Hydrogen-Free Plasma Nitriding Process for Fabrication of Expanded Austenite Layer on AISI 316 Stainless Steel Surface
Abstract
1. Introduction
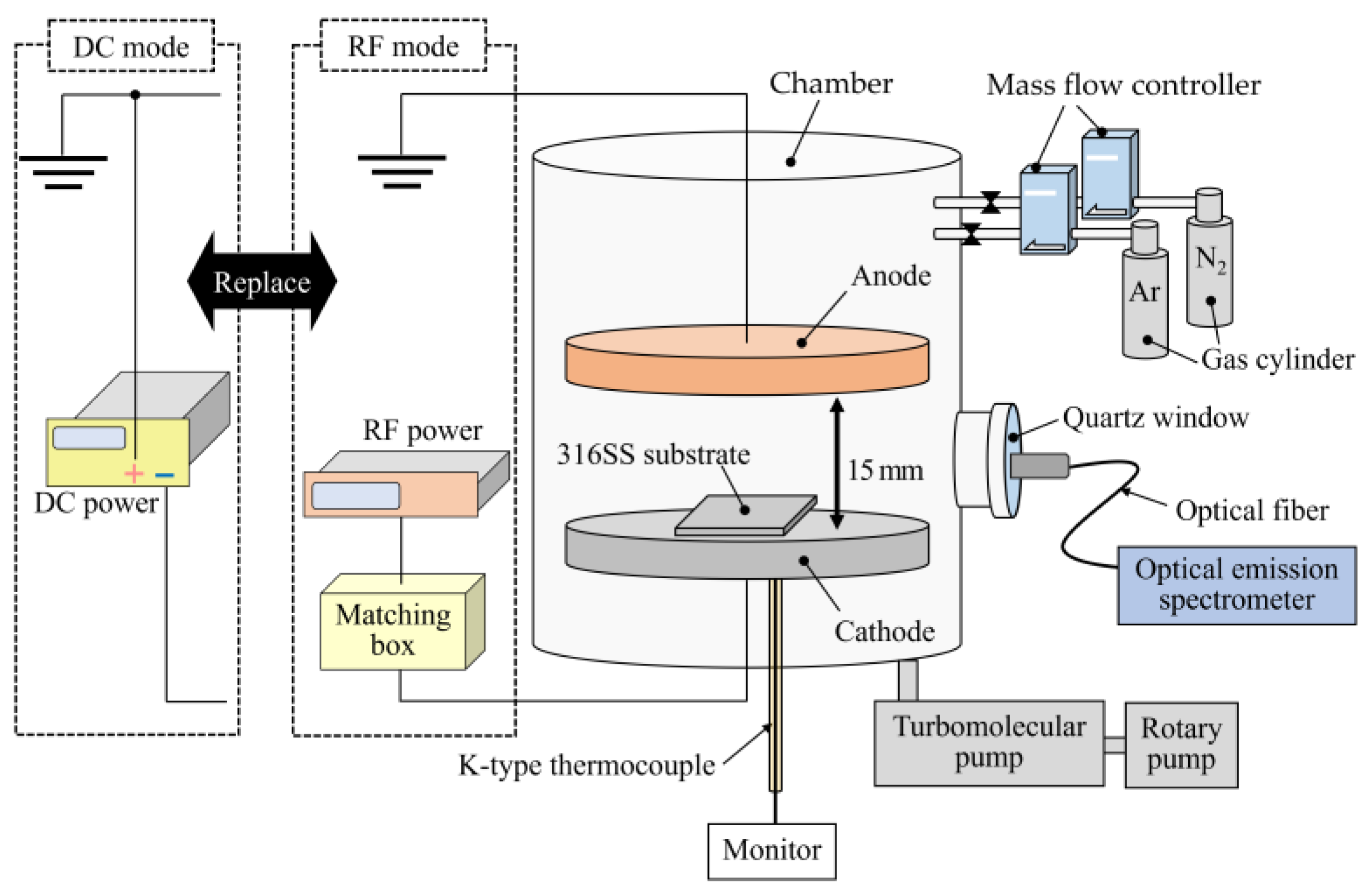
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Specimen Preparation
2.2. Surface Analysis
3. Results
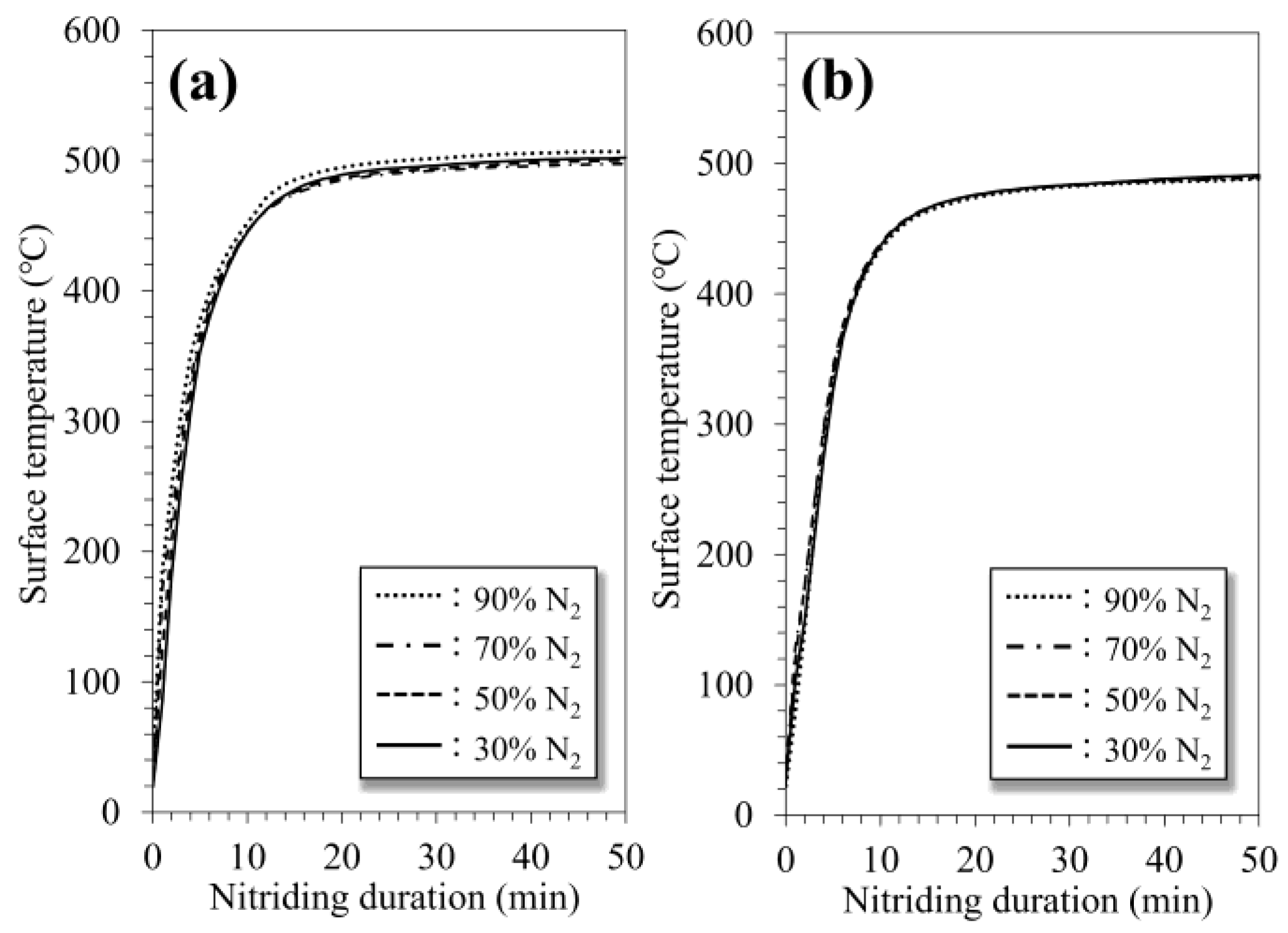
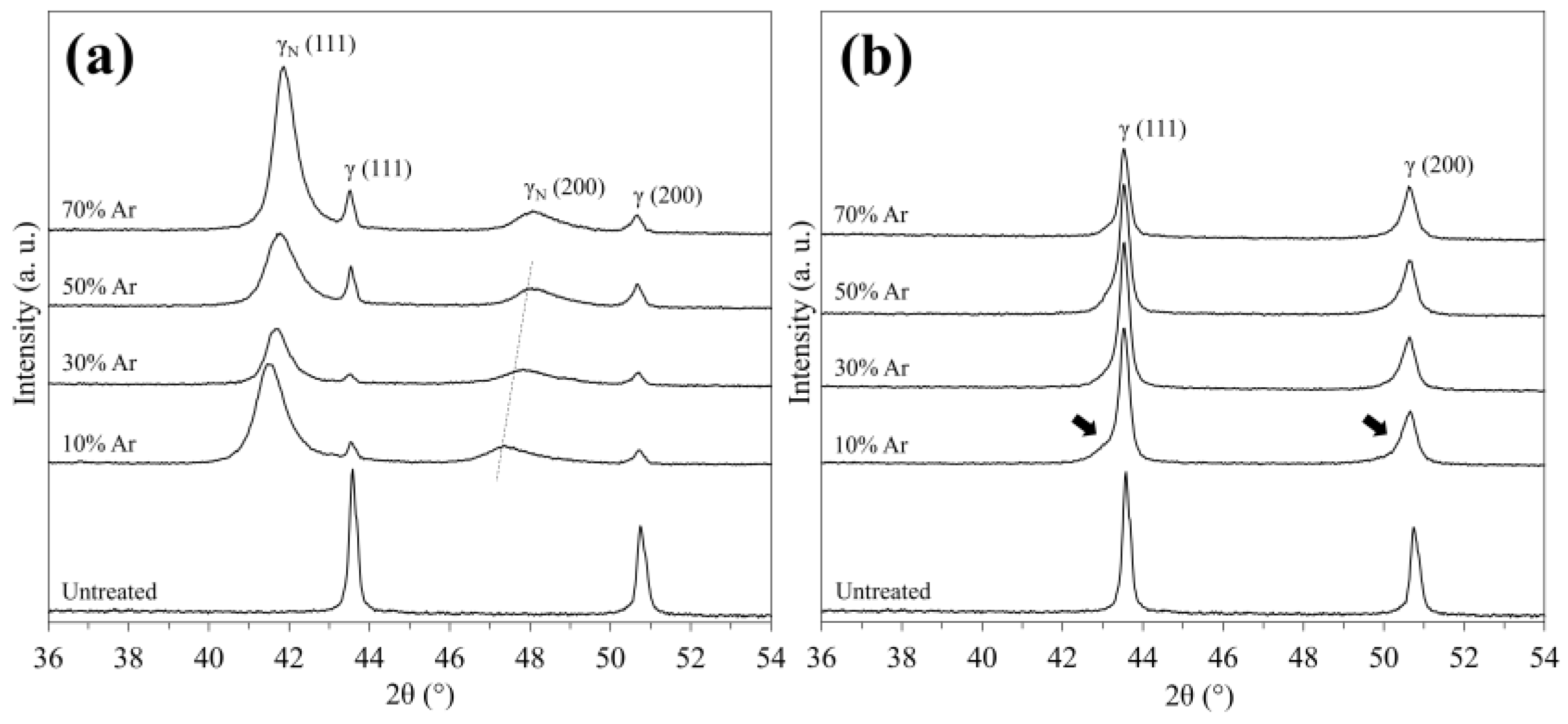
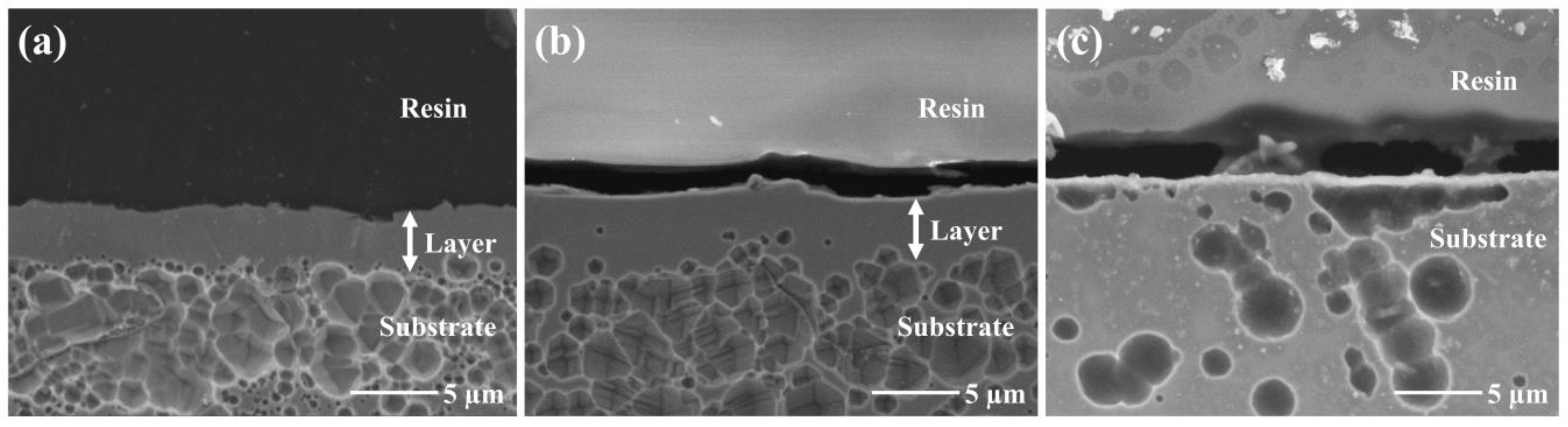
3.1. Characteristics of 316SS Surface Nitrided in N2-Ar Plasma Discharged by RF and DC Modes
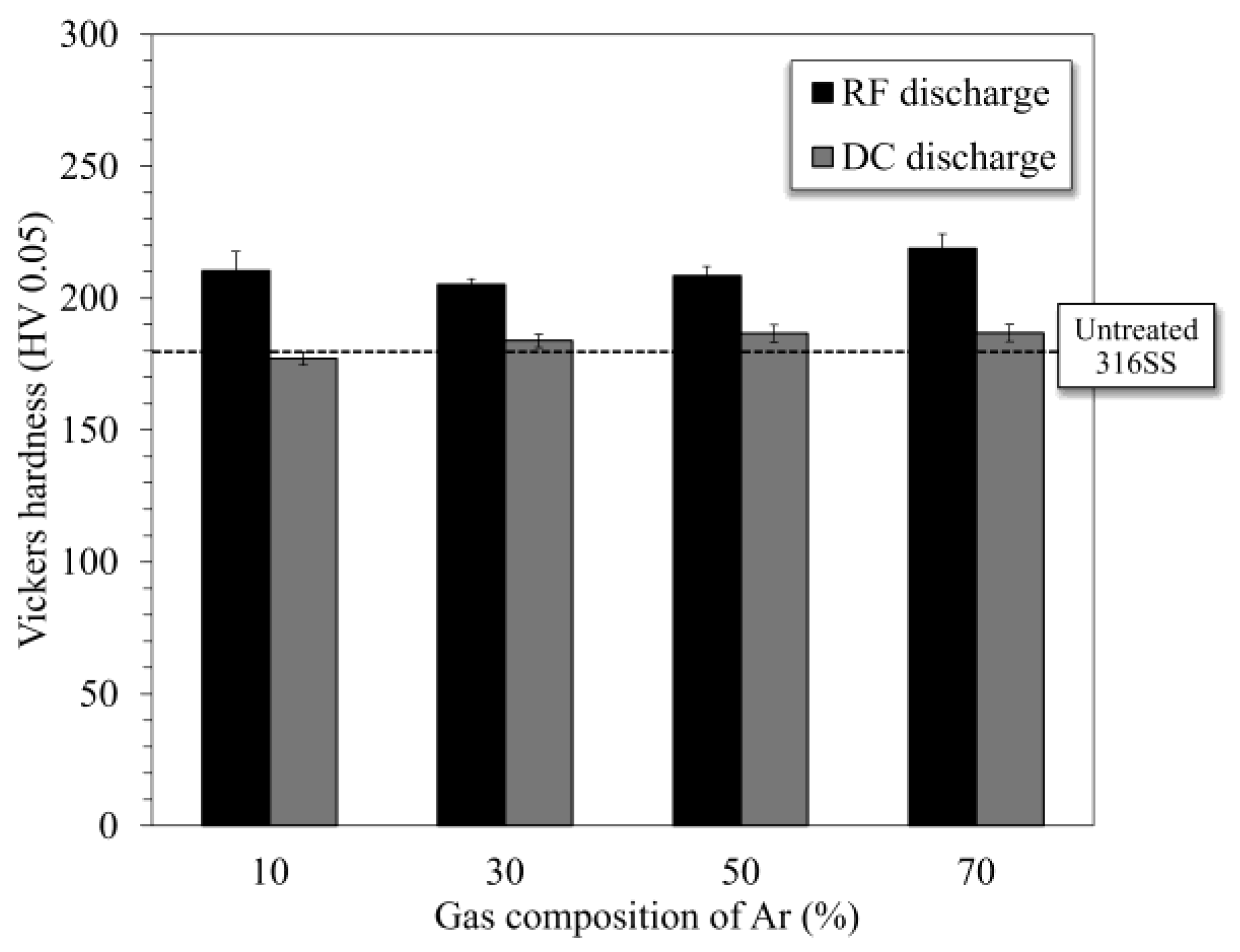
3.2. Vickers Hardness of Nitrided 316SS Surface
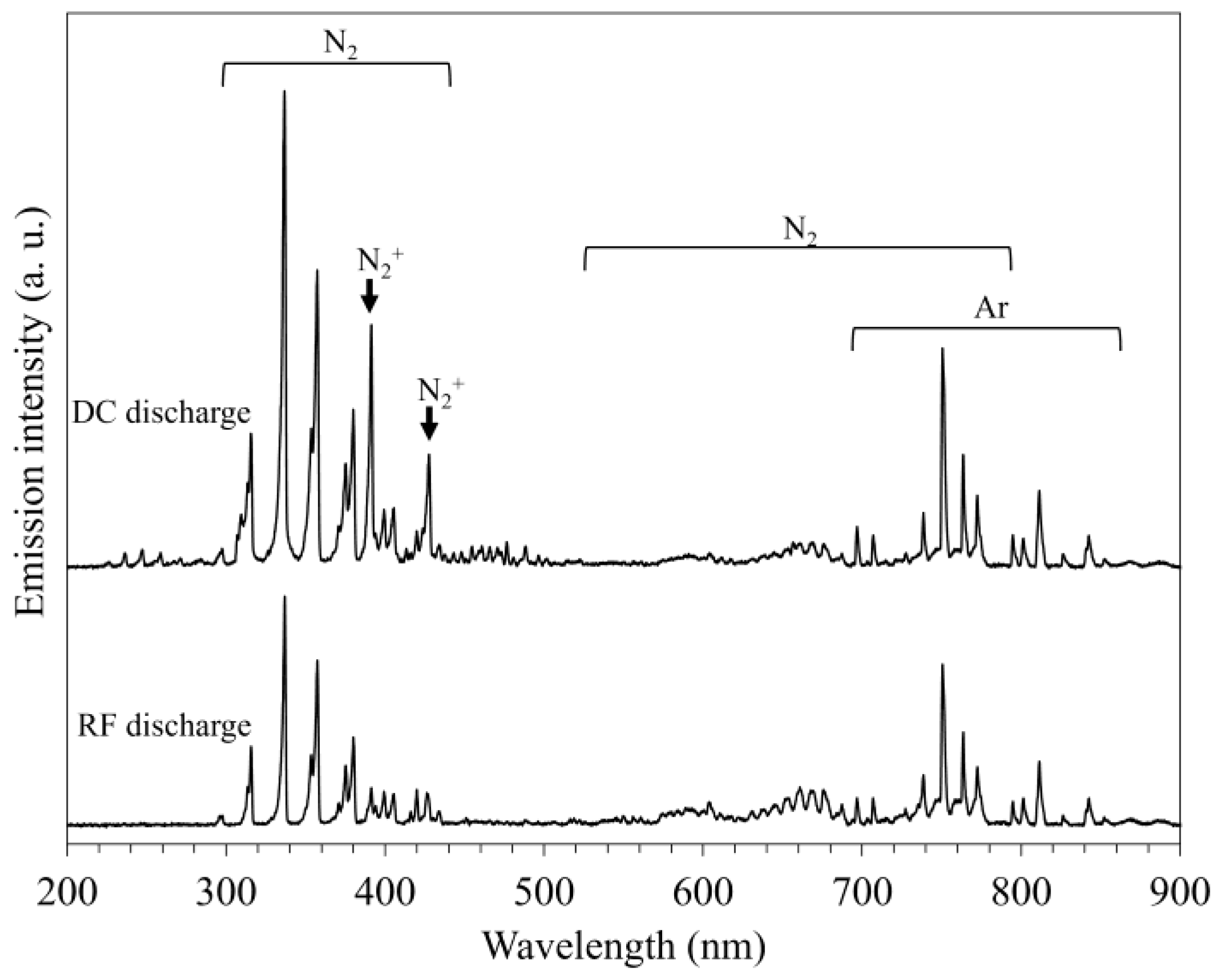
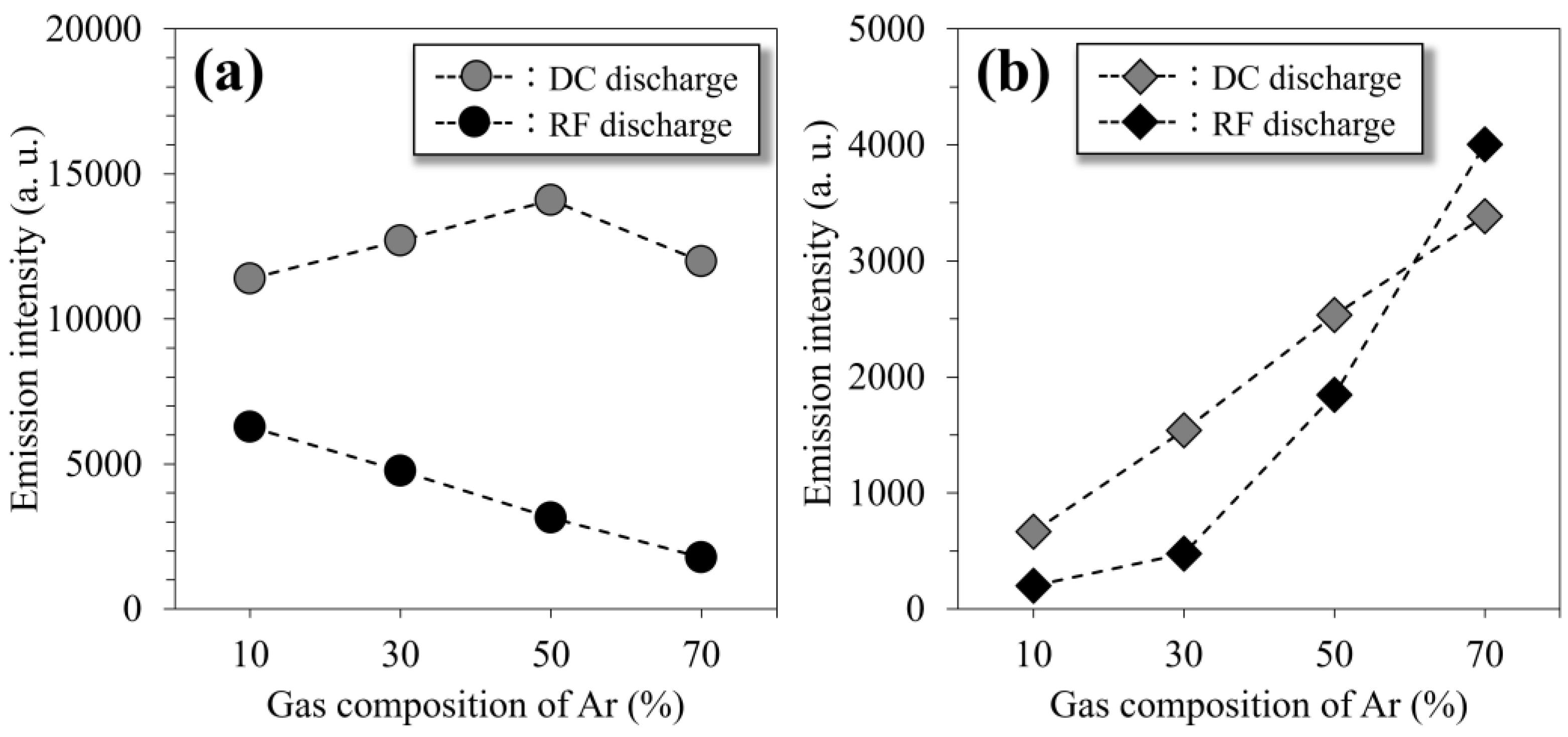
3.3. Plasma Diagnosis of RF and DC Glow-Discharged N2-Ar Plasma
4. Discussion
4.1. Effect of Discharge Mode on Nitrogen Penetration During N2-Ar Plasma Nitriding Process
4.2. Industrial Application of N2-Ar Plasma Nitriding Process Employing RF Discharge Mode
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Larisch, B.; Brusky, U.; Spies, H.J. Plasma nitriding of stainless steels at low temperatures. Surf. Coat. Technol. 1999, 116–119, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fossati, A.; Borgioli, F.; Galvanetto, E.; Bacci, T. Glow-discharge nitriding of AISI 316L austenitic stainless steel: Influence of treatment time. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2006, 200, 3511–3517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Zhao, X.; Wang, S.; Li, J.; Wei, W.; Hu, J. Performance enhancement by plasma nitriding at low gas pressure for 304 austenitic stainless steel. Vacuum 2017, 145, 334–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Li, X.Y.; Bell, T. X-ray diffraction characterisation of low temperature plasma nitrided austenitic stainless steels. J. Mater. Sci. 1999, 34, 4793–4802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stinville, J.C.; Villechaise, P.; Templier, C.; Riviere, J.P.; Drouet, M. Plasma nitriding of 316L austenitic stainless steel: Experimental investigation of fatigue life and surface evolution. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2010, 204, 1947–1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menthe, E.; Bulak, A.; Olfe, J.; Zimmermann, A.; Rie, K.T. Improvement of the mechanical properties of austenitic stainless steel after plasma nitriding. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2000, 133–134, 259–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Peng, Q.; Li, C.; Wang, Y.; Gao, J.; Chen, S.; Wang, J.; Shen, B. Effect of DC plasma nitriding temperature on microstructure and dry-sliding wear properties of 316L stainless steel. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2008, 202, 2749–2754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, R.P.H.; Chang, C.C.; Darack, S. Hydrogen plasma etching of semiconductors and their oxides. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. 1982, 20, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brecelj, F.; Mozetic, M. Reduction of metal oxide thin layers by hydrogen plasma. Vacuum 1990, 40, 177–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moskalioviene, T.; Galdikas, A. Mechanisms of the hydrogen influence on the diffusivity of nitrogen during plasma nitriding austenitic stainless steel. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2019, 50, 1021–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohtsu, N.; Miura, K.; Hirano, M.; Kodama, K. Investigation of admixed gas effect on plasma nitriding of AISI316L austenitic stainless steel. Vacuum 2021, 193, 110545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garamoon, A.; Rashed, U.M.; Abouelela, A.; Eissa, M.A.; Saudi, A.H.; El-Zeer, D.M.; El-Hossary, F. Hydrogen effect on nitriding process of 304L austenitic stainless steel. IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 2006, 34, 1066–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priest, J.M.; Baldwin, M.J.; Fewell, M.P. The action of hydrogen in low-pressure r.f.-plasma nitriding. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2001, 145, 152–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Ghadiani, H.; Jalilvand, V.; Farhat, Z.; Islam, M.A. Hydrogen impact: A review on diffusibility, embrittlement mechanisms, and characterization. Materials 2024, 17, 965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousefi, A.; Itoh, G.; Ghorani, Z.; Kuramoto, S. Effect of strain rates on mechanical properties of a duplex stainless-steel sheet charged in hydrogen plasma. ISIJ Int. 2023, 63, 390–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Depover, T.; Wan, D.; Wang, D.; Barnoush, A.; Verbeken, K. The effect of hydrogen on the crack initiation site of TRIP-assisted steels during in-situ hydrogen plasma micro-tensile testing: Leading to an improved ductility? Mater. Charact. 2020, 167, 110493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, D.; Ma, Y.; Sun, B.; Razavi, S.M.J.; Wang, D.; Lu, X.; Song, W. Evaluation of hydrogen effect on the fatigue crack growth behavior of medium-Mn steels via in-situ hydrogen plasma charging in an environmental scanning electron microscope. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2021, 85, 30–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wang, X.; Hu, Y.; Luo, L.; Jiang, C.; Liu, F.; Jin, W.; Zhu, K.; Long, Z.; Liu, K. Effect of hydrogen on microstructure and mechanical properties of plasma-nitrided pure titanium by cathodic cage plasma nitriding. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2023, 456, 129231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsukuda, N.; Kuramoto, E.; Tokunaga, K.; Muroga, T.; Yoshida, N.; Itoh, S. Plasma-induced surface degradation in 304 stainless steel used for TRIAM-1M limiter. J. Nucl. Mater. 1994, 212–215, 1303–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawabe, T.; Kaminaga, M.; Fukazawa, M.; Nakazato, K.; Hayashi, T.; Sato, S. Discharge cleaning and gas trapping by use of a glow-mode plasma source. Vacuum 1990, 41, 1977–1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katayama, K.; Uchida, Y.; Fujiki, T.; Nishikawa, M.; Fukada, S.; Ashikawa, N.; Uda, T. Hydrogen release from deposition layers formed from 316 stainless steel by hydrogen plasma sputtering. J. Nucl. Mater. 2009, 390–391, 689–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, C.; Kyrsta, S.; Cremer, R.; Neuschütz, D. Application of argon r.f. plasma etching for the removal of oxidic scales on ULC steels. Surf. Interface Anal. 2002, 34, 396–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrasonis, G.; Rivière, J.P.; Templier, C.; Muzard, S.; Pranevicius, L. Influence of surface preparation and ion flux on the nitriding efficiency of austenitic stainless steel. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2005, 196, 279–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogaerts, A.; Gijbels, R.; Goedheer, W. Comparison between a radio-frequency and direct current glow discharge in argon by a hybrid Monte Carlo–fluid model for electrons, argon ions and fast argon atoms. Spectrochim. Acta Part B At. Spectrosc. 1999, 54, 1335–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez, C.; Pereiro, R.; Bordel, N.; Sanz-Medel, A. Effect of operation parameters on the sputtering and emission processes in radiofrequency glow discharge. A comparison with the direct-current mode. Spectrochim. Acta Part B At. Spectrosc. 1998, 53, 1541–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.; Hu, B.; Ye, Y.; Marcus, R.K. Comparison of fundamental characteristics between radio-frequency and direct current powering of a single glow discharge atomic emission spectroscopy source. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 1998, 13, 1159–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efimova, V.; Hoffmann, V.; Eckert, J. Sputter crater formation in the case of microsecond pulsed glow discharge in a Grimm-type source. Comparison of direct current and radio frequency modes. Spectrochim. Acta Part B 2012, 76, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Baldwin, M.J.; Fewell, M.P.; Haydon, S.C.; Short, K.T.; Collins, G.A.; Tendys, J. The effect of hydrogen on the growth of the nitrided layer in r.f.-plasma-nitrided austenitic stainless steel AISI316. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2000, 123, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Templier, C.; Stinville, J.C.; Villechaise, P.; Renault, P.O.; Abrasonis, G.; Rivière, J.P.; Martinavičius, A.; Drouet, M. On lattice plane rotation and crystallographic structure of the expanded austenite in plasma nitrided AISI 316L steel. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2010, 204, 2551–2558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suraj, K.S.; Bharathi, P.; Prahlad, V.; Mukherjee, S. Near cathode optical emission spectroscopy in N2–H2 glow discharge plasma. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2007, 202, 301–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mavadat, M.; Ricard, A.; Sarra-Bournet, C.; Laroche, G. Determination of ro-vibrational excitations of N2(B, v’) and N2(C, v’) states in N2 microwave discharges using visible and IR spectroscopy. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2011, 44, 155207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes, P.G.; Torres, C.; Martínez, H. Electron temperature and ion density measurements in a glow discharge of an Ar–N2 mixture. Radiat. Eff. Defects Solids 2014, 169, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qayyum, A.; Zeb, S.; Naveed, M.A.; Rehman, N.U.; Ghaurib, S.A.; Zakaullah, M. Optical emission spectroscopy of Ar–N2 mixture plasma. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 2007, 107, 361–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, S.; Hirai, H.; Araki, S.; Wagatsuma, K. Effect of excitation states of nitrogen on the surface nitridation of iron and steel in d.c. glow discharge plasma. Surf. Interface Anal. 2011, 43, 964–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirano, M.; Hashimoto, M.; Miura, K.; Ohtsu, N. Fabrication of antibacterial nanopillar surface on AISI 316 stainless steel through argon plasma etching with direct current discharge. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2021, 406, 126680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, W.; Bin, X.; Zhiwei, Y.; Yaqin, S. The wear and corrosion properties of stainless steel nitrided by low-pressure plasma-arc source ion nitriding at low temperatures. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2000, 130, 304–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Xiong, J.; Peng, Q.; Fan, H.; Wang, Y.; Li, G.; Shen, B. Effects of DC plasma nitriding parameters on microstructure and properties of 304L stainless steel. Mater. Charact. 2009, 60, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naeem, M.; Iqbal, J.; Zakaullah, M.; Shafiq, M.; Mujahid, Z.I.; Díaz-Guillén, J.C.; Lopez-Badillo, C.M.; Sousa, R.R.M.; Khan, M.A. Enhanced wear and corrosion resistance of AISI-304 steel by duplex cathodic cage plasma treatment. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2019, 375, 34–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hirano, M.; Miura, K.; Ohtsu, N. Hydrogen-Free Plasma Nitriding Process for Fabrication of Expanded Austenite Layer on AISI 316 Stainless Steel Surface. Materials 2025, 18, 140. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18010140
Hirano M, Miura K, Ohtsu N. Hydrogen-Free Plasma Nitriding Process for Fabrication of Expanded Austenite Layer on AISI 316 Stainless Steel Surface. Materials. 2025; 18(1):140. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18010140
Chicago/Turabian StyleHirano, Mitsuhiro, Koyo Miura, and Naofumi Ohtsu. 2025. "Hydrogen-Free Plasma Nitriding Process for Fabrication of Expanded Austenite Layer on AISI 316 Stainless Steel Surface" Materials 18, no. 1: 140. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18010140
APA StyleHirano, M., Miura, K., & Ohtsu, N. (2025). Hydrogen-Free Plasma Nitriding Process for Fabrication of Expanded Austenite Layer on AISI 316 Stainless Steel Surface. Materials, 18(1), 140. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18010140





