Effects of Laser Cutting Parameters on the Magnetic Properties of 50W350 High-Grade Non-Oriented Electrical Steel
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Sample Preparation
2.3. Magnetic Properties Measurement and Evaluation
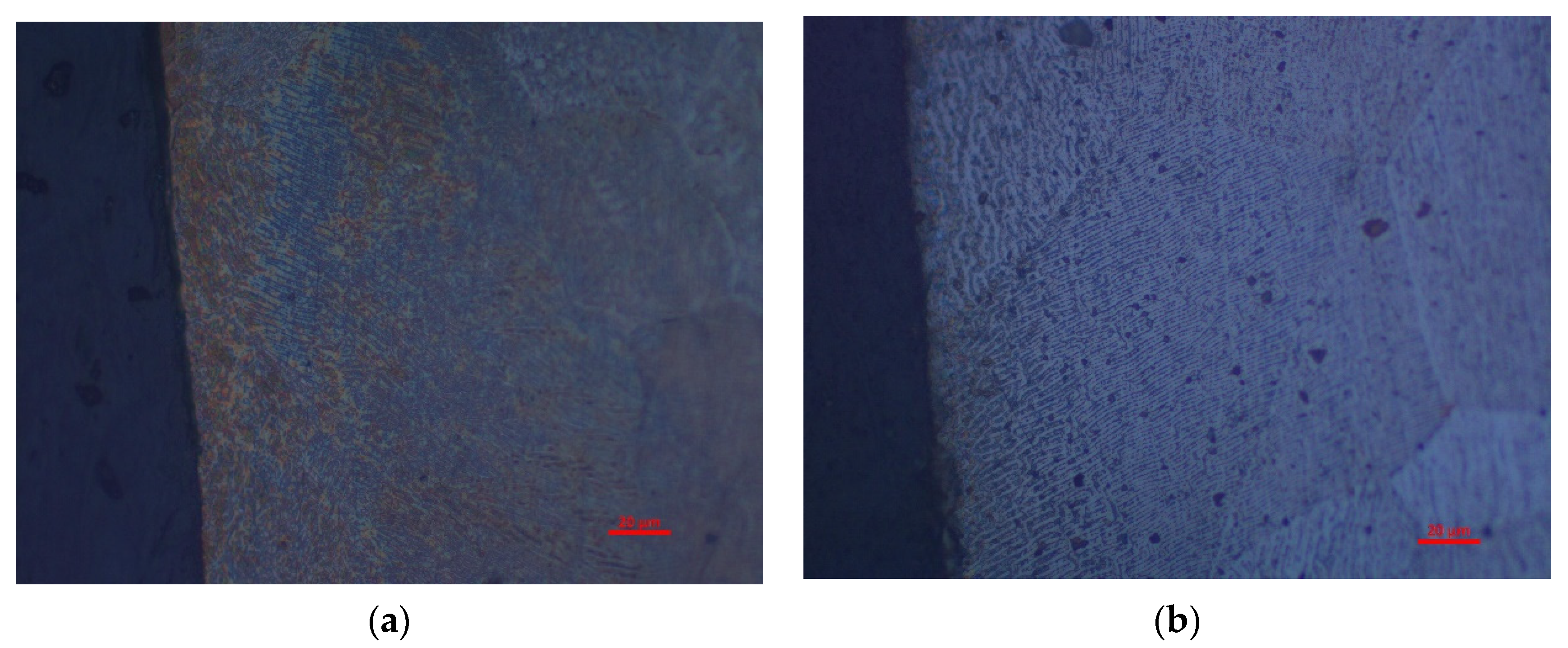
2.4. Observation of Cutting Edge and Magnetic Domain
2.5. Optimization of the Laser Cutting Parameters
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Magnetic Properties under Different Laser Cutting Parameters
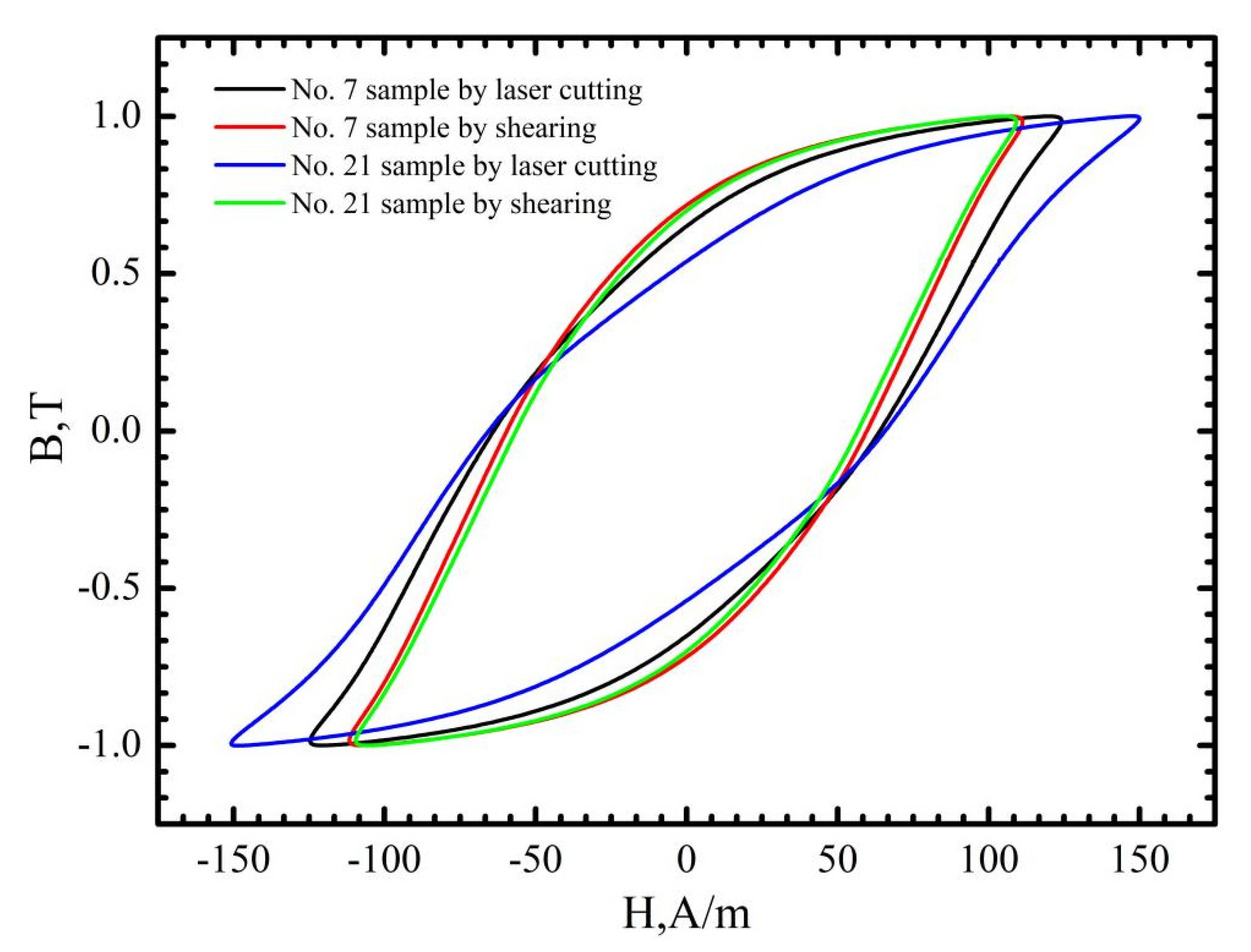
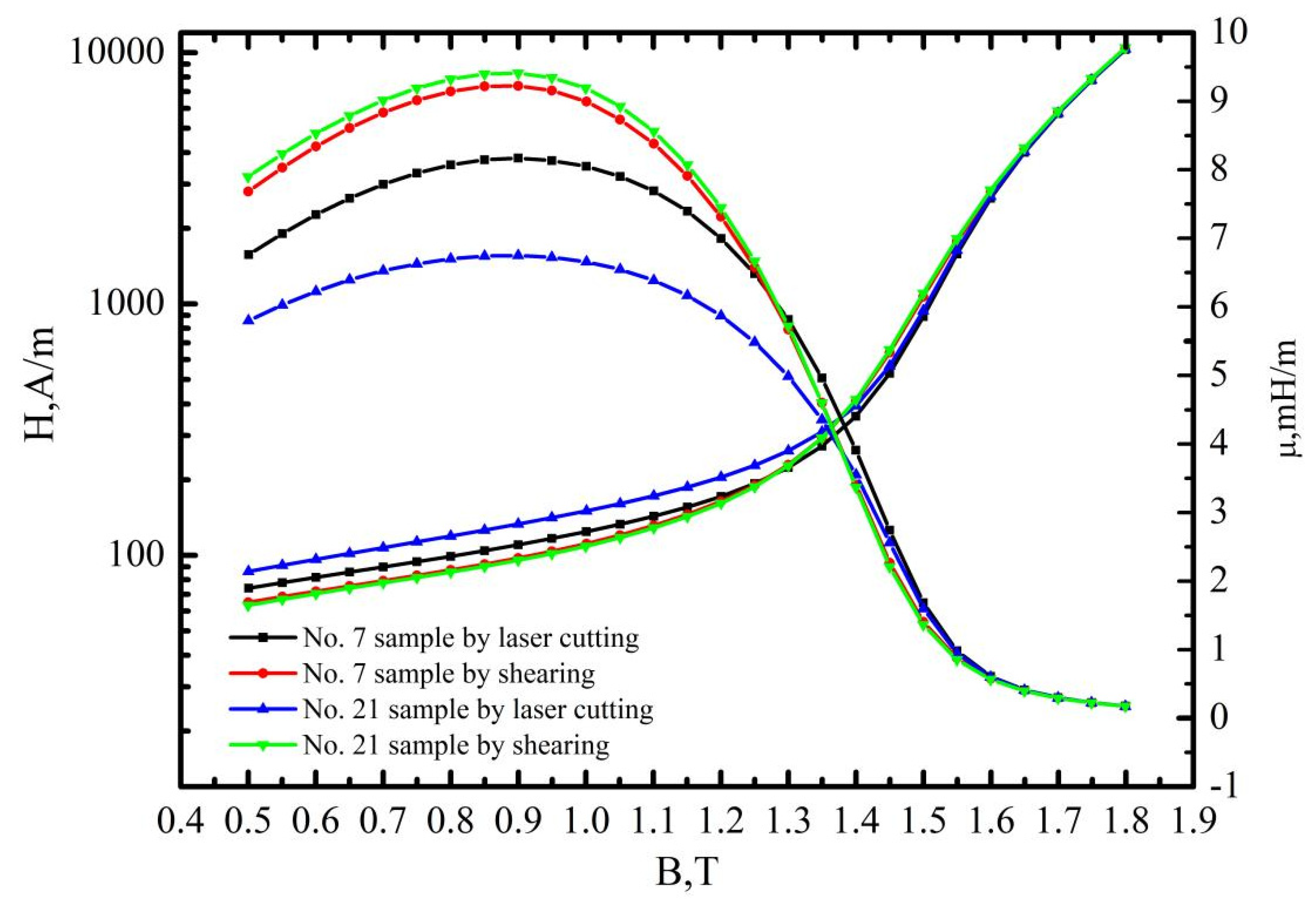
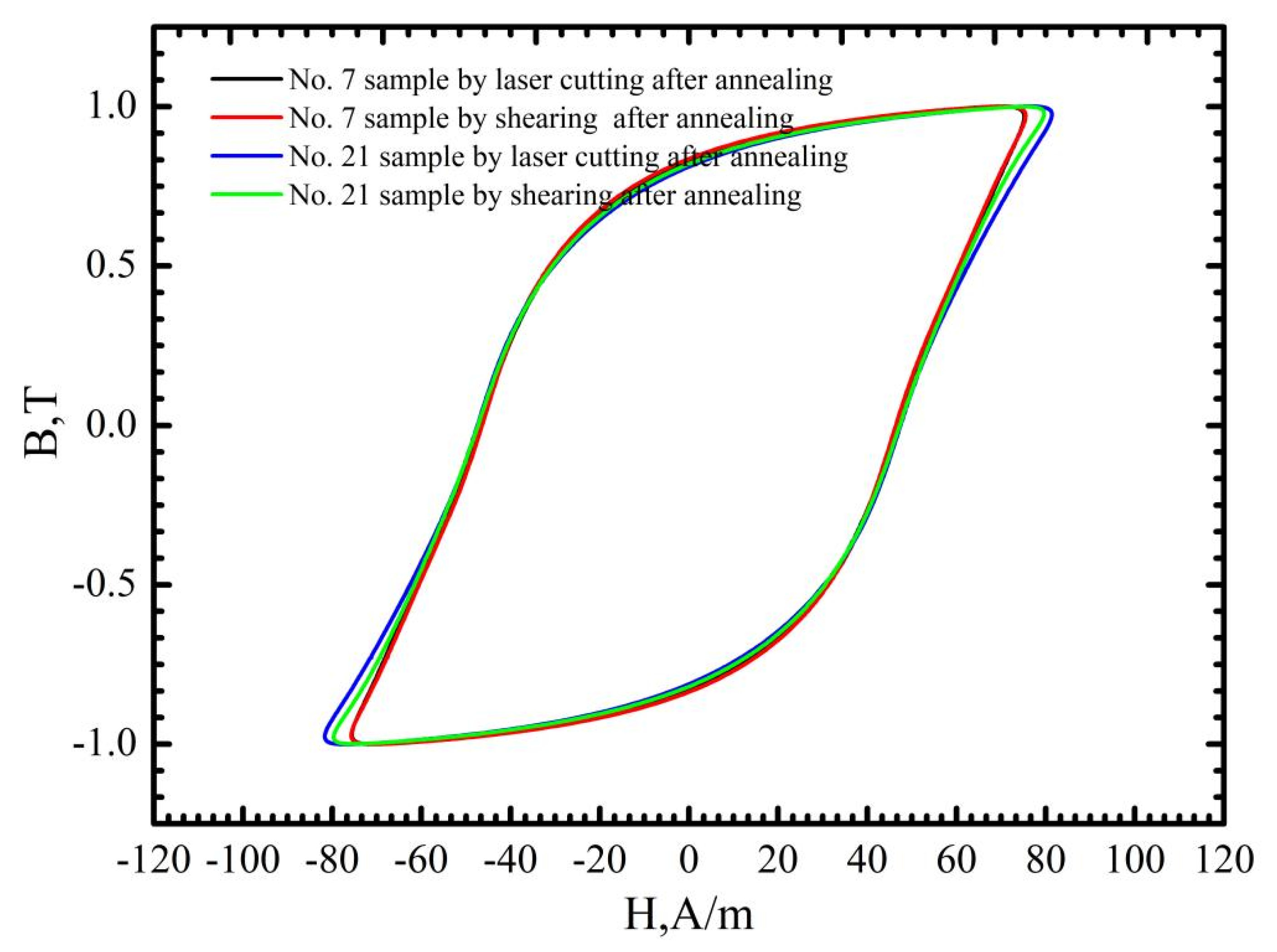
3.2. The Effects of Cutting Parameters on the B-H, H-B and μ-B Curves
3.3. Optimization of the Laser Cutting Parameters
4. Summary
- (1)
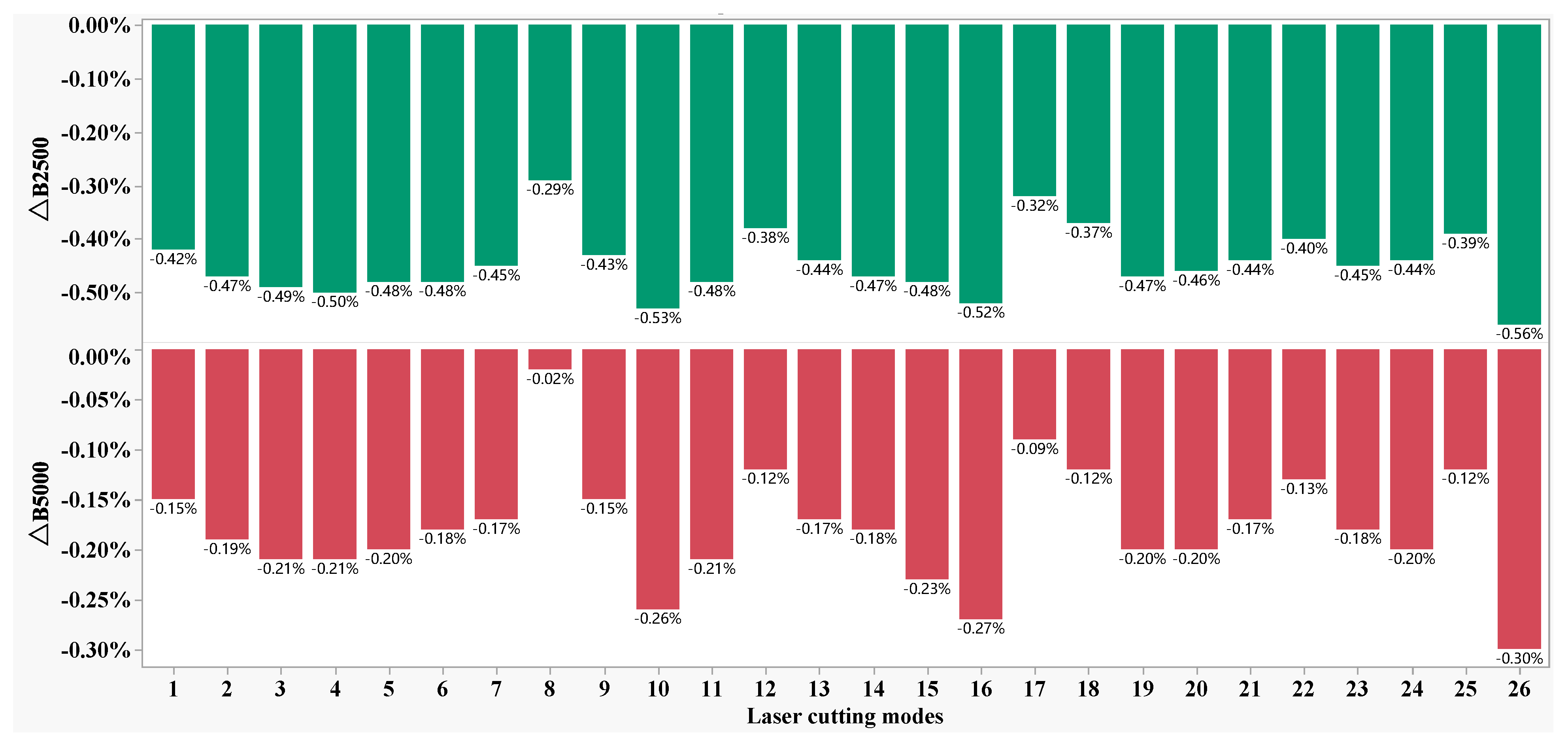
- The laser cutting process changed the magnetic domain structures near the cutting edge, which dominated the hysteresis loss increment compared with the annealed samples for the investigated 50W350 high-grade non-oriented electrical steel.
- (2)
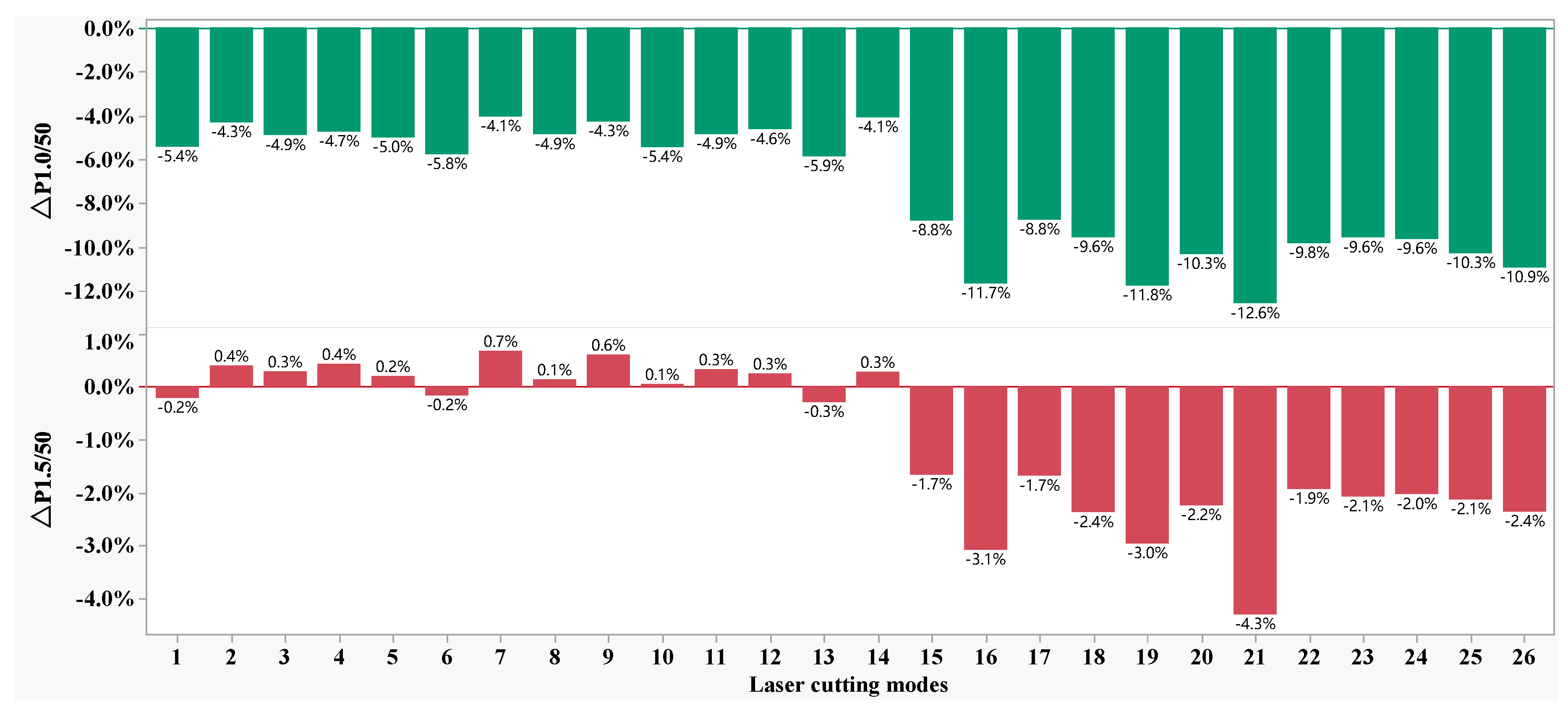
- Compared to mechanic shearing, the influencing of laser cutting on permeability depend on the magnetic induction intensity with a critical value of about 1.3 T. At the lower magnetic induction intensity (less than 1.3 T) the permeability was significantly decreased, whereas the permeability was slightly enhanced at the higher magnetic induction intensity (larger than 1.3 T), which induced the lower score at the index of ΔP1.0/50 but improved the score at the index ΔP1.5/50.
- (3)
- The parameters of laser cutting demonstrated non-linear effects on the magnetic properties of the cut samples. The mechanic shearing is superior to laser cutting regarding the index P1.0/50 in all of the cases. However, laser cutting is superior to mechanic shearing in some cases regarding index P1.5/50. Meanwhile, both P1.0/50 and P1.5/50 can be further improved by optimizing the laser cutting parameters.
- (4)
- Laser cutting is completely acceptable for 50W350 high-grade non-oriented electrical steel. If the working magnetic induction intensity is more than 1.3 T, the optimized laser cutting parameters can be directly utilized. If the working magnetic induction intensity is less than 1.3 T, laser cutting may result in a 3.5% deterioration compared with mechanic shearing in regard to index P1.0/50. However, stress relief annealing can be applied to restore the magnetic properties.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kurosaki, Y.; Mogi, H.; Fujii, H.; Kubota, T.; Shiozaki, M. Importance of punching and workability in non-oriented electrical steel sheets. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2008, 320, 2474–2480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peksoz, A.; Erdem, S.; Derebasi, N. Mathematical model for cutting effect on magnetic flux distribution near the cut edge of non-oriented electrical steels. Comput. Mater. Sci. 2008, 43, 1066–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.H.; Lin, C.K.; Tung, P.C.; Cuong, N.V.; Ho, J.R. An extreme learning machine for predicting kerf waviness and heat affected zone in pulsed laser cutting of thin non-oriented silicon steel. Opt. Laser Eng. 2020, 134, 106244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, D.T.; Ho, J.R.; Tung, P.C.; Lin, C.K. An improved real-time temperature control for pulsed laser cutting of non-oriented electrical steel. Opt. Laser Technol. 2021, 136, 106783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohman, M.N.; Ho, J.R.; Tung, P.C.; Lin, C.T.; Lin, C.K. Prediction and optimization of dross formation in laser cutting of electrical steel sheet in different environments. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2022, 18, 1977–1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohman, M.N.; Ho, J.R.; Tung, P.C.; Tsui, H.P.; Lin, C.K. Prediction and optimization of geometrical quality for pulsed laser cutting of non-oriented electrical steel sheet. Opt. Laser Technol. 2022, 149, 107847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleem, A.; Alatawneh, N.; Rahman, T.; Lowther, D.A.; Chromik, R.R. Effects of Laser Cutting on Microstructure and Magnetic Properties of Non-Orientation Electrical Steel Laminations. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2020, 56, 6100609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belhadj, A.; Baudouin, P.; Breaban, F.; Deffontaine, A.; Dewulf, M.; Houbaert, Y. Effect of laser cutting on microstructure and on magnetic properties of grain non-oriented electrical steels. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2003, 256, 20–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bali, M.; Muetze, A. Modeling the Effect of Cutting on the Magnetic Properties of Electrical Steel Sheets. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2017, 64, 2547–2556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Liu, J.; Li, C. Effect of cutting techniques on the structure and magnetic properties of a high-grade non-oriented electrical steel. J. Wuhan Univ. Technol.-Mater. Sci. Ed. 2014, 29, 1246–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naumoski, H.; Riedmüller, B.; Minkow, A.; Herr, U. Investigation of the influence of different cutting procedures on the global and local magnetic properties of non-oriented electrical steel. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2015, 392, 126–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baudouin, P.; Belhadj, A.; Breaban, F.; Deffontaine, A.; Houbaert, Y. Effects of laser and mechanical cutting modes on the magnetic properties of low and medium Si content nonoriented electrical steels. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2002, 38, 3213–3215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loisos, G.; Moses, A.J. Effect of mechanical and Nd:YAG laser cutting on magnetic flux distribution near the cut edge of non-oriented steels. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2005, 161, 151–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Gallaugher, M.; Brodusch, N.; Gauvin, R.; Chromik, R.R. Effect of a Coating Induced Residual Stress on Magnetic Domain Structure in Non-Oriented Electrical Steels. Microsc. Microanal. 2014, 20, 894–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bali, M.; Muetze, A. The Degradation Depth of Non-grain Oriented Electrical Steel Sheets of Electric Machines Due to Mechanical and Laser Cutting: A State-of-the-Art Review. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2019, 55, 366–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puchý, V.; Kováč, F.; Falat, L.; Petryshynets, I.; Džunda, R.; Fides, M.; Podobová, M.; Mrázek, J.; Baravets, Y.; Honzátko, P.; et al. The effects of CO2 laser and thulium-doped fibre laser scribing on magnetic domains structure, coercivity, and nanohardness of Fe-3.2Si grain-oriented electrical steel sheets. Kov. Mater. 2018, 56, 389–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paltanea, G.; Manescu, P.V.; Gavrila, H.; Nemoianu, I.V.; Andrei, P.C.; Ciuceanu, R.M. Application of orientation distribution functions’ theory in the case of grain-oriented steels cut through classical and non-conventional technologies. Int. J. Appl. Electromagn. Mech. 2019, 61, S131–S139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tung, A.T.; Park, B.H.; Liang, D.H.; Niemeyer, G. Laser-machined shape memory alloy sensors for position feedback in active catheters. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2008, 147, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balasubramaniyan, C.; Rajkumar, K.; Santosh, S. Fiber Laser Cutting of Cu-Zr Added Quaternary NiTi Shape Memory Alloy: Experimental Investigation and Optimization. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balasubramaniyan, C.; Santosh, S.; Rajkumar, K. Surface quality and morphology of NiTiCuZr shape memory alloy machined using thermal-energy processes: An examination of comparative topography. Surf. Topogr. Metrol. Prop. 2022, 3, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IEC-60404-2-2010; Magnetic Materials-Part 2: Methods of Measurement of the Magnetic Properties of Electrical Steel Strip and Sheet by Means of an Epstein Frame. International Electro Technical Commission: Geneva, Switzerland, 2008.
- Tumansk, S. Handbook of Magnetic Measurements; China Machine Press: Beijing, China, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, W.M.; Yang, P. Material Science Principles on Electrical Steels; Higher Education Press: Beijing, China, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Araujo, E.; Schneider, J.; Verbeken, K.; Pasquarella, G.; Houbaert, Y. Dimensional effects on magnetic properties of Fe-Si steels due to laser and mechanical cutting. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2010, 46, 213–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emura, M.; Landgraf, F.J.G.; Ross, W.; Barreta, J. The influence of cutting technique in the magnetic properties of electrical steels. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2003, 254, 358–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdul-Zade, E.A.; Gasanov, A.K.; Talybov, R.M. Influence of laser cutting on the electromagnetic characteristics of electrical steels. Elektrotekhnika 1988, 59, 59–60. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, T.J. Experimental Investigation for Improvement of Efficiency of the Electric Machine by the Annealing of the Stator. Electr. Mach. Medium Small Size 2000, 27, 54–55. [Google Scholar]


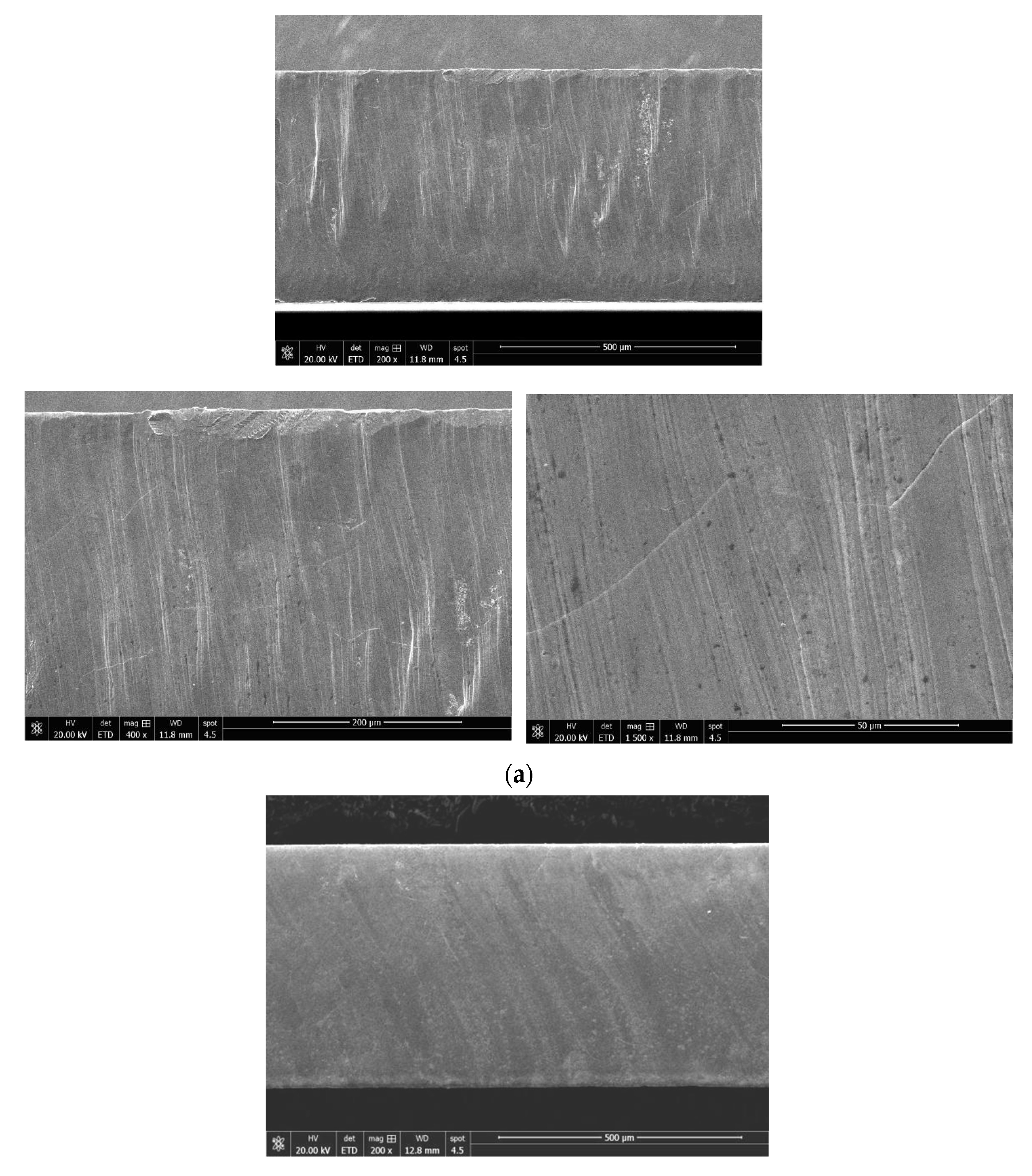
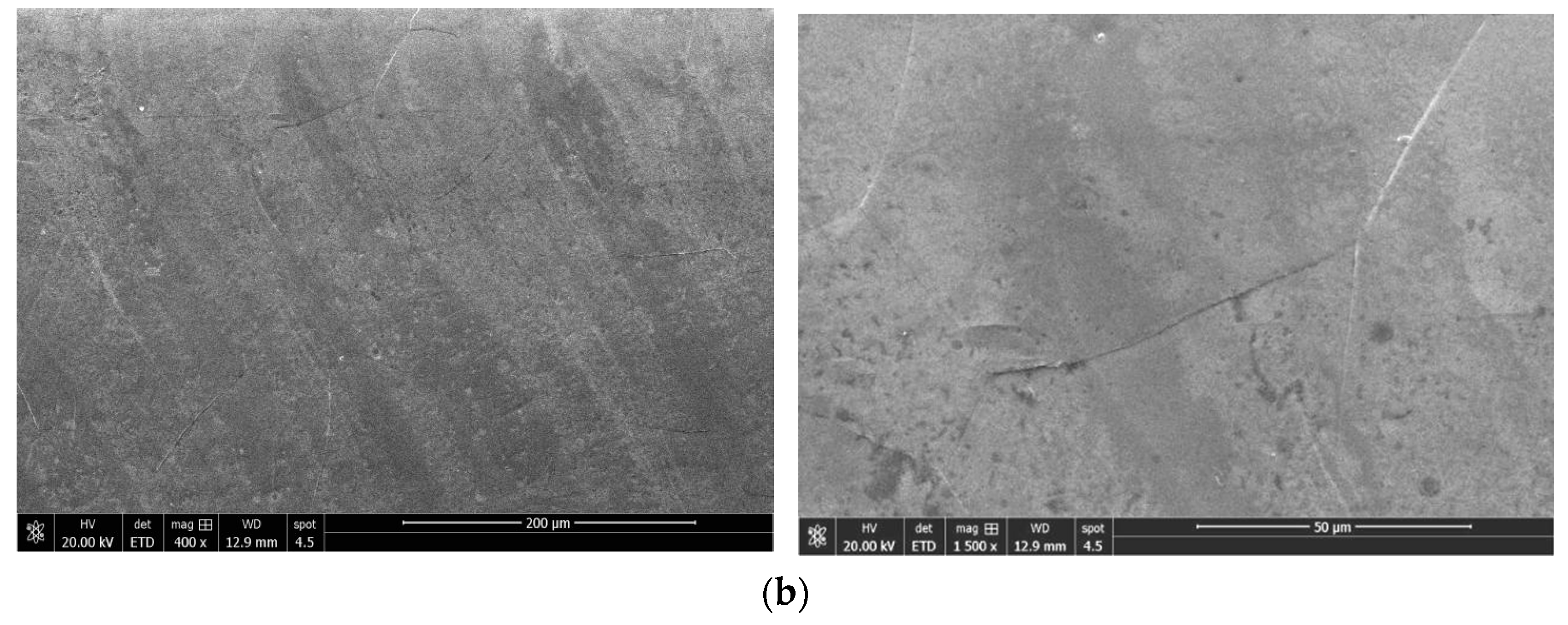

| No. | Laser Model | Cutting Speed, m/min | Power, W | N2 Pressure, MPa | Defocus Value, mm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0+−0 | 25 | 1600 | 1.00 | 0.5 |
| 2 | 0++0 | 25 | 1600 | 1.50 | 0.5 |
| 3 | 0+0+ | 25 | 1600 | 1.25 | 1.0 |
| 4 | ++00 | 30 | 1600 | 1.25 | 0.5 |
| 5 | −−00 | 20 | 1200 | 1.25 | 0.5 |
| 6 | +−00 | 30 | 1200 | 1.25 | 0.5 |
| 7 | −0+0 | 20 | 1400 | 1.50 | 0.5 |
| 8 | 0+0− | 25 | 1600 | 1.25 | 0.0 |
| 9 | 0 | 25 | 1400 | 1.25 | 0.5 |
| 10 | +0+0 | 30 | 1400 | 1.50 | 0.5 |
| 11 | −00− | 20 | 1400 | 1.25 | 0.0 |
| 12 | 00+− | 25 | 1400 | 1.50 | 0.0 |
| 13 | +0−0 | 30 | 1400 | 1.00 | 0.5 |
| 14 | 0−+0 | 25 | 1200 | 1.50 | 0.5 |
| 15 | −00+ | 20 | 1400 | 1.25 | 1.0 |
| 16 | 00−+ | 25 | 1400 | 1.00 | 1.0 |
| 17 | −0−0 | 20 | 1400 | 1.00 | 0.5 |
| 18 | +00− | 30 | 1400 | 1.25 | 0.0 |
| 19 | 0−−0 | 25 | 1200 | 1.00 | 0.5 |
| 20 | 0−0− | 25 | 1200 | 1.25 | 0.0 |
| 21 | 00−− | 25 | 1400 | 1.00 | 0.0 |
| 22 | 0−0+ | 25 | 1200 | 1.25 | 1.0 |
| 23 | 00++ | 25 | 1400 | 1.50 | 1.0 |
| 24 | 0 | 25 | 1400 | 1.25 | 0.5 |
| 25 | −+00 | 20 | 1600 | 1.25 | 0.5 |
| 26 | +00+ | 30 | 1400 | 1.25 | 1.0 |
| No. | P1.0/50-s | P1.0/50-B | ΔP1.0/50 | P1.5/50-s | P1.5/50-B | ΔP1.5/50 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1.186 | 1.231 | −3.7% | 2.677 | 2.666 | 0.4% |
| 2 | 1.182 | 1.223 | −3.4% | 2.650 | 2.632 | 0.7% |
| 3 | 1.174 | 1.217 | −3.5% | 2.648 | 2.629 | 0.7% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xiang, Q.; Cheng, L.; Wu, K. Effects of Laser Cutting Parameters on the Magnetic Properties of 50W350 High-Grade Non-Oriented Electrical Steel. Materials 2023, 16, 1642. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16041642
Xiang Q, Cheng L, Wu K. Effects of Laser Cutting Parameters on the Magnetic Properties of 50W350 High-Grade Non-Oriented Electrical Steel. Materials. 2023; 16(4):1642. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16041642
Chicago/Turabian StyleXiang, Qian, Lin Cheng, and Kaiming Wu. 2023. "Effects of Laser Cutting Parameters on the Magnetic Properties of 50W350 High-Grade Non-Oriented Electrical Steel" Materials 16, no. 4: 1642. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16041642
APA StyleXiang, Q., Cheng, L., & Wu, K. (2023). Effects of Laser Cutting Parameters on the Magnetic Properties of 50W350 High-Grade Non-Oriented Electrical Steel. Materials, 16(4), 1642. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16041642





