Experimental Research on the Anti-Reflection Crack Performance of Basalt Fiber Modified Rubber Asphalt Stress-Absorbing Layer
Abstract
1. Introduction
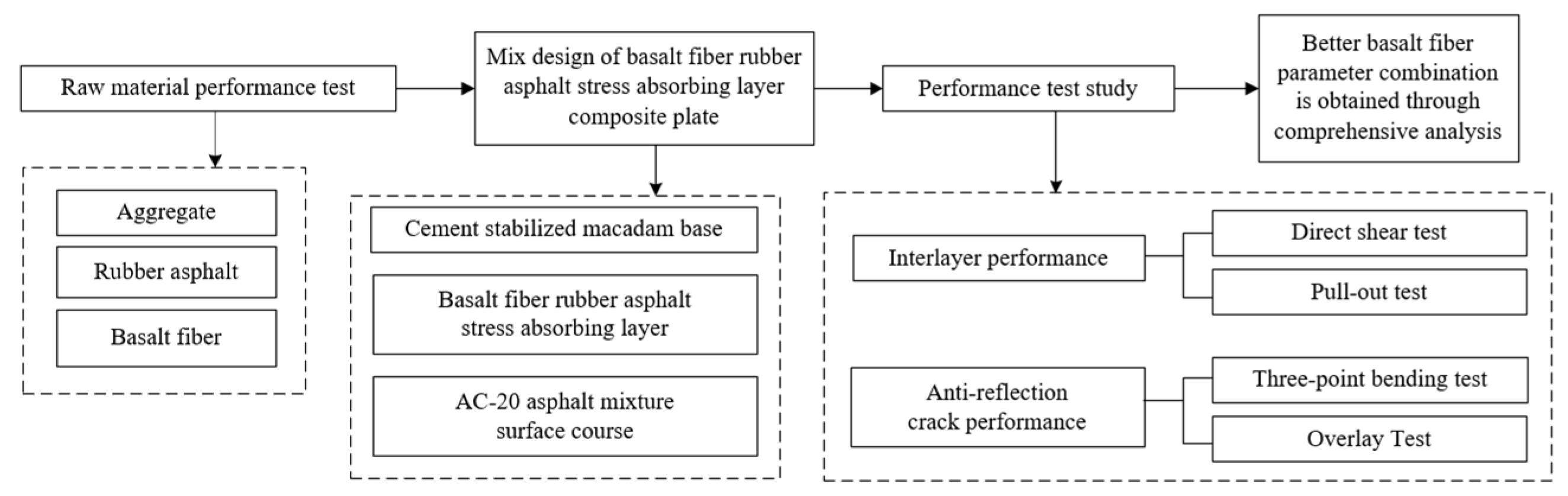
2. Raw Material Performance Test and Mix Proportion Composition Design
2.1. Raw Material Performance Test
2.2. Mix Proportion Design and Composite Specimen Forming
2.2.1. Mix Proportion Design of Cement-Stabilized Macadam Base
2.2.2. Mix Proportion Design of AC-20 Asphalt Mixture Surface Course
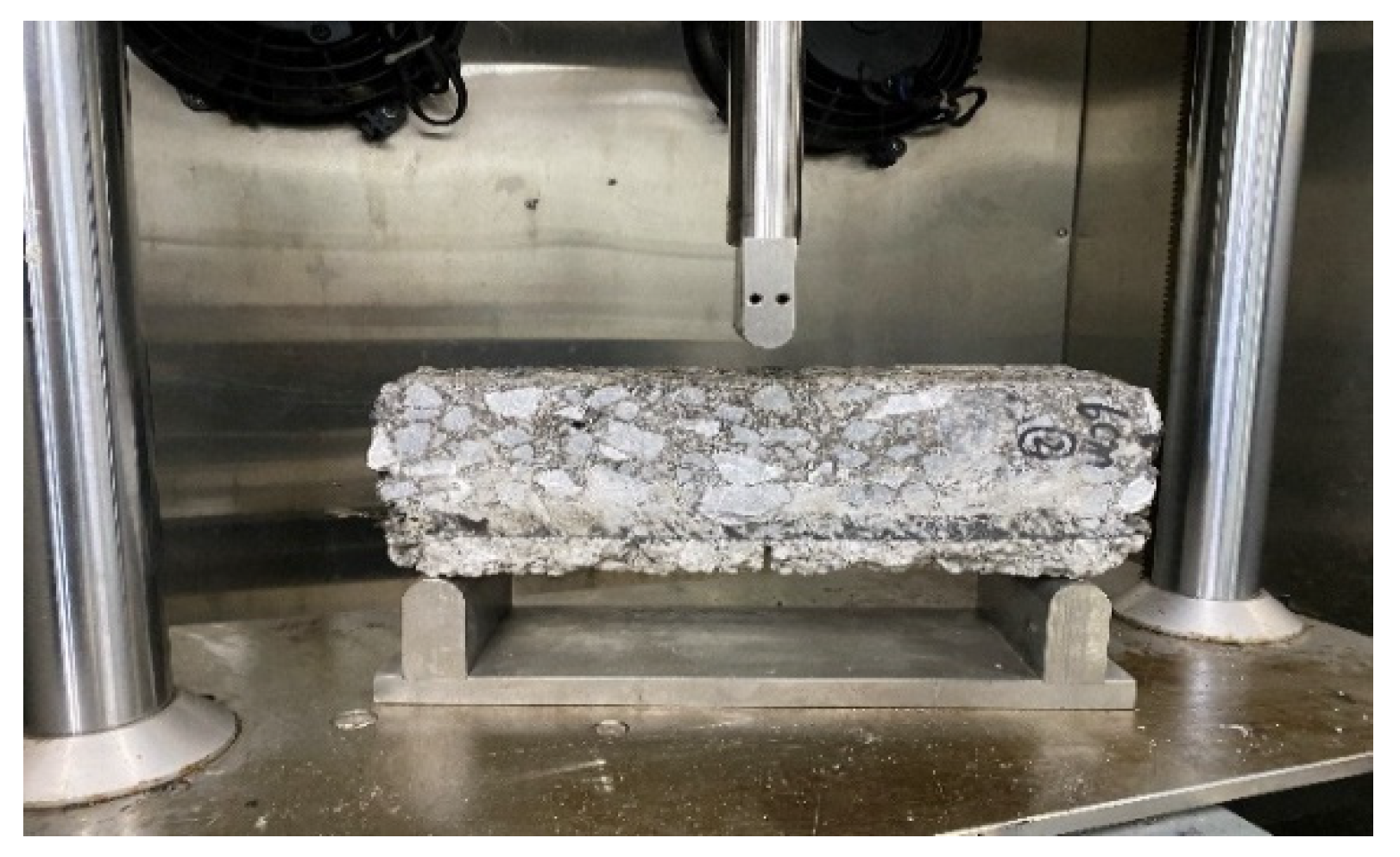
2.2.3. Preparation of Basalt Fiber Rubber Asphalt Stress-Absorbing Layer Composite Board
3. Test Methods
3.1. Raw Material Performance Test
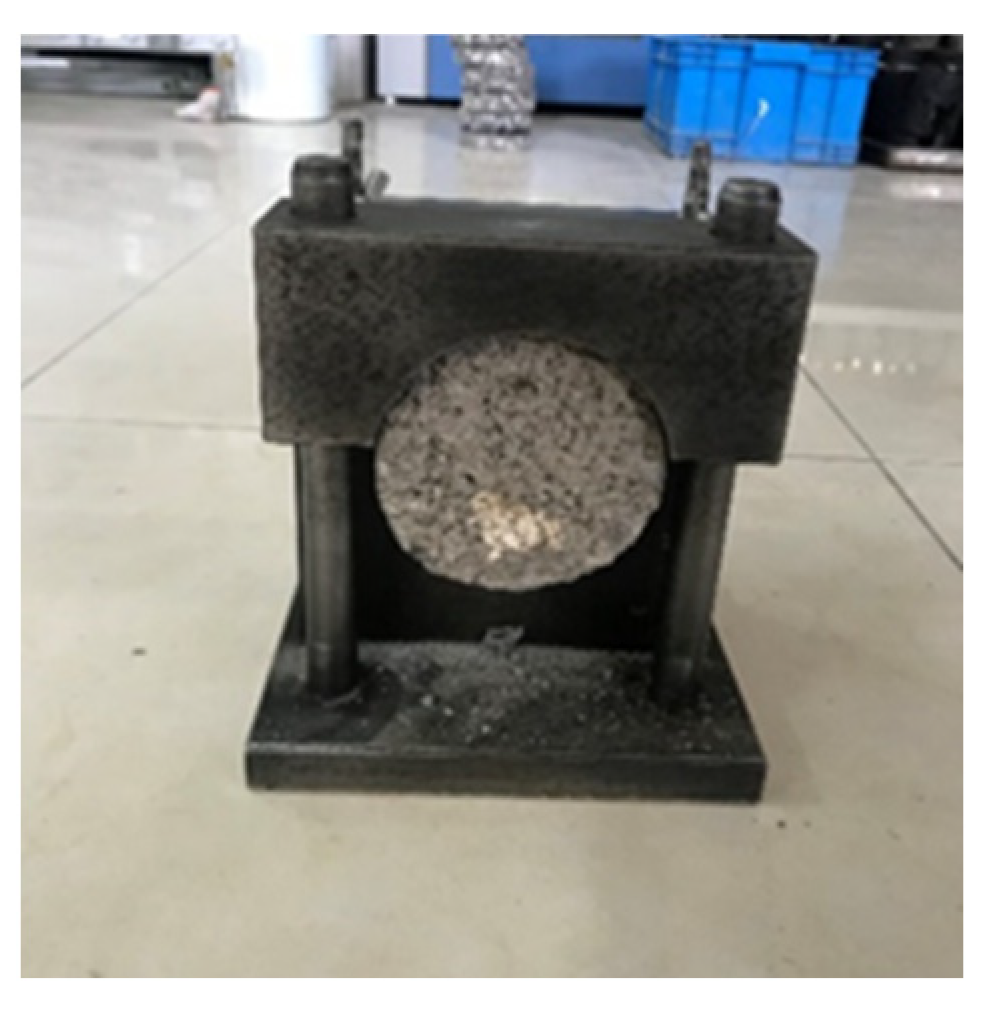
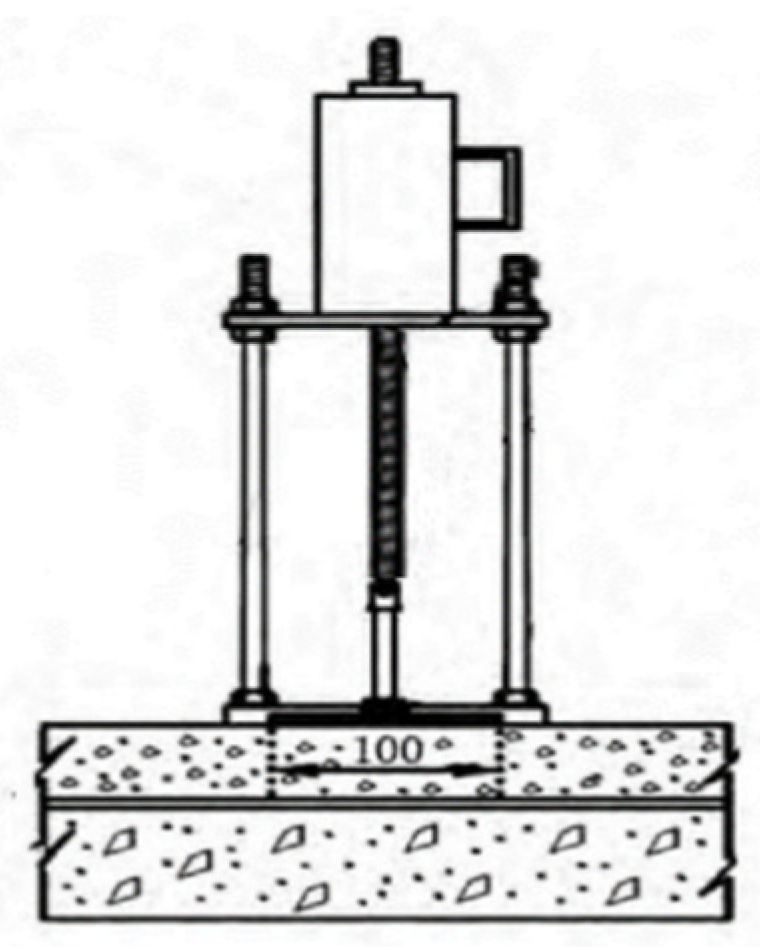
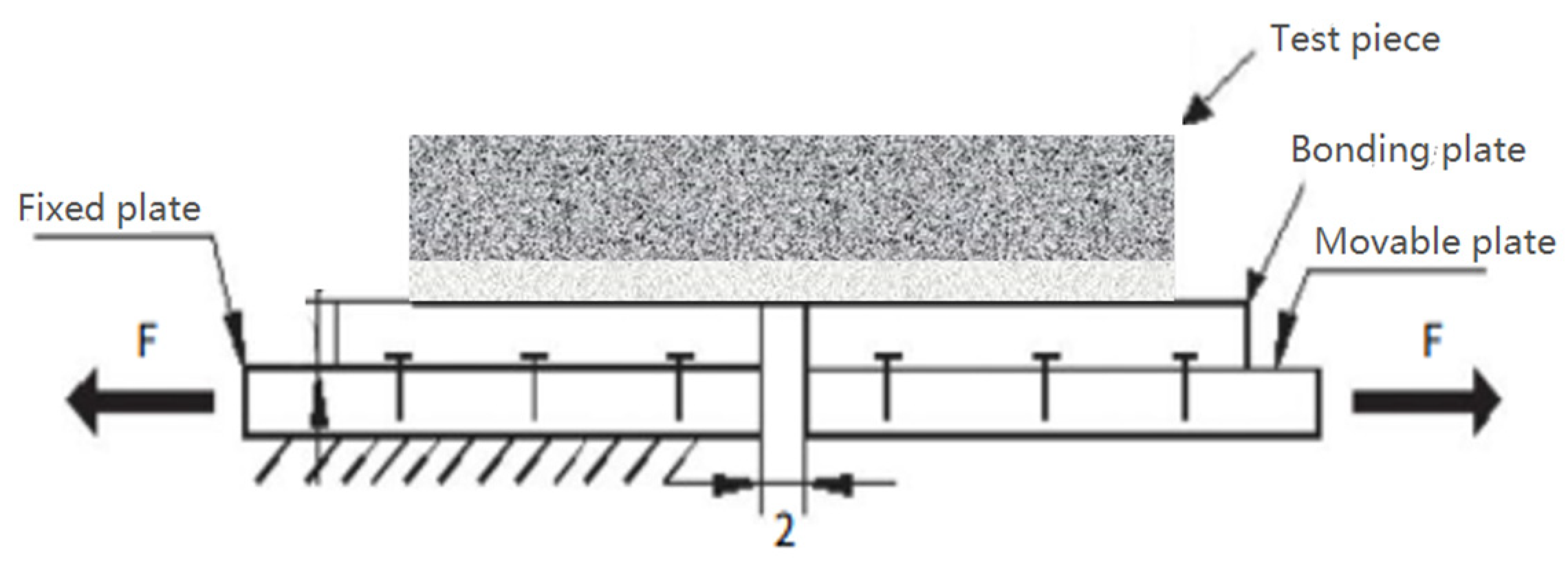
3.2. Interlayer Pull-Out Test
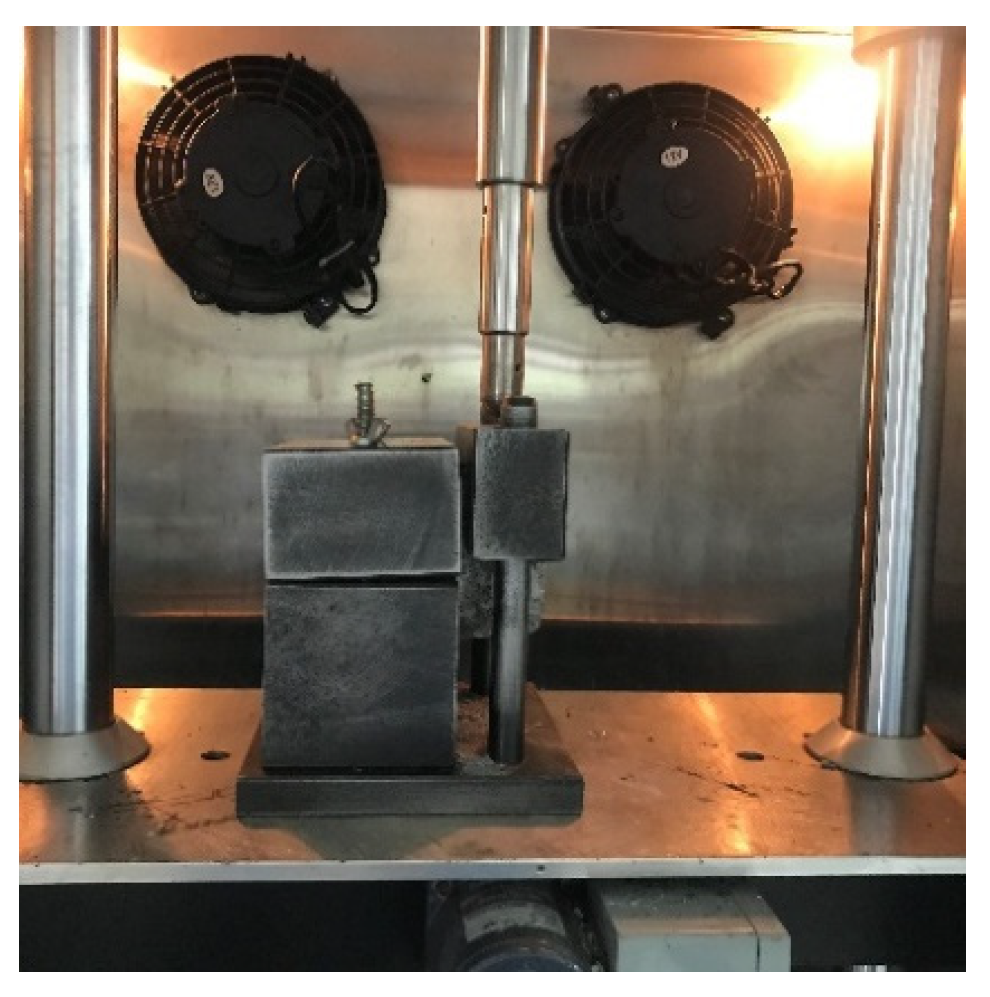
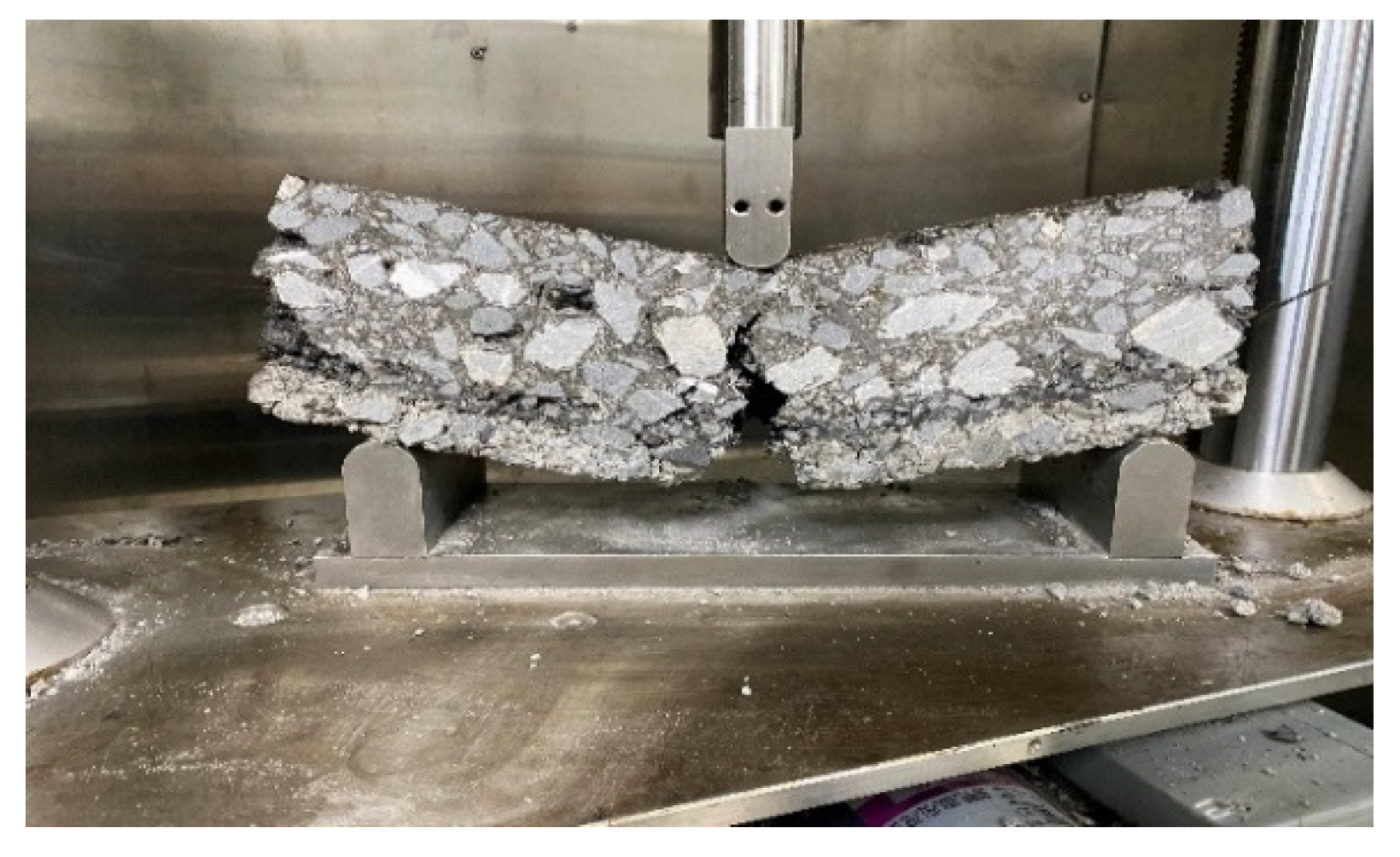
3.3. Three-Point Bending Test
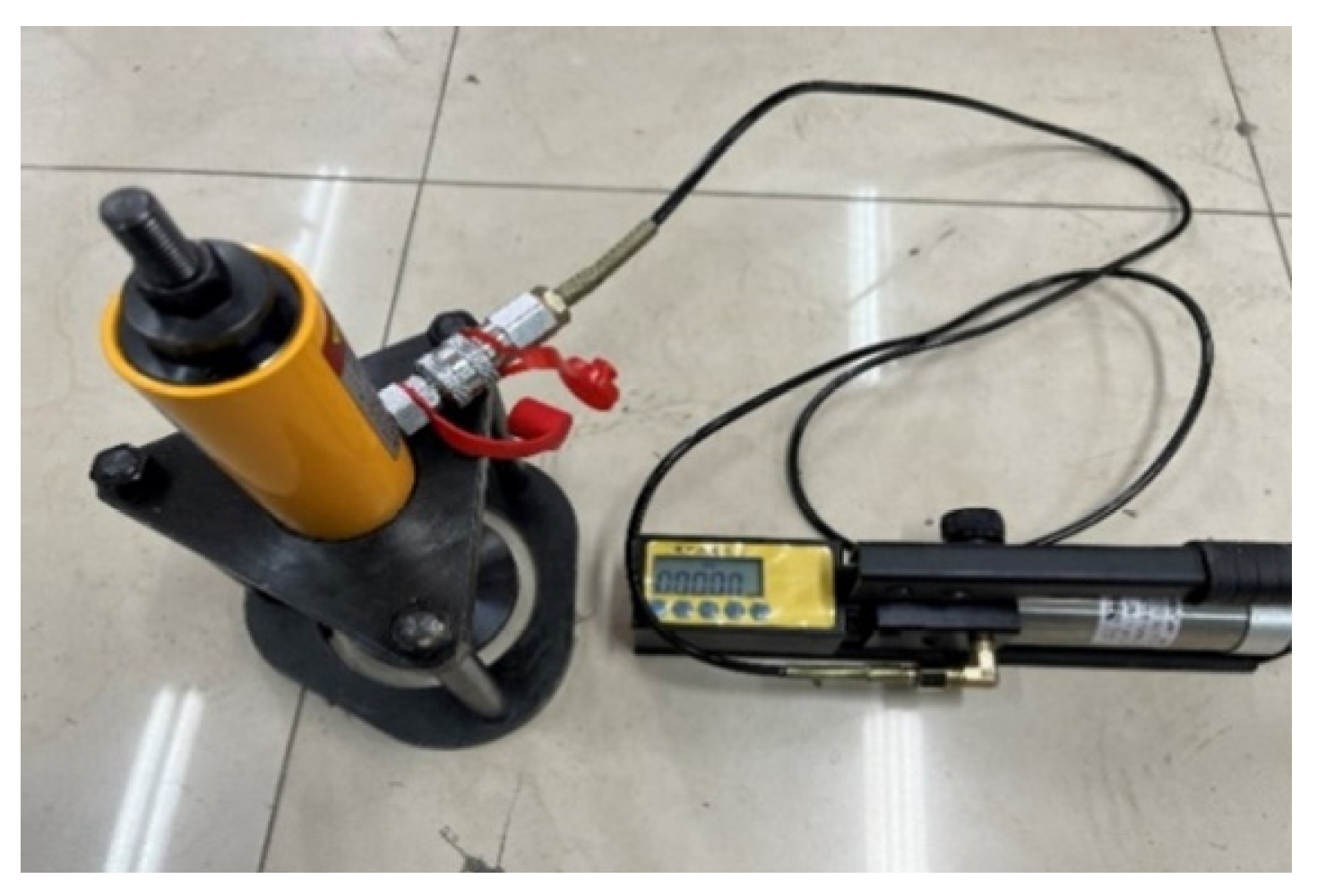
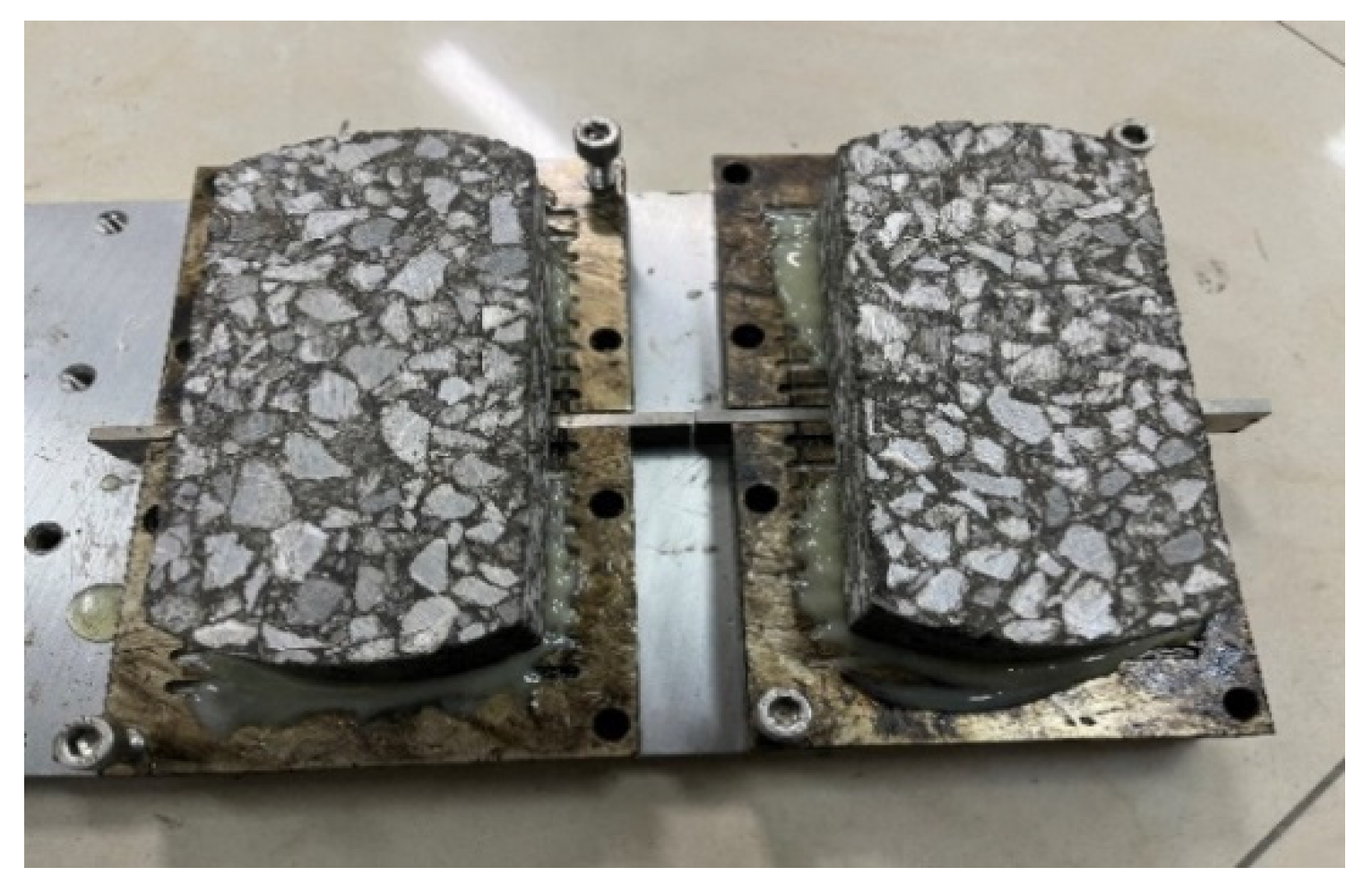
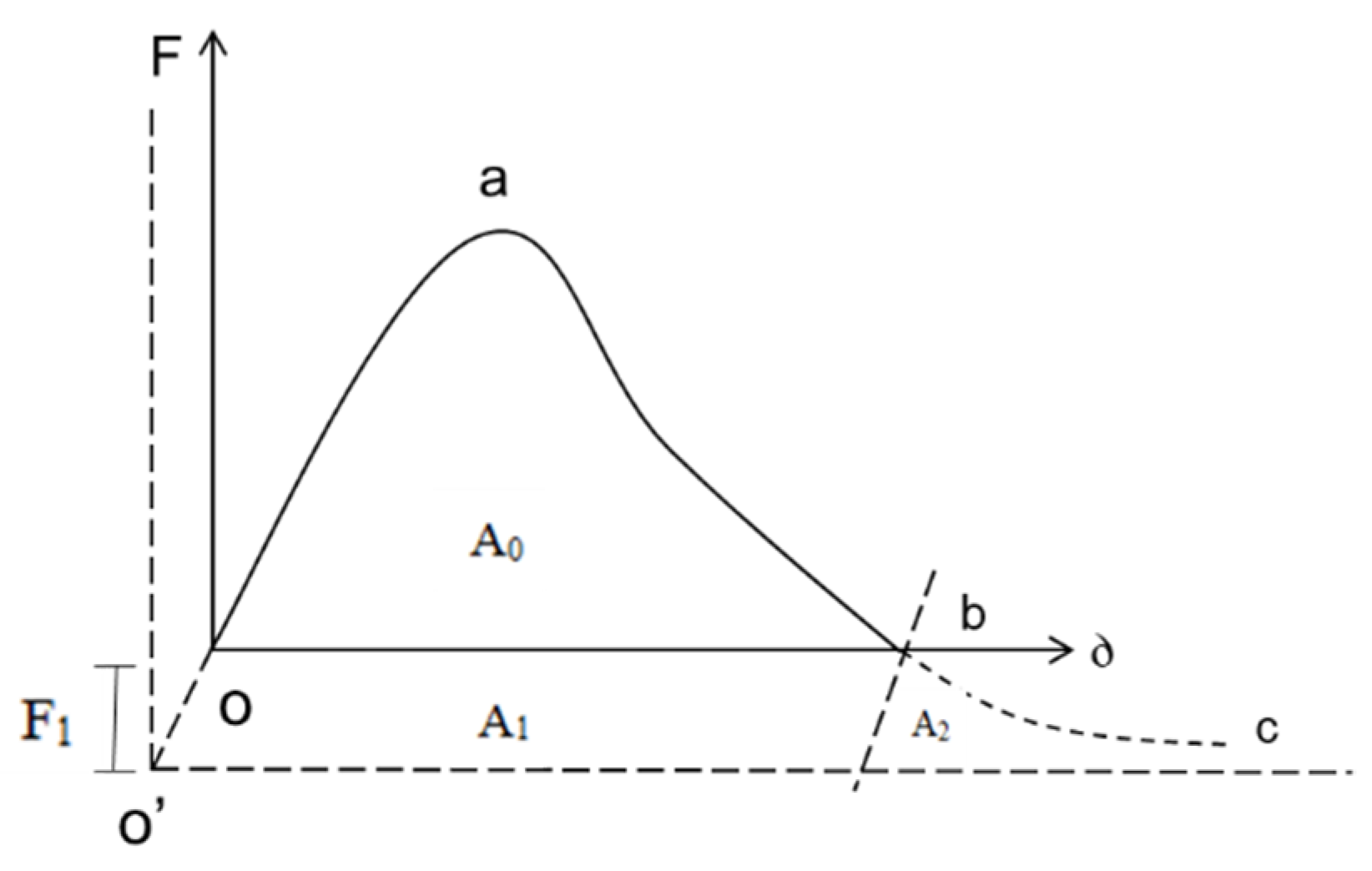
3.4. Overlay Test
4. Test Results and Analysis
4.1. Interlaminar Direct Shear Test
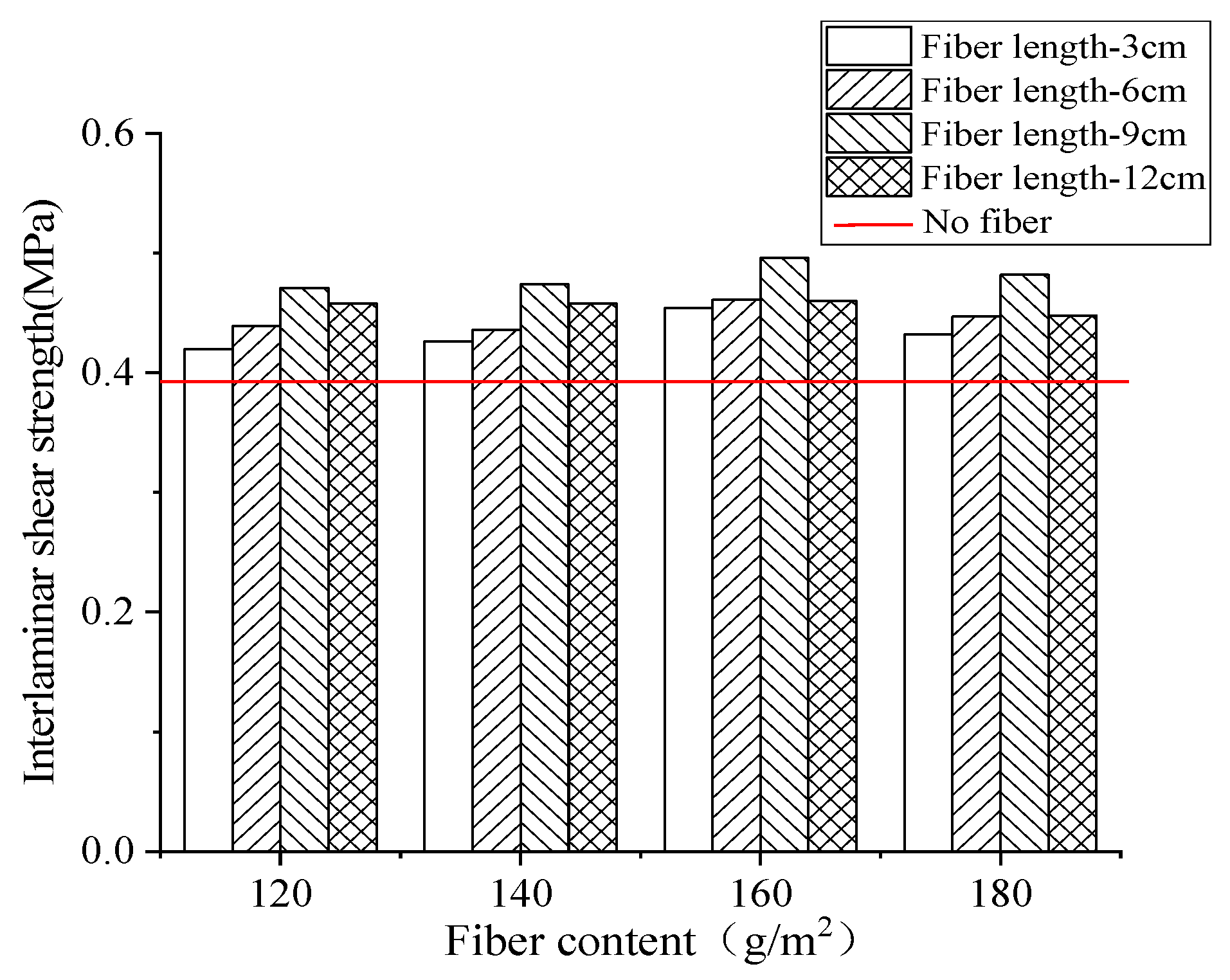
4.2. Interlayer Pull-Out Test
4.3. Three-Point Bending Test
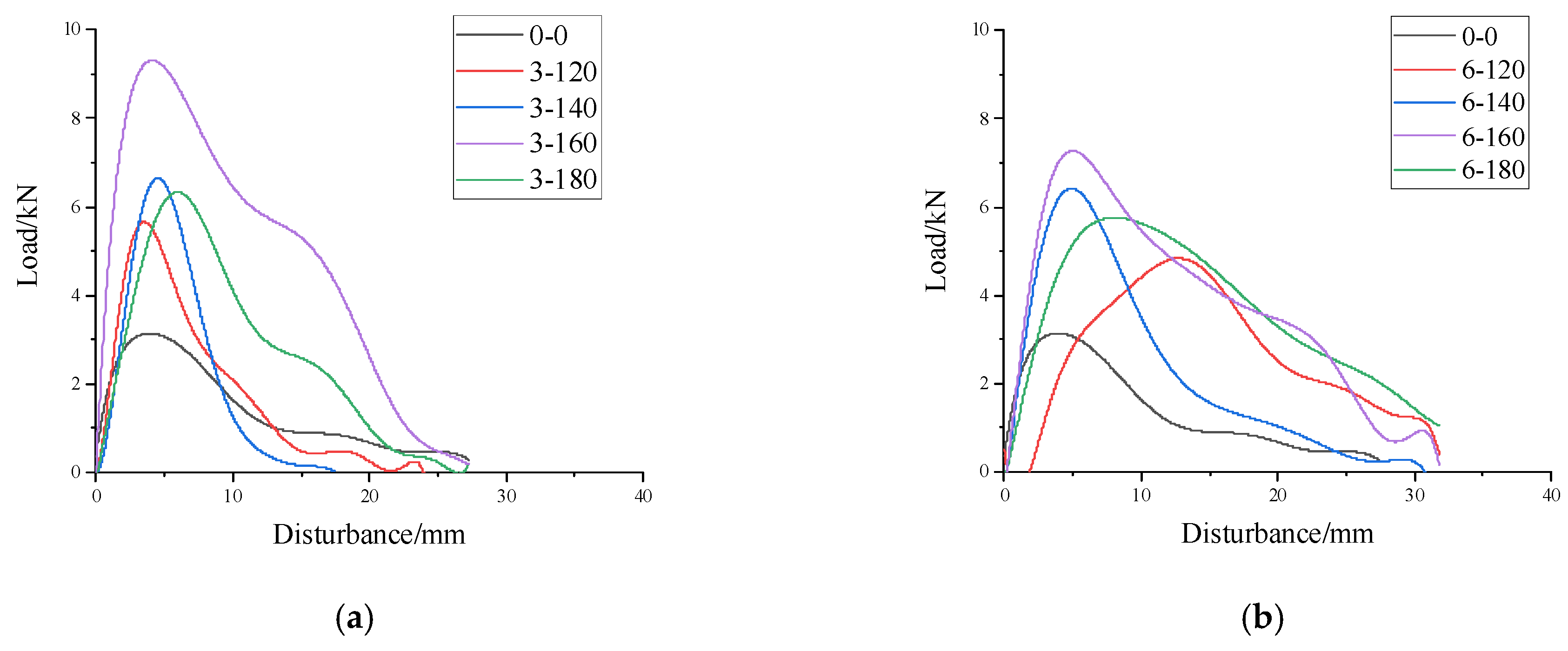
4.3.1. Test Results
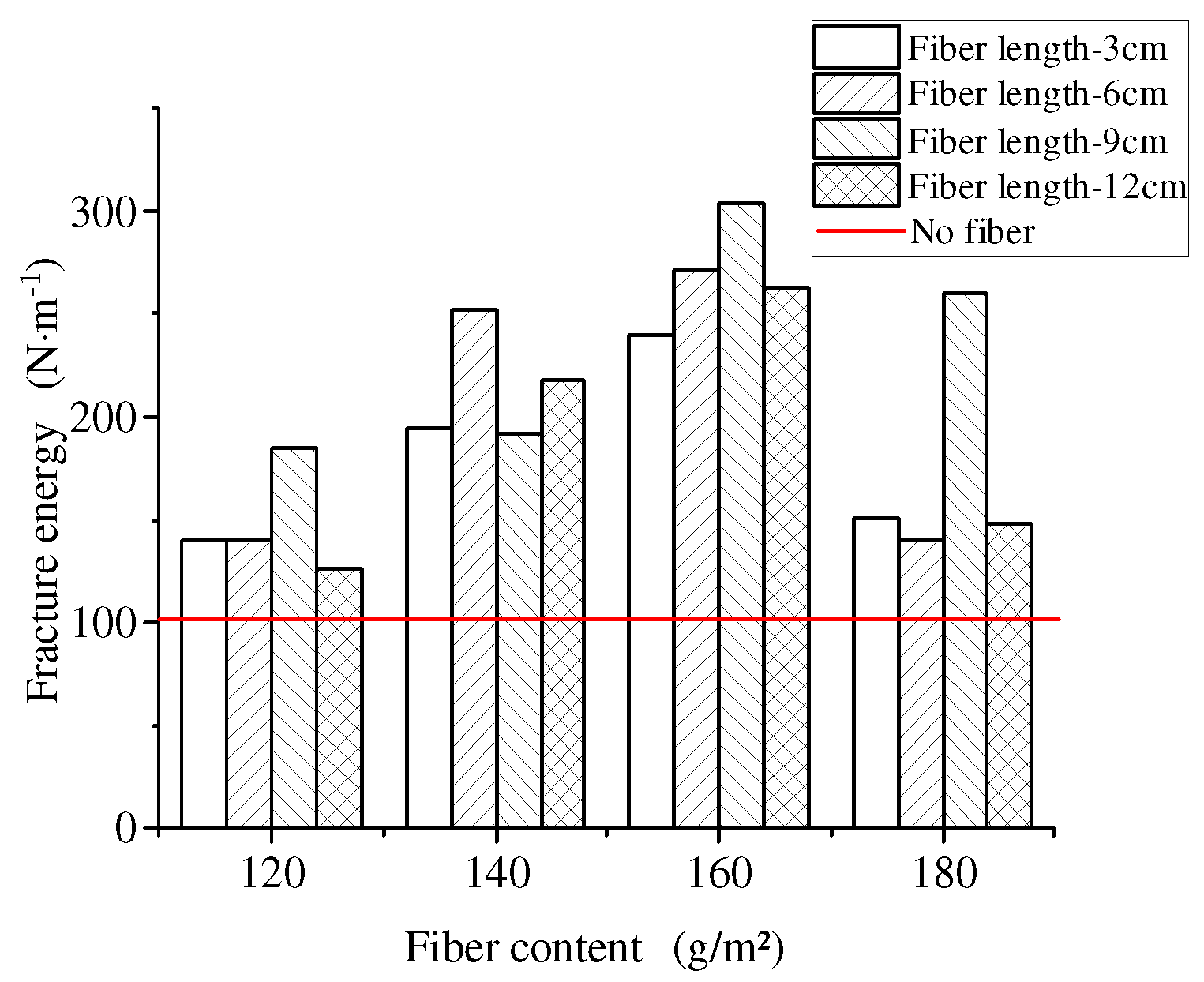
4.3.2. Effect of Basalt Fiber on Bending Fracture Energy
4.4. Overlay Test
4.4.1. Test Results
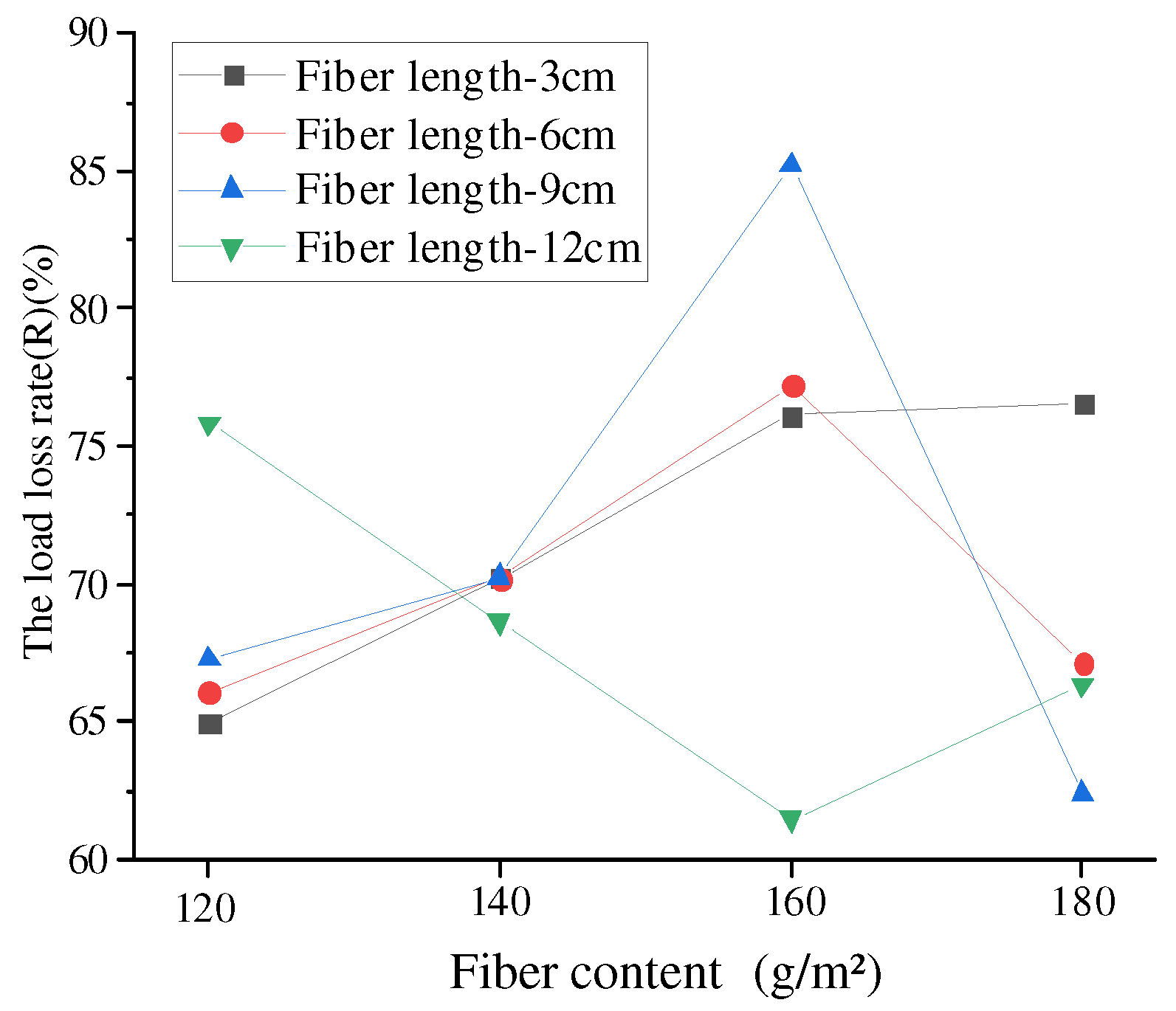
4.4.2. Effect of Basalt Fiber on Anti-Reflection Crack Performance
4.4.3. OT Test Curve Fitting
4.5. Comprehensive Engineering Analysis
4.5.1. Engineering Performance Analysis
4.5.2. Engineering Economic Analysis
5. Conclusions
- From the perspective of interlayer bonding performance, compared with the neat samples without fiber addition, the improvement in interlayer bonding strength of basalt fiber modified samples significantly achieves up to 114%, while the improvement of interlayer direct shear strength is not very significant, with a maximum reinforcement amplitude of only 20%. The reinforcement of the addition of basalt fiber mainly reflect in the improvement of the cohesion of asphalt binder rather than the interface strength.
- Based on the three-point bending test, the fracture energy of basalt fiber modified samples increases by 305.5% compared with the neat samples. Basalt fiber can enhance the anti-cracking performance some extent under one-time failure loads. Furthermore, optimal fiber content should be determined since excessive fiber will cause negative effect on the anti-cracking performance.
- Based on the overlay test, the maximum increase in fracture energy of basalt fiber-modified samples can reach up to 200.3%, compared with the neat samples. Basalt fibers possess a significant impact on the anti-reflection cracking performance under cyclic loads. Similarly, optimal fiber content should be determined since the fracture energy first increases and then decreases with an increasing fiber content.
- According to range analysis, the main factor affecting the anti-reflection cracking performance was the fiber content rather than the fiber length.
- Based on comprehensive performance and cost-effectiveness analysis, it was recommended that the basalt fiber parameter combination with the length of 9 cm and fiber content of 160 g/m2 can be used to prepare the new type of basalt fiber modified rubber asphalt stress absorption layer.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lv, S.; Yuan, J.; Peng, X.; Zhang, N.; Liu, H.; Luo, X. A structural design for semi-rigid base asphalt pavement based on modulus optimization. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 302, 124216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, S.; Guo, Y.; Xia, C.; Wang, X.; You, L.; Cabrera, M.B.; Li, J. Unified approach to characterize the strength of cement stabilized macadam subjected to different loading modes. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 265, 120143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhong, Y. Reflective crack in semi-rigid base asphalt pavement under temperature-traffic coupled dynamics using XFEM. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 214, 280–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Torre, I.; Calzada-Perez, M.A.; Vega-Zamanillo, A.; Castro-Fresno, D. Evaluation of reflective cracking in pavements using a new procedure that combine loads with different frequencies. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 75, 368–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, S.; Wu, Q.; Jiao, Y.; Du, Y. Cracking behavior of asphalt pavement with a graded gravel layer based on computational granular mechanics. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 345, 128199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Zhang, H.; Sun, W. Effect of coating optimization on performances of glass fiber geogrid for semi-rigid base asphalt pavement. Geotext. Geomembr. 2022, 50, 337–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhong, Y. Influence of tack coat on reflective cracking propagation in semi-rigid base asphalt pavement. Eng. Fract. Mech. 2019, 213, 172–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, A.; Bhuyan, M.R.; Khattak, M.J.; Zhang, Q. Mitigating reflective cracking in composite pavements through the use of a ductile concrete interlayer. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 259, 120383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Torre, I.; Calzada-Perez, M.A.; Vega-Zamanillo, A.; Castro-Fresno, D. Experimental study of the behaviour of different geosynthetics as anti-reflection cracking systems using a combined-load fatigue test. Geotext. Geomembr. 2015, 43, 345–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamora-Barraza, D.; Calzada-Pérez, M.A.; Castro-Fresno, D.; Vega-Zamanillo, A. Evaluation of anti-reflection cracking systems using geosynthetics in the interlayer zone. Geotext. Geomembr. 2011, 29, 130–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Xiao, P.; Kang, A.; Wu, Z.; Kou, C.; Ren, Z. Research on the road performance of self-adhesive basalt fiber geotextiles based on the background of long-life pavements. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 392, 131776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, F.; Li, T.; Li, X.; Li, Y.; Guo, M. Research on the Anti-Reflective Cracking Performance of a Full-Depth Asphalt Pavement. Sustainability 2021, 3, 9499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, C.; Liu, Q.; Xia, Y.; Cui, Y.; Cao, Z.; Qian, Y.; Liu, M.; Mu, C.; Wang, H. Influence of Crack Spacing/Layer Thickness Value on Reflection Crack Propagation Mechanism Under Low Temperatures. Front. Earth Sci. 2021, 9, 810964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Yan, T.; Wu, C.; Sun, X.; Wang, J.; Yuan, X. Analysis of the Fatigue Crack Propagation Process of the Stress-Absorption Layer of Composite Pavement Based on Reliability. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 2093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, F.-L.; Lytton, R.L.; Lee, S. Prediction of reflection cracking in hot-mix asphalt overlays. Transp. Res. Rec. 2010, 2155, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanzadeh, R.; Tanzadeh, J.; Honarmand, M.; Tahami, S.A. Experimental study on the effect of basalt and glass fibers on behavior of open-graded friction course asphalt modified with nano-silica. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 212, 467–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; He, Z.; Li, D.; Xu, H.; Kong, L. Experimental Study on Basalt Fiber Crack Resistance of Asphalt Concrete Based on Acoustic Emission. Materials 2021, 14, 4096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, B.; Meng, W.; Xia, J.; Xiao, P. Influence of Basalt Fibers on the Crack Resistance of Asphalt Mixtures and Mechanism Analysis. Materials 2021, 15, 744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, R.; Li, Y. Effect of warm mix rubber modified asphalt mixture as stress absorbing layer on anti-crack performance in cold region. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 251, 118985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Gao, P.; Zhang, Z.; Pan, Y. Experimental study of the performance of a stress-absorbing waterproof layer for use in asphalt pavements on bridge decks. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 254, 119290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Han, L.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Gao, T.; Gao, T. Mechanical analysis of preventing reflection cracks based on stress absorbing layer. Adv. Civ. Eng. 2022, 2022, 8016215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, D.; Wang, S.; Sun, P.; Huang, C. Study on anti-crack effect of semi-rigid base pavement with stress absorbing layer. J. Eng. Appl. Sci. 2023, 70, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norambuena-Contreras, J.; Gonzalez-Torre, I.; Fernandez-Arnau, D.; Lopez-Riveros, C. Mechanical damage evaluation of geosynthetics fibres used as anti-reflection cracking systems in asphalt pavements. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 109, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, P.; Wang, H. Finite element analysis of thermal-in duced reflective cracking in composite pavement with mitigation strategies. Eng. Fract. Mech. 2022, 266, 108396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Gu, Q.; Kang, A.; Ding, X.; Ma, T. Characterization of mesoscale fracture damage of asphalt mixtures with basalt fiber by environmental scanning electron microscopy. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 344, 128188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Q.; Kang, A.; Li, B.; Xiao, P.; Ding, H. Effect of fiber characteristic parameters on the high and low temperature rheological properties of basalt fiber modified asphalt mortar. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2022, 17, e01247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Pei, Z.; Xiao, P.; Lou, K.; Wu, X. Influence of fiber-asphalt interface property on crack resistance of asphalt mixture. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2022, 17, e01703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Shi, F.; Cao, P.; Liu, K. The fracture toughness analysis on the basalt fiber reinforced asphalt concrete with prenotched three-point bending beam test. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2022, 16, e01079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, T.; Wang, L. Optimize the design by evaluating the performance of asphalt mastic reinforced with different basalt fiber lengths and contents. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 363, 129698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, K.; Xiao, P.; Tang, Q.; Wu, Y.; Wu, Z.; Pan, X. Research on the micro-nano characteristic of basalt fiber and its impact on the performance of relevant asphalt mastic. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 318, 126048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, K.; Xiao, P.; Kang, A.; Wu, Z.; Li, B.; Lu, P. Performance evaluation and adaptability optimization of hot mix asphalt reinforced by mixed lengths basalt fibers. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 292, 123373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Liu, X.; Liu, Z. Interlaminar shear fatigue and damage characteristics of asphalt layer for asphalt overlay on rigid pavement. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 68, 341–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudarsanan, N.; Fonte, B.R.; Kim, Y.R. Application of time-temperature superposition principle to pull-off tensile strength of asphalt tack coats. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 262, 120798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noorvand, H.; Mobasher, B.; Underwood, S.; Kaloush, K. Development of an analytical framework for evaluation of critical fiber length in asphalt concrete with a fiber pullout test. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 360, 129561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.; Li, J.; Cai, D.; Cheng, H.; Xiao, F. Characterizing thermal fatigue behaviors of asphalt concrete waterproofing layer in high-speed railway using customized overlay test. Int. J. Fatigue 2022, 165, 107176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Oh, J.; Naik, B.; Simate, G.S.; Walubita, L.F. Laboratory characterization of cracking-resistance potential of asphalt mixes using overlay tester. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 70, 130–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walubita, L.F.; Faruk, A.N.; Alvarez, A.E.; Scullion, T. The Overlay Tester (OT): Using the Fracture Energy Index concept to analyze the OT monotonic loading test data. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 40, 802–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gou, H.; Zhu, H.; Zhou, H.; Yang, Z. Reinforcement mechanism of orientally distributed steel fibers on ultra-high-performance concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 281, 122646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walubita, L.F.; Fuentes, L.; Lee, S.I.; Guerrero, O.; Mahmoud, E.; Naik, B.; Simate, G.S. Correlations and preliminary validation of the laboratory monotonic overlay test (OT) data to reflective cracking performance of in-service field highway sections. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 267, 121029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
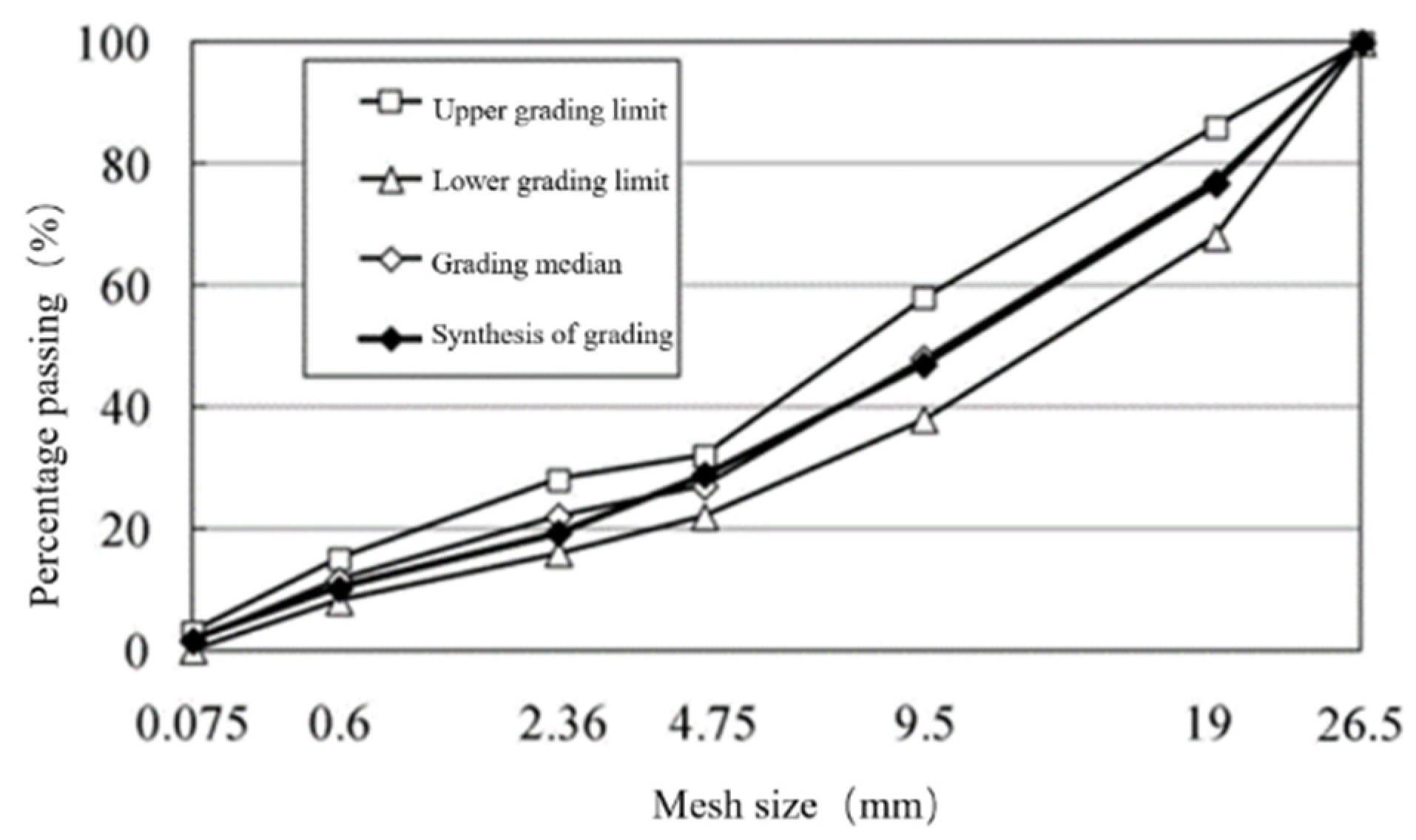
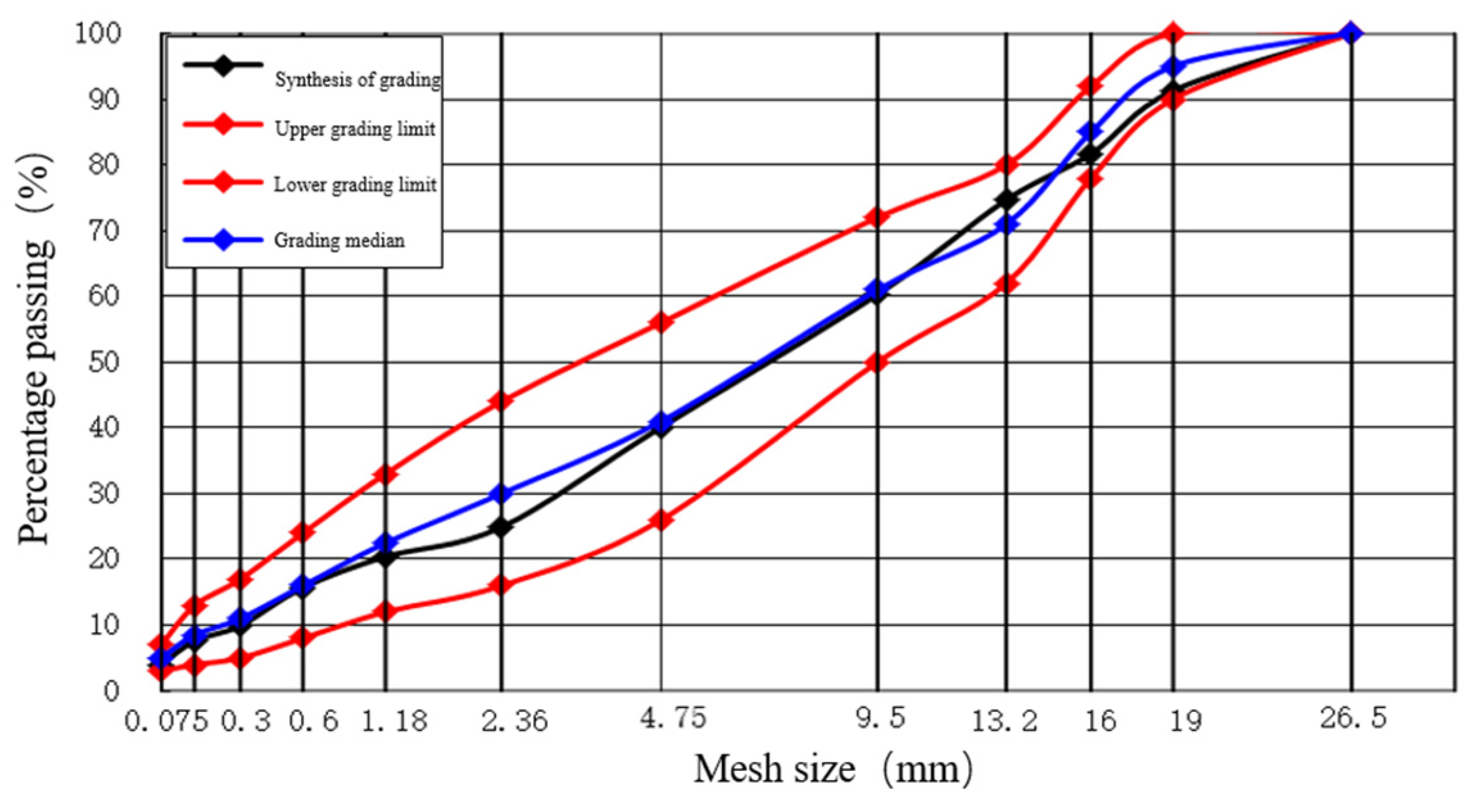
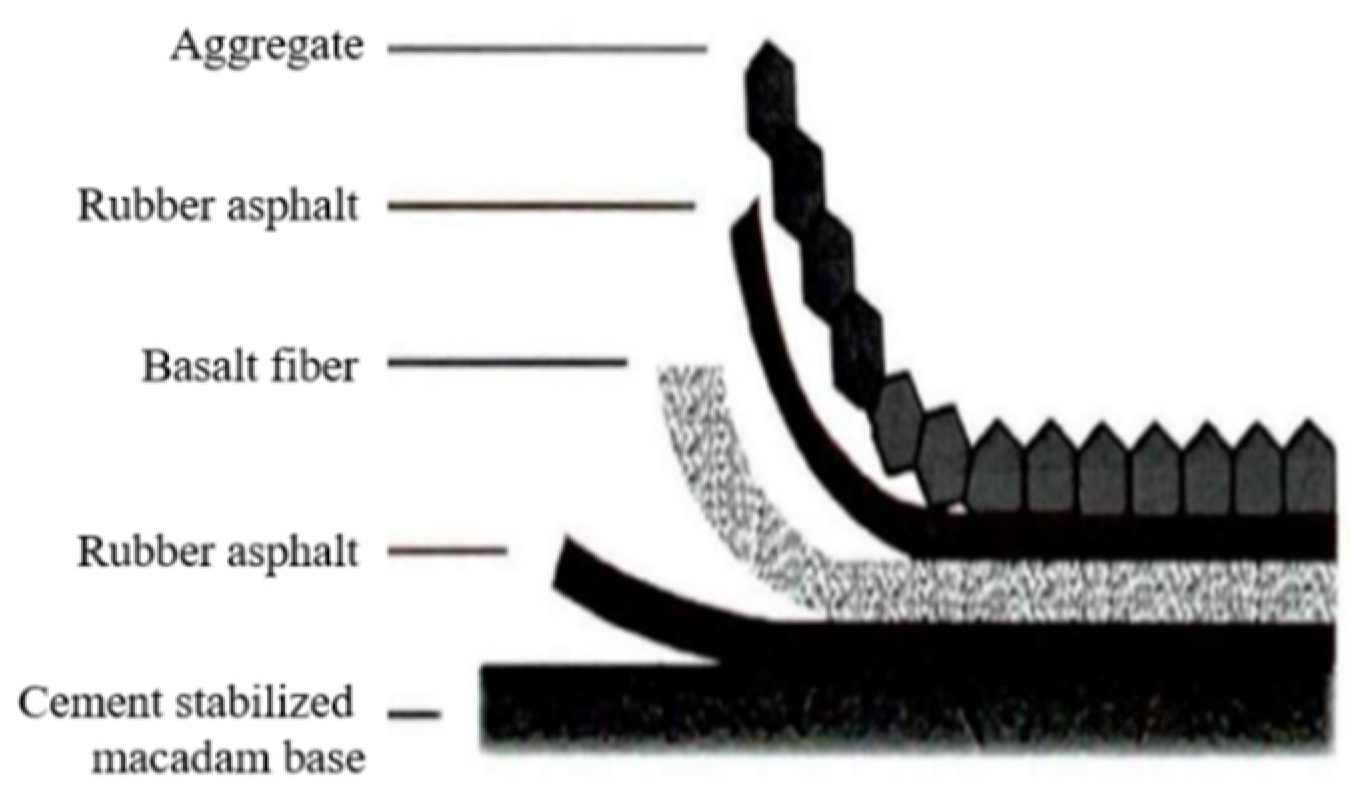








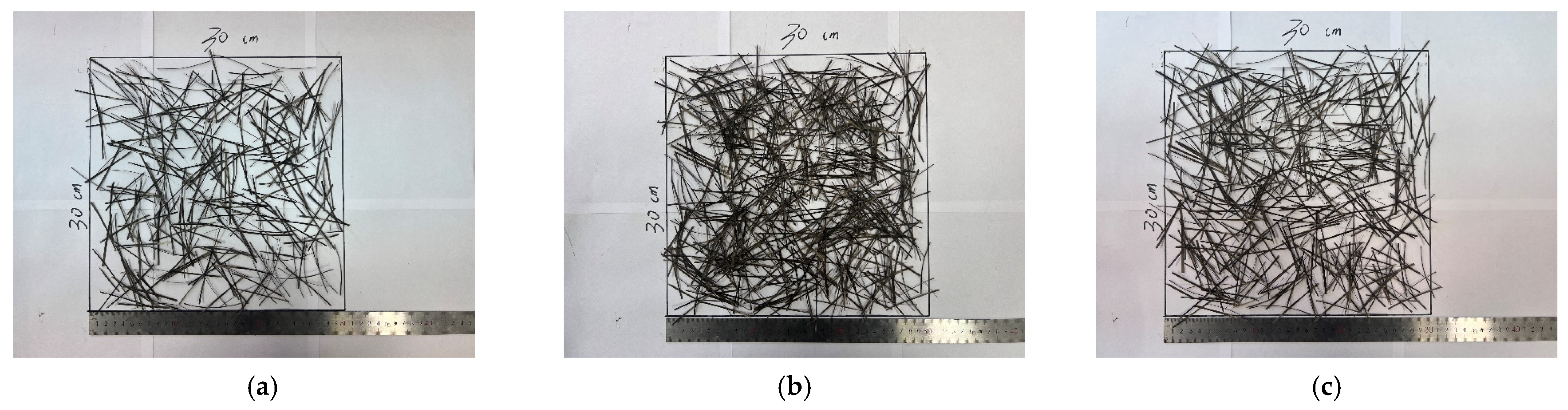






| Types | Apparent Relative Density | Relative Density of Gross Volume | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Limestone | 1# (19–13.2 mm) | 2.724 | 2.683 |
| 2# (13.2–2.36 mm) | 2.715 | 2.695 | |
| Basalt | 3# (4.75–0.15 mm) | 2.975 | 2.888 |
| 4# (0.15–0.075 mm) | 2.970 | 2.863 | |
| Test Index | Test Result | Specification Requirements | Test Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| Crushing value/% | 14 | ≤26 | T0316 |
| Los Angeles abrasion value/% | 16 | ≤28 | T0317 |
| Apparent relative density/g/m2 | 2.883 | ≥2.6 | T0304 |
| Water absorption/% | 0.7 | ≤2 | T0305 |
| Adhesion to asphalt/grade | 5 | ≥4 | T0616 |
| Water washing method < 0.075 particle content/% | 0.4 | ≤1 | T0310 |
| Test Index | Test Result | Specification Requirements | Test Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| Apparent relative density/g/m2 | 2.762 | ≥2.5 | T0330 |
| Firmness (>0.3)/% | 9 | ≤12 | T0340 |
| Sand equivalent/% | 66 | ≥60 | T0334 |
| Test Index | Test Result | Specification Requirements | Test Method | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Penetration (25 °C)/0.1 mm | 44 | 30~60 | T0604 | |
| Penetration index (PI) | 0.8 | ≥0 | T0604 | |
| Softening point/°C | 68 | ≮60 | T0606 | |
| Ductility (5 cm/min, 5 °C)/cm | 9 | ≮5 | T0605 | |
| Elastic recovery (25 °C)/% | 86 | ≮60 | T0662 | |
| Segregation (Softening point difference)/°C | 1.8 | ≯3 | T0661 | |
| Residue after RTFOT | Quality change/% | −0.06 | ±1.0 | T0610 |
| Penetration ratio/% | 76 | ≮60 | T0604 | |
| 15 °C residual ductility/cm | 28 | ≮10 | T0605 | |
| Test Index | Specification Requirements | Test Result |
|---|---|---|
| Elongation at break/% | ≤3.1 | 2.71 |
| Breaking strength/MPa | ≥1200 | 2218 |
| Oil absorption rate/% | ≥50 | 52 |
| Heat resistance, breaking strength retention/% | ≥85 | 93 |
| Alkali resistance, breaking strength retention/% | ≥75 | 89 |
| Length (cm)–Content (g/m2) | Fitting Formula | R2 | a | b |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0–0 | 0.9783 | 1.8246 | 0.6364 | |
| 3–120 | 0.9657 | 1.364 | 0.4644 | |
| 3–140 | 0.9816 | 1.266 | 0.4732 | |
| 3–160 | 0.976 | 0.8547 | 0.3558 | |
| 3–180 | 0.9872 | 1.343 | 0.419 | |
| 6–120 | 0.9693 | 1.2139 | 0.4738 | |
| 6–140 | 0.9693 | 1.4131 | 0.4121 | |
| 6–160 | 0.9859 | 0.9539 | 0.3162 | |
| 6–180 | 0.9739 | 1.3 | 0.3312 | |
| 9–120 | 0.9869 | 1.3307 | 0.3503 | |
| 9–140 | 0.9554 | 1.157 | 0.287 | |
| 9–160 | 0.9865 | 0.6807 | 0.131 | |
| 9–180 | 0.9782 | 1.4184 | 0.175 | |
| 12–120 | 0.9782 | 1.5192 | 0.431 | |
| 12–140 | 0.9861 | 1.762 | 0.412 | |
| 12–160 | 0.9713 | 1.389 | 0.373 | |
| 12–180 | 0.9725 | 1.837 | 0.427 |
| Performance Index | Fiber Length | Fiber Content | Average Value of Test Data | Increase Range Compared with That without Fiber |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Interlaminar shear strength | 9 cm | 160 g/m2 | 0.496 | 25.2% |
| Interlayer bonding strength | 0.669 | 114.4% | ||
| Bending fracture energy | 20,422.454 | 305.5% | ||
| Total breaking energy | 303.405 | 200.2% |
| Project | Pavement Layer | Pavement Plan | Gate Treatment Plan |
|---|---|---|---|
| Double Layer Cover Scheme | Milling and Laying Double Layers + Cover Scheme | ||
| Pavement Structure Design Drawing | 1 | Overlay 4 cm SMA-13 (PG76-22 + 3‰ Anti stripping agent) | Overlay 4 cm modified asphalt SMA-13 (PG76-22 + 3‰ Anti stripping agent) |
| 2 | Pave 6 cm modified asphalt high modulus material | Milling and laying back 10 cm modified asphalt Sup-20 (+3‰ basalt fiber) | |
| 3 | Rubber asphalt stress absorption layer | Rubber asphalt stress absorption layer | |
| 4 | Original surface layer | Original surface layer | |
| Applicable road section | K284 + 398~K286 + 762 | Service area runs through lanes and gates | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shen, C.; Wu, Z.; Xiao, P.; Kang, A.; Wang, Y. Experimental Research on the Anti-Reflection Crack Performance of Basalt Fiber Modified Rubber Asphalt Stress-Absorbing Layer. Materials 2024, 17, 2013. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17092013
Shen C, Wu Z, Xiao P, Kang A, Wang Y. Experimental Research on the Anti-Reflection Crack Performance of Basalt Fiber Modified Rubber Asphalt Stress-Absorbing Layer. Materials. 2024; 17(9):2013. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17092013
Chicago/Turabian StyleShen, Cheng, Zhengguang Wu, Peng Xiao, Aihong Kang, and Yangbo Wang. 2024. "Experimental Research on the Anti-Reflection Crack Performance of Basalt Fiber Modified Rubber Asphalt Stress-Absorbing Layer" Materials 17, no. 9: 2013. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17092013
APA StyleShen, C., Wu, Z., Xiao, P., Kang, A., & Wang, Y. (2024). Experimental Research on the Anti-Reflection Crack Performance of Basalt Fiber Modified Rubber Asphalt Stress-Absorbing Layer. Materials, 17(9), 2013. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17092013




