Preparation of Photocurable Organic–Inorganic Hybrid Composites for Continuous Manufacturing of 3D-Patterned Abrasive
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
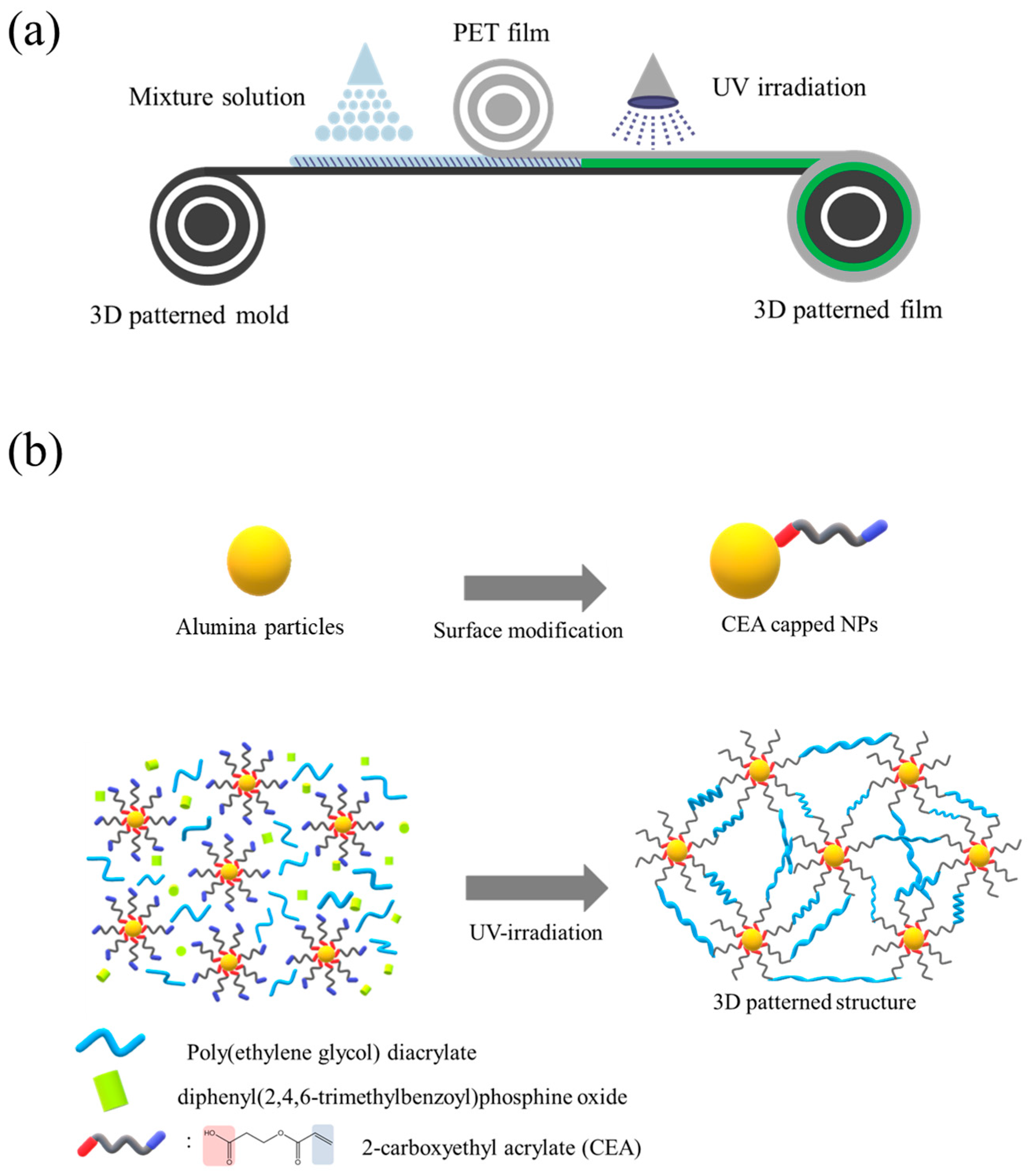
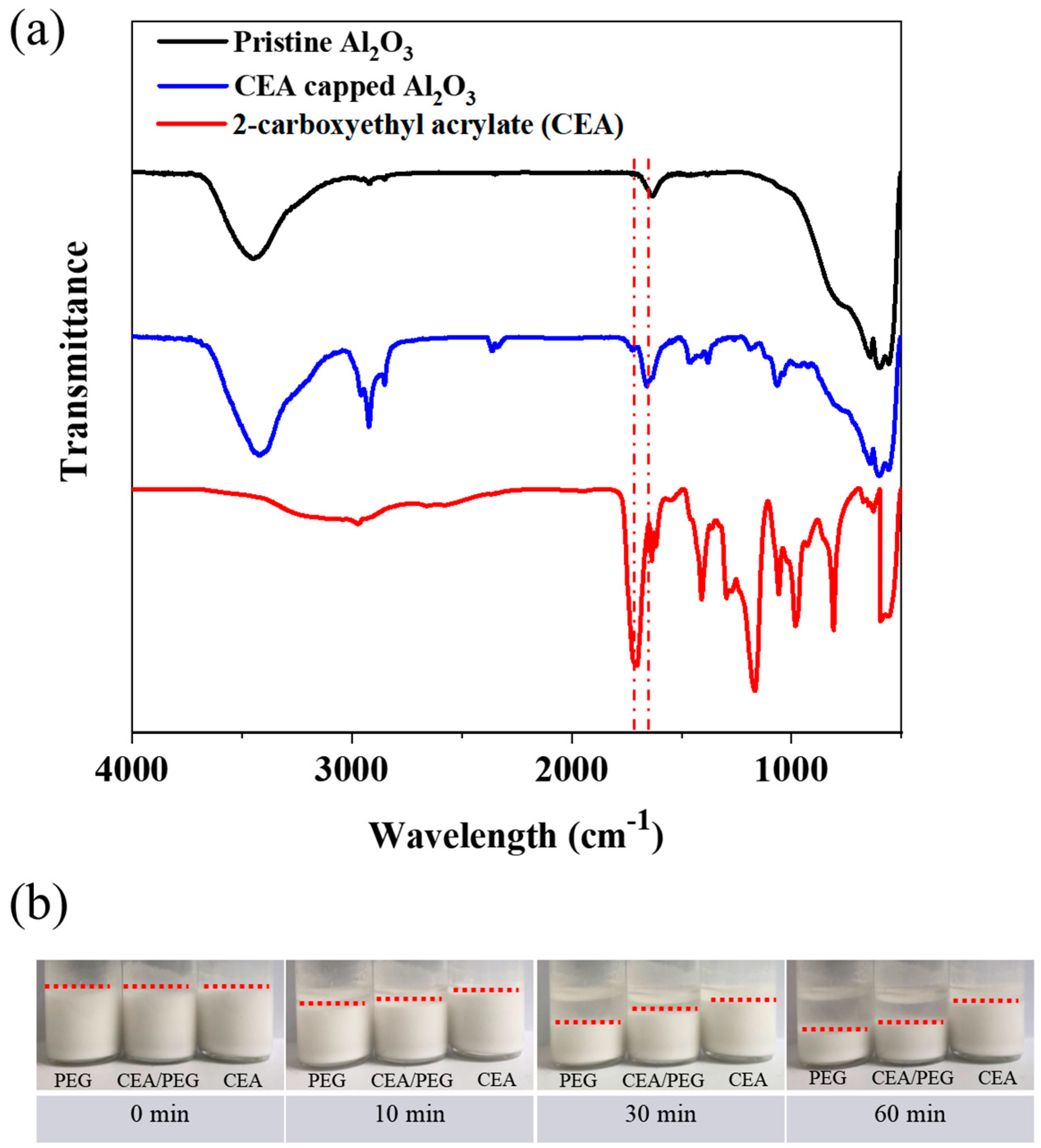
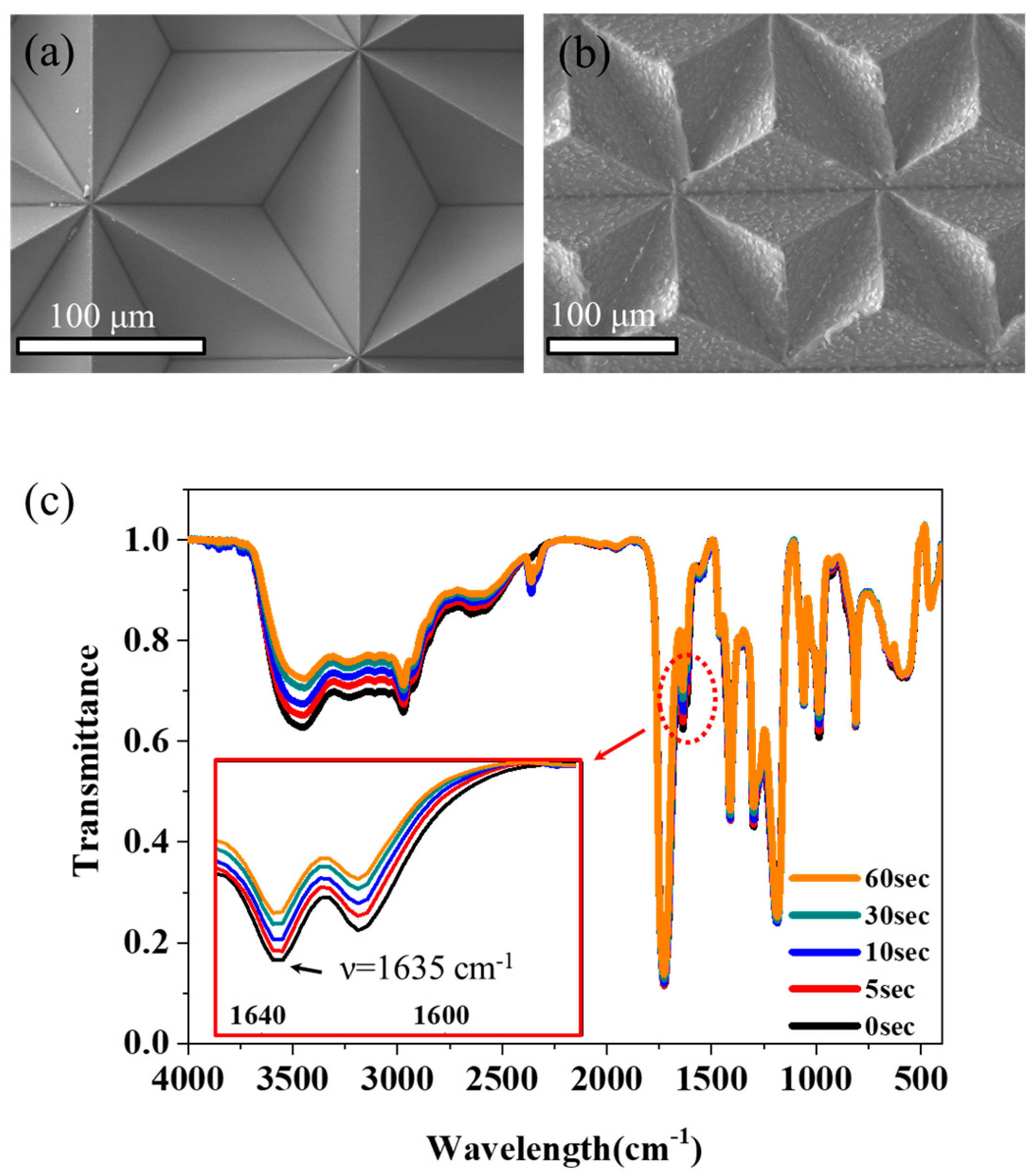
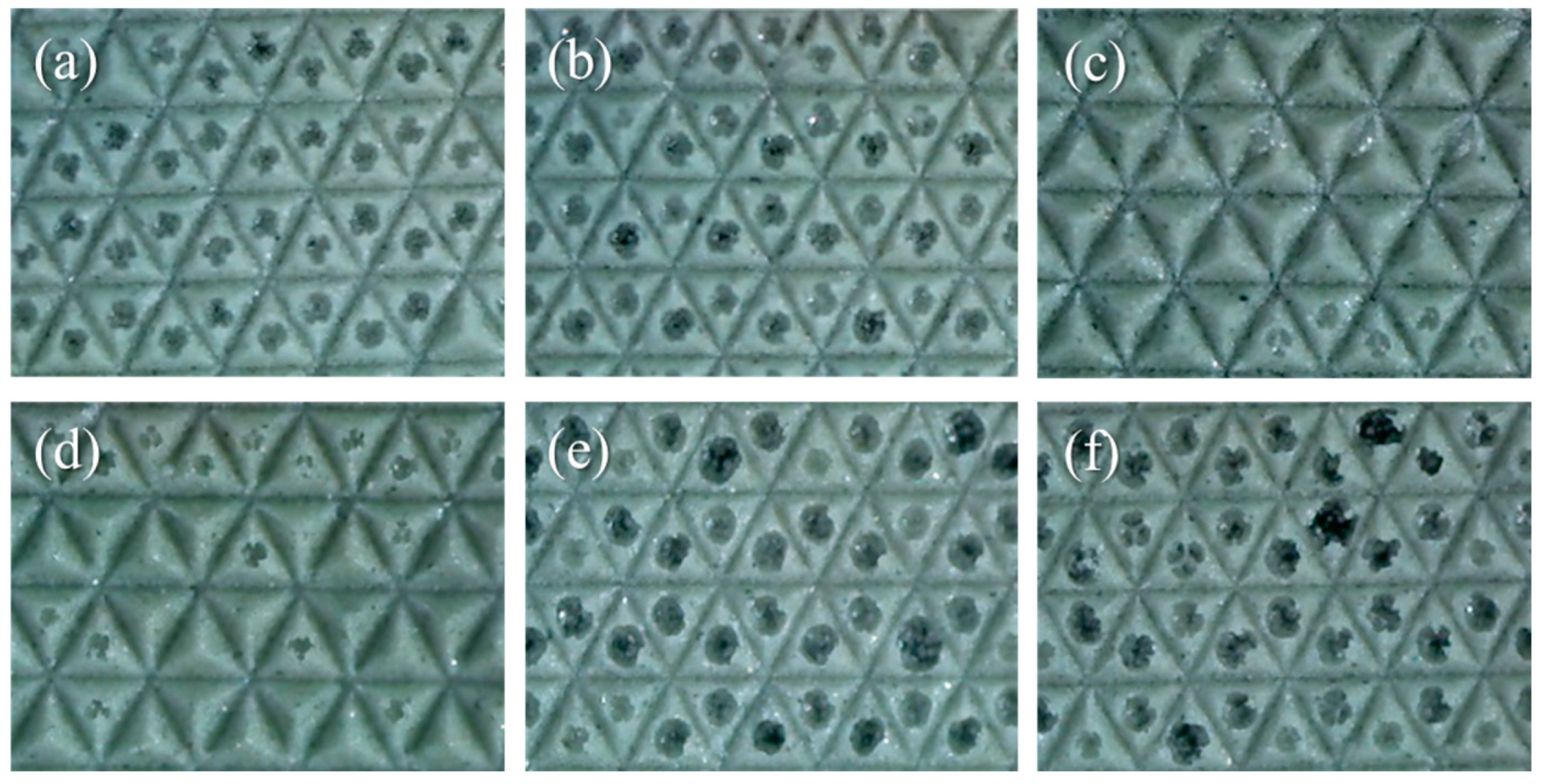
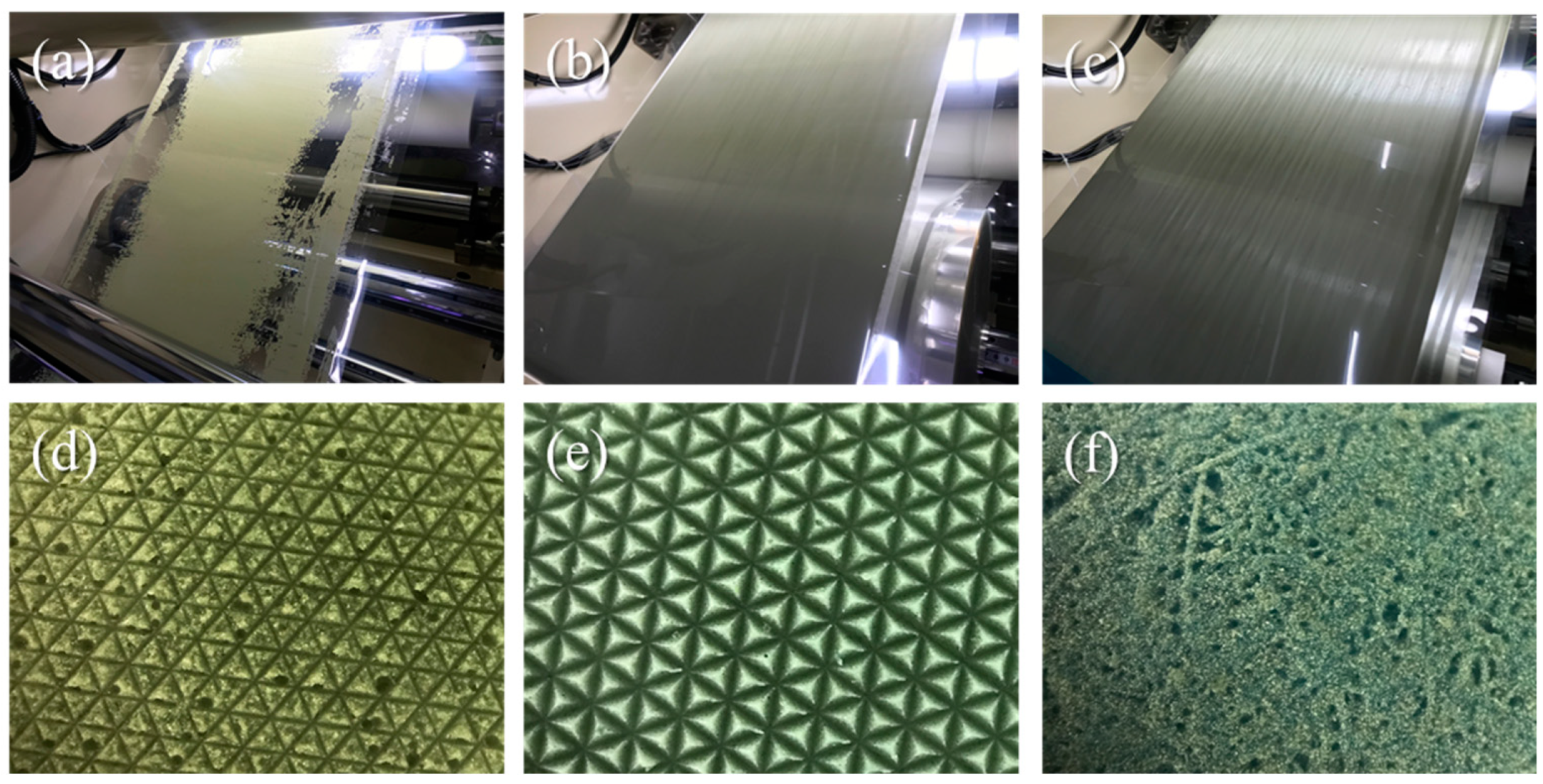
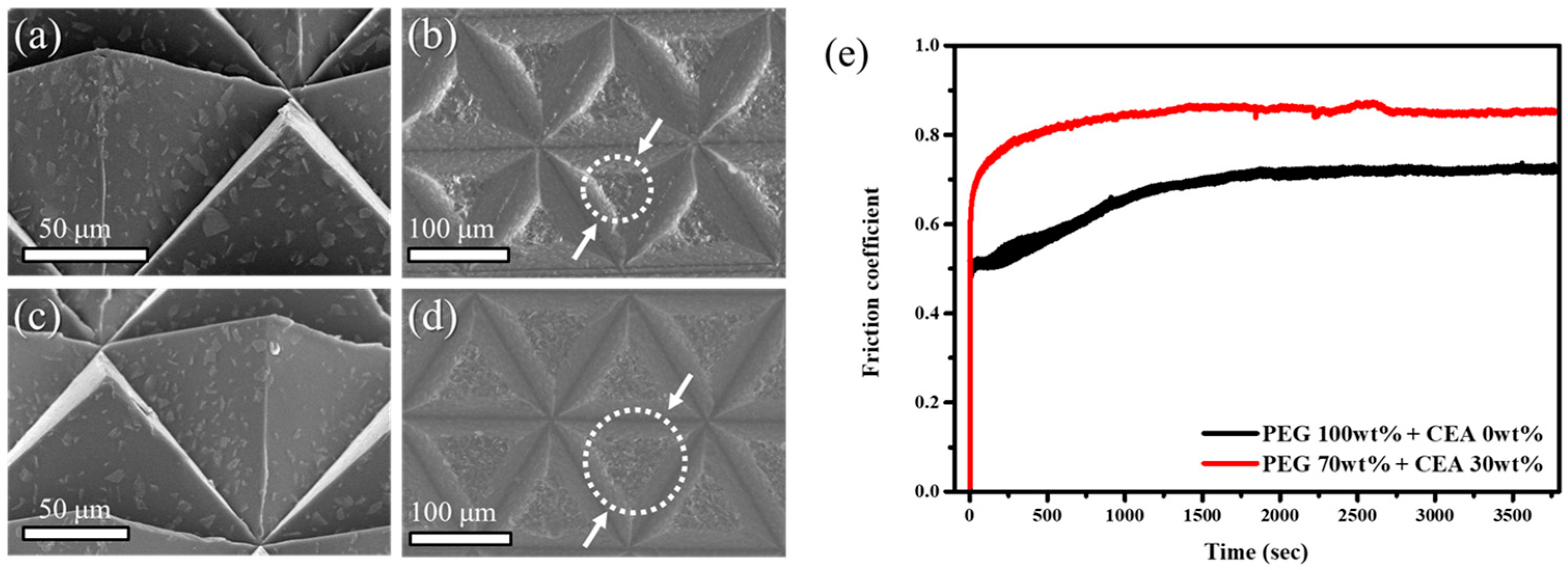
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Komanduri, R.; Lucca, D.A.; Tani, Y. Technological Advances in Fine Abrasive Processes. CIRP Ann. 1997, 46, 545–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.-K.; Wang, Z.-K.; Zhu, Y.-W.; Su, J.-X. Effect of lapping slurry on critical cutting depth of spinel. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 347, 849–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khruschov, M.M. Principles of abrasive wear. Wear 1974, 28, 69–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linke, B.S. A review on properties of abrasive grits and grit selection. Int. J. Abras. Technol. 2015, 7, 46–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhopadhyay, A.K.; Yiu-Wing, M. Grain size effect on abrasive wear mechanisms in alumina ceramics. Wear 1993, 162–164, 258–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zhao, L.; Li, Z.Y.; Feng, L.; Bai, X. Surface characteristics of Ti-6Al-4V by SiC abrasive-mixed EDM with magnetic stirring. Mater. Manuf. Process. 2017, 32, 83–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, J.B.; Kim, D.W.; Parks, R.E.; Burge, J.H. New approach for pre-polish grinding with low subsurface damage. In Proceedings of the SPIE—The International Society for Optical Engineering; SPIE: Bellingham, MA, USA, 2011; p. 81261E. [Google Scholar]
- Chung, S.; Im, Y.; Choi, J.; Jeong, H. Microreplication techniques using soft lithography. Microelectron. Eng. 2004, 75, 194–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihlbachler, M.C.; Foy, M.; Beatty, B.L. Surface Replication, Fidelity and Data Loss in Traditional Dental Microwear and Dental Microwear Texture Analysis. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tseng, W.-T.; Rafie, S.; Ticknor, A.; Devarapalli, V.; Truong, C.; Majors, C.; Zabasajja, J.; Sokol, J.; Laraia, V.; Fritz, M. Microreplicated Conditioners for Cu Barrier Chemical-Mechanical Planarization (CMP). ECS J. Solid State Sci. Technol. 2015, 4, P5001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gåhlin, R.; Björkman, H.; Rangsten, P.; Jacobson, S. Designed abrasive diamond surfaces. Wear 1999, 233–235, 387–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.; Wang, H.; Song, X.; Sun, F. Fabrication and grinding performance of CVD diamond abrasive tool. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part B J. Eng. Manuf. 2023, 237, 192–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gäbler, J.; Schäfer, L.; Menze, B.; Hoffmeister, H.-W. Micro abrasive pencils with CVD diamond coating. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2003, 12, 707–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Lu, M.; Zhang, C.; Sun, F. Optimization of deposition parameters for the growth of micro-edge diamond abrasive grains using HFCVD method. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2023, 140, 110548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.-M.; Park, H.; Kim, J.; Chun, D.-M. Fabrication of a superhydrophobic surface using a fused deposition modeling (FDM) 3D printer with poly lactic acid (PLA) filament and dip coating with silica nanoparticles. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 467–468, 979–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fina, F.; Goyanes, A.; Gaisford, S.; Basit, A.W. Selective laser sintering (SLS) 3D printing of medicines. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 529, 285–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weng, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Lin, W.; Senthil, T.; Wu, L. Structure-property relationship of nano enhanced stereolithography resin for desktop SLA 3D printer. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2016, 88, 234–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Goyanes, A.; Gaisford, S.; Basit, A.W. Stereolithographic (SLA) 3D printing of oral modified-release dosage forms. Int. J. Pharm. 2016, 503, 207–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, J. Continuous manufacturing of 3D patterned hybrid film via a roll-to-roll process with UV curing. Mod. Phys. Lett. B 2020, 34, 2040039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noh, H.S.; Jung, J. Synthesis of Organic-Inorganic Hybrid Nanocomposites via a Simple Two-Phase Ligands Exchange. Sci. Adv. Mater. 2020, 12, 326–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, J.; Yoon, Y.J.; Lin, Z. Semiconducting organic-inorganic nanocomposites by intimately tethering conjugated polymers to inorganic tetrapods. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 8887–8898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, C.H.; Son, I.; Kim, J.H.; Yoo, J.Y.; Lee, B.; Moon, G.; Lee, E.; Lee, J.H. New UV/Heat Dual-curable Sealant Containing Flexible Di-functional Acrylate Resin for Liquid Crystal Device with High Adhesive Strength and Low Moisture Permeability. Mol. Cryst. Liq. Cryst. 2019, 687, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crouse, C.A.; Pierce, C.J.; Spowart, J.E. Influencing Solvent Miscibility and Aqueous Stability of Aluminum Nanoparticles through Surface Functionalization with Acrylic Monomers. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2010, 2, 2560–2569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, T.Y.; Roper, T.M.; Jonsson, E.S.; Kudyakov, I.; Viswanathan, K.; Nason, C.; Guymon, C.A.; Hoyle, C.E. The kinetics of vinyl acrylate photopolymerization. Polymer 2003, 44, 2859–2865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.-H.; Choi, J.-H.; Kim, H.-J. Coating performance and characteristics for UV-curable aliphatic urethane acrylate coatings containing norrish type I photoinitiators. J. Coat. Technol. Res. 2006, 3, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, Y.; Kawaguchi, S.-i.; Nomoto, A.; Ogawa, A. Photoinduced Coupling Reaction of Diphenyl(2,4,6-trimethylbenzoyl)phosphine Oxide with Interelement Compounds: Application to the Synthesis of Thio- or Selenophosphinates. Synthesis 2017, 49, 3558–3567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godfrey, D. Friction oscillations with a pin-on-disc tribometer. Tribol. Int. 1995, 28, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegadekatte, V.; Huber, N.; Kraft, O. Modeling and Simulation of Wear in a Pin on Disc Tribometer. Tribol. Lett. 2006, 24, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, K.; Jung, J. Preparation of Photocurable Organic–Inorganic Hybrid Composites for Continuous Manufacturing of 3D-Patterned Abrasive. Materials 2024, 17, 3977. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17163977
Kim K, Jung J. Preparation of Photocurable Organic–Inorganic Hybrid Composites for Continuous Manufacturing of 3D-Patterned Abrasive. Materials. 2024; 17(16):3977. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17163977
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Kitae, and Jaehan Jung. 2024. "Preparation of Photocurable Organic–Inorganic Hybrid Composites for Continuous Manufacturing of 3D-Patterned Abrasive" Materials 17, no. 16: 3977. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17163977
APA StyleKim, K., & Jung, J. (2024). Preparation of Photocurable Organic–Inorganic Hybrid Composites for Continuous Manufacturing of 3D-Patterned Abrasive. Materials, 17(16), 3977. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17163977






