A Study on the Mechanical and Wear-Resistance Properties of Hybrid Fiber Mortar Composites with Low Water–Cement Ratios
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Main Test Materials
2.2. Mix Design for the Experiment
2.3. Sample Preparation
2.4. Test Methods
2.4.1. Mechanical Performance Testing
Flexural and Compressive Strength Tests
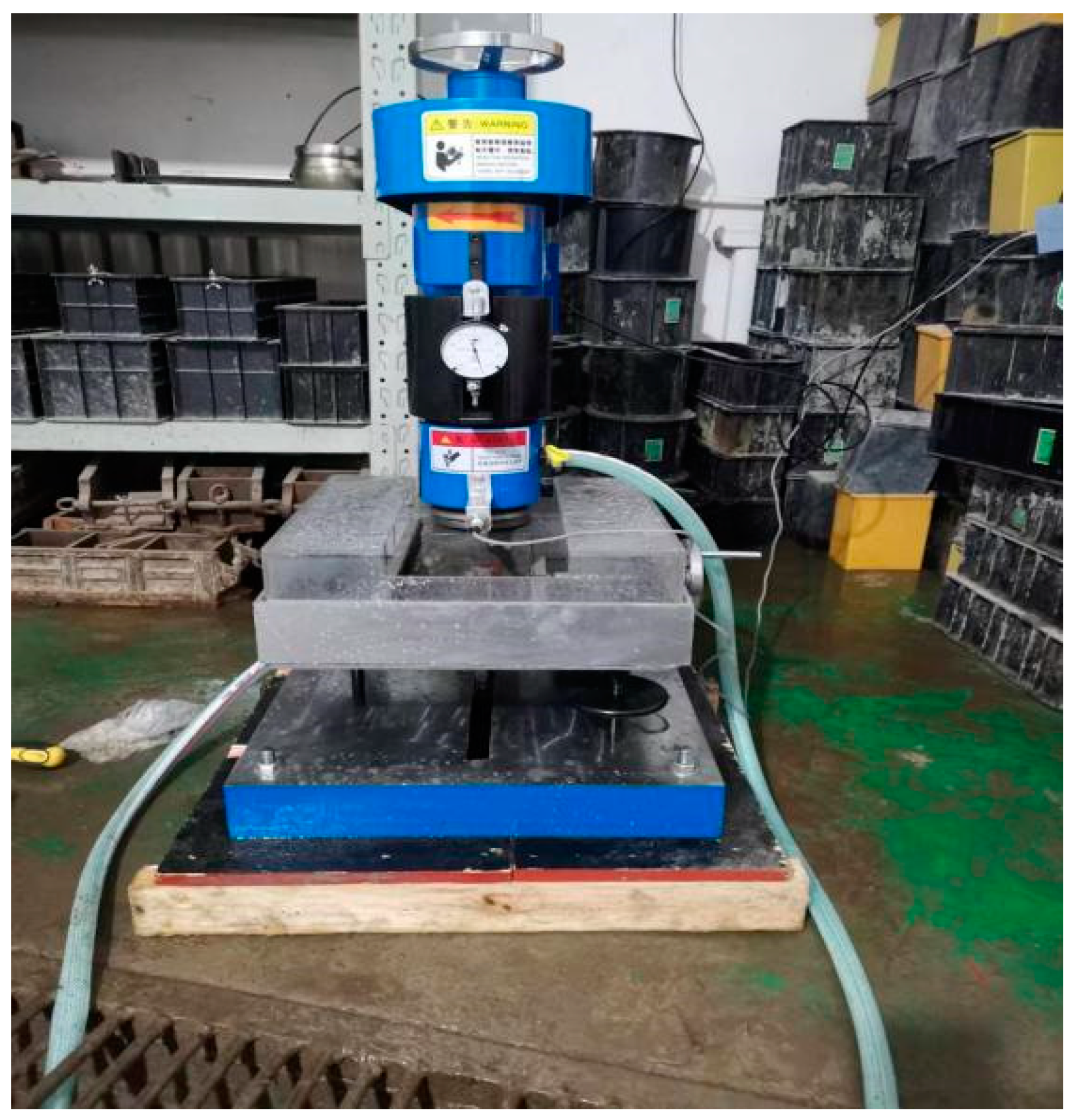
2.4.2. Abrasion-Resistance Test
2.4.3. Microstructure Test
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Mechanical Properties
3.1.1. Compressive Strength
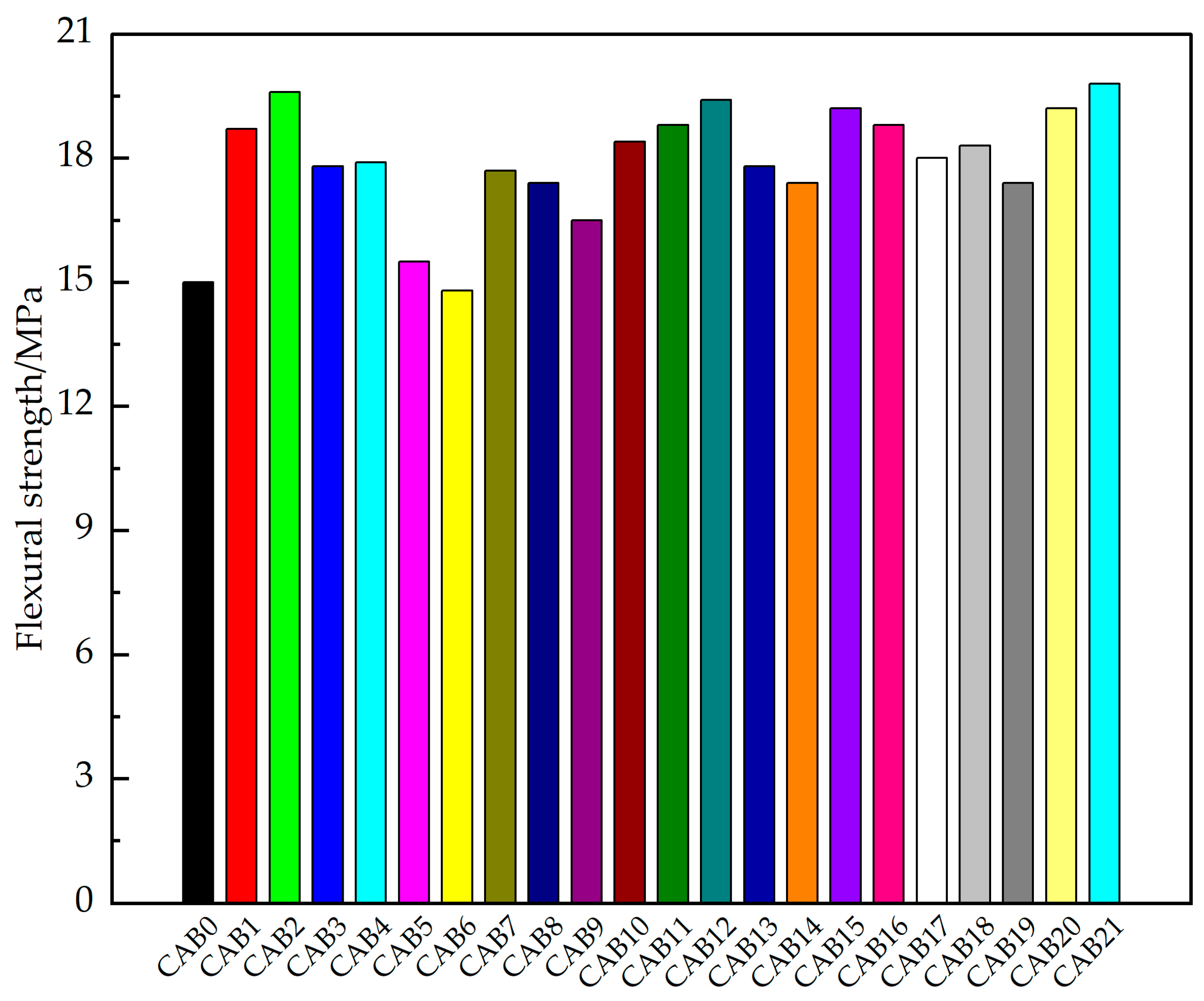
3.1.2. Flexural Strength
3.2. Abrasion Resistance
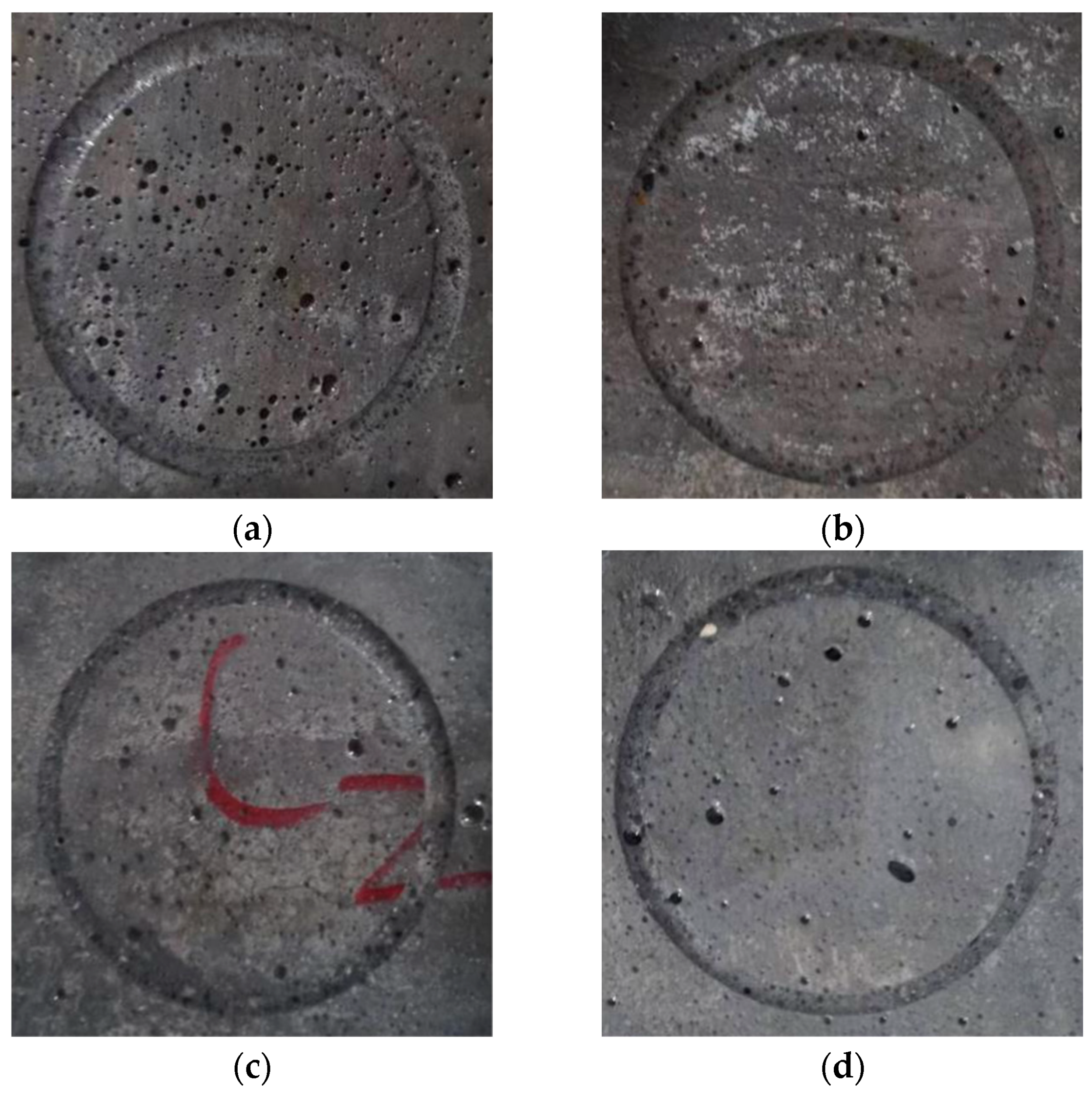
3.3. Appearance after Specimen Wear
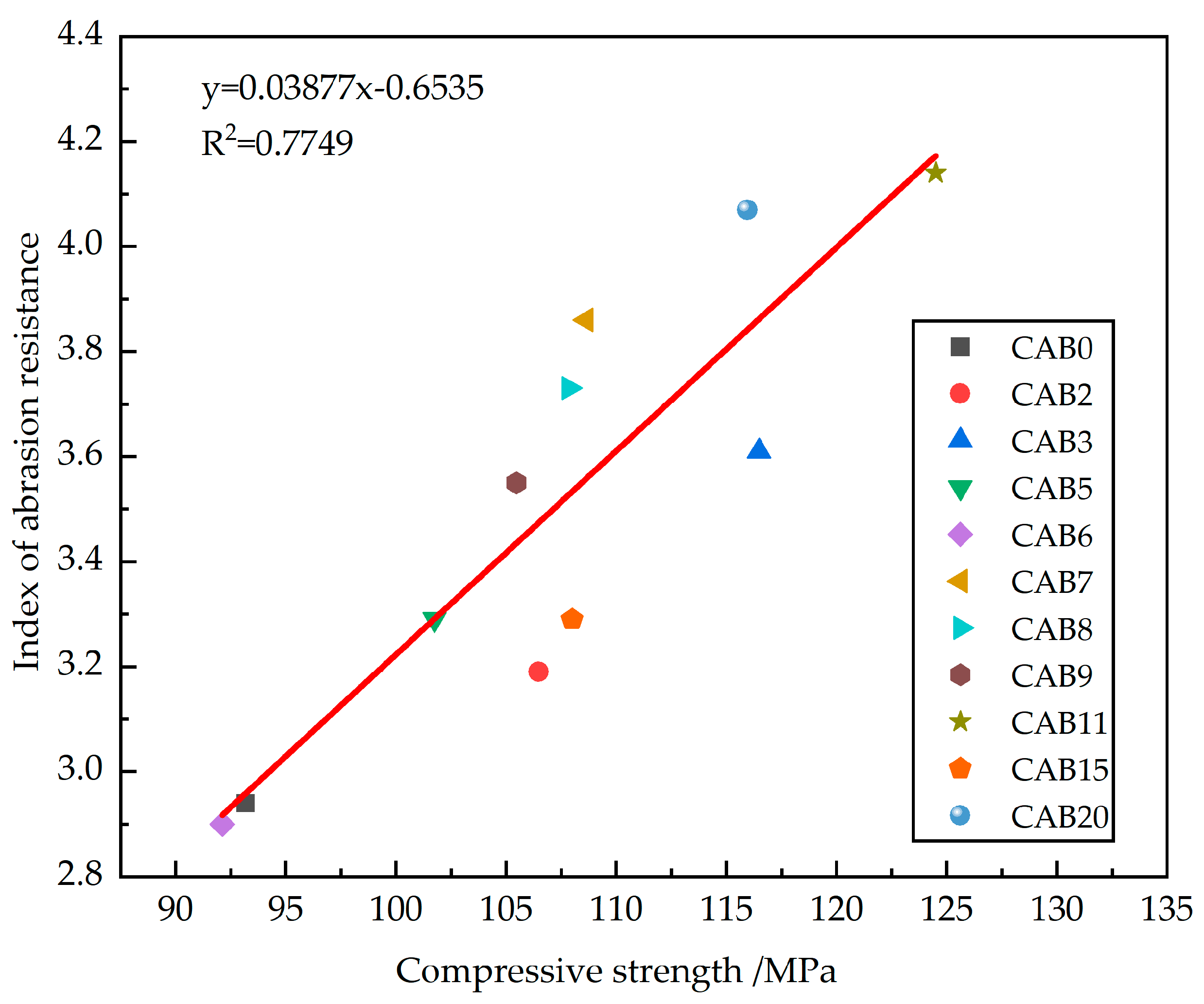
3.4. Relationship between Wear-Resistance Index and Compressive Strength
3.5. Microstructure
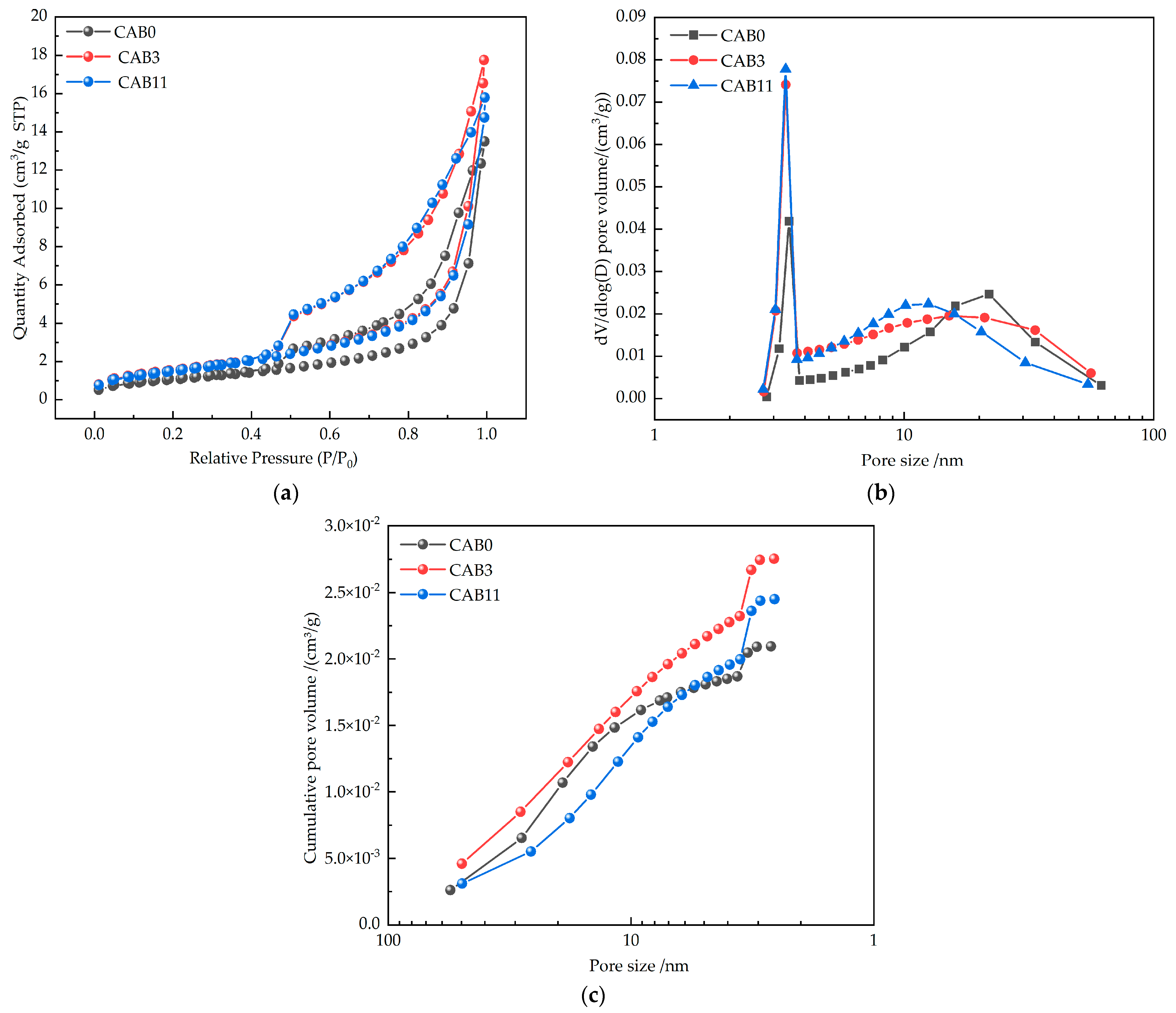
3.6. Pore Structure
3.7. Mechanism of Wear-Resistance Enhancement
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Thongchom, C.; Refahati, N.; Roodgar Saffari, P.; Roudgar Saffari, P.; Niyaraki, M.N.; Sirimontree, S.; Keawsawasvong, S. An Experimental Study on the Effect of Nanomaterials and Fibers on the Mechanical Properties of Polymer Composites. Buildings 2022, 12, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilir, T.; Yüksel, I.; Topcu, I.B.; Gencel, O. Effects of bottom ash and granulated blast furnace slag as fine aggregate on abrasion resistance of concrete. Sci. Eng. Compos. Mater. 2017, 24, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alguhi, H.; Tomlinson, D. Crack behaviour and flexural response of steel and chopped glass fibre-reinforced concrete: Experimental and analytical study. J. Build. Eng. 2023, 75, 106914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, J.; Liang, N.; Liu, X.; Zhong, Z.; Zhou, C. Investigation on early-age cracking resistance of basalt-polypropylene fiber reinforced concrete in restrained ring tests. J. Build. Eng. 2023, 70, 106155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.; Cao, M.; Ali, M. Cracking behaviour and constitutive modelling of hybrid fibre reinforced concrete. J. Build. Eng. 2020, 30, 101272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, P.S.; Hwang, S. Mechanical properties of high-strength steel fiber-reinforced concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2004, 18, 669–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bentur, P.; Mindess, S. Fibre Reinforced Cementitious Composites, 2nd ed.; CRC: London, UK, 2006; p. 624. [Google Scholar]
- Aly, T.; Sanjayan, J.G.; Collins, F. Effect of polypropylene fibers on shrinkage and cracking of concretes. Mater. Struct. 2008, 41, 1741–1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banthia, N.; Gupta, R. Influence of polypropylene fiber geometry on plastic shrinkage cracking in concrete, Cem. Concr. Res. 2006, 36, 1263–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, J.; He, Y.; Huang, G.; Li, J.; Niu, Z.; Gao, B. A review on durability of basalt fiber reinforced concrete. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2022, 225, 109519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behera, B.K.; Pattanayak, A.K.; Mishra, R. Prediction of fabric drape behavior using finite element method. J. Text. Eng. 2008, 54, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhand, V.; Mittal, G.; Rhee, K.Y.; Park, S.-J.; Hui, D. A short review on basalt fiber reinforced polymer composites. Compos. Part B Eng. 2015, 73, 166–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayub, T.; Shafiq, N.; Nuruddin, M.F. Mechanical properties of high-performance concrete reinforced with basalt fibers. Procedia Eng. 2014, 77, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Jia, B.; Huang, H.; Mou, Y. Experimental Study on Basic Mechanical Properties of Basalt Fiber Reinforced Concrete. Materials 2020, 13, 1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, C.; Fan, K.; Wu, F.; Chen, D. Experimental study on the mechanical properties and microstructure of chopped basalt fiber reinforced concrete. Mat. Des. 2014, 58, 187–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabay, N. Abrasion resistance and fracture energy of concretes with basalt fiber. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 50, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talikoti, S.R.; Kandekar, S.B. Strength and durability study of concrete structures using aramid-fiber-reinforced polymer. Fibers 2019, 7, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhanesh, S.; Kumar, K.S.; Maruthur, P.; Rejumon, R.; Usmanasha, G.S. Experimental investigation of strength of aramid kelvar and chopped carbon reinforced concrete beam. Mater. Today. Proc. 2021, 45, 1269–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walton, P.L.; Majumdar, A.J. Properties of cement composites reinforced with Kevlar fibres. J. Mater. Sci. 1978, 13, 1075–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, R.J.; Li, V.C. Dependence of Flexural Behavior of Fiber Reinforced Material Fracture Resistance and Beam Size. Mater. J. 1990, 87, 627–637. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.F.; Wang, H.F.; Syu, J.Y.; Ramanathan, G.K.; Tsai, Y.K. Investigating the Mechanical Performance on Static and Shock Wave Loading of Aramid Fiber-Reinforced Concrete. Fibers 2022, 10, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhuang, X.; Querol, X.; Font, O.; Moreno, N. A review on the applications of coal combustion products in China. Int. Geol. Rev. 2018, 60, 671–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, L.; Pan, R.; Jun, X.U. Mechanical Properties and Microstructure of CaSO4 Whisker Reinforced Cement Mortar. J. Wuhan Univ. Technol. Mater. Sci. Ed. 2019, 34, 1170–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, K.; Li, C.; Xiang, L.; Li, H.; Ning, P. Influence of temperature and solution composition on the formation of calcium sulfates. Particuology 2010, 8, 240–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.G.; Ye, K.; Luo, K.B.; Li, H.P.; Su, Y.; Li, G.B.; Mei, Y. Research Progress on Modification and Applications in the Material Fields of Calcium Sulfate Whisker. Bull. Chin. Ceram. Soc. 2017, 36, 1590–1593. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, K.; Liu, G.; Li, H.; Huang, Z. Mechanical Properties and Microstructure of Calcium Sulfate Whisker-Reinforced Cement-Based Composites. Materials 2022, 15, 947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, Y.; Yao, J.; Deng, F.; Li, H.; Wang, K.; Tang, S. Hydration Behavior and Strength Development of Supersulfated Cement Prepared by Calcined Phosphogypsum and Slaked Lime. J. Build. Eng. 2023, 80, 108075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, C.; Tobon, J.I. Influence of Calcined Clay/Limestone, Sulfate and Clinker Proportions on Cement Performance. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 251, 119050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stawiski, B.; Kania, T. Examining the Distribution of Strength across the Thickness of Reinforced Concrete Elements Subject to Sulphate Corrosion Using the Ultrasonic Method. Materials 2019, 12, 2519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.H.; Ju, Y.Z.; Shen, H.; Xu, L.B. Mechanical properties of high performance concrete reinforced with basalt fiber and polypropylene fiber. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 197, 464–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.X.; Song, Y.; Xie, Z.H.; Guo, Y.C.; Yuan, B.; Zeng, J.J.; Wei, X. Static and dynamic mechanical behavior of engineered cementitious composites with PP and PVA fibers. J. Build. Eng. 2020, 29, 101097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Htet, P.; Chen, W.; Hao, H.; Shaikh, F. Influence of micro basalt and recycled macro polypropylene hybrid fibre on physical and mechanical properties of recycled aggregate concrete. J. Build. Eng. 2023, 76, 107083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Li, X.; Li, C.; Zhao, J.; Cheng, S. Mechanical Properties of Fully Recycled Aggregate Concrete Reinforced with Steel Fiber and Polypropylene Fiber. Materials 2024, 17, 1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palanisamy, E.; Ramasamy, M. Dependency of sisal and banana fiber on mechanical and durability properties of polypropylene hybrid fiber reinforced concrete. J. Nat. Fibers 2020, 19, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganta, J.K.; Seshagiri Rao, M.V.; Mousavi, S.S.; Srinivasa Reddy, V.; Bhojaraju, C. Hybrid steel/glass fiber-reinforced selfconsolidating concrete considering packing factor: Mechanical and durability characteristics. Structures 2020, 28, 956–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teja Prathipati, S.R.R.; Rao, C.B.K. A study on the uniaxial behavior of hybrid graded fiber reinforced concrete with glass and steel fibers. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 32, 764–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köksal, F.; Gencel, O.; Unal, B.; Durgun, M.Y. Durability properties of concrete reinforced with steel-polypropylene hybrid fibers. Sci. Eng. Compos. Mater. 2012, 19, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhou, L.; Nie, Q.; Wu, H.; Wu, L. Effects of calcium sulfate whiskers and basalt fiber on gas permeability and microstructure of concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 411, 134369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Z.; Li, C.; Chen, Z.; Ke, L. Study on mechanical properties and optimum fiber content for basalt/polyacrylonitrile hybrid fiber reinforced concrete. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2022, 2022, 4181638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Li, D.; Bian, L.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Y. Study on Mechanical and Impact Properties of Aramid Fiber Reinforced Cement Cementitious Composites. Mater. Rep. 2021, 35, 634–637. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- GBT 31387-2015; Reactive Powder Concrete. China Standard Press: Beijing, China, 2015. (In Chinese)
- GB/T 17671-2021; Test Method of Cement Mortar Strength (ISO Method). China Standard Press: Beijing, China, 2021.
- GB/T 16925-1997; Test Method for Abrasion Resistance of Concrete and Its Products (Ball Bearing Method). State Bureau of Technical Supervision: Beijing, China, 1997.
- Militký, J.; Mishra, R.; Jamshaid, H. Basalt Fibers, 2nd ed.; Woodhead: London, UK, 2018; pp. 805–840. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Q.; Song, P.; Li, L.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X.Y.; Fang, J. The effect of basalt fiber addition on cement concrete: A review focused on basalt fiber shotcrete. Front. Mater. 2022, 9, 1048228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, C.; Chen, X.; Mao, W.; Xing, S.; Chen, J.; Zhou, J. Experimental Study on Flexural Fatigue Resistance of Recycled Fine Aggregate Concrete Incorporating Calcium Sulfate Whiskers. Sustainability 2023, 15, 16357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemalatha, T.; Ramesh, G. Mitigation of plastic shrinkage in fly ash concrete using basalt fibres. Can. J. Civil. Eng. 2019, 46, 759–769. [Google Scholar]
- Simões, T.; Costa, H.; Dias-da-Costa, D.; Júlio, E. Influence of Fibres on the Mechanical Behaviour of Fibre Reinforced Concrete Matrixes. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 137, 548–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banthia, N.; Gupta, R. Hybrid fiber reinforced concrete (HyFRC): Fiber synergy in high strength matrices. Mater. Struct. 2004, 37, 707–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, Y.; Yang, Z.; Liu, J.; Xu, D.; Li, L.; Zhou, H. Application of high performance aramid fiber in cement based composite materials. Concrete 2015, 94–97. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Koksal, F.; Yıldırım, M.S.; Benli, A.; Gencel, O. Hybrid effect of micro-steel and basalt fibers on physico-mechanical properties and durability of mortars with silica fume. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2021, 15, e00649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Song, Q.; Wang, X.; Yang, L. Enhancement Performance of Desulfuration Gypsum Whisker on Cementitious Materials. Bull. Chin. Ceram. Soc. 2017, 36, 1298–1302. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, F.; Pham, T.M.; Hao, H.; Hao, Y.F. Post-cracking behaviour of basalt and macro polypropylene hybrid fibre reinforced concrete with different compressive strengths. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 262, 120108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Q.; Xu, W.R.; Bu, M.X.; Guo, B.B.; Niu, D.T. Effect and action mechanism of fibers on mechanical behavior of hybrid basalt-polypropylene fiber-reinforced concrete. Structures 2021, 34, 3596–3610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.-G.; Seo, D.-J.; Heo, G.-H. Impact Resistance and Flexural Performance Properties of Hybrid Fiber-Reinforced Cement Mortar Containing Steel and Carbon Fibers. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 9439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, G.; Zhao, C.; Guo, J.; Yi, R.; Luo, M.; Peng, Z.; Wang, X. Experimental Study on Mechanical Properties of Basalt Fiber Cement Mortar. Hydroelectr. Power. 2024, 50, 108–113. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Grzeszczyk, S.; Matuszek-Chmurowska, A.; Vejmelková, E.; Černý, R. Reactive Powder Concrete Containing Basalt Fibers: Strength, Abrasion and Porosity. Materials 2020, 13, 2948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, G.; Liao, Y.; Sha, X.; Liu, G.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, R.; Yue, Y. Application of Calcium Sulfate Whiskers to Cement-Based Materials: A Review. Materials. 2024, 17, 1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siddique, R.; Kapoor, K.; Kadri, E.-H.; Bennacer, R. Effect of polyester fibres on the compressive strength and abrasion resistance of HVFA concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2012, 29, 270–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warudkar, A.; Elavenil, S.; Arunkumar, A. Assessment of abrasion resistance of concrete pavement for durability. Int. J. Civ. Eng. Technol. 2018, 9, 1176–1181. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, B.; Jia, L.; Tian, M.; Ning, N.; Zhang, L.; Wang, W. Surface and interface modification of aramid fiber and its reinforcement for polymer composites: A review. Eur. Polym. J. 2021, 147, 110352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Mei, J.; LI, H.; Dai, J.; Xie, A. Mechanical Properties of Polyformaldehyde—Basalt Hybrid Fiber Reinforced Mortar. Bull. Chin. Ceram. Soc. 2023, 42, 3454–3461. [Google Scholar]
- Nia, A.; Hedayatian, M.; Nili, M.; Afrough, V. An experimental and numerical study on how steel and polypropylene fibers affect the impact resistance in fiber-reinforced concrete. Int. J. Impact Eng. 2012, 46, 62–73. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, M.; Cong, Z.; Lv, H.; Xu, L. Characterization of mechanical behavior and mechanism of calcium carbonate whisker-reinforced cement mortar. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 66, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Yi, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, D.; Ran, J. The Effects of Hybrid Steel/Basalt Fibers on the Durability of Concrete Pavement against Freeze–Thaw Cycles. Materials 2023, 16, 7137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Lian, H. High Performance Concrete; China Railway Publishing House: Beijing, China, 1999; pp. 41–43. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Li, D.; Bianm, L.; Feng, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, H. Effect of Cutting Aramid Fiber Content on Strength and Pore Structure of Cement-based Composites. Mater. Rep. 2021, 35, 638–641. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhai, S.; Liu, G.; Pang, B.; Liu, C.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Liu, L.; Yang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, Y. Investigation on the influence of modified waste rubber powder on the abrasion resistance of concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 357, 129409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, K.; Liang, K.; Chang, J.; Lau, D. Investigation of the macro performance, mechanism, and durability of multiscale steel fiber reinforced low-carbon ecological UHPC. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 327, 126921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Chen, C.; Wang, Y.; Jiu, S.; Chen, Y. Influence of modified calcium sulfate hemihydrate whisker on the physical, mechanical, and microscopic properties of gypsum matrix composites. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 394, 132280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Su, Y.; Tan, K.H.; Zheng, X.; Sheng, J. Pore structure and splitting tensile strength of hybrid Basalt–Polypropylene fiber reinforced concrete subjected to carbonation. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 297, 123779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Raw Materials | SiO2 | Al2O3 | CaO | Fe2O3 | SO3 | MgO | K2O | Others |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cement (%) | 20.34 | 4.4 | 62.92 | 3.2 | 2.8 | 1.78 | 0.45 | 0.3 |
| Silica Fume (%) | 88% | 1.63 | 0.4 | 1.15 | 0.05 | 0.8 | 0.49 | 3.21 |
| Fly Ash (%) | 48.62 | 35.41 | 6.61 | 6.26 | 0.63 | 0.58 | 0.91 | 1.25 |
| Raw Materials | O | Si | S | Ca | C | Al | N |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AF (%) | 15.95 | - | - | - | 79.43 | - | 4.62 |
| BF (%) | 58.93 | 26.43 | 0.59 | 4.93 | 9.12 | ||
| CSW (%) | 30.27 | 27.56 | 40.46 | 1.71 |
| Fiber | Single Filament Diameter (μm) | Length (um) | Bulk Density (g·cm−3) | Absolute Density (g·cm−3) | PH Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Calcium Sulfate Whiskers | 1–4 | 10–200 | ≤0.5 | 2.69 | 6.5–7.5 |
| Fiber | Single Filament Diameter (μm) | Length (mm) | Specific Gravity (g·cm−3) | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Elastic Modulus (GPa) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aramid Fiber | 12 | 6 | 1.68 | 2880 | 94 |
| Basalt Fiber | 15 | 12 | 2.64 | 2070 | 84.2 |
| Parameter | Water (kg·m−3) | Fly Ash (kg·m−3) | Silica Fume (kg·m−3) | Cement (kg·m−3) | Sand (kg·m−3) | Water-Reducing Agent (kg·m−3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Value | 180 | 90 | 63 | 747 | 890 | 9 |
| Specimen Number | AF and BF Combination Ratio | Fiber Content (%) | Specimen Number | AF and BF Combination Ratio | Fiber Content (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AF | BF | CSW | AF | BF | CSW | ||||
| CAB0 | - | 0 | 0 | 0.00 | CAB11 | - | 0.100 | 0 | 2.00 |
| CAB1 | - | 0 | 0 | 1.00 | CAB12 | - | 0.100 | 0 | 3.00 |
| CAB2 | - | 0 | 0 | 2.00 | CAB13 | - | 0.100 | 0 | 4.00 |
| CAB3 | - | 0 | 0 | 3.00 | CAB14 | - | 0 | 0.100 | 1.00 |
| CAB4 | - | 0 | 0 | 4.00 | CAB15 | - | 0 | 0.100 | 2.00 |
| CAB5 | - | 0.100 | 0 | 0.00 | CAB16 | - | 0 | 0.100 | 3.00 |
| CAB6 | - | 0 | 0.100 | 0 | CAB17 | - | 0 | 0.100 | 4.00 |
| CAB7 | 2:1 | 0.067 | 0.033 | 0 | CAB18 | 2:1 | 0.067 | 0.033 | 1.00 |
| CAB8 | 1:1 | 0.050 | 0.050 | 0 | CAB19 | 2:1 | 0.067 | 0.033 | 2.00 |
| CAB9 | 1:2 | 0.033 | 0.067 | 0 | CAB20 | 2:1 | 0.067 | 0.033 | 3.00 |
| CAB10 | - | 0.100 | 0 | 1.00 | CAB21 | 2:1 | 0.067 | 0.033 | 4.00 |
| Specimen Number | Average Pore Diameter (nm) | Most Probable Pore Diameter (mL/g) | Harmless Pore Volume (mL/g) | Slightly Harmful Pore Volume (mL/g) | Harmful Pore Volume (mL/g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAB0 | 11.2914 | 0.0419 | 0.26035 | 0.00652 | 0.00261 |
| CAB3 | 8.9263 | 0.07412 | 0.31199 | 0.01308 | - |
| CAB11 | 7.8503 | 0.07781 | 0.261 | 0.00862 | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, S.; Dang, Z.; Jiang, C.; Xia, X. A Study on the Mechanical and Wear-Resistance Properties of Hybrid Fiber Mortar Composites with Low Water–Cement Ratios. Materials 2024, 17, 3798. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17153798
Li S, Dang Z, Jiang C, Xia X. A Study on the Mechanical and Wear-Resistance Properties of Hybrid Fiber Mortar Composites with Low Water–Cement Ratios. Materials. 2024; 17(15):3798. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17153798
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Shuangxi, Zimin Dang, Chunmeng Jiang, and Xinguang Xia. 2024. "A Study on the Mechanical and Wear-Resistance Properties of Hybrid Fiber Mortar Composites with Low Water–Cement Ratios" Materials 17, no. 15: 3798. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17153798
APA StyleLi, S., Dang, Z., Jiang, C., & Xia, X. (2024). A Study on the Mechanical and Wear-Resistance Properties of Hybrid Fiber Mortar Composites with Low Water–Cement Ratios. Materials, 17(15), 3798. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17153798






