Protection of Patinated Bronze with Long-Chain Phosphonic Acid/Organic Coating Combined System
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Sample Preparation
2.3. Electrochemical Measurements
2.4. Surface Analysis
2.5. Exposure in a Corrosion Chamber
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Evaluation of Patinated Bronze Protection by PA
3.2. Evaluation of Patinated Bronze Protection by PA/Paraloid System
3.3. Surface Studies
3.4. Exposure in a Corrosion Chamber
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bartuli, C.; Cigna, R.; Fumei, O. Prediction of durability for outdoor exposed bronzes: Estimation of the corrosivity of the atmospheric environment of the Capitoline Hill in Rome. Stud. Conserv. 1999, 44, 245–252. [Google Scholar]
- Strandberg, H. Reactions of copper patina compounds-I. Influence of some air pollutants. Atmos. Environ. 1998, 32, 3511–3520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosec, T.; Legat, A.; Milošev, I. The comparison of organic protective layers on bronze and copper. Prog. Org. Coat. 2010, 69, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiavari, C.; Colledan, A.; Frignani, A.; Brunoro, G. Corrosion evaluation of traditional and new bronzes for artistic castings. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2006, 95, 252–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardi, E.; Chiavari, C.; Lenza, B.; Martini, C.; Morselli, L.; Ospitali, F.; Robbiola, L. The atmospheric corrosion of quaternary bronzes: The leaching action of acid rain. Corros. Sci. 2009, 51, 59–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardi, E.; Chiavari, C.; Martini, C.; Morselli, L. The atmospheric corrosion of quaternary bronzes: An evaluation of the dissolution rate of the alloying elements. Appl. Phys. A Mater. Sci. Process. 2008, 92, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiavari, C.; Bernardi, E.; Martini, C.; Passarini, F.; Ospitali, F.; Robbiola, L. The atmospheric corrosion of quaternary bronzes: The action of stagnant rain water. Corros. Sci. 2010, 52, 3002–3010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masi, G.; Esvan, J.; Josse, C.; Chiavari, C.; Bernardi, E.; Martini, C.; Bignozzi, M.C.; Gartner, N.; Kosec, T.; Robbiola, L. Characterisation of typical patinas simulating bronze corrosion in outdoor condition. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2017, 200, 308–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Di Turo, F.; Proietti, C.; Screpanti, A.; Fornasier, M.F.; Cionni, I.; Favero, G.; De Marco, A. Impacts of air pollution on cultural heritage corrosion at European level: What has been achieved and what are the future scenarios. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 218, 586–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikić, D.; Ćurković, H.O.; Kosec, T.; Peko, N. An electrochemical and spectroscopic study of surfaces on bronze sculptures exposed to urban environment. Materials 2021, 14, 2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandberg, J.; Odnevall Wallinder, I.; Leygraf, C.; Le Bozec, N. Corrosion-induced copper runoff from naturally and pre-patinated copper in a marine environment. Corros. Sci. 2006, 48, 4316–4338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández, R.D.P.B.; Aoki, I.V.; Tribollet, B.; De Melo, H.G. Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy investigation of the electrochemical behaviour of copper coated with artificial patina layers and submitted to wet and dry cycles. Electrochim. Acta 2011, 56, 2801–2814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letardi, P. Testing new coatings for outdoor bronze monuments: A methodological overview. Coatings 2021, 11, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krätschmer, A.; Odnevall Wallinder, I.; Leygraf, C. The evolution of outdoor copper patina. Corros. Sci. 2002, 44, 425–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robbiola, L.; Rahmouni, K.; Chiavari, C.; Martini, C.; Prandstraller, D.; Texier, A.; Takenouti, H.; Vermaut, P. New insight into the nature and properties of pale green surfaces of outdoor bronze monuments. Appl. Phys. A Mater. Sci. Process. 2008, 92, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiavari, C.; Bernardi, E.; Martini, C.; Morselli, L.; Ospitali, F.; Robbiola, L.; Textier, A. Predicting the corrosion behaviour of outdoor bronzes: Assessment of artificially exposed and real outdoor. In Proceedings of the Interim Meeting of the ICOM-CC Metal Working Group, Metal 2010, Charleston, SC, USA, 11–15 October 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Masi, G.; Aufray, M.; Balbo, A.; Bernardi, E.; Bignozzi, M.C.; Chiavari, C.; Esvan, J.; Gartner, N.; Grassi, V.; Josse, C.; et al. B-IMPACT project: Eco-friendly and non-hazardous coatings for the protection of outdoor bronzes. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 949, 012097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cano, E.; Lafuente, D. Corrosion inhibitors for the preservation of metallic heritage artefacts. In Corrosion and Conservation of Cultural Heritage Metallic Artefacts; Dillmann, P., Watkinson, D., Angelini, E., Adriaens, A., Eds.; Wood-head Publishing Limited: Cambridge, UK, 2013; pp. 570–590. [Google Scholar]
- Moffett, D.L. Wax Coatings on Ethnographic Metal Objects: Justifications for Allowing a Tradition to Wane. Source J. Am. Inst. Conserv. 1996, 35, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watkinson, D. Preservation of metallic cultural heritage. In Shreir’s Corrosion; Cottis, B., Graham, M., Lindsay, R., Lyon, S., Richardson, T., Scantlebury, D., Stott, H., Eds.; Elsevier Science: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2010; pp. 3307–3340. [Google Scholar]
- Ehrhardt, D.; Hopwood, W.; Padfield, T. The Durability of Incralac: Examination of a Ten Year Old Treatment. In Proceedings of the ICOM Conservation Committee, 7th Triennial Meeting, Copenhagen, Denmark, 10–14 September 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Wolfe, J.; Grayburn, R. A review of the development and testing of Incralac lacquer. J. Am. Inst. Conserv. 2017, 56, 225–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNamara, C.J.; Breuker, M.; Helms, M.; Perry, T.D.; Mitchell, R. Biodeterioration of Incralac used for the protection of bronze monuments. J. Cult. Herit. 2004, 5, 361–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C. Biodeterioration of Acrylic Polymers Paraloid B-72 and B-44: Report on Field Trials. AAS 2012, 15, 283–290. [Google Scholar]
- Argyropoulos, V.; Boyatzis, S.; Giannoulaki, M. The role of standards in conservation methods for metals in cultural heritage. In Corrosion and Conservation of Cultural Heritage Metallic Artefacts; Dillmann, P., Watkinson, D., Angelini, E., Adriaens, A., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing Limited: Cambridge, UK, 2013; pp. 478–512. [Google Scholar]
- Rocca, E.; Mirambet, F. Corrosion inhibitors for metallic artefacts: Temporary protection. In Corrosion of Metallic Heritage Artefacts; Woodhead Publishing Limited: Cambridge, UK, 2007; pp. 308–350. [Google Scholar]
- Otmačić Ćurković, H.; Kosec, T.; Marušić, K.; Legat, A. An electrochemical impedance study of the corrosion protection of artificially formed patinas on recent bronze. Electrochim. Acta 2012, 83, 28–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cano, E.; Lafuente, D.; Bastidas, D.M. Use of EIS for the evaluation of the protective properties of coatings for metallic cultural heritage: A review. J. Solid State Electrochem. 2010, 14, 381–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marušić, K.; Otmačić Ćurković, H.; Horvat-Kurbegović, Š.; Takenouti, H.; Stupnišek-Lisac, E. Comparative studies of chemical and electrochemical preparation of artificial bronze patinas and their protection by corrosion inhibitor. Electrochim. Acta 2009, 54, 7106–7113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muresan, L.; Varvara, S.; Stupnišek-Lisac, E.; Otmačić, H.; Marušić, K.; Horvat-Kurbegović, S.; Robbiola, L.; Rahmouni, K.; Takenouti, H. Protection of bronze covered with patina by innoxious organic substances. Electrochim. Acta 2007, 52, 7770–7779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valek, L.; Martinez, S. Copper corrosion inhibition by Azadirachta indica leaves extract in 0.5 M sulphuric acid. Mater. Lett. 2007, 61, 148–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albini, M.; Letardi, P.; Mathys, L.; Brambilla, L.; Schröter, J.; Junier, P.; Joseph, E. Comparison of a bio-based corrosion inhibitor versus benzotriazole on corroded copper surfaces. Corros. Sci. 2018, 143, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popoola, L.T. Organic green corrosion inhibitors (OGCIs): A critical review. Corros. Rev. 2019, 37, 71–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varvara, S.; Caniglia, G.; Izquierdo, J.; Bostan, R.; Găină, L.; Bobis, O.; Souto, R.M. Multiscale electrochemical analysis of the corrosion control of bronze in simulated acid rain by horse-chestnut (Aesculus hippocastanum L.) extract as green inhibitor. Corros. Sci. 2020, 165, 108381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varvara, S.; Bostan, R.; Bobis, O.; Găină, L.; Popa, F.; Mena, V.; Souto, R.M. Propolis as a green corrosion inhibitor for bronze in weakly acidic solution. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 426, 1100–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Favre-Quattropani, L.; Groening, P.; Ramseyer, D.; Schlapbach, L. The protection of metallic archaeological objects using plasma polymer coatings. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2000, 125, 377–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artesani, A.; Di Turo, F.; Zucchelli, M.; Traviglia, A. Recent advances in protective coatings for cultural heritage—An overview. Coatings 2020, 10, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kosec, T.; Novak, Ž.; Fabjan, E.Š.; Škrlep, L.; Sever Škapin, A.; Ropret, P. Corrosion protection of brown and green patinated bronze. Prog. Org. Coat. 2021, 161, 106510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosec, T.; Novak, Ž.; Fabjan, E.Š.; Škrlep, L.; Finšgar, M. Exploring the protection mechanism of a combined fluoropolymer coating on sulphide patinated bronze. Prog. Org. Coat. 2022, 172, 107071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosec, T.; Škrlep, L.; Švara Fabjan, E.; Sever Škapin, A.; Masi, G.; Bernardi, E.; Chiavari, C.; Josse, C.; Esvan, J.; Robbiola, L. Development of multi-component fluoropolymer based coating on simulated outdoor patina on quaternary bronze. Prog. Org. Coat. 2019, 131, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faraldi, F.; Cortese, B.; Caschera, D.; Di Carlo, G.; Riccucci, C.; de Caro, T.; Ingo, G.M. Smart conservation methodology for the preservation of copper-based objects against the hazardous corrosion. Thin Solid Film. 2017, 622, 130–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argyropoulos, V.; Giannoulaki, M.; Michalakakos, G.P.; Siatou, A. A survey of the types of corrosion inhibitors and protective coatings used for the conservation of metal objects from museum collections in the Mediterranean basin. In Strategies for Saving Our Cultural Heritage. Proceedings of the International Conference on Conservation Strategies for Saving Indoor Metallic Collections, TEI of Athens, Athens, Cairo, Egypt, 25 February–1 March 2007; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2007; pp. 166–170. [Google Scholar]
- Ntelia, E.; Karapanagiotis, I. Superhydrophobic Paraloid B72. Prog. Org. Coat. 2020, 139, 105224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cano, E.; Bastidas, D.M.; Argyropoulos, V.; Fajardo, S.; Siatou, A.; Bastidas, J.M.; Degrigny, C. Electrochemical characterization of organic coatings for protection of historic steel artefacts. J. Solid State Electrochem. 2010, 14, 453–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kosec, T.; Otmačić Ćurković, H.; Legat, A. Electrochimica Acta Investigation of the corrosion protection of chemically and electrochemically formed patinas on recent bronze. Electrochim. Acta 2010, 56, 722–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikić, D.; Otmačić Ćurković, H.; Hosseinpour, S. Bronze corrosion protection by long-chain phosphonic acids. Corros. Sci. 2022, 205, 110445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristan Mioč, E.; Hajdari Gretić, Z.; Otmačić Ćurković, H. Modification of cupronickel alloy surface with octadecylphosphonic acid self–assembled films for improved corrosion resistance. Corros. Sci 2018, 134, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashkenazi, D.; Nusbaum, I.; Shacham-Diamand, Y.; Cvikel, D.; Kahanov, Y.; Inberg, A. A method of conserving ancient iron artefacts retrieved from shipwrecks using a combination of silane self-assembled monolayers and wax coating. Corros. Sci. 2017, 123, 88–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiavari, C.; Balbo, A.; Bernardi, E.; Martini, C.; Bignozzi, M.C.; Abbottoni, M.; Monticelli, C. Protective silane treatment for patinated bronze exposed to simulated natural environments. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2013, 141, 502–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapitanović, A.; Otmačić Ćurković, H. The Effect of Corrosion Conditions on Aging of Artificial Patina on Three Bronzes. Coatings 2022, 12, 936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristan Mioč, E.; Otmačić Ćurković, H. Protective films of stearic and octadecylphosphonic acid formed by spray coating. J. Electrochem. Sci. Eng. 2020, 10, 161–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorhout, J.M.; Anderson, A.S.; Batista, E.; Carlson, R.K.; Currier, R.P.; Martinez, R.K.; Clegg, S.M.; Wilkerson, M.P.; Nowak-Lovato, K. NOx speciation from copper dissolution in nitric acid/water solutions using FTIR spectroscopy. J. Mol. Spectrosc. 2020, 372, 111334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Pauli, M.; Castro Prado, M.; Souza Matos, M.J.; Nogueira Fontes, G.; Perez, C.A.; Carvalho Mazzoni, M.S.; Almeida Neves, B.R.; Malachias, A. Thermal stability and ordering study of long- and short-alkyl chain phosphonic acid multilayers. Langmuir 2012, 28, 15124–15133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quiñones, R.; Raman, A.; Gawalt, E.S. Functionalization of nickel oxide using alkylphosphonic acid self-assembled monolayers. Thin Solid Film. 2008, 516, 8774–8781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, M.S.; Smiley, K.J.; Gawalt, E.S. Thermally Driven Stability of Octadecylphosphonic Acid Thin Films Grown on SS316L. Scanning 2010, 32, 304–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marušić, K.; Otmačić Ćurković, H.; Takenouti, H. Inhibiting effect of 4-methyl-1-p-tolylimidazole to the corrosion of bronze patinated in sulphate medium. Electrochim. Acta 2011, 56, 7491–7502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansfeld, F. Use of electrochemical impedance spectroscopy for the study of corrosion protection by polymer coatings. J. Appl. Electrochem. 1995, 25, 187–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
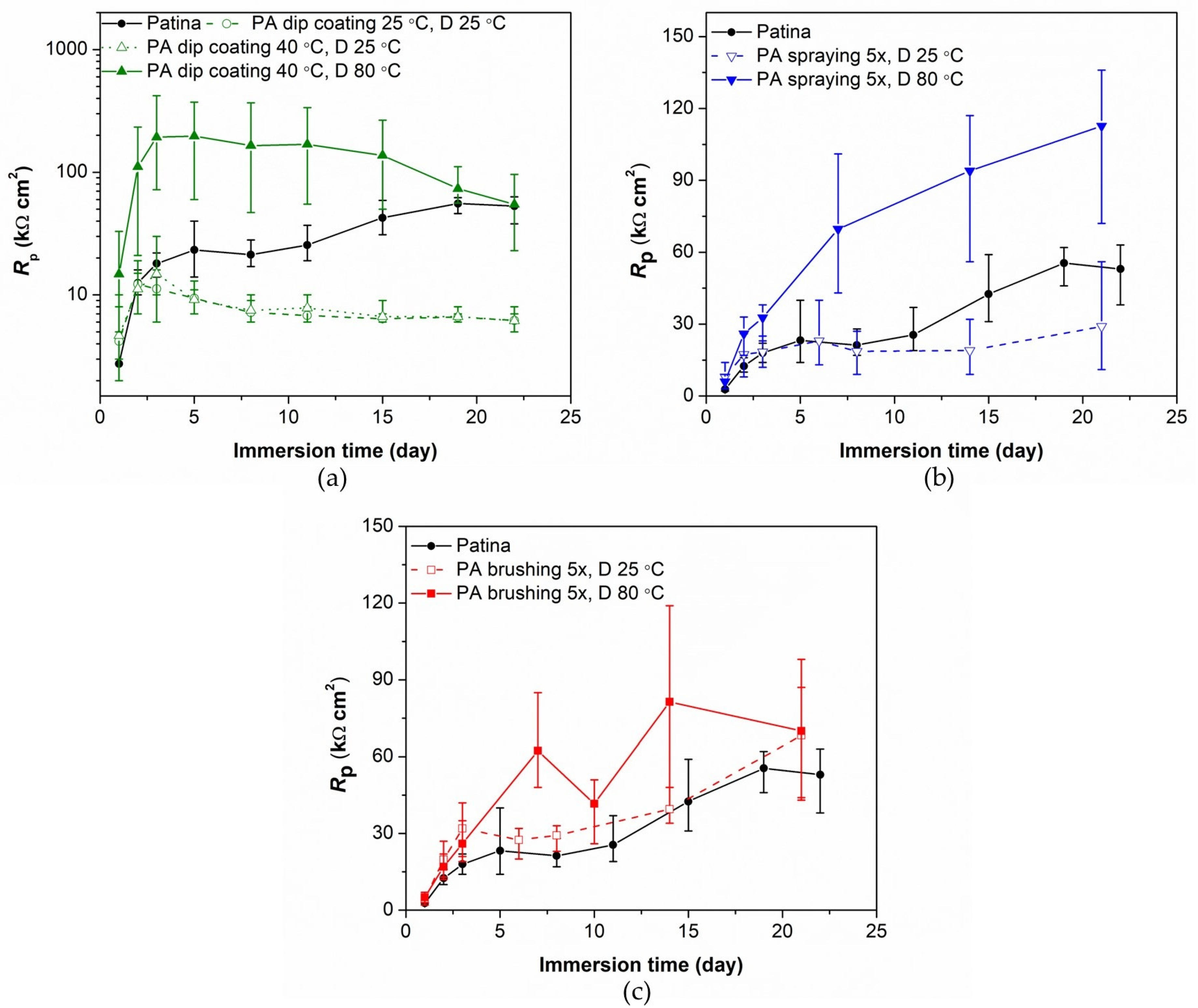
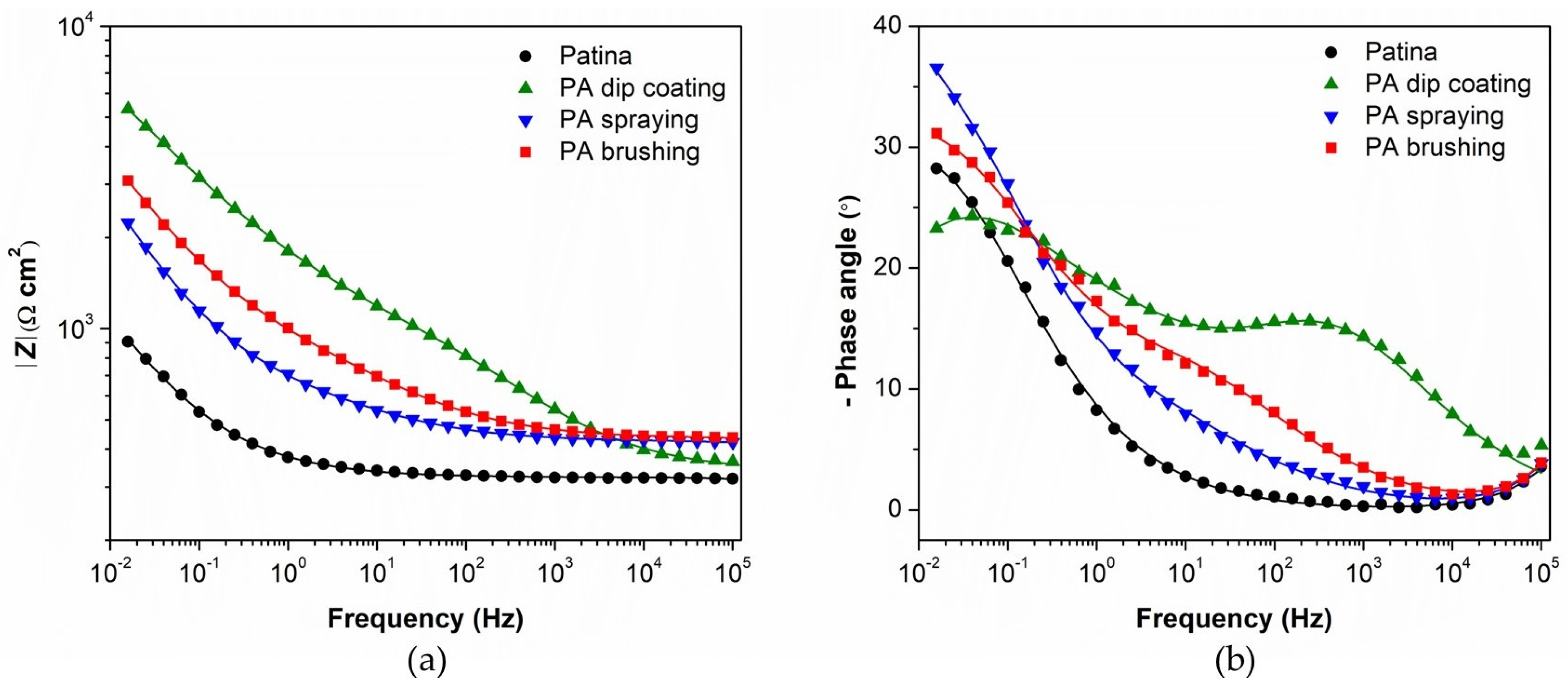


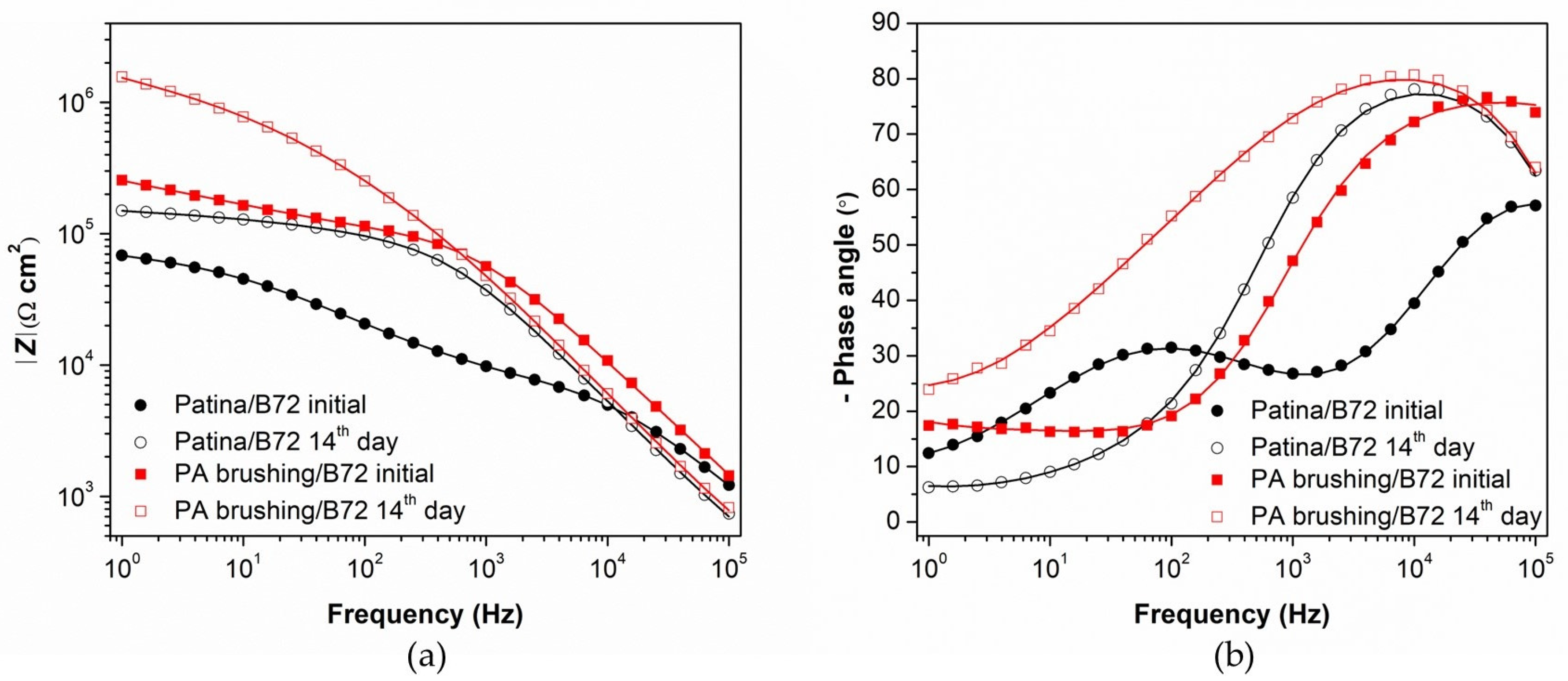

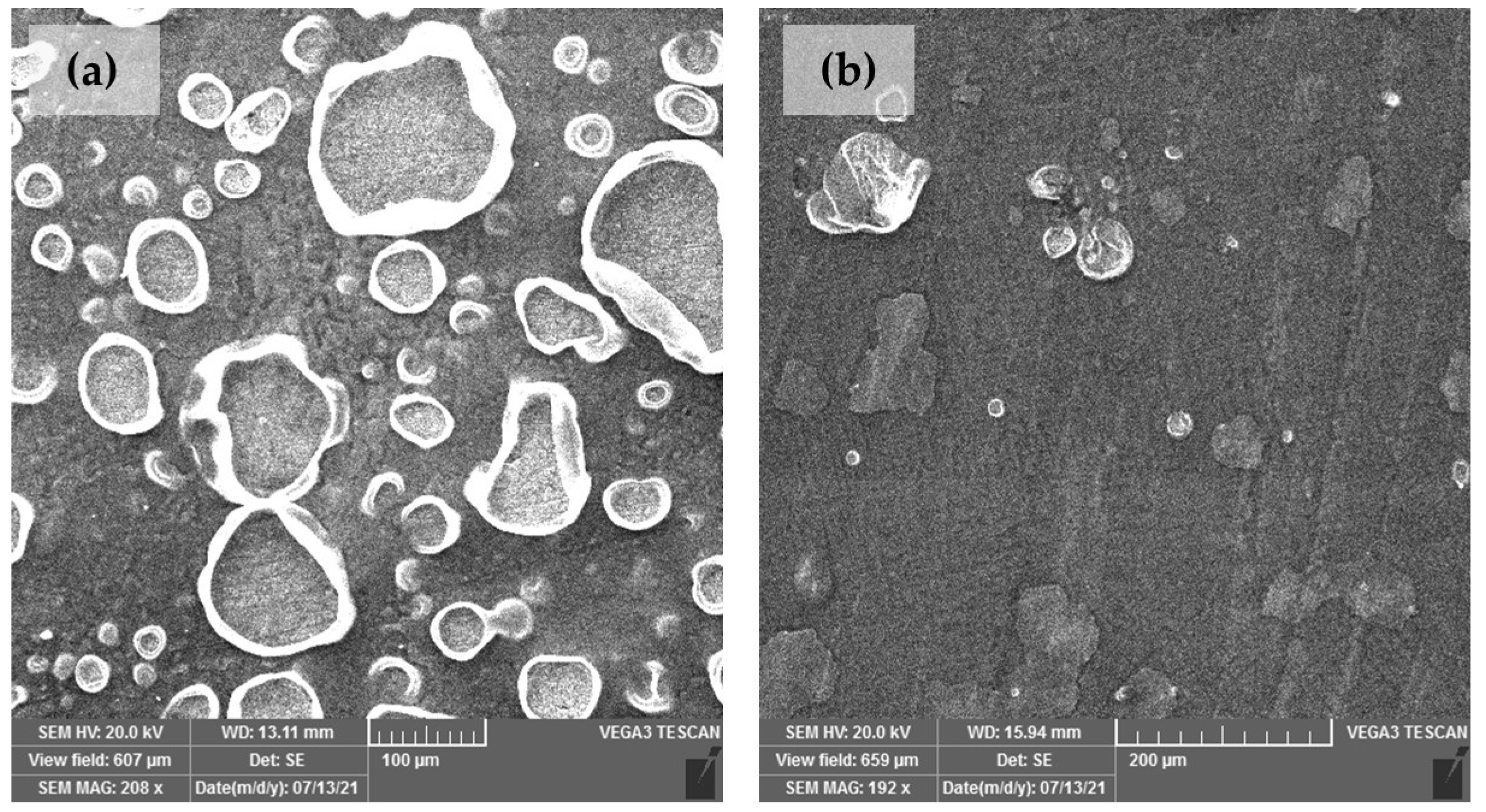
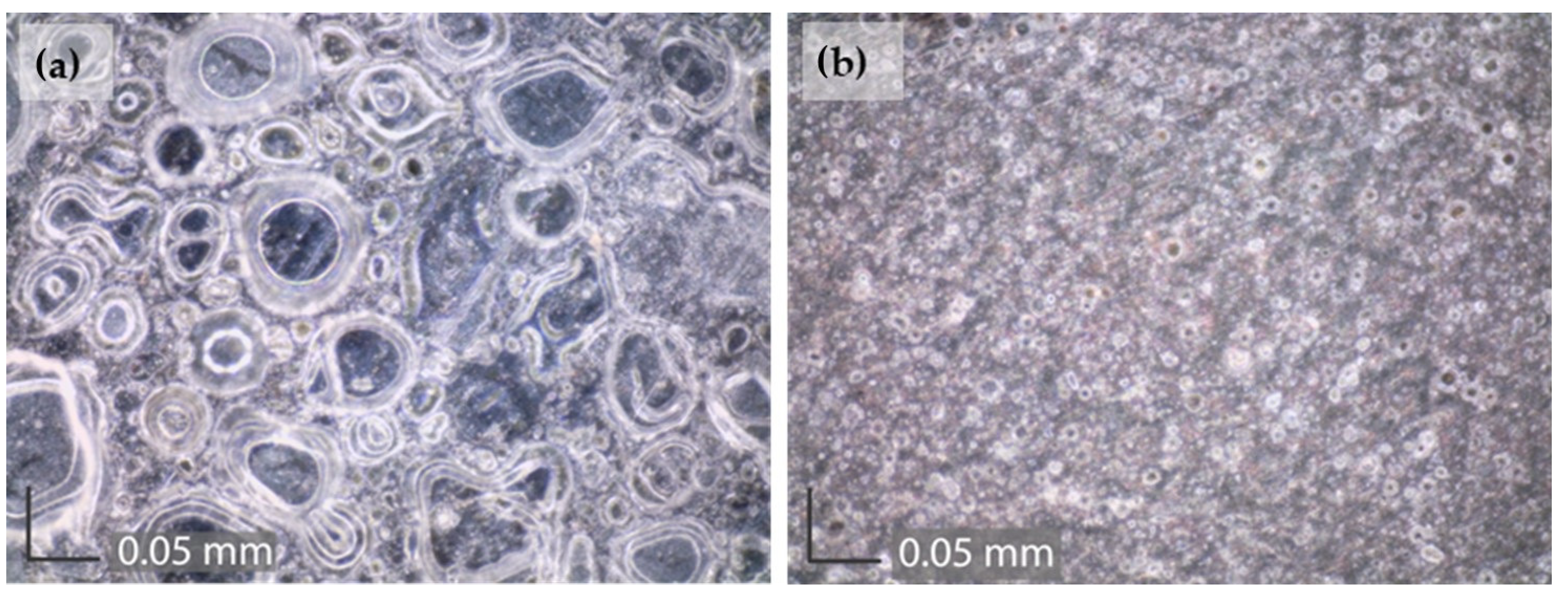
| Element | Cu | Sn | Pb | Ni | P | Zn | Rest |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wt. (%) | 87.94 | 11.02 | 0.54 | 0.29 | 0.10 | 0.07 | 0.04 |
| Method | Adsorption | Drying | Sample |
|---|---|---|---|
| Patina | |||
| Dip coating | 20 h at 25 °C | 20 h at 25 °C | PA dip coating 25 °C, D 25 °C |
| 20 h at 40 °C | 20 h at 25 °C | PA dip coating 40 °C, D 25 °C | |
| 20 h at 40 °C | 5 h at 80 °C | PA dip coating 40 °C, D 80 °C | |
| Spraying | 5× at room temp. * | 20 h at 25 °C | PA spraying 5×, D 25 °C |
| 5× at room temp. * | 5 h at 80 °C | PA spraying 5×, D 80 °C | |
| Brushing | 5× at room temp. * | 20 h at 25 °C | PA brushing 5×, D 25 °C |
| 5× at room temp. * | 5 h at 80 °C | PA brushing 5×, D 80 °C | |
| Patina/Paraloid B-72 | |||
| Dip coating | 20 h at 40 °C | 5 h at 80 °C | PA dip coating 40 °C, D 80 °C/B72 |
| Brushing | 1× at room temp. | 20 h at 25 °C | PA brushing 1×, D 25 °C/B72 |
| 1× at room temp. | 5 h at 80 °C | PA brushing 1×, D 80 °C/B72 | |
| 5× at room temp. * | 20 h at 25 °C | PA brushing 5×, D 25 °C/B72 | |
| 5× at room temp. * | 5 h at 80 °C | PA brushing 5×, D 80 °C/B72 | |
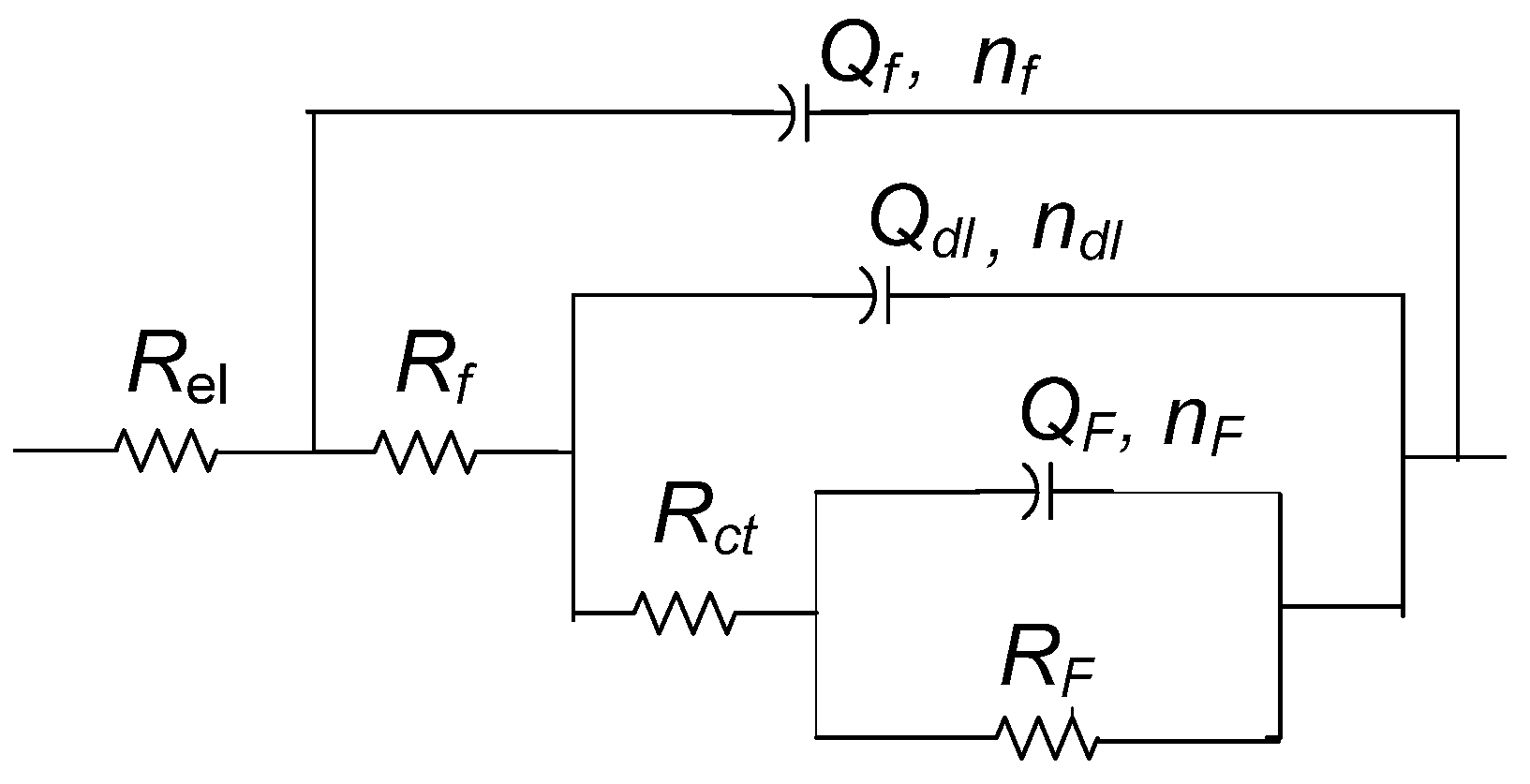
| Rf (kΩ cm2) | Qf (µS Sn cm−2) | nf | Rct (kΩ cm2) | Qdl (µS Sn cm−2) | ndl | RF (kΩ cm2) | QF (µS Sn cm−2) | nF | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Patina | |||||||||
| 1st day | 0.14 | 4097 | 0.50 | 4.69 | 776 | 0.84 | |||
| After 2 weeks | 2.94 | 1.01 | 0.76 | 5.25 | 4.30 | 0.71 | 38 | 98 | 0.57 |
| After 3 weeks | 2.55 | 0.87 | 0.77 | 8.72 | 7.77 | 0.60 | 56 | 80 | 0.68 |
| Patina/PA dip coating 40 °C, D 80 °C | |||||||||
| 1st day | 2.18 | 285 | 0.50 | 10 | 331 | 0.50 | |||
| After 2 weeks | 16 | 0.33 | 0.87 | 28 | 4.76 | 0.50 | 91 | 95 | 0.50 |
| After 3 weeks | 40 | 0.11 | 1 | 23 | 1.34 | 0.71 | 46 | 108 | 0.50 |
| Patina/PA spraying 5×, D 80 °C | |||||||||
| 1st day | 0.38 | 696 | 0.50 | 33 | 1143 | 0.54 | |||
| After 2 weeks | 6.46 | 1.78 | 0.69 | 7.80 | 3.51 | 0.75 | 110 | 51 | 0.61 |
| After 3 weeks | 6.09 | 1.68 | 0.70 | 15 | 6.60 | 0.59 | 93 | 45 | 0.74 |
| Patina/PA brushing 5×, 80 °C | |||||||||
| 1st day | 0.66 | 295 | 0.50 | 21 | 915 | 0.50 | |||
| After 2 weeks | 8.24 | 13.38 | 0.53 | 5.99 | 21 | 1 | 104 | 63 | 0.72 |
| After 3 weeks | 8.50 | 15.53 | 0.55 | 11.55 | 38 | 1 | 92 | 73 | 0.76 |
| Rpo (kΩ cm2) | Qcoat (nS Sn cm−2) | ncoat | Rct (kΩ cm2) | Qdl (µS Sn cm−2) | ndl | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Paraloid B-72 | ||||||
| 1st day | 8 | 20 | 0.82 | 66 | 1.19 | 0.60 |
| After 2 weeks | 77 | 6.64 | 0.93 | 73 | 0.86 | 0.50 |
| After 3 weeks | 76 | 8.58 | 0.93 | 89 | 0.60 | 0.55 |
| PA brushing 5×, D 80 °C /Paraloid B-72 | ||||||
| 1st day | 97 | 6.00 | 0.87 | 215 | 1.15 | 0.50 |
| After 2 weeks | 128 | 5.04 | 0.94 | 1741 | 0.11 | 0.50 |
| After 3 weeks | 126 | 5.34 | 0.94 | 1844 | 0.13 | 0.50 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mikić, D.; Otmačić Ćurković, H. Protection of Patinated Bronze with Long-Chain Phosphonic Acid/Organic Coating Combined System. Materials 2023, 16, 1660. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16041660
Mikić D, Otmačić Ćurković H. Protection of Patinated Bronze with Long-Chain Phosphonic Acid/Organic Coating Combined System. Materials. 2023; 16(4):1660. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16041660
Chicago/Turabian StyleMikić, Dajana, and Helena Otmačić Ćurković. 2023. "Protection of Patinated Bronze with Long-Chain Phosphonic Acid/Organic Coating Combined System" Materials 16, no. 4: 1660. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16041660
APA StyleMikić, D., & Otmačić Ćurković, H. (2023). Protection of Patinated Bronze with Long-Chain Phosphonic Acid/Organic Coating Combined System. Materials, 16(4), 1660. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16041660







