Sustainable Alkaline Hydrolysis of Polyester Fabric at Low Temperature
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Material
2.2. Modification
2.3. Characterization Methods
2.4. Model for Kinetics of Polyester Dissolution
3. Results and Discussion
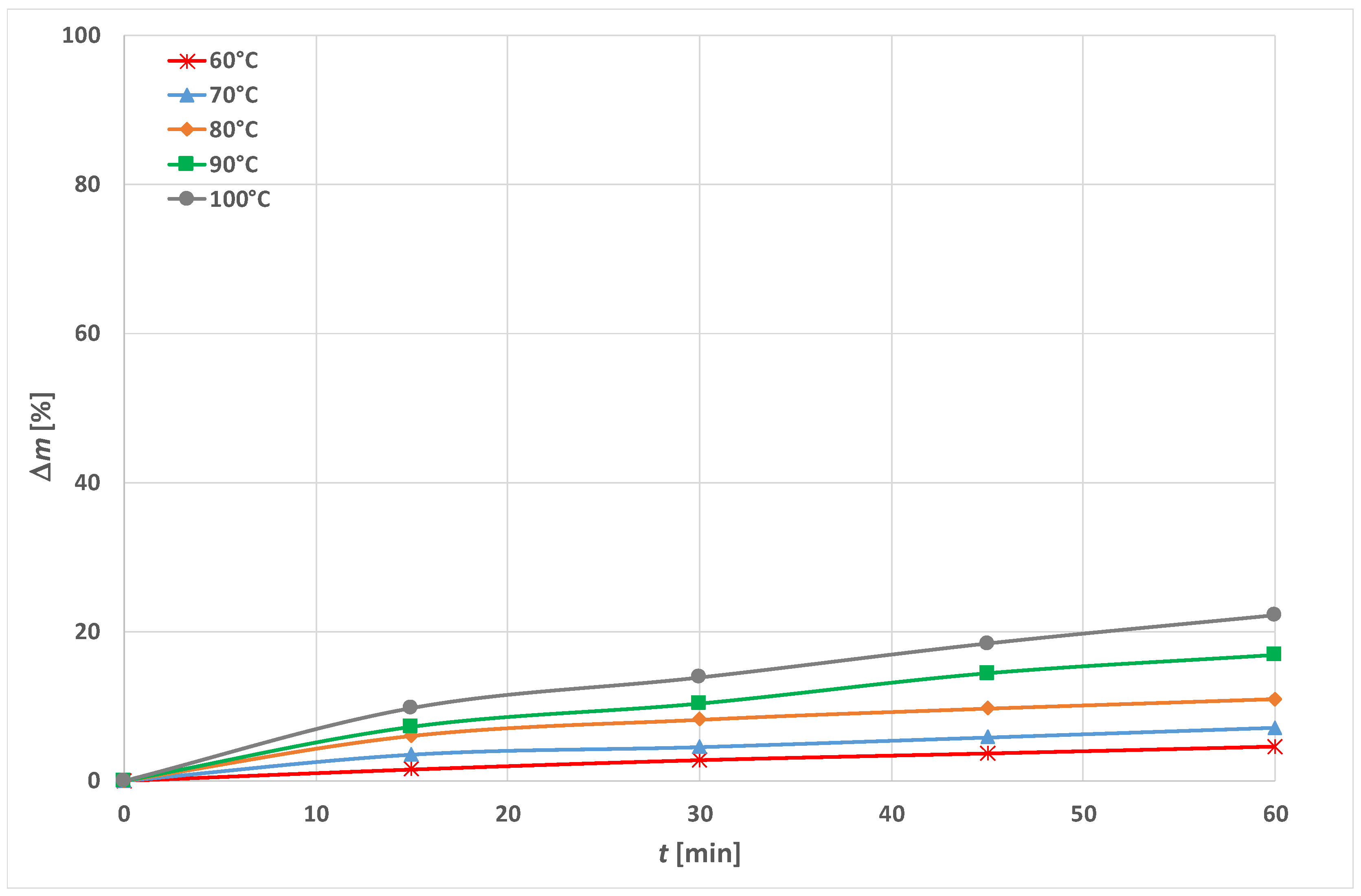
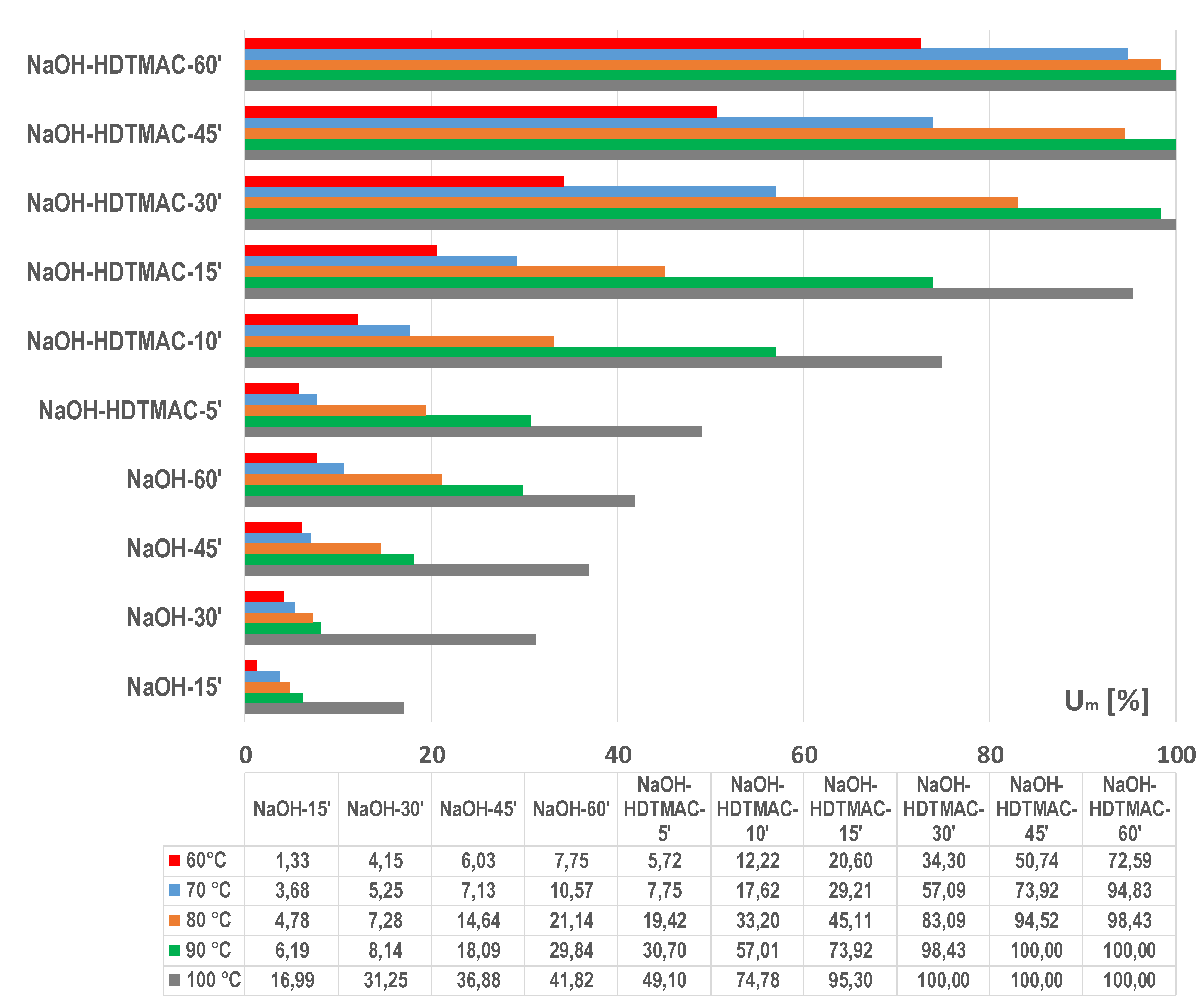
3.1. Optimization of Energy Efficient Process
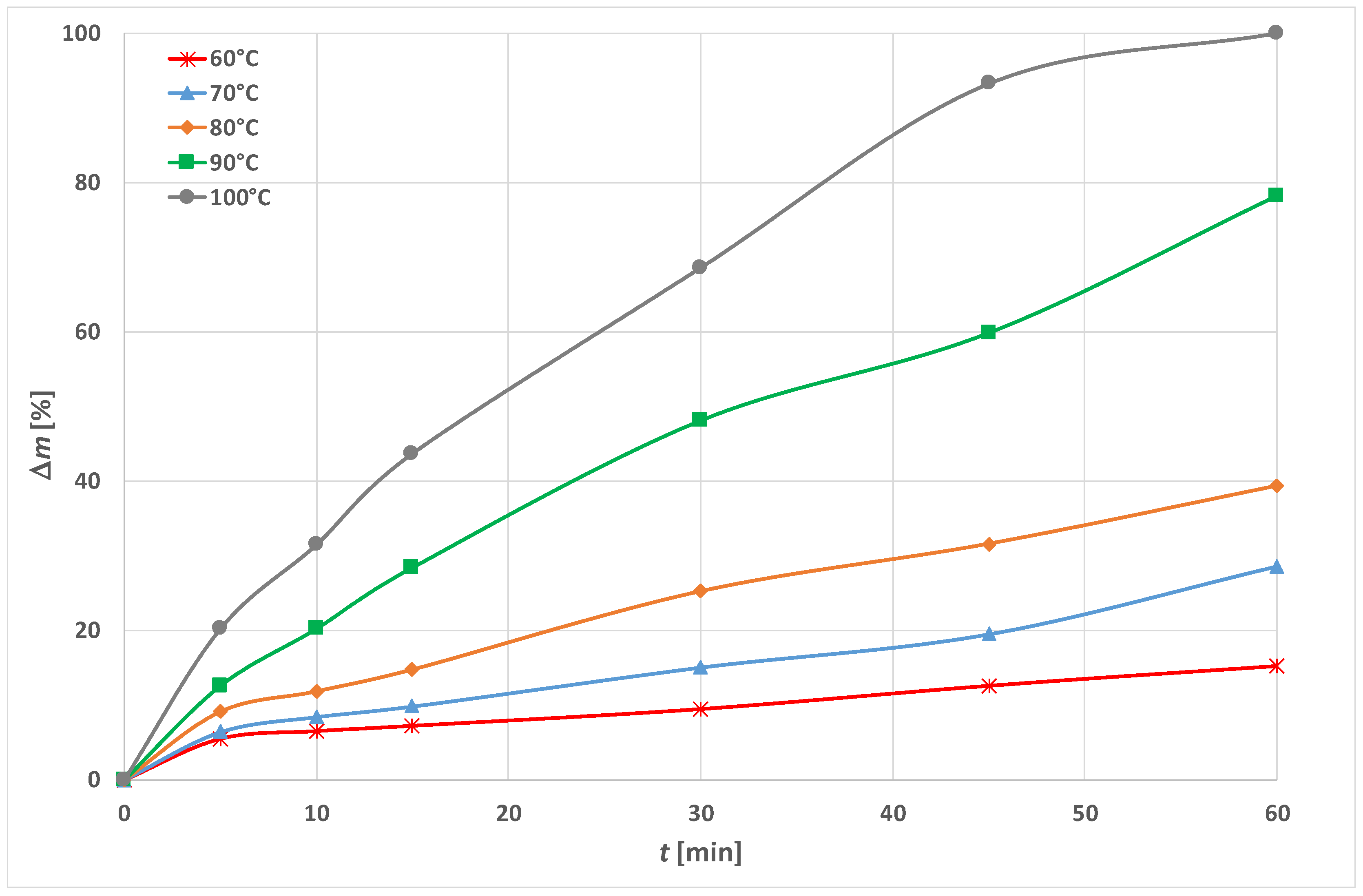
3.2. Model for Kinetics of PET Fabric Dissolution with HDTMAC as an Accelerator
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- BISFA: Terminology of Man-Made Fibres. 2017. Available online: https://bisfa.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/08/2017-BISFA-Terminology-final-update.pdf (accessed on 12 December 2021).
- Spaseka, D.; Civkaroska, M. Alkaline hydrolysis of poly(ethylene terephthalate) recycled from the postconsumer soft-drink bottles. J. Univ. Chem. Technol. Matallurgy 2010, 45, 379–384. [Google Scholar]
- Čorak, I.; Pušić, T.; Tarbuk, A. Enzimi za hidrolizu poliestera (Enzymes for Polyester Hydrolysis). Tekstil 2019, 68, 142–151. [Google Scholar]
- Pfeifer, H. Uber den Abbau von Polyester fasern durch Hydrolyse und Aminolyse; Westdeutscher Verlag: Köln, Germany, 1964. [Google Scholar]
- Bendak, A.; El-Marsafi, S.M. Effect of Chemical Modifications on Polyester Fibre. J. Islamic Acad. Sci. 1991, 4, 275–284. [Google Scholar]
- Gawish, S.M.; Ambroise, G. Alkaline Hydrolysis of Polyester Fabrics. Am. Dyest. Report. 1986, 75, 30–32. [Google Scholar]
- Gawish, S.M.; Bourgeois, M.; Ambroise, G. Cationic Polymers for the Alkaline Saponification of Polyester Fabrics. Am. Dyest. Report. 1985, 74, 35–36. [Google Scholar]
- Gawish, S.M.; Bourgeois, M.; Ambroise, G. Effect of Cationic Surfactants on the Alkaline Hydrolysis of Polyester Fabrics. Am. Dyest. Report. 1986, 75, 19–24. [Google Scholar]
- Gawish, S.M.; Mosleh, S.; Ramadan, A.M. Synthesis of a new cationic surfactant for the alkaline hydrolysis of solvent-pretreated polyester fabrics. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2002, 85, 1652–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grancarić, A.M.; Soljačić, I.; Rukavina, I.; Čavar, T. Utjecaj obrade na efekte alkalne hidrolize poliestera. Tekstil 1988, 37, 689–694. [Google Scholar]
- Kallay, N.; Grancarić, A.M.; Tomić, M. Kinetics of Polyester Fibre Dissolution. Text. Res. J. 1990, 60, 663–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grancarić, A.M.; Kallay, N. Kinetics of polyester fiber alkaline hydrolysis: Effect of temperature and cationic surfactants. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1993, 49, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grancarić, A.M.; Pušić, T.; Kallay, N. Modifikacija poliesterskog vlakna alkalnom hidrolizom. Polimeri 1991, 12, 141–145. [Google Scholar]
- Hsieh, Y.L. Surface Characteristics of Polyester Fibers. In Chapter 2 in Surface Characteristics of Fibers and Textiles, 1st ed.; Pastore, C., Kiekens, P., Eds.; Marcel Dekker: Basel, Switzerland, 2001; pp. 33–58. [Google Scholar]
- Mousazadegan, F.; Saharkhiz, S.; Maroufi, M. Weight reduction of the microfibre polyester fabric and its effect on physical and mechanical properties. J. Text. Inst. 2010, 101, 716–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dave, J.; Kumar, R.; Srivastava, H.C. Studies on modification of polyester fabrics I: Alkaline hydrolysis. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1987, 33, 455–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shet, R.T.; Zeronian, S.H.; Needles, H.L.; Siddiqui, S.A. Modification of Polyester and Polyester/Cotton by Alkali Treatment. Text. Chem. Colorist 1982, 14, 233–237. [Google Scholar]
- Zeronian, S.H.; Collins, M.J. Surface modification of polyester by alkaline treatments. Text. Progr. 1989, 20, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grancarić, A.M.; Tarbuk, A.; Kallay, N.; Tomašić, V. Topochemical Modification of Poly(ethylene terephtalate) Fibers—Kinetic of Fiber Alkaline Hydrolysis. In Book of Papers of 3rd AUTEX World Textile Conference; Krucinska, I., Ed.; Gdansk, Poland, 2003; pp. 29–33. Available online: https://www.bib.irb.hr/127149 (accessed on 20 December 2021).
- Jemaitaitis, A.J.; Rubezene, V.P.; Jemaitaitiene, R.-J.R. Einsatz kationischer Polymere beim alkalischen Abschaelen von Polyesterfasern (Use of cationic polymers in the alkaline peeling of polyester fibers). Textilveredlung 1993, 28, 146–148. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, J.; Meng, C.; Cheng, X.; Pan, X. Surface alkali deweighting and dyeing of polyester fabric by one-bath and one-step process. Surf. Innov. 2019, 7, 104–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Meng, C.; Cao, Y.; Yan, K.; Li, Y. Alkali deweighting processing of polyester fiber with imidazole ionic liquid. HERO 2017, 54, 21–25. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, J.; Meng, C.; Cao, Y.; Yan, K.; Wu, N.; Wang, C. Alkali deweighting of polyester fabrics using alkyl imidazolium Gemini ionic liquid. J. Text. Res. 2018, 39, 79–83. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Dong, Z.; Chen, G. Alkaline Hydrolysis of Polyester in the Presence of Ionic Liquids. Adv. Mater. Res. 2012, 441, 661–665. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, F.; Xiao, C.; Yu, S.; Zhuo, L.; Xiaoping, G. Hydrolysis Reaction of Poly(ethylene terephthalate) Using Ionic Liquids as Solvent and Catalyst. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2009, 114, 3561–3565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musale, R.M.; Shukla, S.R. Weight reduction of polyester fabric using sodium hydroxide solutions with additives cetyltrimethylammonium bromide and [BMIM]Cl. J. Text. Inst. 2017, 108, 467–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuhara, M. Innovation in Polyester Fibers: From Silk-Like to New Polyester. Text. Res. J. 1993, 63, 387–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solbrig, C.M.; Obendorf, S.K. Alkaline hydrolysis of titanium dioxide delustered poly (ethylene terephthalate) yarns. Text. Res. J. 1991, 61, 177–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ömeroğullari Başyiğit, Z. Effects of Chemical and Surface Modification on Mechanical and Chemical Properties of Polyester Fabrics. Düzce Univ. J. Sci. Technol. 2018, 6, 1344–1353. [Google Scholar]
- Vesel, A.; Junkar, I.; Cvelbar, U.; Kovac, J.; Mozetic, M. Surface Modification of Polyester by Oxygen and Nitrogen-Plasma Treatment. Surf. Interface Anal. 2008, 40, 1444–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Q.; Liu, Y.; Hou, D.; Huang, F. Dynamic wetting behavior of plasma treated PET fibers. J. Mater. Processing Technol. 2007, 194, 89–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bide, M.; Zhong, T.; Ukponmwan, J.; Phaneuf, M.; Quist, W.; Logerfo, F. Bifunctional surface modification of polyester. AATCC Rev. 2003, 3, 24–28. [Google Scholar]
- Grancarić, A.M.; Tarbuk, A. EDA Modified PET Fabric Treated with Activated Natural Zeolite Nanoparticles. Mater. Technol. Advan. Perform. Mater. 2009, 24, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avny, Y.; Rebenfeld, L. Chemical modification of polyester fiber surfaces by amination reactions with multifunctional amines. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1986, 32, 4009–4025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guebitz, G.M.; Cavaco-Paulo, A. Enzymes go big: Surface hydrolysis and functionalization of synthetic polymers. Trends Biotechnol. 2008, 26, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vertommen, M.A.M.E.; Nierstrasz, V.A.; van der Veer, M.; Warmoeskerken, M.M.C.G. Enzymatic surface modification of poly(ethylene terephthalate). J. Biotechnol. 2005, 120, 376–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quartinello, F.; Gübitz, G.M. Bioprocessing of polyesters. In Chapter 3 Advances in Textile Biotechnology; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2019; pp. 37–48. [Google Scholar]
- Quartinello, F.; Vajnhandl, S.; Valh, J.V.; Farmer, T.J.; Voncina, B.; Lobnik, A.; Herrero Acero, E.; Pellis, A.; Guebitz, G.M. Synergistic chemo-enzymatic hydrolysis of poly(ethylene terephthalate) from textile waste. Microbial. Biotechnol. 2017, 10, 1376–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brueckner, T.; Eberl, A.; Heumann, S.; Rabe, M.; Guebitz, G.M. Enzymatic and Chemical Hydrolysis of Poly(ethylene terephthalate) Fabrics. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 2008, 46, 6435–6443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donelli, I.; Taddei, P.; Smet, P.F.; Poelman, D.; Nierstrasz, V.A.; Freddi, G. Enzymatic surface modification and functionalization of PET: A water contact angle, FTIR, and fluorescence spectroscopy study. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2009, 103, 845–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donelli, I.; Freddia, G.; Nierstrasz, V.A.; Taddeic, P. Surface structure and properties of poly-(ethylene terephthalate) hydrolyzed by alkali and cutinase. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2010, 95, 1542–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Đorđević, D.; Petronijević, Ž.; Dimitrijević, S.; Đorđević, S. Primjena komercijalnog i laboratoriskog enzimskog preparata lipaze u obradi poliesterske tkanine radi poboljšanja sorpcijskih i bojadiarskih svojstava (Commercial and Laboratory Application of Enzymatic Lipase Preparation in the Polyester Fabric Processing to Improve the Sorption and Dyebility Properties). Tekstil 2006, 55, 410–418. [Google Scholar]
- Tarbuk, A.; Grancarić, A.M.; Čorak, I. Cutinase Hydrolisis of Poly(ethylene-terephtalate) Fabric. In Proceedings of the 8th Central European Conference on Fiber-grade Polymers, Chemical Fibers and Special Textiles, Zagreb, Croatia, 16–18 September 2015; Dekanić, T., Tarbuk, A., Eds.; University of Zagreb Faculty of Textile Technology: Zagreb, Croatia, 2015; pp. 97–102. [Google Scholar]
- Tarbuk, A.; Grancarić, A.M.; Đorđević, D.; Demirović, O.; Majcen Le Marechal, A. Eco Surface Modifications of PET Fabric. In Proceedings of the 7th International Textile, Colthing & Design Conference, Dubrovnik, Croatia, 5–8 October 2014; Dragčević, Z., Hursa Šajatović, A., Vujasinović, E., Eds.; University of Zagreb Faculty of Textile Technology: Zagreb, Zagre, 2014; pp. 250–255. [Google Scholar]
- Mazrouei-Sebdani, Z.; Khoddami, A. Alkaline hydrolysis: A facile method to manufacture superhydrophobic polyester fabric by fluorocarbon coating. Prog. Org. Coat. 2011, 72, 638–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, M.S.; Park, Y.; Park, C.H. Development of superhydrophobic polyester fabrics using alkaline hydrolysis and coating with fluorinated polymers. Fibers Polym. 2016, 17, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, C.-H.; Li, Y.-R.; Zhang, P.; Ma, J.-Z.; Jia, S.-T. Washable and Wear-Resistant Superhydrophobic Surfaces with Self-Cleaning Property by Chemical Etching of Fibers and Hydrophobization. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 10153–10161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youn, S.; Park, C. Development of breathable Janus superhydrophobic polyester fabrics using alkaline hydrolysis and blade coating. Text. Res. J. 2018, 89, 959–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yan, X.; Yi, L.; Cai, Y.; Tang, Z. Novel coating system on poly(ethylene terephthalate) fabrics with mechanically durable liquid-repellence: Application as flexible materials with striking loading capacity. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 457, 332–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pušić, T.; Grancarić, A.M.; Tarbuk, A.; Šauperl, O.; Soljačić, I. Adsorption and Desorption of Ionic Surfactants. Tenside Surfactants Deterg. 2010, 47, 173–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarbuk, A. Adsorpcija Ionskih Tenzida na Tekstilna Vlakna (Adsorption of Ionic Surfactants to Textile Fibers). Master’s Thesis, University of Zagreb Faculty of Textile Technology, Zagreb, Croatia, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Pušić, T.; Soljačić, I.; Grancarić, A.M.; Tarbuk, A. Adsorption of Surfactants on Textile Fibers. In Proceedings of the 3rd Central European Conference—Fibre-grade Polymers, Chemical Fibers and Special Textiles, Portorose, Slovenia, 10–12 September 2003; University of Maribor: Portorose, Slovenia, 2003; pp. 48–52. [Google Scholar]
- Pušić, T.; Soljačić, I.; Grancarić, A.M.; Tarbuk, A. The Influence of the Textile Fiber Composition on Surfactant Adsorption and Desorption. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Textile, Colthing & Design Conference, Dubrovnik, Croatia, 3–6 10 October 2004; Dragčević, Z., Ed.; University of Zagreb Faculty of Textile Technology: Zagreb, Croatia, 2004; pp. 444–449. [Google Scholar]
- Grancarić, A.M.; Tarbuk, A.; Pušić, T. Electrokinetic Properties of Textile Fabrics. Coloration Technol. 2005, 121, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawahara, Y.; Yoshioka, T.; Takarada, W.; Kikutani, T.; Tsuji, M. Alkaline Hydrolysis Kinetics of Poly(ethylene terephthalate) Fibers. J. Fiber Sci. Technol. 2016, 72, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarbuk, A.; Grancarić, A.M.; Jančijev, I.; Sharma, S. Zaštita od ultraljubičastog zračenja površinski modificiranom poliesterskom tkaninom (Protection against UV radiation using a modified polyester fabric). Tekstil 2006, 55, 383–394. [Google Scholar]
- Grancarić, A.M.; Tarbuk, A.; McCall, D. Modifikacija površine poliesterske tkanine nanočesticama tribomehanički aktiviranog prirodnog zeolita (TMAZ) (Surface Modification of Polyester Fabric with Tribomechanically Activated Natural Zeolite (TMAZ) Nanoparticles). Polimeri 2007, 28, 219–224. [Google Scholar]
- Haji, A.; Malek, R.M.A.; Mazaheri, F. Comparative study of exhaustion and pad-steam methods for improvement of handle, dye uptake and water absorption of polyester/cotton fabric. CI&CEQ 2011, 17, 359–365. [Google Scholar]
- Haji, A. The role of quaternary ammonium compound and reducing agent in environmentally friendly alkali treatment of PET (cotton fabric). J. Bio. Env. Sci. 2014, 5, 417–422. [Google Scholar]
- Hsieh, Y.-L.; Miller, A.; Thompson, J. Wetting, Pore Structure, and Liquid Retention of Hydrolyzed Polyester Fabrics. Text. Res. J. 1996, 66, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarbuk, A.; Grancarić, A.M. Interface Phenomena of Cotton Cationized in Mercerization. In Chapter 6 Cellulose and Cellulose Derivatives: Synthesis, Modification and Applications, Part I: Cellulose Synthesis and Modification. Mondal, I.H., Ed.; Nova Science Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 103–126. [Google Scholar]
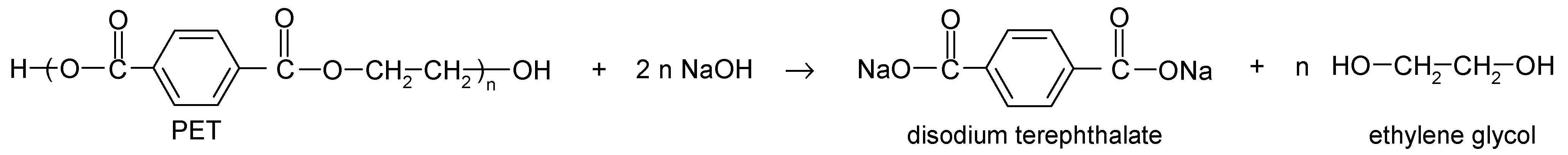

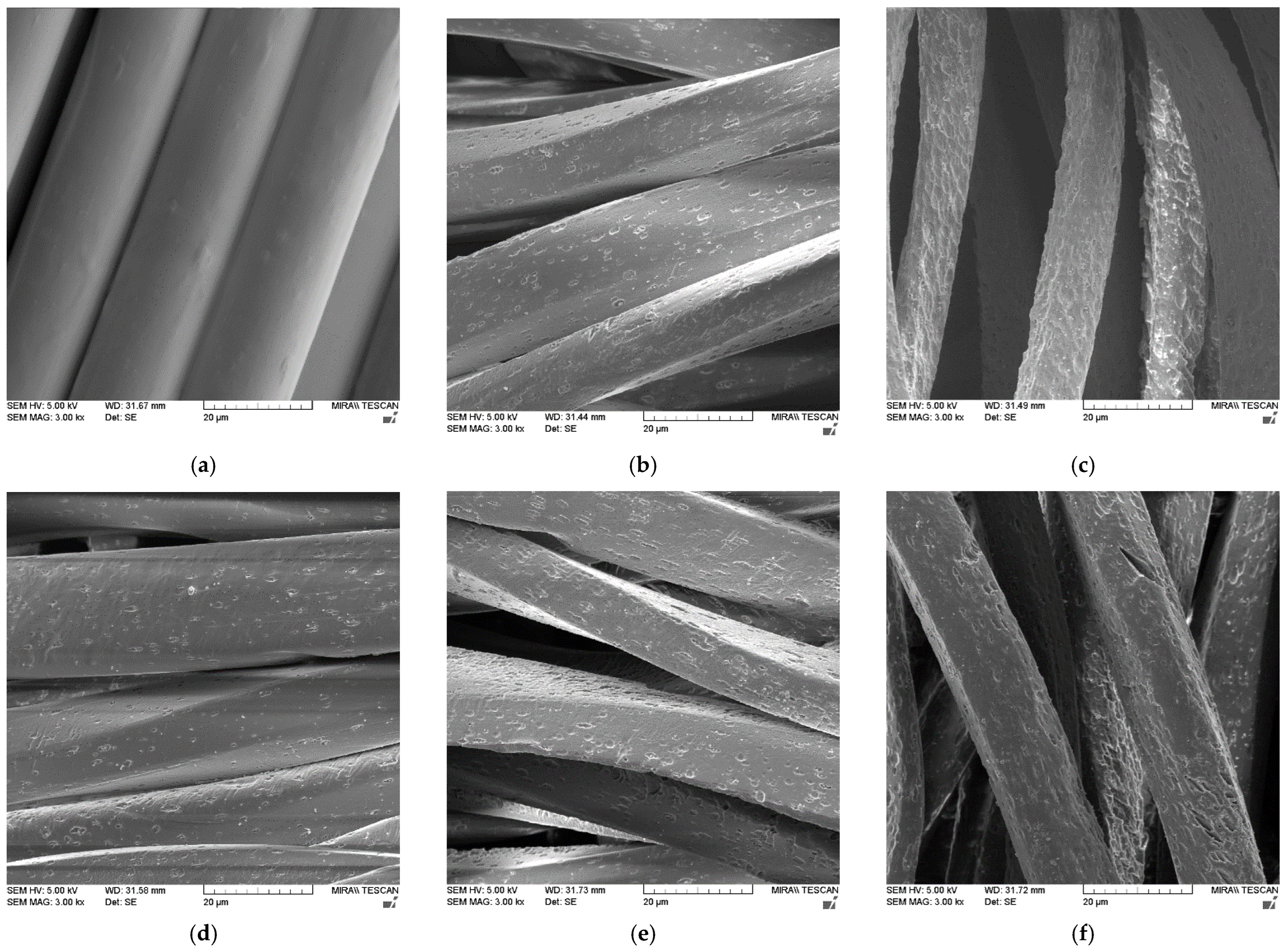
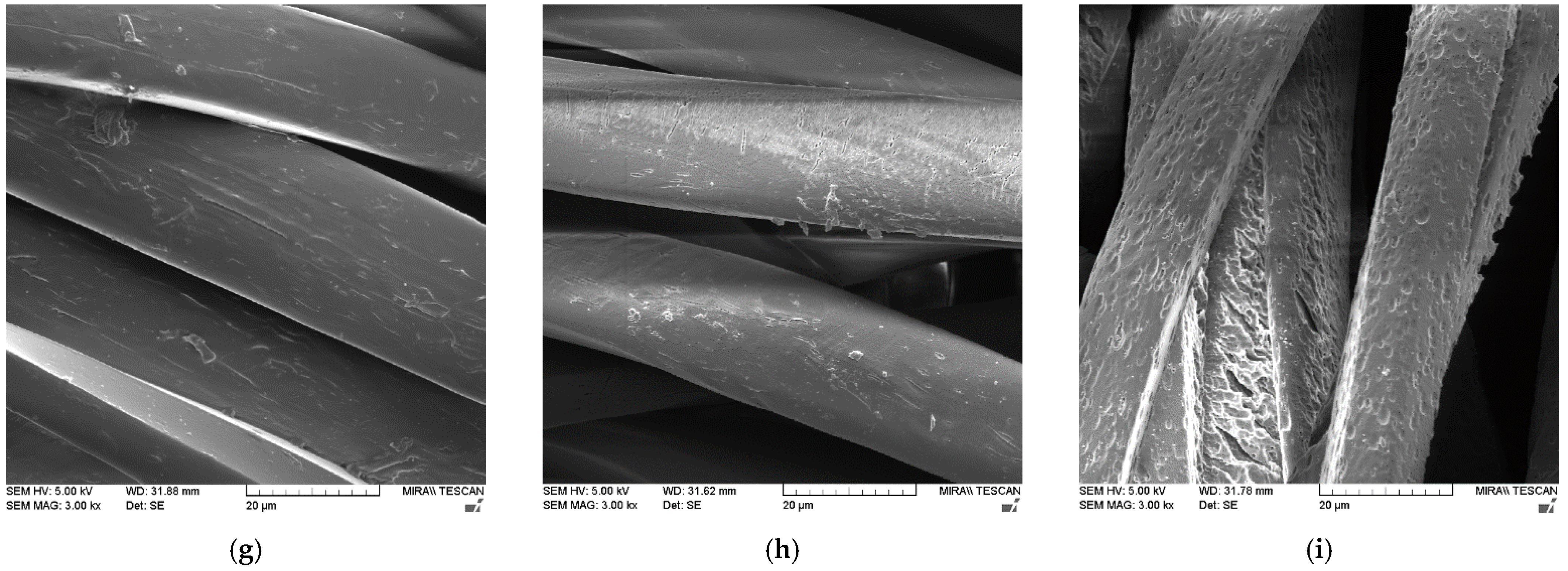
| Treatment | F [N] | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| t [min] | 60 °C | 70 °C | 80 °C | 90 °C | 100 °C | |
| PET | 0 | 638.50 | 638.50 | 638.50 | 638.50 | 638.50 |
| NaOH | 15 | 630.00 | 615.00 | 608.00 | 599.00 | 530.00 |
| 30 | 612.00 | 605.00 | 592.00 | 586.50 | 439.00 | |
| 45 | 600.00 | 593.00 | 545.00 | 523.00 | 403.00 | |
| 60 | 589.00 | 571.00 | 503.50 | 448.00 | 371.50 | |
| NaOH + HDTMAC | 5 | 602.00 | 589.00 | 514.50 | 442.50 | 325.00 |
| 10 | 560.50 | 526.00 | 426.50 | 274.50 | 161.00 | |
| 15 | 507.00 | 452.00 | 350.50 | 166.50 | 30.00 | |
| 30 | 419.50 | 274.00 | 108.00 | 10.00 | 0.00 | |
| 45 | 314.50 | 166.50 | 35.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | |
| 60 | 175.00 | 33.00 | 10.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | |
| Treatment | ε [%] | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| t [min] | 60 °C | 70 °C | 80 °C | 90 °C | 100 °C | |
| PET | 0 | 34.200 | 34.200 | 34.200 | 34.200 | 34.200 |
| NaOH | 15 | 33.050 | 34.000 | 34.520 | 35.260 | 33.240 |
| 30 | 29.910 | 29.910 | 30.000 | 36.924 | 32.700 | |
| 45 | 29.550 | 26.400 | 28.600 | 33.050 | 32.100 | |
| 60 | 29.367 | 29.367 | 26.280 | 32.400 | 31.891 | |
| NaOH + HDTMAC | 5 | 32.009 | 31.926 | 26.132 | 29.050 | 25.781 |
| 10 | 30.637 | 29.163 | 23.145 | 24.238 | 22.224 | |
| 15 | 27.218 | 25.087 | 23.189 | 18.741 | 18.030 | |
| 30 | 23.111 | 18.750 | 12.242 | 10.420 | 0.000 | |
| 45 | 19.772 | 13.180 | 10.376 | 0.000 | 0.000 | |
| 60 | 13.161 | 12.095 | 8.045 | 0.000 | 0.000 | |
| Treatment | t [s] | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| t [min] | 60 °C | 70 °C | 80 °C | 90 °C | 100 °C | |
| PET | 0 | 12.08 | ||||
| NaOH | 15 | 9.92 | 9.88 | 9.45 | 9.35 | 8.98 |
| 30 | 8.12 | 7.99 | 7.80 | 7.05 | 5.29 | |
| 45 | 8.56 | 8.23 | 7.75 | 7.25 | 6.33 | |
| 60 | 9.88 | 9.70 | 7.47 | 9.46 | 7.12 | |
| NaOH + HDTMAC | 5 | 9.23 | 8.90 | 5.81 | 8.22 | 7.59 |
| 10 | 8.88 | 8.57 | 7.08 | 6.21 | 9.77 | |
| 15 | 8.85 | 8.85 | 7.96 | 7.75 | 7.17 | |
| 30 | 8.56 | 9.89 | 6.15 | 9.99 | - | |
| 45 | 8.33 | 7.99 | 6.16 | - | - | |
| 60 | 7.98 | 6.63 | 6.82 | - | - | |
| Parameter | NaOH | NaOH + HDTMAC |
|---|---|---|
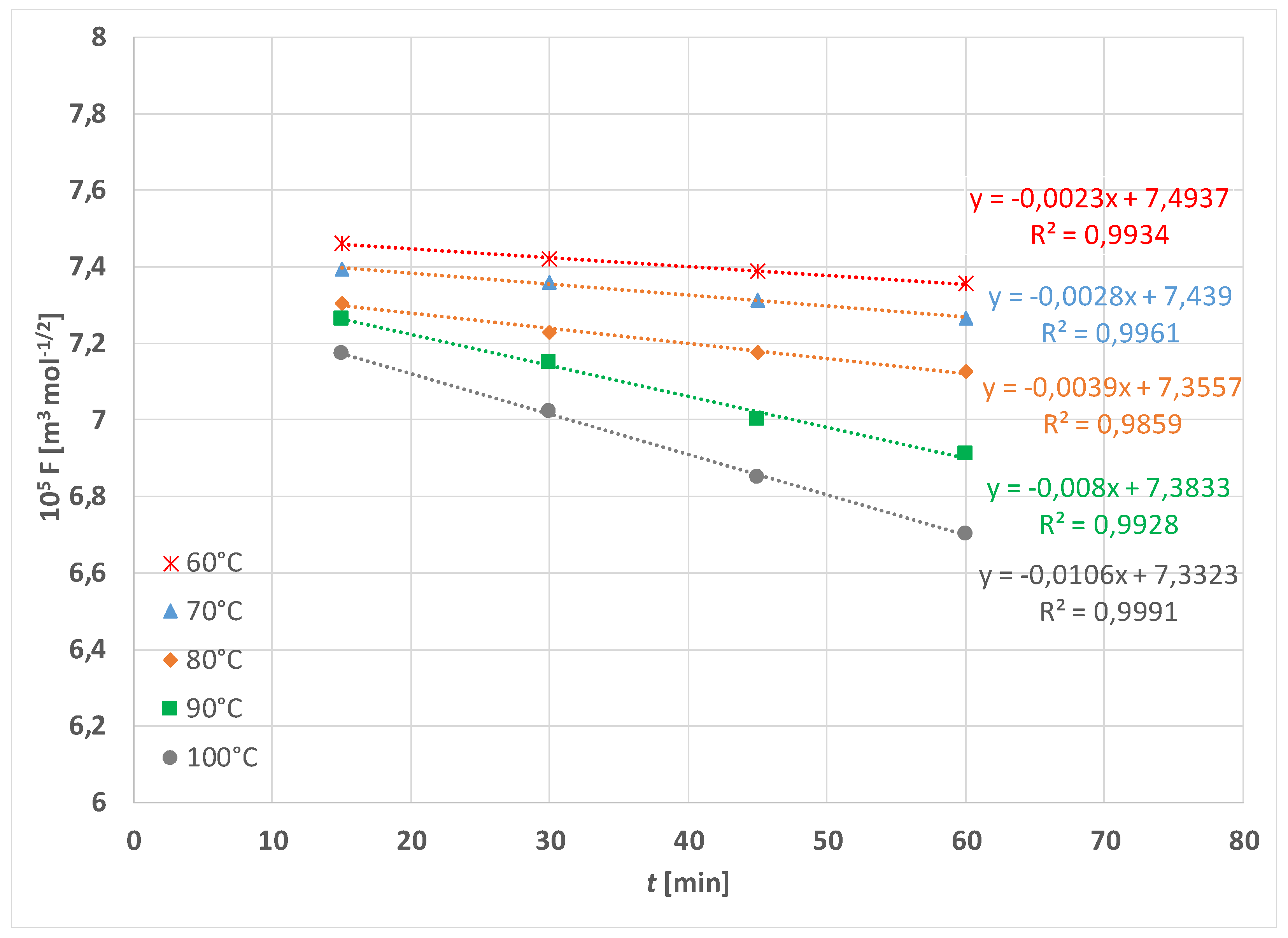
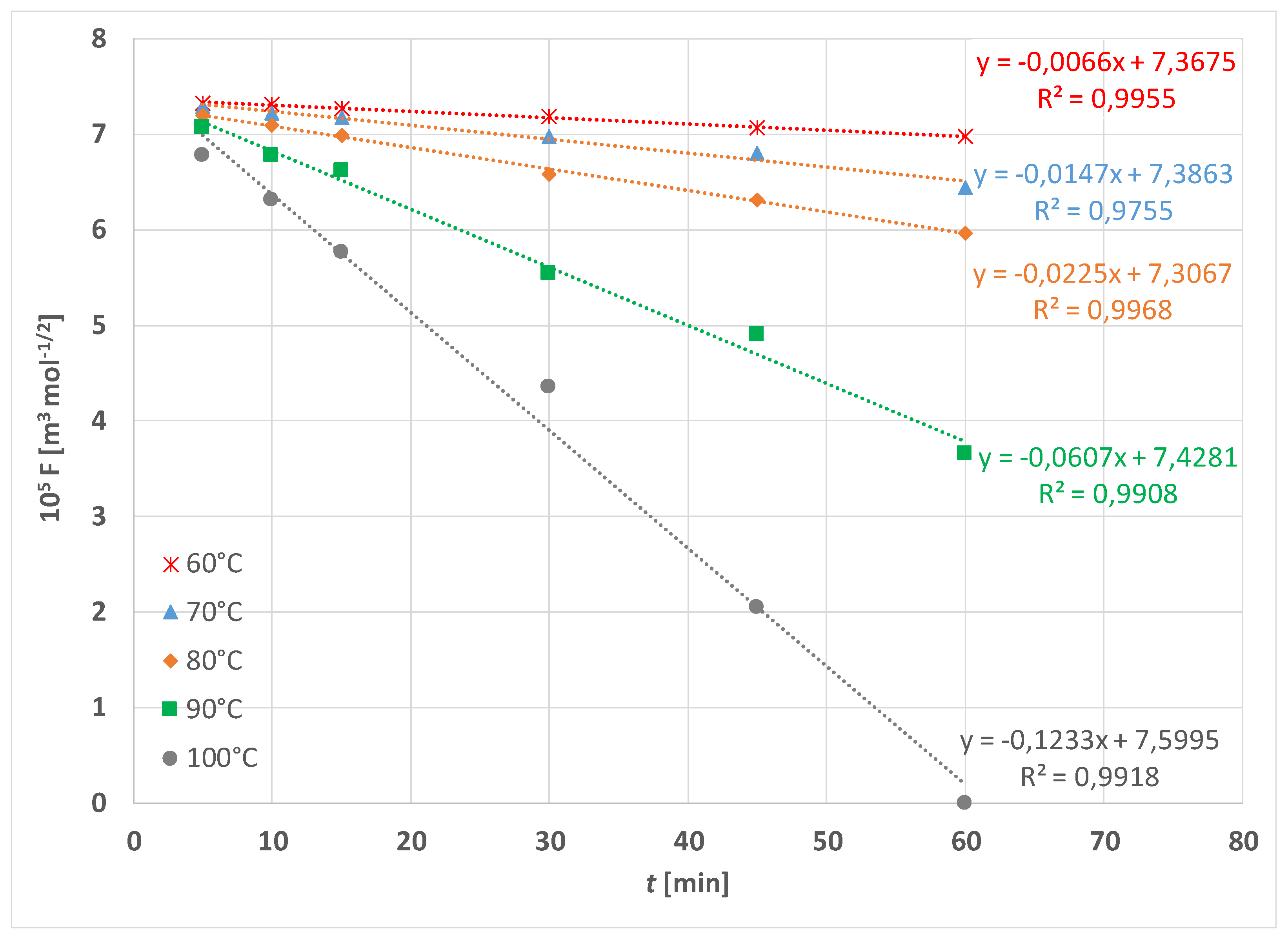
| k-60 °C | 2.21 × 10−8 m3 mol−1/2 s−1 | 6.94 × 10−8 m3 mol−1/2 s−1 |
| k-70 °C | 2.84 × 10−8 m3 mol−1/2 s−1 | 1.55 × 10−7 m3 mol−1/2 s−1 |
| k-80 °C | 3.47 × 10−8 m3 mol−1/2 s−1 | 2.36 × 10−7 m3 mol−1/2 s−1 |
| k-90 °C | 9.46 × 10−8 m3 mol−1/2 s−1 | 6.38 × 10−7 m3 mol−1/2 s−1 |
| k-100 °C | 1.13 × 10−7 m3 mol−1/2 s−1 | 1.29 × 10−6 m3 mol−1/2 s−1 |
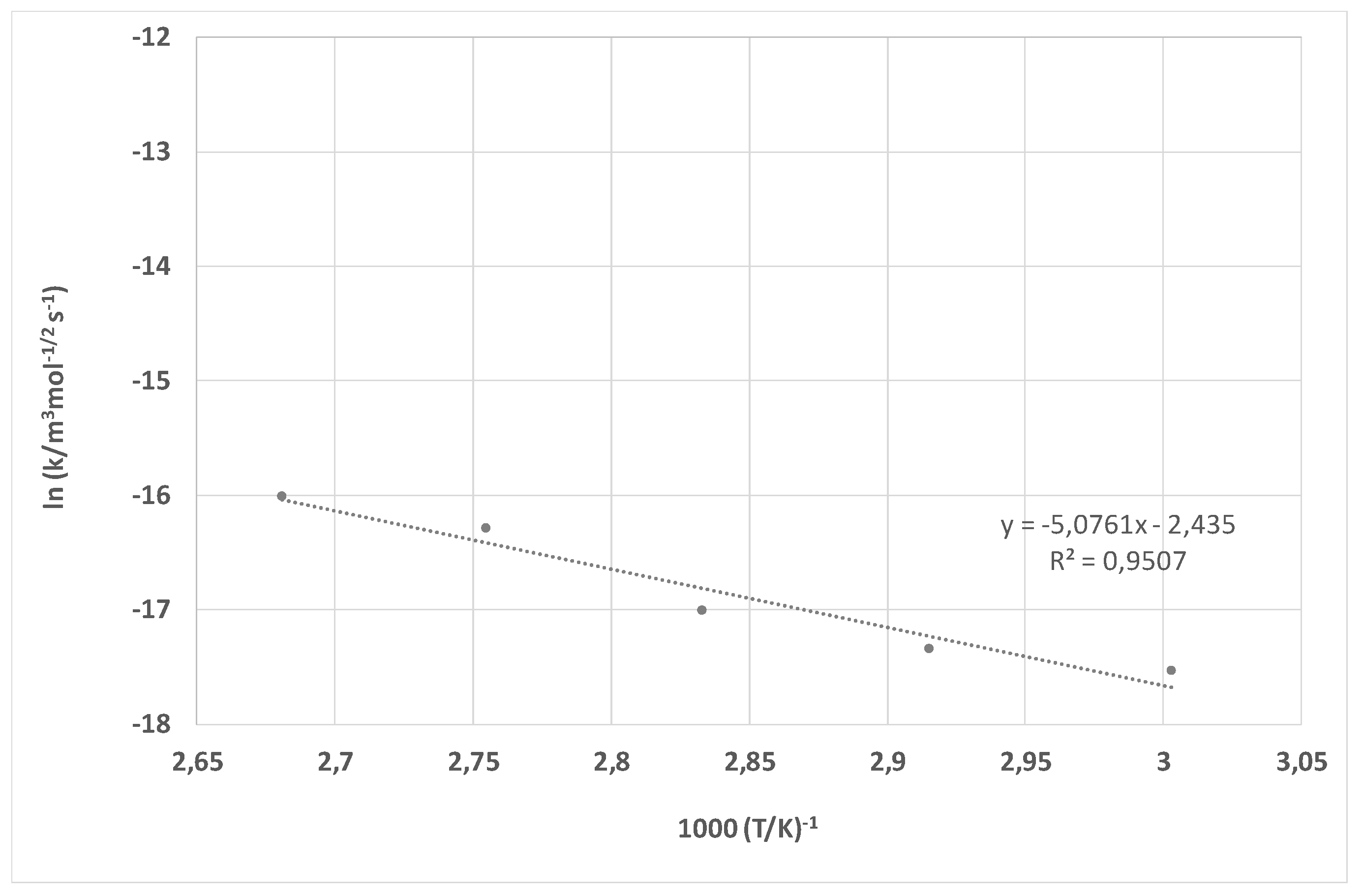
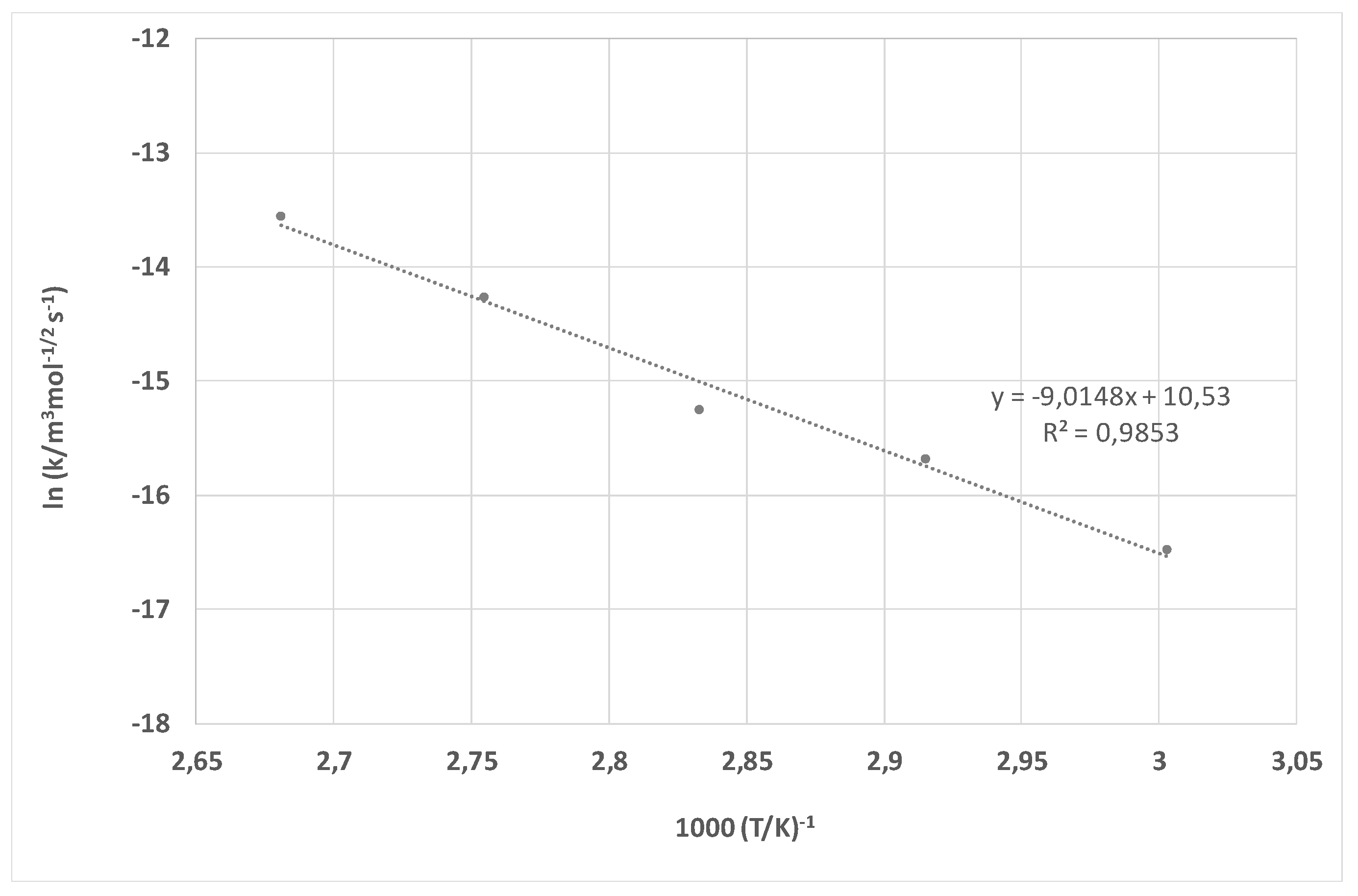
| Ea | 42.34 kJ mol−1 | 75.19 kJ mol−1 |
| B | 8.76 × 10−6 m3 mol−1/2 s−1 | 3.74 × 105 m3 mol−1/2 s−1 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Čorak, I.; Tarbuk, A.; Đorđević, D.; Višić, K.; Botteri, L. Sustainable Alkaline Hydrolysis of Polyester Fabric at Low Temperature. Materials 2022, 15, 1530. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15041530
Čorak I, Tarbuk A, Đorđević D, Višić K, Botteri L. Sustainable Alkaline Hydrolysis of Polyester Fabric at Low Temperature. Materials. 2022; 15(4):1530. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15041530
Chicago/Turabian StyleČorak, Ivana, Anita Tarbuk, Dragan Đorđević, Ksenija Višić, and Lea Botteri. 2022. "Sustainable Alkaline Hydrolysis of Polyester Fabric at Low Temperature" Materials 15, no. 4: 1530. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15041530
APA StyleČorak, I., Tarbuk, A., Đorđević, D., Višić, K., & Botteri, L. (2022). Sustainable Alkaline Hydrolysis of Polyester Fabric at Low Temperature. Materials, 15(4), 1530. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15041530







