A Review of Welding Process for UNS S32750 Super Duplex Stainless Steel
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Recent Researches on Welding UNS S32750
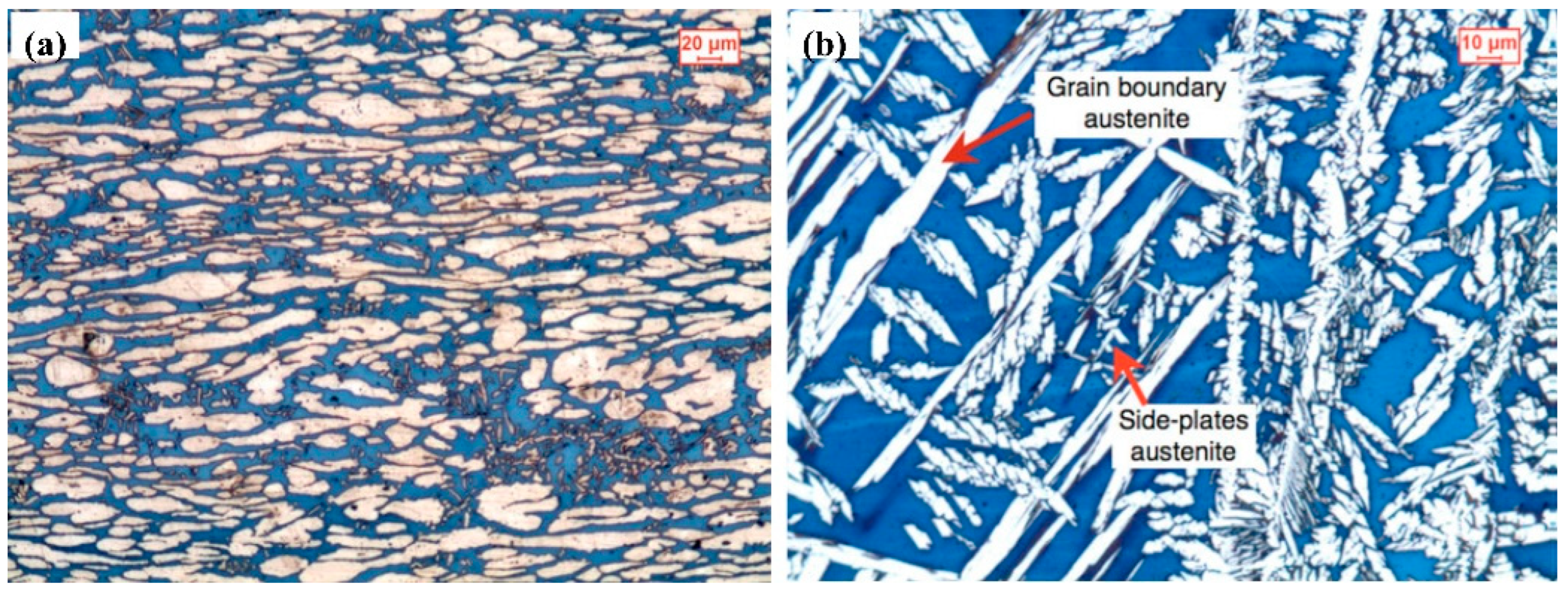
2.1. UNS S32750 Welding by GTAW Process
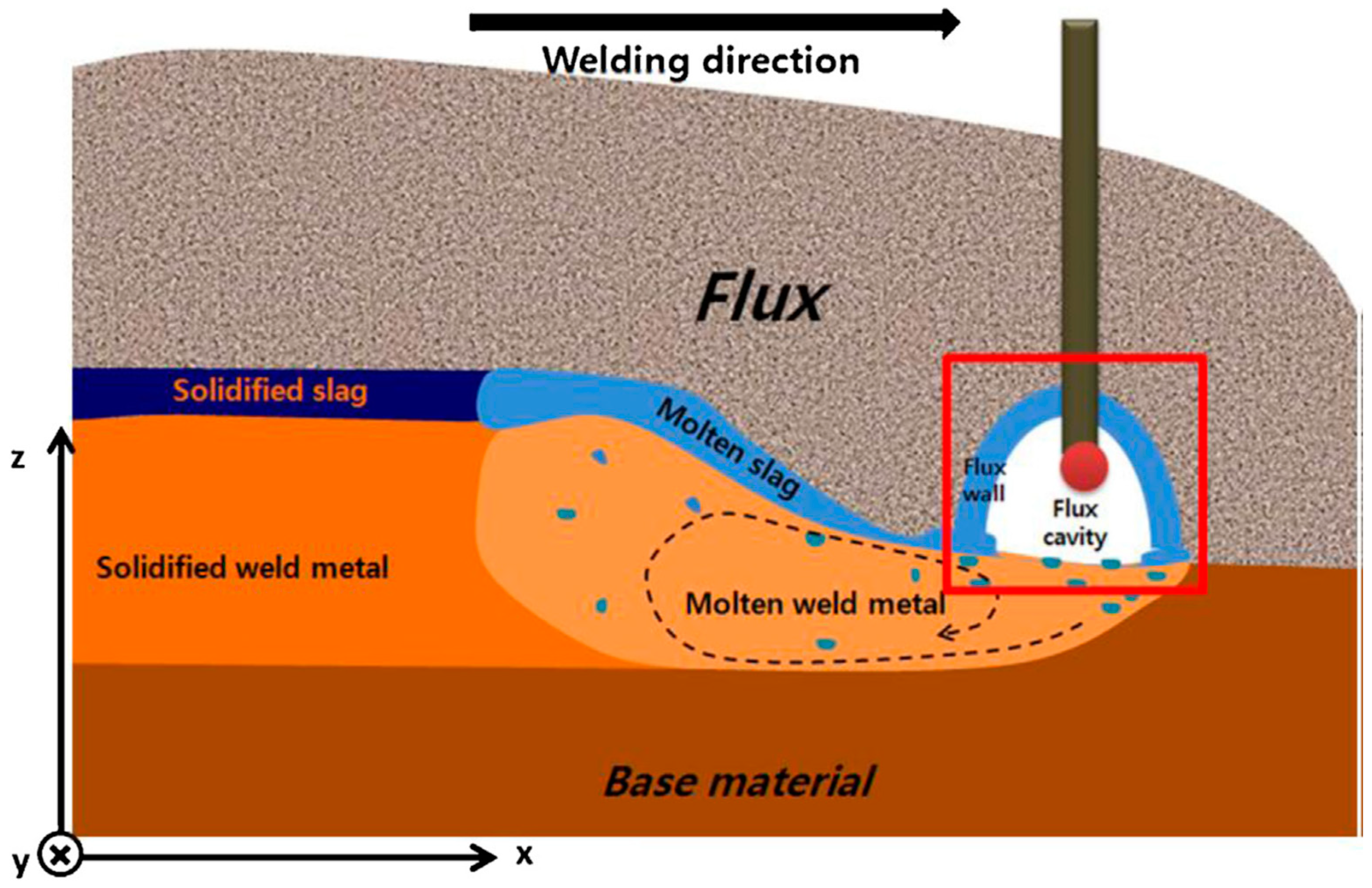
2.2. UNS S32750 Welding by SAW Process
2.3. UNS S32750 Welding by PAW Process
2.4. UNS S32750 Welding by LBW Process
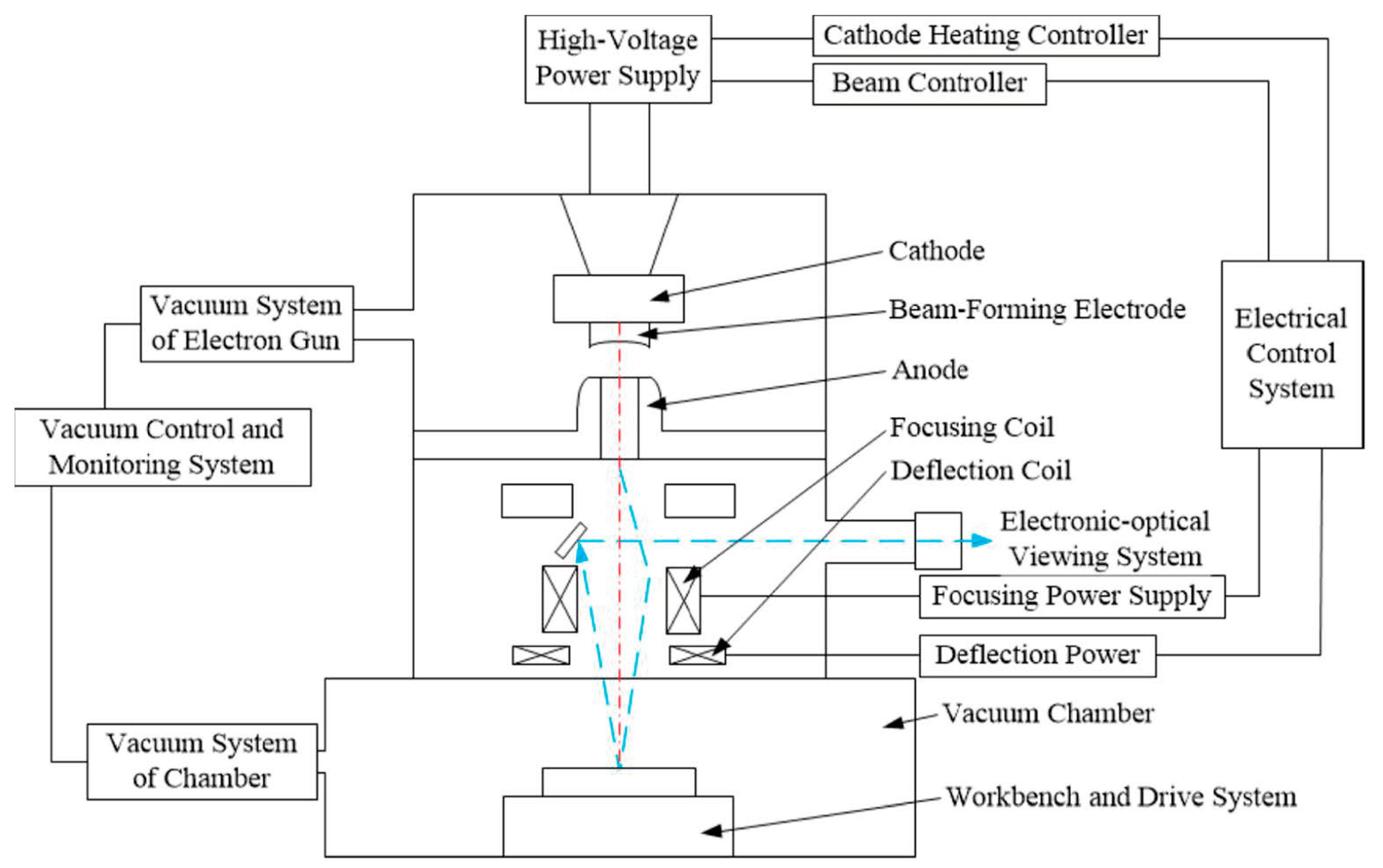
2.5. UNS S32750 Welding by EBW Process
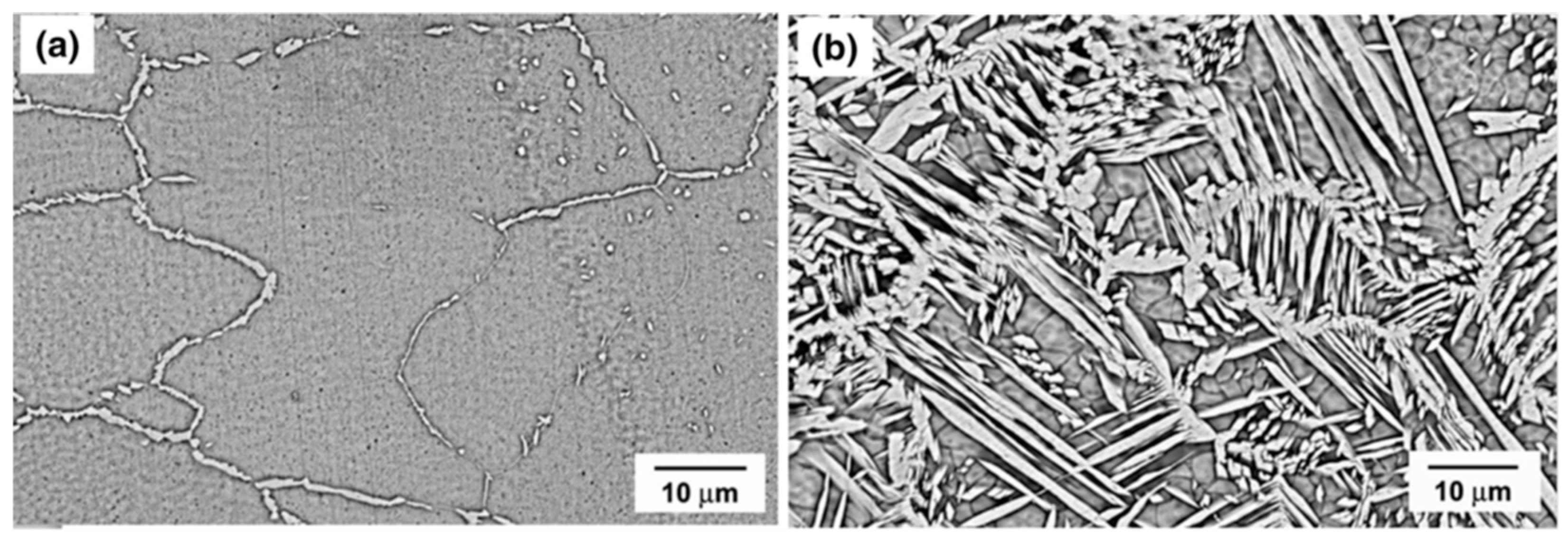
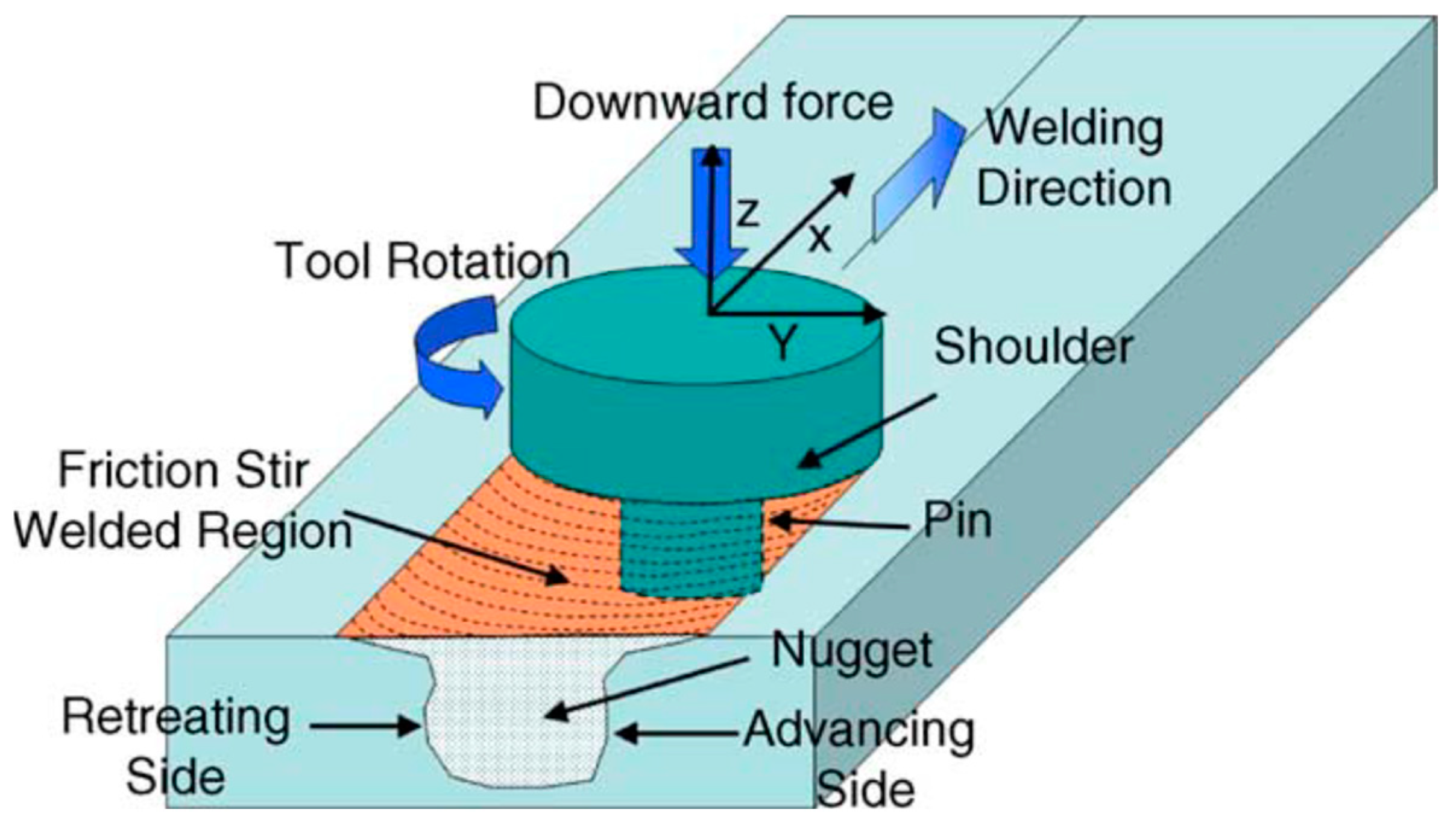
2.6. UNS S32750 Welding by FSW Process
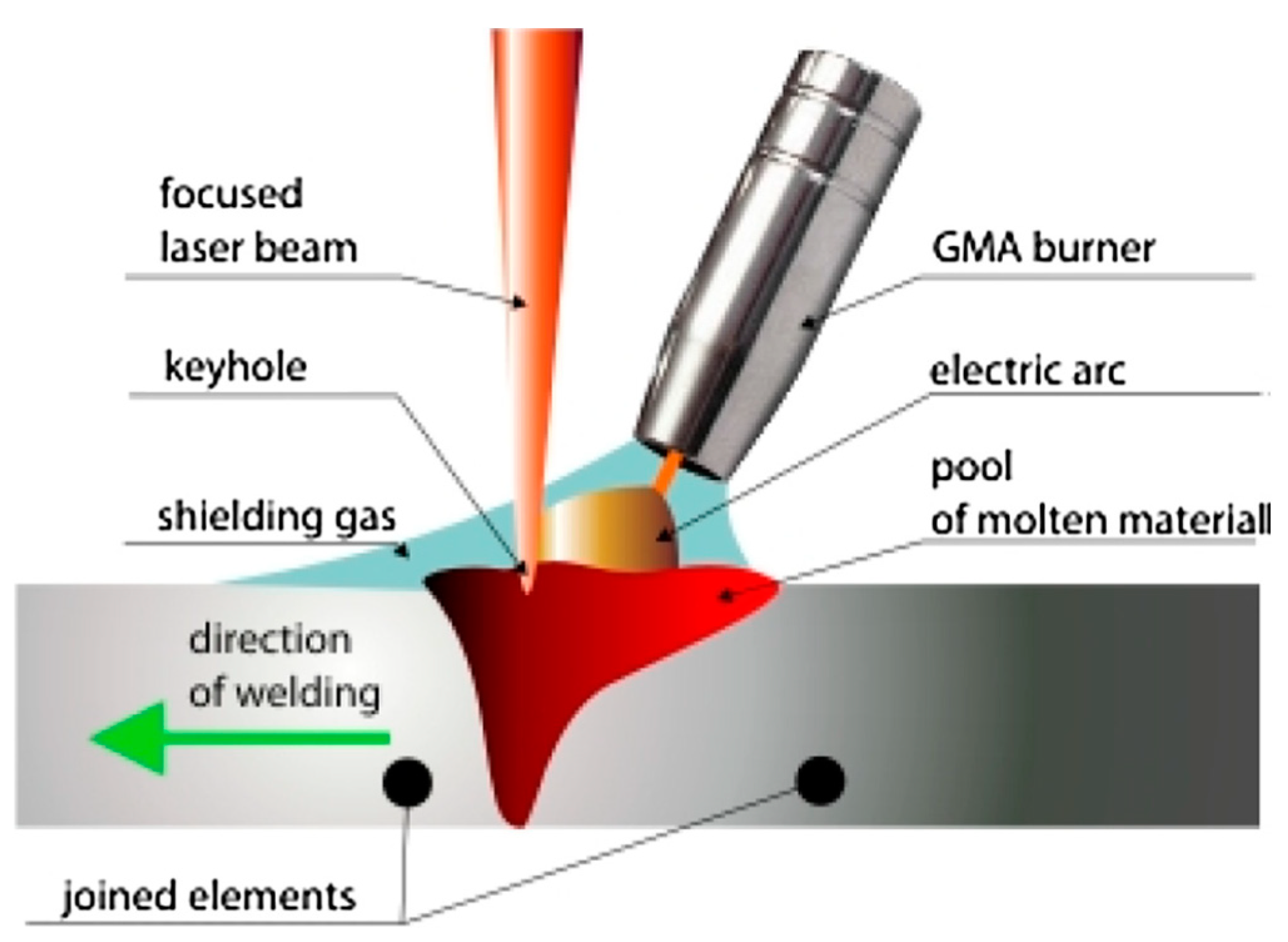
2.7. UNS S32750 Welding by Laser-MIG Hybrid Welding Process
3. Critical Challenge in Welding UNS S32750
4. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Farrer, J.C.M. The Alloy Tree: A Guide to Low-Alloy Steels, Stainless Steels, and Nickel-Base Alloys; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Sharafi, S. Microstructure of Super-Duplex Stainless Steels. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Cambridge, Cambridge, UK, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Dandekar, T.R.; Gupta, A.; Khatirkar, R.K.; Kumar, R.; Gaikwad, A.D. Evolution of Microstructure and Texture in Uns S32750 Super Duplex Stainless Steel Weldments. Trans. Indian Inst. Met. 2021, 74, 2267–2283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kangazian, J.; Shamanian, M. Effect of Pulsed Current on the Microstructure, Mechanical Properties and Corrosion Behavior of Ni-Based Alloy/Super Duplex Stainless Steel Dissimilar Welds. Trans. Indian Inst. Met. 2019, 72, 2403–2416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.-Q.; Bai, Y.; Xu, B.-Z.; Pan, W.; Li, J.-X.; Qiao, L.-J. Effect of Hydrogen on Pitting Susceptibility of 2507 Duplex Stainless Steel. Corros. Sci. 2013, 70, 140–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurya, A.K.; Pandey, C.; Chhibber, R. Dissimilar Welding of Duplex Stainless Steel with Ni Alloys: A Review. Int. J. Press. Vessel. Pip. 2021, 192, 104439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, P.; Leo Dev Wins, K.; Ebenezer Jacob Dhas, D.S.; George, P.; Beatrice, B.A. Machinability, Weldability and Surface Treatment Studies of Sdss 2507 Material-a Review. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 46, 7682–7687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pramanik, A.; Littlefair, G.; Basak, A.K. Weldability of Duplex Stainless Steel. Mater. Manuf. Process. 2015, 30, 1053–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gowthaman, P.S.; Jeyakumar, S.; Saravanan, B.A. Machinability and Tool Wear Mechanism of Duplex Stainless Steel—A Review. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 26, 1423–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-T.; Jang, S.-H.; Lee, I.-S.; Park, Y.-S. Effects of Solution Heat-Treatment and Nitrogen in Shielding Gas on the Resistance to Pitting Corrosion of Hyper Duplex Stainless Steel Welds. Corros. Sci. 2011, 53, 1939–1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Z.-Y.; Wang, L.-W.; Ni, H.-T.; Hao, W.-K.; Man, C.; Chen, S.-S.; Wang, X.; Liu, Z.-Y.; Li, X.-G. Influence of Temperature on the Electrochemical and Passivation Behavior of 2507 Super Duplex Stainless Steel in Simulated Desulfurized Flue Gas Condensates. Corros. Sci. 2017, 118, 31–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, J.; Taiwade, R.V. Effect of Welding Processes and Conditions on the Microstructure, Mechanical Properties and Corrosion Resistance of Duplex Stainless Steel Weldments—A Review. J. Manuf. Process. 2017, 25, 134–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patra, S.; Agrawal, A.; Mandal, A.; Podder, A.S. Characteristics and Manufacturability of Duplex Stainless Steel: A Review. Trans. Indian Inst. Met. 2021, 74, 1089–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Migiakis, K.; Daniolos, N.; Papadimitriou, G.D. Plasma Keyhole Welding of Uns S32760 Super Duplex Stainless Steel: Microstructure and Mechanical Properties. Mater. Manuf. Process. 2010, 25, 598–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saravanan, S.; Sivagurumanikandan, N.; Raghukandan, K. Effect of Process Parameters in Microstructural and Mechanical Properties of Nd: Yag Laser Welded Super Duplex Stainless Steel. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 39, 1248–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, V.A.; Wessman, S.; Hurtig, K.; Karlsson, L. Nitrogen Loss and Effects on Microstructure in Multipass Tig Welding of a Super Duplex Stainless Steel. Mater. Des. 2016, 98, 88–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taban, E. Toughness and Microstructural Analysis of Superduplex Stainless Steel Joined by Plasma Arc Welding. J. Mater. Sci. 2008, 43, 4309–4315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Cruz Junior, E.J.; Franzini, O.D.; Calliari, I.; Ventrella, V.A. Effects of Nickel Addition on the Microstructure of Laser-Welded Uns S32750 Duplex Stainless Steel. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2019, 50, 1616–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holländer Pettersson, N.; Lindell, D.; Lindberg, F.; Borgenstam, A. Formation of Chromium Nitride and Intragranular Austenite in a Super Duplex Stainless Steel. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2019, 50, 5594–5601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettersson, N.; Pettersson, R.F.A.; Wessman, S. Precipitation of Chromium Nitrides in the Super Duplex Stainless Steel 2507. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2015, 46, 1062–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez, A.J.; Lippold, J.C.; Brandi, S.D. The Relationship between Chromium Nitride and Secondary Austenite Precipitation in Duplex Stainless Steels. Metall. Mater. Trans. A. 2003, 34, 1575–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardal, J.M.; Tavares, S.S.M.; Fonseca, M.C.; de Souza, J.A.; Côrte, R.R.A.; de Abreu, H.F.G. Influence of the Grain Size on Deleterious Phase Precipitation in Superduplex Stainless Steel Uns S32750. Mater. Charact. 2009, 60, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, V.A.; Karlsson, L.; Wessman, S.; Fuertes, N. Effect of Sigma Phase Morphology on the Degradation of Properties in a Super Duplex Stainless Steel. Materials 2018, 11, 933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paulraj, P.; Garg, R. Effect of Intermetallic Phases on Corrosion Behavior and Mechanical Properties of Duplex Stainless Steel and Super-Duplex Stainless Steel. Adv. Sci. Technol. Res. J. 2015, 9, 87–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Zou, D.-N.; Zhang, W.; Yu, J.-H.; Qiao, Y.-Y. Influence of Sigma Phase Precipitation on Pitting Corrosion of 2507 Super-Duplex Stainless Steel. Mater. Sci. Forum 2010, 658, 380–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messer, B.; Oprea, V.; Wright, A. Duplex Stainless Steel Welding: Best Practices. Stainl. Steel World 2007, 53, 53–63. [Google Scholar]
- Mishra, M.K.; Rao, A.G.; Balasundar, I.; Kashyap, B.P.; Prabhu, N. On the Microstructure Evolution in Friction Stir Processed 2507 Super Duplex Stainless Steel and Its Effect on Tensile Behaviour at Ambient and Elevated Temperatures. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2018, 719, 82–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.-Y.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, R.-X.; Li, D.-G.; Shu, F.-Y.; Song, X.-G.; Zhao, Y.-Q. Enhancement in Mechanical Properties and Corrosion Resistance of 2507 Duplex Stainless Steel Via Friction Stir Processing. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2020, 9, 8296–8305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, H.-Y.; Jang, M.-H.; Lee, T.-H.; Moon, J. Understanding the Relation between Phase Fraction and Pitting Corrosion Resistance of Uns S32750 Stainless Steel. Mater. Charact. 2015, 106, 338–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devendranath Ramkumar, K.; Thiruvengatam, G.; Sudharsan, S.P.; Mishra, D.; Arivazhagan, N.; Sridhar, R. Characterization of Weld Strength and Impact Toughness in the Multi-Pass Welding of Super-Duplex Stainless Steel Uns 32750. Mater. Des. 2014, 60, 125–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darji, R.; Badheka, V.; Mehta, K.; Joshi, J.; Yadav, A.; Chakraborty, A.K. Investigation on Stability of Weld Morphology, Microstructure of Processed Zones, and Weld Quality Assessment for Hot Wire Gas Tungsten Arc Welding of Electrolytic Tough Pitch Copper. Mater. Manuf. Process. 2021, 37, 908–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhari, R.; Ingle, A. Experimental Investigation of Dissimilar Metal Weld of Sa335 P11 and Sa312 Tp304 Formed by Gas Tungsten Arc Welding (Gtaw). Trans. Indian Inst. Met. 2019, 72, 1145–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tathgir, S.; Bhattacharya, A. Activated-Tig Welding of Different Steels: Influence of Various Flux and Shielding Gas. Mater. Manuf. Process. 2015, 31, 335–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.-S. Introduction to Welding Manufacturing; China Machine Press: Beijing, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, C.-M.; Liu, J.-J.; Tsai, H.-L.; Cheng, C.-M. Evolution of Microstructures and Mechanical Properties of Az31b Magnesium Alloy Weldment with Active Oxide Fluxes and Gtaw Process. J. Chin. Inst. Eng. 2011, 34, 1013–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandya, D.; Badgujar, A.; Ghetiya, N. A Novel Perception toward Welding of Stainless Steel by Activated Tig Welding: A Review. Mater. Manuf. Process. 2020, 36, 877–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anbarasu, P.; Yokeswaran, R.; Godwin Antony, A.; Sivachandran, S. Investigation of Filler Material Influence on Hardness of Tig Welded Joints. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 21, 964–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, H.C.; Albert, S.K.; Bhaduri, A.K.; Mudali, U.K. Activated Flux Tig Welding of Titanium. Weld. World 2013, 57, 903–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arunkumar, V.; Vasudevan, M.; Maduraimuthu, V.; Muthupandi, V. Effect of Activated Flux on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of 9cr-1mo Steel Weld Joint. Mater. Manuf. Process. 2012, 27, 1171–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senthur Vaishnavan, S.; Jayakumar, K. Performance Analysis of Tig Welded Dissimilar Aluminium Alloy with Scandium Added Er5356 Filler Rods. J. Chin. Inst. Eng. 2021, 44, 718–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tathgir, S.; Rathod, D.W.; Batish, A. A-Tig Welding Process for Enhanced-Penetration in Duplex Stainless-Steel: Effect of Activated Fluxes. Mater. Manuf. Process. 2019, 34, 1659–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, V.A.; Hurtig, K.; Karlsson, L. Effect of Multipass Tig Welding on the Corrosion Resistance and Microstructure of a Super Duplex Stainless Steel. Mater. Corros. 2017, 68, 405–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, V.A.; Valiente Bermejo, M.A.; Gårdstam, J.; Hurtig, K.; Karlsson, L. Influence of Multiple Thermal Cycles on Microstructure of Heat-Affected Zone in Tig-Welded Super Duplex Stainless Steel. Weld. World 2016, 60, 233–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, D.-F.; Liu, J.; Li, G.-P.; Liu, J.-M. Effect of N2 Addition on Microstructure and Properties of Saf 2507 Duplex Stainless Steels Gtaw Welded Joint. Mater. Sci. Forum 2012, 724, 127–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westin, E.M.; Johansson, M.M.; Bylund, L.Å.; Pettersson, R.F.A. Effect on Microstructure and Properties of Super Duplex Stainless Steel Welds When Using Backing Gas Containing Nitrogen and Hydrogen. Weld. World 2014, 58, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramkumar, K.D.; Goutham, P.S.; Radhakrishna, V.S.; Tiwari, A.; Anirudh, S. Studies on the Structure–Property Relationships and Corrosion Behaviour of the Activated Flux Tig Welding of Uns S32750. J. Manuf. Process. 2016, 23, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.-Y.; Zhao, H.; Zhang, H.-Z.; Hu, J.; Jin, J.-R. Microstructure Evolution and Pitting Corrosion Behavior of Uns S32750 Super Duplex Stainless Steel Welds after Short-Time Heat Treatment. Corros. Sci. 2017, 121, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.-Y.; Zhang, H.-Z.; Hu, J.; Qi, X.-X.; Bian, Y.; Shen, A.; Xu, P.-P.; Zhao, Y.-Q. Microstructure Evolution and Mechanical Properties of Briefly Heat-Treated Saf 2507 Super Duplex Stainless Steel Welds. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 168, 338–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, I.J.; Jang, B.S.; Koh, J.H. Heat Treatment Effect on Pitting Corrosion of Super Duplex Stainless Steel Uns S32750 Gta Welds. Adv. Mater. Res. 2013, 746, 467–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nath, R.K.; Maji, P.; Sinha, A.K.; Karmakar, R.; Paul, P. Effect of Different Electrode Angles as Well as Weld Direction on the Bead Geometry of Submerge Arc Welding Process. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 49, 1793–1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohal, S.; Chaitanya, S.; Singh, M.; Goyal, R.; Kumar, A.; Saini, G. Analyzing the Response of Submerged Arc Welding Process Parameters on Form Factor and Dilution. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 56, 2556–2562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Singh, R.P. A Review of Effect of Welding Parameters on the Mechanical Properties of Weld in Submerged Arc Welding Process. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 26, 1714–1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, D.-W.; Song, W.-H.; Cho, M.-H.; Na, S.-J. Analysis of Submerged Arc Welding Process by Three-Dimensional Computational Fluid Dynamics Simulations. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2013, 213, 2278–2291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cervo, R.; Ferro, P.; Tiziani, A. Annealing Temperature Effects on Super Duplex Stainless Steel Uns S32750 Welded Joints. I: Microstructure and Partitioning of Elements. J. Mater. Sci. 2010, 45, 4369–4377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cervo, R.; Ferro, P.; Tiziani, A.; Zucchi, F. Annealing Temperature Effects on Superduplex Stainless Steel Uns S32750 Welded Joints. Ii: Pitting Corrosion Resistance Evaluation. J. Mater. Sci. 2010, 45, 4378–4389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pragatheswaran, T.; Rajakumar, S.; Balasubramanian, V. Optimization of the Weld Characteristics of Plasma-Arc Welded Titanium Alloy Joints: An Experimental Study. Mater. Manuf. Process. 2021, 37, 896–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ureña, A.; Otero, E.; Utrilla, M.V.; Múnez, C.J. Weldability of a 2205 Duplex Stainless Steel Using Plasma Arc Welding. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2007, 182, 624–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.-S.; Wang, L.; Ren, W.-J.; Zhang, X.-Y. Plasma Arc Welding: Process, Sensing, Control and Modeling. J. Manuf. Process. 2014, 16, 74–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, A.; Tripathy, S. Development in Plasma Arc Welding Process: A Review. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 41, 363–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correa, E.O.; Costa, S.C.; Santos, J.N. Weldability of Iron-Based Powder Metal Materials Using Pulsed Plasma Arc Welding Process. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2008, 198, 323–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.-M.; Cui, S.-L.; Luo, Z.; Zhang, C.-Z.; Wang, Z.-M.; Zhang, Y.-C. Plasma Arc Welding: Process Variants and Its Recent Developments of Sensing, Controlling and Modeling. J. Manuf. Process. 2016, 23, 315–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taban, E.; Kaluc, E. Welding Behaviour of Duplex and Superduplex Stainless Steels Using Laser and Plasma Arc Welding Processes. Weld. World 2011, 55, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, F.-J.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, Y.-F.; Jin, Y.-J.; Li, J.-P.; Hou, W.-T. Effects of Beam Offset on the Macro Defects, Microstructure and Mechanical Behaviors in Dissimilar Laser Beam Welds of Sdss2507 and Q235. J. Manuf. Process. 2020, 55, 335–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Oliveira, J.P.; Li, Y.-L.; Tan, C.-W.; Gao, C.-K.; Zhao, Y.-X.; Yu, Z.-S. Laser Techniques for Dissimilar Joining of Aluminum Alloys to Steels: A Critical Review. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2022, 301, 117443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva Leite, C.G.; Da Cruz Junior, E.J.; Lago, M.; Zambon, A.; Calliari, I.; Ventrella, V.A. Nd: Yag Pulsed Laser Dissimilar Welding of Uns S32750 Duplex with 316l Austenitic Stainless Steel. Materials 2019, 12, 2906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, B.; Luo, T.-W.; Feng, M.-J. Effect of Nitrogen Content on the Microstructure and Properties of the Laser-Arc Hybrid Welding Joint of High Nitrogen Steel. Optik 2021, 243, 167478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marimuthu, P.; Dinesh Babu, P.; Ram Prabhu, T. Laser Welding of Ze41 Mg Alloy: Experimental Investigations on the Effect of Parameters and Nondestructive Testing. Trans. Indian Inst. Met. 2020, 73, 1587–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saravanan, S.; Sivagurumanikandan, N.; Raghukandan, K. Effect of Heat Input on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Nd: Yag Laser Welded Super Duplex Stainless Steel-Numerical and Experimental Approach. Optik 2019, 185, 447–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolenic, F.; Kovac, L.; Drimal, D. Effect of Laser Welding Conditions on Austenite/Ferrite Ratio in Duplex Stainless Steel 2507 Welds. Weld. World 2011, 55, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saravanan, S.; Raghukandan, K.; Sivagurumanikandan, N. Pulsed Nd: Yag Laser Welding and Subsequent Post-Weld Heat Treatment on Super Duplex Stainless Steel. J. Manuf. Process. 2017, 25, 284–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhury, B.; Chandrasekaran, M. Microstructural Investigation and Integrated Optimization of Weld Bead Characteristics in Electron Beam Welding of Inconel 825. Trans. Indian Inst. Met. 2021, 74, 2681–2701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.-Q.; Jing, H.-Y.; Xu, L.-Y.; Han, Y.-D.; Zhao, L.; Lv, X.-Q.; Zhang, J.-Y. Influence of Heat Input in Electron Beam Process on Microstructure and Properties of Duplex Stainless Steel Welded Interface. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 435, 352–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Turner, R.; Brooks, J.; Basoalto, H. A Study of Process-Induced Grain Structures During Steady State and Non-Steady State Electron-Beam Welding of a Titanium Alloy. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2022, 113, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tóth, T.; Krasnorutskyi, S.; Hensel, J.; Dilger, K. Electron Beam Welding of 2205 Duplex Stainless Steel Using Pre-Placed Nickel-Based Filler Material. Int. J. Press. Vessel. Pip. 2021, 191, 104354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.-M.; Dong, Q.-L.; Wang, P.-F.; Chen, H. Review of Electron Beam Welding Technology in Space Environment. Optik 2021, 225, 165720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramkumar, K.D.; Mishra, D.; Vignesh, M.K.; Ganesh Raj, B.; Arivazhagan, N.; Naren, S.V.; Suresh Kumar, S. Metallurgical and Mechanical Characterization of Electron Beam Welded Super-Duplex Stainless Steel Uns 32750. J. Manuf. Process. 2014, 16, 527–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.-W.; Huang, Y.-F.; Aoh, J.-N. Strengthening Mechanisms of Aluminum Matrix Composite Containing Cu-Coated Sic Particles Produced by Friction Stir Processing. J. Chin. Inst. Eng. 2019, 42, 653–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suresha, C.N.; Rajaprakash, B.M.; Upadhya, S. A Study of the Effect of Tool Pin Profiles on Tensile Strength of Welded Joints Produced Using Friction Stir Welding Process. Mater. Manuf. Process. 2011, 26, 1111–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chien, C.-H.; Lin, W.-B.; Chen, T. Optimal Fsw Process Parameters for Aluminum Alloys Aa5083. J. Chin. Inst. Eng. 2011, 34, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babu, K.T.; Muthukumaran, S.; Kumar, C.H.B. The Role of Material Location on the First Mode of Metal Transfer and Weld Formation in Dissimilar Friction Stir Welded Thin Sheets. Trans. Indian Inst. Met. 2019, 72, 1589–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajesh, S.; Badheka, V. Influence of Heat Input/Multiple Passes and Post Weld Heat Treatment on Strength/Electrochemical Characteristics of Friction Stir Weld Joint. Mater. Manuf. Process. 2018, 33, 156–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayabalakrishnan, D.; Balasubramanian, M. Eccentric-Weave Fsw between Cu and Aa 6061-T6 with Reinforced Graphene Nanoparticles. Mater. Manuf. Process. 2017, 33, 333–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, R.S.; Ma, Z.Y. Friction Stir Welding and Processing. Mater. Sci. Eng. R Rep. 2005, 50, 1–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giorjão, R.A.R.; Pereira, V.F.; Terada, M.; Fonseca, E.B.d.; Marinho, R.R.; Garcia, D.M.; Tschiptschin, A.P. Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Friction Stir Welded 8 Mm Pipe Saf 2507 Super Duplex Stainless Steel. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2019, 8, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, M.K.; Gunasekaran, G.; Rao, A.G.; Kashyap, B.P.; Prabhu, N. Effect of Multipass Friction Stir Processing on Mechanical and Corrosion Behavior of 2507 Super Duplex Stainless Steel. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2016, 26, 849–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; He, D.-Y.; Guo, F.; Li, X.-Y.; Jiang, J.-M. Effect of Fiber Laser–Mig Hybrid Process Parameters on Weld Bead Shape and Tensile Properties of Commercially Pure Titanium. Mater. Manuf. Process. 2010, 25, 1309–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.-A.; Gao, X.-D.; Zhang, N.-F.; Ye, G.-W.; Liu, G.-Q.; Zhang, Y.-X. Monitoring of 304 Austenitic Stainless-Steel Laser-Mig Hybrid Welding Process Based on Emd-Svm. J. Manuf. Process. 2022, 73, 736–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagger, C.; Olsen, F.O. Review of Laser Hybrid Welding. J. Laser Appl. 2005, 17, 2–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acherjee, B. Hybrid Laser Arc Welding: State-of-Art Review. Opt. Laser Technol. 2018, 99, 60–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, K.; Li, R.-F.; Wang, G.-J.; Sun, Z. Structure and Mechanical Properties of Laser-Mig Hybrid Welded Saf 2507 Super Duplex Stainless Steel Joints. Int. J. Mod. Phys. B 2019, 33, 1940037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, K.; Li, R.-F.; Wang, G.-J.; Li, G.-Z.; Liu, B.; Wu, M.-F. Microstructure and Corrosion Properties of Laser-Welded Saf 2507 Super Duplex Stainless Steel Joints. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2018, 28, 287–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
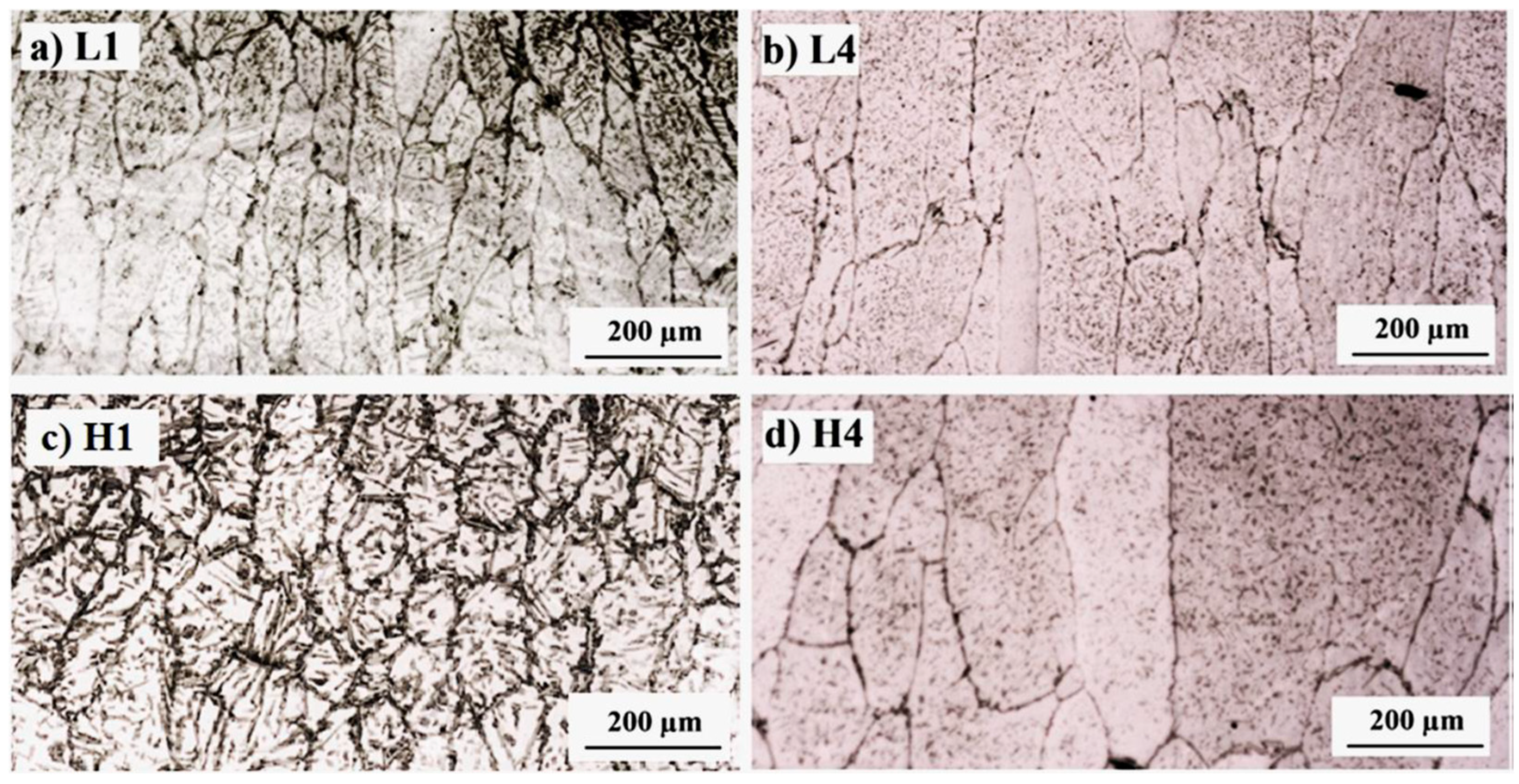

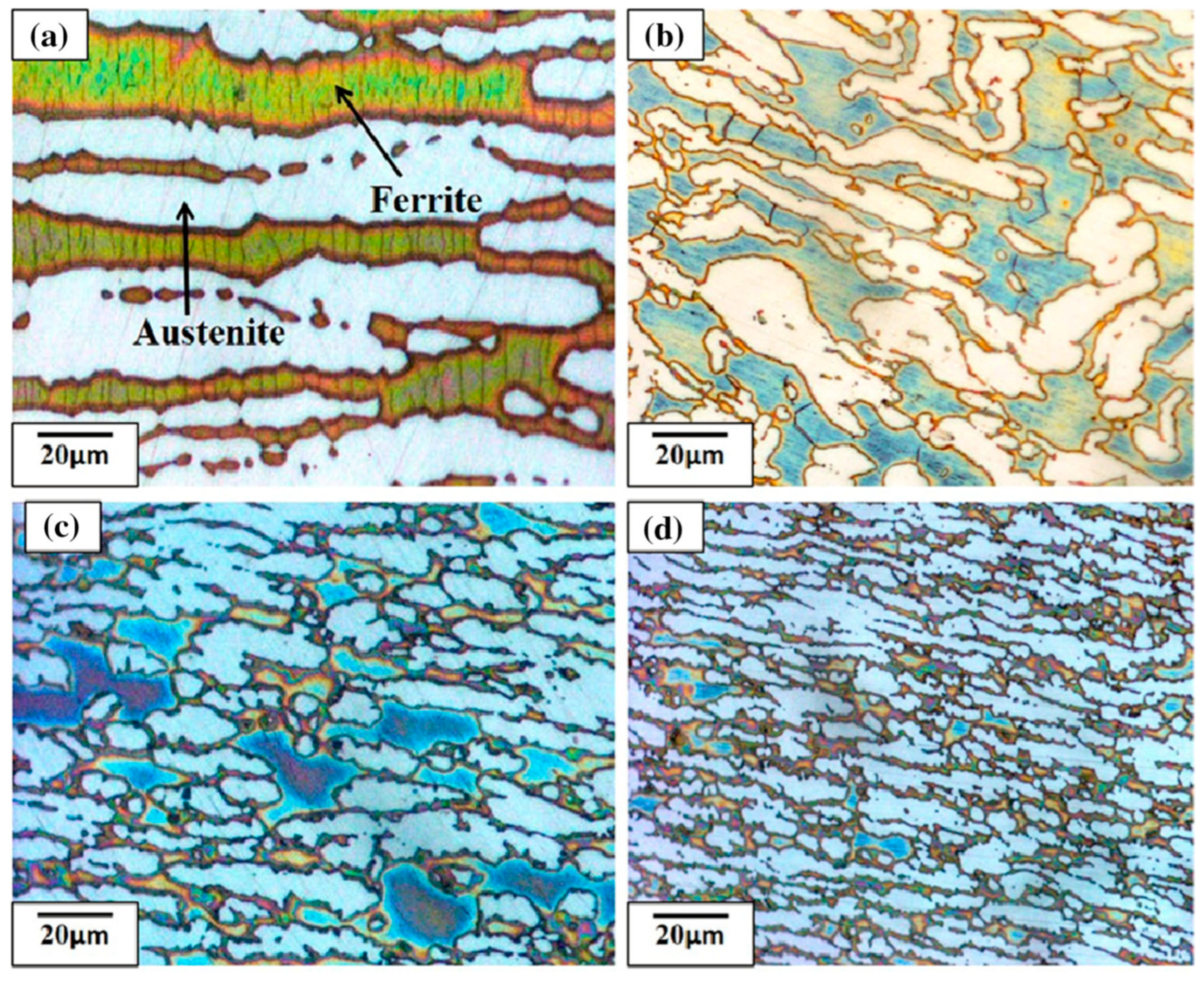
| BM | L1 | L2 | L3 | L4 | H1 | H2 | H3 | H4 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nitrogen content (wt.%) | 0.28 | 0.23 | 0.21 | 0.18 | 0.17 | 0.21 | 0.19 | 0.13 | 0.10 |
| Ferrite content (%) | 55 ± 3 | 51 ± 3 | 57 ± 3 | 65 ± 3 | 75 ± 3 | 51 ± 3 | 56 ± 3 | 73 ± 3 | 79 ± 3 |
| Ferrite grain width (μm) | - | 56 ± 5 | 61 ± 5 | 92 ± 10 | 85 ± 3 | 85 ± 3 | 105 ± 6 | 125 ± 10 | 133 ± 12 |
| Welding Process | Author | Observation |
|---|---|---|
| GTAW | Hosseini VA et al. [16,23,42,43] | Compared with base metal, after four passes, the nitrogen content of samples with low and high heat input reduced 0.11 wt.% and 0.17 wt.%, respectively. The nitrogen loss resulted in an increase in nitride precipitates and the content and grain size of ferrite. |
| Du DF et al. [44] | The austenite content increases with the increase in the content of N2 in shielding gas. When using Ar +2~3% N2 as shielding gas, the austenite content was 51~53%. | |
| Ramkumar KD et al. [30,46] | When employing activated flux tungsten inert gas welding, the addition of flux (NiO, MoO3, and SiO2) can obtain a complete penetrated joint but has no significant effect on the content and grain size of ferrite. | |
| Zhang Z et al. [47,48] | Post-weld short duration heat treatment can reduce the ferrite content in the HAZ and WM and adjust the distribution of elements to improve the pitting corrosion resistance of welded joints. | |
| Moon IJ et al. [49] | A slow cooling rate after post-weld heat treatment may result in the σ phase precipitation in the weld joint, which is harmful to the pitting corrosion resistance. | |
| SAW | Cervo R et al. [54,55] | Even if nickel-rich filler metal is used, the austenite content of weld metal, compared with base metal, is lower due to the high cooling rate of the welding process. Post-weld heat treatment can increase the austenite content and pitting corrosion resistance of the weld joint. |
| PAW | Taban E et al. [62] | By controlling the heat input, the weld joints can exhibit a reasonable two-phase ratio and good low-temperature toughness. Compared with LBW, the austenite content of PAW joints is higher. |
| LBW | Saravanan S et al. [68,70] | A fully penetrated and defect-free weld joint can be obtained with high heat input. As the heat input increases, the hardness and tensile strength of the weld joint both increase firstand then decrease. After post-weld short duration heat treatment, the austenite content and pitting corrosion resistance of the weld joint increase while the hardness and tensile strength decrease. |
| Da Cruz Junior EJ et al. [18] | When electrolytic nickel foil is used as an added metal, a large amount of intragranular austenite forms in the weld metal and the ferrite–austenite ratio is similar to the base metal. | |
| Koleni D-IF et al. [69] | By controlling short-term heat input on the weld joint after welding, the ferrite–austenite ratio can be adjusted to a reasonable range. | |
| EBW | Zhang Z.-Q et al. [72], Tóth T. et al. [74] | A sound weld joint can be obtained by EBW. The ferrite–austenite ratio is similar to the base metal. The hardness and tensile strength of the weld joint is higher than that of the base metal while toughness is lower. |
| FSW | Giorjão RAR et al. [84] | An excellent weld joint without surface defects can be obtained, and grain refinement can be observed at the root of the weld joint due to the low thermal cycle hindering dynamic recrystallization. |
| Mishra MK et al. [83,85] | Both ferrite and austenite in the weld joint exhibit obvious grain refinement, and with the increase in the number of welding passes, the grain size of ferrite and austenite may become smaller. The micro-hardness, yield strength, tensile strength, lower ductility, and pitting corrosion resistance of welded joints are better than that of base material. | |
| Hybrid Welding | Qi K et al. [90,91] | Compared with LBW, the laser-MIG hybrid weld metal exhibits a higher austenite content and better pitting corrosion resistance. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, T.; Wang, K.; Lei, Y. A Review of Welding Process for UNS S32750 Super Duplex Stainless Steel. Materials 2024, 17, 5215. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17215215
Li T, Wang K, Lei Y. A Review of Welding Process for UNS S32750 Super Duplex Stainless Steel. Materials. 2024; 17(21):5215. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17215215
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Tianqing, Kai Wang, and Yucheng Lei. 2024. "A Review of Welding Process for UNS S32750 Super Duplex Stainless Steel" Materials 17, no. 21: 5215. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17215215
APA StyleLi, T., Wang, K., & Lei, Y. (2024). A Review of Welding Process for UNS S32750 Super Duplex Stainless Steel. Materials, 17(21), 5215. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17215215







