Structure and Physical Properties of Conductive Bamboo Fiber Bundle Fabricated by Magnetron Sputtering
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Raw Materials
2.2. Fiber Treatment
2.3. Preparation of Conductive Bamboo Fiber Bundle
3. Methodology
4. Results and Discussion
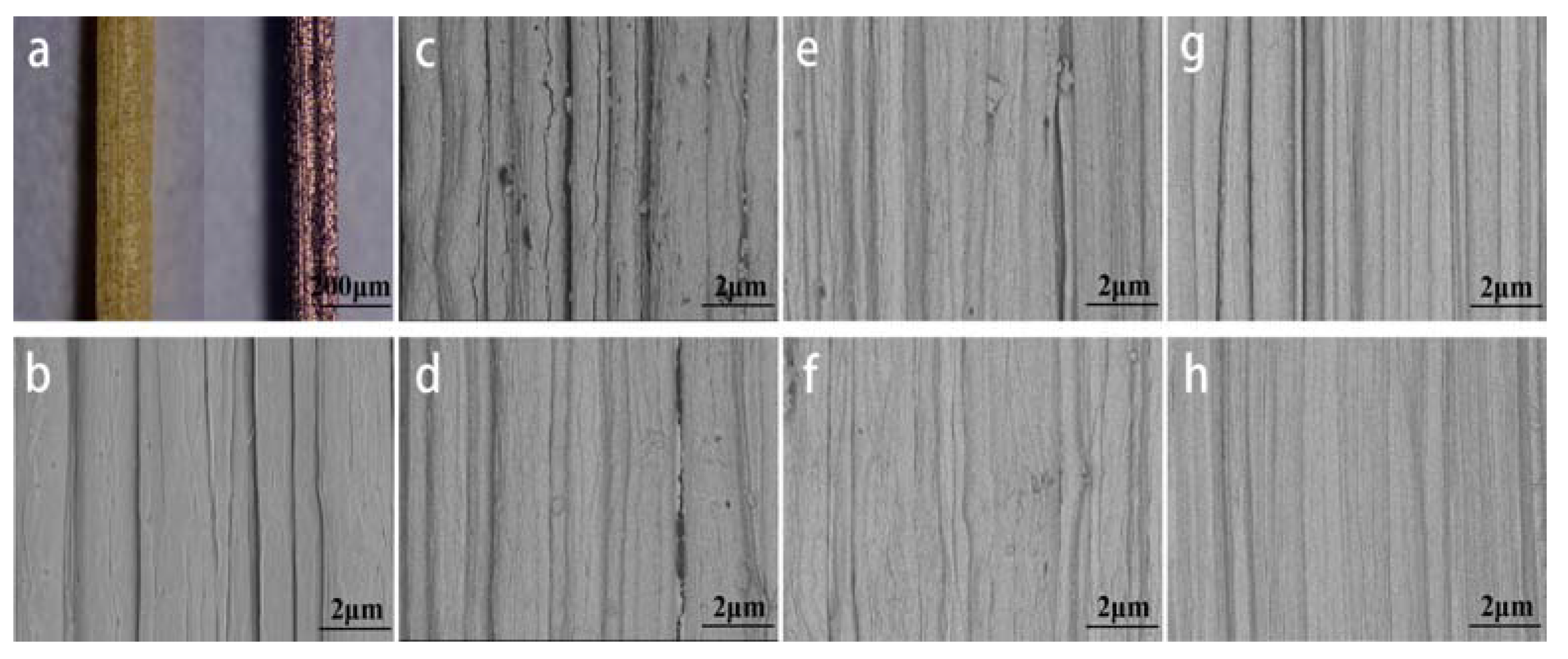
4.1. Morphology Study of Conductive Bamboo Fiber Bundle
4.2. Resistivity Analysis
4.3. Tensile Strength Analysis
4.4. XRD Analysis
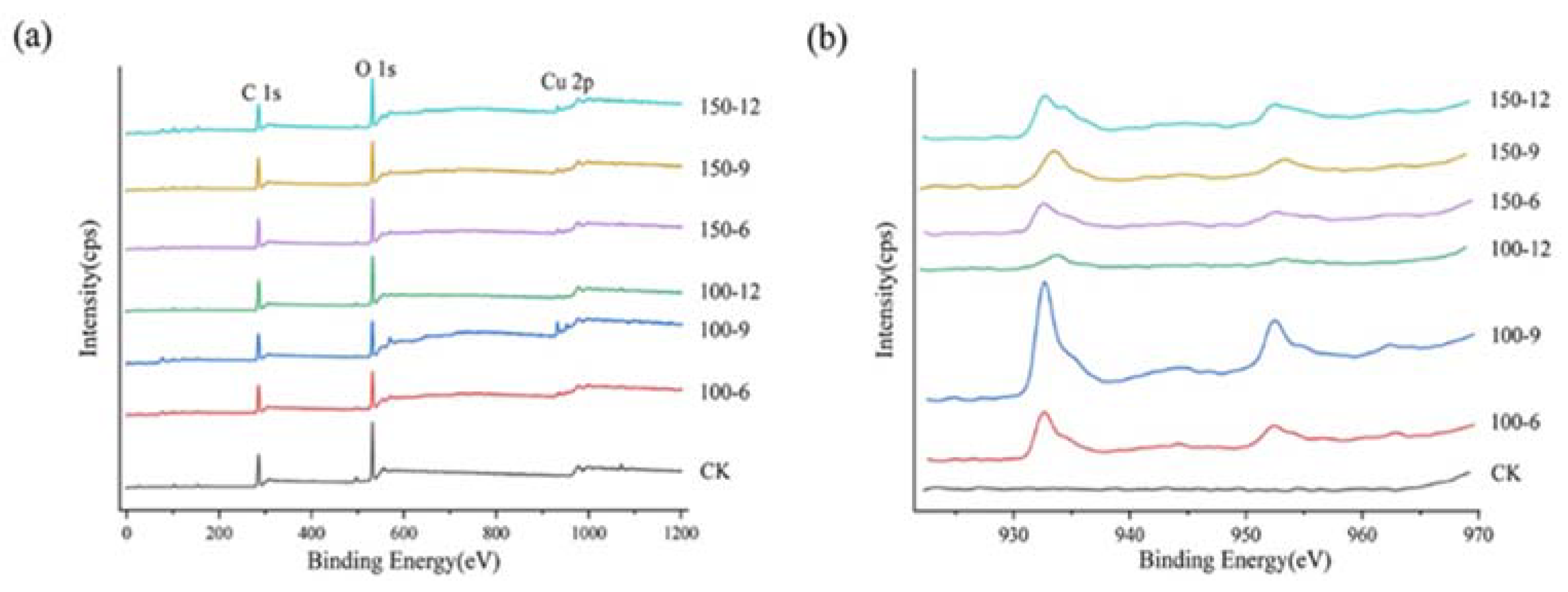
4.5. XPS Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chin, S.C.; Tee, K.F.; Tong, F.S.; Ong, H.R.; Gimbun, J. Thermal and mechanical properties of bamboo fiber reinforced composites. Mater. Today Commun. 2020, 23, 100876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Xiao, L.; Huang, J.; Wang, Y.; Nie, X.; Chen, J. Bio-based epoxy vitrimer for recyclable and carbon fiber reinforced materials: Synthesis and structure-property relationship. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2022, 227, 109575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- József, K.; Haroon, M.; Alessandro, P. Recent advances in fiber/matrix interphase engineering for polymer composites. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2015, 73, 1–43. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Y.; Zhu, R.; Wu, B.; Hu, Y.A.; Yu, W. Fabrication, material properties, and application of bamboo scrimber. Wood Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 83–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nkeuwa, W.N.; Zhang, J.; Semple, K.E.; Chen, M.; Xia, Y.; Dai, C. Bamboo-based composites: A review on fundamentals and processes of bamboo bonding. Compos. Part B Eng. 2022, 235, 109776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Chen, C.; Xie, H.; Yao, Y.; Zhang, X.; Brozena, A.; Li, J.; Ding, Y.; Zhao, X.; Hong, M.; et al. Sustainable high-strength macrofibres extracted from natural bamboo. Nat. Sustain. 2021, 5, 235–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Chen, S.; Peng, Y.; Zheng, Z.; Li, J.; Zhong, F. Materials, Preparation Strategies, and Wearable Sensor Applications of Conductive Fibers: A Review. Sensors 2022, 22, 3028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, W.; Shu, L.; Li, Q.; Chen, S.; Wang, F.; Tao, X.M. Fiber-Based Wearable Electronics: A Review of Materials, Fabrication, Devices, and Applications. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 5310–5336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qureshi, Y.; Tarfaoui, M.; Lafdi, K.K.; Lafdi, K. Real-time strain monitoring performance of flexible Nylon/Ag conductive fiber. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2019, 295, 612–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Li, X.; Li, X.; Xu, T.; Song, C.; Ogino, K.; Gu, Z. Preparation of Conductive Polyester Fibers Using Continuous Two-Step Plating Silver. Materials 2018, 11, 2033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashir, T.; Skrifvars, M.; Persson, N.K. Production of highly conductive textile viscose yarns by chemical vapor deposition technique: A route to continuous process. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2011, 22, 2214–2221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Xin, B.; Chen, Z.; Liu, Y. Flexible and highly conductive Ag/G-coated cotton fabric based on graphene dipping and silver magnetron sputtering. Cellulose 2018, 25, 3691–3701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarakinos, K.; Alami, J.; Wuttig, M. Process characteristics and film properties upon growth of TiOx films by high power pulsed magnetron sputtering. Journal of Physics, D. Appl. Phys. A Europhys. J. 2007, 40, 2108. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Zhu, T.; Wang, J.; Zheng, Z.; Li, Y.; Li, J.; Lai, Y. Functionalized Fiber-Based Strain Sensors: Pathway to Next-Generation Wearable Electronics. Nano-Micro Lett. 2022, 14, 96–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Q.; Hu, J.; Huang, Y.; Lin, Q.; Yu, W. Facile preparation of multifunctional bamboo with superhydrophobic, conductive, and flame-retardant properties. Ind. Crops Prod. 2022, 188, 115676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Q.; Liu, S.; Wang, X.; Huang, Y.; Yu, W. Preparation of ultra-conductive bamboo cellulose fiber via a facile pretreatment. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2022, 575, 151700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Wang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Wang, X.; Shi, J. Effects of Different Delignification and Drying Methods on Fiber Properties of Moso Bamboo. Polymers 2022, 14, 5464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rode, D.L.; Gaddam, V.R.; Yi, J.H. Subnanometer surface roughness of dc magnetron sputtered Al films. J. Appl. Phys. 2007, 102, 024303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, S.K.; Joshi, L.; Barhai, P.K. A comparative study of nanocrystalline Cu film deposited using anodic vacuum arc and dc magnetron sputtering. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2011, 205, 4582–4595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, P.; Wei, A.; Wang, Y.; Li, D.; Zhang, J.; Lucia, L.A.; Wei, Q. Copper nanoparticles-sputtered bacterial cellulose nanocomposites displaying enhanced electromagnetic shielding, thermal, conduction, and mechanical properties. Cellulose 2016, 23, 55–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasheed, H.S.; Ahmed, N.M.; Matjafri, M.Z.; Sabah, F.A.; Al-Rawi, H.N. The Effect of the Annealing on the Properties of ZnO/Cu/ZnO Multilayer Structures. Procedia Chem. 2016, 19, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Dong, D.; Gong, S.; Brassart, L.; Wang, Y.; An, T.; Cheng, W. A Moss-Inspired Electroless Gold-Coating Strategy Toward Stretchable Fiber Conductors by Dry Spinning. Adv. Electron. Mater. 2018, 5, 1800462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Z.; He, Y.; Sang, J.; Hirahara, H.; Chen, D. Superhydrophobic and Conductive Cotton Fabric Composite with Excellent Corrosion Resistance for Wearable Electronics. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 8, 2100651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Tian, G.; Jin, G.; Xin, Y.; Tao, R.; Lubineau, G. Buckled Conductive Polymer Ribbons in Elastomer Channels as Stretchable Fiber Conductor. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 1907316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Ding, C.; Yuan, W.; Xie, R.; Zhou, X.; Zhao, Y.; Yu, M.; Yang, Z.; Sun, J.; Tian, Q.; et al. Highly Stretchable and Permeable Conductors Based on Shrinkable Electrospun Fiber Mats. Adv. Fiber Mater. 2021, 3, 302–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Han, J.; Shi, Z.; Chen, K.; Xu, N.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, R.; Tao, Y.; Sun, Q.; Wang, Z.L.; et al. Biodegradable, Super-Strong, and Conductive Cellulose Macrofibers for Fabric-Based Triboelectric Nanogenerator. Nanomicro. Lett. 2022, 14, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Mensah, A.; Liao, S.; Lv, P.; Wei, Q. Scalable, ultra-high stretchable and conductive fiber triboelectric nanogenerator for biomechanical sensing. Nano Energy 2023, 109, 108291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.F.; Fang, S.; Moura, F.A.; Ding, J.N.; Jiang, N.; Di, J.; Zhang, M.; Lepró, X.; Galvao, D.S.; Haines, C.S.; et al. Hierarchically buckled sheath-core fibers for superelastic electronics, sensors, and muscles. Science 2015, 349, 400–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.; Ren, P.; Guo, H.; Jin, Y.; Yan, D.; Li, Z. Highly Sensitive and Stretchable Polyurethane Fiber Strain Sensors with Embedded Silver Nanowires. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 23649–23658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilsson, E.; Rigdahl, M.; Hagström, B. Electrically conductive polymeric bi-component fibers containing a high load of low-structured carbon black. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2015, 132, 42255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Wang, Y.; Xu, J.; Miao, D.; Shang, S.; Peng, L.; Guo, R. Fabrication and characterization of copper coated polyamide-6 fibers with magnetron sputtering technology. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2017, 28, 18936–18943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Zhao, J.; Li, S.; Zhang, X.; Yong, Z.; Li, Q. Continuous electrodeposition for lightweight, highly conducting and strong carbon nanotube-copper composite fibers. Nanoscale 2011, 3, 4215–4219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soldán, J.; Musil, J. Structure and mechanical properties of DC magnetron sputtered TiC/Cu films. Vacuum 2006, 81, 531–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellison, M.S.; Zeronian, S.H.; Alger, K.W.; Aboul-Fadl, S.M.; Soler, T.M. Interrelationships between selected mechanical properties of individually-tested polymeric fibers. Polym. Eng. Sci. 1989, 29, 1738–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.; Chen, S.; Chen, Y.; Wang, B.; Pei, Q.; Wang, H. Macrofibers with High Mechanical Performance Based on Aligned Bacterial Cellulose Nanofibers. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 20330–20339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walther, A.; Timonen JV, I.; Díez, I.; Laukkanen, A.; Ikkala, O. Multifunctional high-performance biofibers based on wet-extrusion of renewable native cellulose nanofibrils. Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, 2924–2928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Z.; Sun, H.; Zhao, X.; Gao, C. Ultrastrong fibers assembled from giant graphene oxide sheets. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 188–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morkavuk, S.; Köklü, U.; Bağcı, M.; Gemi, L. Cryogenic machining of carbon fiber reinforced plastic (CFRP) composites and the effects of cryogenic treatment on tensile properties: A comparative study. Compos. Part B 2018, 147, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tae, H.L.; So, H.L.; Sang, Y.Y. Highly conductive polymer/metal/carbon nanotube composite fiber prepared by the melt-spinning process. Text. Res. J. 2017, 87, 593–606. [Google Scholar]
- Keisuke, T.; Takahisa, N.; Tatsuya, S.; Yamamoto, H. Changes in the cellulose crystallinity of moso bamboo cell walls during the growth process by X-ray diffraction techniques. J. Wood Sci. 2015, 61, 517–524. [Google Scholar]
- Alfred, D.F. Idealized powder diffraction patterns for cellulose polymorphs. Cellulose 2014, 21, 885–896. [Google Scholar]
- Boo, J.H.; Jung, M.J.; Park, H.K.; Nam, K.H.; Han, J.G. High-rate deposition of copper thin films using newly designed high-power magnetron sputtering source. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2004, 188, 721–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niraj, J.; Debnath, A.K.; Aswal, D.K.; Muthe, K.; Kumar, M.S.; Gupta, S.; Yakhmi, J. Morphology and resistivity of Al thin films grown on Si (111) by molecular beam epitaxy. Vacuum 2005, 79, 178–185. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, G.; Wang, L.; Liu, J.; Wu, J. FTIR and XPS analysis of the changes in bamboo chemical structure decayed by white-rot and brown-rot fungi. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2013, 280, 799–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zang, L.; Shen, F.; Wang, J.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, L. Preparation of Cu modified g-C3N4 nanorod bundles for efficiently photocatalytic CO2 reduction. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 622, 336–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.K.; Yin, M.; O’Brien, S.; Koberstein, J.T. Quantitative analysis of copper oxide nanoparticle composition and structure by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. Chem. Mater. A Publ. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 18, 6054–6058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huijing, W.; Jun, Z.; Pu, W.; Yin, L.; Tian, Y.; Li, J. Bifunctional copper modified graphitic carbon nitride catalysts for efficient tetracycline removal:Synergy of adsorption and photocatalytic degradation. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2020, 31, 2789–2794. [Google Scholar]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, W.; Li, J.; Shi, J.; Jiao, Y.; Wang, X.; Xia, C. Structure and Physical Properties of Conductive Bamboo Fiber Bundle Fabricated by Magnetron Sputtering. Materials 2023, 16, 3154. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16083154
Wang W, Li J, Shi J, Jiao Y, Wang X, Xia C. Structure and Physical Properties of Conductive Bamboo Fiber Bundle Fabricated by Magnetron Sputtering. Materials. 2023; 16(8):3154. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16083154
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Wenqing, Jiayao Li, Jiangtao Shi, Yue Jiao, Xinzhou Wang, and Changlei Xia. 2023. "Structure and Physical Properties of Conductive Bamboo Fiber Bundle Fabricated by Magnetron Sputtering" Materials 16, no. 8: 3154. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16083154
APA StyleWang, W., Li, J., Shi, J., Jiao, Y., Wang, X., & Xia, C. (2023). Structure and Physical Properties of Conductive Bamboo Fiber Bundle Fabricated by Magnetron Sputtering. Materials, 16(8), 3154. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16083154









