Fully Physically Crosslinked Hydrogel with Ultrastretchability, Transparency, and Freezing-Tolerant Properties for Strain Sensor
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Fabrication of PHEAA–Gl–NaCl Hydrogels
2.3. Characterization
2.4. Mechanical Test
2.5. Electrical Test
2.6. Application of PHEAA–Gl–NaCl Hydrogel-Based Sensor
3. Results
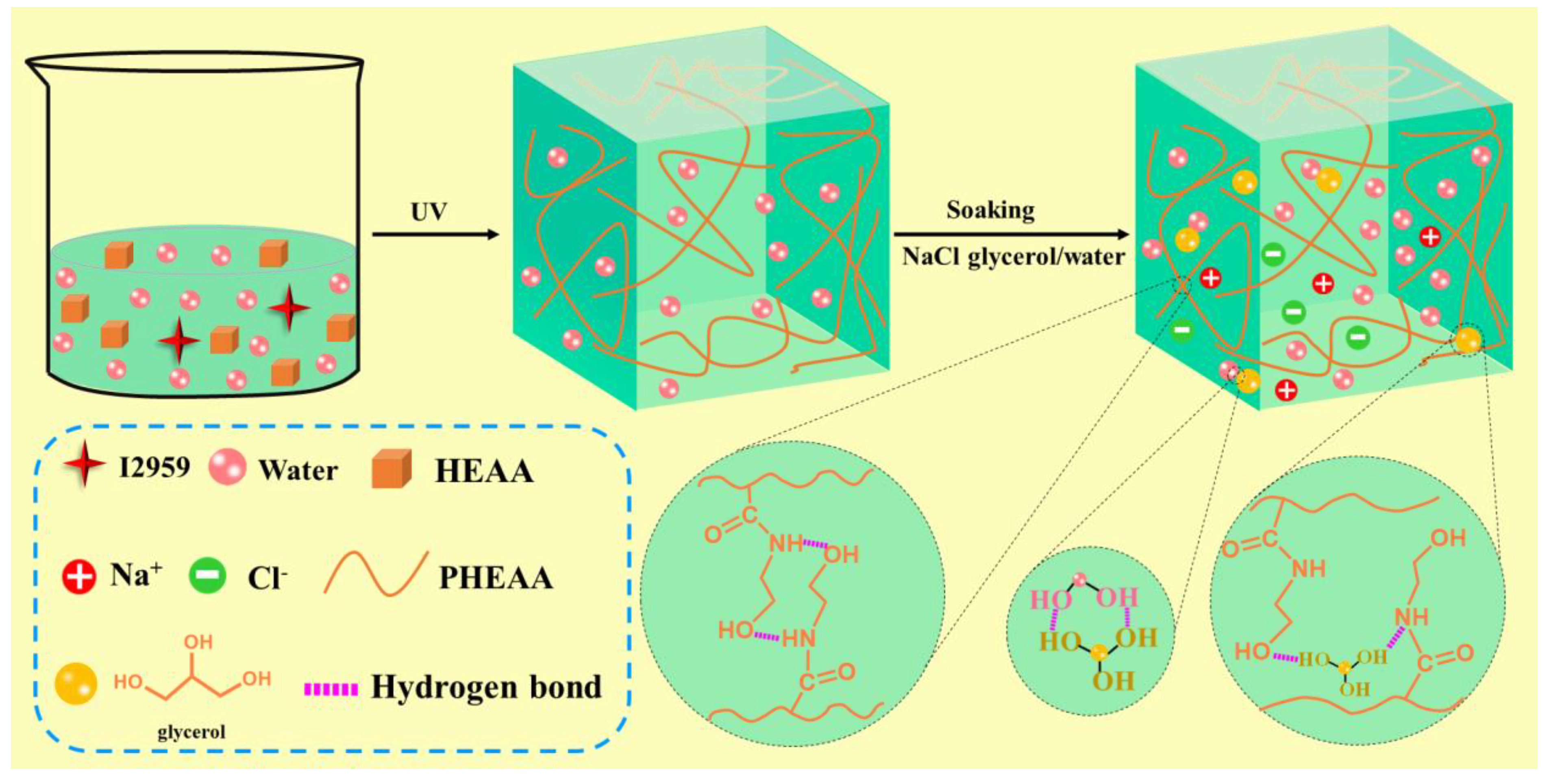
3.1. Preparation of PHEAA–Gl–NaCl Hydrogel
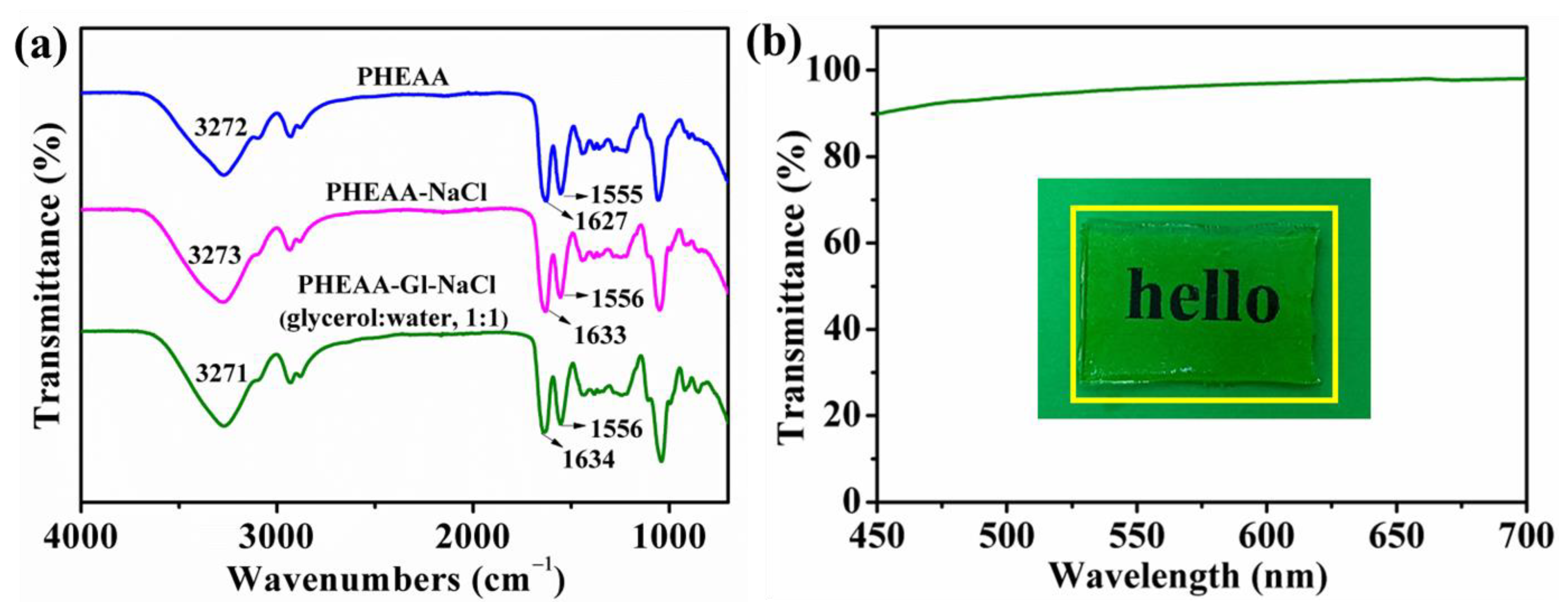
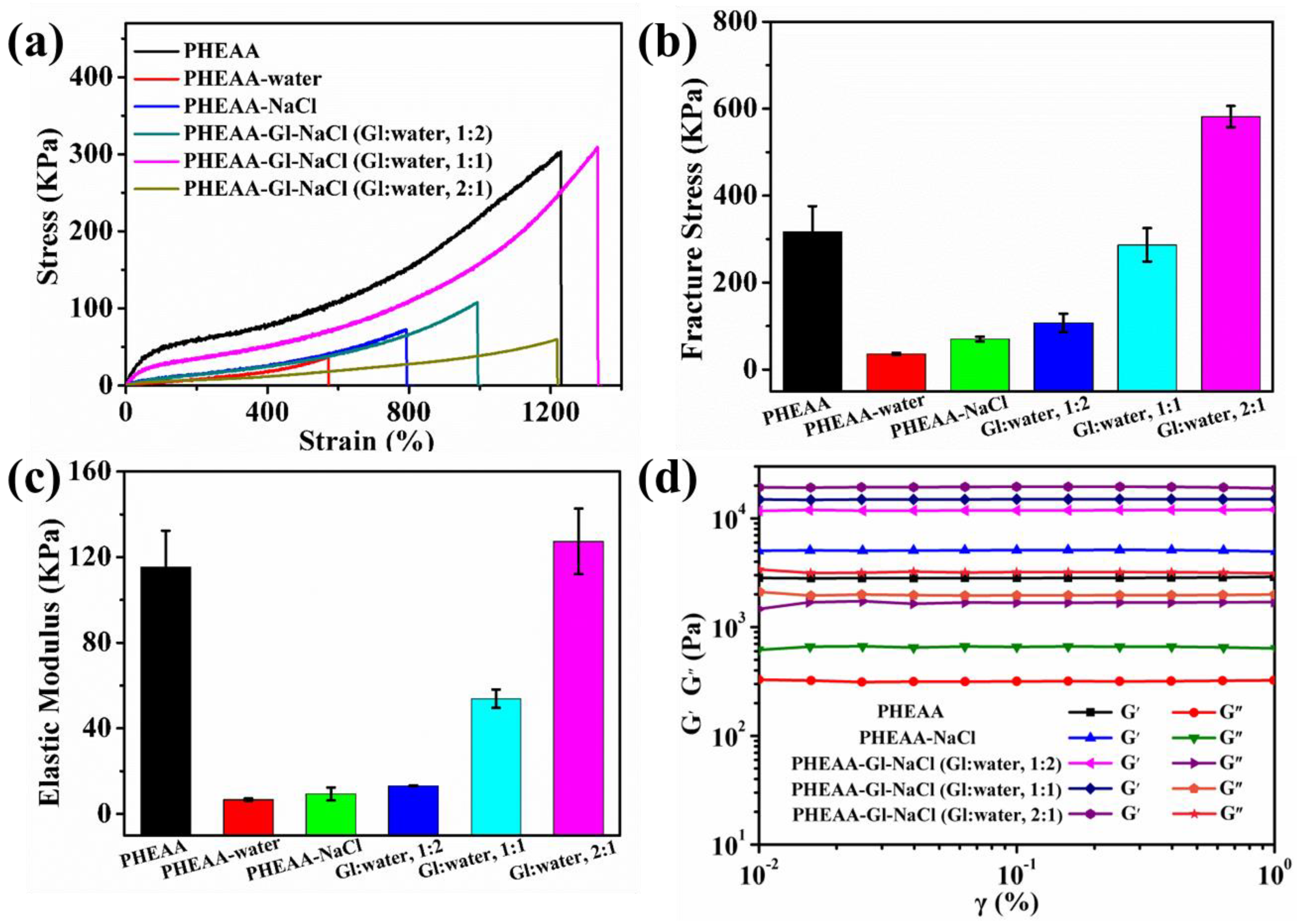
3.2. Mechanical Properties of PHEAA–Gl–NaCl Hydrogel
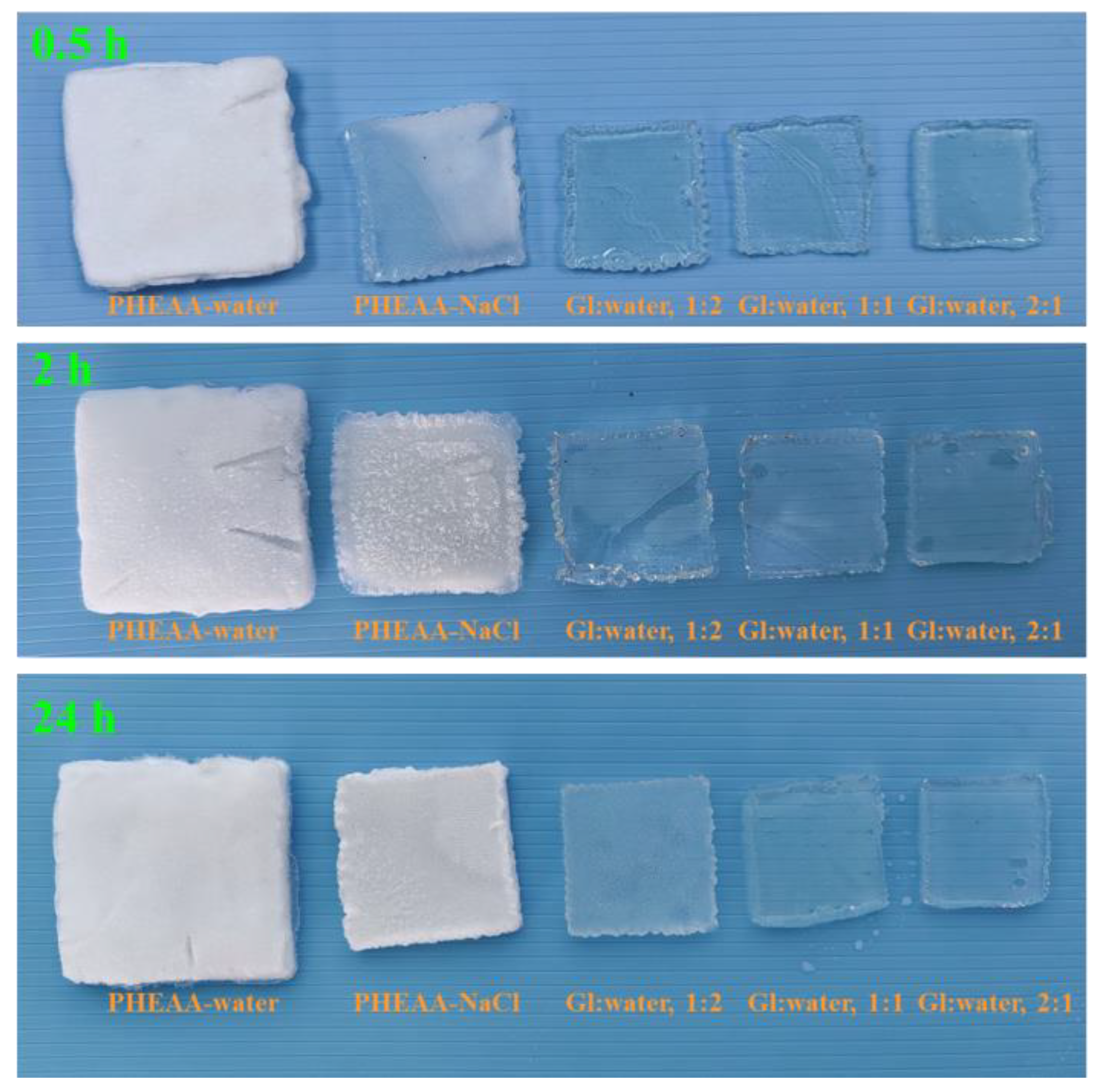
3.3. Anti-Freezing Properties of PHEAA–Gl–NaCl Hydrogel
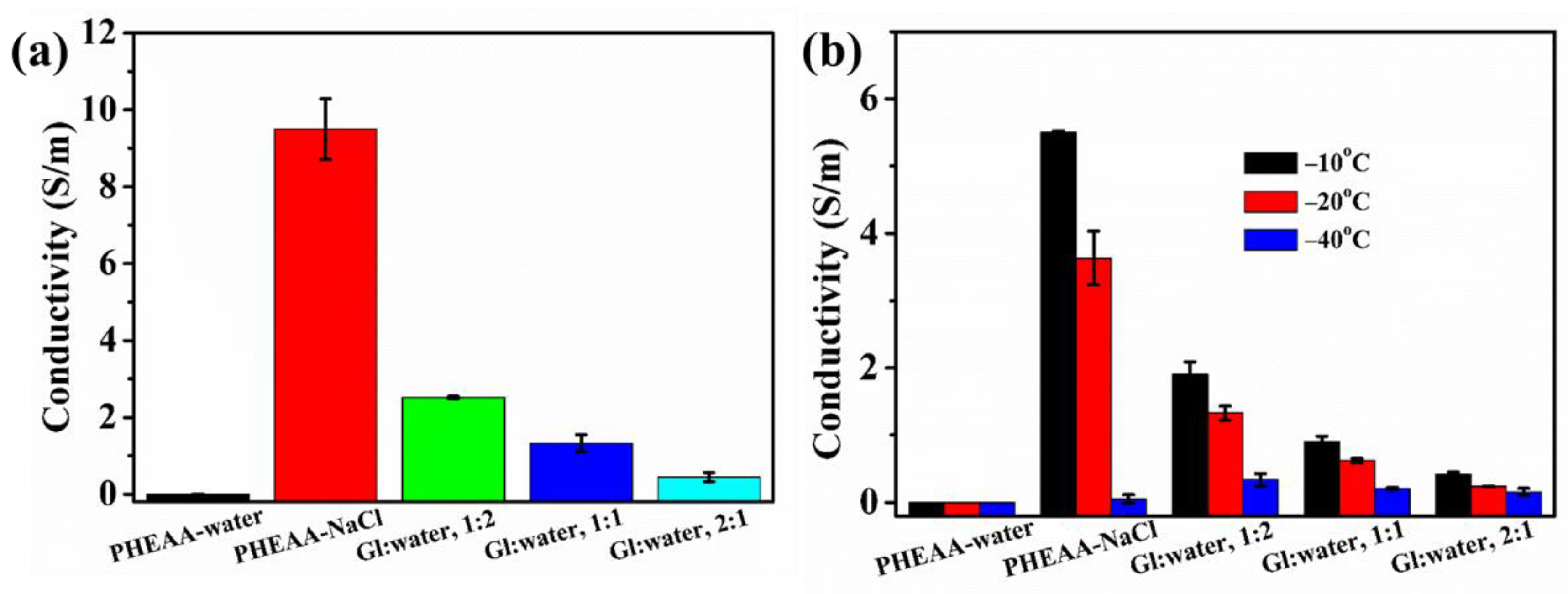
3.4. Conductivity of PHEAA–Gl–NaCl Hydrogel
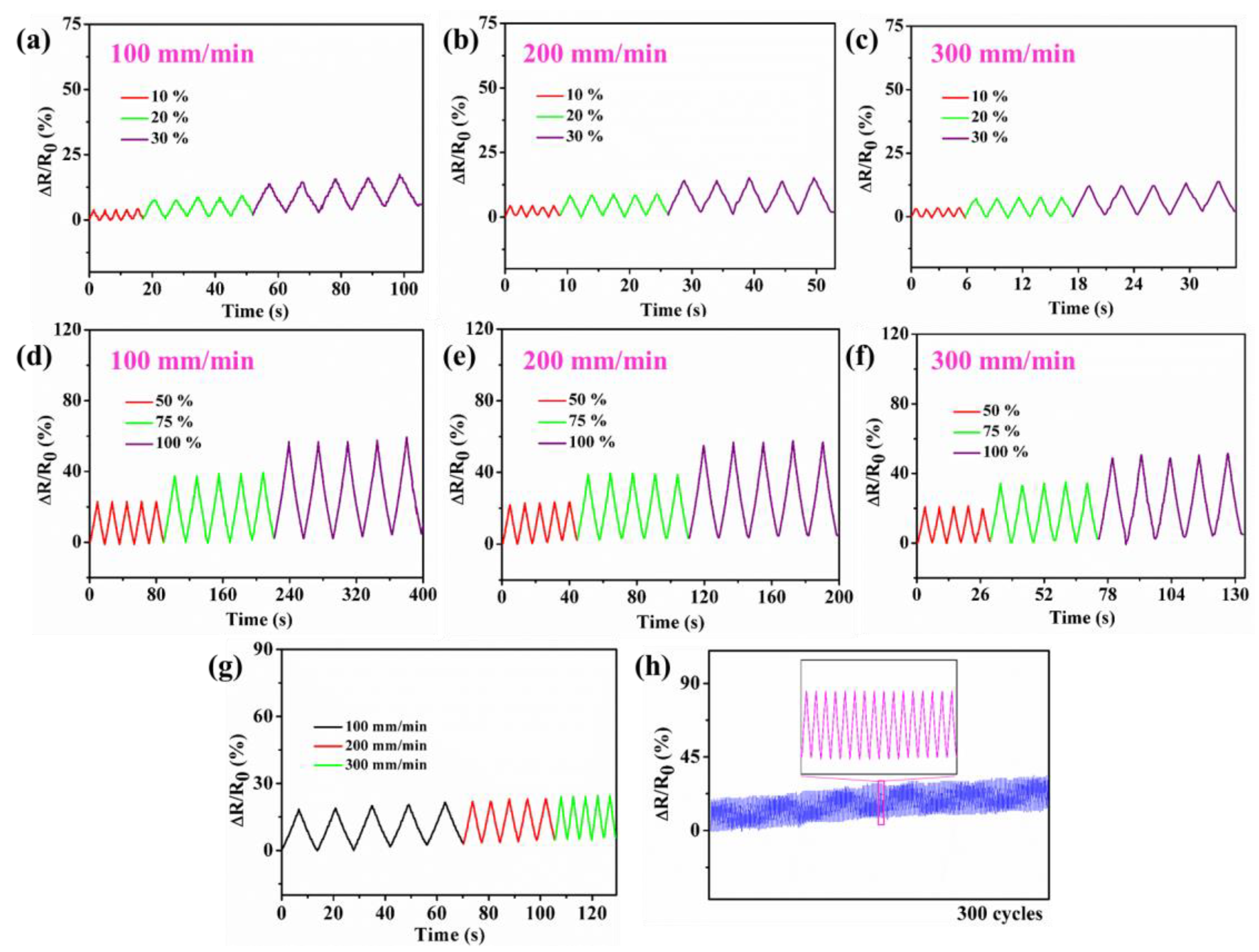
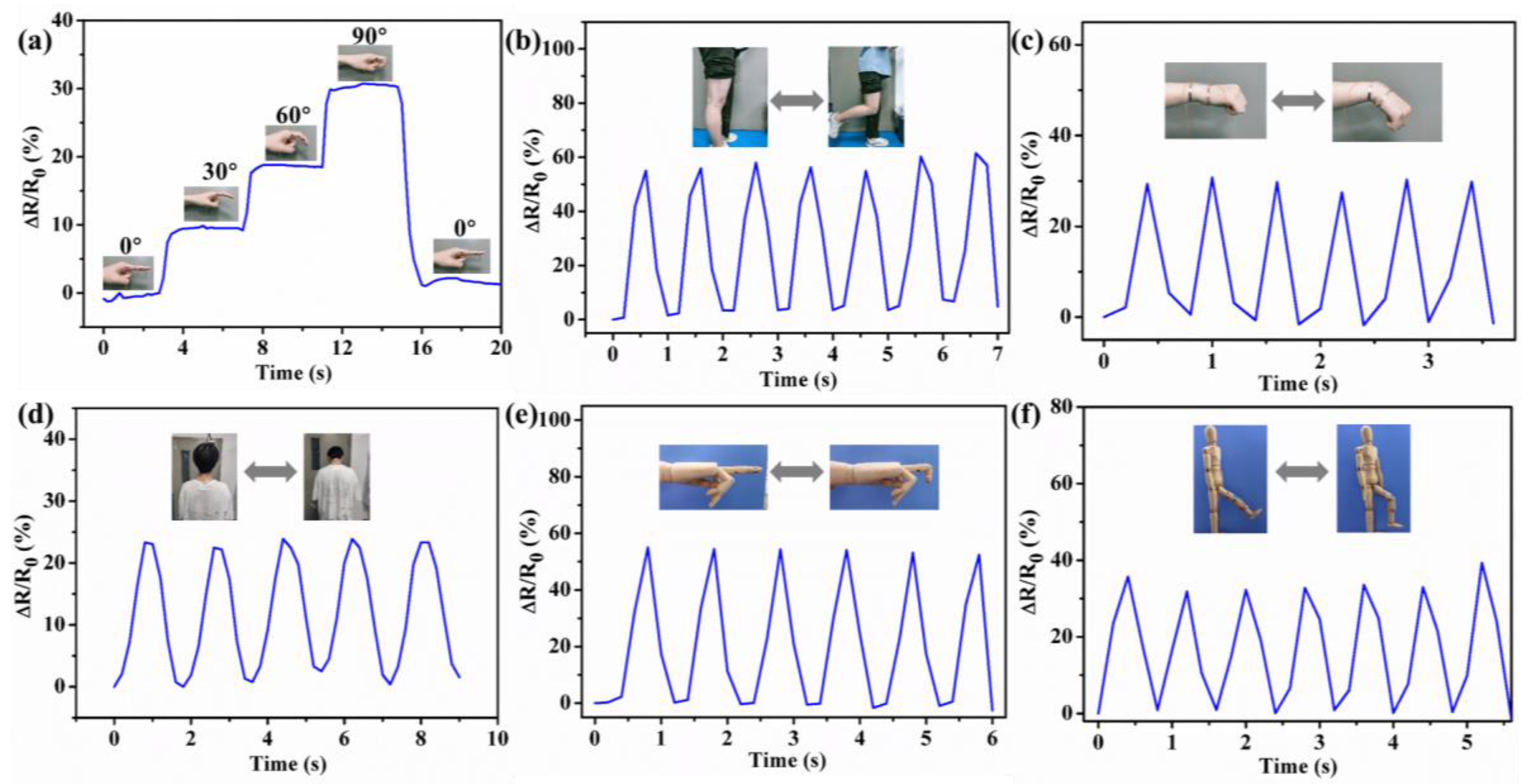
3.5. Performance as Strain Sensor
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhao, Y.; Jin, K.; Li, J.; Sheng, K.; Huang, W.; Liu, Y. Flexible and stretchable electrochemical sensors for biological monitoring. Adv. Mater. 2023, 202305917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Z.; Duan, S.; Liu, M.; Dang, C.; Qian, S.; Zhang, L.; Wang, H.; Yan, W.; Zhu, M. Insights into materials, physics, and applications in flexible and wearable acoustic sensing technology. Adv. Mater. 2024, 36, 202306880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Zhuo, F.; Zhou, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Dong, S.; Liu, X.; Elmarakbi, A.; Duan, H.; Fu, Y. Advances in graphene-based flexible and wearable strain sensors. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 464, 142576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Yao, Z.; Meng, X.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Z.; Wang, J.; Ma, G.; Liu, L.; Zhang, J.; Niu, S.; et al. High-fidelity, low-hysteresis bionic flexible strain sensors for soft machines. ACS Nano 2024, 18, 2520–2530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, Q.; Liu, W.; Liu, J.; Zhao, L.; Ren, Z.; Gu, H. Highly sensitive and robust polysaccharide-based composite hydrogel sensor integrated with underwater repeatable self-adhesion and rapid self-healing for human motion detection. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 24741–24754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yue, X.; Zhang, L.; Han, X.; Hong, J. Graphene-decorated polyurethane nanofiber membrane flexible sensor with different fiber orientation. Sensor. Actuat. A Phys. 2024, 376, 115628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.; Kumar, V.; Lee, D.; Choi, J. Synergistically toughened silicone rubber nanocomposites using carbon nanotubes and molybdenum disulfide for stretchable strain sensors. Compos. Part B Eng. 2023, 259, 110759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Wei, D.; Song, T.; Dou, C.; Shi, Y.; Li, X.; Kong, Z.; Zhang, Q. A self-compensating stretchable conductor based on a viscous fluid for wide-range flexible sensors. J. Mater. Chem. C 2023, 11, 10923–10930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Kong, L.; Huang, B.; Lin, B.; Fu, L.; Xu, C. A high-sensitive rubber-based sensor with integrated strain and humidity responses enabled by bionic gradient structure. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2024, 34, 202400789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, M.; Wang, Y.; Ma, D.; Wu, X.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, L.; Wan, P. Wearable MXene nanocomposites-based strain sensor with tile-like stacked hierarchical microstructure for broad-range ultrasensitive sensing. Nano Energy 2020, 78, 105187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Wei, Q.; Zhao, M. Flexible and stretchable poly(styrene-butadiene-styrene)/Mxene nanosheet composite and coaxial fibers for wearable strain sensors. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 6, 8743–8751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, T.; Zhu, Z.; Chen, M.; Yan, X.; Li, Y. Functional hydrogel strain sensors for smart electronic devices: Strategies and recent progress. ACS Appl. Electron. Mater. 2024, 6, 5402–5428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaidi, S.; Saeed, A.; Heo, J.; Lee, J. Multifunctional small biomolecules as key building blocks in the development of hydrogel-based strain sensors. J. Mater. Chem. A 2023, 11, 13844–13875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Tian, B.; Liang, J.; Wu, W. Functional conductive hydrogels: From performance to flexible sensor applications. Mater. Chem. Front. 2023, 7, 2925–2957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Pan, S.; Xia, M.; Yin, J.; Li, H.; Sun, Z.; Zhan, Y.; Zhang, Y. Transparent, highly stretchable, fully self-recoverable ionic hydrogel for flexible ultra-sensitive sensors. Mater. Res. Bull. 2022, 146, 111627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Z.; Liu, S.; Bai, J.; Yin, J.; Li, N.; Jiao, T. Ionic conductive hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose reinforced hydrogels with extreme stretchability, self-adhesion and anti-freezing ability for highly sensitive skin-like sensors. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 220, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, M.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, T.; Wang, Y.; Sheng, L.; Li, J.; Peng, J.; Zhai, M. Mechanically excellent, notch-insensitive, and highly conductive double-network hydrogel for flexible strain sensor. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2024, 16, 22604–22613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Dai, L.; Sun, T.; Qin, C.; Wang, J.; Sun, J.; Dai, L. A transparent, self-adhesive and fully recyclable conductive pva based hydrogel for wearable strain sensor. Polymer 2023, 283, 126281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Liu, B.; Hu, N.; Fan, Q.; Zhan, F.; Zhang, Z.; Ni, Z.; Li, X.; Hu, T. A biodegradable, highly sensitive and multifunctional mechanical sensor based on rgo-silk fibroin hydrogel for human motion detection and gesture recognition. J. Mater. Chem. A 2024, 12, 3283–3293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, S.; Gao, Z.; Bi, D.; Qu, N.; Huang, S.; Zhao, X.; Li, R. Highly conductive and tough polyacrylamide/sodium alginate hydrogel with uniformly distributed polypyrrole nanospheres for wearable strain sensors. Carbohydr. Polym. 2023, 315, 120953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, D.; Won, S.; Patil, T.; Dutta, S.; Lim, K.; Han, S. Unzipped carbon nanotubes assisted 3d printable functionalized chitosan hydrogels for strain sensing applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 265, 131025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, B.; He, S.; Yao, M.; Tan, Z.; Li, X.; Liu, M.; Yu, C.; Liang, L.; Zhao, Z.; Guo, Z.; et al. MXene-containing anisotropic hydrogels strain sensors with enhanced sensing performance for human motion monitoring and wireless transmission. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 461, 142099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Song, L.; Wang, Q.; Wang, L.; Li, S.; Du, H.; Wang, C.; Wang, Y.; Xue, P.; Nie, W.; et al. Multifunctional acetylated distarch phosphate based conducting hydrogel with high stretchability, ultralow hysteresis and fast response for wearable strain sensors. Carbohydr. Polym. 2023, 318, 121106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ara, L.; Khan, M.; Ullah, R.; Shah, L. Hydrophobically associated ionic conductive hydrogels as strain, pressure, and an electronic sensor for human motions detection. sensor. Actuat. A Phys. 2023, 362, 114618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Zhou, H.; Zheng, B.; Wei, C.; Ma, A.; Jin, X.; Chen, W.; Liu, H. Stable flexible electronic devices under harsh conditions enabled by double-network hydrogels containing binary cations. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2024, 16, 7768–7779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, W.; Sheng, N.; Zhang, X.; Luan, Z.; Qi, P.; Lin, M.; Tan, Y.; Xia, Y.; Li, Y.; Sui, K. Design of injectable Agar/NaCl/polyacrylamide ionic hydrogels for high performance strain sensors. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 211, 322–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Ren, X.; Jia, F.; Gao, G. Highly conductive hydrogel sensors driven by amylose with freezing and dehydration resistances. J. Mater. Chem. C 2022, 10, 12873–12882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Hu, O.; Zhang, J.; Hou, L.; Ye, D.; Jiang, X.; Xiao, G. Preparation of tough and ionic conductive pva/carboxymethyl chitosan bio-based organohydrogels with long-term stability for strain sensor. Cellulose 2022, 29, 9323–9339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Gao, S.; Jian, J.; Shi, X.; Lai, C.; Wang, C.; Xu, F.; Chu, F.; Zhang, D. Skin-mimicking strategy to fabricate strong and highly conductive anti-freezing cellulose-based hydrogels as strain sensors. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 227, 462–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Liu, Y.; Ren, B.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, J.; Xu, L.; Chen, Q.; Zheng, J. Super bulk and interfacial toughness of physically crosslinked double-network hydrogels. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2017, 27, 201703086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, L.; Gao, G. Stretchable organohydrogel with adhesion, self-healing, and environment-tolerance for wearable strain sensors. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 28993–29003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Guo, Z.; Chen, Y.; Luo, Y.; Xie, S.; Zhang, Y.; Tan, H.; Xu, L.; Zheng, J. Tough, adhesive, self-healing, fully physical crosslinked κ-CG-K+/PHEAA double-network ionic conductive hydrogels for wearable sensors. Polymer 2021, 236, 124321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Tian, G.; Du, Y.; Shi, P.; Li, N.; Li, Y.; Qin, Z.; Jiao, T.; He, X. Highly stretchable, low-hysteresis, and adhesive TA@MXene-composited organohydrogels for durable wearable sensors. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2024, 34, 202315813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, F.; Jiang, M.; Yu, Q.; Hao, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, J.; Luo, S.; Li, J. Ionic conductive organohydrogel with ultrastretchability, self-healable and freezing-tolerant properties for wearable strain sensor. Front. Chem. 2021, 9, 758844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, M.; Hao, X.; Ye, L.; Luo, S.; Ji, F. Preparation and properties of poly(N-hydroxyethyl acrylamide)-gelatin-based hydrogel sensor. Polym. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2022, 38, 149–158. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, F.; Zeng, Y.; Yu, Q.; Zhu, J.; Xu, J.; Guo, J.; Zhou, Q.; Luo, S.; Li, J. Fully physically crosslinked organohydrogel with ultrastretchability, transparency, freezing-tolerant, self-healing, and adhesion properties for strain sensor. Polymer 2023, 268, 125718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Jia, F.; Gao, G. Ionic conductive hydrogels toughened by latex particles for strain sensors. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 2021, 64, 827–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, S.; Song, S.; Jia, F.; Gao, G. A flexible, adhesive and self-healable hydrogel-based wearable strain sensor for human motion and physiological signal monitoring. J. Mater. Chem. B 2019, 7, 4638–4648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Wang, H.; Luo, J.; Ren, G.; Wang, J.; Chen, Y.; Jia, P. Ultrastretchable, adhesive, anti-freezing, conductive, and self-healing hydrogel for wearable devices. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 4, 1784–1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Jia, F.; Gao, G. Transparent and conductive amino acid-tackified hydrogels as wearable strain sensors. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 375, 121915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, X.; Zhu, K.; Chen, H.; Ye, S.; Cui, P.; Dou, L.; Ma, J.; Zhao, C.; He, J.; Feng, P. Recyclable, anti-freezing and anti-drying silk fibroin-based hydrogels for ultrasensitive strain sensors and all-hydrogel-state super-capacitors. Mater. Today Chem. 2023, 32, 101624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Jiang, L.; Yan, M.; Bi, H.; Wang, Q. Highly stretchable, tough and conductive chitin nanofiber composite hydrogel as a wearable sensor. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 242, 124780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, F.; Shang, P.; Lai, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhang, G.; Lin, D.; Xu, J.; Cai, D.; Qin, Z. Fully physically crosslinked conductive hydrogel with ultrastretchability, transparency, and self-healing properties for strain sensors. Materials 2023, 16, 6491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shang, P.; Ji, Y.; Ji, F. Fully Physically Crosslinked Hydrogel with Ultrastretchability, Transparency, and Freezing-Tolerant Properties for Strain Sensor. Materials 2024, 17, 5102. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17205102
Shang P, Ji Y, Ji F. Fully Physically Crosslinked Hydrogel with Ultrastretchability, Transparency, and Freezing-Tolerant Properties for Strain Sensor. Materials. 2024; 17(20):5102. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17205102
Chicago/Turabian StyleShang, Pengbo, Yang Ji, and Feng Ji. 2024. "Fully Physically Crosslinked Hydrogel with Ultrastretchability, Transparency, and Freezing-Tolerant Properties for Strain Sensor" Materials 17, no. 20: 5102. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17205102
APA StyleShang, P., Ji, Y., & Ji, F. (2024). Fully Physically Crosslinked Hydrogel with Ultrastretchability, Transparency, and Freezing-Tolerant Properties for Strain Sensor. Materials, 17(20), 5102. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17205102



