The Formation and Phase Stability of A-Site High-Entropy Perovskite Oxides
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Procedure
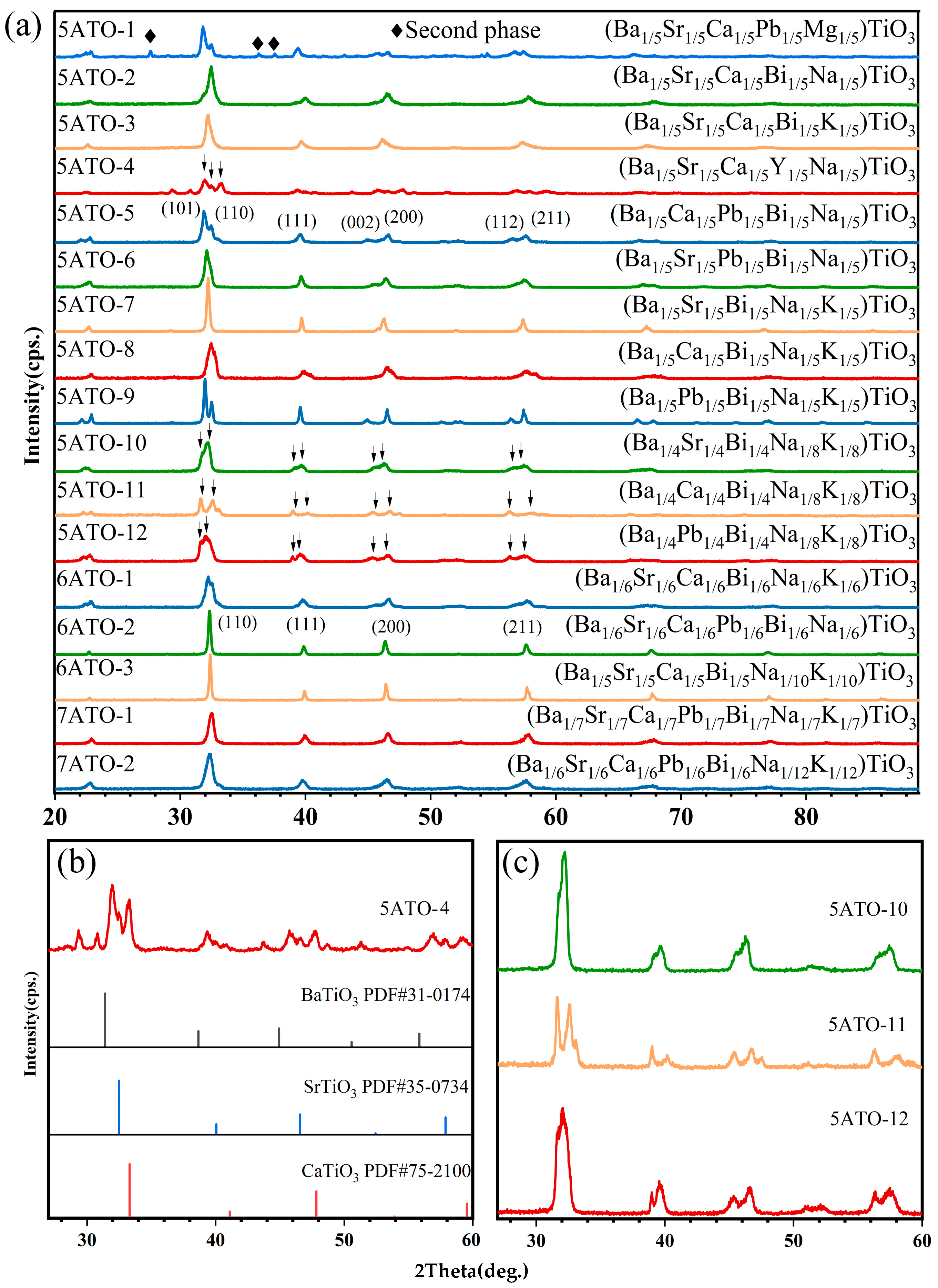
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yeh, J.W.; Chen, S.K.; Lin, S.J. Nanostructured high-entropy alloys with multiple principal elements: Novel alloy design concepts and outcomes. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2004, 6, 299–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantor, B.; Chang, I.; Knight, P.; Vincent, A. Microstructural development in equiatomic multicomponent alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A. 2004, 375, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavel, A.L.; Alexander, D.F.; Samat, K.M.; Olga, S.M. Manufacturing of metal-diamond composites with high-strength CoCrCuxFeNi high-entropy alloy used as a binder. Materials 2023, 16, 1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rost, C.M.; Sachet, E.; Borman, T.; Moballegh, A.; Dickey, E.C.; Hou, D. Entropy-stabilized oxides. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 8485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, Y.; Zhao, X.; An, Y. High-entropy (La0.2Nd0.2Sm0.2Eu0.2Gd0.2)2Ce2O7: A potential thermal barrier material with improved thermo-physical properties. J. Adv. Ceram. 2022, 11, 615–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.H.; Li, J.S.; Yang, S.Z. Microstructures and dielectric properties of novel (La0.2Pr0.2Nd0.2Sm0.2Eu0.2)2Ce2O7 high entropy ceramics. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2021, 32, 27860–27870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrew, J.; Wright, A.; Wang, Q.Y. From high-entropy ceramics to compositionally-complex ceramics: A case study of fluorite oxides. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2020, 40, 2120–2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spiridigliozzi, L.; Ferone, C.; Cioffi, R. A simple and effective predictor to design novel fluorite-structured high entropy oxides (HEOs). Acta Mater. 2021, 202, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Wei, M.; Xu, J. Influence of order-disorder transition on the mechanical and thermophysical properties of A2B2O7 high-entropy ceramics. J. Adv. Ceram. 2022, 11, 1222–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Qi, J.; Zhang, M. Pyrochlore-based high-entropy ceramics for capacitive energy storage. J. Adv. Ceram. 2022, 11, 1179–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, H.; Li, C.; Chen, G. Design and synthesis of high-entropy pyrochlore ceramics based on valence combination. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2022, 42, 5973–5983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, A.J.; Wang, Q.; Ko, S.T. Size disorder as a descriptor for predicting reduced thermal conductivity in medium- and high-entropy pyrochlore oxides. Scr. Mater. 2020, 181, 76–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Xu, X.; Bi, L. A high-entropy spinel ceramic oxide as the cathode for proton-conducting solid oxide fuel cells. Adv. Ceram. 2022, 11, 794–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Zhao, B.; Xiang, H. High-entropy spinel ferrites MFe2O4 (M = Mg, Mn, Fe, Co, Ni, Cu, Zn) with tunable electromagnetic properties and strong microwave absorption. J. Adv. Ceram. 2022, 11, 754–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.Y.; Huang, C.W.; Wu, M.C. Atomic-scale investigation of lithiation/delithiation mechanism in high-entropy spinel oxide with superior electrochemical performance. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 420, 129838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, C.Q.; Tian, K.; Li, X. New spinel high-entropy oxides (FeCoNiCrMnXLi)3O4 (X = Cu, Mg, Zn) as the anode material for lithium-ion batteries. Ceram. Int. 2021, 47, 32025–32032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Zou, M.; Zhang, W. Electrical and thermal transport behaviours of high-entropy perovskite thermoelectric oxides. J. Adv. Ceram. 2021, 10, 377–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.Y.; Pu, Y.P.; Zhao, X.Y. Dielectric temperature stability and energy storage performance of NBT-based ceramics by introducing high-entropy oxide. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2022, 105, 4796–4804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Xu, S.; Li, T. Microstructure and ferroelectric properties of high-entropy perovskite oxides with A-site disorder. Ceram. Int. 2021, 47, 33039–33046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, G. High-entropy La(Fe0.2Co0.2Ni0.2Cr0.2Mn0.2)O3 ceramic exhibiting high emissivity and low thermal conductivity. Int. J. Appl. Ceram. Technol. 2022, 19, 2963–2966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eiselt, L.; Kruk, R.; Hahn, H. Hole-doped high entropy ferrites: Structure and charge compensation mechanisms in (Gd0.2La0.2Nd0.2Sm0.2Y0.2)1−xCaxFeO3. Int. J. Appl. Ceram. Technol. 2023, 20, 213–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.; Cao, Z.; Jiang, Z. High entropy oxide nanofiber by electrospun method and its application for lithium battery anode material. Int. J. Appl. Ceram. Technol. 2022, 19, 2004–2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Wu, Y. High-entropy transparent ceramics: Review of potential candidates and recently studied cases. Int. J. Appl. Ceram. Technol. 2022, 19, 644–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, T.Y.; Han, Z.; Huang, Y.Q. Piezoelectric calcium/manganese-doped barium titanate nanofibers with improved osteogenic activity. Ceram. Int. 2021, 47, 28778–28789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahesh, M.; Bhanuprasad, V.V.; James, A.R. Enhanced piezoelectric properties and tunability of lead-free ceramics prepared by high-energy ball milling. J. Electron. Mater. 2013, 42, 3547–3551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Han, F.; Liu, M. High-temperature dielectric and relaxation behavior of tantalum-doped sodium bismuth titanate-barium titanate ceramics. J. Electron. Mater. 2020, 49, 6643–6655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Li, P.; Zhang, X. Effect of configurational entropy on dielectric properties of high-entropy perovskite oxides (Ce0.5,K0.5)x[(Bi0.5,Na0.5)0.25Ba0.25Sr0.25Ca0.25]1-xTiO3. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2022, 33, 20721–20730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Li, J.; Zhou, C. Research on the dielectric energy storage characteristics of the [(Bi0.5Na0.5)0.2Ba0.2Sr0.2Ca0.2Mg0.2]TiO3 equal ratio high-entropy ceramics. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2022, 33, 23792–23805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Shrivastava, V.; Thakur, O.P. Cumulative effect of yttrium and tin co-doping on the structural and ferroelectric properties of sol-gel derived barium titanate. J. Sol-Gel. Sci. Technol. 2023, 105, 304–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chawla, A.; Verma, S.; Godara, S. Understanding phase segregation using rietveld analysis and the dielectric, ferroelectric properties of Ba(1-x)CaxTiO3 solid solutions. J. Electron. Mater. 2020, 49, 4111–4122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, Y.; Pu, Y.; Zhang, Q. Effect of configuration entropy on dielectric relaxor, ferroelectric properties of high-entropy (NaBiBa)x(SrCa)(1-3x)/2TiO3 ceramics. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2022, 33, 5359–5369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Pu, Y.; Zhang, Q. Microstructure and dielectric properties of high entropy Ba(Zr0.2Ti0.2Sn0.2Hf0.2Me0.2)O3 perovskite oxides. Ceram. Int. 2020, 46, 7430–7437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Q.; Yan, J.; Zhang, X. Phase evolution and dielectric properties of Ba(Ti1/6Sn1/6Zr1/6Hf1/6Nb1/6Ga1/6)O3 high-entropy perovskite ceramics. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2020, 31, 7760–7765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Hu, T.; Gild, J. A new class of high-entropy perovskite oxides. Scr. Mater. 2018, 142, 116–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Li, Z.M.; Chen, K.P. High-entropy oxides based on valence combinations: Design and practice. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2020, 104, 1953–1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Chen, K.P.; Li, C. High-entropy stoichiometric perovskite oxides based on valence combinations. Ceram. Int. 2021, 47, 24348–24352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, A.; Djenadic, R.; Wang, D. Rare earth and transition metal based entropy stabilised perovskite type oxides. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2017, 38, 2318–2327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramadass, N. ABO3-type oxides-their structure and properties-a bird’s eye view. Mater. Sci. Eng. 1978, 36, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.J.; Qiu, W.F.; Yang, Y. Atomic-size and lattice-distortion effects in newly developed high-entropy alloys with multiple principal elements. Intermetallics 2015, 64, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eshelby, J.D. The continuum theory of lattice defects. Solid State Phys. 1956, 3, 79–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhou, Y.J.; Lin, J.P. Solid-solution phase formation rules for multi-component alloys. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2008, 10, 534–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miracle, D.B.; Senkov, O.N. A critical review of high entropy alloys and related concepts. Acta. Mater. 2017, 122, 448–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, Z.; Tan, Y.; Zeng, S. Preparation and phase evolution of high-entropy oxides A2B2O7 with multiple elements at A and B sites. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2021, 41, 3614–3620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, A.; Breitung, B.; Hahn, H. High entropy oxides: The role of entropy, enthalpy and synergy. Scr. Mater. 2020, 187, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akrami, S.; Edalati, P.; Fuji, M. High-entropy ceramics: Review of principles, production and applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. R Rep. 2021, 146, 100644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Ren, K.; Ma, C. Dielectric and energy storage properties of flash-sintered high-entropy (Bi0.2Na0.2K0.2Ba0.2Ca0.2)TiO3 ceramic. Ceram. Int. 2020, 46, 20576–20581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, Y.P.; Zhang, Q.W.; Li, R. Dielectric properties and electrocaloric effect of high-entropy (Na0.2Bi0.2Ba0.2Sr0.2Ca0.2)TiO3 ceramic. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2019, 115, 223901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bragg, W. The reflection of X-rays by crystals. Nature 1913, 91, 477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krad, I.; Bidault, O.; Geoffroy, N. Preparation and characterization of K0.5Bi0.5TiO3 particles synthesized by a stirring hydrothermal method. Ceram. Int. 2016, 42, 3751–3756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Ma, J.X.; Chen, K.P. Design and investigate the electrical properties of Pb(Mg0.2Zn0.2Nb0.2Ta0.2W0.2)O3-PbTiO3 high-entropy ferroelectric ceramics-sciencedirect. Ceram. Int. 2022, 48, 12848–12855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldschmidt, V.M. Die gesetze der krystallochemie. Naturwissenschaften 1926, 14, 477–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nong, Z.S.; Zhu, J.C.; Cao, Y. Stability and structure prediction of cubic phase in as cast high entropy alloys. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2014, 30, 363–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| No. | Composition | Phase | t | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5ATO-1 | (Ba1/5Sr1/5Ca1/5Pb1/5Mg1/5)TiO3 | F | 1.609R | 1.376 | 0.98 | 18.30 | - |
| 5ATO-2 | (Ba1/5Sr1/5Ca1/5Bi1/5Na1/5)TiO3 | C | 1.432 | 1.00 | 6.60 | 0.37 | |
| 5ATO-3 | (Ba1/5Sr1/5Ca1/5Bi1/5K1/5)TiO3 | C | 1.482 | 1.02 | 8.19 | 0.39 | |
| 5ATO-4 | (Ba1/5Sr1/5Ca1/5Y1/5Na1/5)TiO3 | F | 1.372 | 0.98 | 12.67 | - | |
| 5ATO-5 | (Ba1/5Ca1/5Pb1/5Bi1/5Na1/5)TiO3 | T | 1.442 | 0.99 | 6.76 | 0.43 | |
| 5ATO-6 | (Ba1/5Sr1/5Pb1/5Bi1/5Na1/5)TiO3 | T | 1.462 | 1.00 | 5.73 | 0.44 | |
| 5ATO-7 | (Ba1/5Sr1/5Bi1/5Na1/5K1/5)TiO3 | T | 1.492 | 1.02 | 7.43 | 0.40 | |
| 5ATO-8 | (Ba1/5Ca1/5Bi1/5Na1/5K1/5)TiO3 | T | 1.472 | 1.00 | 8.59 | 0.40 | |
| 5ATO-9 | (Ba1/5Pb1/5Bi1/5Na1/5K1/5)TiO3 | T | 1.502 | 1.01 | 7.19 | 0.46 | |
| 5ATO-10 | (Ba1/4Sr1/4Bi1/4Na1/8K1/8)TiO3 | F | 1.560R | 1.486 | 1.00 | 7.15 | - |
| 5ATO-11 | (Ba1/4Ca1/4Bi1/4Na1/8K1/8)TiO3 | F | 1.461 | 1.01 | 8.52 | - | |
| 5ATO-12 | (Ba1/4Pb1/4Bi1/4Na1/8K1/8)TiO3 | F | 1.499 | 1.03 | 6.87 | - | |
| 6ATO-1 | (Ba1/6Sr1/6Ca1/6Pb1/6Bi1/6Na1/6)TiO3 | T | 1.790R | 1.442 | 0.99 | 6.17 | 0.44 |
| 6ATO-2 | (Ba1/6Sr1/6Ca1/6Bi1/6Na1/6K1/6)TiO3 | C | 1.467 | 1.00 | 7.91 | 0.36 | |
| 6ATO-3 | (Ba1/5Sr1/5Ca1/5Bi1/5Na1/10K1/10)TiO3 | C | 1.748R | 1.457 | 0.99 | 7.66 | 0.38 |
| 7ATO-1 | (Ba1/7Sr1/7Ca1/7Pb1/7Bi1/7Na1/7K1/7)TiO3 | C | 1.946R | 1.470 | 1.00 | 7.33 | 0.45 |
| 7ATO-2 | (Ba1/6Sr1/6Ca1/6Pb1/6Bi1/6Na1/12K1/12)TiO3 | C | 1.907R | 1.463 | 0.98 | 7.02 | 0.44 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, J.; Liu, S.; Tian, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, Z. The Formation and Phase Stability of A-Site High-Entropy Perovskite Oxides. Materials 2023, 16, 2214. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16062214
Zhang J, Liu S, Tian Z, Zhang Y, Shi Z. The Formation and Phase Stability of A-Site High-Entropy Perovskite Oxides. Materials. 2023; 16(6):2214. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16062214
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Junzhan, Shangyi Liu, Zhifeng Tian, Ying Zhang, and Zongmo Shi. 2023. "The Formation and Phase Stability of A-Site High-Entropy Perovskite Oxides" Materials 16, no. 6: 2214. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16062214
APA StyleZhang, J., Liu, S., Tian, Z., Zhang, Y., & Shi, Z. (2023). The Formation and Phase Stability of A-Site High-Entropy Perovskite Oxides. Materials, 16(6), 2214. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16062214





