Non-Isothermal Analysis of the Crystallization Kinetics of Amorphous Mg72Zn27Pt1 and Mg72Zn27Ag1 Alloys
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
- -
- The background resulting from the scattering of X-rays in air and the optics of the incident and diffracted beam (slits/collimators) were measured.
- -
- The sample was then measured in the same way. The optics of the incident beam were set to illuminate only the sample surface and exclude the signal from the fixture.
- -
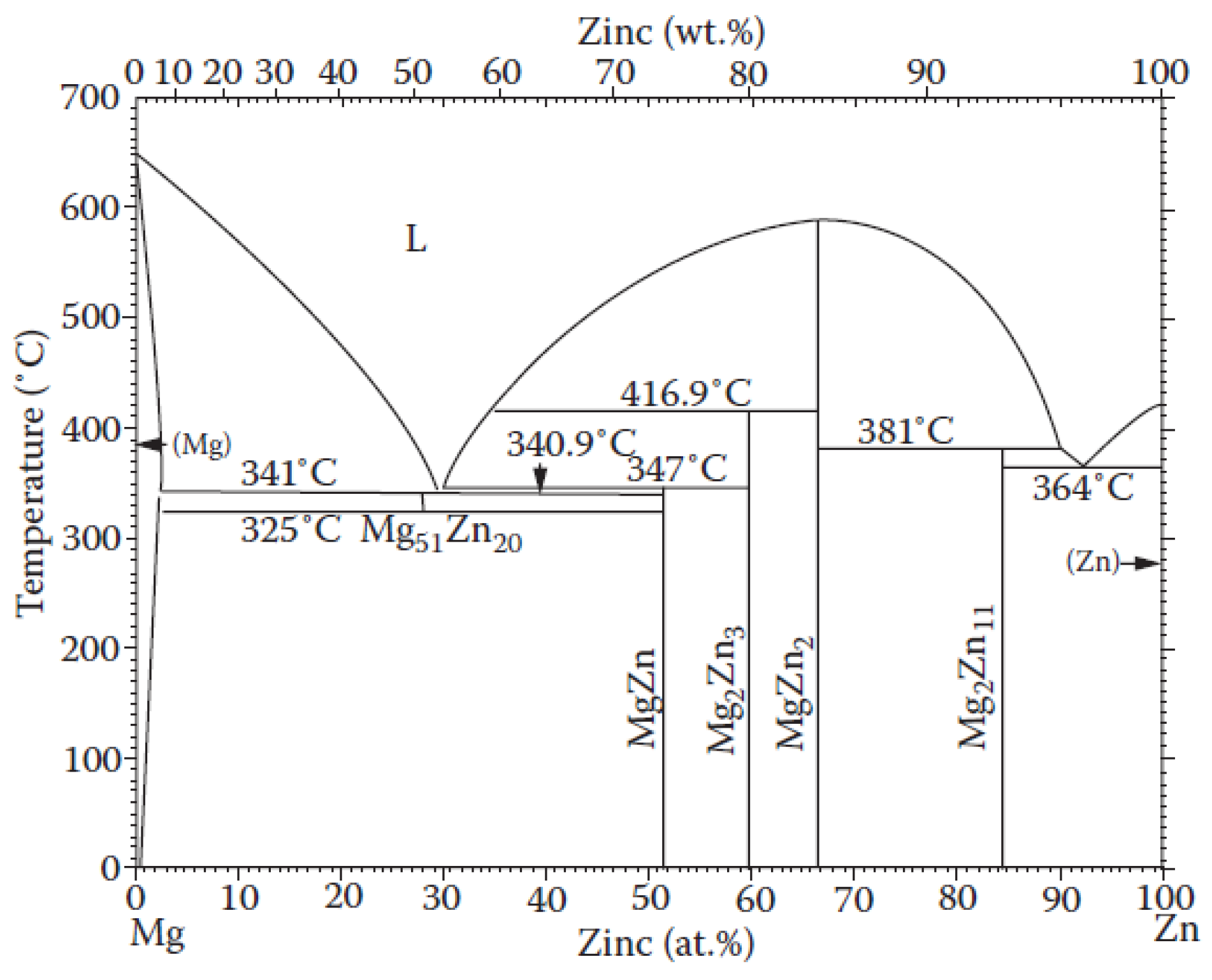
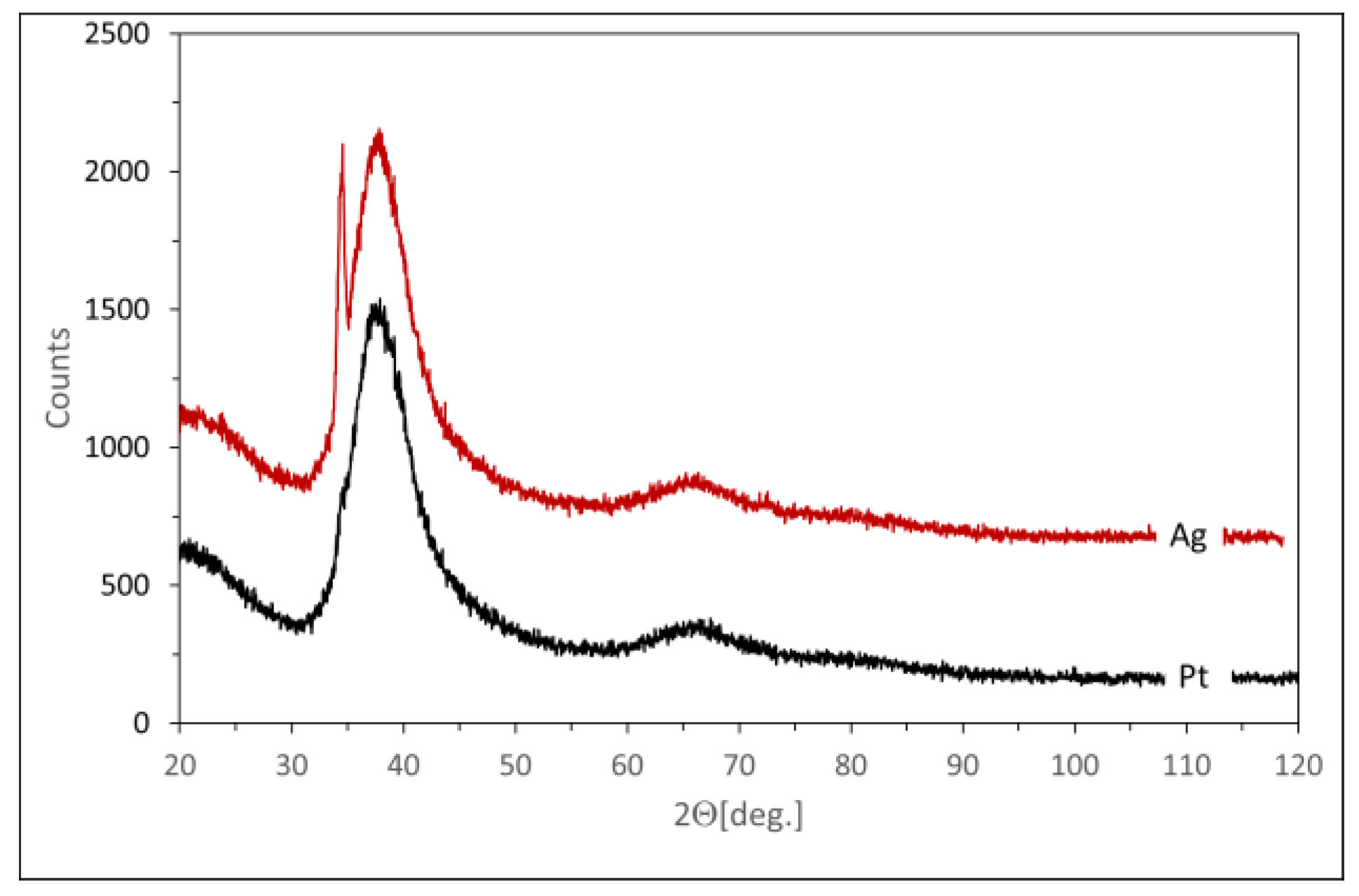
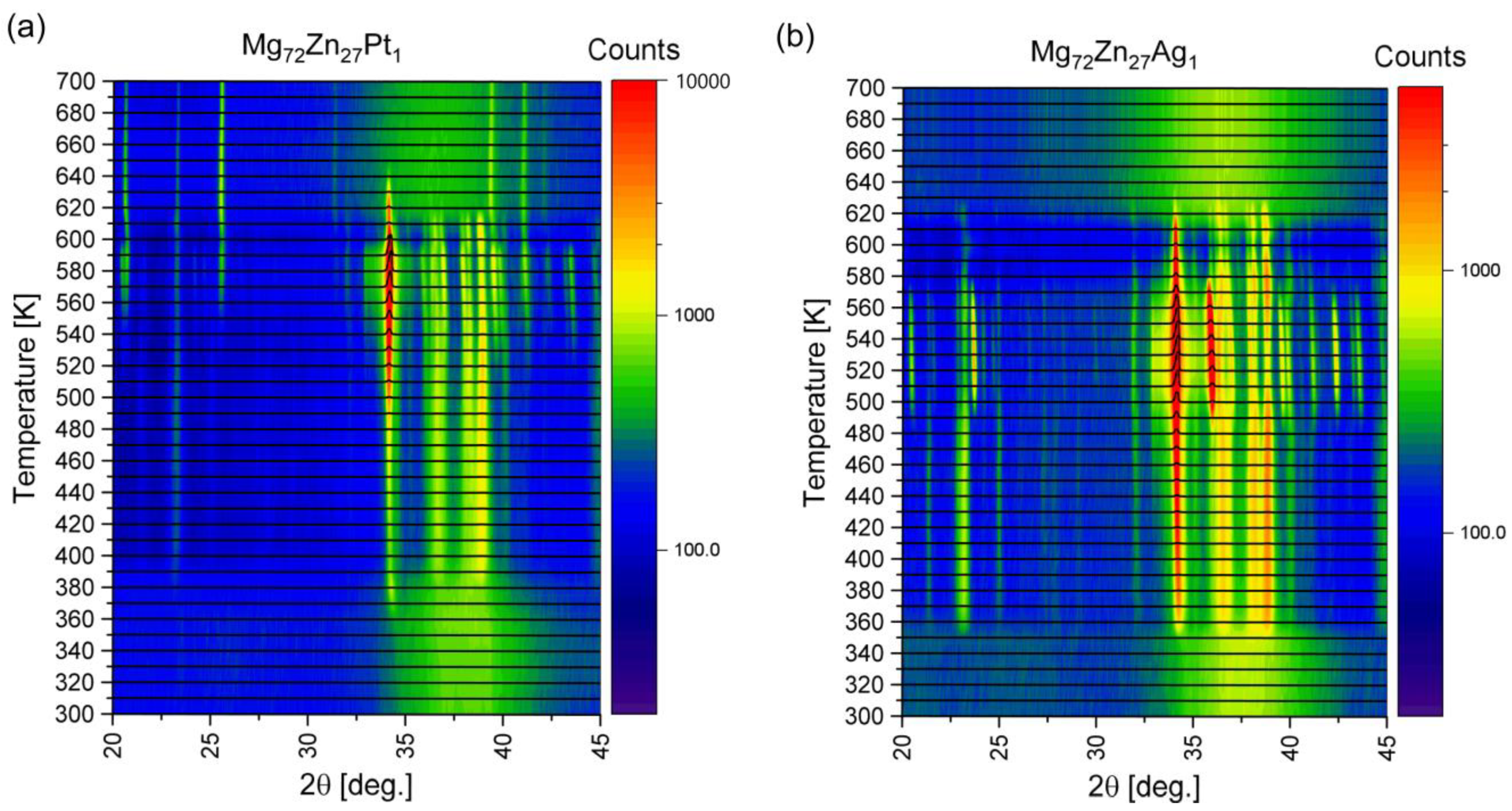
- A background scan was then extracted from the sample scan, and a procedure was used to compare the surface under the reflections with the total surface. This procedure can be used because, according to EDS data, the amorphous and crystalline phases have the same composition. Therefore, no correction was required for different scattering lengths. The maximum amorphous contribution corresponds to interplanar distances of 2.9–1.9 Å. This correlates quite well with the expected metallic radius of Mg, Zn, and Ag, which are 1.6, 1.37, and 1.75 Å, respectively.
4. Conclusions
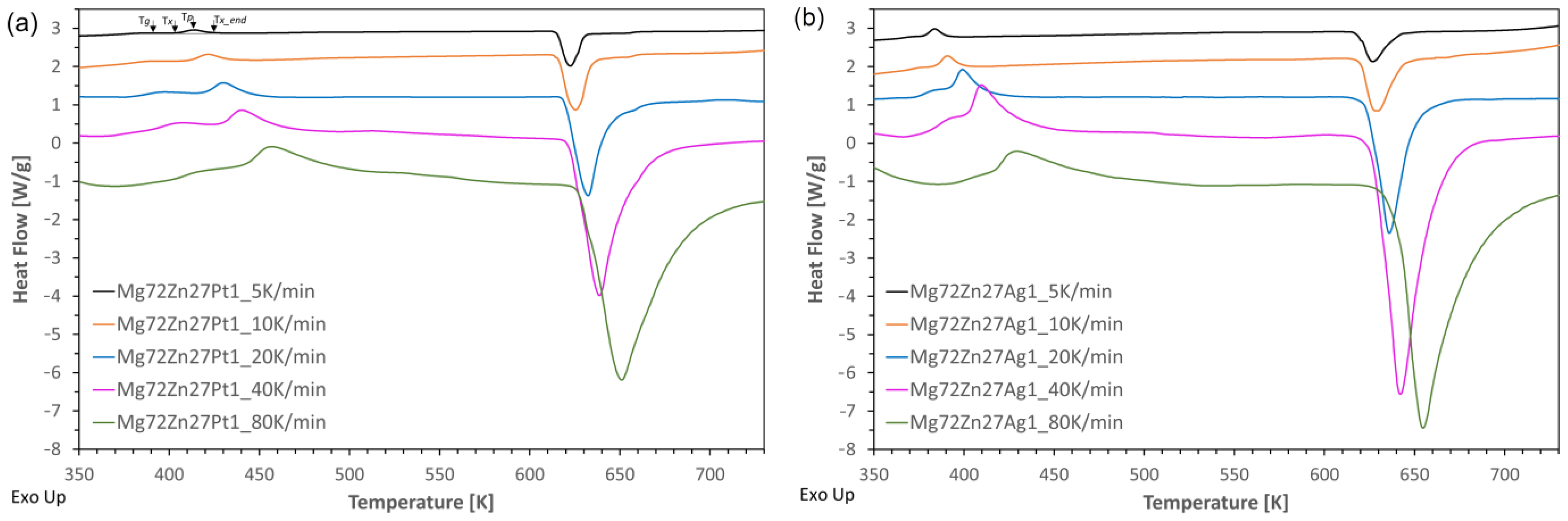
- The addition of platinum and silver causes crystallization with one distinct crystallization peak and shifts the onset of crystallization towards higher temperatures compared to the two-component Mg72Zn28 alloy [20], but Pt has the greatest influence;
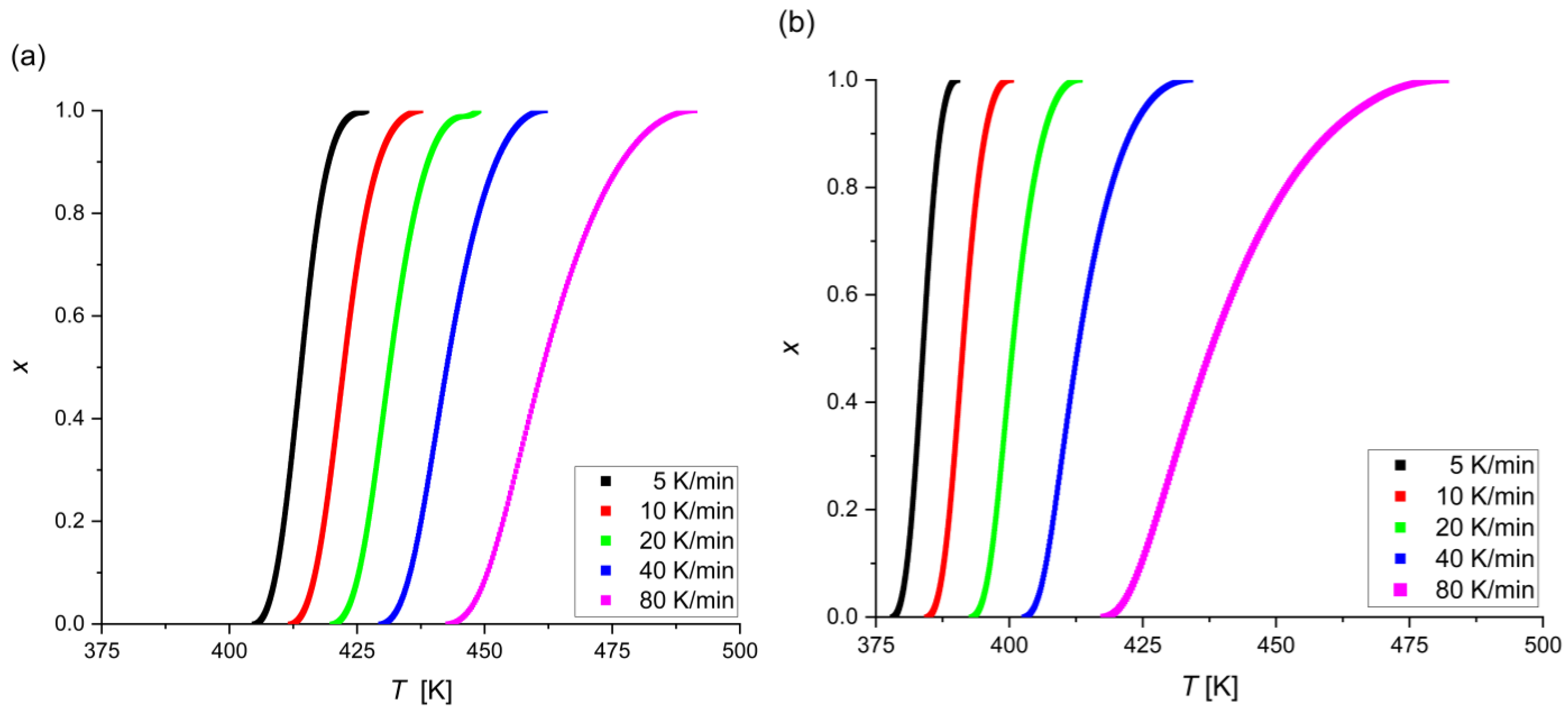
- The crystallization in the Mg72Zn27Ag1 alloy occurs faster than in the Mg72Zn27Pt1 alloy, and the Mg72Zn27Pt1 alloy has higher (temporary) thermal stability due to the difference in the size of the atoms of all alloy components;
- The crystallization in Mg72Zn27Pt1 and Mg72Zn27Ag1 is mainly based on the growth of a single and a two-dimensional crystal and the constant/decreasing nucleation rate during the process;
- The higher values of n for Mg72Zn27Pt1 indicate a greater number of nuclei and grains and, therefore, a more fine-grained structure;
- The XRD tests indicate the presence of α-Mg and Mg12Zn13 phases for both Mg72Zn27Pt1 and Mg72Zn27Ag1, as in the case of a two-component Mg72Zn28 alloy [20];
- The phase contribution is the greatest for Mg72Zn27Ag1, but for Mg72Zn27Pt1, it is also greater than for the binary Mg72Zn28 alloy [20].
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jin, C.; Liu, Z.; Yu, W.; Qin, C.; Yu, H.; Wang, Z. Biodegradable Mg–Zn–Ca-Based Metallic Glasses. Materials 2022, 15, 2172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meagher, P.; O’Cearbhaill, E.D.; Byrne, J.H.; Browne, D.J. Bulk metallic glasses for implantable medical devices and surgical tools. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 5755–5762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Homayun, B.; Afshar, A. Microstructure, mechanical properties, corrosion behavior and cytotoxicity of Mg–Zn–Al–Ca alloys as biodegradable materials. J. Alloys Compd. 2014, 607, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M. A brief overview of bulk metallic glasses. NPG Asia Mater. 2011, 3, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Zadorozhnyy, V. Review of the Recent Development in Metallic Glass and Its Composites. Metals 2021, 11, 1933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, X.; Sun, G.Y.; Zhang, C.M.; Liu, S.N.; Wang, E.R.; Wang, M.L.; Chen, G.L. Mg-Cu-Y-Ag bulk metallic glasses with enhanced compressive strength and plasticity. J. Alloys Compd. 2010, 504, S6–S9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janovszky, D.; Sveda, M.; Sycheva, A.; Kristaly, F.; Zámborszky, F.; Koziel, T.; Bala, P.; Czel, G.; Kaptay, G. Amorphous alloys and differential scanning calorimetry (DSC). J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2022, 147, 7141–7157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, W.A.; Mehl, R.F. Reaction Kinetics in Processes of Nucleation and Growth. Trans. Am. Inst. Min. Metall. Eng. 1939, 135, 416–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avrami, M. Granulation, phase change, and microstructure kinetics of phase change. III. J. Chem. Phys. 1941, 9, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kissinger, H.E. Reaction kinetics in differential thermal analysis. Anal. Chem. 1957, 29, 1702–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, X. Synthesis and Characterization of Bulk Metallic Glasses Prepared by Laser Direct Deposition. Master’s Thesis, Purdue University, West Lafayette, IN, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Lelito, J. Crystallization kinetics analysis of the amorphous Mg72Zn24Ca4 alloy at the isothermal annealing temperature of 507 K. Materials 2020, 13, 2815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Opitek, B.; Lelito, J.; Szucki, M.; Piwowarski, G.; Gondek, Ł.; Rogal, Ł. Analysis of the crystallization kinetics and thermal stability of the amorphous Mg72Zn24Ca4 alloy. Materials 2021, 14, 3583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Xie, X.; Li, H.; Wang, X.; Zhao, M.; Zhang, E.; Bai, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Qin, L. Biodegradable CaMgZn bulk metallic glass for potential skeletal applictaion. Acta Biomater. 2011, 7, 3196–3208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dambatta, M.; Izman, S.; Yahaya, B.; Lim, J.; Kurniawan, D. Mg-based bulk metallic glasses for biodegradable implant materials: A review on glass forming ability, mechanical properties, and biocompatibility. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2015, 426, 110–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matias, T.; Roche, V.; Nogueira, R.; Asato, G.; Kiminami, C.; Bolfarini, C.; Botta, W.; Jorge, A. Mg–Zn–Ca amorphous alloys for application as temporary implant: Effect of Zn content on the mechanical and corrosion properties. Mater. Des. 2016, 110, 188–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.; Zheng, Y.; Zhong, S.; Xi, T.; Wang, J.; Wang, W. Corrosion of, and cellular responses to Mg-Zn-Ca bulk metallic glasses. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 1093–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y. Magnesium Alloys as Degradable Biomaterials; CRC Press Taylor & Francis Group, LLC: Abingdon, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Busch, R.; Kim, Y.J.; Johnson, W.L. Thermodynamics and kinetics of the undercooled liquid and the glass transition of the Zr41.2Ti13.8Cu12.5Ni10.0Be22.5 alloy. J. Appl. Phys. 1995, 77, 4039–4043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opitek, B.; Gracz, B.; Lelito, J.; Krajewski, W.K.; Łucarz, M.; Bała, P.; Kozieł, T.; Gondek, Ł.; Szucki, M. Crystallization Kinetics Analysis of the Binary Amorphous Mg72Zn28 Alloy. Materials 2023, 16, 2727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habashi, F. Two hundred years platinum group metals. Metall-Magazin 2003, 57, 798–805. [Google Scholar]
- Rashidi, R.; Malekana, M.; Gholamipour, R. Crystallization kinetics of Cu47Zr47Al6 and (Cu47Zr47Al6)99Sn1 bulk metallic glasses. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2018, 498, 272–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Center for Biotechnology Information. Atomic Radius in the Periodic Table of Elements. 2023. Available online: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/periodic-table/atomic-radius (accessed on 7 November 2023).
- Saengsuwan, S.; Tongkasee, P.; Sudyoadsuk, T.; Promarak, V.; Keawin, T.; Jungsuttiwong, S. Non-isothermal crystallization kinetics and thermal stability of the in situ reinforcing composite films based on thermotropic liquid crystalline polymer and polypropylene. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2011, 103, 1017–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeziorny, A. Parameters characterizing the kinetics of the non-isothermal crystallization of poly(ethylene terephthalate) determined by d.s.c. Polymer 1978, 19, 1142–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.; He, S.; Li, J.; Zhou, Y. On the crystallization kinetics of Zr60Al15Ni25 amorphous alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2004, 368, 175–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.C.; Ma, G.T.; Nollmann, N.; Wilde, G.; Zeng, M.; Hu, C.H.; Li, L.; Tang, C. Comparative study of thermal stability and crystallization kinetics between melt-spun and bulk Pd77.5Cu6Si16.5 metallic glasses. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2022, 17, 2203–2219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
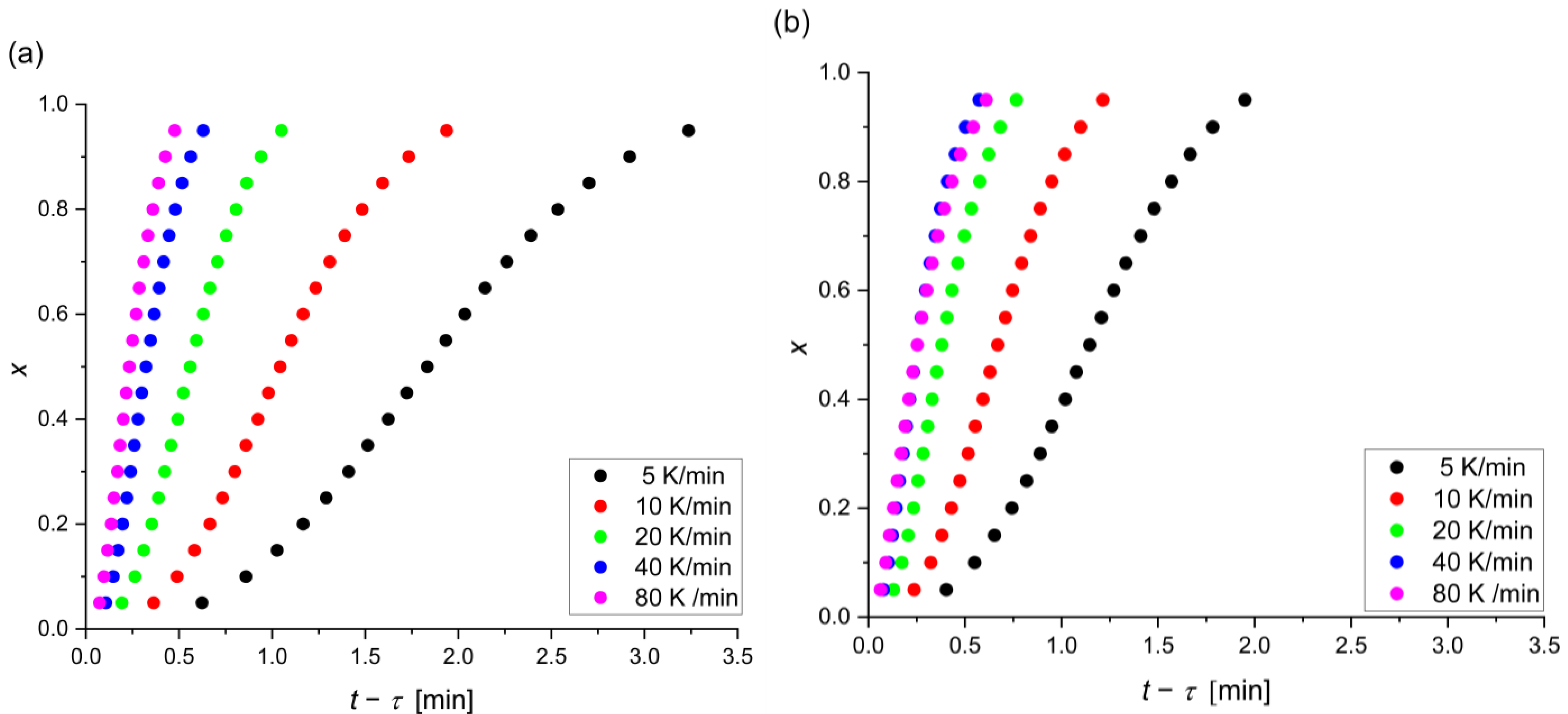
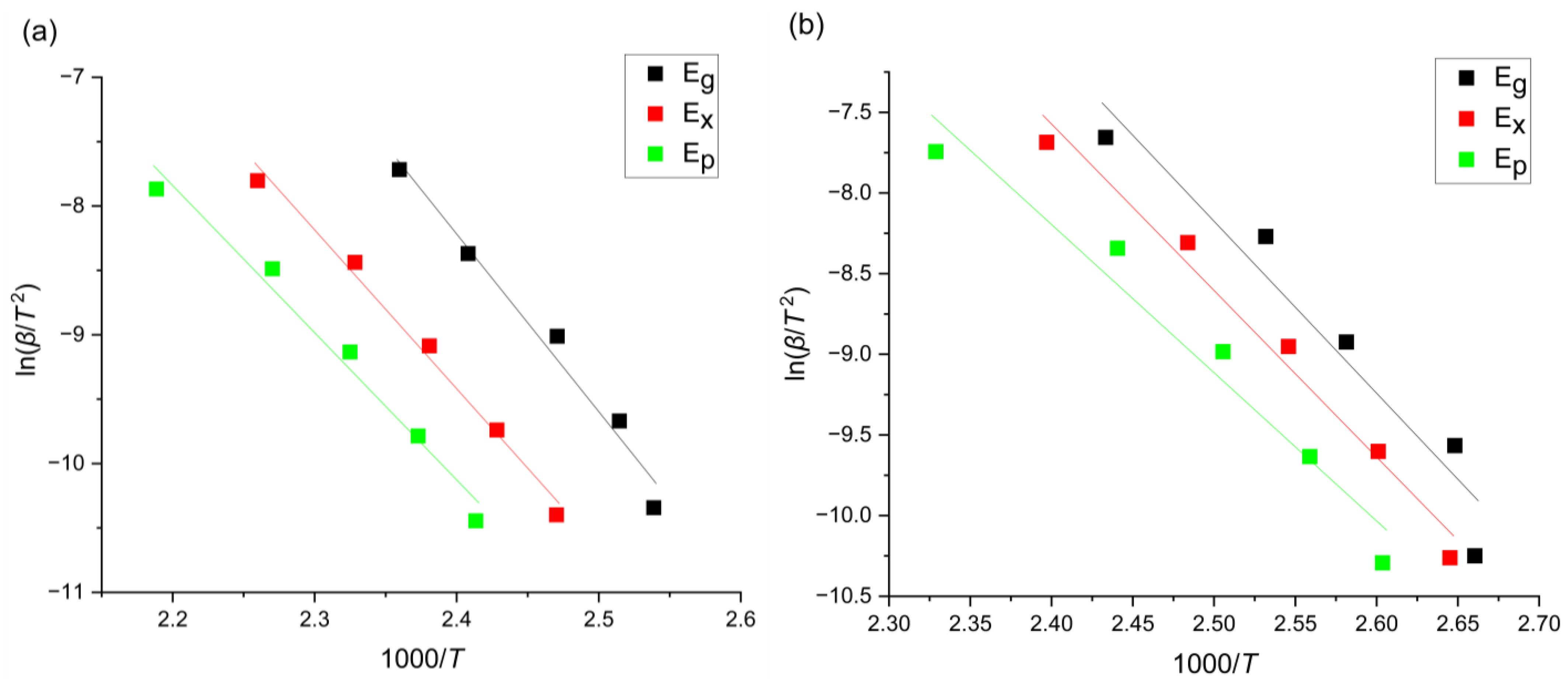
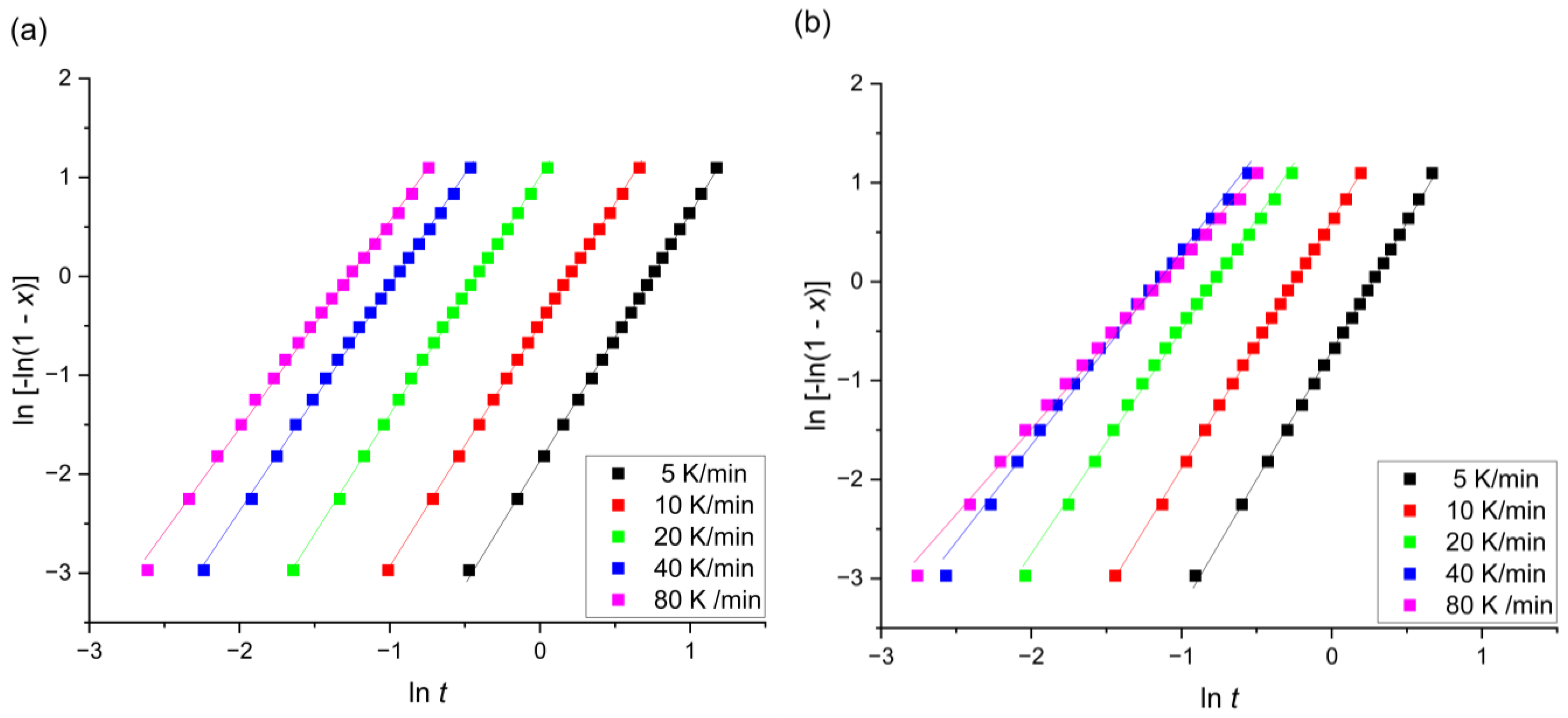

| Alloy | β [K/min] | [min] | [K] | [K] | [K] | [K] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mg72Zn27Pt1 | 5 | 21.43 | 393.90 | 404.82 | 414.35 | 426.88 |
| 10 | 11.98 | 397.69 | 411.85 | 421.45 | 437.47 | |
| 20 | 6.53 | 404.75 | 420.07 | 430.14 | 448.85 | |
| 40 | 3.18 | 415.29 | 429.50 | 440.50 | 461.86 | |
| 80 | 1.92 | 423.80 | 442.57 | 456.93 | 491.17 | |
| Mg72Zn27Ag1 | 5 | 13.26 | 375.89 | 378.07 | 384.09 | 390.32 |
| 10 | 9.30 | 377.64 | 384.48 | 390.81 | 400.36 | |
| 20 | 4.31 | 387.39 | 392.82 | 399.14 | 413.26 | |
| 40 | 2.51 | 394.98 | 402.62 | 409.75 | 433.96 | |
| 80 | 1.57 | 410.98 | 417.19 | 429.41 | 481.76 |
| Alloy | [kJ/mol] | [kJ/mol] | [kJ/mol] |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mg72Zn27Pt1 | 114.56 | 102.52 | 95.01 |
| Mg72Zn27Ag1 | 88.60 | 85.78 | 76.38 |
| Alloy | β [K/min] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mg72Zn27Pt1 | 5 | 2.5 | 0.474 | 0.095 |
| 10 | 2.4 | 0.820 | 0.082 | |
| 20 | 2.4 | 1.523 | 0.076 | |
| 40 | 2.3 | 2.603 | 0.065 | |
| 80 | 2.1 | 3.554 | 0.044 | |
| Mg72Zn27Ag1 | 5 | 2.6 | 0.764 | 0.153 |
| 10 | 2.5 | 1.281 | 0.128 | |
| 20 | 2.3 | 2.185 | 0.109 | |
| 40 | 2.0 | 3.182 | 0.080 | |
| 80 | 1.7 | 3.122 | 0.039 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pierwoła, A.; Lelito, J.; Krawiec, H.; Szucki, M.; Gondek, Ł.; Kozieł, T.; Babilas, R. Non-Isothermal Analysis of the Crystallization Kinetics of Amorphous Mg72Zn27Pt1 and Mg72Zn27Ag1 Alloys. Materials 2024, 17, 408. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17020408
Pierwoła A, Lelito J, Krawiec H, Szucki M, Gondek Ł, Kozieł T, Babilas R. Non-Isothermal Analysis of the Crystallization Kinetics of Amorphous Mg72Zn27Pt1 and Mg72Zn27Ag1 Alloys. Materials. 2024; 17(2):408. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17020408
Chicago/Turabian StylePierwoła, Aleksandra, Janusz Lelito, Halina Krawiec, Michał Szucki, Łukasz Gondek, Tomasz Kozieł, and Rafał Babilas. 2024. "Non-Isothermal Analysis of the Crystallization Kinetics of Amorphous Mg72Zn27Pt1 and Mg72Zn27Ag1 Alloys" Materials 17, no. 2: 408. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17020408
APA StylePierwoła, A., Lelito, J., Krawiec, H., Szucki, M., Gondek, Ł., Kozieł, T., & Babilas, R. (2024). Non-Isothermal Analysis of the Crystallization Kinetics of Amorphous Mg72Zn27Pt1 and Mg72Zn27Ag1 Alloys. Materials, 17(2), 408. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17020408





