Microstructure Evolution and Mechanical Properties of High-Temperature Carburized 18Cr2Ni4WA Steel
Abstract
1. Introduction
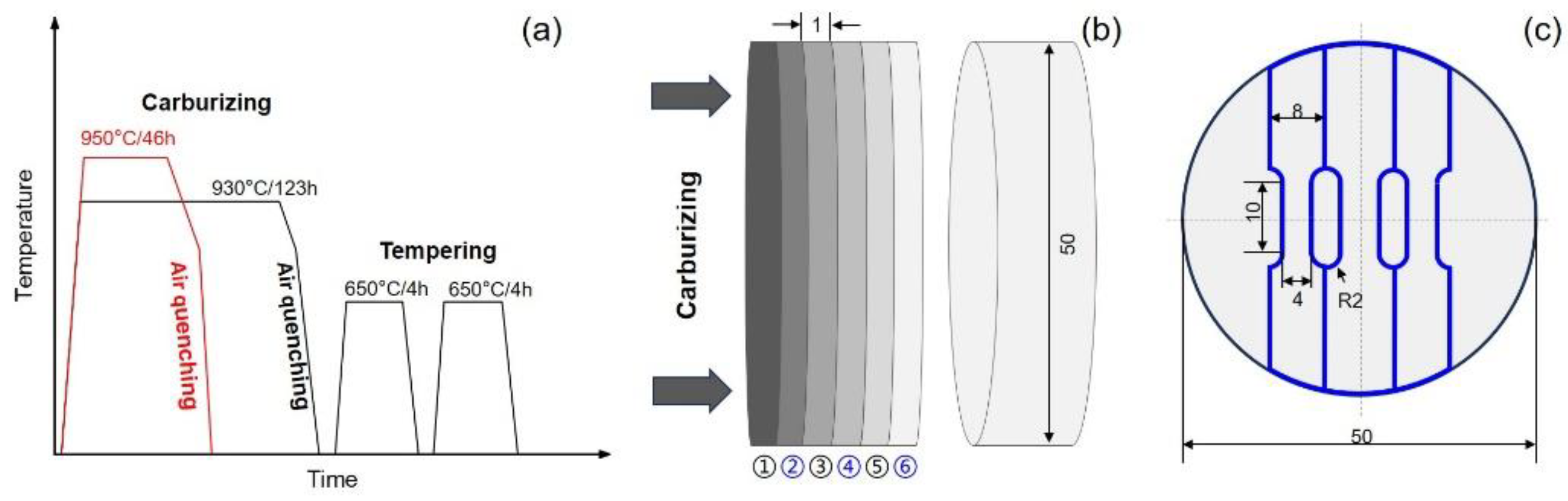
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
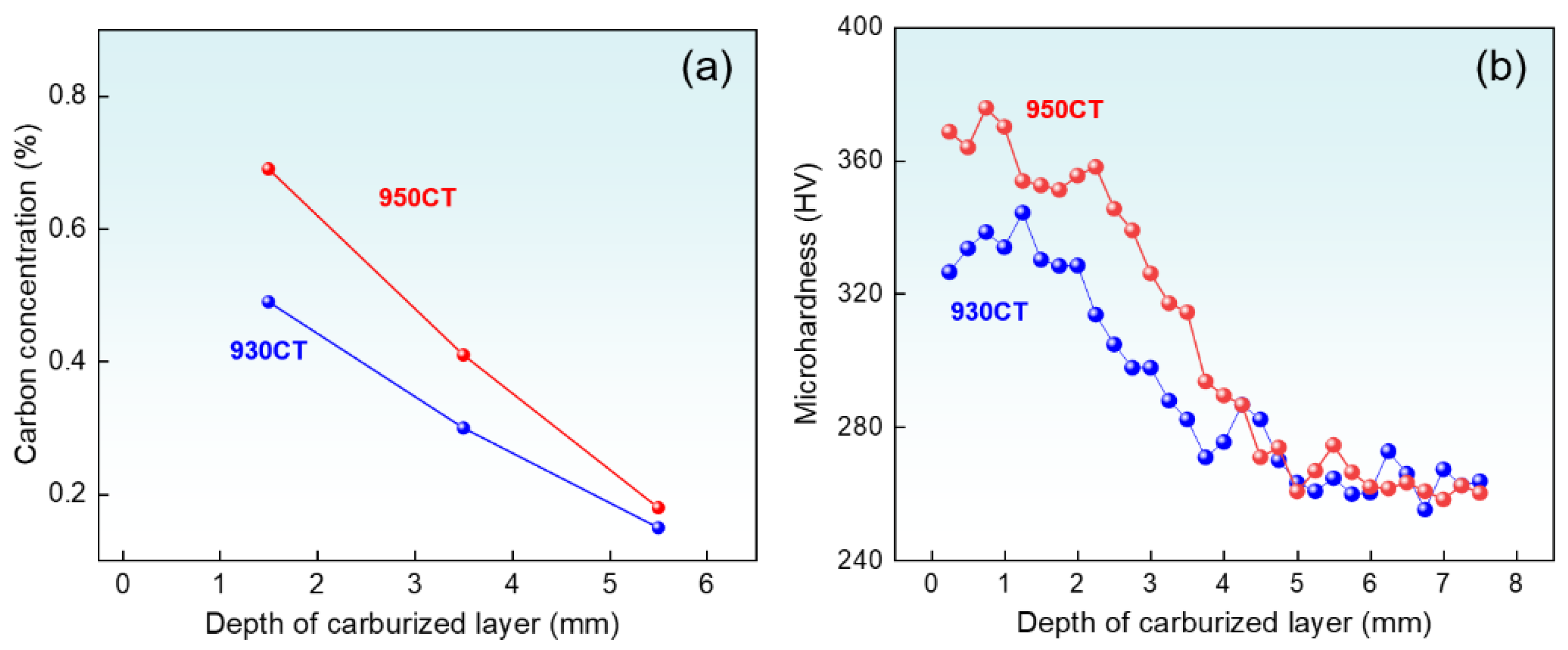
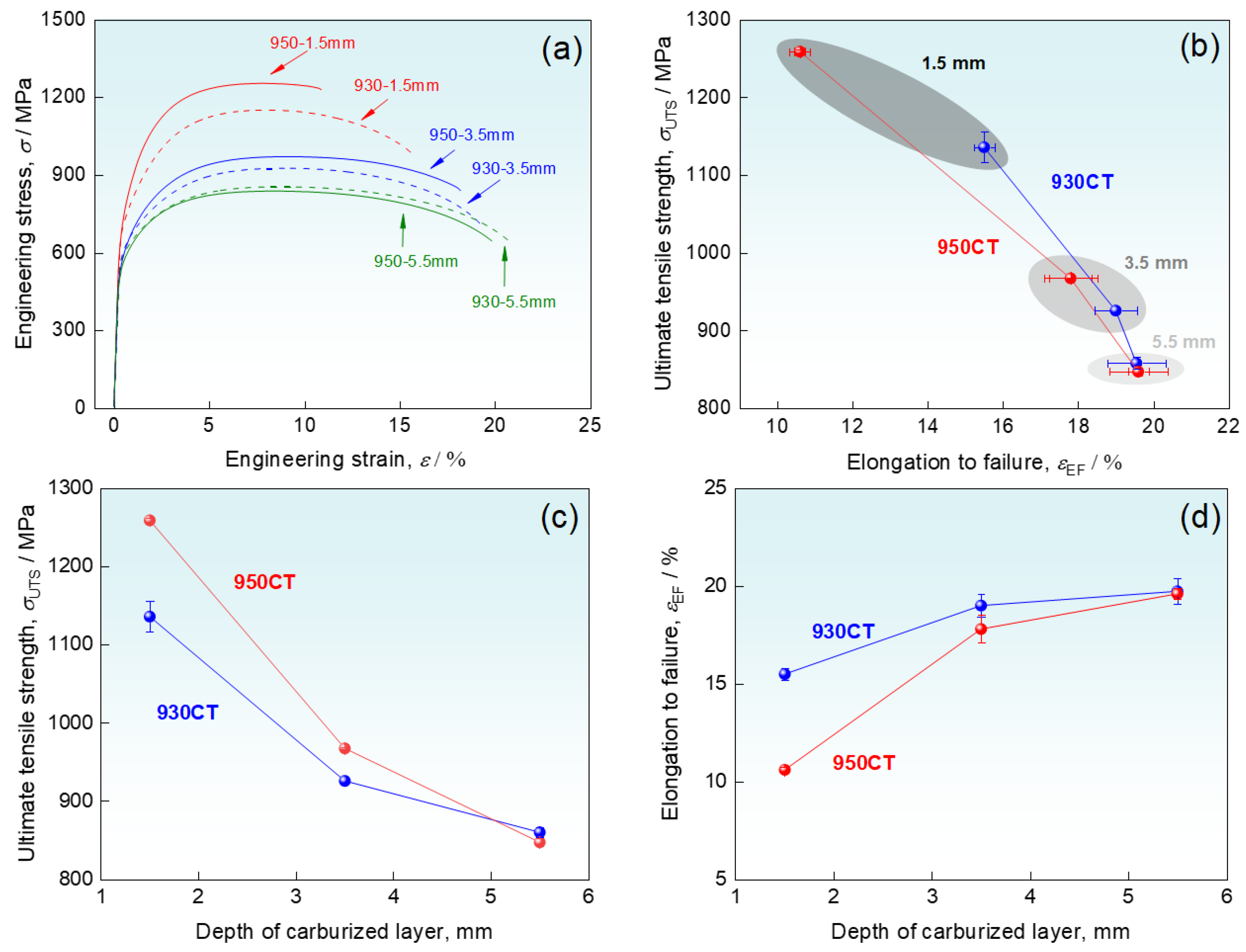
3.1. Carbon Content and Mechanical Properties
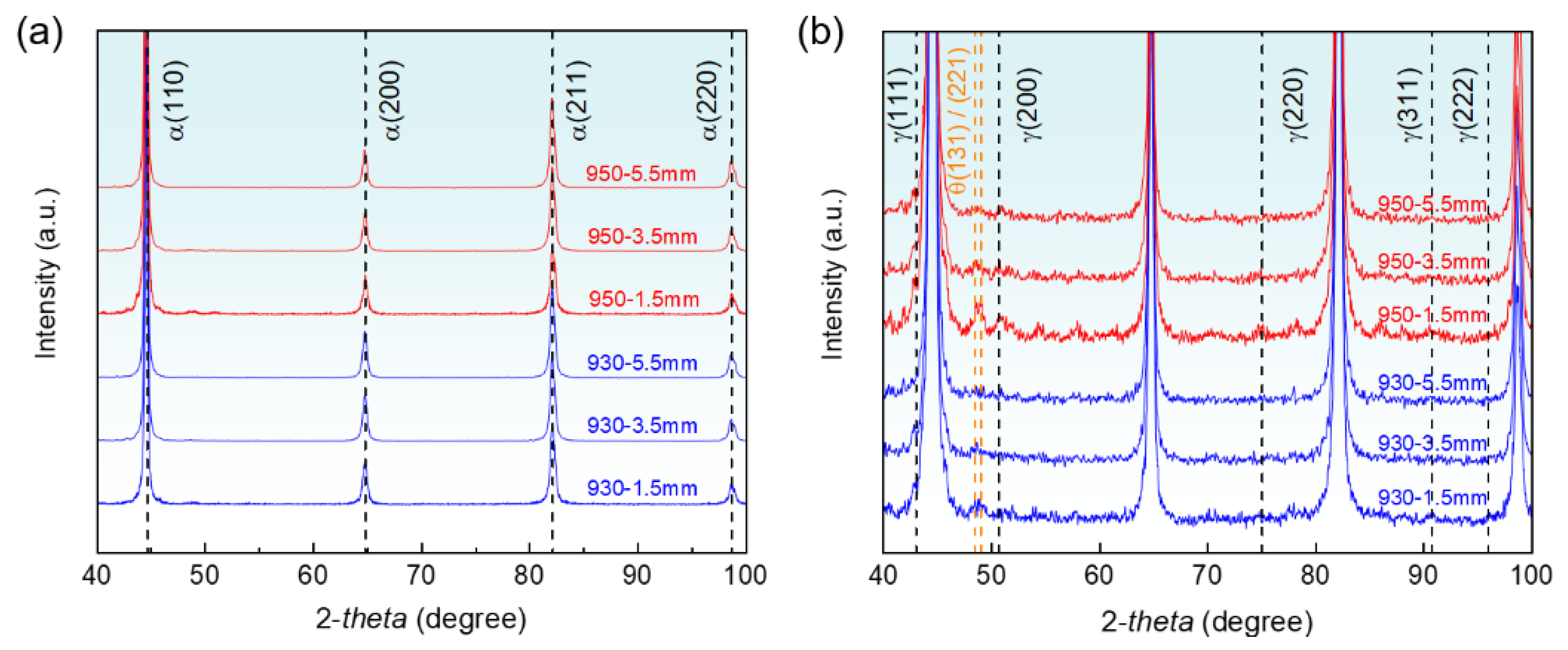
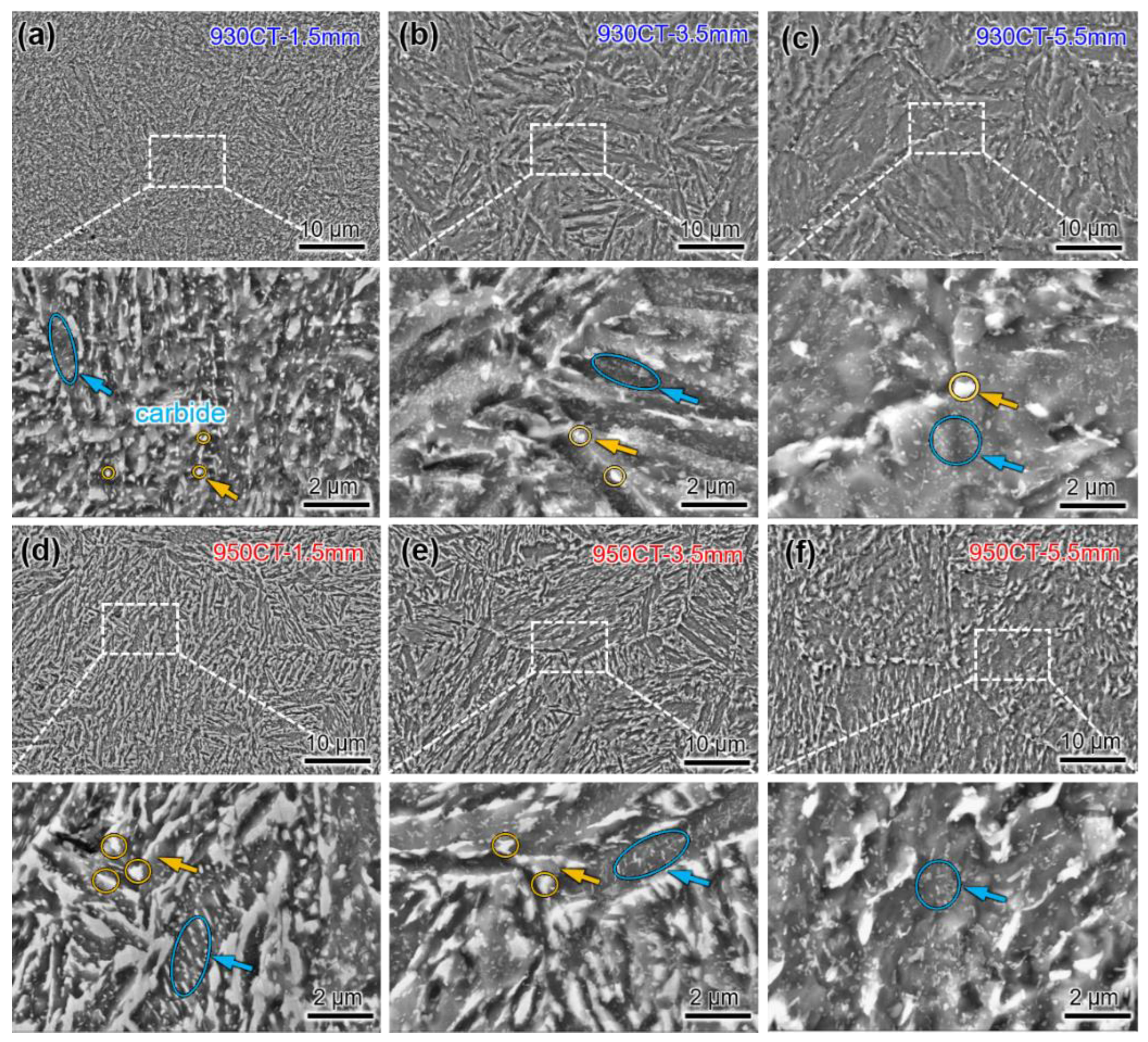
3.2. Microstructures in Different Carburized Layers
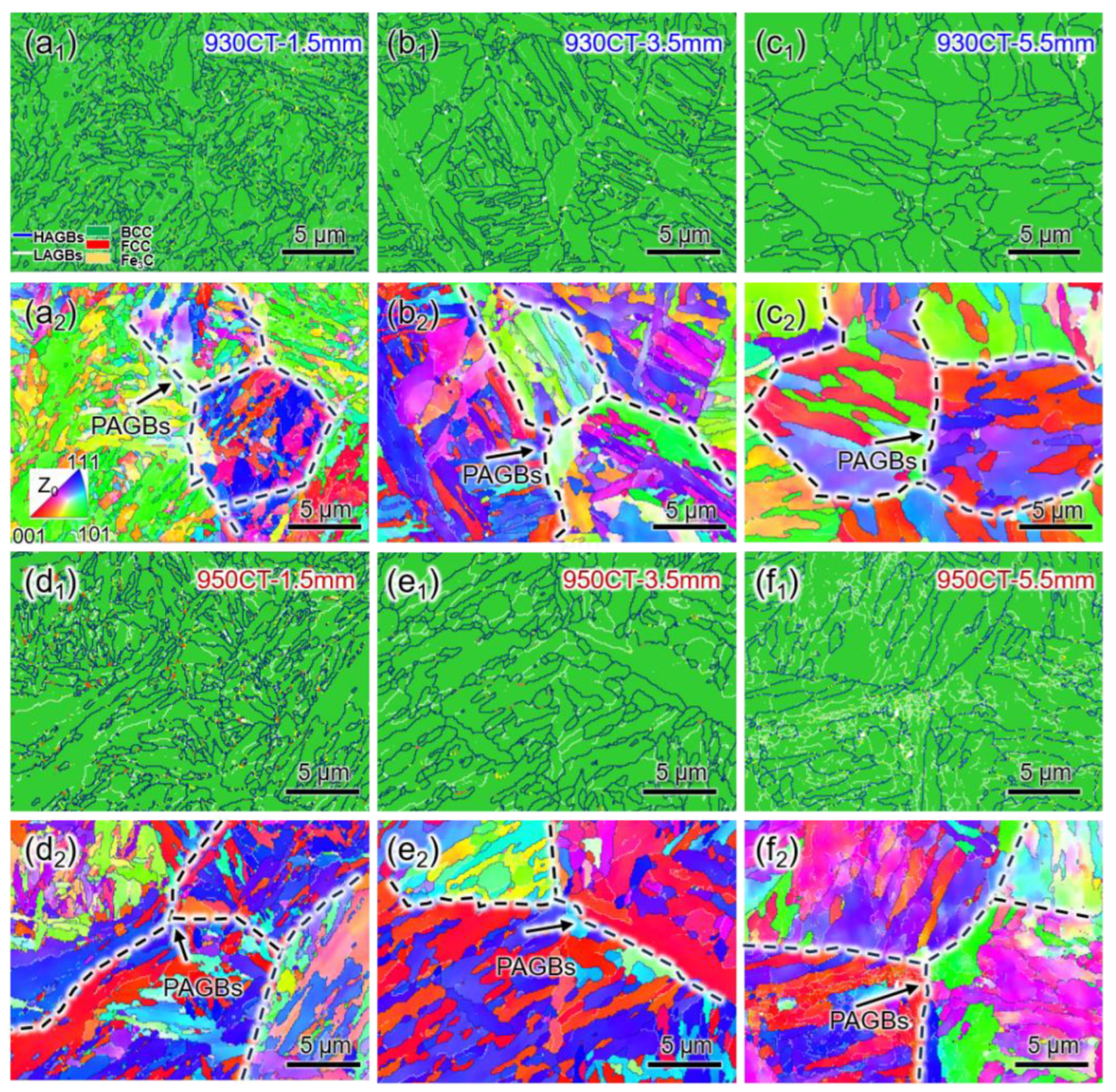
3.3. Grain Size at Different Carburizing Temperatures
4. Discussion
4.1. Effect of Carbon Content on Microstructures in Different Carburized Layers
4.2. Effect of Carburizing Temperature on Strength at Different Locations
5. Conclusions
- The 950 °C carburized sample achieved a higher level of carbon content, resulting in a high carburized layer of 5 mm. High carbon content and high-density dislocations are retained at the depth of 1.5 mm, and the grain boundaries are pinned efficiently. The strength is enhanced by a higher degree of solid solution strengthening and dislocation strengthening, which make the 950 °C carburized sample excellent comprehensive performance without excessive loss of plasticity.
- The difference in carbon content between the two samples is not significant, and the pinning effect of carbides on the boundaries is weakened at the depth of 3.5 mm. High-temperature carburizing increases the grain size and the density of carbides, leading to a decrease in grain boundary strengthening and an increase in precipitation strengthening. The bilateral effects make the slightly increased strength for the 950 °C carburized sample.
- At a depth of 5.5 mm, the carbon contents are similar for the two specimens and greatly reduced. Equiaxed ferrite is obtained after tempering, and the grain size becomes the dominant factor for strengthening, which ultimately leads to the strength decrease after high-temperature carburizing.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, Z.; Yuan, Q.; Zhang, Q. Microstructure and mechanical properties of a cold rolled gradient medium-carbon martensitic steel. Acta Metall. Sin. 2023, 59, 821–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Deng, S.; Liu, B. Experimental study on the influence of different carburized layer depth on gear contact fatigue strength. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2020, 107, 104225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Ma, Z.; Li, Q.; Li, C. Dry friction performance analysis of FeS coating on the surface of 20CrMnTi gear steel. Acta Metall. Sin. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, B.; Mei, Z.; Zhou, L.; Liu, G.; Wang, Z.; Huang, B.; Liu, Y. High toughness and multiphase microstructure transition product of carburizing steel by a novel heat treatment cooling process. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2016, 675, 361–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Liu, K.; Luo, Z.; Wang, M.; Wang, X. Effect of cryogenic treatment on microstructure, mechanical properties and distortion of carburized gear steels. Metals 2021, 11, 1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Wang, M.; Chen, J.; Dong, H. Microstructure and mechanical properties of gear steels after high temperature carburization. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 2013, 20, 140–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, R.; Yang, G.; Sun, X.; Zhao, G. Austenite grain growth behavior of vanadium microalloying medium manganese martensitic wear-resistant steel. Acta Metall. Sin. 2022, 58, 1589–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Pang, K. Elastoplastic behavior of Case-Carburized 18Cr2Ni4WA steel by indenter testing. J. Aerosp. Eng. 2019, 32, 04019045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, C.B.; Tu, M.W.; Pan, Q.J. Performance and property of Ni base Coatings by using plasma arc technology for 18Cr2Ni4WA steel repairing. Adv. Mat. Res. 2011, 189–193, 311–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhadeshia, H.K.D.H. Steels for bearings. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2012, 57, 268–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Liu, P.; Li, W.; Ma, F.; Guo, Z.; Rong, Y. Enhancement of the strength and ductility of martensitic steels by carbon. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2018, 716, 87–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, D.; Wu, L.; Wang, F.; Deng, S.; Yin, F.; Jiang, S. Tailored Carburization Gradient Microstructure and Enhanced Wear Properties of M50NiL Steel via Introduced Prior Cold Rolling. Wear 2024, 540–541, 205265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeddi, D.; Lieurade, H.-P. Effect of retained austenite on high cycle fatigue behavior of carburized 14NiCr11 steel. Proc. Eng. 2010, 2, 1927–1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walvekar, A.A.; Sadeghi, F. Rolling contact fatigue of case carburized steels. Int. J. Fatigue 2017, 95, 264–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asi, O.; Can, A.Ç.; Pineault, J.; Belassel, M. The effect of high temperature gas carburizing on bending fatigue strength of SAE 8620 steel. Mater Des. 2009, 30, 1792–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Wang, J.; Pan, Z.; Tao, Q. Effect of carbon partition and precipitation on wear resistance of carburized layer in heavy-duty gear. Materials 2021, 14, 6958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; He, Y.; Liu, Y.; Tian, Y.; You, J.; Misra, R.D.K.; Wang, Z.; Wang, G. Thermodynamics of phase transformation and microstructure evolution of 18Cr2Ni4WA carburized steel during high-temperature tempering. Steel Res. Int. 2020, 91, 2000094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Z.; Liu, T.; Li, J.; Wang, L.; Zhang, T.; Wang, J.; Tao, Q. Improving mechanical properties of a forged High-Manganese alloy by regulating carbon content and carbide precipitation. Metals 2022, 12, 473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera-Díaz-del-Castillo, P.E.J.; Hayashi, K.; Galindo-Nava, E.I. Computational design of nanostructured steels employing irreversible thermodynamics. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2013, 29, 1206–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galindo-Nava, E.I.; Rivera-Díaz-del-Castillo, P.E.J. Understanding the factors controlling the hardness in martensitic steels. Scr. Mater. 2016, 110, 96–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; He, Y.; Liu, Y.; Tian, Y.; You, J.; Wang, Z.; Wang, G. Mechanism of the Microstructural Evolution of 18Cr2Ni4WA Steel during Vacuum Low-Pressure Carburizing Heat Treatment and Its Effect on Case Hardness. Materials 2020, 13, 2352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popov, A.A.; Yang, S. Endohedral fullerenes. Chem. Rev. 2013, 113, 5989–6113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrow, A.T.W.; Kang, J.-H.; Rivera-Díaz-del-Castillo, P.E.J. The ϵ→η→θ transition in 100Cr6 and its effect on mechanical properties. Acta Mater. 2012, 60, 2805–2815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, F.; Yang, Z.; Lv, B.; Zheng, C. Rolling Contact Fatigue Performances of Carburized and High-C Nanostructured Bainitic Steels. Materials 2016, 9, 960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, G.; Zhang, N.; Wan, S. The carburizing behavior of high-temperature short-time carburizing gear steel: Effect of Nb microalloying. Steel Res. Int. 2022, 93, 2200427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Q.; Wang, J.; Galindo-Nava, E.I. Effect of low-temperature tempering on confined precipitation and mechanical properties of carburized steels. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2021, 822, 141688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.G.; Li, M.Q.; Dang, X.L. Effect of heating temperature and heating rate on austenite in the heating process of 300M steel. Mater. Sci. Forum 2013, 749, 260–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Huang, M.X. Abnormal TRIP effect on the work hardening behavior of a quenching and partitioning steel at high strain rate. Acta Mater. 2020, 188, 551–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perdahcıoğlu, E.S.; Geijselaers, H.J.M. Mechanical Behavior of Multi-Phase Steels Comprising Retained Austenite. Materials 2022, 15, 498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Huang, X.; Liu, J. Microstructure regulation and strengthening mechanisms of a hot-rolled & intercortical annealed medium-Mn steel containing Mn-segregation band. Acta Metall. Sin. 2023, 59, 1448–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Xia, S.L.; Zhang, F.C.; Branco, R.; Long, X.Y.; Li, Y.G.; Li, J.H. Effect of Tempering Temperature on Monotonic and Low-Cycle Fatigue Properties of a New Low-Carbon Martensitic Steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2021, 826, 141939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Chen, K.; Sun, Y. Effect of H2O(g) on decarburization of 55SiCr spring steel during the heating process. Acta Metall Sin. 2018, 54, 1350–1358. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Z.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Jiang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Yuan, Y.; Xue, Y.; Wang, X. Effect of Microstructure on Wear Resistance during High Temperature Carburization Heat Treatment of Heavy-Duty Gear Steel. Mater. Today Commun. 2024, 40, 109486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, X.; Cao, W.; Zhang, X.; Yu, J. Suppress Austenite Grain Coarsening by Nb Alloying in High–Temperature–Pseudo–Carburized Bearing Steel. Materials 2024, 17, 2962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, K.; Jiang, Z.; Liu, F.; Li, H.; Ma, X.; Zhao, B.; Kang, C.; Li, Y. Enhanced Mechanical Properties by Retained Austenite in Medium–Carbon Si-Rich Microalloyed Steel Treated by Quenching–Tempering, Austempering and Austempering–Tempering Processes. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2020, 790, 139742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Wang, P.; Li, D.; Li, Y. Influence of the decomposition behavior of retained austenite during tempering on the mechanical properties of 2.25Cr-1Mo-0.25 V steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2019, 742, 540–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidalgo, J.; Findley, K.O.; Santofimia, M.J. Thermal and mechanical stability of retained austenite surrounded by martensite with different degrees of tempering. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2017, 690, 337–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Li, S.X.; Zhang, Z.F. General Relationship between Strength and Hardness. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2011, 529, 62–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Li, L.; Li, J.; Yang, Y.; Li, S.; Qin, G. Correlating Strength and Hardness of High-Entropy Alloys. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2021, 23, 2001514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlina, E.J.; Van Tyne, C.J. Correlation of Yield Strength and Tensile Strength with Hardness for Steels. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2008, 17, 888–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galindo-Nava, E.I.; Rivera-Díaz-del-Castillo, P.E.J. A model for the microstructure behaviour and strength evolution in lath martensite. Acta Mater. 2015, 98, 81–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Shen, Y.; Jia, N.; Wang, J.; Zhao, S. Acicular martensite induced superior strength-ductility combination in a 20Cr2Ni2MoV steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2022, 848, 143400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauzay, M.; Kubin, L.P. Scaling Laws for Dislocation Microstructures in Monotonic and Cyclic Deformation of Fcc Metals. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2011, 56, 725–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Q.; Liang, J.; Stoica, A.D.; Li, R.; Yang, P.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, J.; Lan, H.; Li, R.; An, K. In-Situ Neutron Diffraction Study on the Tension-Compression Fatigue Behavior of a Twinning Induced Plasticity Steel. Scr. Mater. 2017, 137, 83–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.; Boucard, E.; Sourmail, T.; San Martín, D.; Gey, N.; Rivera-Díaz-del-Castillo, P.E.J. The influence of silicon in tempered martensite: Understanding the microstructure–properties relationship in 0.5–0.6 wt.% C steels. Acta Mater. 2014, 68, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Drouven, C.; Galindo-Nava, E. Carbon Redistribution in Martensite in High-C Steel: Atomic-Scale Characterization and Modelling. Metals 2018, 8, 577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Samples | ρ/1014 m−2 | D/μm | fp/% | rP/μm |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 930CT-1.5mm | 2.782 | 2.5 | 7.59 | 0.049 |
| 950CT-1.5mm | 4.079 | 2.8 | 12.68 | 0.069 |
| 930CT-3.5mm | 1.652 | 3.3 | 6.37 | 0.034 |
| 950CT-3.5mm | 1.114 | 4.9 | 9.37 | 0.036 |
| 930CT-5.5mm | 0.293 | 5.9 | 4.69 | 0.027 |
| 950CT-5.5mm | 0.244 | 6.6 | 5.64 | 0.031 |
| Samples | /MPa | /MPa | /MPa | HV1 | HV0 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 930CT-1.5 mm | 365.6 | 268.1 | 392.1 | 121.1 | 458.7 | 334.1 |
| 950CT-1.5 mm | 470.1 | 324.6 | 370.5 | 119.9 | 514.1 | 370.2 |
| 930CT-3.5 mm | 288.2 | 169.7 | 343.4 | 150.8 | 373.2 | 297.9 |
| 950CT-3.5 mm | 366.1 | 206.6 | 281.2 | 174.7 | 397.7 | 326.2 |
| 930CT-5.5 mm | 236.3 | 87.1 | 255.3 | 154.6 | 289.1 | 263.5 |
| 950CT-5.5 mm | 244.7 | 79.4 | 241.3 | 156.3 | 284.3 | 260.8 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Z.; Wu, Z.; Yuan, Y.; Wang, X.; Tian, Y. Microstructure Evolution and Mechanical Properties of High-Temperature Carburized 18Cr2Ni4WA Steel. Materials 2024, 17, 4820. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17194820
Zhang Z, Wu Z, Yuan Y, Wang X, Tian Y. Microstructure Evolution and Mechanical Properties of High-Temperature Carburized 18Cr2Ni4WA Steel. Materials. 2024; 17(19):4820. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17194820
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Zhenyang, Zehua Wu, Yuedong Yuan, Xiaonan Wang, and Yanzhong Tian. 2024. "Microstructure Evolution and Mechanical Properties of High-Temperature Carburized 18Cr2Ni4WA Steel" Materials 17, no. 19: 4820. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17194820
APA StyleZhang, Z., Wu, Z., Yuan, Y., Wang, X., & Tian, Y. (2024). Microstructure Evolution and Mechanical Properties of High-Temperature Carburized 18Cr2Ni4WA Steel. Materials, 17(19), 4820. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17194820







