Accuracy of Four Intra-Oral Scanners in Subgingival Vertical Preparation: An In Vitro 3-Dimensional Comparative Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
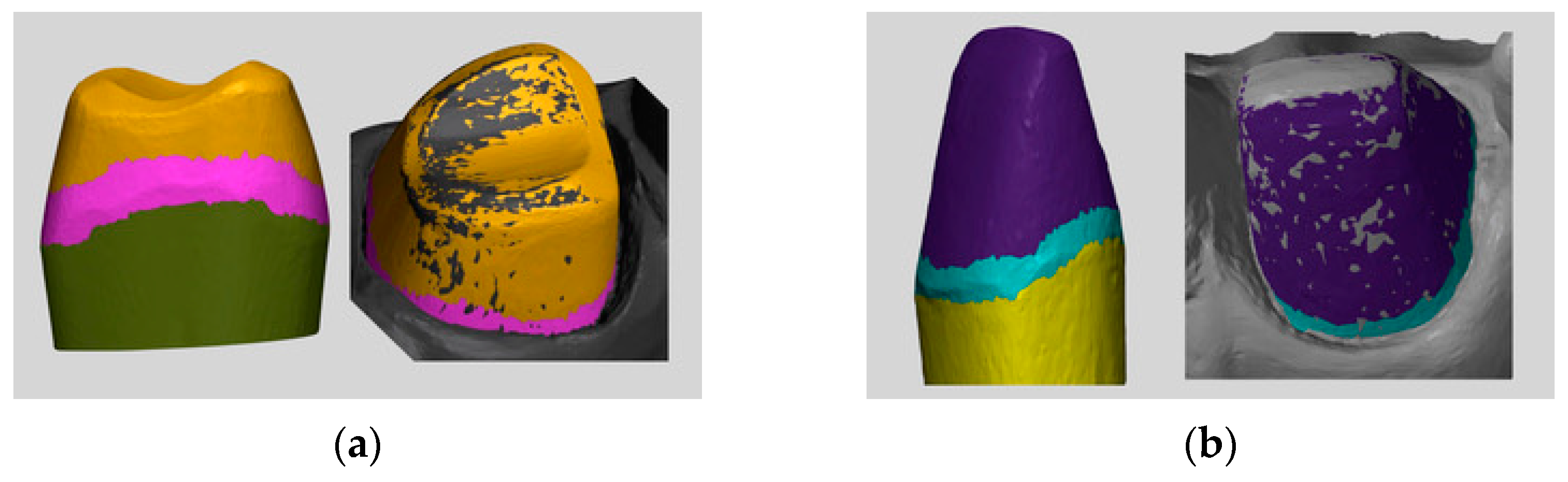
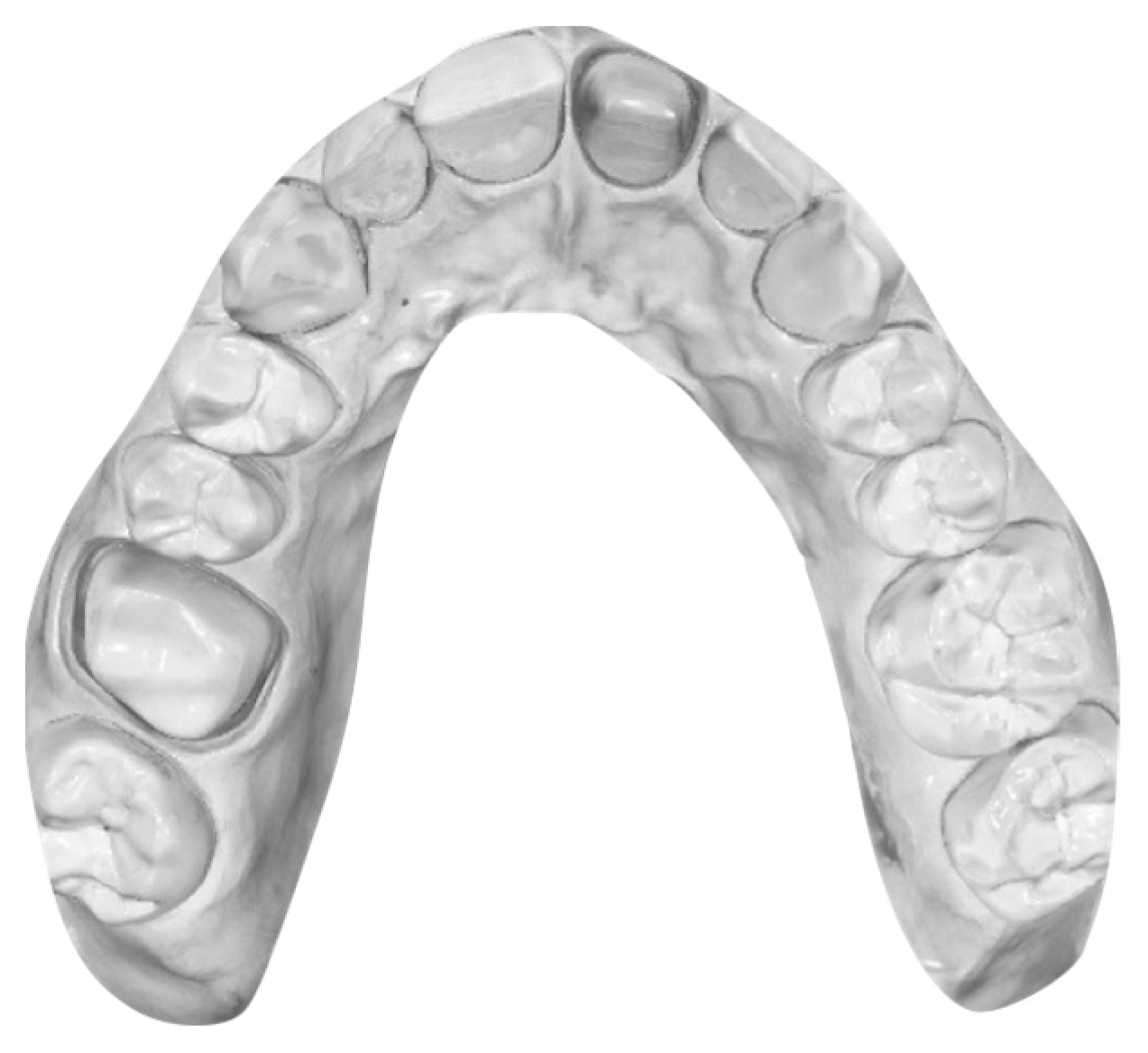
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. RMS Evaluations
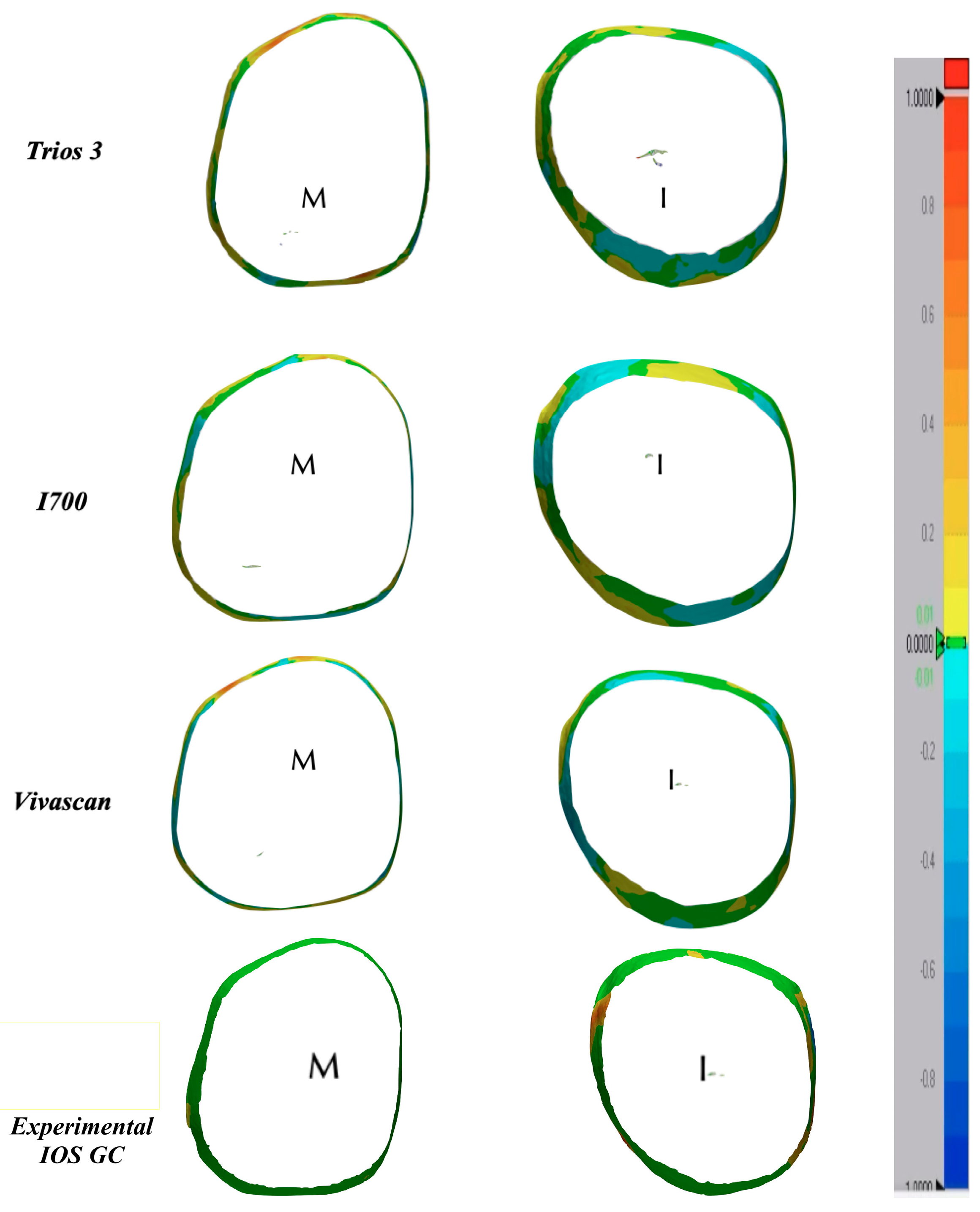
3.2. Accuracy at the Subgingival Marginal Level
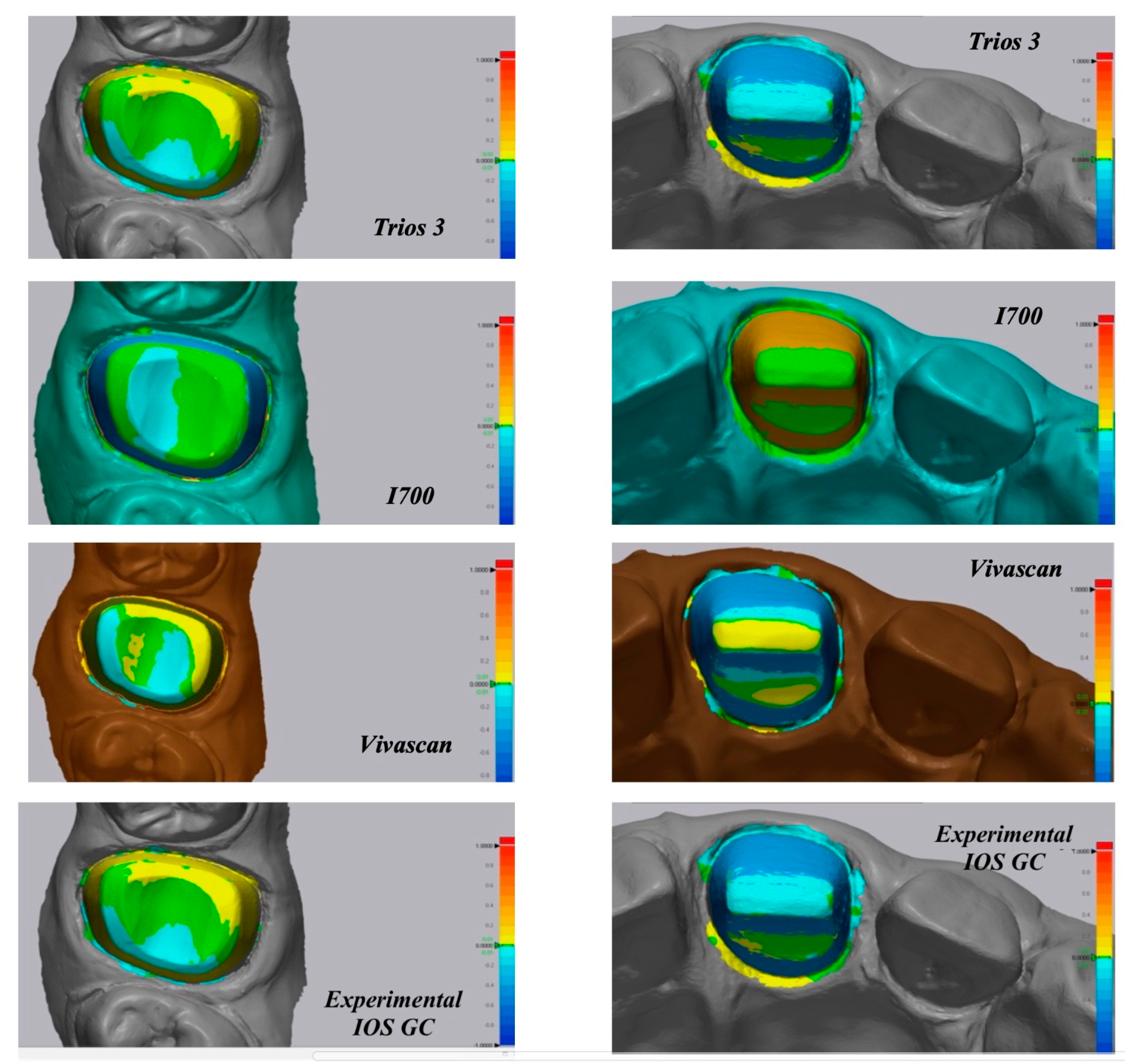
3.3. Color Map Evaluations
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- The trueness deviations of the analyzed scanners were significantly different in the full abutment surface of the molar and incisor.
- At the subgingival marginal level, the accuracy results were not clinically acceptable for all the IOS, probably due to the “joining the dots” effect.
- More studies are required to validate the behavior of IOS in vertical preparations.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Richert, R.; Goujat, A.; Venet, L.; Viguie, G.; Viennot, S.; Robinson, P.; Farges, J.C.; Fages, M.; Ducret, M. Intraoral scanner technologies: A review to make a successful impression. J. Healthc. Eng. 2017, 2017, 8427595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alghazzawi, T.F. Advancements in CAD/CAM technology: Options for practical implementation. J. Prosthodont. Res. 2016, 60, 72–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chochlidakis, K.M.; Papaspyridakos, P.; Geminiani, A.; Chen, C.J.; Feng, I.J.; Ercoli, C. Digital versus conventional impressions for fixed prosthodontics: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2016, 116, 184–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueda, K.; Beuer, F.; Stimmelmayr, M.; Erdelt, K.; Keul, C.; Güth, J.F. Fit of 4-unit FDPs from CoCr and zirconia after conventional and digital impressions. Clin. Oral. Investig. 2016, 20, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Memari, Y.; Mohajerfar, M.; Armin, A.; Kamalian, F.; Rezayani, V.; Beyabanaki, E. Marginal adaptation of CAD/CAM all-ceramic crowns made by different impression methods: A literature review. J. Prosthodont. 2019, 28, 536–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahlholm, P.; Sipilä, K.; Vallittu, P.; Jakonen, M.; Kotiranta, U. Digital versus conventional impressions in fixed prosthodontics: A review. J. Prosthodont. 2018, 27, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuzbasioglu, E.; Kurt, H.; Turunc, R.; Bilir, H. Comparison of digital and conventional impression techniques: Evaluation of patients’ perception, treatment comfort, effectiveness and clinical outcomes. BMC Oral. Health 2014, 14, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glossary of Digital Dental Terms, 2nd Edition: American College of Prosthodontists and ACP Education Foundation. J. Prosthodont. 2021, 30, 172–181. [CrossRef]
- ISO 5725-1; Accuracy (Trueness and Precision) of Measurement Methods and Results. Part 1: General Principles and Definitions. International Organization for Standardization: Berlin, Germany, 1994. Available online: http://www.iso.org/iso/home.html (accessed on 5 May 2023).
- Sim, J.Y.; Jang, Y.; Kim, W.C.; Kim, H.Y.; Lee, D.H.; Kim, J.H. Comparing the accuracy (trueness and precision) of models of fixed dental prostheses fabricated by digital and conventional workflows. J. Prosthodont. Res. 2019, 63, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wesemann, C.; Muallah, J.; Mah, J.; Bumann, A. Accuracy and efficiency of full-arch digitalization and 3D printing: A comparison between desktop model scanners, an intraoral scanner, a CBCT model scan, and stereolithographic 3D printing. Quintessence Int. 2017, 48, 41–50. [Google Scholar]
- Amornvit, P.; Rokaya, D.; Sanohkan, S. Comparison of Accuracy of Current Ten Intraoral Scanners. BioMed Res. Int. 2021, 2021, 2673040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nedelcu, R.G.; Persson, A.S. Scanning accuracy and precision in 4 intraoral scanners: An in vitro comparison based on 3-dimensional analysis. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2014, 112, 1461–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Latham, J.; Ludlow, M.; Mennito, A.; Kelly, A.; Evans, Z.; Renne, W. Effect of scan pattern on complete-arch scans with 4 digital scanners. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2020, 123, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, H.; Mickesh, G.J.; Cho, D.; Sorensen, J.A. Effect of finish line location and saliva contamination on the accuracy of crown finish line scanning. J. Prosthodont. 2023. Online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keeling, A.; Wu, J.; Ferrari, M. Confounding factors affecting the marginal quality of an intra-oral scan. J. Dent. 2017, 59, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukazawa, S.; Odaira, C.; Kondo, H. Investigation of accuracy and reproducibility of abutment position by intraoral scanners. J. Prosthodont. Res. 2017, 61, 450–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guth, J.F.; Keul, C.; Stimmelmayr, M.; Beuer, F.; Edelhoff, D. Accuracy of digital models obtained by direct and indirect data capturing. Clin. Oral. Investig. 2013, 17, 1201–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari Cagidiaco, E.; Zarone, F.; Discepoli, N.; Joda, T.; Ferrari, M. Analysis of The Reproducibility of Subgingival Vertical Margins Using Intraoral Optical Scanning (IOS): A Randomized Controlled Pilot Trial. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, Y.T.; Son, K.; Lee, K.B. Trueness of intraoral scanners according to subgingival depth of abutment for fixed prosthesis. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 20786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, K.; Lee, K.B. Effect of finish line locations of tooth preparation on the accuracy of intraoral scanners. Int. J. Comput. Dent. 2021, 24, 29–40. [Google Scholar]
- García-Gil, I.; Perez de la Calle, C.; Lopez-Suarez, C.; Pontevedra, P.; Suarez, M.J. Comparative analysis of trueness between conventional and digital impression in dental-supported fixed dental prosthesis with vertical preparation. J. Clin. Exp. Dent. 2020, 12, e896–e901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marani, R.; Reno, V.; Nitti, M.; D’Orazio, T.; Stella, E. A modified iterative closest point algorithm for 3D point cloud registration. Comput. Aided Civil. Infrastruct. Eng. 2016, 31, 515–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlsson, S. The fit of Procera titanium crowns. An in vitro and clinical study. Acta Odontol. Scand. 1993, 51, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gardner, F.M. Margins of complete crowns—Literature review. J. Prosthet. Dent. 1982, 48, 396–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bader, J.D.; Rozier, R.G.; McFall, W.T., Jr.; Ramsey, D.L. Effect of crown margins on periodontal conditions in regularly attending patients. J. Prosthet. Dent. 1991, 65, 75–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLean, J.W.; Von Fraunhofer, J.A. The estimation of cement film thickness by an in vivo technique. Br. Dent. J. 1971, 131, 107–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verniani, G.; Ferrari Cagidiaco, E.; Marruganti, C.; Kamposiora, P.; Ferrari, M. Comparison of marginal fit and sealing ability of luted lithium disilicate crowns fabricated with CAD/CAM technology using two different intraoral scanners. J. Osseointegr. 2021, 13, S299–S304. [Google Scholar]
- Brawek, P.K.; Wolfart, S.; Endres, L.; Kirsten, A.; Reich, S. The clinical accuracy of single crowns exclusively fabricated by digital workflow—The comparison of two systems. Clin. Oral. Investig. 2013, 17, 2119–2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shim, J.S.; Lee, J.S.; Lee, J.Y.; Choi, Y.J.; Shin, S.W.; Ryu, J.J. Effect of software version and parameter settings on the marginal and internal adaptation of crowns fabricated with the CAD/CAM system. J. Appl. Oral Sci. 2015, 23, 515–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abduo, J.; Elseyoufi, M. Accuracy of Intraoral Scanners: A Systematic Review of Influencing Factors. Eur. J. Prosthodont. Restor. Dent. 2018, 26, 101–121. [Google Scholar]


| Trueness #16 [µm] | Trueness #21 [µm] | Precision #16 [µm] | Precision #21 [µm] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Trios 3 | 60.2 ± 4.9 a | 68.7 ± 4.0 b | 31.7± 13.1 bc | 18.0 ± 2.7 ab |
| I700 | 58.0 ± 8.9 a | 83.3± 5.6 c | 15.8 ± 2.7 b | 29.8 ± 3.7 b |
| Vivascan | 69.6 ± 6.9 b | 56.0 ± 1.21 a | 41.4 ± 20.2 c | 49.9 ± 19.6 c |
| Experimental IOS, GC | 55.4 ± 5.6 a | 59.2 ± 2.7 a | 10.7 ± 2.1 a | 16.9 ± 1.3 a |
| Marginal #16 [µm] | Marginal #21 [µm] | |
|---|---|---|
| Trios 3 | 166.0 ± 0.34 b | 147.4 ± 2.18 a |
| I700 | 96.3 ± 0.13 a | 154.2 ± 1.89 a |
| Vivascan | 141.2 ± 2.20 b | 170.0 ± 1.33 b |
| Experimental IOS, GC | 145.2 ± 1.87 b | 135.7 ± 0.825 a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Casucci, A.; Verniani, G.; Habib, R.; Ricci, N.M.; Carboncini, C.; Ferrari, M. Accuracy of Four Intra-Oral Scanners in Subgingival Vertical Preparation: An In Vitro 3-Dimensional Comparative Analysis. Materials 2023, 16, 6553. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16196553
Casucci A, Verniani G, Habib R, Ricci NM, Carboncini C, Ferrari M. Accuracy of Four Intra-Oral Scanners in Subgingival Vertical Preparation: An In Vitro 3-Dimensional Comparative Analysis. Materials. 2023; 16(19):6553. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16196553
Chicago/Turabian StyleCasucci, Alessio, Giulia Verniani, Ralph Habib, Nicolò Maria Ricci, Clelia Carboncini, and Marco Ferrari. 2023. "Accuracy of Four Intra-Oral Scanners in Subgingival Vertical Preparation: An In Vitro 3-Dimensional Comparative Analysis" Materials 16, no. 19: 6553. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16196553
APA StyleCasucci, A., Verniani, G., Habib, R., Ricci, N. M., Carboncini, C., & Ferrari, M. (2023). Accuracy of Four Intra-Oral Scanners in Subgingival Vertical Preparation: An In Vitro 3-Dimensional Comparative Analysis. Materials, 16(19), 6553. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16196553







