Effect of Shot Peening on the Low-Cycle Fatigue Behavior of an AA2519-T62 Friction-Stir-Welded Butt Joint
Abstract
:1. Introduction
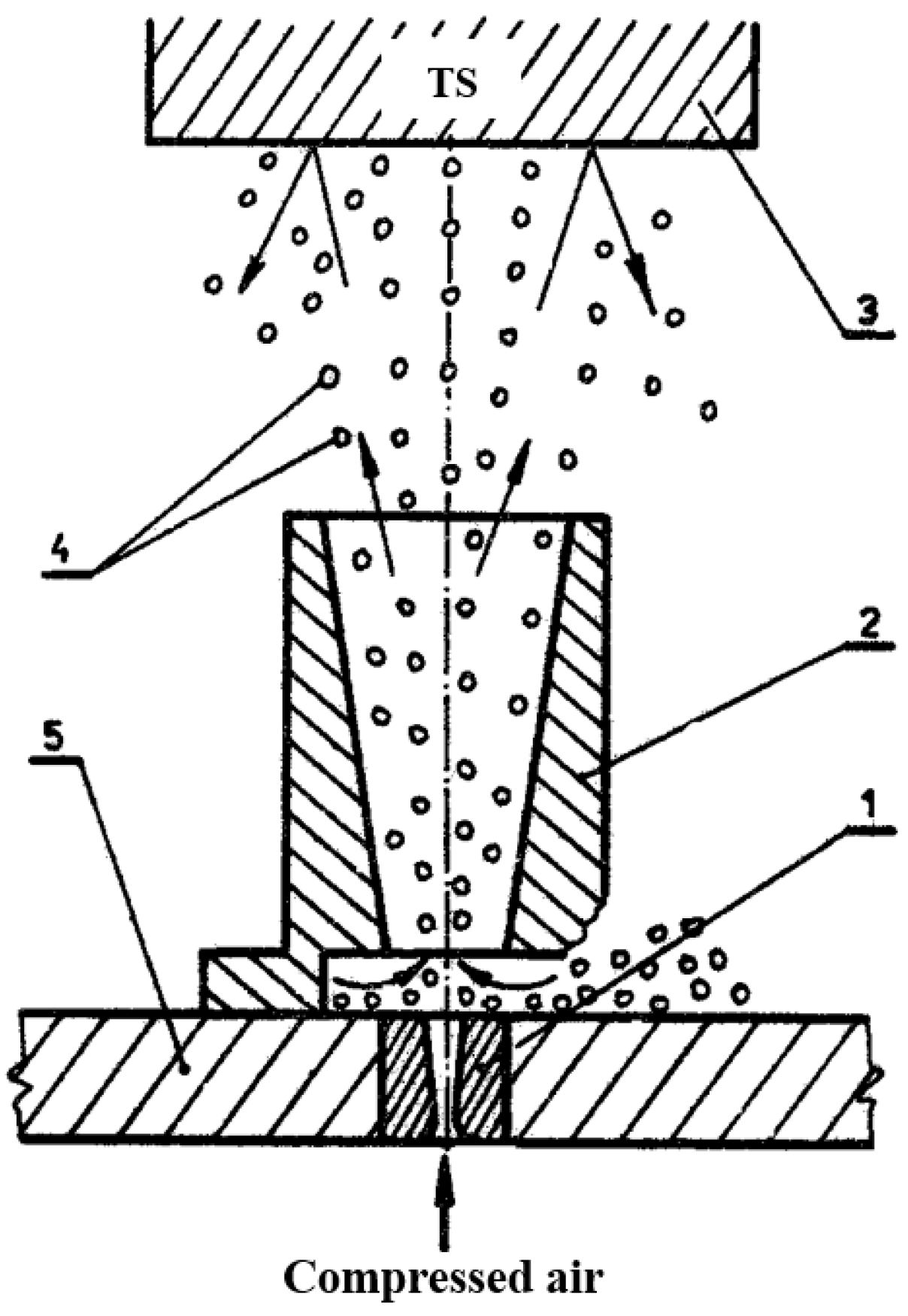
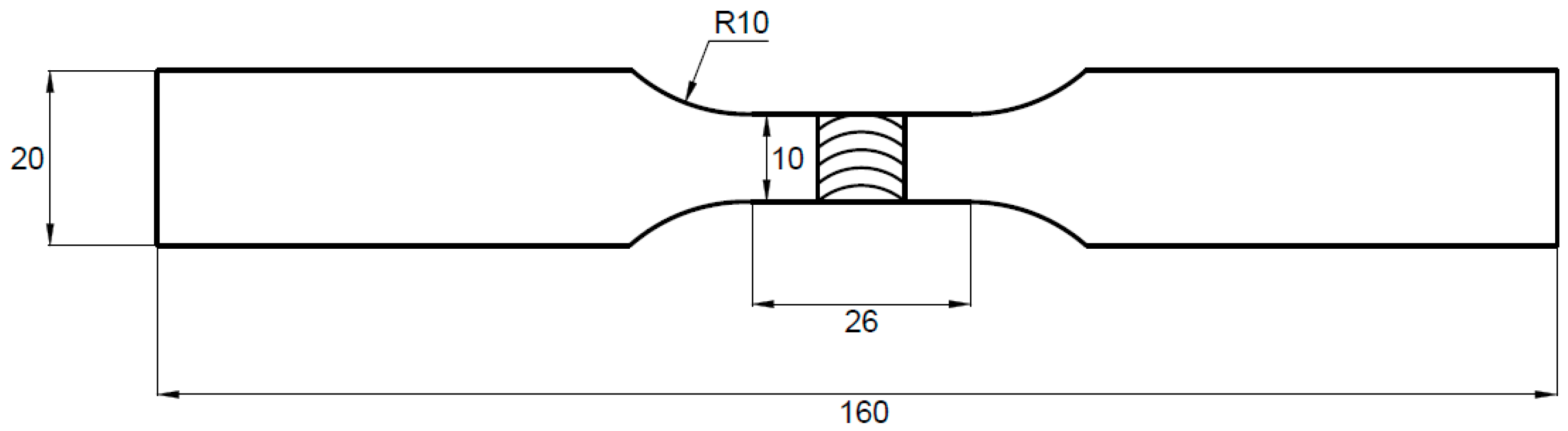
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
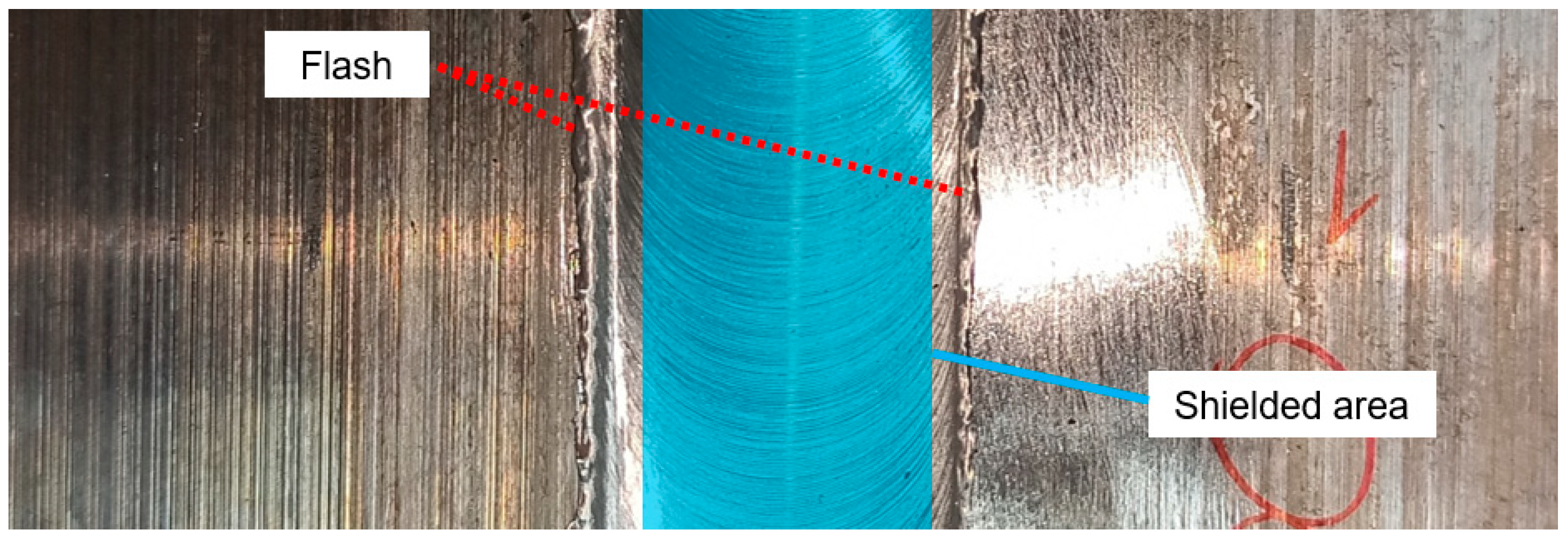
3.1. Macrostructural Observations
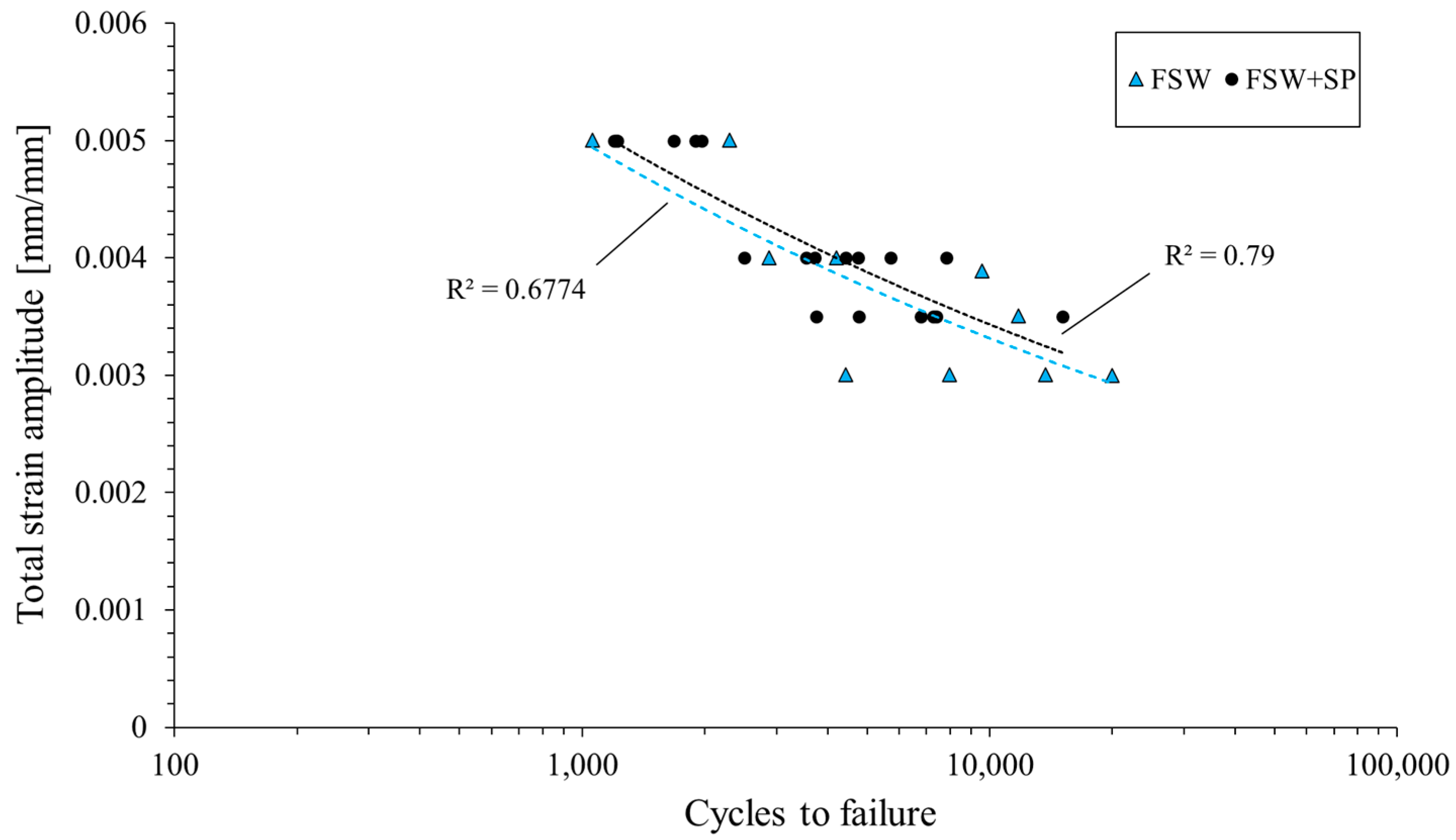
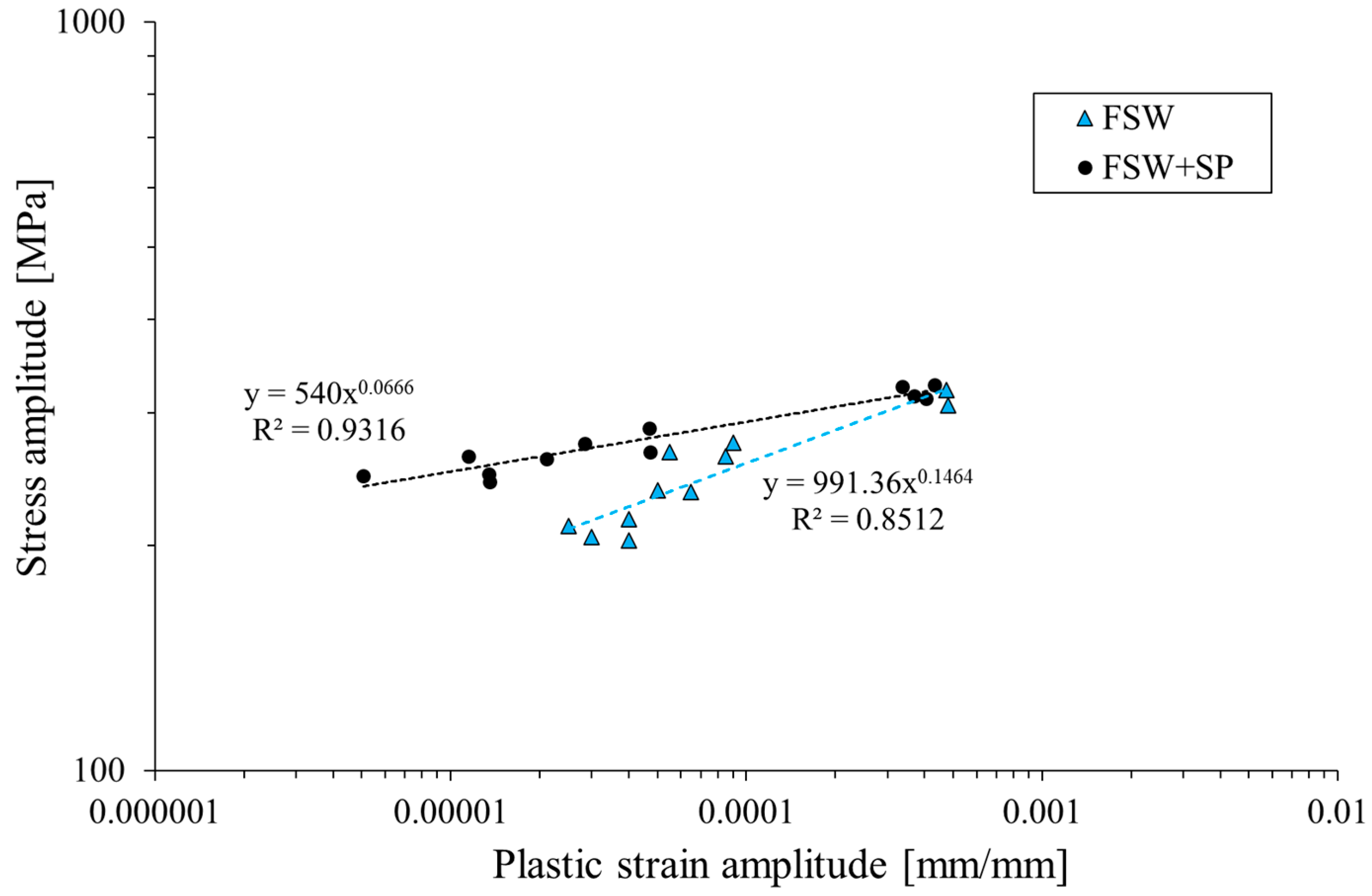
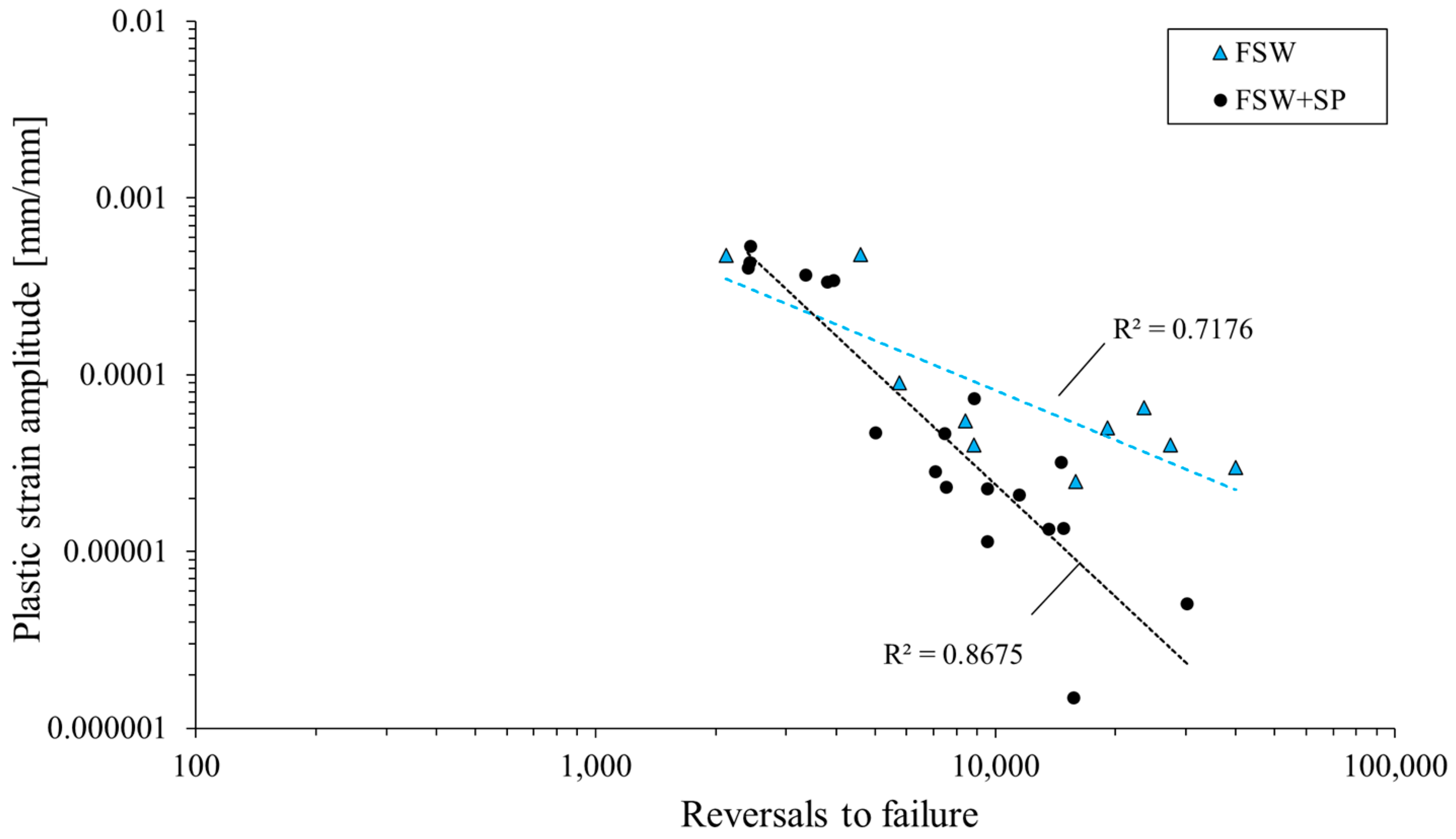
3.2. Low-Cycle Fatigue Properties
3.3. Fracture Behavior
4. Conclusions
- The performed shot peening process caused the plastic deformation of large near-surface grains, but also introduced small microcracks into the stir zone at a depth of about 30 µm.
- The shot-peened welds are characterized by a higher value of stress amplitude, a lower value of plastic strain amplitude, and their fatigue life slightly increased. The cyclic strength coefficient and the cyclic strain hardening exponent were reduced by 45% and 55%, respectively, as the result of the surface layer hardening.
- The shot peening process had no noticeable effect on the character of crack initiation and propagation. Almost in all cases, the cracking started in the area under the weld face, located close to the boundary between the thermo-mechanically affected zone and the stir zone at the advancing side. Only in the heaviest loads (εac = 0.5%) were the cracks initiated out of the FSW region at the retreating side.
- Despite the introduction of small cracks into the stir zone, their presence did not affect the decohesion character of the welded joint with failure occurring in the thermo-mechanically affected zone at the advancing side.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xu, W.F.; Liu, J.H.; Chen, D.L.; Luan, G.H. Low-Cycle Fatigue of a Friction Stir Welded 2219-T62 Aluminum Alloy at Different Welding Parameters and Cooling Conditions. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2014, 74, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosturek, R.; Torzewski, J.; Joska, Z.; Wachowski, M.; Sniezek, L. The Influence of Tool Rotation Speed on the Low-Cycle Fatigue Behavior of AA2519-T62 Friction Stir Welded Butt Joints. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2022, 142, 106756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Gao, J.; Li, Q. Fatigue of Friction Stir Welded Aluminum Alloy Joints: A Review. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 2626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zhang, H.; Yu, L. Mechanical Properties of Underwater Friction Stir Welded 2219 Aluminum Alloy. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2010, 20, 1387–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabari, S.S.; Malarvizhi, S.; Balasubramanian, V. The Effect of Pin Profiles on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Underwater Friction Stir Welded AA2519-T87 Aluminium Alloy. Int. J. Mech. Mater. Eng. 2016, 11, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bocchi, S.; D’Urso, G.; Giardini, C.; Maccarini, G. Effects of Cooling Conditions on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Friction Stir Welded Butt Joints of Different Aluminum Alloys. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 5069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.J.; Zhang, H.J.; Yu, L. Effect of Welding Speed on Microstructures and Mechanical Properties of Underwater Friction Stir Welded 2219 Aluminum Alloy. Mater. Des. 2011, 32, 1548–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aruri, D.; Kishan, V. Influence of Cryogenic Cooling (Liquid Nitrogen) on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Friction Stir Welded 2014-T6 Aluminum Alloy. Mater. Today Proc. 2018, 5, 1585–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwaszko, J. New Trends in Friction Stir Processing: Rapid Cooling—A Review. Trans. Indian Inst. Met. 2022, 75, 1681–1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bucior, M.; Kluz, R.; Kubit, A.; Ochał, K. Analysis of the Possibilities of Improving the Selected Properties Surface Layer of Butt Joints Made Using the FSW Method. Adv. Sci. Technol. Res. J. 2020, 14, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.; An, X.; Rodopoulos, C.; Brown, M.; O’Hara, P.; Levers, A.; Gardiner, S. The Effect of Controlled Shot Peening on the Fatigue Behaviour of 2024-T3 Aluminium Friction Stir Welds. Int. J. Fatigue 2007, 29, 1531–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatamleh, O.; Forth, S.; Reynolds, A.P. Fatigue Crack Growth of Peened Friction Stir-Welded 7075 Aluminum Alloy under Different Load Ratios. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2010, 19, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosturek, R.; Śnieżek, L.; Wachowski, M.; Torzewski, J. The Influence of Post-Weld Heat Treatment on the Microstructure and Fatigue Properties of Sc-Modified AA2519 Friction Stir-Welded Joint. Materials 2019, 12, 583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lezaack, M.B.; Simar, A. Avoiding Abnormal Grain Growth in Thick 7XXX Aluminium Alloy Friction Stir Welds during T6 Post Heat Treatments. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2021, 807, 140901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bucior, M.; Kluz, R.; Kubit, A.; Ochał, K. The Effect of Brushing on Residual Stress and Surface Roughness of EN AW-2024-T3 Aluminum Alloy Joints Welded Using the FSW Method. Adv. Sci. Technol. Res. J. 2023, 17, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jambor, M.; Trško, L.; Klusák, J.; Fintová, S.; Kajánek, D.; Nový, F.; Bokůvka, O. Effect of Severe Shot Peening on the Very-High Cycle Notch Fatigue of an AW 7075 Alloy. Metals 2020, 10, 1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malopheyev, S.; Vysotskiy, I.; Zhemchuzhnikova, D.; Mironov, S.; Kaibyshev, R. On the Fatigue Performance of Friction-Stir Welded Aluminum Alloys. Materials 2020, 13, 4246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, V.; Chattopadhyay, K.; Santhi Srinivas, N.C.; Singh, V. Role of Ultrasonic Shot Peening on Low Cycle Fatigue Behavior of 7075 Aluminium Alloy. Int. J. Fatigue 2017, 103, 426–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Huang, Y.; Cao, J.; Shen, J.; dos Santos, J.F. Recent progress on control strategies for inherent issues in friction stir welding. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2021, 115, 100706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saravanakumar, R.; Rajasekaran, T.; Pandey, C. Influence of Tool Probe Profiles on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Underwater Friction Stir Welded AA5083 material. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2022, 31, 8433–8450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saravanakumar, R.; Rajasekaran, T.; Pandey, C. Underwater Friction Stir Welded Armour Grade AA5083 Aluminum Alloys: Experimental Ballistic Performance and Corrosion Investigation. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2023, 32, 10175–10190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosturek, R.; Ślęzak, T.; Torzewski, J.; Wachowski, M.; Sniezek, L. Study on Tensile and Fatigue Failure in the Low-Hardness Zone of AA2519-T62 FSW Joint. Manuf. Rev. 2022, 9, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 12106:2017; Metallic Materials—Fatigue Testing—Axial-Strain-Controlled Method. Vernier: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017.
- Baklouti, M.; Mnif, R.; Elleuch, R. Impact of Surface Hardening Treatment Generated by Shot Peening on the Fatigue Life of Brass Alloy. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 2012, 26, 2711–2717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marohnić, T.; Basan, R.; Franulović, M. Evaluation of Methods for Estimation of Cyclic Stress-Strain Parameters from Monotonic Properties of Steels. Metals 2017, 7, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trško, L.; Fintová, S.; Nový, F.; Bokůvka, O.; Jambor, M.; Pastorek, F.; Florková, Z.; Oravcová, M. Study of Relation between Shot Peening Parameters and Fatigue Fracture Surface Character of an AW 7075 Aluminium Alloy. Metals 2018, 8, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhong, H.; Li, S.; Zhao, H.; Chen, J.; Qi, L. Microstructure, mechanical properties and fatigue crack growth behavior of friction stir welded joint of 6061-T6 aluminum alloy. Int. J. Fatigue 2020, 135, 105556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Si | Fe | Cu | Mn | Mg | Ni | Zn | Ti | Zr | Sc | V | Al |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.08 | 0.11 | 6.32 | 0.17 | 0.33 | 0.02 | 0.05 | 0.008 | 0.19 | 0.16 | 0.10 | Base |
| Young Modulus, E | Yield Strength, R0.2 | Tensile Strength, Rm | Elongation, A |
|---|---|---|---|
| 78 GPa | 312 MPa | 469 MPa | 19% |
| Young Modulus, E | Yield Strength, R0.2 | Tensile Strength, Rm | Elongation, A |
|---|---|---|---|
| 72 GPa | 265 MPa | 410 MPa | 9% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kosturek, R.; Ślęzak, T.; Torzewski, J.; Bucior, M.; Zielecki, W.; Śnieżek, L.; Sęp, J. Effect of Shot Peening on the Low-Cycle Fatigue Behavior of an AA2519-T62 Friction-Stir-Welded Butt Joint. Materials 2023, 16, 7131. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16227131
Kosturek R, Ślęzak T, Torzewski J, Bucior M, Zielecki W, Śnieżek L, Sęp J. Effect of Shot Peening on the Low-Cycle Fatigue Behavior of an AA2519-T62 Friction-Stir-Welded Butt Joint. Materials. 2023; 16(22):7131. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16227131
Chicago/Turabian StyleKosturek, Robert, Tomasz Ślęzak, Janusz Torzewski, Magdalena Bucior, Władysław Zielecki, Lucjan Śnieżek, and Jarosław Sęp. 2023. "Effect of Shot Peening on the Low-Cycle Fatigue Behavior of an AA2519-T62 Friction-Stir-Welded Butt Joint" Materials 16, no. 22: 7131. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16227131
APA StyleKosturek, R., Ślęzak, T., Torzewski, J., Bucior, M., Zielecki, W., Śnieżek, L., & Sęp, J. (2023). Effect of Shot Peening on the Low-Cycle Fatigue Behavior of an AA2519-T62 Friction-Stir-Welded Butt Joint. Materials, 16(22), 7131. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16227131










