Effect of Ball-Milling Process on Microwave Absorption Behaviors of Flaky Carbonyl Iron Powders
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Flaky CIP
2.3. Selection of Ball-Milling Parameters
2.4. Test and Characterizations
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Effect of Ball-Milling Parameters on Microstructure of F-CIPs
3.2. Effect of Ball-Milling Parameters on Phase Composition of F-CIPs
3.3. Effect of Ball-Milling Parameters on EM Properties of F-CIPs
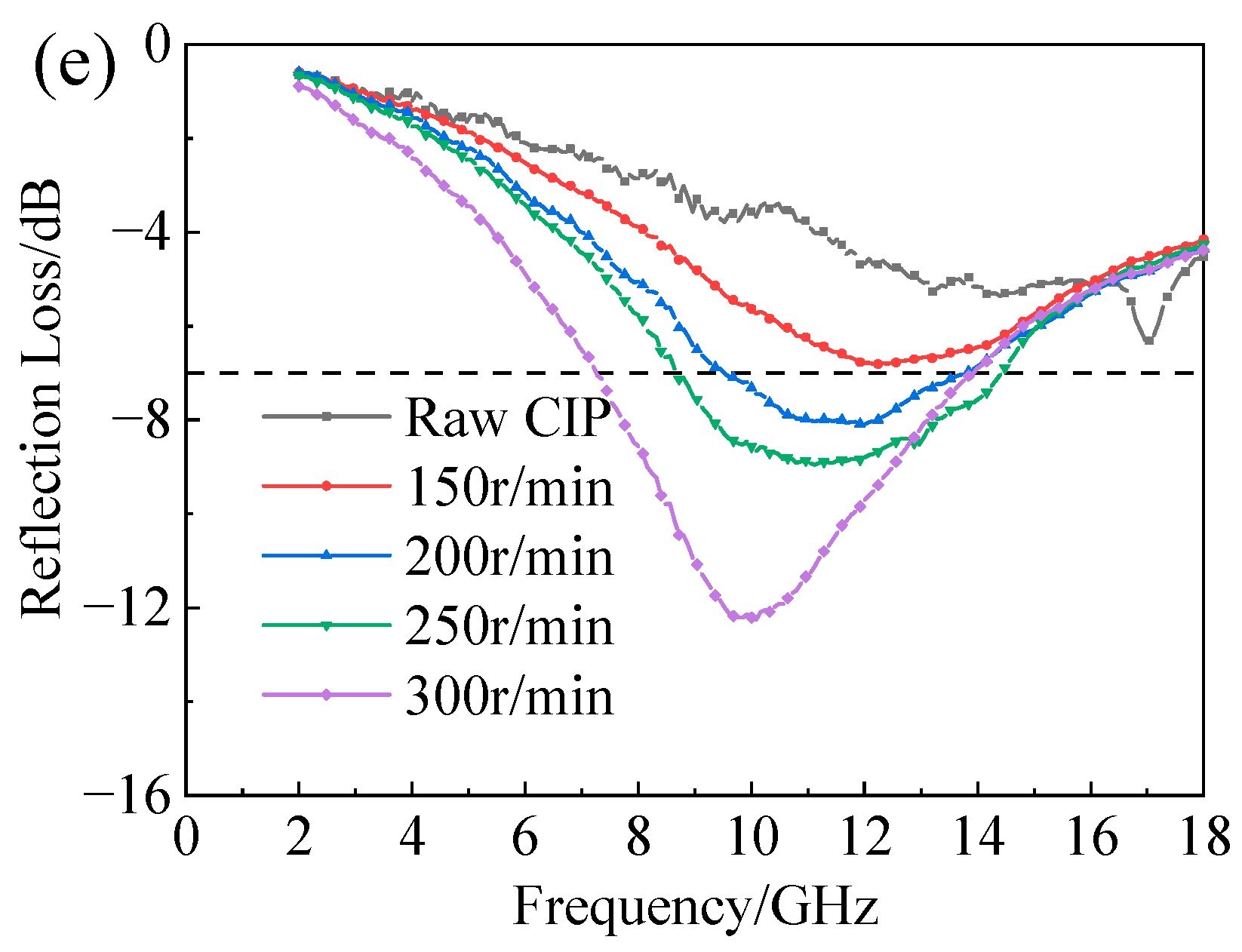
3.4. Effect of Ball-Milling Parameters on Absorbing Behaviors of F-CIPs
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Meisak, D.; Plyushch, A.; Macutkevič, J.; Grigalaitis, R.; Sokal, A.; Lapko, K.N.; Selskis, A.; Kuzhir, P.P.; Banys, J. Effect of Temperature on Shielding Efficiency of Phosphate-Bonded Cofe2O4–Xbatio3 Multiferroic Composite Ceramics in Microwaves. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 24, 1939–1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Sun, C.; Zhou, H.; Huang, H.; Chen, Y.; Duan, X.; Huang, S.; Li, J. Extremely Low-Frequency Electromagnetic Field Impairs the Development of Honeybee (Apis Cerana). Animals 2022, 12, 2420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Xu, Y.; Zheng, D.; Zhou, L.; Li, X.; Liu, L. Fabrication and Absorbing Property of the Tower-Like Absorber Based On 3D Printing Process. Phys. B Condens. Matter 2019, 553, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, Z.; Xu, Y.; Wei, F.; Liu, T.; Su, D. Electromagnetic Property of a Novel Gradient Honeycomb Composite Fabricated by 3D Forming. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2020, 493, 165742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Li, G.; Li, H.; Lü, L.; He, L. Ceramsite Containing Iron Oxide and its Use as Functional Aggregate in Microwave Absorbing Cement-Based Materials. J. Wuhan Univ. Technol. Mater. Sci. Ed. 2018, 33, 133–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Xie, B.; Li, H.; Tian, R.; Zhang, Q. Mechanical Properties and Electromagnetic Absorption Characteristics of Foam Cement-Based Absorbing Materials. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 330, 127221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Huang, J.; Song, L.; Yi, M. A Study on Zoning Coating Method of Absorbing Materials for Stealth Aircraft. Optik 2020, 208, 163912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayalakshmi, C.G.; Inamdar, A.; Anand, A.; Kandasubramanian, B. Polymer Matrix Composites as Broadband Radar Absorbing Structures for Stealth Aircrafts. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2018, 136, 47241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Wei, C.; Tai, N. Composition Tunable Manganese-Doped Magnetite Microwave Absorber Composites for Radio Frequency Identification Communication. Ceram. Int. 2022, 48, 15105–15115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, F.; Zhang, J.; Yan, B.; Gu, Y.; Jiang, K. Preparation and Properties of Epoxy Matrix Composite Absorbing Materials. Surf. Technol. 2022, 51, 325–334. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Tian, X.; Wang, J.; Ma, L.; Li, C.; Qin, Z.; Qu, S. Ternary Heterogeneous Core-Shell Structure Cip@Ppy/Mwcnts Composites for Broadband Microwave Absorption. Diam. Relat. Mat. 2022, 130, 109420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Wang, Z.; Shi, R.; Pei, J.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, X. EM and Microwave Absorption Properties of Ti Doped Li–Zn Ferrites. J. Alloy. Compd. 2019, 805, 934–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, J.; Kang, Y. EM Wave Absorbing Properties of Ni-Zn Ferrite Powder–Epoxy Composites in Ghz Range. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2020, 513, 167075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vovchenko, L.L.; Len, T.A.; Matzui, L.Y.; Yakovenko, O.S.; Oliynyk, V.V.; Zagorodnii, V.V.; Ischenko, O.V. Electrical and Shielding Properties of Epoxy Composites with Combined Fillers (Sio2-Fe2O3)/Cnt and (Sio2-Fe3O4)/Cnt. Appl. Compos. Mater. 2023, 30, 635–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Zhu, Z.; Xiong, C.; Zheng, X.; Lin, Q. The Influence of Different Ni Contents on the Radar Absorbing Properties of Feni Nano Powders. Rsc Adv. 2016, 6, 16413–16418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Dong, Y.; Li, Q.; He, A.; Chang, C.; Wang, X. Enhanced Magnetic Properties of Fe-Based Nanocrystalline Composites by Addition of Carbonyl Iron Powders. Sn Appl. Sci. 2019, 1, 902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, B.; Jiang, X.; Wan, W.; Yin, L.; Agathopoulos, S.; Van Bui, H.; Xie, J.; Zhang, L.; Lu, H.; et al. Silicone-Encapsulated Carbonyl Iron Filler for Corrosion-Resistant EM Shielding. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2022, 282, 125918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, W.; Chen, F.; Luo, H.; Xiong, Y.; Wang, X.; Cheng, Y.; Gong, R. Synthesis of Yolk-Shell Structured Carbonyl Iron@Void@Nitrogen Doped Carbon for Enhanced Microwave Absorption Performance. J. Alloy. Compd. 2020, 812, 152083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, W.; Yang, G.; Bi, S.; Zhang, J.; Hou, Z. Construction of Caterpillar-Like Hierarchically Structured Co/Mno/Cnts Derived From Mno2/Zif-8@Zif-67 for EM Wave Absorption. Carbon 2021, 173, 521–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Li, Q.; Xu, S. Microwave Absorption Properties of Cementitious Composites Containing Carbonyl Iron Powder (Cip) and Fly Ash: Formation and Effect of Cip Core–Shell Structure. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2022, 131, 104559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Hou, X.; Zheng, K.; Yang, P.; Yu, M. Effect of carbonyl iron powder morphology on the absorption properties of microwave. J. Chongqing Univ. 2017, 40, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.; Wang, W.; Long, C.; Li, W.; Guan, J.; Gu, H.; Xu, G. Facile Preparation, Formation Mechanism and Microwave Absorption Properties of Porous Carbonyl Iron Flakes. J. Mater. Chem. C 2014, 2, 3769–3776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walser, R.K.; Win, W.; Valanju, P.M. Shape-Optimized Ferromagnetic Particles with Maximum Theoretical Microwave Susceptibility. IEEE Trans. Magn. 1998, 34, 1390–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Xie, H.; Tao, S.; Zhou, W. Effect of Milling Time on Microwave Absorbing Property ofFeSi Alloy. Mater. Rep. 2018, 32, 2738–2742, 2777. [Google Scholar]
- Zhai, Y.; Zhu, D.; Luo, F.; Nan, H.; Ruan, X. Effects of Milling Time on EM and Microwave Absorbing Properties of Epoxy Resin/FeSiCr Composites. Eng. Plast. Appl. 2020, 48, 13–18. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Huang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wei, S.; Wang, B.; Huang, W.; Xin, W.; Wang, X. Effect of Ball Milling on the Absorption Properties of Fe3O4. Materials 2020, 13, 883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, Y.; Zhu, D.; Zhou, W.; Min, D.; Luo, F. Enhanced Impedance Matching and Microwave Absorption Properties of the Mams by Using Ball-Milled Flaky Carbonyl Iron-Bafe12O19 as Compound Absorbent. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2018, 467, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Xu, B.; Wang, J.; Cai, X. Multivariate parameters regulation of flake carbonyl iron absorbing properties in low-frequency. J. Magn. Mater. Devices 2017, 48, 45–48. [Google Scholar]
- Golchinvafa, S.; Masoudpanah, S.M.; Alamolhoda, S. Ultra-Broadband Feni3/Niznfe2O4/Zno Composite Powders for Microwave Absorption. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2022, 21, 1737–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Wang, J.; Hu, X.; Wang, L.; Fan, Y.; Jiang, W. Construction of Plate–Like Magnetic Heterostructure for Synergistic Microwave Absorption. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2023, 106, 410–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Ma, T.; Chai, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Zhu, M.; Tang, X.; Zhao, X.; Lu, Y.; Lan, Q.; Wang, Z.; et al. Graphene-Based Magnetic Composite Foam with Hierarchically Porous Structure for Efficient Microwave Absorption. Carbon 2023, 207, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, M.; Chen, X. Recent Progress of Nanomaterials for Microwave Absorption. J. Mater. 2019, 5, 503–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Zhou, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Gu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Jiang, K. Microwave Absorption Properties of Carbon Black-Carbonyl Iron/Polylactic Acid Composite Filament for Fused Deposition Modeling. Materials 2022, 15, 5455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, F.; Zhang, J.; Li, P.; Jiang, K. Ultra–Broadband and Wide–Angle Metamaterial Absorber with Carbon Black/Carbonyl Iron Composites Fabricated by Direct–Ink–Write 3D Printing. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2023, 25, 2201236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Dong, Y.; Pan, F.; Xiang, Z.; Liu, Z.; Deng, B.; Zhang, X.; Shi, Z.; Lu, W. Covalent Organic Framework-Derived Hollow Core-Shell Fe/Fe3O4@Porous Carbon Composites with Corrosion Resistance for Lightweight and Efficient Microwave Absorption. Compos. Commun. 2021, 25, 100731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Perez, F.; López-Estrada, S.M.; Tolentino-Hernández, R.V.; Caballero-Briones, F. Carbon-Based Radar Absorbing Materials: A Critical Review. J. Sci. Adv. Mater. Devices 2022, 7, 100454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Drew, M.G.B. A Re-Evaluation of the Mechanism of Microwave Absorption in Film–Part 3: Inverse Relationship. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2022, 290, 126521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, C.; Cao, Y.; Fan, J.; Bai, L.; Ding, F.; Yuan, F. Synthesis of Hollow Carbonyl Iron Microspheres Via Pitting Corrosion Method and their Microwave Absorption Properties. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2013, 270, 432–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
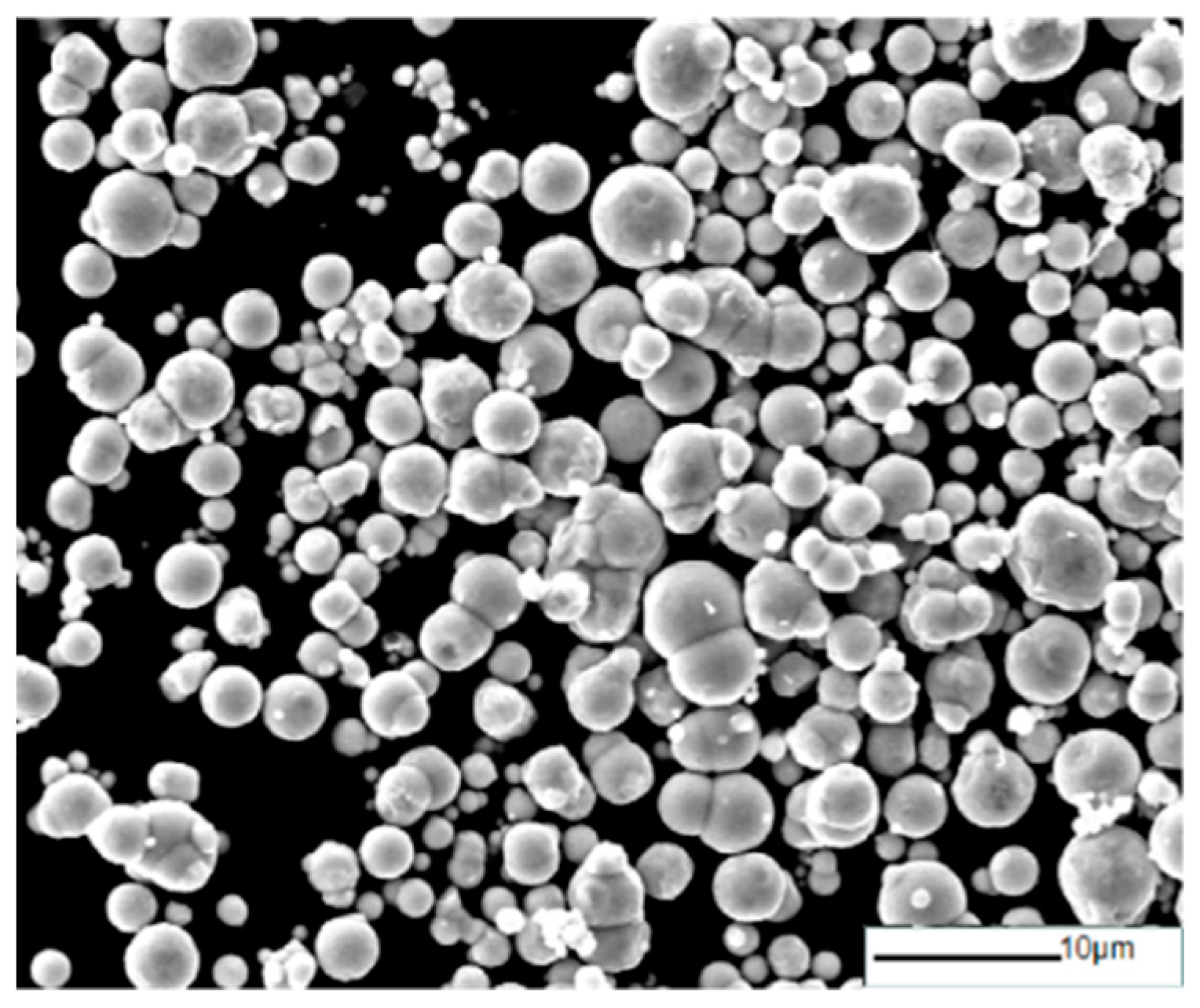


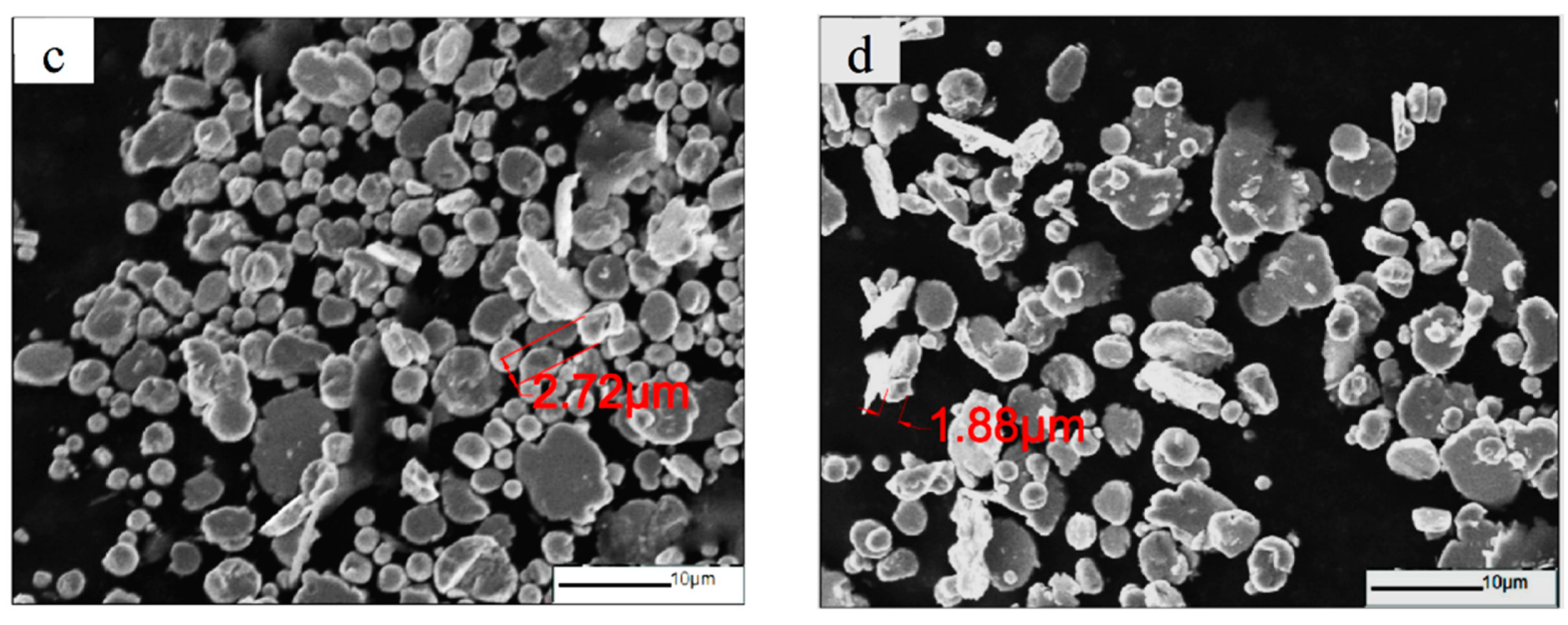
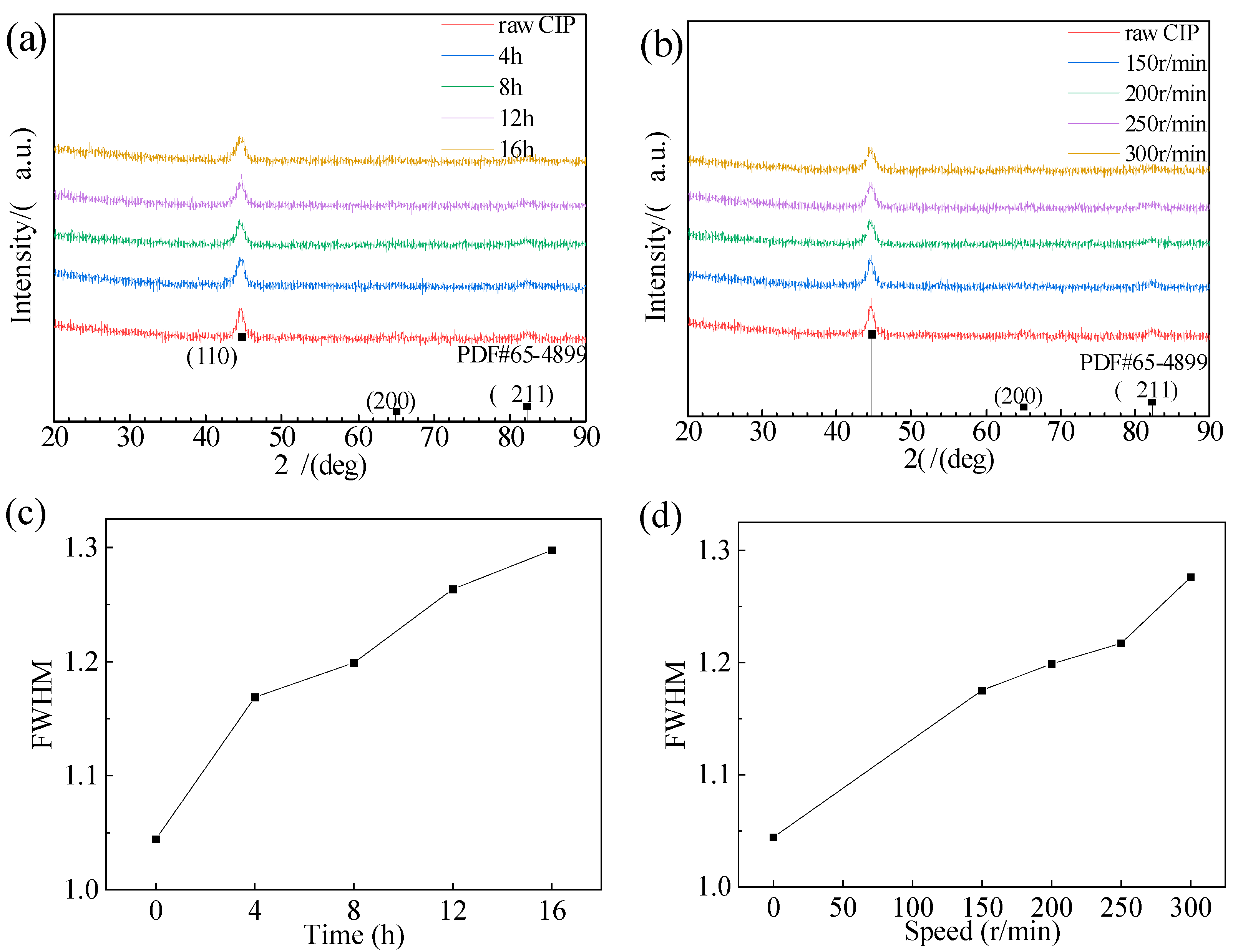
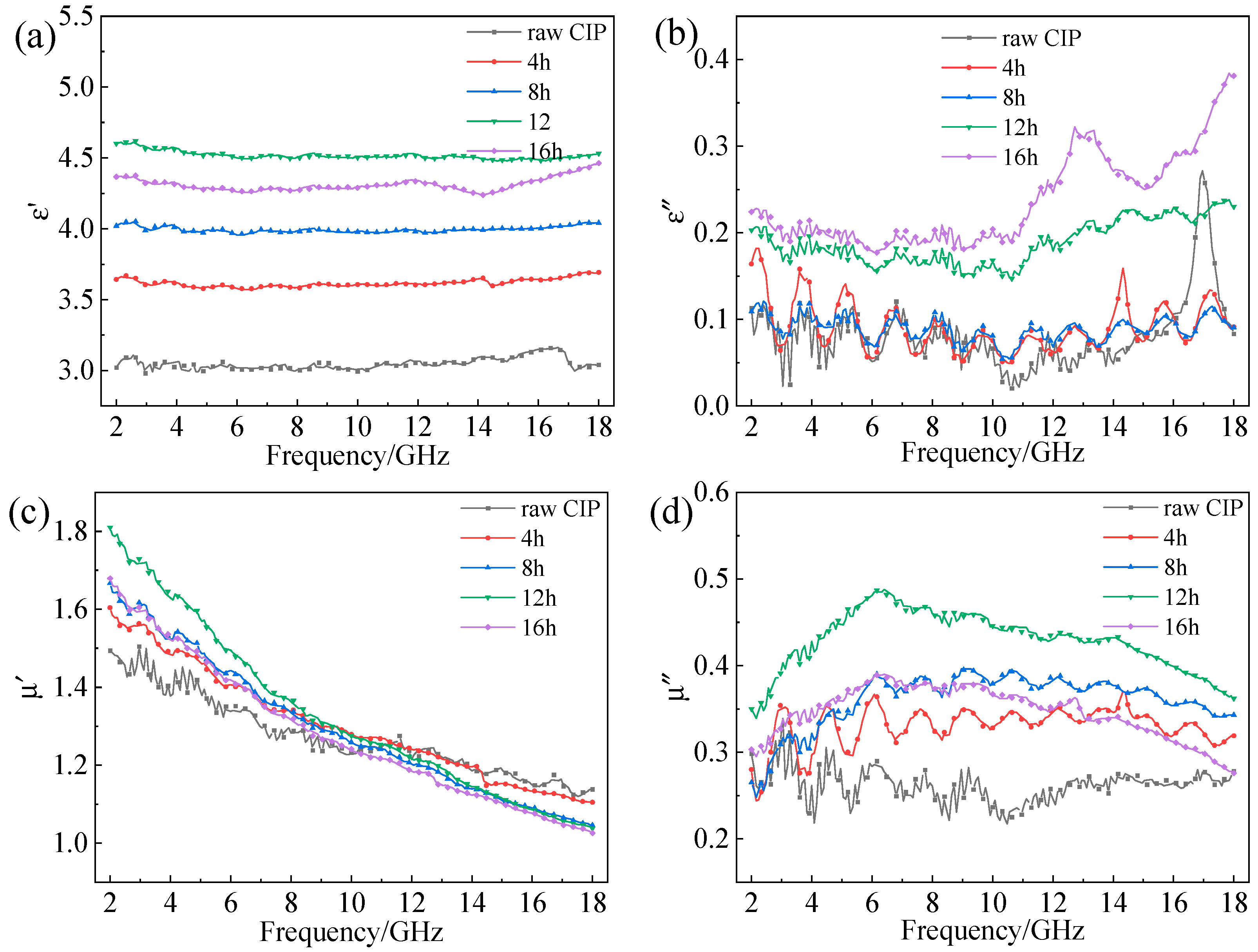
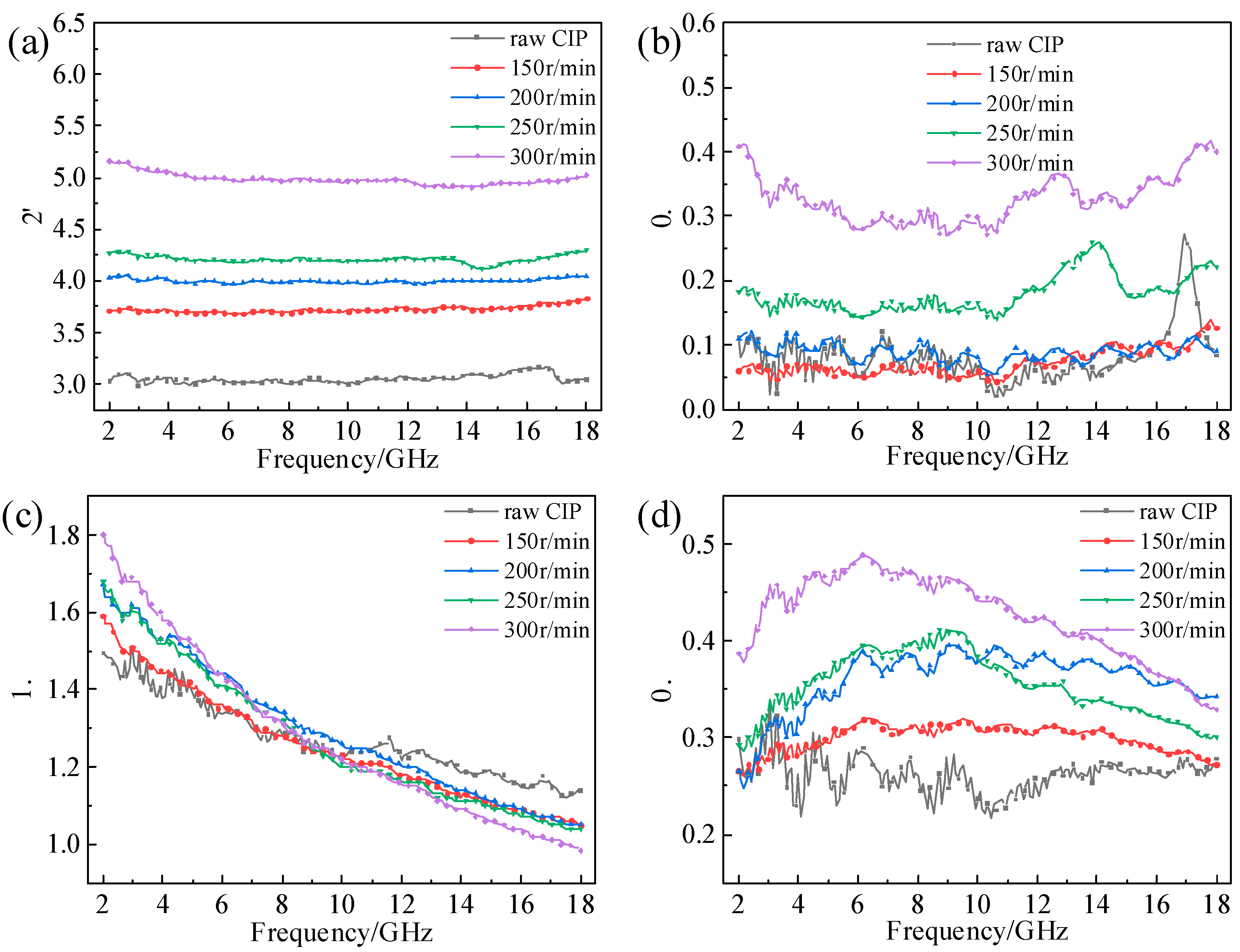
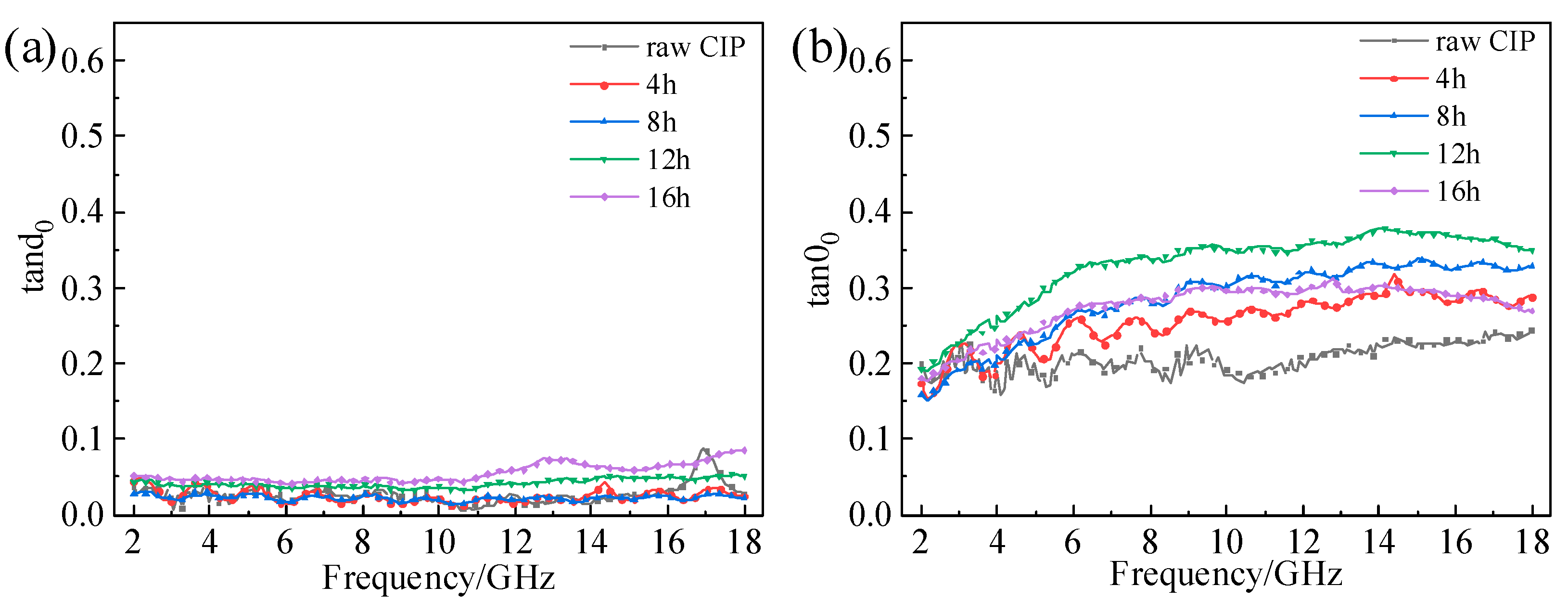

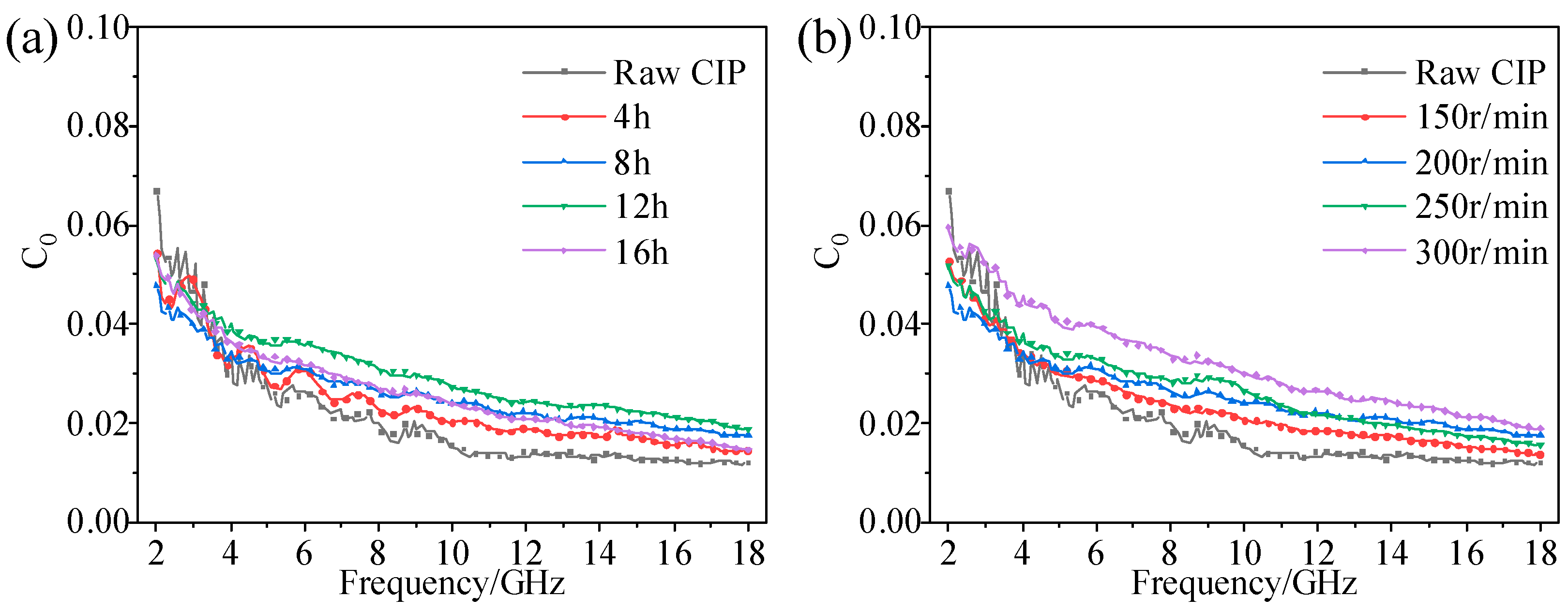
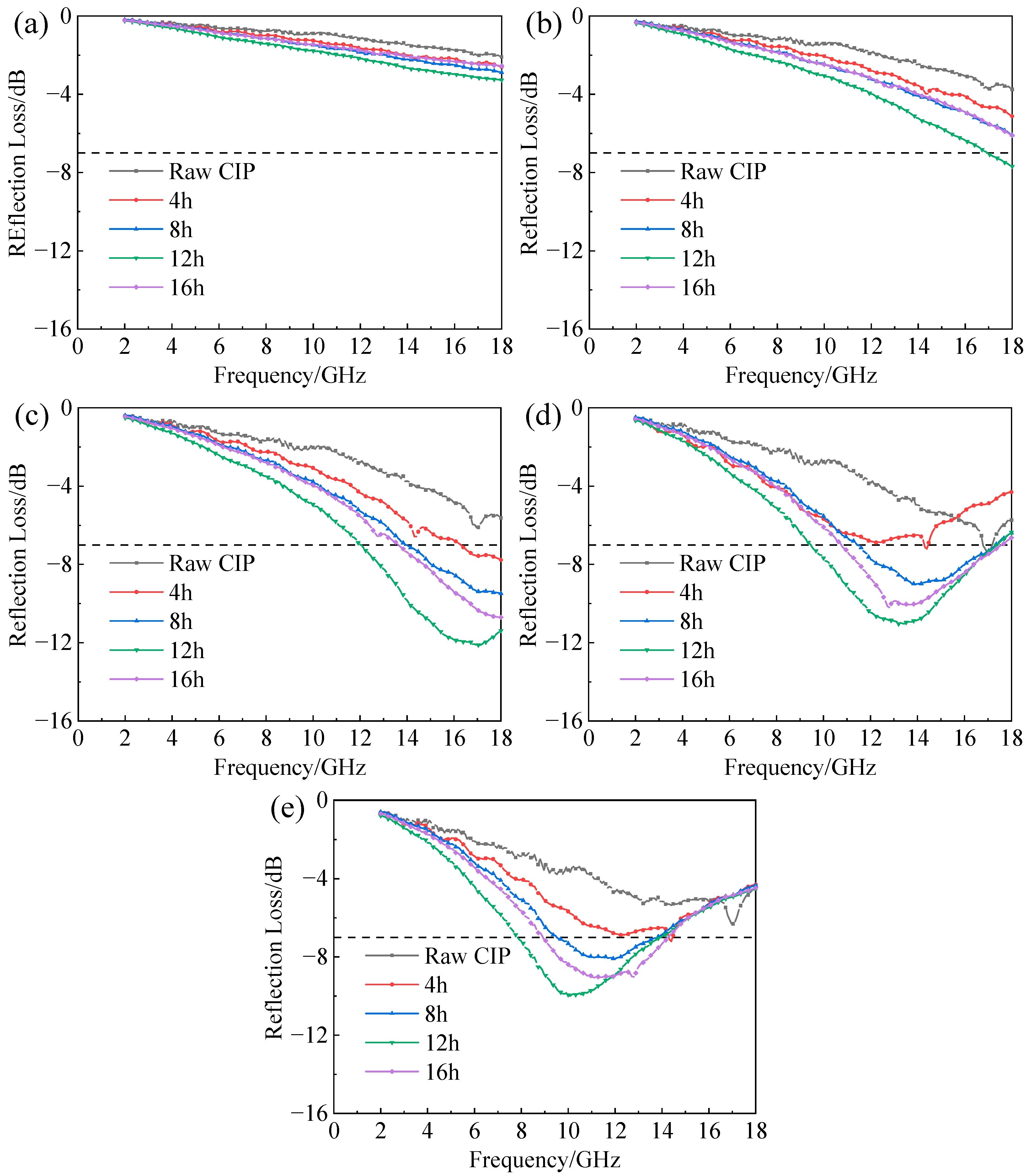


| Time | 4 h | 8 h | 12 h | 16 h |
| rotation speed | 200 r/min | 200 r/min | 200 r/min | 200 r/min |
| Time | 8 h | 8 h | 8 h | 8 h |
| rotation speed | 150 r/min | 200 r/min | 250 r/min | 300 r/min |
| Absorber and Content | EAB/GHz (RL < −10 dB) | Minimum RL/dB | Thickness at Minimum RL/mm | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dendritic CIP (60%) | 5.2 | −47.14 | 2.68 | [19] |
| Porous carbonyl iron flakes (20%) | 2 | −28 | 2 | [20] |
| Hollow carbonyl iron (55.5%) | 3 | −11 | 1 | [38] |
| Flaky CIPs (50%) | 4.5 | −14 | 2 | This work |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, S.; Wang, F.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, J.; Jiang, K. Effect of Ball-Milling Process on Microwave Absorption Behaviors of Flaky Carbonyl Iron Powders. Materials 2023, 16, 4397. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16124397
Yang S, Wang F, Zhang Z, Liu Z, Zhang J, Jiang K. Effect of Ball-Milling Process on Microwave Absorption Behaviors of Flaky Carbonyl Iron Powders. Materials. 2023; 16(12):4397. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16124397
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Siyuan, Fei Wang, Zhe Zhang, Zhiming Liu, Jiliang Zhang, and Kaiyong Jiang. 2023. "Effect of Ball-Milling Process on Microwave Absorption Behaviors of Flaky Carbonyl Iron Powders" Materials 16, no. 12: 4397. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16124397
APA StyleYang, S., Wang, F., Zhang, Z., Liu, Z., Zhang, J., & Jiang, K. (2023). Effect of Ball-Milling Process on Microwave Absorption Behaviors of Flaky Carbonyl Iron Powders. Materials, 16(12), 4397. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16124397






