Optimization of a Ge2Sb2Te5-Based Electrically Tunable Phase-Change Thermal Emitter for Dynamic Thermal Camouflage
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
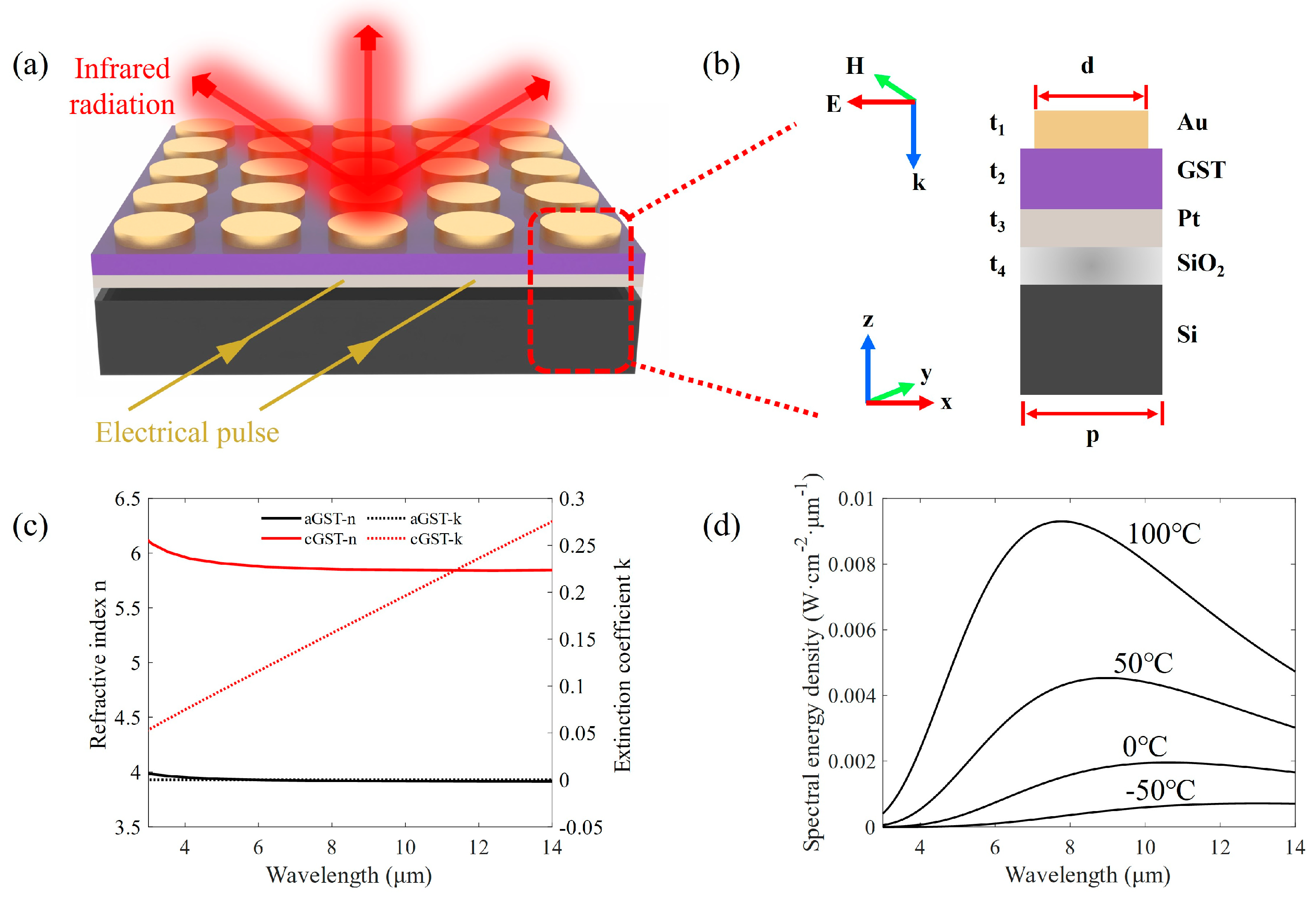
2.1. Materials and Structures
2.2. Emissivity and Radiation Intensity
2.3. Simulation Modeling
3. Results and Discussion
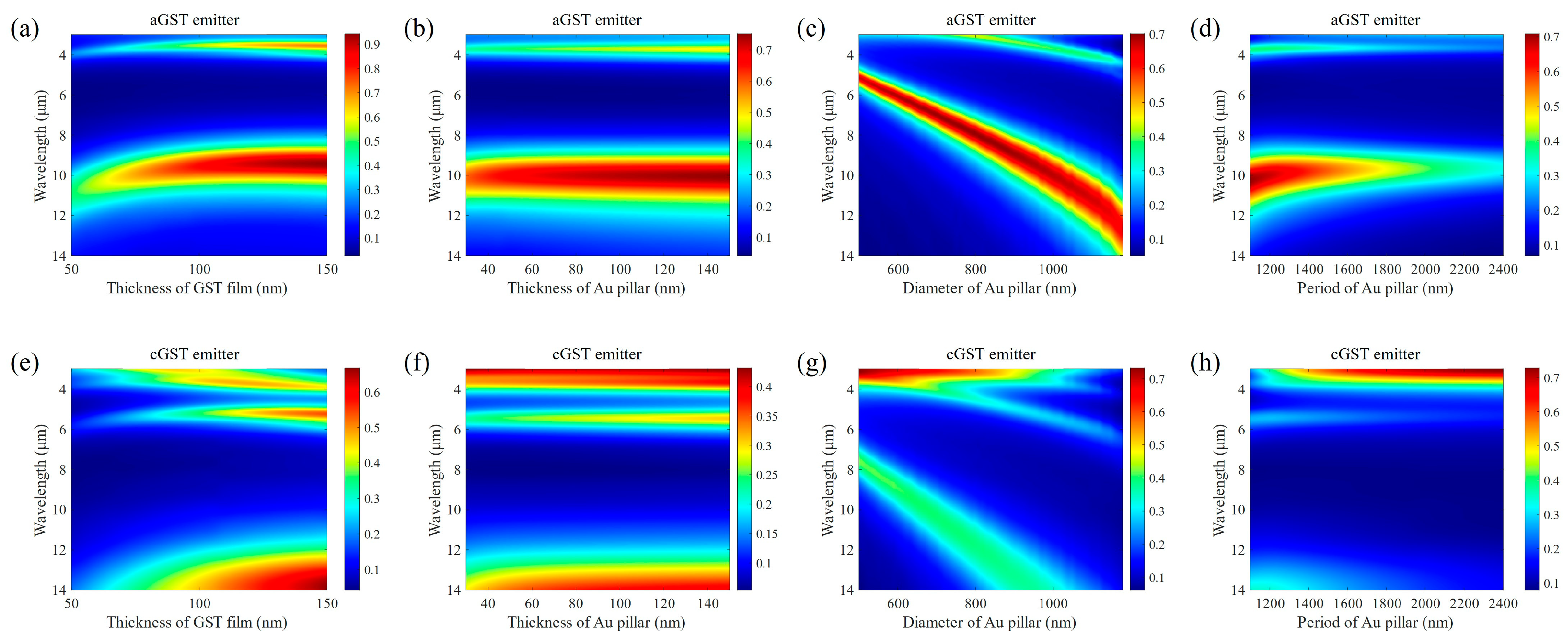
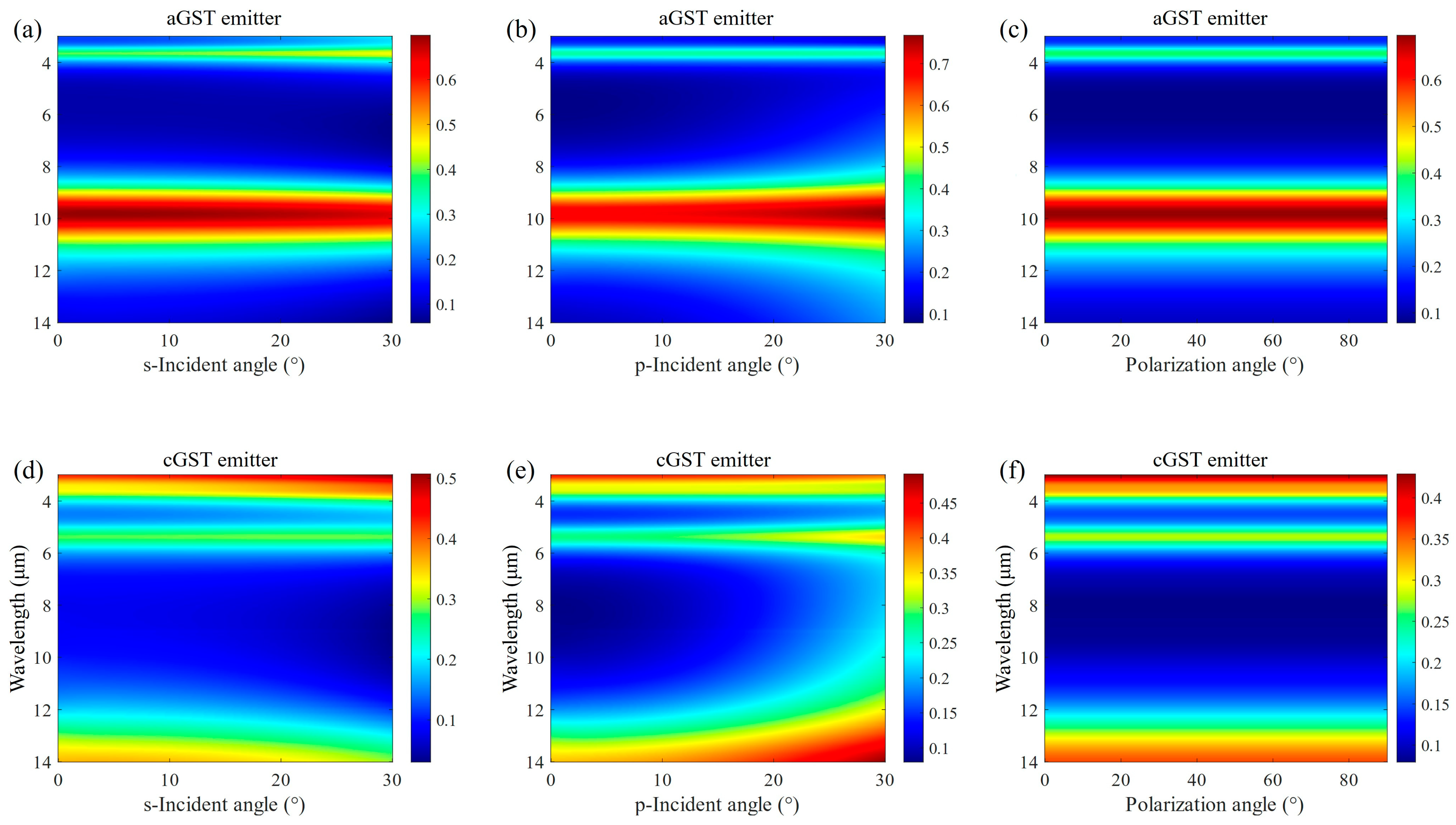
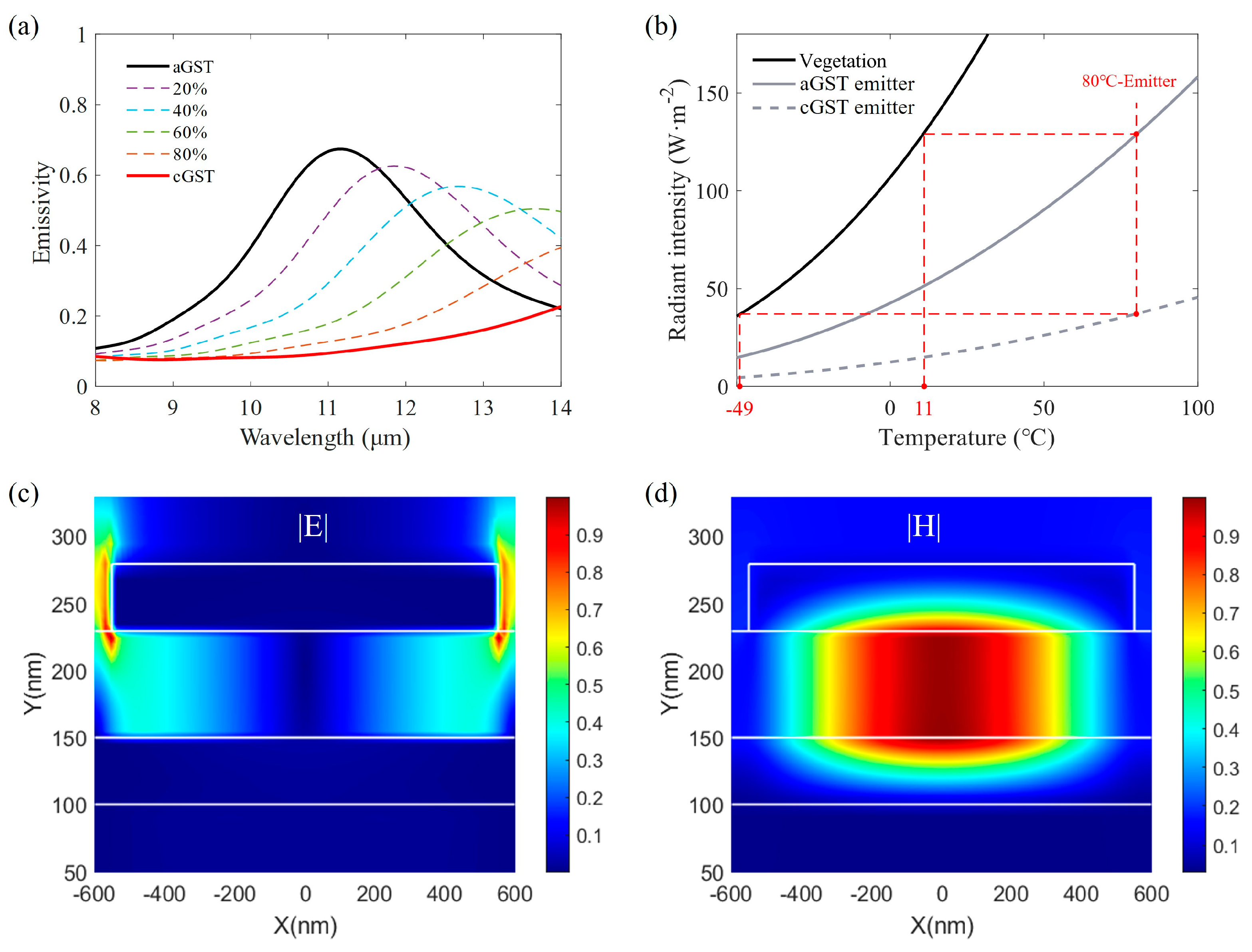
3.1. Optical Simulation
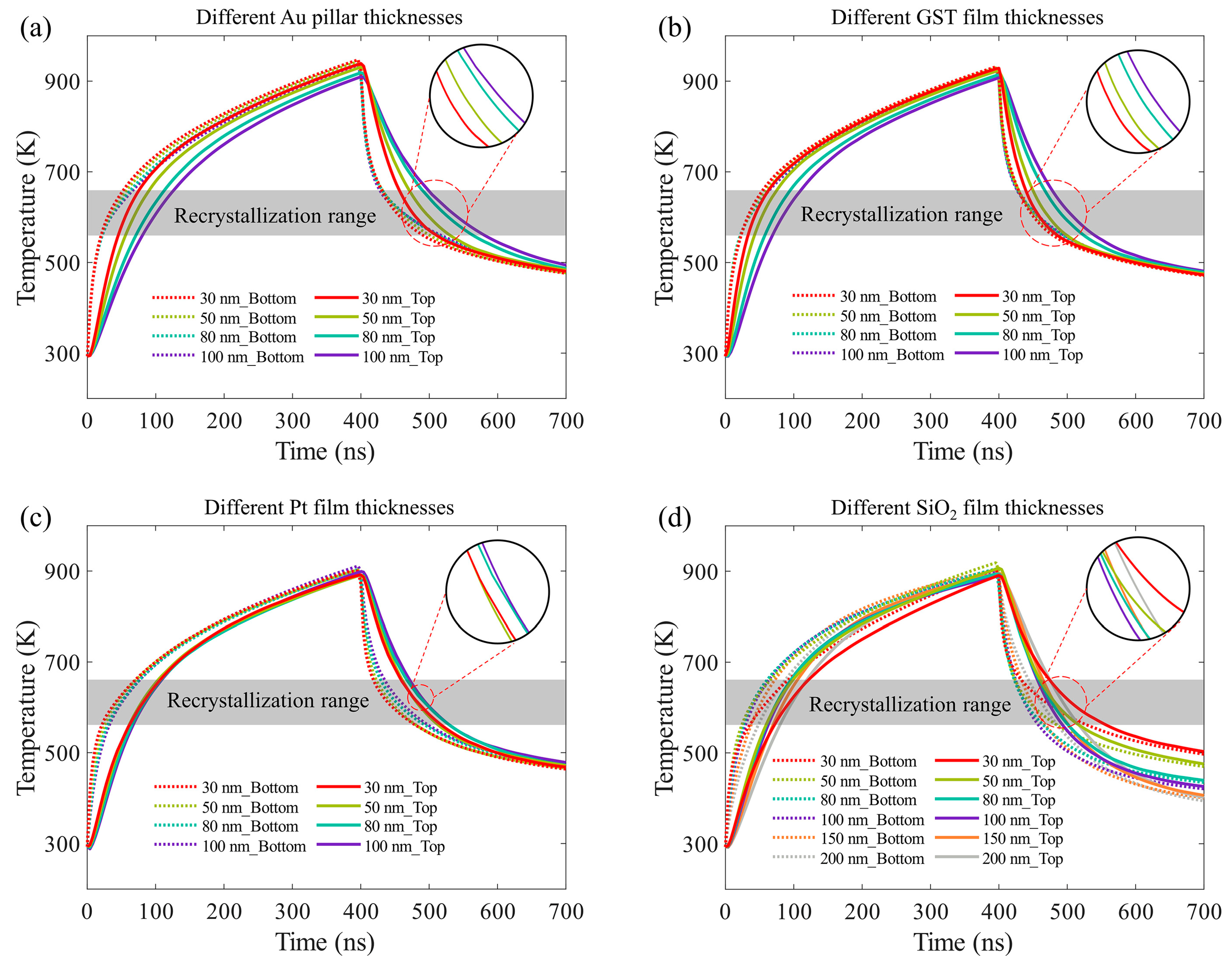
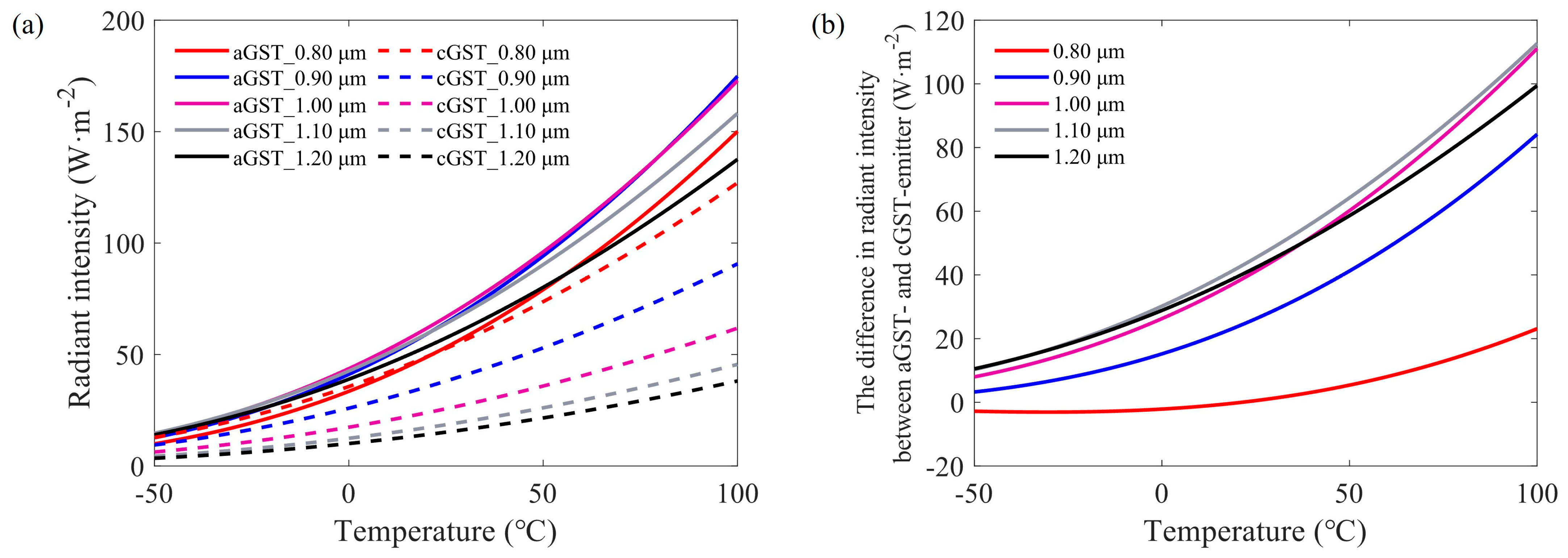
3.2. Thermal Simulation
3.3. Thermal Camouflage Application
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fu, L.C.; He, Y.M.; Zheng, J.J.; Hu, Y.X.; Xue, J.Y.; Li, S.; Ge, C.Y.; Yang, X.K.; Peng, M.; Li, K.H.; et al. TexSe1–x Photodiode Shortwave Infrared Detection and Imaging. Adv. Mater. 2023, 35, e2211522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martyniuk, P.; Rogalski, A. Van der Waals two-color infrared detection. Light-Sci. Appl. 2022, 11, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, R.; Xi, W.; Liu, Y.; Tang, K.; Song, J.; Luo, X.; Wu, J.; Qiu, C. Thermal camouflaging metamaterials. Mater. Today 2021, 45, 120–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, J.; Lee, N.; Kim, T.; Chang, I.; Nam, J.; Cho, H.H. Multiresonant Selective Emitter with Enhanced Thermal Management for Infrared Camouflage. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2024, 16, 15416–15425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buhara, E.; Ghobadi, A.; Khalichi, B.; Kocer, H.; Ozbay, E. Mid-infrared adaptive thermal camouflage using a phase-change material coupled dielectric nanoantenna. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2021, 54, 265105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raman, A.P.; Anoma, M.A.; Zhu, L.X.; Rephaeli, E.; Fan, S.H. Passive radiative cooling below ambient air temperature under direct sunlight. Nature 2014, 515, 540–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ono, M.; Chen, K.F.; Li, W.; Fan, S.H. Self-adaptive radiative cooling based on phase change materials. Opt. Express 2018, 26, A777–A787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandal, J.; Yang, Y.; Yu, N.; Raman, A.P. Paints as a scalable and effective radiative cooling technology for buildings. Joule 2020, 4, 1350–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenert, A.; Bierman, D.M.; Nam, Y.; Chan, W.R.; Celanovic, I.; Soljacic, M.; Wang, E.N. A nanophotonic solar thermophotovoltaic device. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2014, 9, 126–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyf, H.R.; Henrya, A. Thermophotovoltaics: A potential pathway to high efficiency concentrated solar power. Energy Environ. Sci. 2016, 9, 2654–2665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.F.; Santhanam, P.; Fan, S.H. Suppressing sub-bandgap phonon-polariton heat transfer in near-field thermophotovoltaic devices for waste heat recovery. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2015, 107, 091106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.K.; Morsy, A.M.; Povinelli, M.L. Design of VO2-coated silicon microspheres for thermally-regulating paint. Opt. Express 2019, 27, 21788–21793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, H.Z.; Li, Q.; Zheng, C.Q.; Hong, Y.; Xu, Z.Q.; Wang, H.; Shen, W.D.; Kaur, S.; Ghosh, P.; Qiu, M. High-temperature infrared camouflage with efficient thermal management. Light-Sci. Appl. 2020, 9, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, W.; Chettiar, U.K.; Kildishev, A.V.; Shalaev, V.M. Optical cloaking with metamaterials. Nat. Photonics 2007, 1, 224–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabrielli, L.H.; Cardenas, J.; Poitras, C.B.; Lipson, M. Silicon nanostructure cloak operating at optical frequencies. Nat. Photonics 2009, 3, 461–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larciprete, M.C.; Albertoni, A.; Belardini, A.; Leahu, G.; Voti, R.L.; Mura, F.; Sibilia, C.; Nefedov, I.; Anoshkin, I.V.; Kauppinen, E.I.; et al. Infrared properties of randomly oriented silver nanowires. J. Appl. Phys. 2012, 112, 083503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, S.C.; Wang, Z.J.; Ye, H. Optimization and preparation of a visible-infrared compatible stealth film based on D/M/D structure. Mater. Res. Express 2019, 6, 106422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Luo, M.Y.; Jiang, X.P.; Luo, S.S.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, Z.F.; Yang, J.B. Color camouflage, solar absorption, and infrared camouflage based on phase-change material in the visible-infrared band. Opt. Mater. Express 2022, 12, 1251–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Y.; Li, Q.; Cai, L.; Pan, M.; Ghosh, P.; Du, K.; Qiu, M. Thermal camouflage based on the phase-changing material GST. Light Sci. Appl. 2018, 7, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnaoutakis, G.E.; Katsaprakakis, D.A. Concentrating Solar Power Advances in Geometric Optics, Materials and System Integration. Energies 2021, 14, 6229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datas, A.; Zeneli, M.; Del Cañizo, C.; Malgarinos, I.; Nikolopoulos, A.; Nikolopoulos, N.; Karellas, S.; Martí, A. Molten silicon storage of concentrated solar power with integrated thermophotovoltaic energy conversion. AIP Conf. Proc. 2018, 2033, 90005. [Google Scholar]
- Iasiello, M.; Braimakis, K.; Andreozzi, A.; Karellas, S. Thermal analysis of a phase change material for a solar organic rankine cycle. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2017, 923, 12042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Ning, J.; Lu, L.; Bosman, M.; Simpson, R.E. A scheme for simulating multi-level phase change photonics materials. NPJ Comput. Mater. 2021, 7, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Mazzarello, R.; Ma, E. Phase-change materials in electronics and photonics. MRS Bull. 2019, 44, 686–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nisar, M.S.; Yang, X.; Lu, L.J.; Chen, J.P.; Zhou, L.J. On-Chip Integrated Photonic Devices Based on Phase Change Materials. Photonics 2021, 8, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, C.D.; Bhaskaran, H.; Pernice, W. Integrated phase-change photonic devices and systems. MRS Bull. 2019, 44, 721–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wredh, S.; Wang, Y.; Yang, J.K.W.; Simpson, R.E. Multi-Level Optical Switching by Amorphization in Single- and Multi-Phase Change Material Structures. Adv. Opt. Mater. 2024, 12, 2301835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Kim, C.; Lee, M. Parallel Laser Printing of a thermal emission Pattern in a phase-change thin film Cavity for Infrared Camouflage and security. Laser Photonics Rev. 2022, 16, 2100545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Y.R.; Li, Q.; Cai, L.; Qiu, M. Polarization switching of thermal emissions based on plasmonic structures incorporating phase-changing material Ge2Sb2Te5. Opt. Mater. Express 2018, 8, 2312–2320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Y.R.; Li, Q.; Du, K.K.; Cai, L.; Lu, J.; Qiu, M. Dynamic thermal emission control based on ultrathin plasmonic metamaterials including phase-changing material GST. Laser Photonics Rev. 2017, 11, 1700091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Q.L.; Li, D.K.; Guo, K.; Gao, J.; Guo, Z.Y. Tunable thermal camouflage based on GST plasmonic metamaterial. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moitra, P.; Wang, Y.Z.; Liang, X.A.; Lu, L.; Poh, A.; Mass, T.; Simpson, R.E.; Kuznetsov, A.I.; Paniagua-Dominguez, R. Programmable Wavefront Control in the Visible Spectrum Using Low-Loss Chalcogenide Phase-Change Metasurfaces. Adv. Mater. 2023, 35, e2205367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, L.; Dong, Z.; Tijiptoharsono, F.; Ng, R.J.H.; Wang, H.; Rezaei, S.D.; Wang, Y.; Leong, H.S.; Lim, P.C.; Yang, J.K.W.; et al. Reversible Tuning of Mie Resonances in the Visible Spectrum. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 19722–19732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barreda, A.; Zou, C.; Sinelnik, A.; Menshikov, E.; Sinev, I.; Pertsch, T.; Staude, I. Tuning and switching effects of quasi-BIC states combining phase change materials with all-dielectric metasurfaces. Opt. Mater. Express 2022, 12, 3132–3142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delaney, M.; Zeimpekis, I.; Lawson, D.; Hewak, D.W.; Muskens, O.L. A New Family of Ultralow Loss Reversible Phase-Change Materials for Photonic Integrated Circuits: Sb2S3 and Sb2Se3. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 2002447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Fowler, C.; Liang, J.; Azhar, B.; Shalaginov, M.Y.; Deckoff-Jones, S.; An, S.; Chou, J.B.; Roberts, C.M.; Liberman, V.; et al. Electrically reconfigurable non-volatile metasurface using low-loss optical phase-change material. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2021, 16, 661–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, Y.; Wang, Y.; Feng, C.; Tian, Y.; Gao, L.; Wang, J.; Zhuo, Z.; Zhao, X. Electrically tunable phase-change metasurface for dynamic infrared thermal camouflage. Photonics Res. 2024, 12, 292–300. [Google Scholar]
- Chew, L.T.; Dong, W.L.; Lu, L.; Zhou, X.L.; Behera, J.; Liu, H.L.; Sreekanth, K.V.; Mao, L.B.; Cao, T.; Yang, J.; et al. Chalcogenide Active Photonics. Act. Photonic Platf. IX 2017, 10345, 58–66. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Lee, J.; Reifenberg, J.P.; Asheghi, M.; Wong, H.P.; Goodson, K.E. In-Plane Thermal Conduction and Conductivity Anisotropy in Ge2Sb2Te5 Films for Phase Change Memory. In Proceedings of the ASME International Mechanical Engineering Congress and Exposition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 12–18 November 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, M.Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, Z.J.; Ma, H.S.; Du, T.; Jiang, X.P.; Zhang, Z.R.; Yang, J.B. Tunable Infrared Detection, Radiative Cooling and Infrared-Laser Compatible Camouflage Based on a Multifunctional Nanostructure with Phase-Change Material. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 2261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aspnes, D.E. Local-field effects and effective-medium theory: A microscopic perspective. Am. J. Phys. 1982, 50, 704–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, C.H.; Tseng, M.L.; Chen, J.; Wu, P.C.; Chen, Y.H.; Wang, H.C.; Chen, T.Y.; Hsieh, W.T.; Wu, H.J.; Sun, G.; et al. Active dielectric metasurface based on phase-change medium. Laser Photonics Rev. 2016, 10, 986–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, T.; Zhang, X.; Dong, W.; Lu, L.; Zhou, X.; Zhuang, X.; Deng, J.; Cheng, X.; Li, G.; Simpson, R.E. Tuneable thermal emission using chalcogenide metasurface. Adv. Opt. Mater. 2018, 6, 1800169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xiong, Y.; Zhang, G.; Tian, Y.; Wang, J.-L.; Wang, Y.; Zhuo, Z.; Zhao, X. Optimization of a Ge2Sb2Te5-Based Electrically Tunable Phase-Change Thermal Emitter for Dynamic Thermal Camouflage. Materials 2024, 17, 1641. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17071641
Xiong Y, Zhang G, Tian Y, Wang J-L, Wang Y, Zhuo Z, Zhao X. Optimization of a Ge2Sb2Te5-Based Electrically Tunable Phase-Change Thermal Emitter for Dynamic Thermal Camouflage. Materials. 2024; 17(7):1641. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17071641
Chicago/Turabian StyleXiong, Yufeng, Guoxu Zhang, Yaolan Tian, Jun-Lei Wang, Yunzheng Wang, Zhuang Zhuo, and Xian Zhao. 2024. "Optimization of a Ge2Sb2Te5-Based Electrically Tunable Phase-Change Thermal Emitter for Dynamic Thermal Camouflage" Materials 17, no. 7: 1641. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17071641
APA StyleXiong, Y., Zhang, G., Tian, Y., Wang, J.-L., Wang, Y., Zhuo, Z., & Zhao, X. (2024). Optimization of a Ge2Sb2Te5-Based Electrically Tunable Phase-Change Thermal Emitter for Dynamic Thermal Camouflage. Materials, 17(7), 1641. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17071641








