Insights into Human Middle Ear Implants: Uncovered Bistability
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Standard Procedure
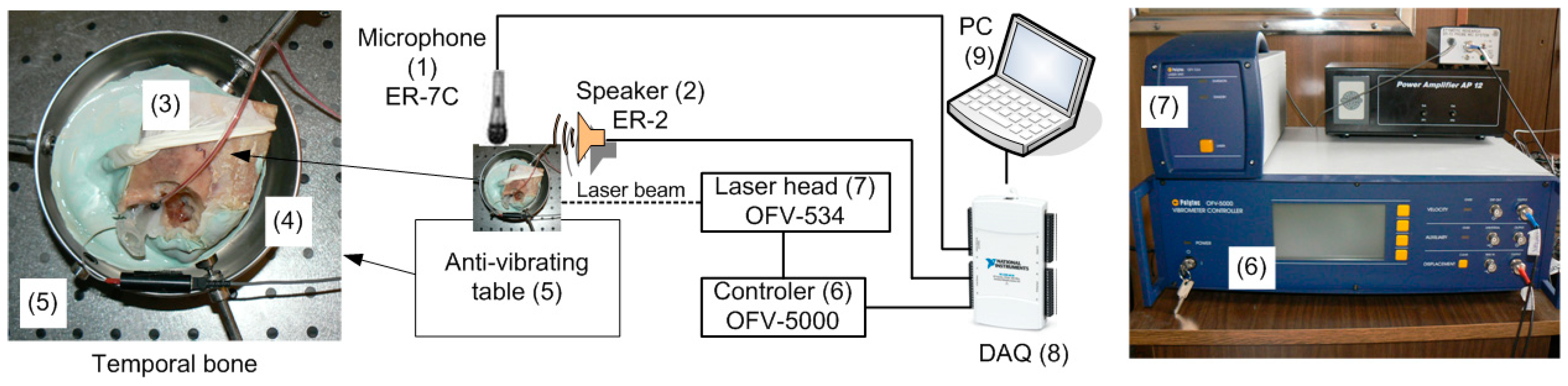
2.2. Temporal Bone Preparing
2.3. Temporal Bone Testing
- —TM sound pressure;
- —stapes footplate velocity.
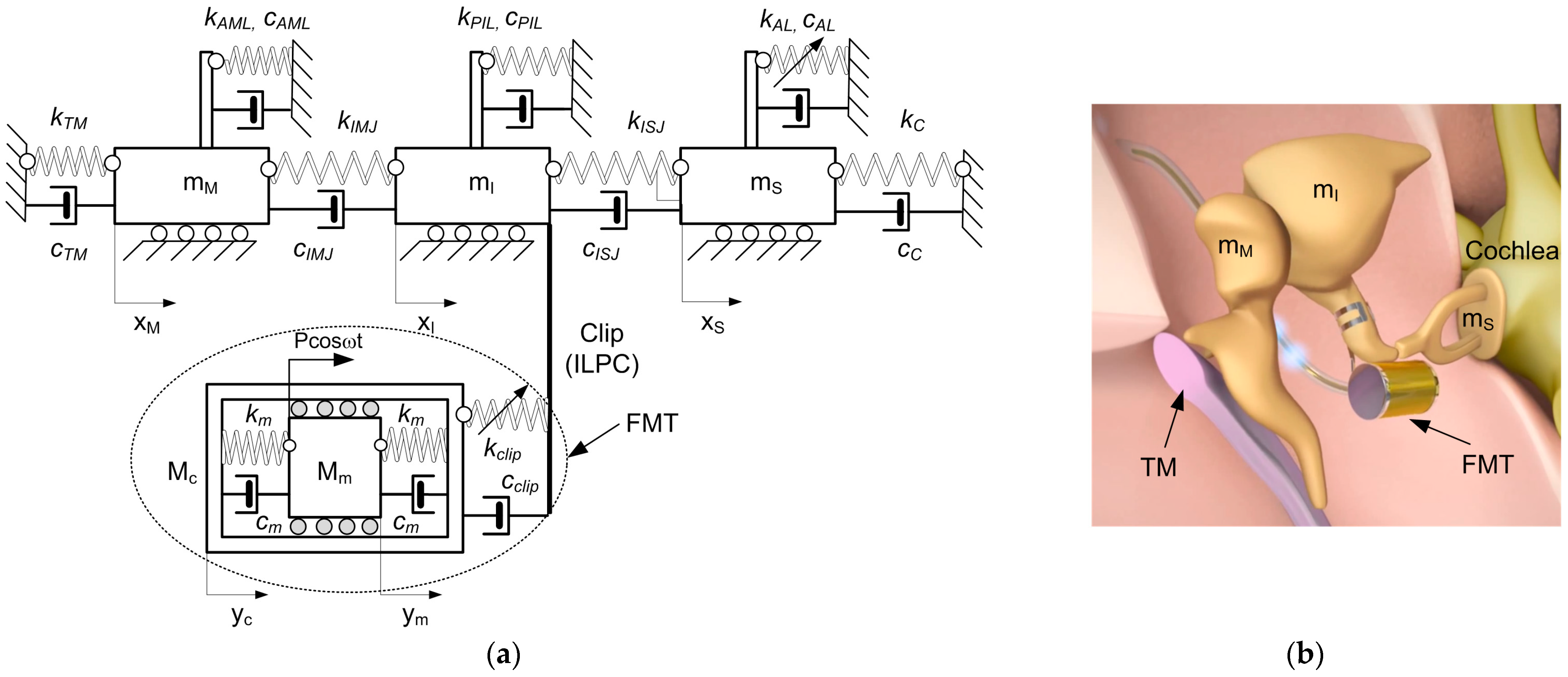
3. Model of the Human Middle Ear with Implant
4. Result Comparisons
4.1. ASTM Standard and Experiment
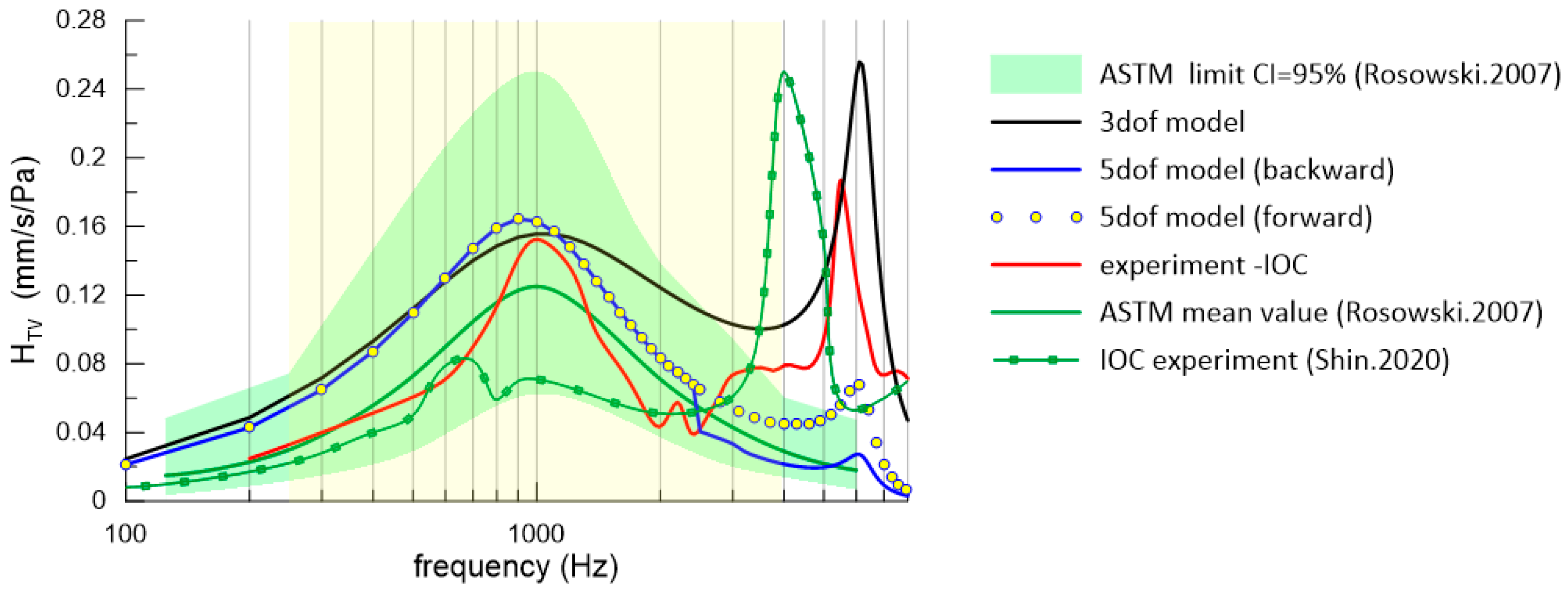
4.2. Numerical Simulation Results
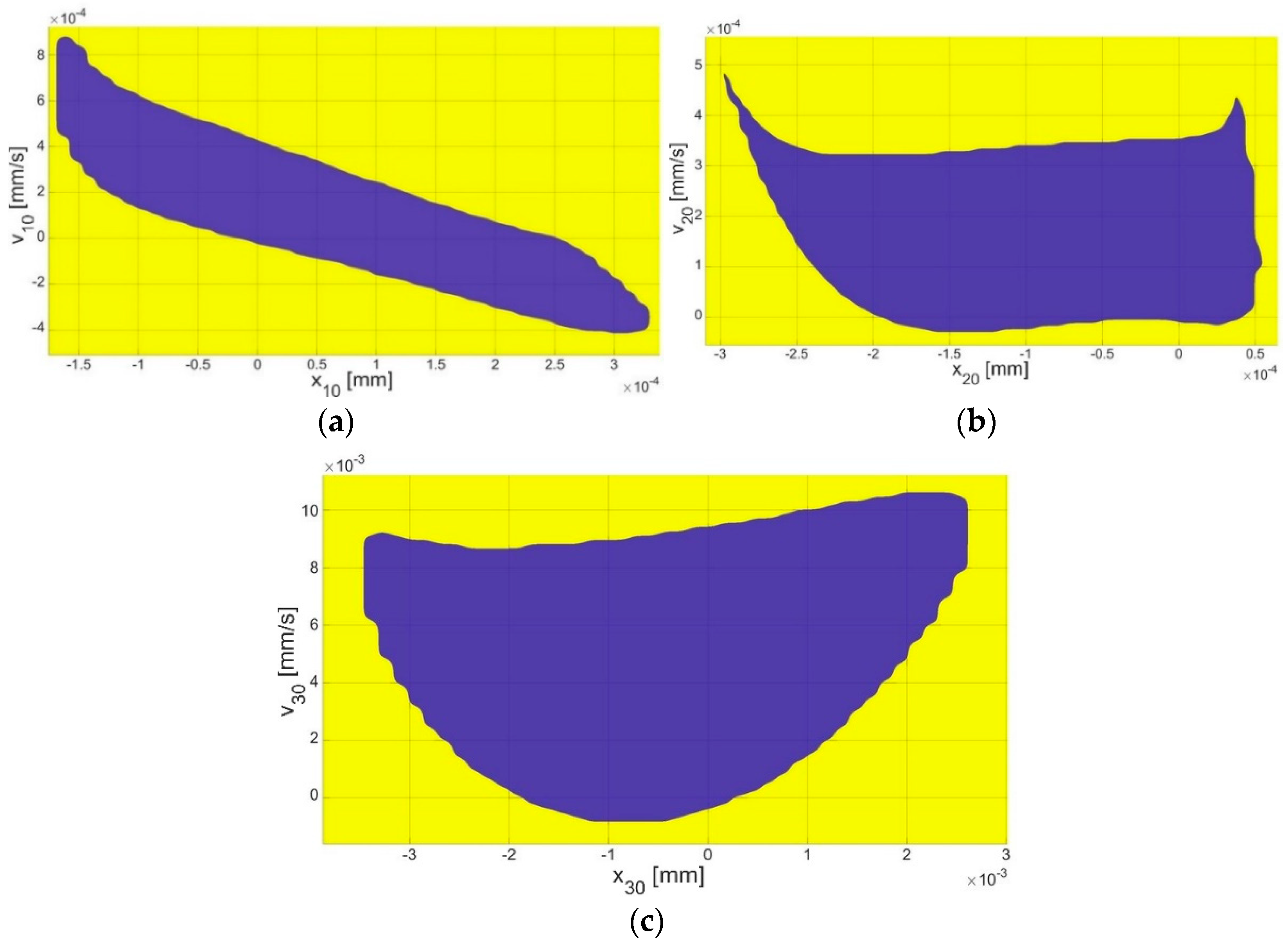
4.3. Bistability Analysis
5. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| LDV | Laser Doppler Vibrometer |
| FRF | Frequency Response Function |
| FMT | Floating Mass Transducer (e.g., VSB) |
| IME | Implanted Middle Ear |
| IOC | Intact Ossicular Chain |
| LML | Lateral Mallear Ligament |
| LPM | Lumped Parameter Model |
| PIL | Posterior Incudal Ligament |
| SML | Superior Mallear Ligament |
| AL | Annular Ligament |
| TM | Tympanic Membrane (Eardrum) |
| TTT | Tensor Tympani Tendon |
| AML | Anterior Mallear Ligament |
| IMJ | Incudomallear Joint |
| ISJ | Incudostapedial Joint |
References
- Hachmeister, J.E. An Abbreviated History of the Ear: From Renaissance to Present. Yale J. Biol. Med. 2003, 76, 81. [Google Scholar]
- Møller, A.R. Network Model of the Middle Ear. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1961, 33, 168–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwislocki, J. Analysis of the Middle-ear Function. Part I: Input Impedance. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1962, 34, 1514–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voss, S.E.; Rosowski, J.J.; Merchant, S.N.; Peake, W.T. Acoustic Responses of the Human Middle Ear. Hear. Res. 2000, 150, 43–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravicz, M.; Peake, W.; Nakajima, H.; Merchant, S.; Rosowski, J. Modeling Flexibility in the Human Ossicular Chain: Comparison to Ossicular Fixation Data. In Middle Ear Mechanics in Research and Otology; World Scientific: Singapore, 2004; pp. 91–98. [Google Scholar]
- Nakajima, H.H.; Ravicz, M.E.; Merchant, S.N.; Peake, W.T.; Rosowski, J.J. Experimental Ossicular Fixations and the Middle Ear’s Response to Sound: Evidence for a Flexible Ossicular Chain. Hear. Res. 2005, 204, 60–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, B.; Gan, R. A Lumped-Parameter Mechanical Model of Human Ear for Sound Transmission. In Proceedings of the Second Joint 24th Annual Conference and the Annual Fall Meeting of the Biomedical Engineering Society, Engineering in Medicine and Biology, Houston, TX, USA, 23–26 October 2002; Volume 1, pp. 267–268. [Google Scholar]
- Lauxmann, M.; Eiber, A.; Haag, F.; Ihrle, S. Nonlinear Stiffness Characteristics of the Annular Ligament. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2014, 136, 1756–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusinek, R.; Szymanski, M.; Zablotni, R. Biomechanics of the Human Middle Ear with Viscoelasticity of the Maxwell and the Kelvin–Voigt Type and Relaxation Effect. Materials 2020, 13, 3779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM F2504-05(2014); Standard Practice for Describing System Output of Implantable Middle Ear Hearing Devices. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2014.
- Rusinek, R.; Kecik, K. Effect of Linear Electromechanical Coupling in Nonlinear Implanted Human Middle Ear. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2021, 151, 107391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosowski, J.; Chien, W.; Ravicz, M.; Merchant, S. Testing a Method for Quantifying the Output of Implantable Middle Ear Hearing Devices. Audiol. Neurotol. 2007, 12, 265–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, M.; Lally, J.; Adams, J.K.; Higgins, S.; Ahmed, M.; Aden, J.; Esquivel, C.; Spear, S.A. Mechanical Energy Dissipation Through the Ossicular Chain and Inner Ear Using Laser Doppler Vibrometer Measurement of Round Window Velocity. Otol. Neurotol. 2020, 41, e387–e391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schraven, S.P.; Dohr, D.; Weiss, N.M.; Mlynski, R.; Dalhoff, E. Laser-Doppler-Vibrometrische Messungen an Humanen Felsenbeinen. HNO 2021, 69, 491–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greene, N.T.; Jenkins, H.A.; Tollin, D.J.; Easter, J.R. Stapes Displacement and Intracochlear Pressure in Response to Very High Level, Low Frequency Sounds. Hear. Res. 2017, 348, 16–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, J.T.; Ghanad, I.; Remenschneider, A.; Rosowski, J. The Onset of Nonlinear Growth of Middle-Ear Responses to High Intensity Sounds. Hear. Res. 2021, 405, 108242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorente-Piera, J.; Manrique-Huarte, R.; Lima, J.P.; Calavia, D.; Manrique, M. Middle Ear Active Implant Indications, Comparative Audiometric Results from Different Approaches, and Coupling with the Vibrant Soundbridge®: A Single Center Experience over More Than 20 Years. Audiol. Res. 2024, 14, 721–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruschini, L.; Canzi, P.; Canale, A.; Covelli, E.; Laborai, A.; Monteforte, M.; Cinquini, M.; Barbara, M.; Beltrame, M.A.; Bovo, R.; et al. Implantable hearing devices in clinical practice. Systematic review and consensus statements. Acta Otorhinolaryngol. Ital. 2023, 44, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusinek, R. Sound Transmission in the First Nonlinear Model of Middle Ear with an Active Implant. Math. Probl. Eng. 2020, 2020, 4580467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Tang, B.; Xiao, X. Time–Frequency Interpretation of Multi-Frequency Signal from Rotating Machinery Using an Improved Hilbert–Huang Transform. Measurement 2016, 82, 221–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aibara, R.; Welsh, J.T.; Puria, S.; Goode, R.L. Human Middle-Ear Sound Transfer Function and Cochlear Input Impedance. Hear. Res. 2001, 152, 100–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, D.H.; Seong, K.W.; Nakajima, H.H.; Puria, S.; Cho, J.-H. A Piezoelectric Bellows Round-Window Driver (PBRD) for Middle-Ear Implants. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 137947–137954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gladiné, K.; Dirckx, J.J.J. Average Middle Ear Frequency Response Curves with Preservation of Curve Morphology Characteristics. Hear. Res. 2018, 363, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schraven, S.P.; Mlynski, R.; Dalhoff, E.; Heyd, A.; Wildenstein, D.; Rak, K.; Radeloff, A.; Hagen, R.; Gummer, A.W. Coupling of an Active Middle-Ear Implant to the Long Process of the Incus Using an Elastic Clip Attachment. Hear. Res. 2016, 340, 179–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, T.; Ren, L.-J.; Yin, D.-M.; Li, J.; Yang, L.; Dai, P.-D.; Zhang, T.-Y. A Comparative Study of MED-EL FMT Attachment to the Long Process of the Incus in Intact Middle Ears and Its Attachment to Disarticulated Stapes Head. Hear. Res. 2017, 353, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Wang, L.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Sun, Y.; Wang, J.; Han, H.; Xiang, S.; Shi, H.; Ding, Q. Nonlinear Dynamic Response and Stability Analysis of the Stapes Reconstruction in Human Middle Ear. Appl. Math. Mech. 2023, 44, 1739–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darvish, B.; Najarian, S.; Shirzad, E.; Khodambashi, R. A Novel Tactile Force Probe for Tissue Stiffness Classification. Am. J. Appl. Sci. 2009, 6, 512–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Aldè, M.; Cantarella, G.; Zanetti, D.; Pignataro, L.; La Mantia, I.; Maiolino, L.; Ferlito, S.; Di Mauro, P.; Cocuzza, S.; Lechien, J.R.; et al. Autosomal Dominant Non-Syndromic Hearing Loss (DFNA): A Comprehensive Narrative Review. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
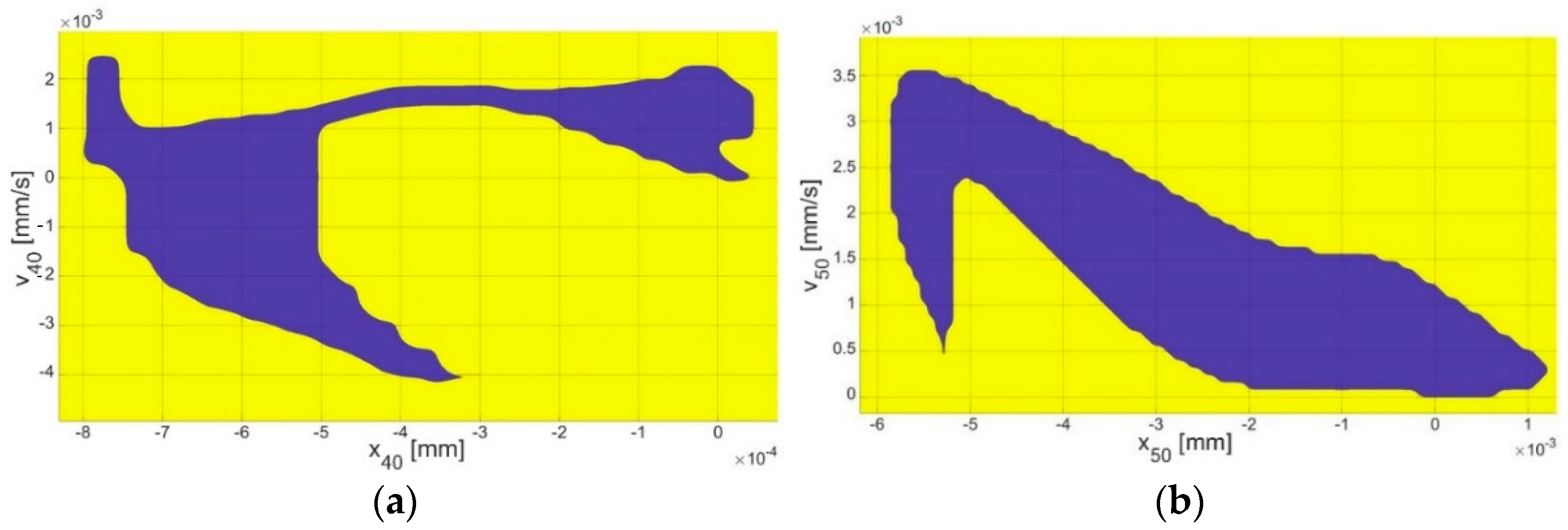
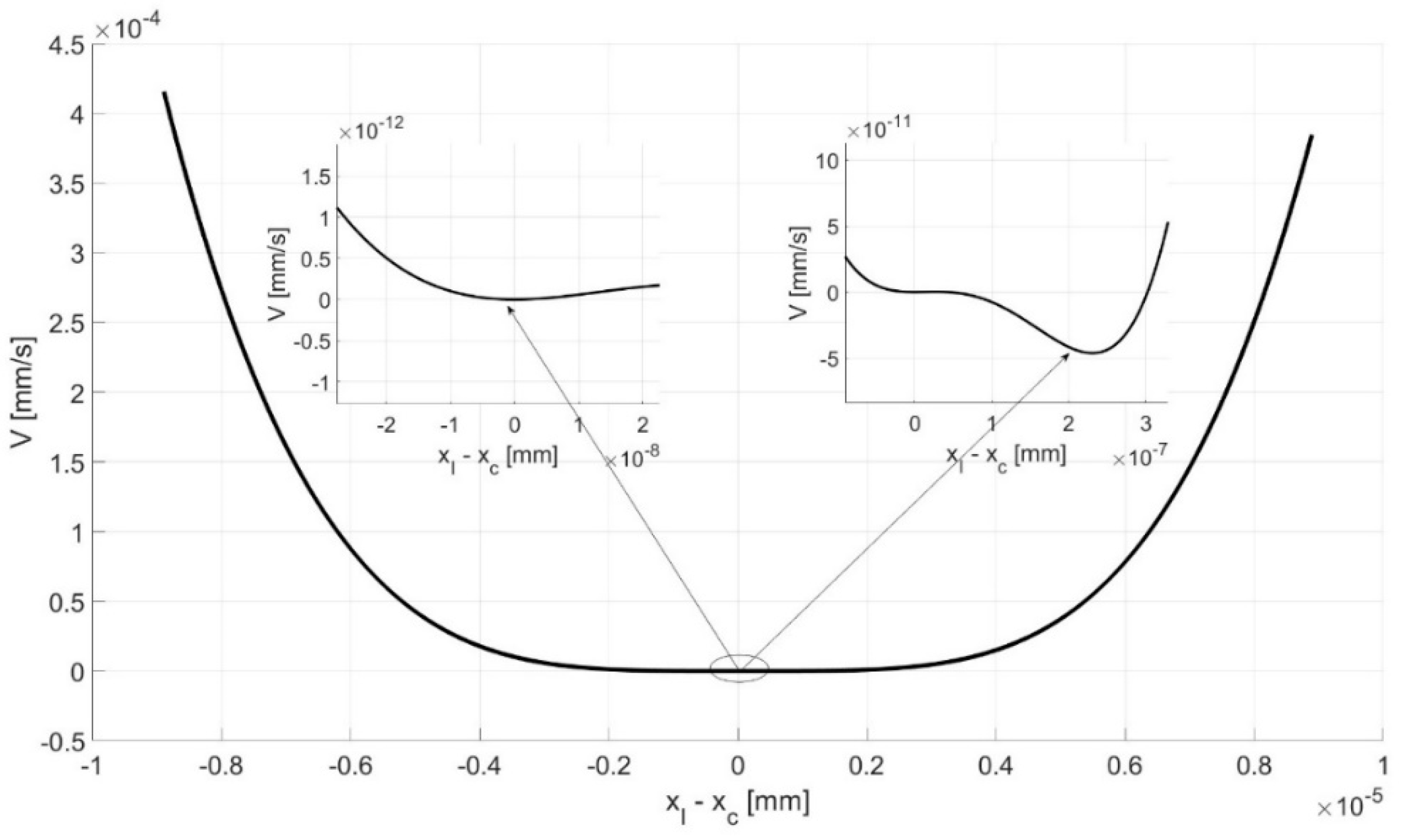
| Frequency [Hz] | Mean Value [mm/s/Pa] | Upper Limit [mm/s/Pa] | Lower Limit [mm/s/Pa] |
|---|---|---|---|
| 125 | 0.015 | 0.048 | 0.004 |
| 250 | 0.030 | 0.074 | 0.012 |
| 500 | 0.073 | 0.180 | 0.029 |
| 1000 | 0.125 | 0.250 | 0.062 |
| 2000 | 0.071 | 0.138 | 0.037 |
| 3000 | 0.043 | 0.094 | 0.020 |
| 4000 | 0.029 | 0.060 | 0.014 |
| 6000 | 0.018 | 0.047 | 0.007 |
| Stiffness Coefficients | Abbreviation | Value [N/m] |
|---|---|---|
| Tympanic membrane stiffness | ktm | 300 |
| Anterior mallear ligament stiffness | kaml | 800 |
| Incudomallear joint stiffness | kimj | 1,000,000 |
| Posterior incudal ligament stiffness | kpil | 400 |
| Incudostapedial joint stiffness | kisj | 1350 |
| Cochlea stiffness | kc | 200 |
| Annular ligament stiffness | kAL | 623 |
| Nonlinear stiffness of the annular ligament | kAL3 | 1.3 × 1011 |
| Stiffness of the mass inside FMT | km | 850 |
| Stiffness of the FMT clip | kclip | 800 |
| Second-order nonlinear stiffness of the FMT clip | kclip2 | −2.2 × 1010 |
| Third-order nonlinear stiffness of the FMT clip | kclip3 | 6.4 × 1016 |
| Damping coefficients | Abbreviation | Value [Ns/m] |
| Tympanic membrane dumping | ctm | 0.06 |
| Anterior mallear ligament dumping | caml | 0.275 |
| Anterior mallear ligament dumping | cimj | 0.359 |
| Incudomallear joint dumping | cpil | 0.055 |
| Posterior incudal ligament dumping | cisj | 0.0079 |
| Incudostapedial joint dumping | cc | 0.0017 |
| Annular ligament dumping | cal | 0.0020 |
| Mass inside the FMT damping | cm | 0.32 |
| Clip of the FMT damping | cclip | 0.15 |
| Masses | Abbreviation | Value [kg] |
| Malleus mass | mM | 2.5 × 10−5 |
| Incus mass | mI | 2.8 × 10−5 |
| Stapes mass | mS | 1.78 × 10−6 |
| Implant mass | Mm | 1.5 × 10−5 |
| Implant clip mass | Mc | 1.5 × 10−5 |
| Mechanical excitation | Abbreviation | Value [N] |
| Mechanical force applied on implant | P | 1.2029 × 10−4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zablotni, R.; Zając, G.; Rusinek, R. Insights into Human Middle Ear Implants: Uncovered Bistability. Materials 2024, 17, 5730. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17235730
Zablotni R, Zając G, Rusinek R. Insights into Human Middle Ear Implants: Uncovered Bistability. Materials. 2024; 17(23):5730. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17235730
Chicago/Turabian StyleZablotni, Robert, Grzegorz Zając, and Rafal Rusinek. 2024. "Insights into Human Middle Ear Implants: Uncovered Bistability" Materials 17, no. 23: 5730. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17235730
APA StyleZablotni, R., Zając, G., & Rusinek, R. (2024). Insights into Human Middle Ear Implants: Uncovered Bistability. Materials, 17(23), 5730. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17235730









