Evaluation of the Antimicrobial Effect of Graphene Oxide Fiber on Fish Bacteria for Application in Aquaculture Systems
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of GO
2.2. Characterization of GO
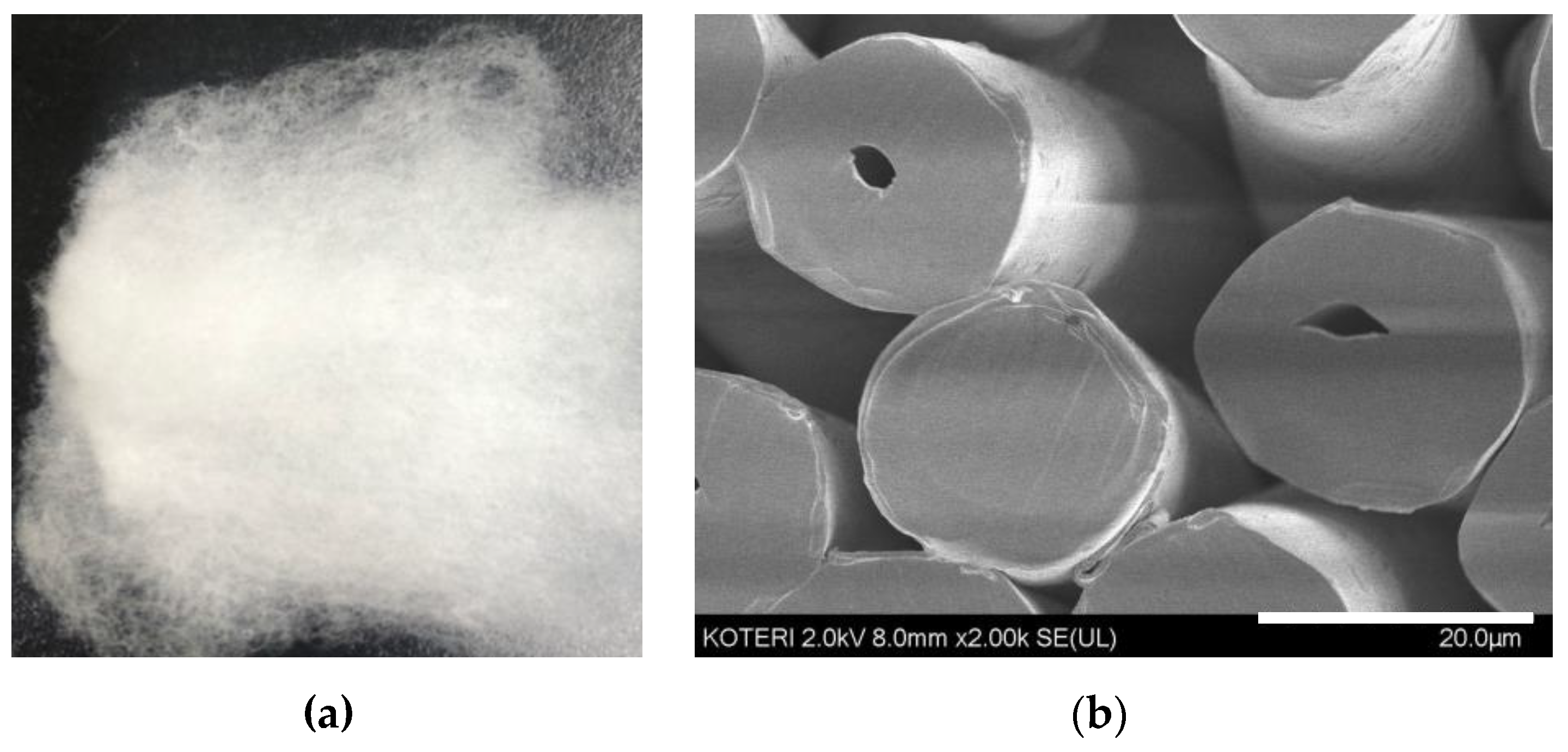
2.3. Preparation of GO Polyester Fiber
2.4. Fish Pathogenic Bacteria
3. Results
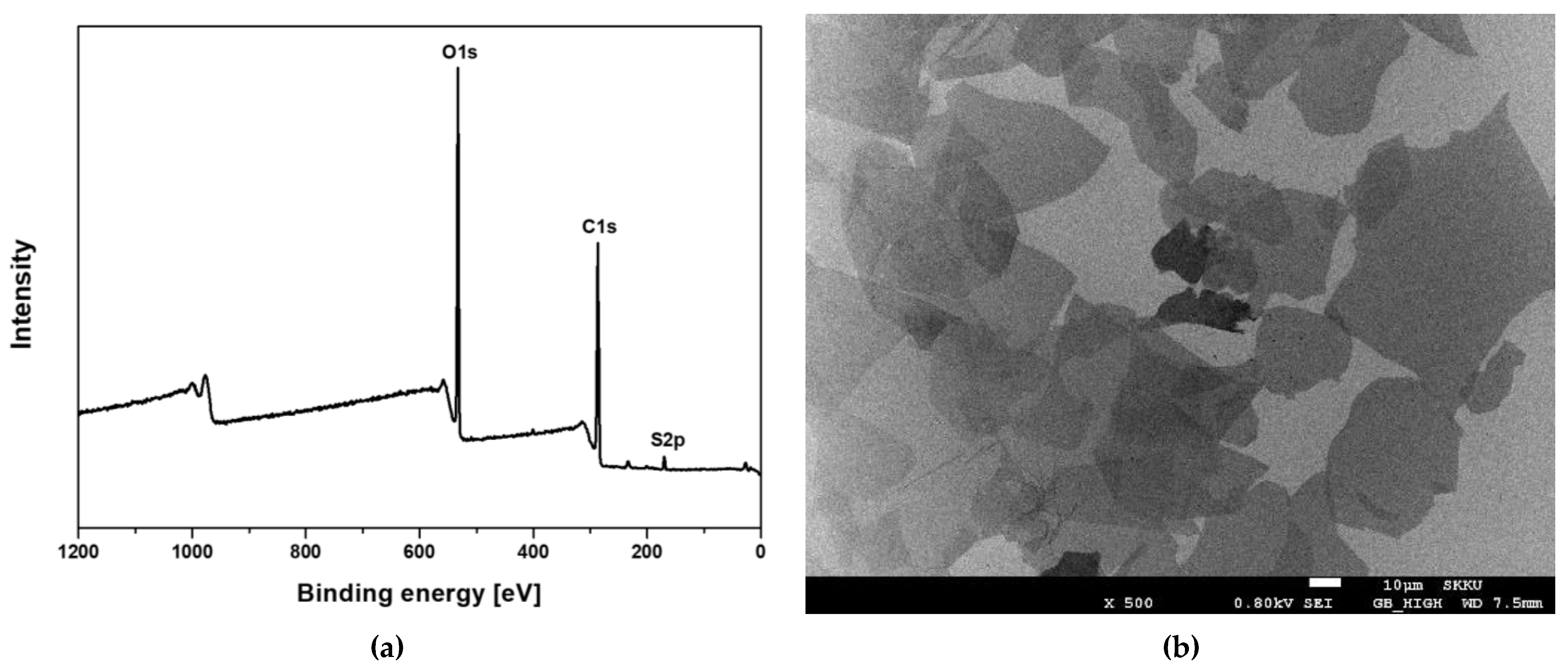
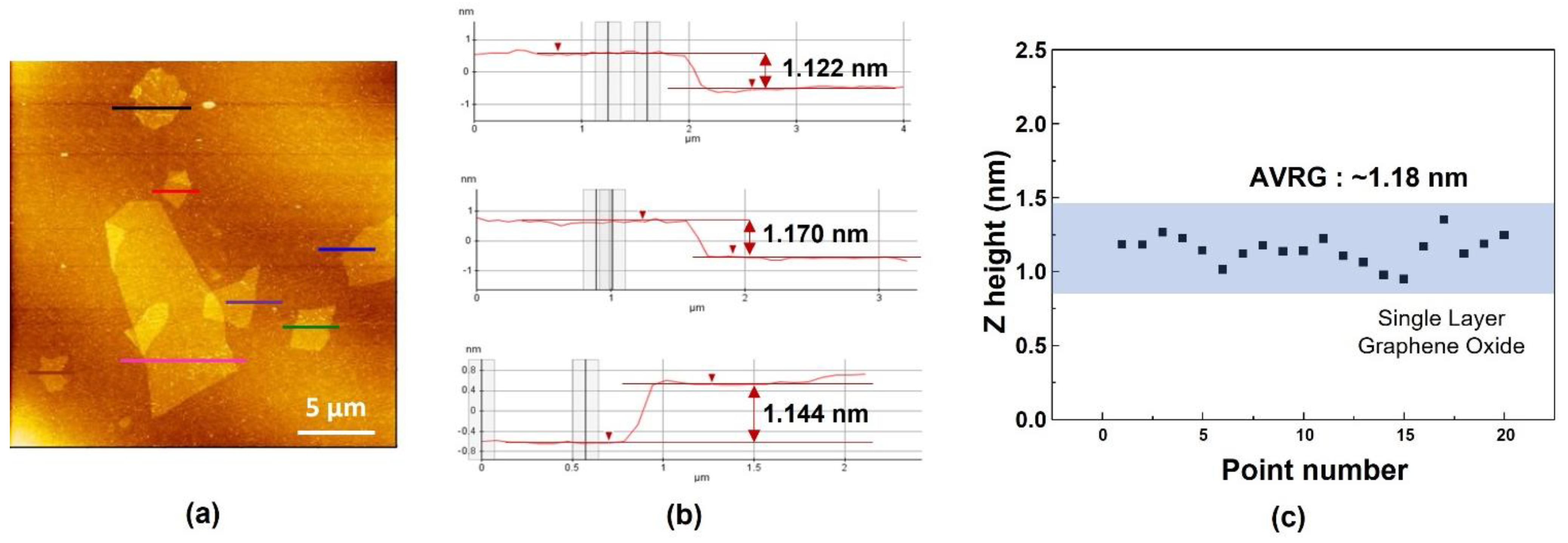
3.1. Characterization of Graphene Oxide (GO)
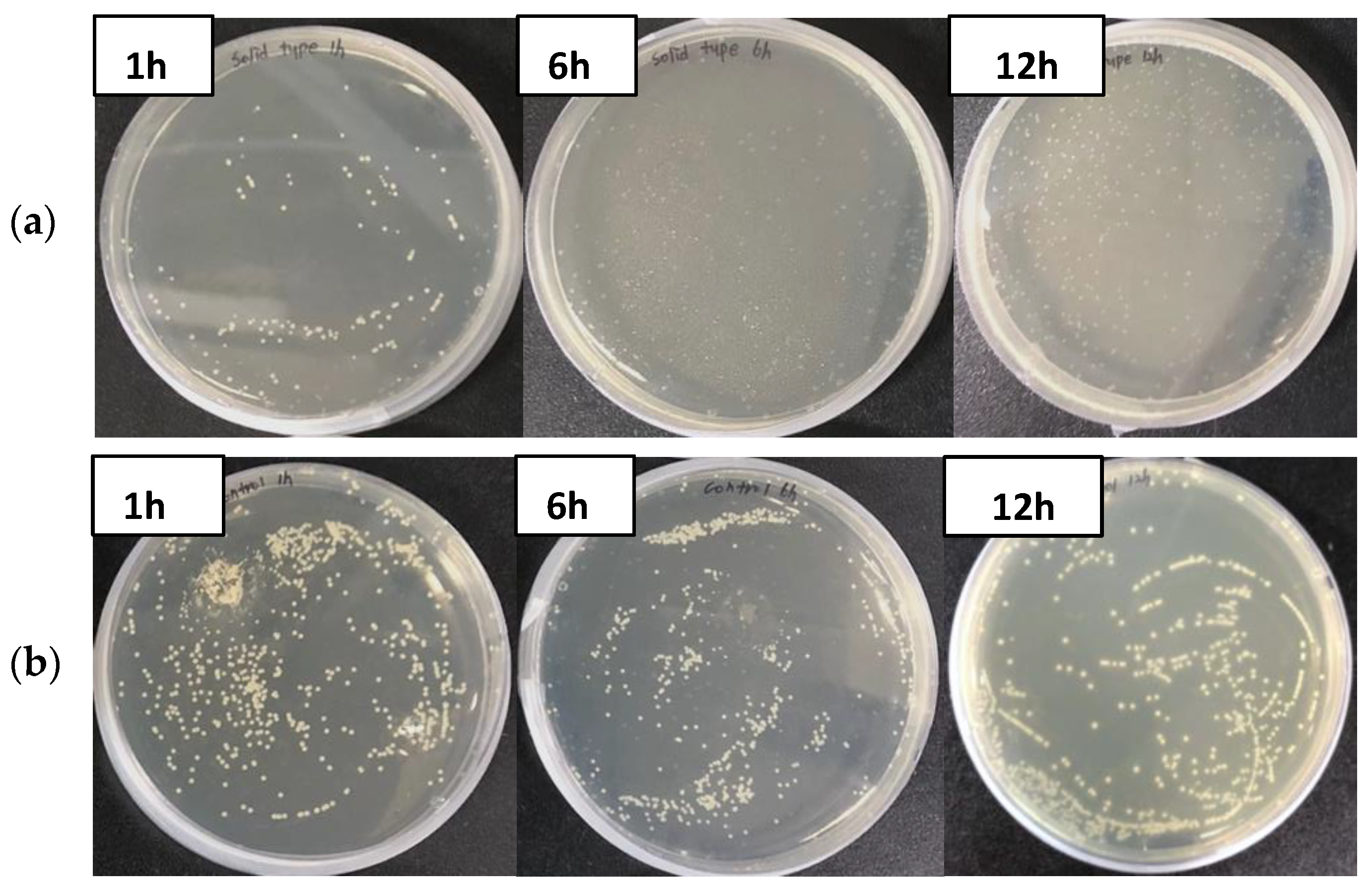
3.2. Antimicrobial Effect of GO Polyester Fiber
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hwang, G.B.; Jung, J.H.; Jeong, T.G.; Lee, B.U. Effect of hybrid UV-thermal energy stimuli on inactivation of S. epidermidis and B. subtilis bacterial bioaerosols. Sci. Total Environ. 2010, 408, 5903–5909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, J.H.; Lee, J.E.; Kim, S.S. Thermal effects on bacterial bioaerosols in continuous air flow. Sci. Total Environ. 2009, 407, 4723–4730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.U.; Yun, S.H.; Ji, J.H.; Bae, G.N. Inactivation of S. epidermidis, B. subtilis, and E. coli bacteria bioaerosols deposited on a filter utilizing airborne silver nanoparticles. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2008, 18, 176–182. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.Y.; Li, C.S. Control effectiveness of ultraviolet germicidal irradiation on bioaerosols. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2002, 36, 474–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peccia, J.; Hernandez, M. UV-induced inactivation rates for airborne Mycobacterium bovis BCG. J. Occup. Environ. 2004, 1, 430–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barhate, R.S.; Ramakrishna, S. Nanofibrous filtering media: Filtration problems and solutions from tiny materials. J. Membr. Sci. 2007, 296, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Chase, H.A. Applications of membrane techniques for purification of natural products. Biotechnol. Lett. 2010, 32, 601–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podgórski, A.; Bałazy, A.; Gradoń, L. Application of nanofibers to improve the filtration efficiency of the most penetrating aerosol particles in fibrous filters. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2006, 61, 6804–6815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porcelli, N.; Judd, S. Chemical cleaning of potable water membranes: A review. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2010, 71, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Przekop, R.; Gradoń, L. Deposition and filtration of nanoparticles in the composites of nano- and microsized fibers. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 483–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, A.; Wang, R.; Ma, H.; Hsiao, B.S.; Chu, B. Novel nanofibrous scaffolds for water filtration with bacteria and virus removal capability. J. Electron Microsc. 2011, 60, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kemp, S.J.; Kuehn, T.H.; Pui, D.Y.H.; Vesley, D.; Streifel, A.J. Growth of microorganisms on HVAC filters under controlled temperature and humidity conditions. ASHRAE Trans. 1995, 1, 305–316. [Google Scholar]
- McFeters, G.A.; Stuart, D.G. Survival of coliform bacteria in natural waters: Field and laboratory studies with membrane-filter chambers. Appl. Microbio. 1972, 24, 805–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Price, D.L.; Simmons, R.B.; Ezeonu, I.M.; Crow, S.A.; Ahearn, D.G. Colonization of fiberglass insulation used in heating, ventilation and air conditioning systems. J. Ind. Microbiol. 1994, 13, 154–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simmons, R.B.; Crow, S.A. Fungal colonization of air filters for use in heating, ventilating, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems. J. Ind. Microbiol. 1995, 14, 41–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borkow, G.; Gabbay, J. Putting copper into action: Copper-impregnated products with potent biocidal activities. FASEB J. 2004, 1, 1728–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Gusseme, B.; Sintubin, L.; Baert, L.; Thibo, E.; Hennebel, T.; Vermeulen, G.; Uyttendaele, M.; Verstraete, W.; Boon, N. Biogenic silver for disinfection of water contaminated with viruses. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 76, 1082–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, T.; Dormitorio, T.V.; Qiao, M.; Huang, T.S.; Weese, J. N-halamine incorporated antimicrobial nonwoven fabrics for use against avian influenza virus. Vet. Microbiol. 2018, 218, 78–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagman, G.H.; Bailey, J.V.; Weinstein, M.J. Binding of aminoglycoside antibiotics to filtration materials. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1975, 7, 316–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Jang, H.M.; Kim, Y.B.; Choi, S.; Lee, Y.; Shin, S.G.; Unno, T.; Kim, Y.M. Prevalence of antibiotic resistance genes from effluent of coastal aquaculture, South Korea. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 233, 1049–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, W.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, T.; Ding, X.; Li, Y.; Wang, M.; Zeng, Z. Antibiotics, Antibiotic Resistance Genes, and Bacterial Community Composition in Fresh Water Aquaculture Environment in China. Microb. Ecol. 2015, 70, 425–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dreyer, D.R.; Park, S.; Bielawski, C.W.; Ruoff, R.S. The Chemistry of Graphene Oxide; Springer: Cham, The Netherlands, 2010; Volume 39, pp. 228–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Ma, R.; Gao, M.; Tian, X.; Li, Y.Q.; Zeng, L.; Li, R. Antibacterial applications of graphene oxides: Structure-activity relationships, molecular initiating events and biosafety. Sci. Bull. 2018, 63, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurunathan, S.; Han, J.W.; Dayem, A.A.; Eppakayala, V.; Kim, J.H. Oxidative stress-mediated antibacterial activity of graphene oxide and reduced graphene oxide in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Int. J. Nanomed. 2012, 7, 5901–5914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Mansukhani, N.D.; Guiney, L.M.; Ji, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Chang, C.H.; French, C.T.; Miller, J.F.; Hersam, M.C.; Nel, A.E.; et al. Identification and Optimization of Carbon Radicals on Hydrated Graphene Oxide for Ubiquitous Antibacterial Coatings. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 10966–10980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.; Zhang, J.; Xiong, Z.; Yong, Y.; Zhao, X.S. Preparation, characterization and antibacterial properties of silver-modified graphene oxide. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 3350–3352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhavan, O.; Ghaderi, E. Toxicity of graphene and graphene oxide nanowalls against bacteria. ACS Nano 2010, 4, 5731–5736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivi, M.; Alfè, M.; Gargiulo, V.; Valle, F.; Mura, F.; Di Giosia, M.; Rapino, S.; Palleschi, C.; Uccelletti, D.; Fiorito, S. Antimicrobial properties of graphene-like nanoparticles: Coating effect on Staphylococcus aureus. J. Nanopart. Res. 2016, 18, 358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canals, R.; Ramirez, S.; Vilches, S.; Horsburgh, G.; Shaw, J.G.; Tomás, J.M.; Merino, S. Polar flagellum biogenesis in Aeromonas hydrophila. J. Bacteriol. 2006, 188, 542–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, I.Y.; Joh, K. Rapid detection of virulence factors of Aeromonas isolated from a trout farm by hexaplex-PCR. Int. J. Nanomed. 2007, 45, 297–304. [Google Scholar]
- Patterson, M.J. Streptococcus. In Medical Microbiology, 4th ed.; Baron, S., Ed.; University of Texas Medical Branch at Galveston: Galveston, TX, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Pier, G.B.; Madin, S.H. Streptococcus iniae sp. nov., a beta hemolytic streptococcus isolated from an Amazon freshwater dolphin, Inia geoffrensis. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 1976, 26, 545–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doménech, A.; Fernández-Garayzábal, J.F.; Pascual, C.; Garcia, J.A.; Cutuli, M.T.; Moreno, M.A.; Collins, M.D.; Dominguez, L. Streptococcosis in cultured turbot, Scophthalmus maximus (L.), associated with Streptococcus parauberis. J. Fish Dis. 1996, 19, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhou, M.; Wang, F.; Wang, E.T.; Du, Z.; Wu, C.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, W.; Xie, Z. Photobacterium proteolyticum sp. Nov., a protease-producing bacterium isolated from ocean sediments of Laizhou Bay. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2017, 67, 1835–1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lo, N.; Jin, H.M.; Jeon, C.O. Photobacterium aestuarii sp. nov., a marine bacterium isolated from a tidal flat. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2014, 64, 625–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.H.; Woo, S.H.; Lee, S.J.; Park, S.I. The Infection Characteristics of Vibrio scophthalmi Isolated from Olive Flounder, Paralichthys olivaceus. J. Fish. Pathol. 2013, 26, 207–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarter, L.L. Polar Flagellar Motility of the Vibrionaceae. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2001, 65, 445–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Austin, B.; Zhang, X.H. Vibrio harveyi: A significant pathogen of marine vertebrates and invertebrates. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2006, 43, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerdà-Cuéllar, M.; Rosselló-Mora, R.A.; Lalucat, J.; Jofre, J.; Blanch, A. Vibrio scophthalmi sp. nov., a new species from turbot (Scophthalmus maximus). Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 1997, 47, 58–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, G.; Lee, D.C.; Woo, S.H.; Li, H.; Xu, D.H.; Park, S.I. Microbiological characteristics of Vibrio scophthalmi isolates from diseased olive flounder Paralichthys olivaceus. Fish. Sci. 2012, 78, 853–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugita, H.; Ito, Y. Identification of intestinal bacteria from Japanese flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus) and their ability to digest chitin. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2006, 43, 336–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Austin, B.; Austin, D.A. Enterobacteriaceae Representatives. In Bacterial Fish Pathogens; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 323–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janda, J.M.; Abbott, S.L.; Kroske-Bystrom, S.; Cheung, W.K.W.; Powers, C.; Kokka, R.P.; Tamura, K. Pathogenic properties of Edwardsiella species. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1991, 29, 35–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Q.; Zhou, M.; Zhu, L.; Zhu, G. Flagella and bacterial pathogenicity. J. Basic Microb. 2013, 53, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossez, Y.; Wolfson, E.B.; Holmes, A.; Gally, D.L.; Holden, N.J. Bacterial Flagella: Twist and Stick, or Dodge across the Kingdoms. PLoS Pathog. 2015, 11, e1004483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, Y.; Lin, G.; Chen, W.; Xu, X.; Yan, Q. Flagellar motility is necessary for Aeromonas hydrophila adhesion. Microb. Pathog. 2016, 98, 160–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Bacteria | 1 h (CFU/mL) | 6 h (CFU/mL) | 12 h (CFU/mL) | Antimicrobial Effect (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A. hydrophila | GO fiber | 1.17 × 104 | 0 | 0 | 100 |
| Control | 5.6 × 104 | 4.5 × 104 | 6.3 × 104 | 0 | |
| S. parauberis | GO fiber | 6.3 × 104 | 1.6 × 103 | 0 | 100 |
| Control | 1.23 × 105 | 1.24 × 105 | 1.2 × 105 | 0 | |
| S. iniae | GO fiber | 5.1 × 104 | 1 × 103 | 3 × 102 | 99 |
| Control | 4.3 × 104 | 8.5 × 104 | 5.7 × 104 | 0 | |
| P. piscicola | GO fiber | 5.5 × 104 | 1.9 × 102 | 0 | 100 |
| Control | 9.2 × 104 | 5 × 104 | 1 × 105 | 0 | |
| E. tarda | GO fiber | 9.2 × 104 | 8 × 104 | 8.8 × 104 | 0 |
| Control | 1 × 105 | 1 × 105 | 5.6 × 104 | 0 | |
| V. scophthalmi | GO fiber | 6 × 103 | 4.4 × 103 | 9.2 × 103 | 0 |
| Control | 2.6 × 105 | 1 × 105 | 1 × 105 | 0 | |
| V. harveyi | GO fiber | 7 × 104 | 2 × 105 | 2.5 × 105 | 0 |
| Control | 5.2 × 104 | 1.5 × 105 | 2.2 × 105 | 0 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, J.H.; Yoo, H.; Ahn, Y.J.; Kim, H.J.; Kwon, S.R. Evaluation of the Antimicrobial Effect of Graphene Oxide Fiber on Fish Bacteria for Application in Aquaculture Systems. Materials 2022, 15, 966. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15030966
Lee JH, Yoo H, Ahn YJ, Kim HJ, Kwon SR. Evaluation of the Antimicrobial Effect of Graphene Oxide Fiber on Fish Bacteria for Application in Aquaculture Systems. Materials. 2022; 15(3):966. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15030966
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Ji Hyun, Heejoun Yoo, Yu Jin Ahn, Hyoung Jun Kim, and Se Ryun Kwon. 2022. "Evaluation of the Antimicrobial Effect of Graphene Oxide Fiber on Fish Bacteria for Application in Aquaculture Systems" Materials 15, no. 3: 966. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15030966
APA StyleLee, J. H., Yoo, H., Ahn, Y. J., Kim, H. J., & Kwon, S. R. (2022). Evaluation of the Antimicrobial Effect of Graphene Oxide Fiber on Fish Bacteria for Application in Aquaculture Systems. Materials, 15(3), 966. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15030966





