Facile Preparation of Irradiated Poly(vinyl alcohol)/Cellulose Nanofiber Hydrogels with Ultrahigh Mechanical Properties for Artificial Joint Cartilage
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Radiation Preparation of PVA/CNF Hydrogels
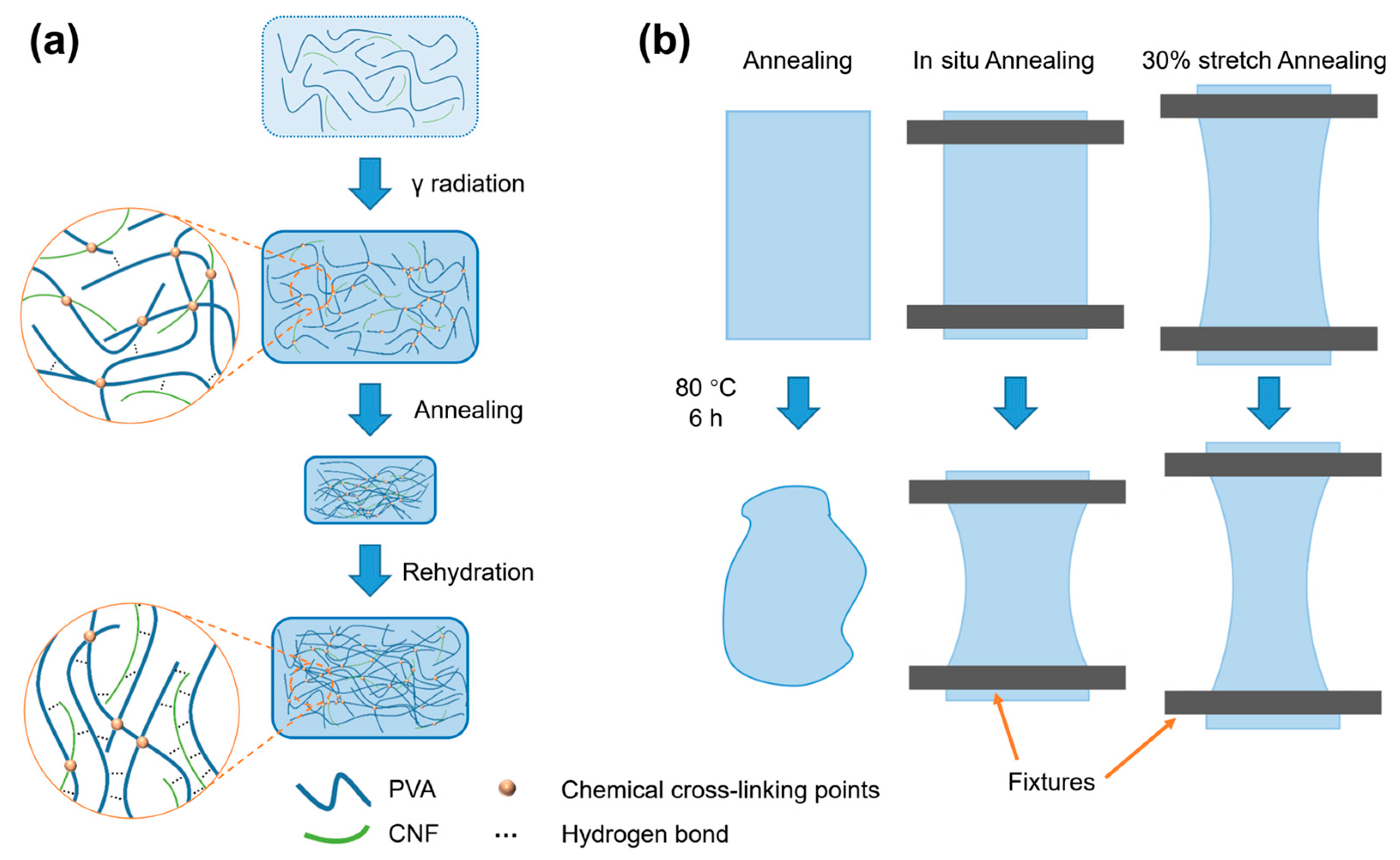
2.3. Preparation of Annealed PVA/CNF Hydrogels
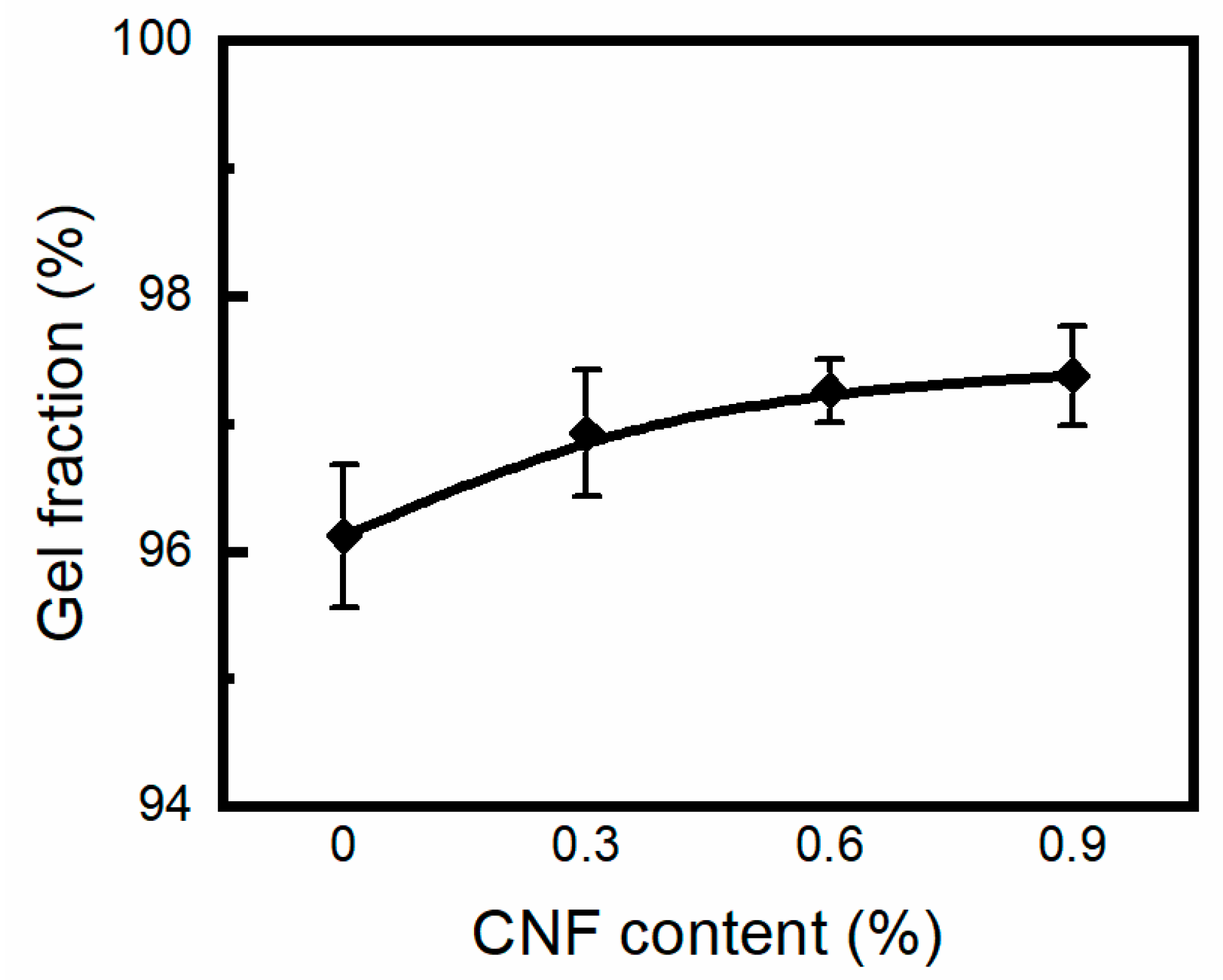
2.4. Gel Fraction Determination
2.5. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectrometer (FTIR) Analysis
2.6. Micromorphology Characterization
2.7. Swelling Test
2.8. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC) Analysis
2.9. Tensile Properties Test
2.10. Friction Properties Test
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Preparation of the PVA/CNF Hydrogels
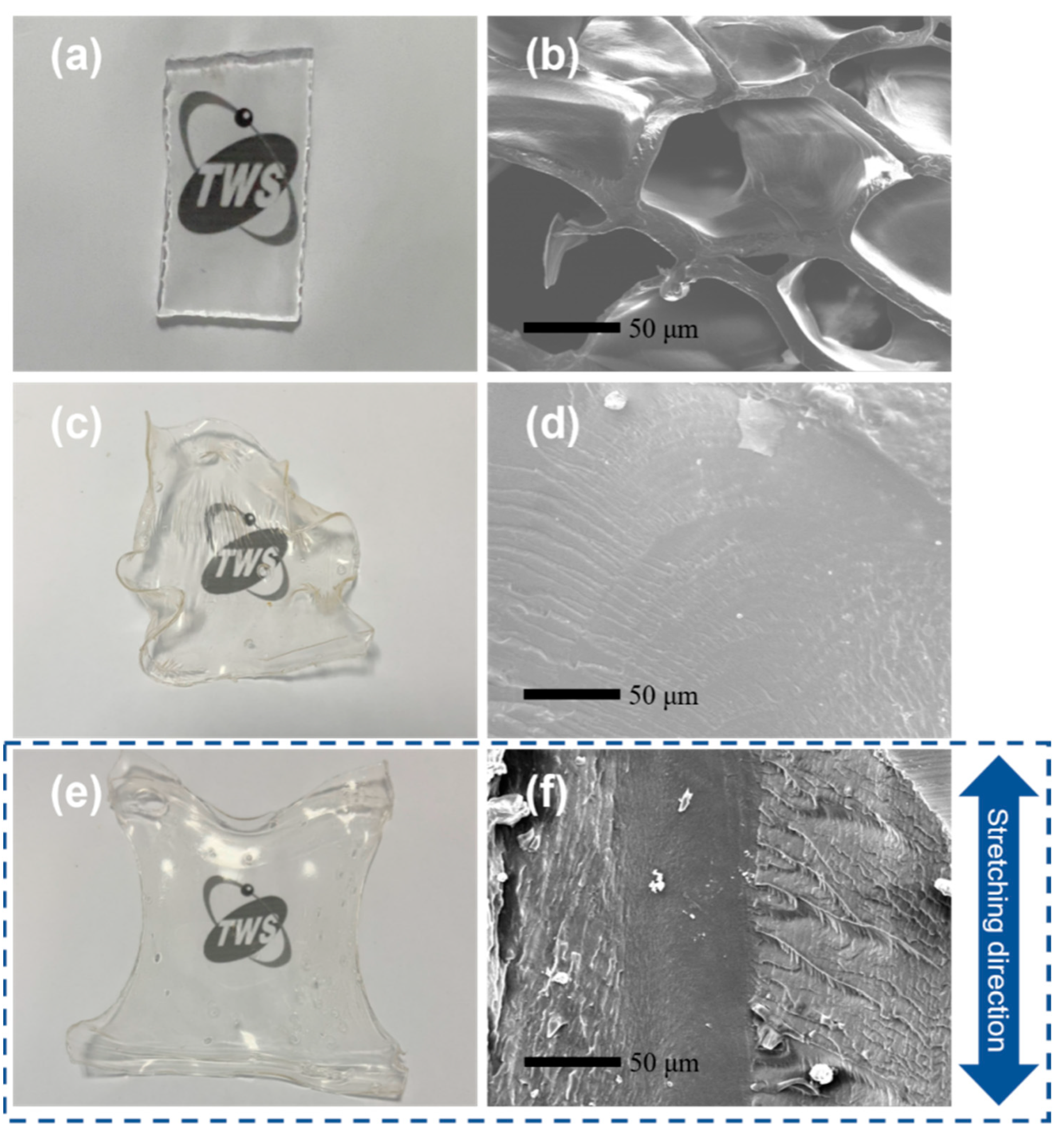
3.2. Morphology of Hydrogels
3.3. Swelling Behavior
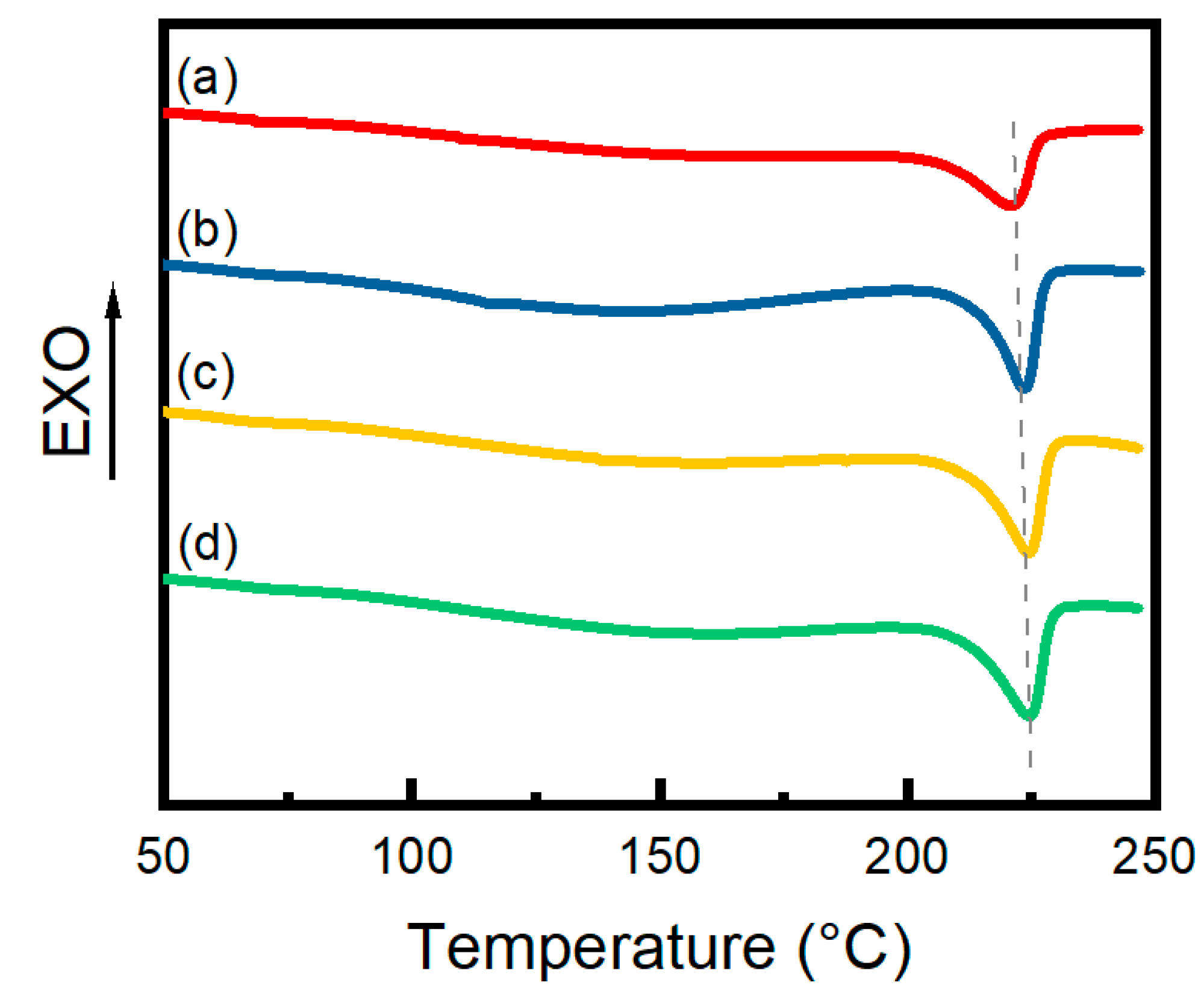
3.4. DSC Analysis
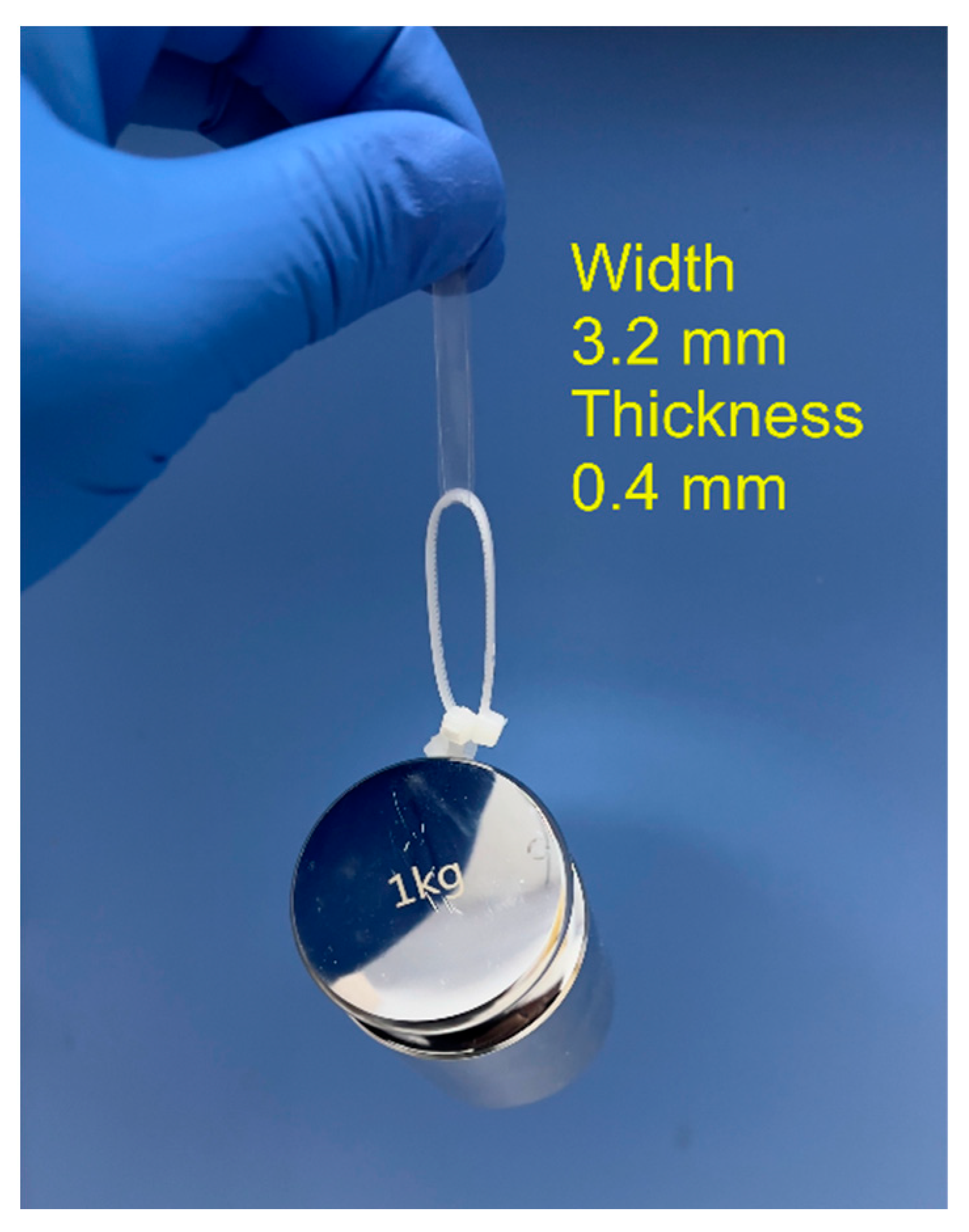
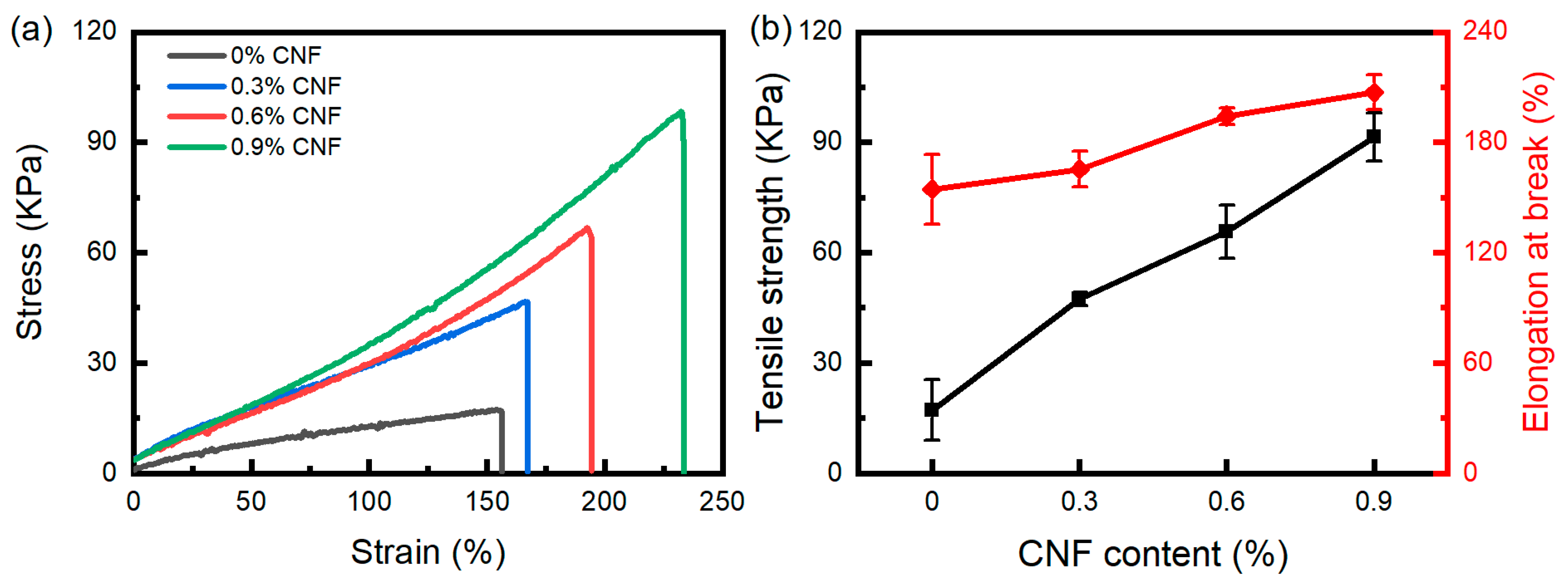
3.5. Tensile Property
3.6. Friction Property
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Roseti, L.; Desando, G.; Cavallo, C.; Petretta, M.; Grigolo, B. Articular cartilage regeneration in osteoarthritis. Cells 2019, 8, 1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Duan, P.; Gao, J.; Guo, R.; Qu, Z.; Li, X.; He, Y.; Yao, H.; Ding, J. Bilayered PLGA/PLGA-HAp composite scaffold for osteochondral tissue engineering and tissue regeneration. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 4, 3506–3521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, H.; Brown, W.E.; Lee, C.A.; Wang, D.; Paschos, N.; Hu, J.C.; Athanasiou, K.A. Surgical and tissue engineering strategies for articular cartilage and meniscus repair. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2019, 15, 550–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Huang, H.; Hao, G.; Zhang, Y.; Ding, H.; Fan, Z.; Sun, L. 3D printing hydrogel scaffolds with nanohydroxyapatite gradient to effectively repair osteochondral defects in rats. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2006697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Bai, J.; Tian, J.; Huang, P.; Zheng, H.; Wang, J. A single integrated osteochondral in situ composite scaffold with a multi-layered functional structure. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2018, 167, 354–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, A.; Su, F.; Chu, P.K.; Sun, J. Articular cartilage inspired bilayer coating on Ti6Al4V alloy with low friction and high load-bearing properties. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 515, 146065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, M.; Rack, H.J. Titanium alloys in total joint replacement—A materials science perspective. Biomaterials 1998, 19, 1621–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Wu, C.; Yu, X.; Zhang, W. Recent advances of PVA-based hydrogels in cartilage repair application. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 24, 2279–2298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, T.; Yarimitsu, S.; Nakashima, K.; Sakai, N.; Yamaguchi, T.; Sawae, Y.; Suzuki, A. Biphasic and boundary lubrication mechanisms in artificial hydrogel cartilage: A review. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. H 2015, 229, 864–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, M.; Hyu, H.S. Development and evaluation of polyvinyl alcohol-hydrogels as an artificial atrticular cartilage for orthopedic implants. Materials 2010, 3, 2753–2771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarimitsu, S.; Sasaki, S.; Murakami, T.; Suzuki, A. Evaluation of lubrication properties of hydrogel artificial cartilage materials for joint prosthesis. Biosurface Biotribology 2016, 2, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Zhang, D.; Cui, X.; Wang, Q. Preparation of ultrahigh-molecular-weight polyethylene grafted with polyvinyl alcohol hydrogel as an artificial joint. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 24215–24223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krklješ, A.; Nedeljković, J.; Kačarević-Popović, Z.M. Fabrication of Ag-PVA hydrogel nanocomposite by γ-irradiation. Polym. Bull. 2007, 58, 271–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Liu, Q.; Chen, X.; Yu, F.; Zhu, Z. Investigation of PVA/ws-chitosan hydrogels prepared by combined γ-irradiation and freeze-thawing. Carbohydr. Polym. 2008, 73, 401–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, H.; Wei, L.; Lin, C.; Ma, Q.; Dai, H.; Zhu, J. Lignin-containing cellulose nanofibril-reinforced polyvinyl alcohol hydrogels. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 4821–4828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Li, J.; Lu, J.; Ding, M.; Chen, Y. Synthesis and properties of poly (vinyl alcohol) hydrogels with high strength and toughness. Polym. Test. 2022, 108, 107516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Lei, T.; Wu, Q. High-water-content mouldable polyvinyl alcohol-borax hydrogels reinforced by well-dispersed cellulose nanoparticles: Dynamic rheological properties and hydrogel formation mechanism. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 102, 306–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Feng, G. When nanocellulose meets hydrogels: The exciting story of nanocellulose hydrogels taking flight. Green Chem. 2023, 25, 8349–8384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tummala, G.K.; Joffre, T.; Lopes, V.R.; Liszka, A.; Buznyk, O.; Ferraz, N.; Persson, C.; Griffith, M.; Mihranyan, A. Hyperelastic nanocellulose-reinforced hydrogel of high water content for ophthalmic applications. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2016, 2, 2072–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tummala, G.K.; Lopes, V.R.; Mihranyan, A.; Ferraz, N. Biocompatibility of nanocellulose-reinforced PVA hydrogel with human corneal epithelial cells for ophthalmic applications. J. Funct. Biomater. 2019, 10, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.-Y.; Li, J.-Y. Enhanced swelling, mechanical and thermal properties of cellulose nanofibrils (CNF)/poly (vinyl alcohol)(PVA) hydrogels with controlled porous structure. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2018, 18, 668–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swaroop, K.; Francis, S.; Somashekarappa, H. Gamma irradiation synthesis of Ag/PVA hydrogels and its antibacterial activity. Mater. Today Proc. 2016, 3, 1792–1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd El-Mohdy, H. Radiation synthesis of nanosilver/poly vinyl alcohol/cellulose acetate/gelatin hydrogels for wound dressing. J. Polym. Res. 2013, 20, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornaggia, A.; Boschetti, F.; Mazzotta, C.; Pandolfi, A. Numerical investigation on epi-off crosslinking effects on porcine corneas. Mech. Soft. Mater. 2020, 2, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahanabadi, R.; Sheikh, N.; Mahdavi, H.; Bagheri, R. Effect of electron-beam irradiation followed by annealing on the physical properties of poly (vinyl alcohol)–chitosan blend films at different weight ratios. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2019, 136, 47820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Tong, H.; Kirillova, A.; Koshut, W.J.; Malek, A.; Brigham, N.C.; Becker, M.L.; Gall, K.; Wiley, B.J. A synthetic hydrogel composite with a strength and wear resistance greater than cartilage. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2205662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.-S.; Kim, H.-A.; Choi, J.-B.; Gwon, H.-J.; Shin, Y.-M.; Lim, Y.-M.; Khil, M.S.; Nho, Y.-C. Effects of annealing and the addition of PEG on the PVA based hydrogel by gamma ray. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2012, 81, 857–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peppas, N.A.; Merrill, E.W. Differential scanning calorimetry of crystallized PVA hydrogels. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1976, 20, 1457–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Yang, M.; Liu, S.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, B.; Chen, Y. Chitosan/polyvinyl alcohol/tannic acid multiple network composite hydrogel: Preparation and characterization. Iran Polym. J. 2021, 30, 1159–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeno, H.; Inoguchi, H.; Hsieh, W.-C. Mechanical and structural properties of cellulose nanofiber/poly (vinyl alcohol) hydrogels cross-linked by a freezing/thawing method and borax. Cellulose 2020, 27, 4373–4387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Sakai, E.; Qiu, J.; Zhu, P. Highly temperature resistant cellulose nanofiber/polyvinyl alcohol hydrogel using aldehyde cellulose nanofiber as cross-linker. Cellulose 2019, 26, 5291–5303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.; Lue, A.; Zhang, L. Effects of crosslinking methods on structure and properties of cellulose/PVA hydrogels. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2008, 209, 1266–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reguieg, F.; Ricci, L.; Bouyacoub, N.; Belbachir, M.; Bertoldo, M. Thermal characterization by DSC and TGA analyses of PVA hydrogels with organic and sodium MMT. Polym. Bull. 2020, 77, 929–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tummala, G.K.; Joffre, T.; Rojas, R.; Persson, C.; Mihranyan, A. Strain-induced stiffening of nanocellulose-reinforced poly (vinyl alcohol) hydrogels mimicking collagenous soft tissues. Soft Matter 2017, 13, 3936–3945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Wang, A.; Wang, C. Analysis of friction between articular cartilage and polyvinyl alcohol hydrogel artificial cartilage. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2016, 27, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Ye, Z.; Hu, F.; Wang, W.; Zhang, S.; Gao, L.; Lu, H. Double-network polyvinyl alcohol composite hydrogel with self-healing and low friction. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2022, 139, 51563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Zhao, W.; Ning, F.; Zhen, J.; Qiang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, F.; Jia, Z. Alginate fiber-enhanced poly (vinyl alcohol) hydrogels with superior lubricating property and biocompatibility. Polymers 2022, 14, 4063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, Y.-S.; Xiong, D.-S.; Ma, R.-Y. A study on the friction properties of poly (vinyl alcohol) hydrogel as articular cartilage against titanium alloy. Wear 2007, 262, 1021–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Sample | PVA Content (wt%) | CNF Content (wt%) | Annealing Treatment |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 9 | / | / |
| 2 | 9 | / | Annealing |
| 3 | 9 | / | In situ annealing |
| 4 | 9 | 0.3 | / |
| 5 | 9 | 0.3 | Annealing |
| 6 | 9 | 0.3 | In situ annealing |
| 7 | 9 | 0.3 | 30% stretch |
| 8 | 9 | 0.6 | / |
| 9 | 9 | 0.6 | Annealing |
| 10 | 9 | 0.6 | In situ annealing |
| 11 | 9 | 0.6 | 30% stretch |
| 12 | 9 | 0.9 | / |
| 13 | 9 | 0.9 | Annealing |
| 14 | 9 | 0.9 | In situ annealing |
| 15 | 9 | 0.9 | 30% stretch |
| 0.6% CNF Hydrogels | Tm (°C) | Xc (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Unannealed | 221.5 | 19.9% |
| Annealed | 223.7 | 22.6% |
| In situ-annealed | 224.4 | 25.6% |
| 30% stretch annealed | 224.7 | 25.8% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, Y.; Yang, M.; Zhang, W.; Guo, W.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, B. Facile Preparation of Irradiated Poly(vinyl alcohol)/Cellulose Nanofiber Hydrogels with Ultrahigh Mechanical Properties for Artificial Joint Cartilage. Materials 2024, 17, 4125. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17164125
Chen Y, Yang M, Zhang W, Guo W, Zhang X, Zhang B. Facile Preparation of Irradiated Poly(vinyl alcohol)/Cellulose Nanofiber Hydrogels with Ultrahigh Mechanical Properties for Artificial Joint Cartilage. Materials. 2024; 17(16):4125. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17164125
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Yang, Mingcheng Yang, Weiwei Zhang, Wenhui Guo, Xiuqiang Zhang, and Benshang Zhang. 2024. "Facile Preparation of Irradiated Poly(vinyl alcohol)/Cellulose Nanofiber Hydrogels with Ultrahigh Mechanical Properties for Artificial Joint Cartilage" Materials 17, no. 16: 4125. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17164125
APA StyleChen, Y., Yang, M., Zhang, W., Guo, W., Zhang, X., & Zhang, B. (2024). Facile Preparation of Irradiated Poly(vinyl alcohol)/Cellulose Nanofiber Hydrogels with Ultrahigh Mechanical Properties for Artificial Joint Cartilage. Materials, 17(16), 4125. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17164125





