Environmentally Friendly Approach for Nd2Fe14B Magnetic Phase Extraction by Selective Chemical Leaching: A Proof-of-Concept Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Material Characterization
2.2. Leaching Procedure
2.3. Magnetic Measurements
2.4. Determination of the Chemical Composition of Powder Samples via ICP-MS
Sample Preparation
2.5. ICP-MS Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
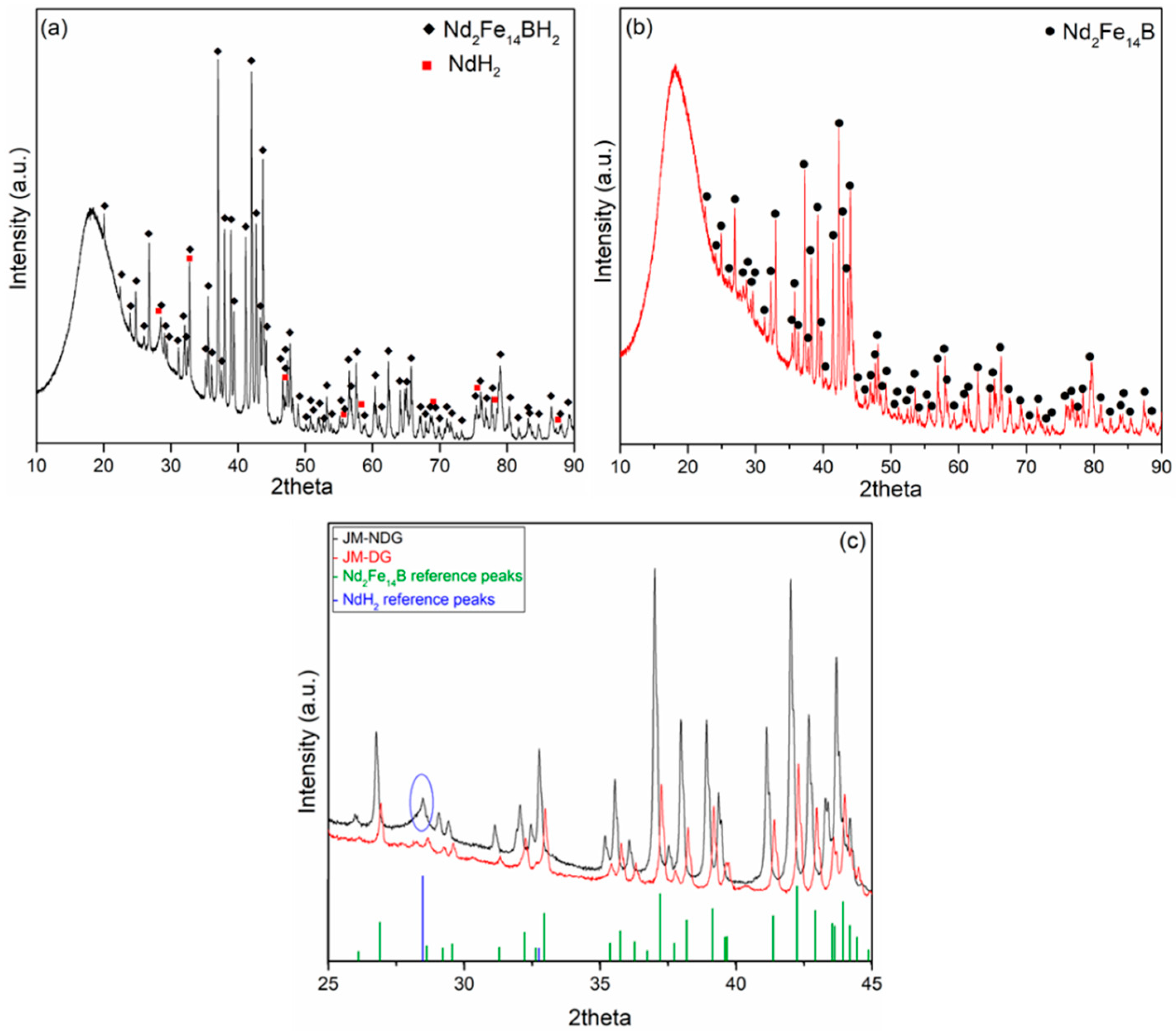
3.1. X-ray Diffraction Analysis of Non-Leached Nd-Fe-B Powders
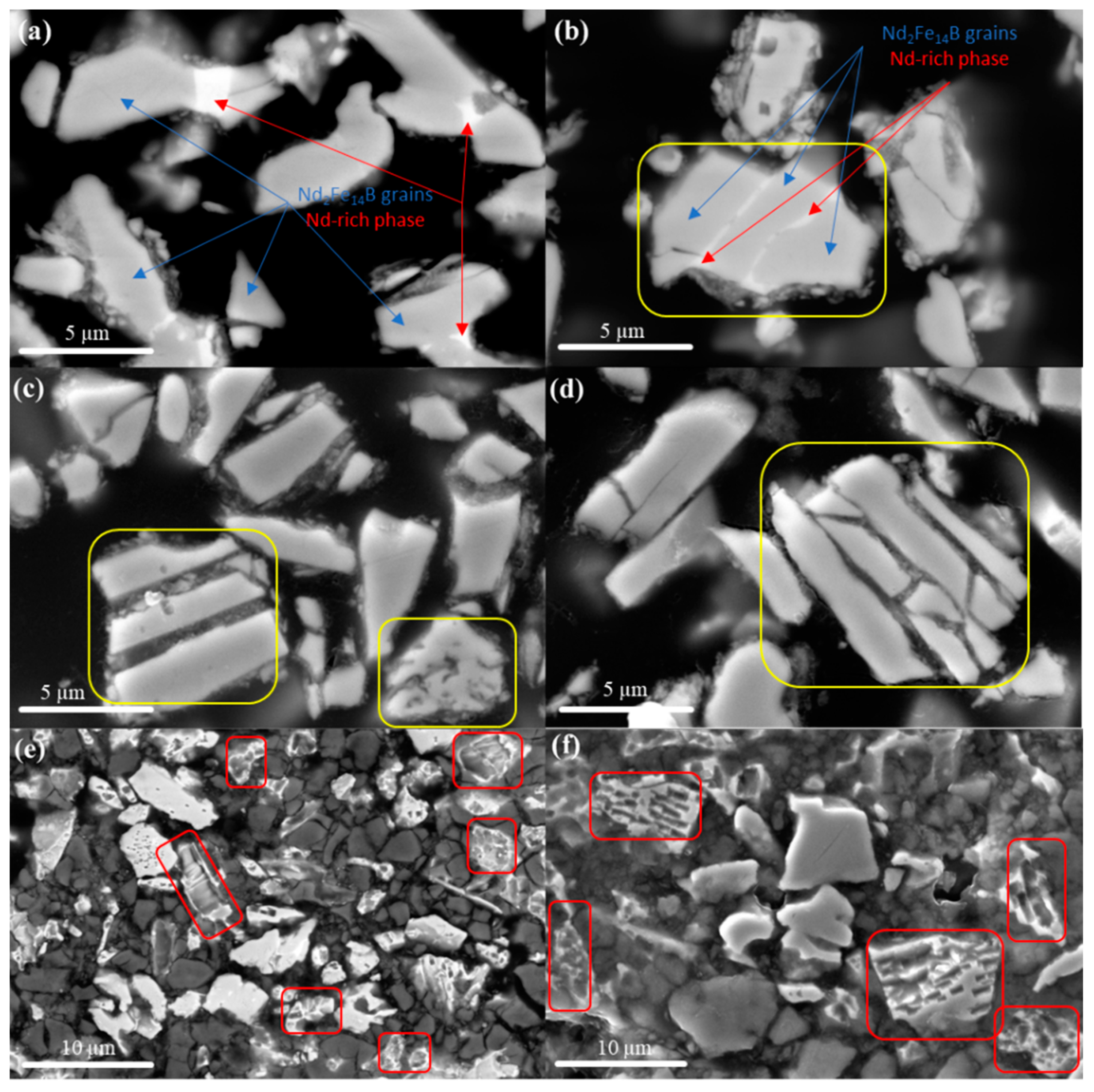
3.2. Microstructure Analysis of Non-Leached and Leached Nd-Fe-B Powders
3.3. Effect of Leaching on the Magnetic Properties of Nd-Fe-B Powders
3.4. ICP-MS Compositional Analysis of Non-Leached and Leached Nd-Fe-B Powders
3.5. Discussion on the Leaching Process of Nd-Fe-B Powders
3.6. Discussion on the Environmental and Economic Impact
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Firdaus, M.; Rhamdhani, M.A.; Durandet, Y.; Rankin, W.J.; McGregor, K. Review of High-Temperature Recovery of Rare Earth (Nd/Dy) from Magnet Waste. J. Sustain. Metall. 2016, 2, 276–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behera, S.S.; Parhi, P.K. Leaching kinetics study of neodymium from the scrap magnet using acetic acid. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2016, 160, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elwert, T.; Goldmann, D.; Römer, F.; Buchert, M.; Merz, C.; Schueler, D.; Sutter, J. Current developments and challenges in the recycling of key components of (Hybrid) electric vehicles. Recycling 2016, 1, 25–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeki, T.; Akahori, T.; Miyamoto, Y.; Kyoi, M.; Okamoto, M.; Okabe, T.H.; Hiroshige, Y.; Nemoto, T. Environment-Friendly Recycling Process for Rare Earth Metals in End-of-Life Electric Products. In Rare Metal Technology; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2014; pp. 103–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, Y.; Guo, S.; Jiang, L.; Tang, K.; Ding, W. Extraction of Rare Earth Elements from Permanent Magnet Scraps by FeO–B2O3 Flux Treatment. J. Sustain. Metall. 2015, 1, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakotnik, M.; Harris, I.R.; Williams, A.J. Multiple recycling of NdFeB-type sintered magnets. J. Alloys Compd. 2009, 469, 314–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombardo, G.; Ebin, B.; Steenari, B.-M.; Alemrajabi, M.; Karlsson, I.; Petranikova, M. Comparison of the effects of incineration, vacuum pyrolysis and dynamic pyrolysis on the composition of NMC-lithium battery cathode-material production scraps and separation of the current collector. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2021, 164, 105142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borra, C.R.; Pontikes, Y.; Binnemans, K.; Van Gerven, T. Leaching of rare earths from bauxite residue (red mud). Miner. Eng. 2015, 76, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Önal, M.A.R.; Borra, C.R.; Guo, M.; Blanpain, B.; Van Gerven, T. Recycling of NdFeB Magnets Using Sulfation, Selective Roasting, and Water Leaching. J. Sustain. Metall. 2015, 1, 199–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, H.S.; Kim, C.J.; Chung, K.W.; Lee, S.J.; Joe, A.R.; Shin, Y.H.; Lee, S.I.; Yoo, S.J.; Kim, J.G. Leaching kinetics of neodymium in sulfuric acid from E-scrap of NdFeB permanent magnet. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2014, 31, 706–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.H.; Chen, Y.J.; Liao, C.H.; Popuri, S.R.; Tsai, S.L.; Hung, C.E. Selective leaching process for neodymium recovery from scrap Nd-Fe-B magnet. Metall. Mater. Trans. A Phys. Metall. Mater. Sci. 2013, 44, 5825–5833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parhi, P.K.; Sethy, T.R.; Rout, P.C.; Sarangi, K. Separation and recovery of neodymium and praseodymium from permanent magnet scrap through the hydrometallurgical route. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2016, 51, 2232–2241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Önal, M.A.R.; Aktan, E.; Borra, C.R.; Blanpain, B.; Van Gerven, T.; Guo, M. Recycling of NdFeB magnets using nitration, calcination and water leaching for REE recovery. Hydrometallurgy 2017, 167, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auerbach, R.; Bokelmann, K.; Stauber, R.; Gutfleisch, O.; Schnell, S.; Ratering, S. Critical raw materials—Advanced recycling technologies and processes: Recycling of rare earth metals out of end of life magnets by bioleaching with various bacteria as an example of an intelligent recycling strategy. Miner. Eng. 2019, 134, 104–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuura, Y.; Hirosawa, S.; Yamamoto, H.; Fujimura, S.; Sagawa, M.; Osamura, K. Phase Diagram of the Nd-Fe-B Ternary System. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 1985, 24, L635–L637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holc, J.; Beseničar, S.; Kolar, D. A study of Nd2Fe14B and a neodymium-rich phase in sintered NdFeB magnets. J. Mater. Sci. 1990, 25, 215–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fidler, J.; Schrefl, T. Overview of Nd-Fe-B magnets and coercivity (invited). J. Appl. Phys. 1996, 79, 5029–5034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Sturm, S.; Samardzija, Z.; Scancar, J.; Markovic, K.; Rozman, K.Z.; Rozman, K.Z. A facile method for the simultaneous recovery of rare-earth elements and transition metals from Nd-Fe-B magnets. Green Chem. 2020, 22, 1105–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Strum, S.; Rozman, K.Z. A Method for Selective Recovery of Rare Earth Elements from Nd-Fe-B Magnet Scraps Based on Electrolysis * EP003795704A1 *. 2021. Available online: https://data.epo.org/publication-server/document?iDocId=6494644&iFormat=0 (accessed on 1 November 2022).
- Laatikainen, M.; Makarova, I.; Sainio, T.; Repo, E. Selective acid leaching of rare earth elements from roasted NdFeB magnets. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 278, 119571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gergoric, M.; Ravaux, C.; Steenari, B.M.; Espegren, F.; Retegan, T. Leaching and recovery of rare-earth elements from neodymium magnet waste using organic acids. Metals 2018, 8, 721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimiabeigi, M.; Sheridan, R.S.; Widmer, J.D.; Walton, A.; Farr, M.; Scholes, B.; Harris, I.R. Production and Application of HPMS Recycled Bonded Permanent Magnets for a Traction Motor Application. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2018, 65, 3795–3804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, A.J.; McGuiness, P.J.; Harris, I.R. Mass spectrometer hydrogen desorption studies on some hydrided NdFeB-type alloys. J. Less-Common Met. 1991, 171, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fredericci, C.; de Campos, M.F.; Braga, A.P.V.; Nazarre, D.J.; Martin, R.V.; Landgraf, F.J.G.; Périgo, E.A. Nd-enriched particles prepared from NdFeB magnets: A potential separation route. J. Alloys Compd. 2014, 615, 410–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verdier, M.; Morros, J.; Pere, D.; Harris, I.R. Hydrogen Absorption Behaviours of Some Nd-Fe-B-Type Alloys. IEEE Trans. Magn. 1994, 30, 660–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardi, J.; Fidler, J.; Sagawa, M.; Hirose, Y. Microstructural analysis of strip cast Nd-Fe-B alloys for high (BH)max magnets. J. Appl. Phys. 1998, 83, 6396–6398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomše, T. Novel Multicomponent Nd-Fe-B Permanent Magnets. Ph.D. Thesis, Jožef Stefan International Postgraduate School, Ljubljana, Slovenia, 2018. Available online: https://plus.cobiss.net/cobiss/si/en/bib/294845696 (accessed on 15 October 2022).
- Banda, R.; Jeon, H.S.; Lee, M.S. Separation of Nd from mixed chloride solutions with Pr by extraction with saponified PC 88A and scrubbing. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2015, 21, 436–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandian, S.; Chandrasekaran, V.; Markandeyulu, G.; Iyer, K.J.L.; Rao, K.V.S.R. Effect of Al, Cu, Ga, Nb additions on the magnetic properties and microstructural features of sintered NdFeB. J. Appl. Phys. 2002, 92, 6082–6086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binnemans, K.; Jones, P.T.; Blanpain, B.; Van Gerven, T.; Yang, Y.; Walton, A.; Buchert, M. Recycling of rare earths: A critical review. J. Clean. Prod. 2013, 51, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Walton, A.; Sheridan, R.; Güth, K.; Gauß, R.; Gutfleisch, O.; Buchert, M.; Steenari, B.-M.; Van Gerven, T.; Jones, P.T.; et al. REE Recovery from End-of-Life NdFeB Permanent Magnet Scrap: A Critical Review. J. Sustain. Metall. 2017, 3, 122–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gergoric, M.; Ekberg, C.; Foreman, M.R.S.J.; Steenari, B.M.; Retegan, T. Characterization and Leaching of Neodymium Magnet Waste and Solvent Extraction of the Rare-Earth Elements Using TODGA. J. Sustain. Metall. 2017, 3, 638–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesan, P.; Hoogerstraete, T.V.; Hennebel, T.; Binnemans, K.; Sietsma, J.; Yang, Y. Selective electrochemical extraction of REEs from NdFeB magnet waste at room temperature. Green Chem. 2018, 20, 1065–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesan, P.; Hoogerstraete, T.V.; Binnemans, K.; Sun, Z.; Sietsma, J.; Yang, Y. Selective Extraction of Rare-Earth Elements from NdFeB Magnets by a Room-Temperature Electrolysis Pretreatment Step. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 9375–9382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schultz, L.; El-Aziz, A.M.; Barkleit, G.; Mummert, K. Corrosion behaviour of Nd-Fe-B permanent magnetic alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 1999, 267, 307–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makarova, I.; Soboleva, E.; Osipenko, M.; Kurilo, I.; Laatikainen, M.; Repo, E. Electrochemical leaching of rare-earth elements from spent NdFeB magnets. Hydrometallurgy 2020, 192, 105264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, J.; Cui, X.; Liu, X.; Cui, H.; Xue, Z.; Jia, Z.; Wang, C.; Ma, J.; Gong, S. Corrosion behavior of NdFeB sintered magnets in HNO3–HF acid mixture solution. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2015, 162, 518–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Song, Z.L.; Mao, S.D.; Yang, H.X. Study on the corrosion behavior of NdFeB permanent magnets in nitric acid and oxalic acid solutions with electrochemical techniques. Mater. Corros. 2011, 62, 346–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gergorić, M. Hydrometallurgical Treatment of Neodymium Magnet Waste; Chalmers University of Technology: Gothenburg, Sweden, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Ismailova, A.G.; Akanova, G.Z.; Kamysbayev, D.K. Acid dissolution of neodymium magnet Nd-Fe-B in different conditions, Bull. Karaganda Univ. Chem. Ser. 2021, 104, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astuti, W.; Hirajima, T.; Sasaki, K.; Okibe, N. Comparison of atmospheric citric acid leaching kinetics of nickel from different Indonesian saprolitic ores. Hydrometallurgy 2016, 161, 138–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonald, R.G.; Whittington, B.I. Atmospheric acid leaching of nickel laterites review. Part I. Sulphuric acid technologies. Hydrometallurgy 2008, 91, 35–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svoronos, D.-R.; Boulhassa, S.; Guillaumont, R.; Quarton, M. Citric complexes and neodymium citrate: NdCit, 3H2O. J. Inorg. Nucl. Chem. 1981, 43, 1541–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, W.; Zhang, L.; Liu, Q.; Shan, A.; Wu, J.; Komuro, M. Dependence of the crystal structure of the Nd-rich phase on oxygen content in an Nd-Fe-B sintered magnet. Scr. Mater. 2008, 59, 179–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodcock, T.G.; Gutfleisch, O. Multi-phase EBSD mapping and local texture analysis in NdFeB sintered magnets. Acta Mater. 2011, 59, 1026–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sepehri-Amin, H.; Ohkubo, T.; Shima, T.; Hono, K. Grain boundary and interface chemistry of an Nd-Fe-B-based sintered magnet. Acta Mater. 2012, 60, 819–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benecki, W.T.; Claggett, T.K.; Trout, S.R. Permanent Magnets 2010-2020: A Comprehensive Overview of the Global Permanent Magnet Industry; Walter T. Benecki LLC: Highland Beach, FL, USA, 2010; Available online: https://www.waltbenecki.com/pub-pm.html (accessed on 27 September 2022).
- Du, X.; Graedel, T.E. Global rare earth in-use stocks in NdFeB permanent magnets. J. Ind. Ecol. 2011, 15, 836–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakotnik, M.; Tudor, C.O.; Peiró, L.T.; Afiuny, P.; Skomski, R.; Hatch, G.P. Analysis of energy usage in Nd–Fe–B magnet to magnet recycling, Environ. Technol. Innov. 2016, 5, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Sample | JM-NDG | JM-NDG-1M CIT | JM-NDG-1M-NIT | JM-DG | JM-DG-1M-CIT | JM-DG-1M-NIT | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Element | Average | Stdev | Average | Stdev | Average | Stdev | Average | Stdev | Average | Stdev | Average | Stdev |
| Nd | 30.26 | 0.49 | 26.22 | 1.05 | 30.12 | 0.75 | 30.28 | 0.53 | 26.76 | 1.90 | 30.35 | 0.61 |
| Dy | 0.95 | 0.01 | 0.98 | 0.01 | 0.93 | 0.03 | 0.93 | 0.01 | 1.00 | 0.04 | 0.95 | 0.02 |
| Fe | 63.95 | 0.86 | 68.21 | 1.89 | 64.33 | 0.98 | 64.08 | 1.00 | 67.34 | 5.60 | 63.94 | 1.41 |
| Pr | 0.56 | 0.01 | 0.45 | 0.01 | 0.54 | 0.02 | 0.55 | 0.01 | 0.49 | 0.02 | 0.56 | 0.01 |
| B | 0.88 | 0.02 | 0.89 | 0.01 | 0.85 | 0.02 | 0.86 | 0.01 | 0.90 | 0.02 | 0.88 | 0.02 |
| Cu | 0.15 | 0.00 | 0.17 | 0.00 | 0.14 | 0.00 | 0.14 | 0.00 | 0.15 | 0.01 | 0.15 | 0.00 |
| Co | 2.92 | 0.04 | 2.84 | 0.02 | 2.78 | 0.09 | 2.84 | 0.03 | 3.04 | 0.15 | 2.87 | 0.03 |
| Ga | 0.18 | 0.00 | 0.09 | 0.00 | 0.17 | 0.01 | 0.17 | 0.00 | 0.15 | 0.01 | 0.17 | 0.00 |
| Al | 0.14 | 0.00 | 0.15 | 0.01 | 0.14 | 0.00 | 0.14 | 0.00 | 0.16 | 0.02 | 0.14 | 0.00 |
| Total | 100 | 1.4 | 100 | 3 | 100 | 2 | 100 | 2 | 100 | 8 | 100 | 2 |
| Powder Type | Nd/Fe | Percent Reduction |
|---|---|---|
| JM-NDG | 0.47 | N/A |
| JM-NDG—1M citric acid leached | 0.38 | −18.8 |
| JM-NDG—1M nitric acid leached | 0.47 | −1.0 |
| JM-DG | 0.47 | N/A |
| JM-DG—1M citric acid leached | 0.40 | −15.9 |
| JM-DG—1M nitric acid leached | 0.47 | +0.4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Khoshsima, S.; Vidmar, J.; Samardžija, Z.; Tomše, T.; Kušter, M.; Mishra, A.; Šturm, S.; Žužek, K. Environmentally Friendly Approach for Nd2Fe14B Magnetic Phase Extraction by Selective Chemical Leaching: A Proof-of-Concept Study. Materials 2023, 16, 5181. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16145181
Khoshsima S, Vidmar J, Samardžija Z, Tomše T, Kušter M, Mishra A, Šturm S, Žužek K. Environmentally Friendly Approach for Nd2Fe14B Magnetic Phase Extraction by Selective Chemical Leaching: A Proof-of-Concept Study. Materials. 2023; 16(14):5181. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16145181
Chicago/Turabian StyleKhoshsima, Sina, Janja Vidmar, Zoran Samardžija, Tomaž Tomše, Monika Kušter, Amit Mishra, Sašo Šturm, and Kristina Žužek. 2023. "Environmentally Friendly Approach for Nd2Fe14B Magnetic Phase Extraction by Selective Chemical Leaching: A Proof-of-Concept Study" Materials 16, no. 14: 5181. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16145181
APA StyleKhoshsima, S., Vidmar, J., Samardžija, Z., Tomše, T., Kušter, M., Mishra, A., Šturm, S., & Žužek, K. (2023). Environmentally Friendly Approach for Nd2Fe14B Magnetic Phase Extraction by Selective Chemical Leaching: A Proof-of-Concept Study. Materials, 16(14), 5181. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16145181







