Effect of Silicon on Dynamic/Static Corrosion Resistance of T91 in Lead–Bismuth Eutectic at 550 °C
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Thermodynamic Calculation
2.3. Structure Observation
2.4. Phase Analysis
2.5. Corrosion Test
2.6. Oxide Film Characterization
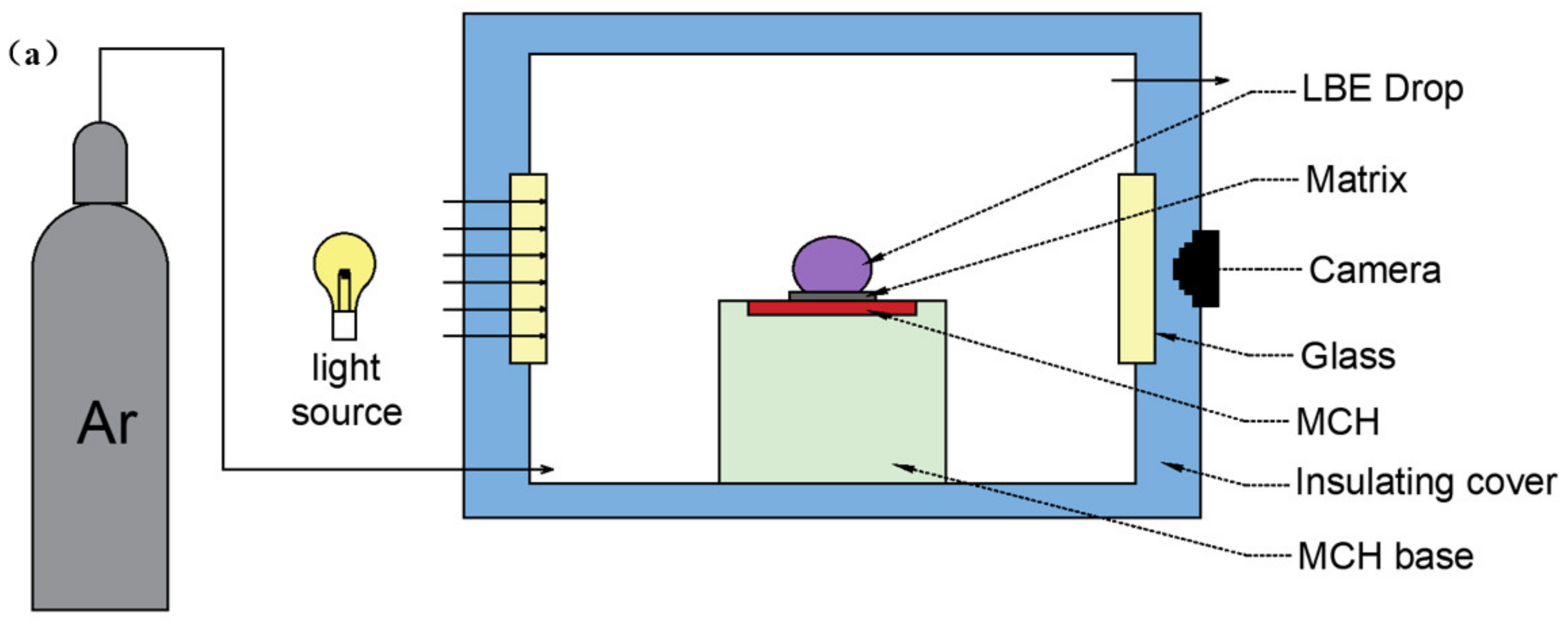
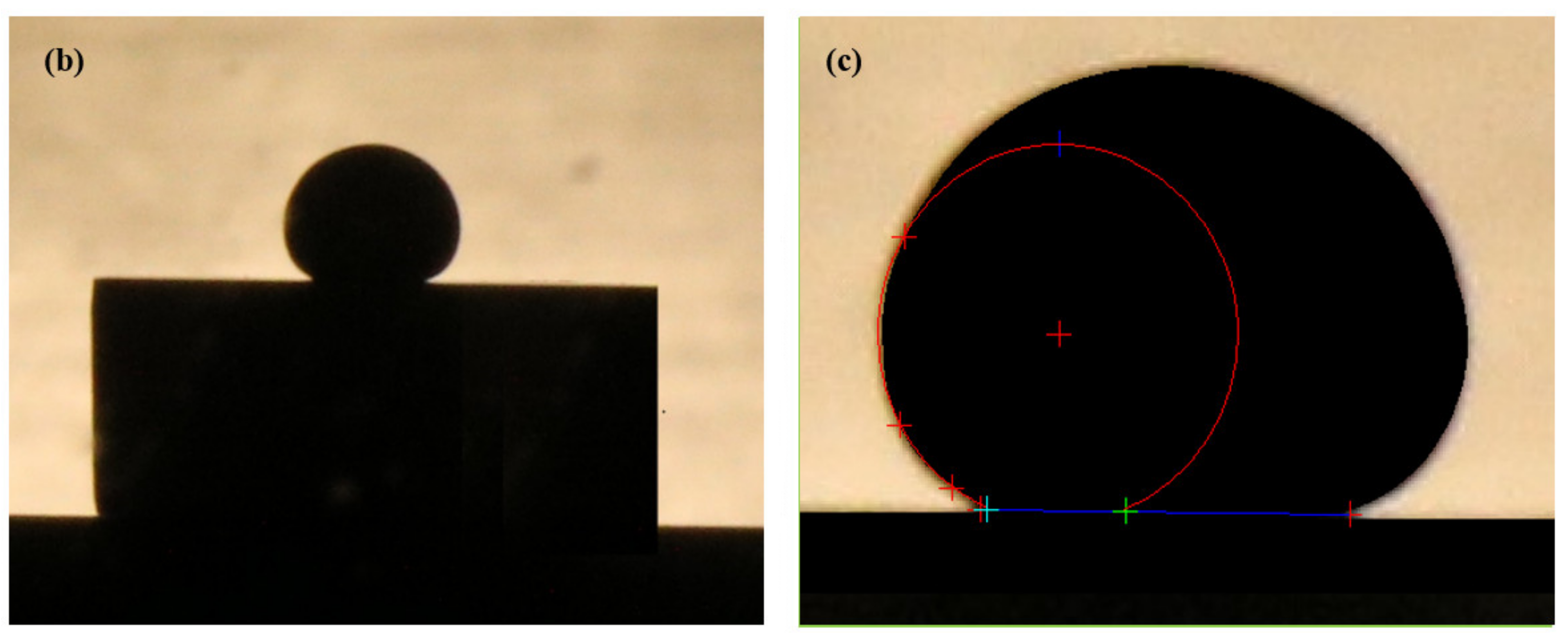
2.7. LBE and Wettability Test
3. Results
3.1. Thermodynamic Calculation
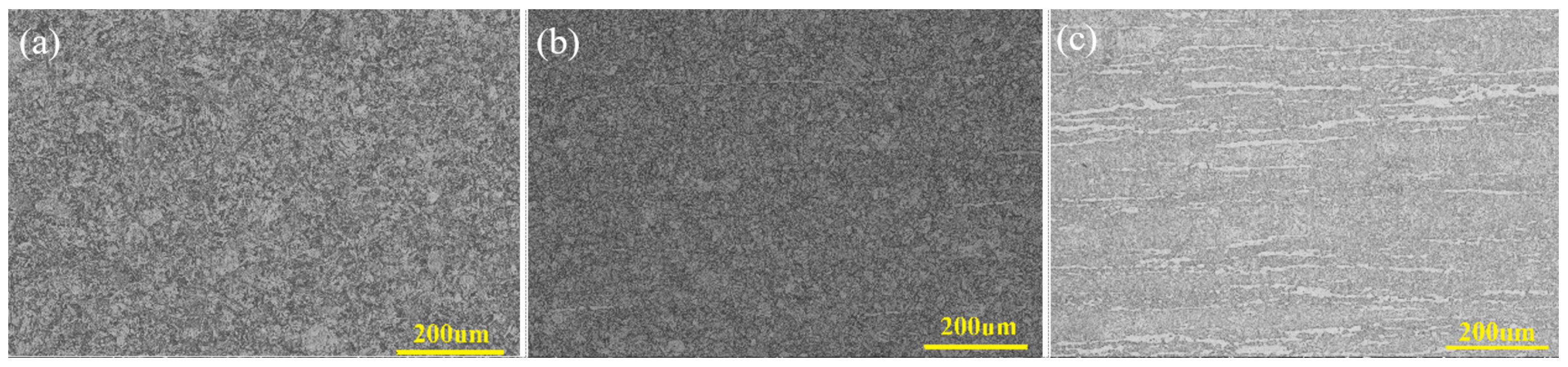
3.2. Structure Observation
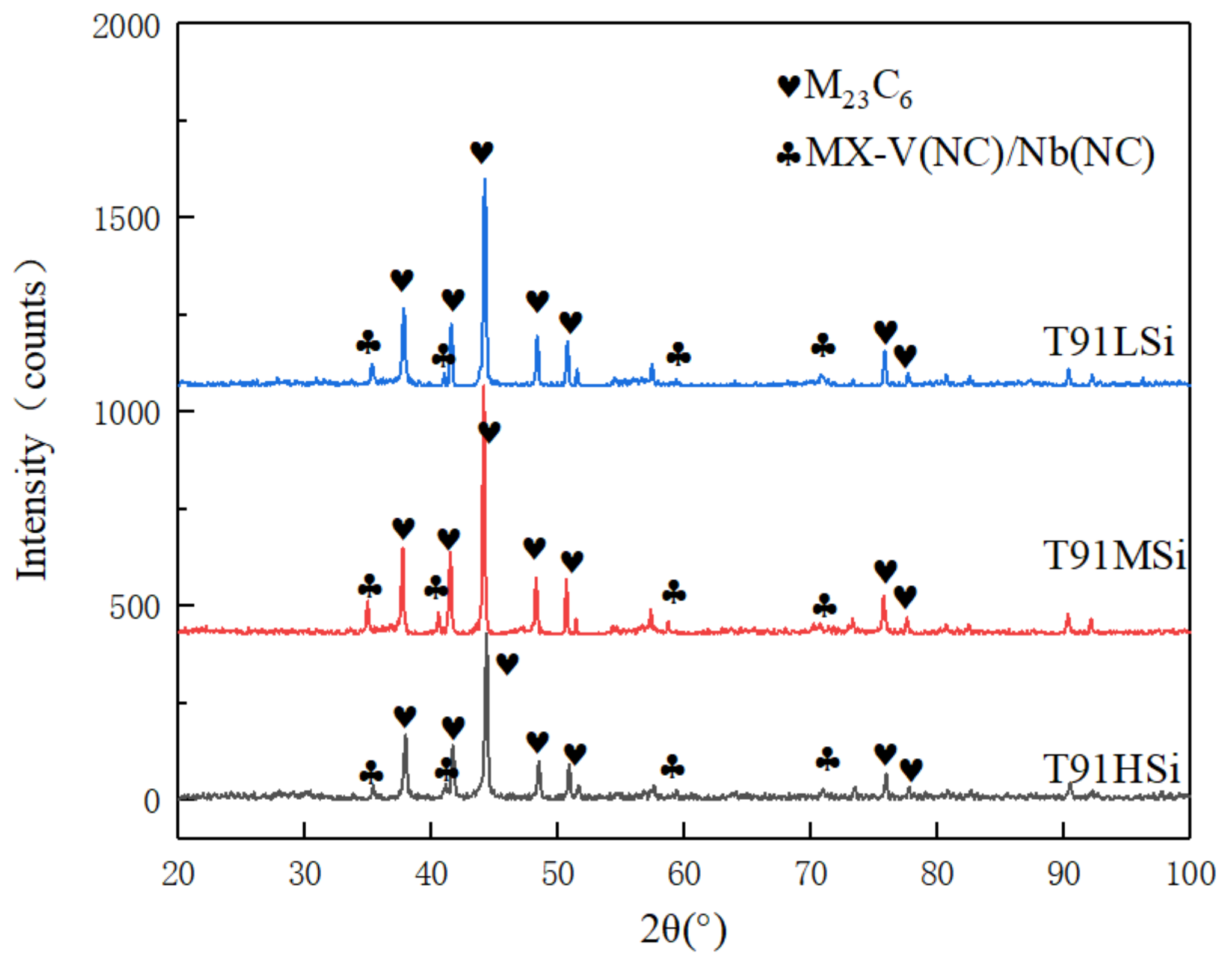
3.3. Phase Analysis
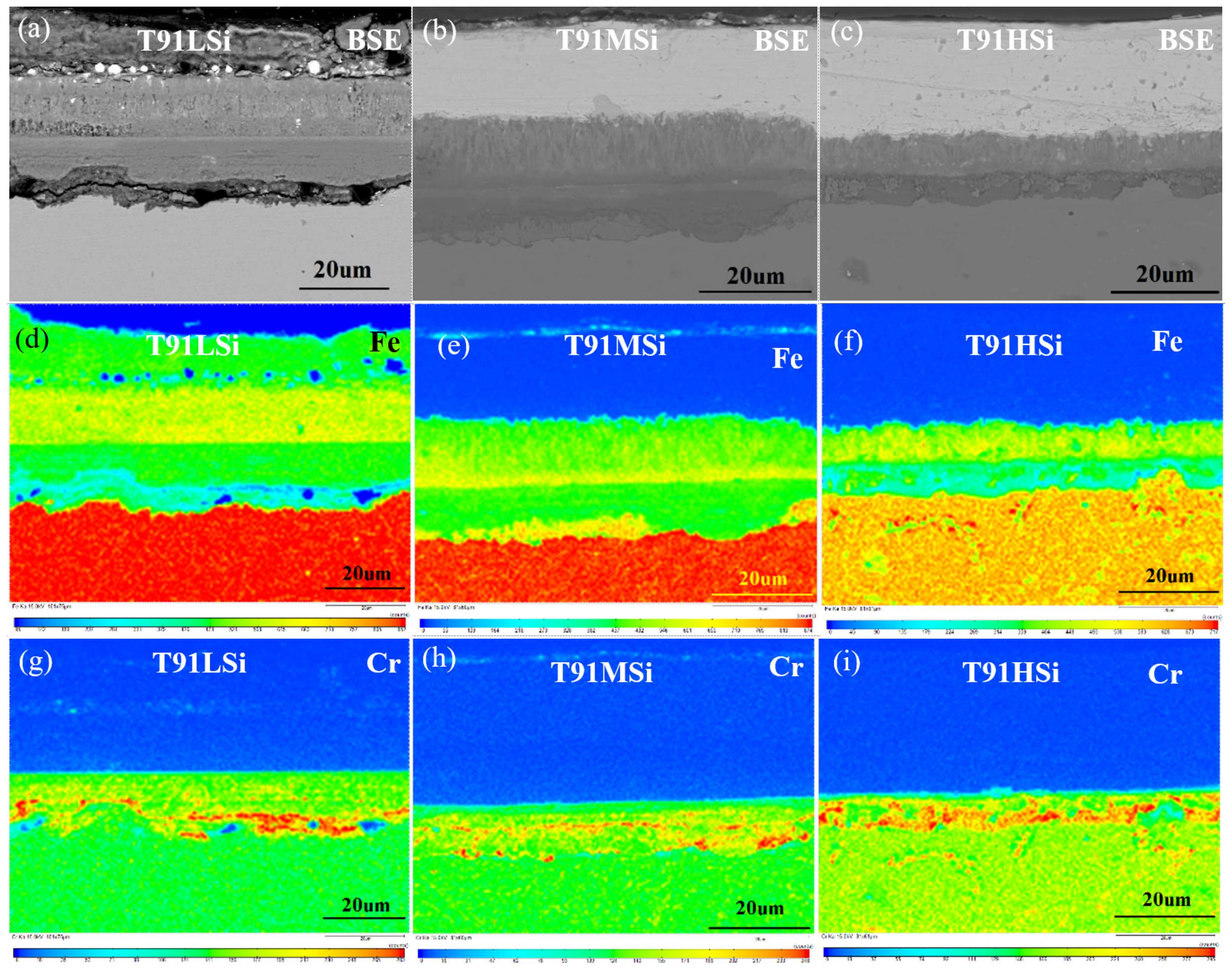
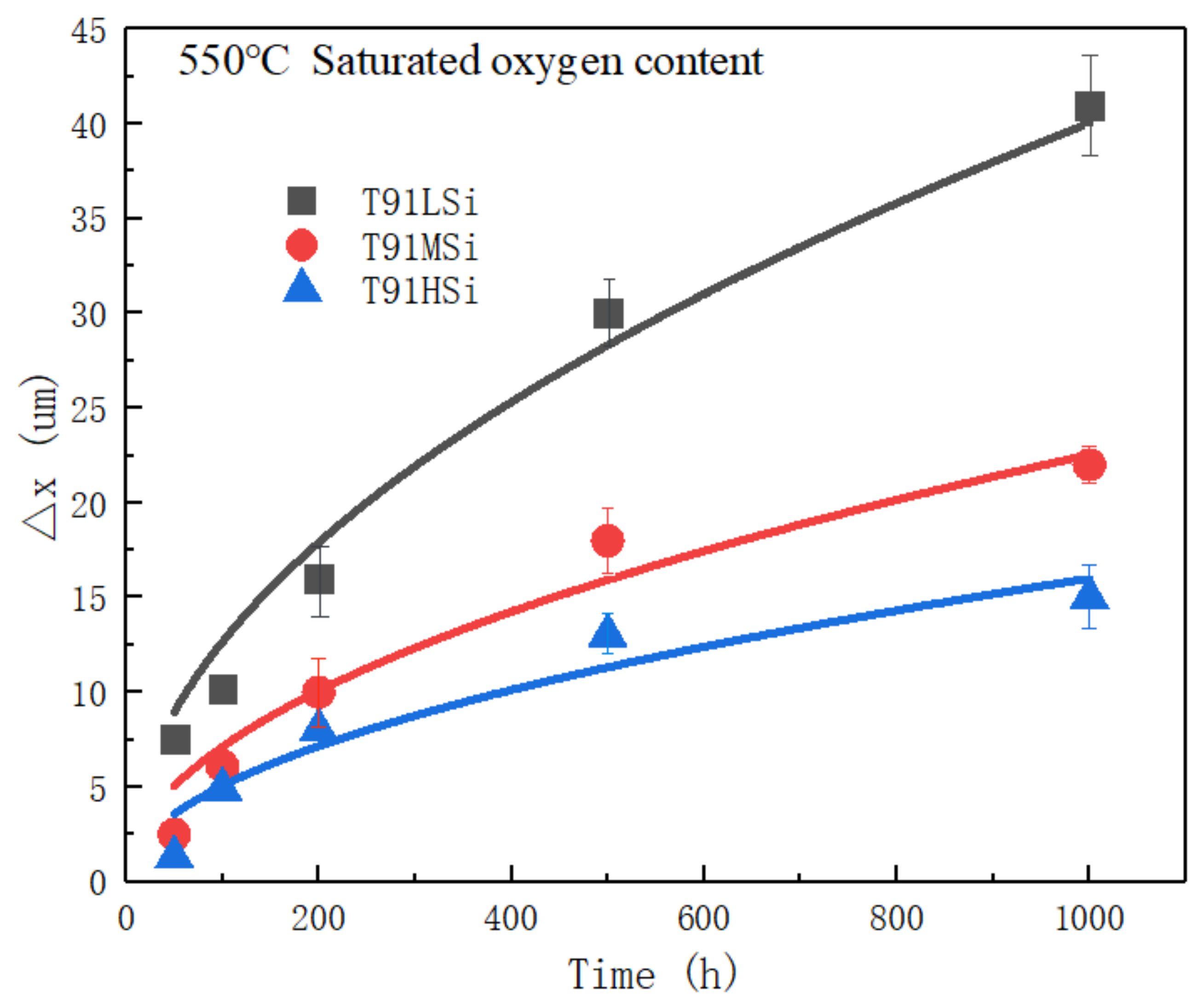
3.4. Characterization of Static Corrosion Oxide Film and Corrosion Kinetics
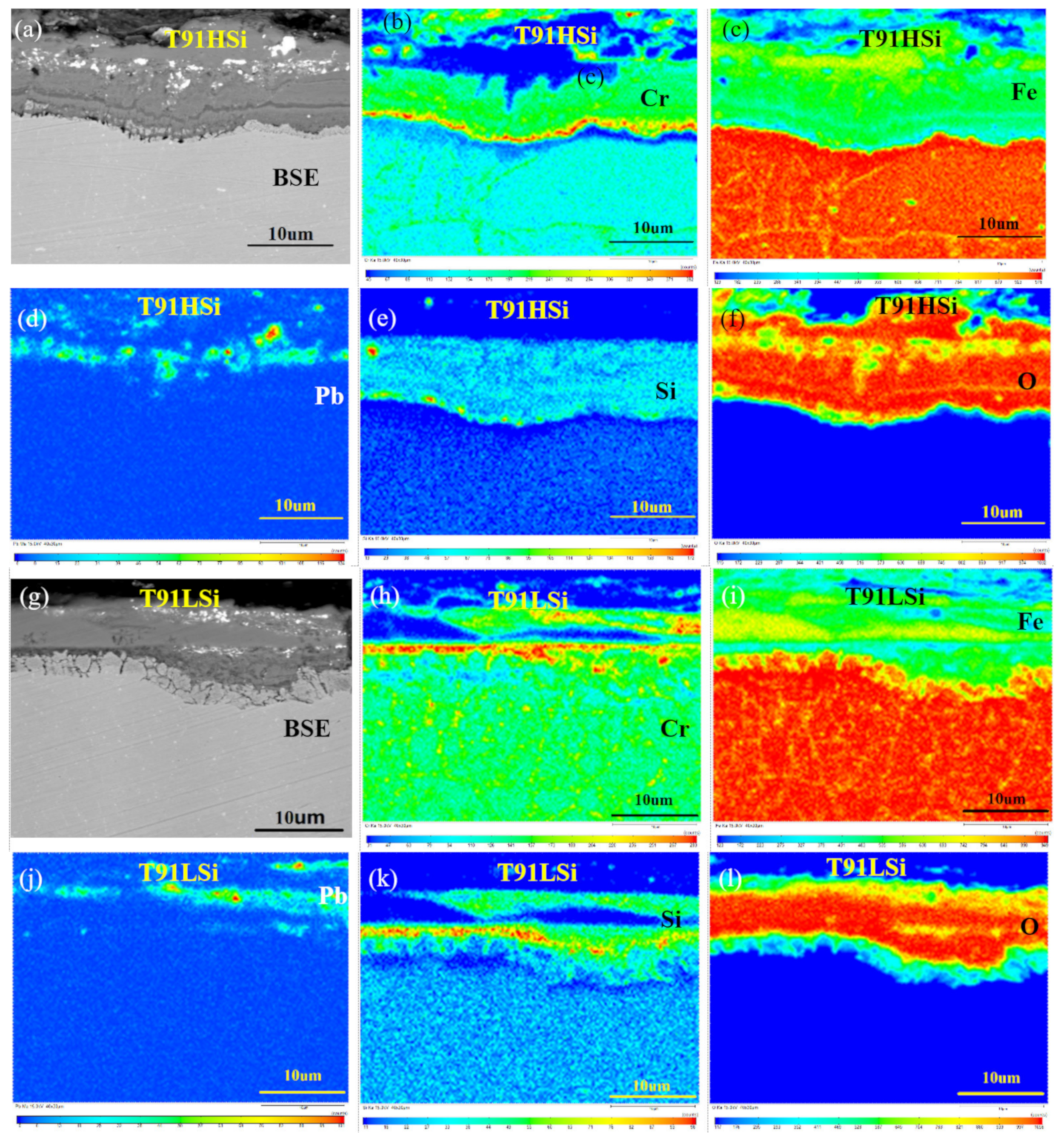
3.5. Characterization of Dynamic Corrosion Oxide Film
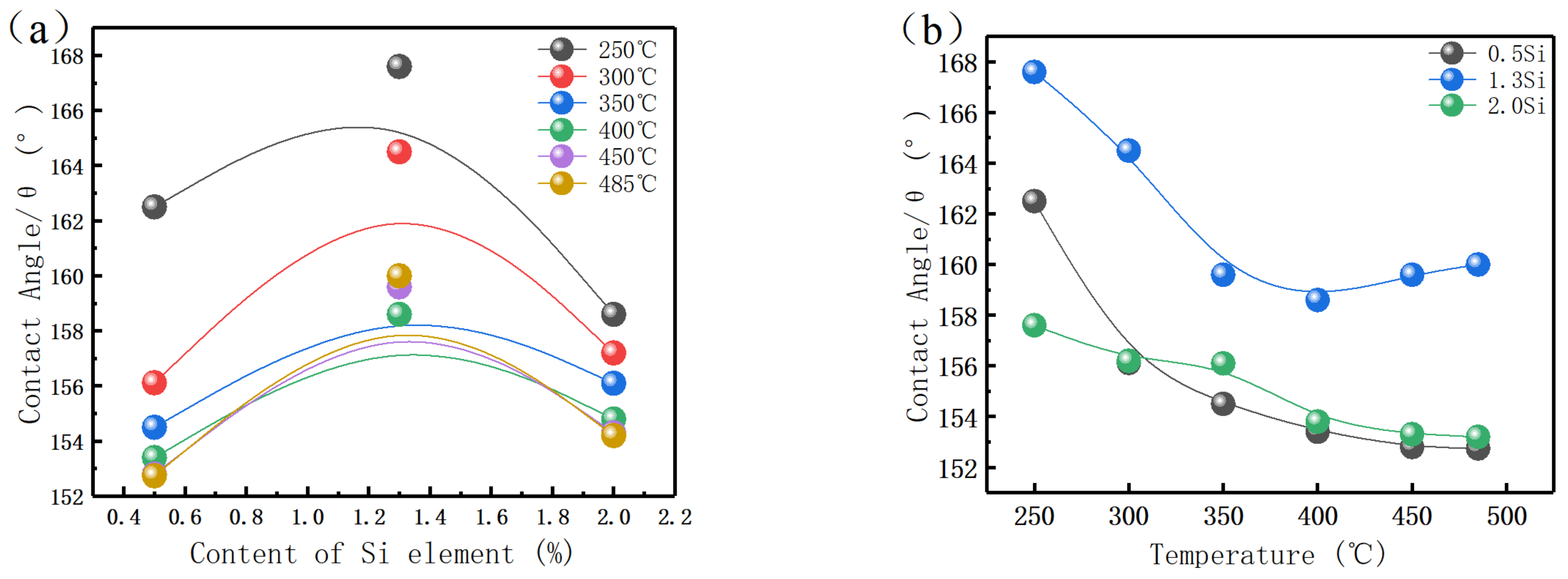
3.6. Wettability Test
4. Discussion
ΔGθ = −773,173 + 148.5T
ΔGθ = −550,858 + 101.3T
ΔGθ = −907,100 + 157T
ΔGθ = −566,095 + 143.9T
5. Conclusions
- The addition of Si effectively reduces the thickness of the oxide film. The thickness of oxide film decreases from 41 μm to 15 μm after exposure at 550 °C LBE for 1000 h. The increase in Si content can help improve the corrosion resistance of T91 steel in LBE. The addition of Si has little effect on carbide, and δ Ferrite will form when Si increases to 2.0 wt.%.
- Corrosion resistance mainly depends on the three-layer film. The outermost film plays a lesser role, while the two films below the original surface play a major role, improving corrosion resistance by forming a stable and dense oxide that hinders diffusion channels. The outer layer Fe3O4 is porous. The intermediate composite layer of Si and Cr plays a critical role in stabilizing the oxide film, which also provides favorable conditions for the formation of Fe Cr spinel in IOZ.
- The increase in Si content can increase the contact angle between the material and LBE droplets when the matrix structure remains unchanged. When ferrite exists in the structure, the dual phase structure of ferrite and martensite affects the interfacial tension between solid and liquid and reduces the contact angle.
- The oxidation model of T91 steel containing Si in the LBE environment is obtained through the analysis of the oxidation process. The model reveals the path of atomic diffusion and the direction of oxide film growth, and shows the hindering effect of Fe2SiO4 on oxygen diffusion channel.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nema, P.K. Application of Accelerators for Nuclear Systems: Accelerator Driven System (ADS). Energy Procedia 2011, 7, 597–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, H.; Du, X.; Liu, X.; Yan, T.; Li, X.; Wang, Y.; Qi, M.; Tu, X. Wetting Behavior of LBE on Corroded Candidate LFR Structural Materials of 316L, T91 and CLAM. Materials 2021, 15, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van, d.B.J.; Coen, G.; Bosch, R.W.; Almazouzi, A. TWIN ASTIR: First tensile results of T91 and 316L steel after neutron irradiation in contact with liquid lead-bismuth eutectic. J. Nucl. Mater. 2010, 398, 68–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gromov, B.F.; Belomitcev, Y.S.; Yefimov, E.I.; Leonchuk, M.P.; Martinov, P.N.; Orlov, Y.I.; Pankratov, D.V.; Pashkin, Y.G.; Toshinsky, G.I.; Chekunov, V.V.; et al. Use of lead-bismuth coolant in nuclear reactors and accelerator-driven systems. Nucl. Eng. Des. 1997, 173, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, X.; Li, R.; Sun, M.; Ren, Q.; Liu, T.; Short, M.P. Opportunities for the LWR ATF materials development program to contribute to the LBE-cooled ADS materials qualification program. J. Nucl. Mater. 2016, 482, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Rong, L.; Li, D.; Lu, S. Effect of welding thermal cycles on the oxidation resistance of 9 wt.% Cr heat resistant steels in 550 °C lead-bismuth eutectic. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 389, 930–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Ning, L. Review of the studies on fundamental issues in LBE corrosion. J. Nucl. Mater. 2008, 373, 351–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Zhang, Q.; Yang, J.; Xie, Z.; Zhang, L.; Liu, R.; Li, Z.; Wang, H.; Fang, Q.; Wang, X. Microstructures and Tensile Properties of 9Cr-F/M Steel at Elevated Temperatures. Materials 2022, 15, 1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patricie, H.; Jan, L.; Anna, H. Microstructural Investigation of LME Crack Initiated in Ferritic/Martensitic Steel T91 Loaded in Liquid Lead-Bismuth Eutectic at 300 °C. Materials 2018, 12, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sapundjiev, D.; Mazouzi, A.A.; Dyck, S.V. A study of the neutron irradiation effects on the susceptibility to embrittlement of A316L and T91 steels in lead–bismuth eutectic. J. Nucl. Mater. 2006, 356, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, B.; Tong, Z.; Gröschel, F.; Dai, Y. Liquid Pb-Bi embrittlement effects on the T91 steel after different heat treatments. J. Nucl. Mater. 2008, 377, 219–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Long, B.; Groeschel, F. Slow strain rate tensile tests on T91 in static lead–bismuth eutectic. J. Nucl. Mater. 2006, 356, 222–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; Wang, P.; Li, D.; Li, Y. Effect of pre-deformation on the oxidation resistance of a high Si ferritic/martensitic steel in oxygen-saturated stagnant lead-bismuth eutectic at 550 °C. Corros. Sci. 2017, 118, 129–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ersoy, F.; Gavrilov, S.; Verbeken, K. Investigating liquid-metal embrittlement of T91 steel by fracture toughness tests. J. Nucl. Mater. 2015, 472, 171–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Bosch, J.; Coen, G.; Almazouzi, A.; Degrieck, J. Fracture toughness assessment of ferritic–martensitic steel in liquid lead–bismuth eutectic. J. Nucl. Mater. 2009, 385, 250–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fazio, C.; Ricapito, I.; Scaddozzo, G.; Benamati, G. Corrosion behaviour of steels and refractory metals and tensile features of steels exposed to flowing PbBi in the LECOR loop. J. Nucl. Mater. 2003, 318, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhary, B.K.; Samuel, E.I.; Sainath, G.; Christopher, J.; Mathew, M.D. Influence of Temperature and Strain Rate on Tensile Deformation and Fracture Behavior of P92 Ferritic Steel. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2013, 44, 4979–4992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auger, T.; Serre, I.; Lorang, G.; Hamouche, Z.; Gorse, D.; Vogt, J.B. Role of oxidation on LME of T91 steel studied by small punch test. J. Nucl. Mater. 2008, 376, 336–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Lu, S.; Rong, L.; Li, D.; Li, Y. Effect of silicon on the oxidation resistance of 9 wt.% Cr heat resistance steels in 550 °C lead-bismuth eutectic. Corros. Sci. 2016, 111, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, A.L.; Loewen, E.P.; Ho, T.T.; Koury, D.; Hosterman, B.; Younas, U.; Welch, J.; Farleyc, J.W. Spectroscopic and microscopic study of the corrosion of iron–silicon steel by lead–bismuth eutectic (LBE) at elevated temperatures. J. Nucl. Mater. 2006, 350, 221–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurata, Y. Corrosion behavior of Si-enriched steels for nuclear applications in liquid lead–bismuth. J. Nucl. Mater. 2013, 437, 401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Shi, Q.; Luan, H.; Yan, W.; Sha, W.; Wang, W.; Shan, Y.; Yang, K. Lead-Bismuth Eutectic Corrosion Behaviors of Ferritic/Martensitic Steels in Low Oxygen Concentration Environment. Oxid. Met. 2015, 84, 383–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Du, X.; Niu, F.; Zhu, H.; Ma, T.; Zhao, Y.; Xiong, W.; Zhang, H. Influence of oxide scale on the wettability of LBE on T91 steel. Fusion Eng. Des. 2017, 125, 378–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, K.; Sawada, K.; Kushima, H. Influence of Chemical Composition and Heat Treatment on Long-term Creep Strength of Grade 91 Steel. Procedia Eng. 2013, 55, 2–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yin, H.F.; Yang, G.; Zhao, J.Q.; Bao, H.S. Mo-rich Laves phase in a 9.5Cr-1.5MoCoVNbNB heat-resistant steel during long-term aging at 620 °C. Mater. Charact. 2021, 182, 111588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, S.; Zhang, J. Corrosion behavior of 316L and T91 steels in stagnant lead-bismuth eutectic at 550 °C. J. Univ. Sci. Technol. China. 2015, 45, 751–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, X.; Stergar, E.; Marmy, P.; Gavrilov, S. Tensile fracture behavior of notched 9Cr-1Mo ferritic-martensitic steel specimens in contact with liquid lead-bismuth eutectic at 350 °C. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2017, 692, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroer, C.; Wedemeyer, O.; Skrypnik, A.; Novotny, J.; Konys, J. Corrosion kinetics of Steel T91 in flowing oxygen-containing lead–bismuth eutectic at 450 °C. J. Nucl. Mater. 2012, 431, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkinson, A. A theoretical analysis of the oxidation of Fe Si alloys. Corros. Sci. 1982, 22, 87–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bischoff, J.; Motta, A.T. Oxidation behavior of ferritic–martensitic and ODS steels in supercritical water. J. Nucl. Mater. 2012, 424, 261–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Material | C | Si | Mn | P | S | Ni | Cr | Mo | V | Nb | N | Fe |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T91LSi | 0.10 | 0.48 | 0.49 | 0.004 | 0.001 | 0.35 | 9.05 | 0.88 | 0.19 | 0.08 | 0.059 | Balance |
| T91MSi | 0.10 | 1.30 | 0.47 | 0.004 | 0.001 | 0.37 | 8.97 | 0.89 | 0.20 | 0.08 | 0.060 | Balance |
| T91HSi | 0.10 | 1.95 | 0.47 | 0.004 | 0.001 | 0.36 | 9.03 | 0.88 | 0.18 | 0.08 | 0.058 | Balance |
| Code | Type of Precipitated Phase | Type of Crystal System | Lattice Constant/nm |
|---|---|---|---|
| T91LSi | M23C6 | FCC | a0 = 1.062~1.064 |
| Nb(CN) | FCC | a0 = 0.440~0.441 | |
| V(CN) | FCC | a0 = 0.411~0.412 | |
| T91MSi | M23C6 | FCC | a0 = 1.062~1.064 |
| Nb(CN) | FCC | a0 = 0.440~0.441 | |
| V(CN) | FCC | a0 = 0.411~0.412 | |
| T91HSi | M23C6 | FCC | a0 = 1.062~1.064 |
| Nb(CN) | FCC | a0 = 0.439~0.440 | |
| V(CN) | FCC | a0 = 0.411~0.412 |
| Code | Cr | Fe | Mo | V | Mn | Ni | C | Σ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T91LSi | 50.80 | 22.15 | 4.05 | 1.02 | 1.00 | 0.30 | 20.69 | 100.00 |
| T91MSi | 50.28 | 22.42 | 3.97 | 1.44 | 0.89 | 0.31 | 20.69 | 100.00 |
| T91HSi | 49.95 | 22.98 | 3.85 | 1.26 | 0.95 | 0.32 | 20.69 | 100.00 |
| Code | V | Nb | Mo | N | C | Σ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T91LSi | 37.27 | 10.88 | 1.85 | 34.13 | 15.87 | 100.00 |
| T91MSi | 34.92 | 11.70 | 3.38 | 34.27 | 15.73 | 100.00 |
| T91HSi | 35.26 | 11.25 | 3.49 | 33.49 | 16.51 | 100.00 |
| Code | 50 h | 100 h | 200 h | 500 h | 1000 h |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T91LSi | 5.5 | 8.6 | 14 | 30 | 41 |
| T91MSi | 2.5 | 6.1 | 10 | 18 | 22 |
| T91HSi | 1.3 | 4.9 | 8 | 13 | 15 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, J.; He, X.; Xu, B.; Tang, Z.; Fang, C.; Yang, G. Effect of Silicon on Dynamic/Static Corrosion Resistance of T91 in Lead–Bismuth Eutectic at 550 °C. Materials 2022, 15, 2862. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15082862
Li J, He X, Xu B, Tang Z, Fang C, Yang G. Effect of Silicon on Dynamic/Static Corrosion Resistance of T91 in Lead–Bismuth Eutectic at 550 °C. Materials. 2022; 15(8):2862. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15082862
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Ji, Xikou He, Bin Xu, Zhengxin Tang, Caishun Fang, and Gang Yang. 2022. "Effect of Silicon on Dynamic/Static Corrosion Resistance of T91 in Lead–Bismuth Eutectic at 550 °C" Materials 15, no. 8: 2862. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15082862
APA StyleLi, J., He, X., Xu, B., Tang, Z., Fang, C., & Yang, G. (2022). Effect of Silicon on Dynamic/Static Corrosion Resistance of T91 in Lead–Bismuth Eutectic at 550 °C. Materials, 15(8), 2862. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15082862





