Comparative Study of the Impurity Effect on SnAgCu and SnZn Solder Joints with Electrodeposited Cu
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
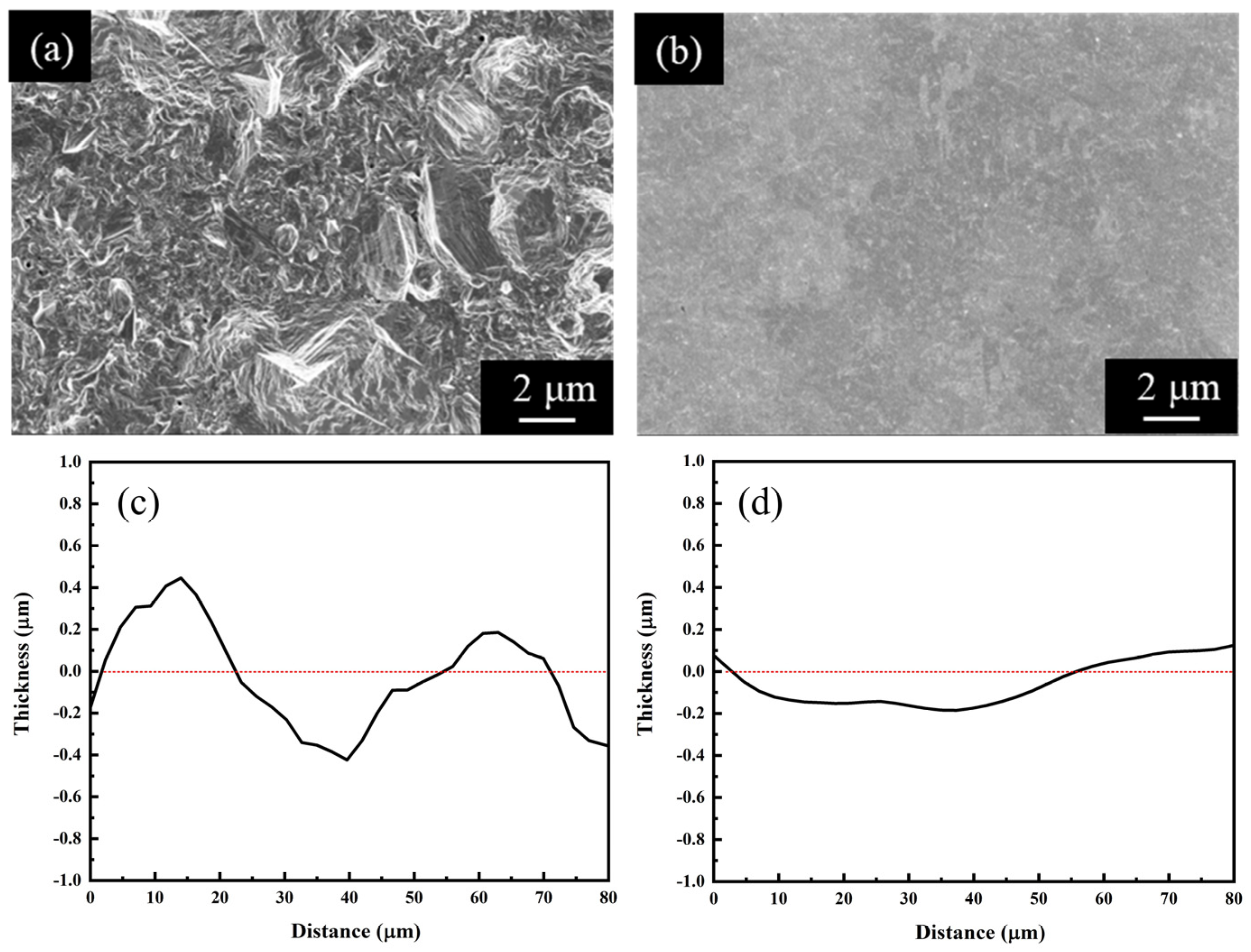
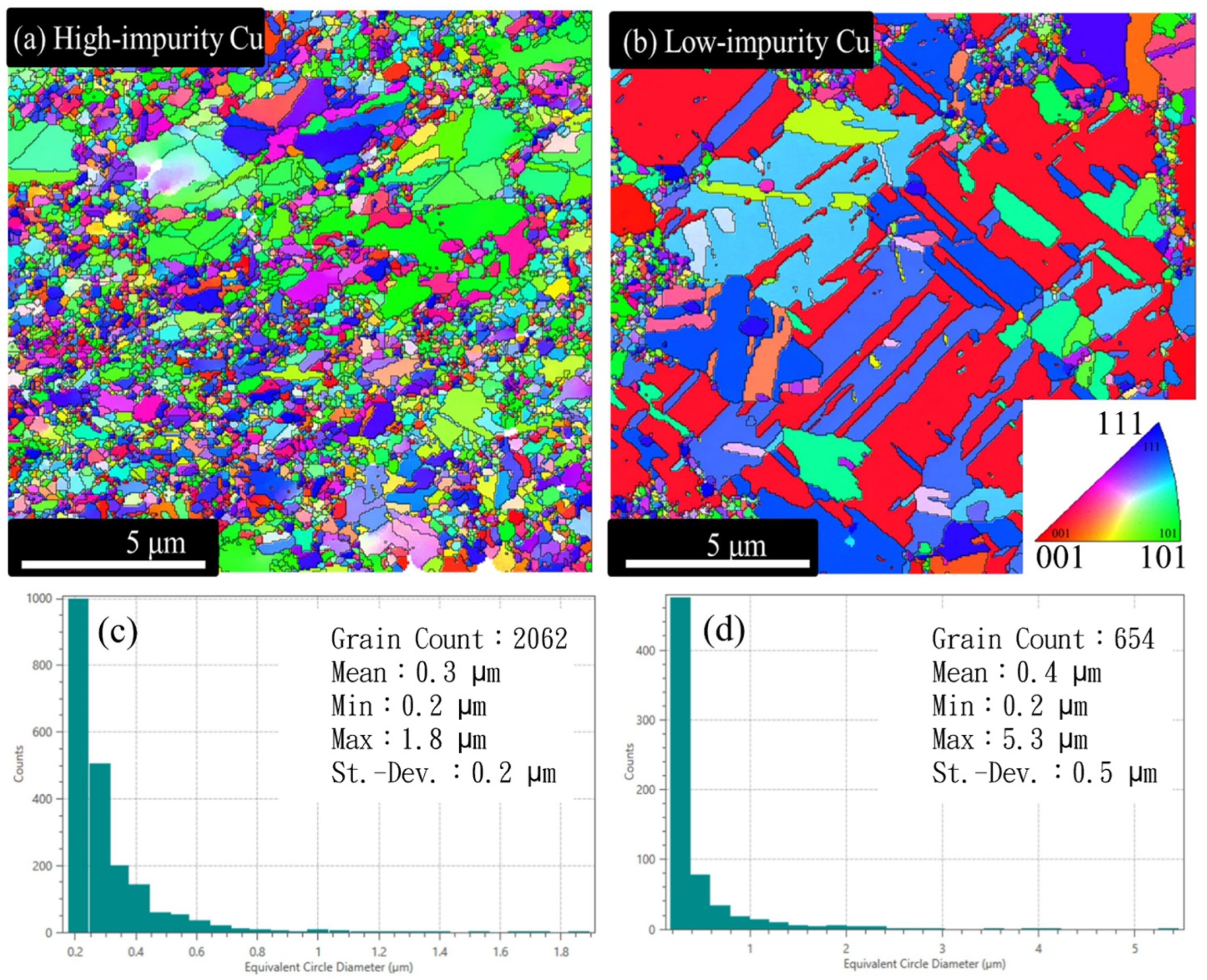
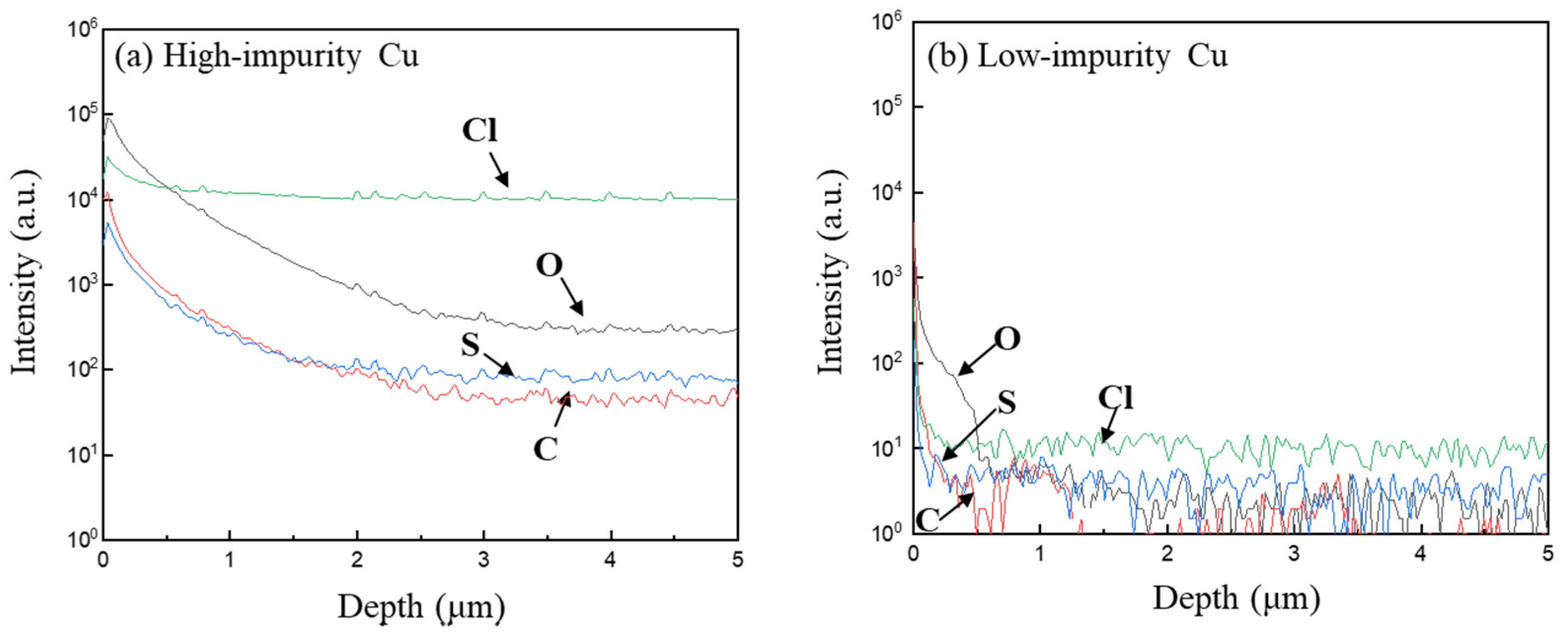
3.1. Effects of Additives on Co-Deposition of Impurities in Electroplated Cu
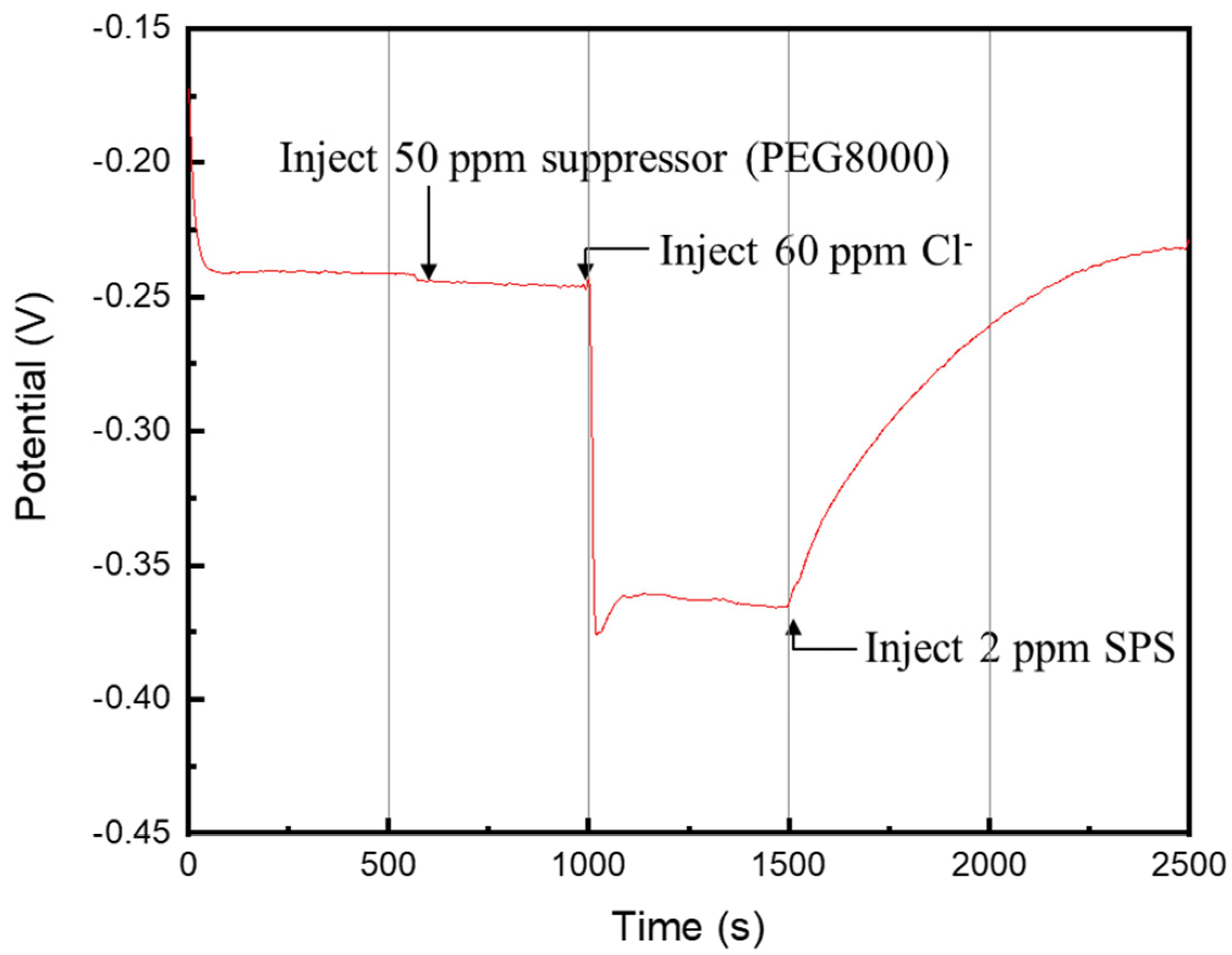
3.2. Molecular Adsorption Mechanisms of Additive Molecules
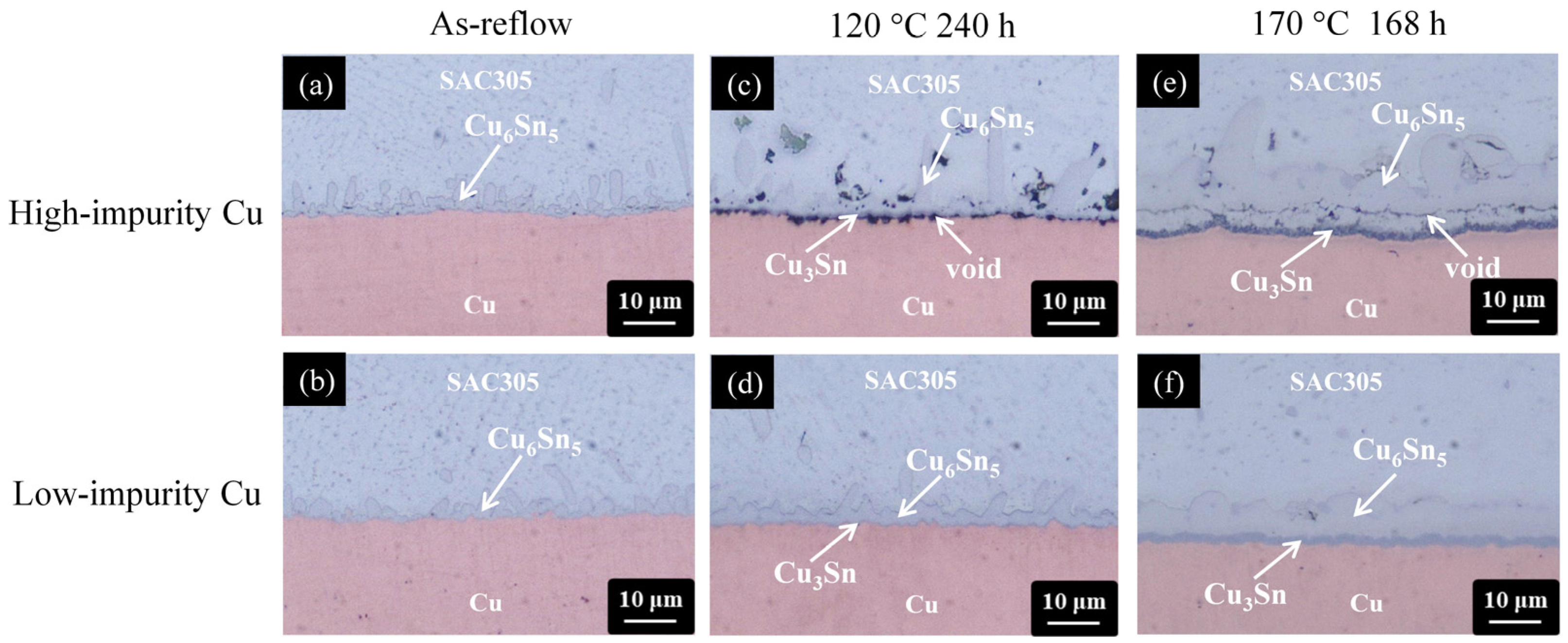
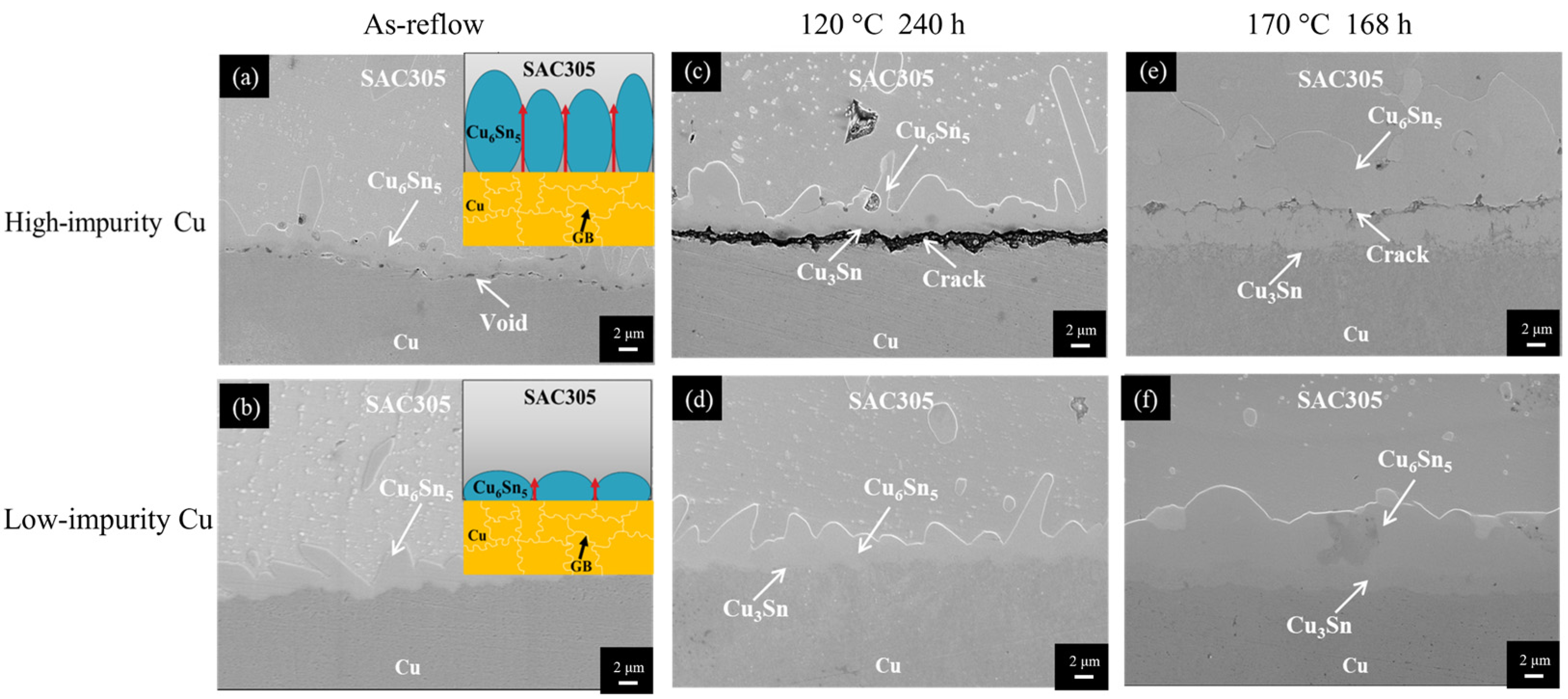
3.3. Impurity Effect on the Microstructural Evolution of the SAC305/Cu Solder Joint
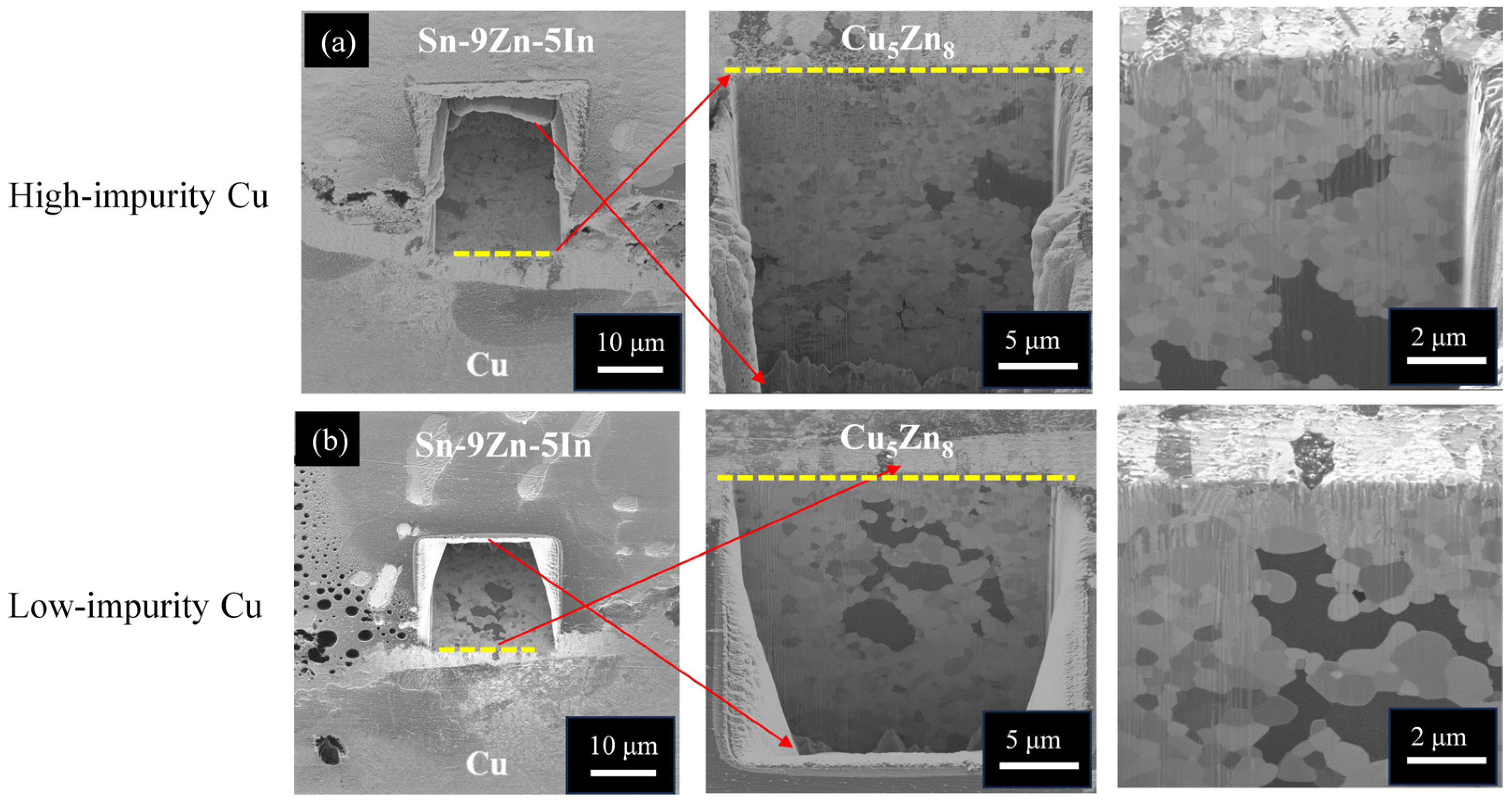
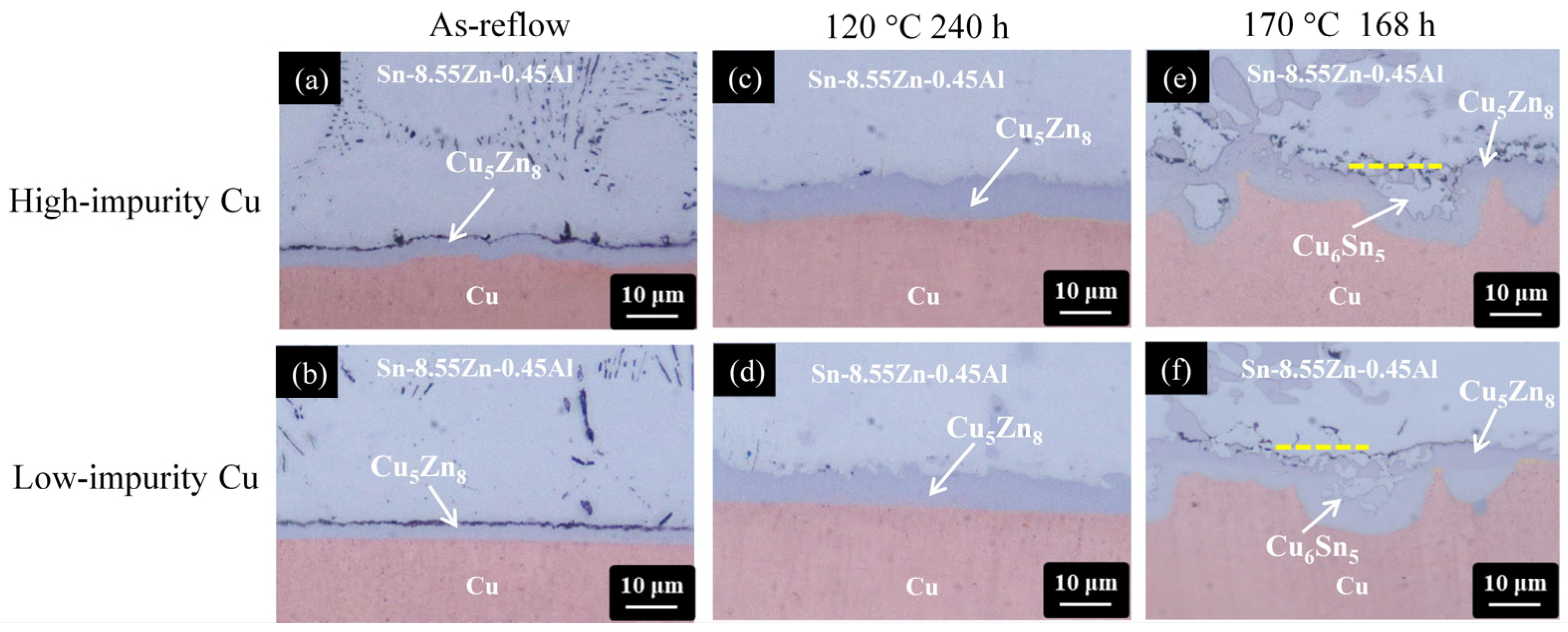
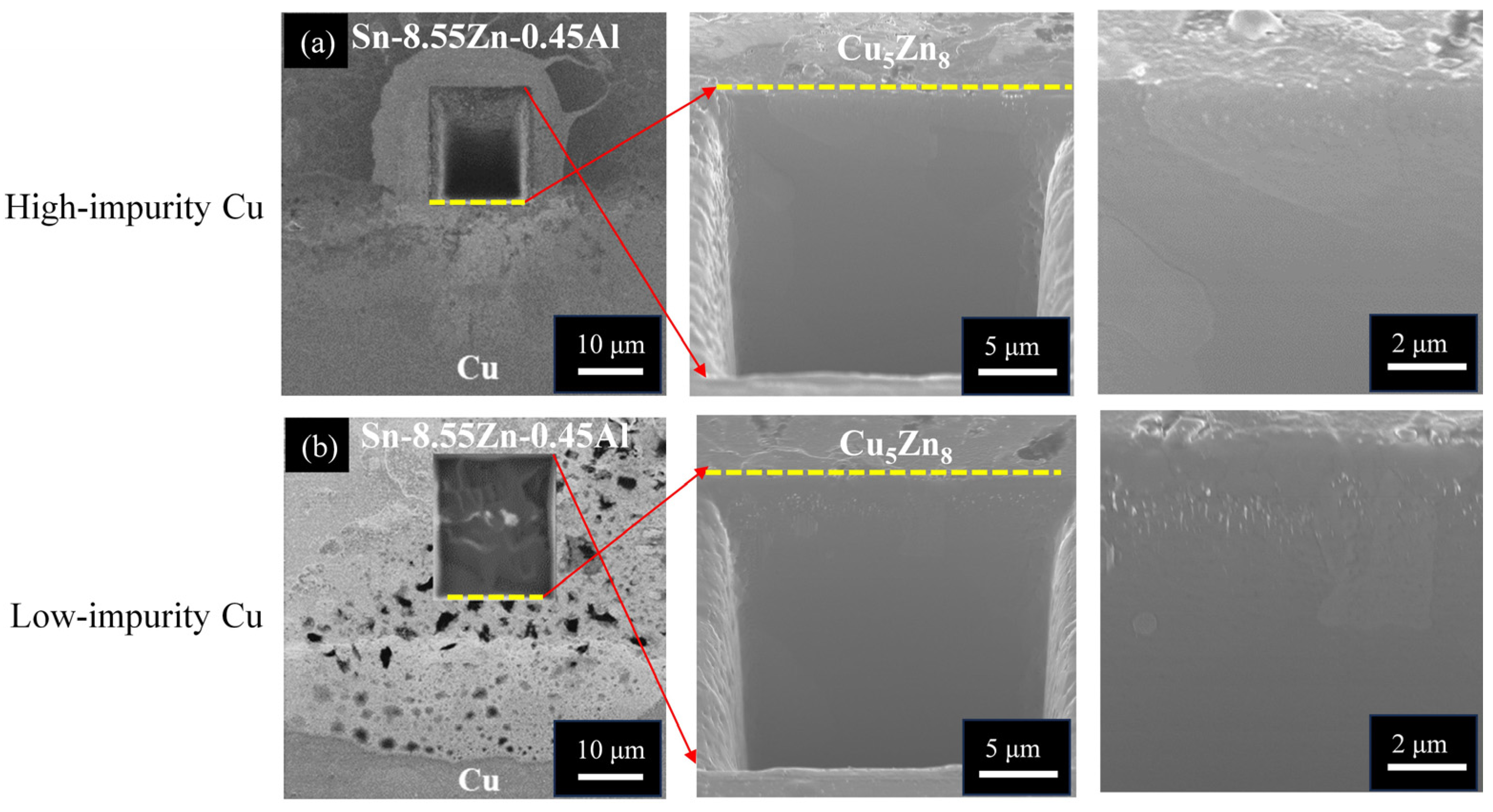
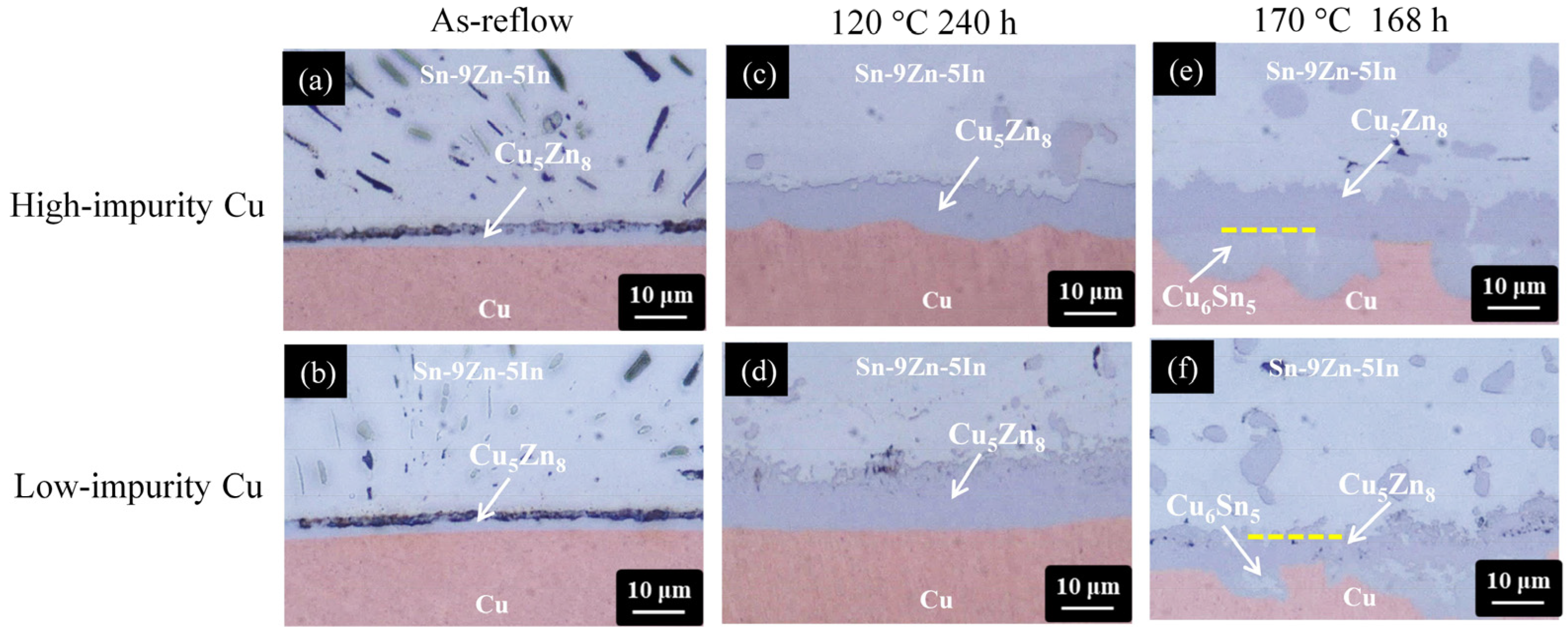
3.4. Impurity Effect on the Microstructural Evolution of the Sn-9Zn/Cu, Sn-8.55Zn-0.45Al/Cu, and Sn-9Zn-5In/Cu Solder Joints
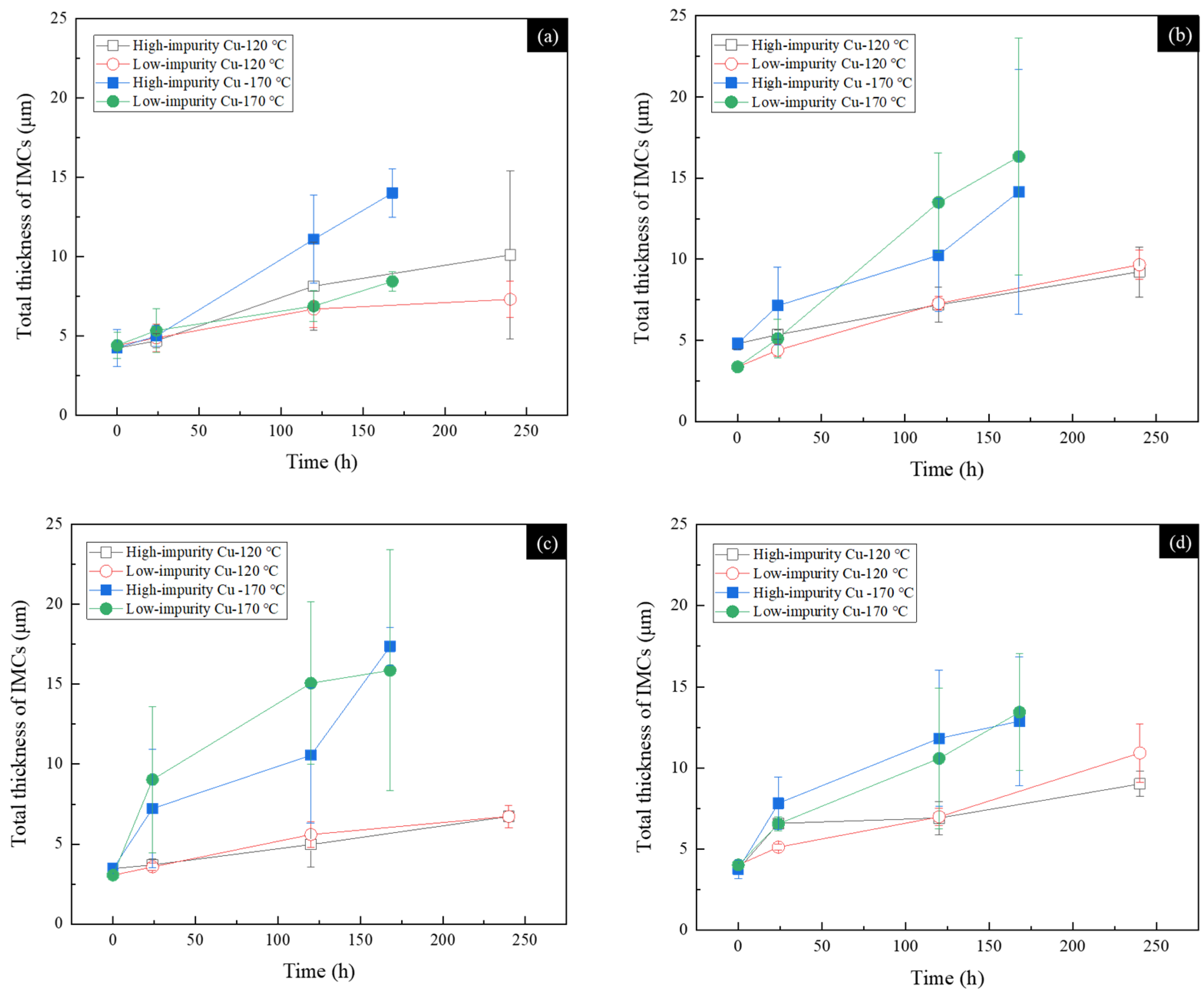
3.5. IMC Growth in the SAC305 and SnZn-Based Solder Joints
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Van Olmen, J.; Huyghebaert, C.; Coenen, J.; Van Aelst, J.; Sleeckx, E.; Van Ammel, A.; Armini, S.; Katti, G.; Vaes, J.; Dehaene, W. Integration challenges of copper through silicon via (TSV) metallization for 3D-stacked IC integration. Microelectron. Eng. 2011, 88, 745–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmann, L.; Ecke, R.; Schulz, S.E.; Gessner, T. Investigations regarding Through Silicon Via filling for 3D integration by Periodic Pulse Reverse plating with and without additives. Microelectron. Eng. 2011, 88, 705–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moffat, T.P.; Josell, D. Extreme bottom-up superfilling of through-silicon-vias by damascene processing: Suppressor disruption, positive feedback and turing patterns. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2012, 159, D208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Huang, Y.T.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, M.; Wang, W.T.; Chung, C.C.; Cherng, S.J.; Tsai, Y.H.; Li, P.C.; Lu, Z. Electrodeposition of (111)-oriented and nanotwin-doped nanocrystalline Cu with ultrahigh strength for 3D IC application. Nanotechnology 2021, 32, 225702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braun, T.M.; Josell, D.; Moffat, T.P. Simulating Cu electrodeposition in high aspect ratio features: Effect of control mode and uncompensated resistance in S-NDR systems. Electrochim. Acta 2021, 375, 137925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stangl, M.; Acker, J.; Oswald, S.; Uhlemann, M.; Gemming, T.; Baunack, S.; Wetzig, K. Incorporation of sulfur, chlorine, and carbon into electroplated Cu thin films. Microelectron. Eng. 2007, 84, 54–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.C.; Yang, C.H.; Wu, Y.S.; Ho, C.E. Depth-dependent self-annealing behavior of electroplated Cu. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2017, 320, 489–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, S.Y.; Chen, C.M.; Song, J.M.; Nishikawa, H. Surface modification of Cu electroplated layers for Cu–Sn transient liquid phase bonding. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2022, 277, 125621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramli, M.I.I.; Salleh, M.A.A.M.; Abdullah, M.M.A.B.; Zaimi, N.S.M.; Sandu, A.V.; Vizureanu, P.; Rylski, A.; Amli, S.F.M. Formation and Growth of Intermetallic Compounds in Lead-Free Solder Joints: A Review. Materials 2022, 15, 1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.; Kim, C.L.; Sohn, Y. Diffusion Barrier Properties of the Intermetallic Compound Layers Formed in the Pt Nanoparticles Alloyed Sn-58Bi Solder Joints Reacted with ENIG and ENEPIG Surface Finishes. Materials 2022, 15, 8419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silvain, J.F.; Constantin, L.; Heintz, J.M.; Bordère, S.; Teule-Gay, L.; Lu, Y.F.; Diot, J.L.; Langlade, R.D.; Feuillet, E. Controlling Interfacial Exchanges in Liquid Phase Bonding Enables Formation of Strong and Reliable Cu–Sn Soldering for High-Power and Temperature Applications. ACS Appl. Electron. Mater. 2021, 3, 921–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chantaramanee, S.; Sungkhaphaitoon, P. Investigation of microstructure, thermal properties, and mechanical performances of Ni-added Sn-5.0Sb-0.5Cu/Cu solder joints. Microelectron. Reliab. 2021, 127, 114421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baheti, V.A.; Kashyap, S.; Kumar, P.; Chattopadhyay, K.; Paul, A. Bifurcation of the Kirkendall marker plane and the role of Ni and other impurities on the growth of Kirkendall voids in the Cu–Sn system. Acta Mater. 2017, 131, 260–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, C.E.; Yang, S.C.; Kao, C.R. Interfacial reaction issues for lead-free electronic solders. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2007, 18, 155–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.W.; Lin, Y.; Kao, C.R. Kirkendall voids formation in the reaction between Ni-doped SnAg lead-free solders and different Cu substrates. Microelectron. Reliab. 2009, 49, 248–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, K.; Stierman, R.; Chiu, T.C.; Edwards, D.; Ano, K.; Tu, K.N. Kirkendall void formation in eutectic SnPb solder joints on bare Cu and its effect on joint reliability. J. Appl. Phys. 2005, 97, 024508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.Y.; Yu, J. Effects of residual impurities in electroplated Cu on the Kirkendall void formation during soldering. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2008, 92, 092109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Kim, J. Effects of residual S on Kirkendall void formation at Cu/Sn–3.5 Ag solder joints. Acta Mater. 2008, 56, 5514–5523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wafula, F.; Liu, Y.; Yin, L.; Bliznakov, S.; Borgesen, P.; Cotts, E.; Dimitrov, N. Impact of key deposition parameters on the voiding sporadically occurring in solder joints with electroplated copper. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2009, 157, D111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wafula, F.; Yin, L.; Borgesen, P.; Andala, D.; Dimitrov, N. Influence of poly(ethylene glycol) degradation on voiding sporadically occurring in solder joints with electroplated Cu. J. Electron. Mater. 2012, 41, 1898–1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, T.Y.; Lee, H.; Hsu, H.L.; Dow, W.P.; Cheng, H.K.; Liu, K.C.; Chen, C.M. Effects of Cu electroplating formulas on the interfacial microstructures of Sn/Cu joints. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2016, 163, D734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Chen, C.M. Impurity effects in electroplated-copper solder joints. Metals 2018, 8, 388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abtew, M.; Selvaduray, G. Lead-free solders in microelectronics. Mater. Sci. Eng. R Rep. 2000, 27, 95–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.Y.; Yang, S.P.; Yang, C.H.; Lu, M.K.; Kuo, T.T.; Ho, C.E. Influence of Pd (P) thickness on the Pd-free solder reaction between eutectic Sn-Ag alloy and Au/Pd (P)/Ni (P)/Cu multilayer. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2020, 395, 125879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, K.; Tu, K.N. Six cases of reliability study of Pb-free solder joints in electronic packaging technology. Mater. Sci. Eng. R Rep. 2002, 38, 55–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.N.; Chan, Y.C.; Rizvi, M.J.; Jillek, W. Investigations of interfacial reactions of Sn–Zn based and Sn–Ag–Cu lead-free solder alloys as replacement for Sn–Pb solder. J. Alloys Compd. 2005, 400, 136–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.A. Effect of indium addition on mechanical, thermal, and soldering properties of eutectic Sn–9Zn alloy. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2024, 315, 128992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.A.; Lin, C.Y.; Chen, C.M. Exploring mechanism of suppressing void formation at Interface of Sn–9Zn and Cu. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2024, 35, 778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Chiang, P.C.; Huang, Y.T.; Wang, W.T.; Li, P.C.; Tsai, Y.H.; Chen, C.M.; Feng, S.P. Study of grain size effect of Cu metallization on interfacial microstructures of solder joints. Microelectron. Reliab. 2019, 99, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, G.; Malmberg, P.; Vuorinen, V.; Paulasto-Krockel, M. The role of ultrafine crystalline behavior and trace impurities in copper on intermetallic void formation. ACS Appl. Electron. Mater. 2019, 1, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, L.; Wafula, F.; Dimitrov, N.; Borgesen, P. Toward a Better Understanding of the Effect of Cu Electroplating Process Parameters on Cu3Sn Voiding. J. Electron. Mater. 2012, 41, 302–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.J.; Choi, S.R.; Kim, J.G.; Kim, H.G. Effect of Molecular Weight of Polyethylene Glycol on Copper Electrodeposition in the Presence of Bis-3-Sulfopropyl-Disulfide. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2016, 11, 10067–10079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kao, Y.J.; Li, Y.J.; Shen, Y.A.; Chen, C.M. Significant Hall–Petch effect in micro-nanocrystalline electroplated copper controlled by SPS concentration. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, Y.J.; Tsai, K.L.; Li, Y.J.; Chen, C.M. Effects of suppressors on the incorporation of impurities and microstructural evolution of electrodeposited Cu solder joints. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2023, 149, 104956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hebert, K.R. Role of chloride ions in suppression of copper electrodeposition by polyethylene glycol. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2005, 152, C283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, N.; Li, N.; Cui, G.; Tian, D.; Yu, S.; Li, Q.; Wu, G. Triblock copolymers as suppressors for microvia filling via copper electroplating. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2013, 160, D188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.V.; Li, X.; Gewirth, A.A. Inhibition due to the interaction of polyethylene glycol, chloride, and copper in plating baths: A surface-enhanced Raman study. J. Phys. Chem. B 2003, 107, 9415–9423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, M.L.; Richter, L.J.; Moffat, T.P. Competitive adsorption of PEG, Cl−, and SPS/MPS on Cu: An in situ ellipsometric study. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2006, 153, C557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yin, L.; Bliznakov, S.; Kondos, P.; Borgesen, P.; Henderson, D.W.; Parks, C.; Wang, J.; Cotts, E.J.; Dimitrov, N. Improving copper electrodeposition in the microelectronics industry. IEEE Trans. Compon. Packag. Technol. 2009, 33, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, M.L.; Richter, L.J.; Moffat, T.P. Potential Dependence of Competitive Adsorption of PEG, Cl−, and SPS/MPS on Cu: An in situ Ellipsometric Study. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2007, 154, D277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willey, M.J.; West, A.C. SPS adsorption and desorption during copper electrodeposition and its impact on PEG adsorption. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2007, 154, D156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.X.; Chu, C.P.; Liao, Y.C. Solderable conductive paste for electronic textiles. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2023, 142, 104616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.H.; Yu, J. Secondary IMC formation induced by Kirkendall voiding in Cu/Sn-3.5 Ag solder joints. J. Mater. Res. 2010, 25, 1854–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, J.W.; Jung, S.B. Interfacial reactions and shear strength on Cu and electrolytic Au/Ni metallization with Sn-Zn solder. J. Mater. Res. 2006, 21, 1590–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suganuma, K.; Murata, T.; Noguchi, H.; Toyoda, Y. Heat resistance of Sn–9Zn solder/Cu interface with or without coating. J. Mater. Res. 2000, 15, 884–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.W.; Lin, K.L. Interfacial reactions of lead-free Sn–Zn based solders on Cu and Cu plated electroless Ni–P/Au layer under aging at 150 °C. J. Mater. Res. 2004, 19, 3560–3568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamoto, H. Supplemental literature review of binary phase diagrams: Ag-Ni, Ag-Zr, Au-Bi, B-Ni, Co-Sb, Cu-Mn, Cu-Si, Cu-Zn, Fe-Zr, Li-Sb, Mg-Pu, and Si-Zr. J. Phase Equilibria Diffus. 2018, 39, 87–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fürtauer, S.; Li, D.; Cupid, D.; Flandorfer, H. The Cu–Sn phase diagram, Part I: New experimental results. Intermetallics 2013, 34, 142–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.C.; Lin, S.C.; Hsieh, K.C. The formation and growth of intermetallic compounds in Sn-Zn and Sn-Zn-Al solder with Ni/Au surface finish bond pad. J. Electron. Mater. 2006, 35, 399–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.W.; Lin, K.L. Morphology of intermetallic compounds formed between lead-free Sn-Zn based solders and Cu substrates. J. Electron. Mater. 2006, 35, 2135–2141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCormack, M.; Jin, S.; Chen, H.; Machusak, D. New lead-free, Sn-Zn-In solder alloys. J. Electron. Mater. 1994, 23, 687–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Sample | Suppressor (PEG) | Bridging Agent (Cl−) | Accelerator (SPS) |
|---|---|---|---|
| High-impurity Cu | 50 ppm | 60 ppm | -- |
| Low-impurity Cu | 50 ppm | 60 ppm | 2 ppm |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Y.-J.; Yen, Y.-W.; Chen, C.-M. Comparative Study of the Impurity Effect on SnAgCu and SnZn Solder Joints with Electrodeposited Cu. Materials 2024, 17, 2149. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17092149
Li Y-J, Yen Y-W, Chen C-M. Comparative Study of the Impurity Effect on SnAgCu and SnZn Solder Joints with Electrodeposited Cu. Materials. 2024; 17(9):2149. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17092149
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Yu-Ju, Yee-Wen Yen, and Chih-Ming Chen. 2024. "Comparative Study of the Impurity Effect on SnAgCu and SnZn Solder Joints with Electrodeposited Cu" Materials 17, no. 9: 2149. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17092149
APA StyleLi, Y.-J., Yen, Y.-W., & Chen, C.-M. (2024). Comparative Study of the Impurity Effect on SnAgCu and SnZn Solder Joints with Electrodeposited Cu. Materials, 17(9), 2149. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17092149







