The Microstructure and Corrosion Resistance of Fe-B-W-Mn-Al Alloy in Liquid Zinc
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Procedures
2.1. Specimens Preparation
2.2. Morphology and Phase Characterization of the Specimen
2.3. Corrosion Test in Molten Zinc
2.4. Vickers Micro-Indentation Fracture Toughness Test
3. Results
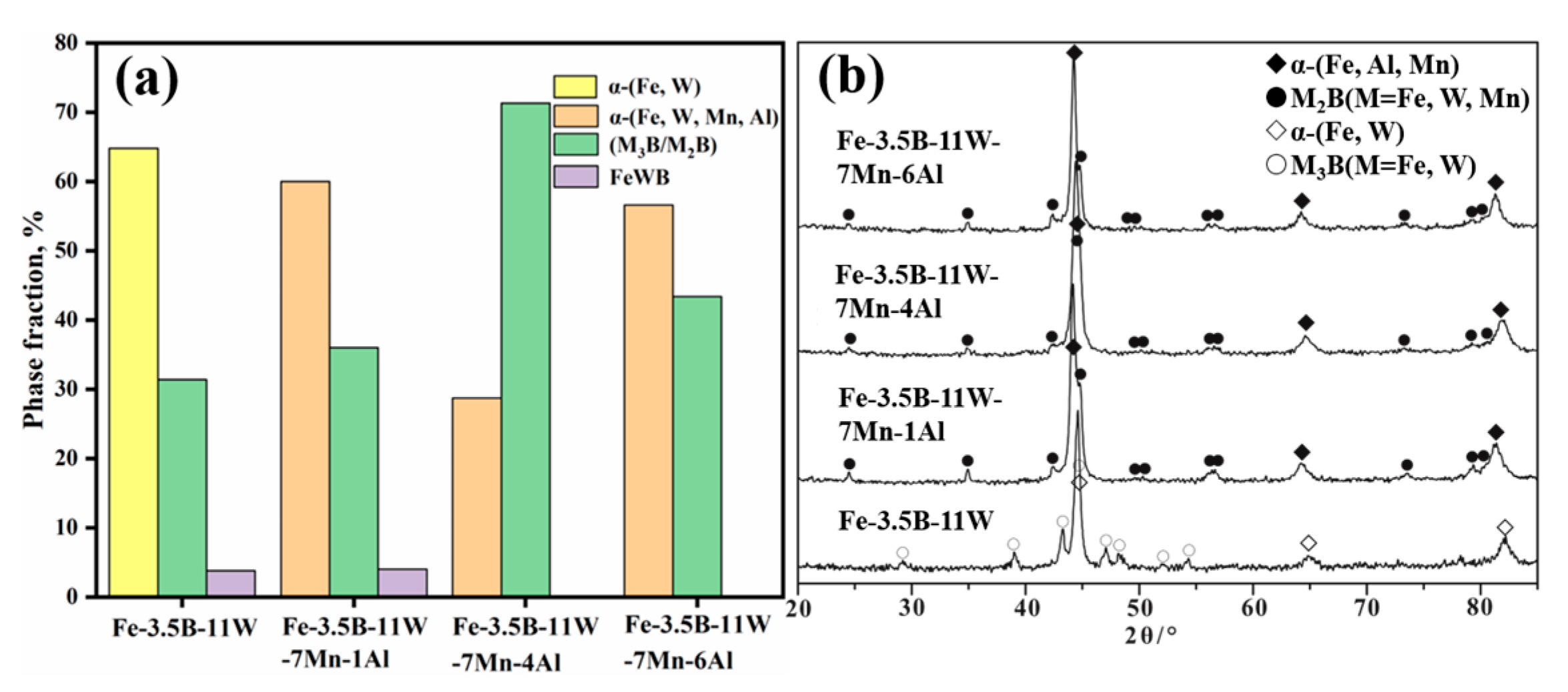
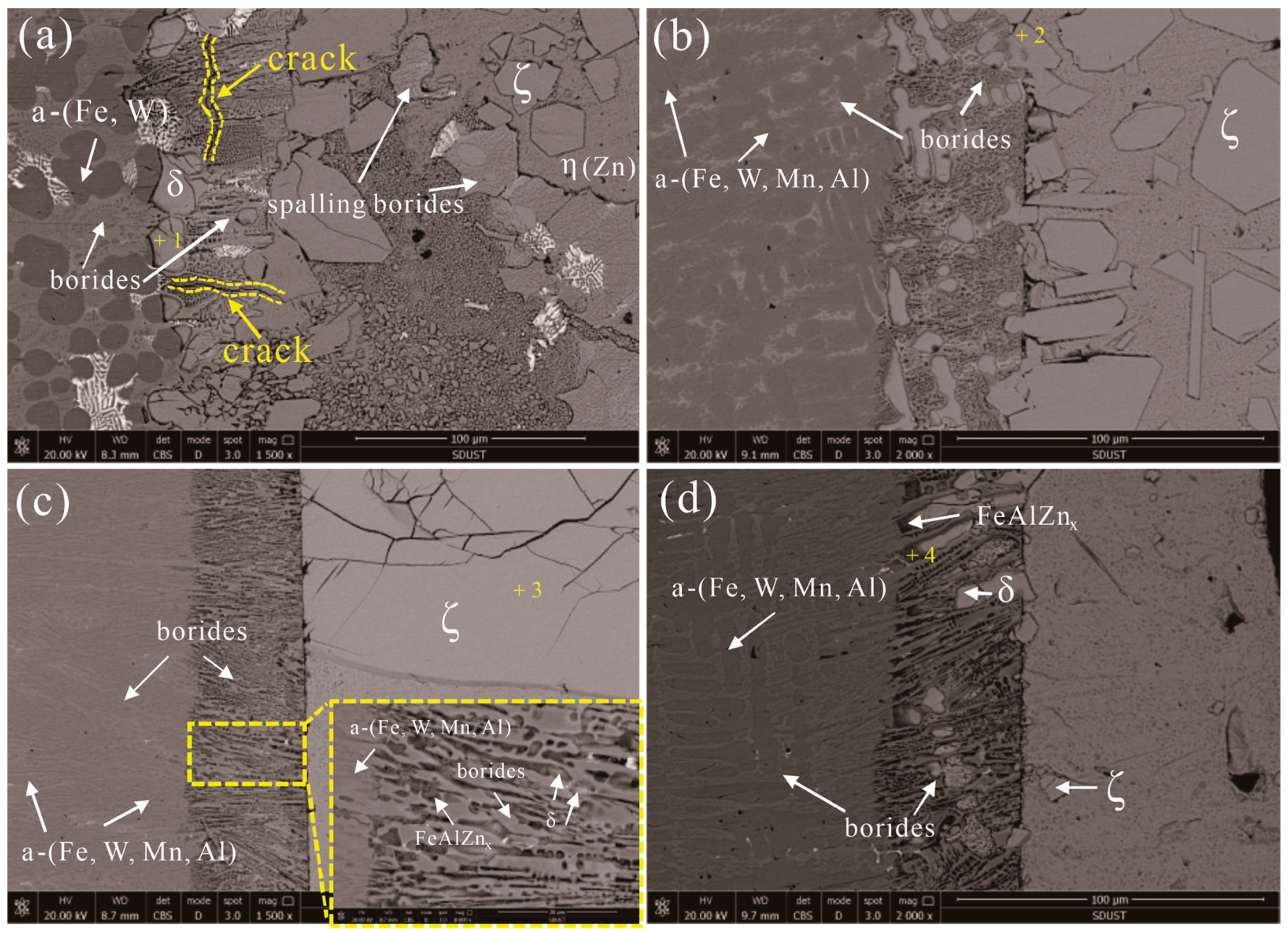
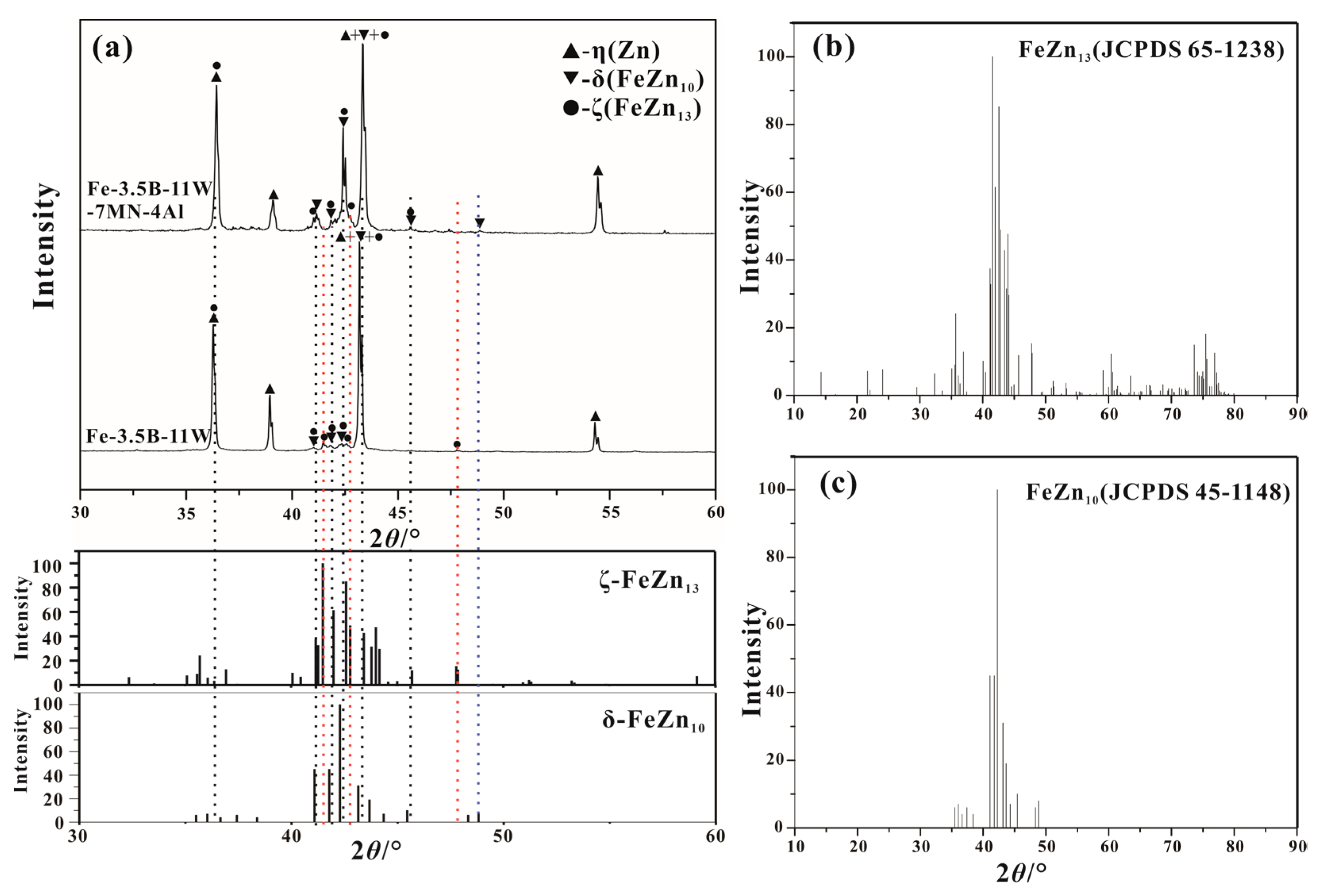
3.1. Microstructural Characteristics
3.2. Micro-Hardness Testing
3.3. Corrosion Kinetics
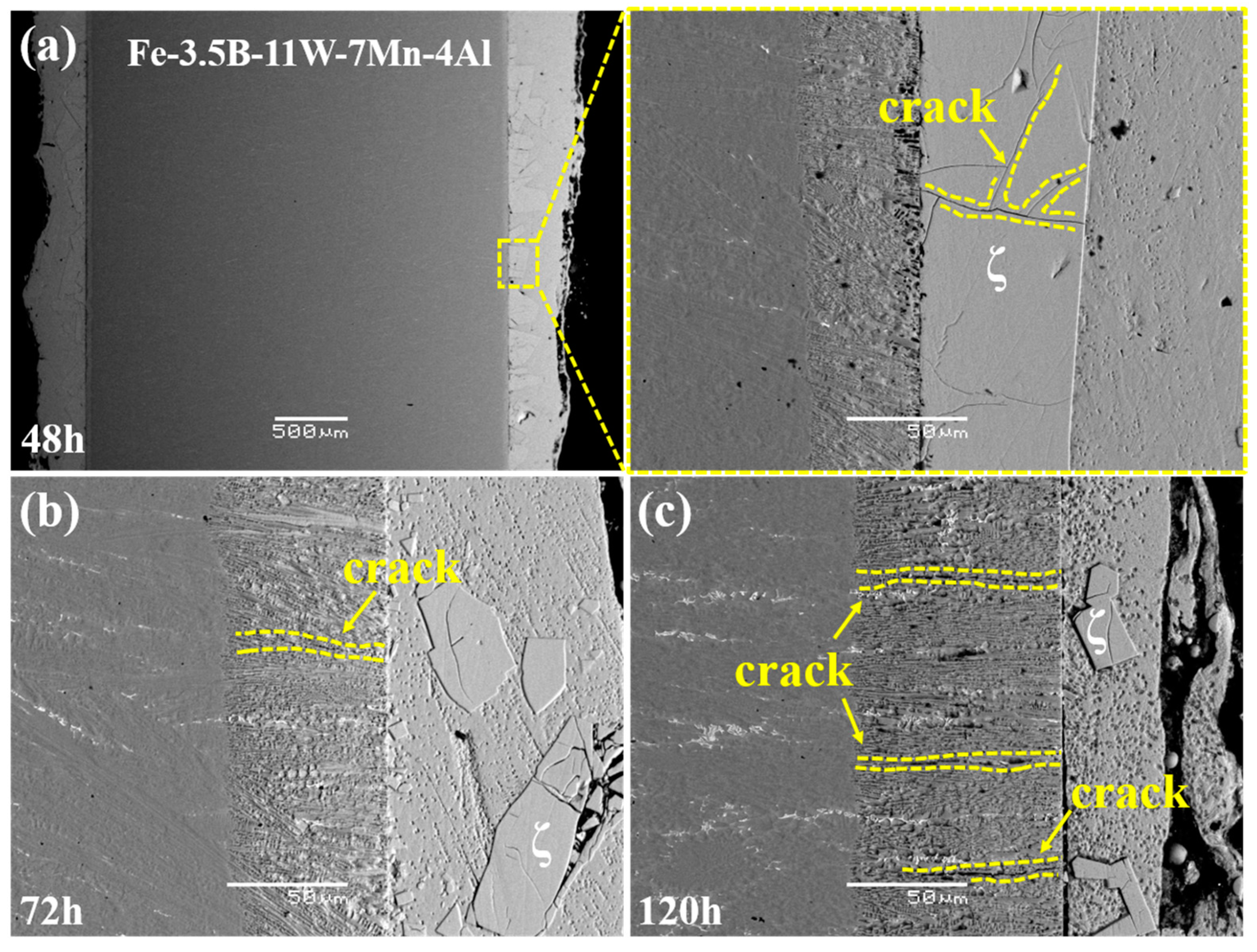
3.4. Corrosion Layer Characterization
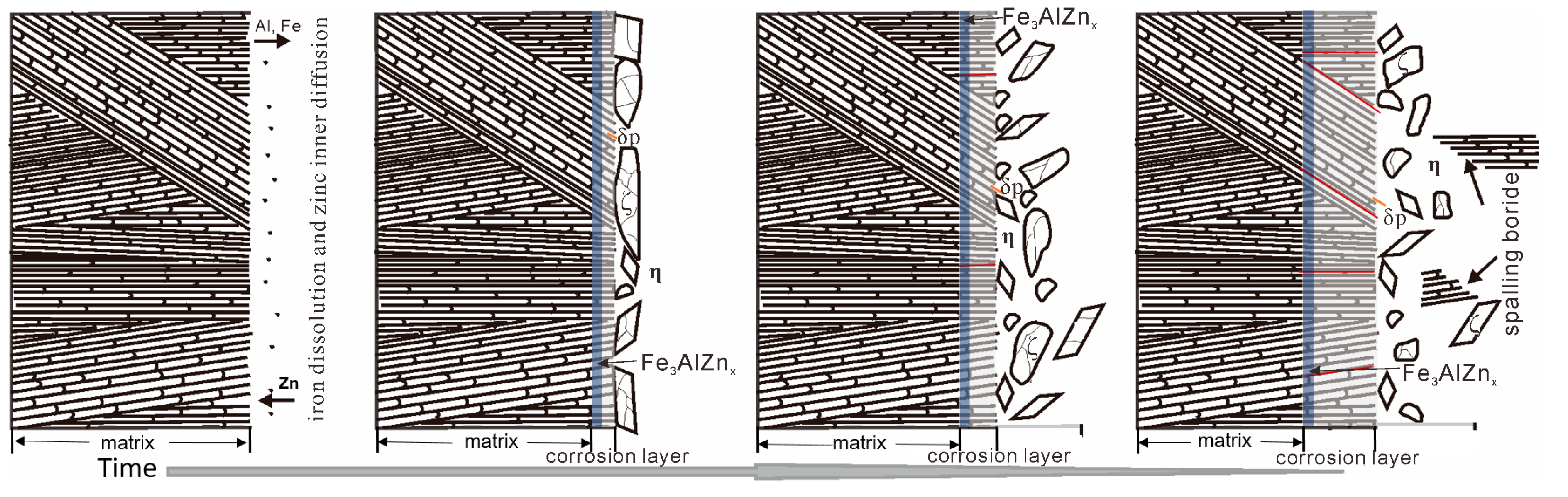
4. Corrosion Mechanism
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- With the addition of Mn to Fe-3.5B-11W, the microstructures of the Fe-3.5B-11W alloys change from hypoeutectic to eutectic, facilitating the formation of M2B-type boride and restraining the formation of M3B-type borides. In the meantime, the fracture toughness obviously increases.
- (2)
- Proper Mn and Fe-3.5B-11W contents can stabilize the Fe2B phase and improve the corrosion resistance in a zinc bath. The Fe-3.5 wt.% B alloy containing 11 wt.% W, 7wt. % Mn, and 4 wt.% Fe-3.5B-11W, with few microcracks, has the best corrosion resistance.
- (3)
- The lamellar borides provide the mechanical protection for α-(Fe, W, Mn, Al). With the fracture toughness of the borides increasing, the thermal stability of the borides improves, thereby suppressing boride spalling and corrosion failure.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Peng, B.; Wang, J.; Su, X.; Li, Z.; Yin, F. Effects of zinc bath temperature on the coatings of hot-dip galvanizing. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2008, 202, 1785–1788. [Google Scholar]
- Verma, A.R.B.; van Ooij, W.J. High-temperature batch hot-dip galvanizing. Part 1. General description of coatings formed at 560 °C. Surf. Coat. Technol. 1997, 89, 132–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudnik, E. Hydrometallurgical recovery of zinc from industrial hot dipping top ash. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2020, 30, 2239–2255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.-t.; Wang, X.-h.; Che, C.-s.; Kong, G.; Chen, J.-h.; Xu, Q.-y. Crystallographic research of spangle on hot dip galvanized steel sheets. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2007, 17, 351–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Townsend, H.E.; Steinbicker, R.N.; Yau, Y.H. Corrosion of Stainless Steel Conductor Rolls in a Continuous Sheet Electrogalvanizing Line. Corrosion 1990, 46, 418–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.J.; Lin, J.P.; Wang, Y.L.; Chen, G.L. The corrosion of intermetallic alloys in liquid zinc. J. Alloys Compd. 2007, 428, 237–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.J.; Lin, J.P.; Wang, Y.L.; Chen, G.L. The corrosion of Fe3Al alloy in liquid zinc. Corros. Sci. 2007, 49, 1340–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Z.Y.; Wang, X.M.; Yin, F.C.; Ouyang, X.M.; Jing-Xian, H.U. Phase equilibria of CoMoZn ternary system. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2020, 30, 417–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan-Tao, H.U.; Zheng, L.; Yan, H.J.; Lian-Kui, W.U.; Jiang, M.Y. Improving hot corrosion resistance of aluminized TiAl alloy by anodization and pre-oxidation. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2021, 31, 193–206. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Barbero, E.; Xu, J.; Burris, M.; Chang, K.-M.; Sikka, V. Liquid metal corrosion of 316L, Fe3Al, and FeCrSi in molten Zn-Al baths. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2005, 36, 2049–2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Xing, J.; Fu, H.; Yi, D.; Zhi, X.; Li, Y. Effects of boron concentration on the corrosion resistance of Fe–B alloys immersed in 460 °C molten zinc bath. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2010, 204, 2208–2214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Xing, J.; Fu, H.; Yi, D.; Li, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, B.; Gao, Y. Microstructure and interface characteristics of Fe–B alloy in liquid 0.25 wt.% Al–Zn at various bath temperatures. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2012, 132, 977–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makuch, N. Nanomechanical properties and fracture toughness of hard ceramic layer produced by gas boriding of Inconel 600 alloy. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2020, 30, 428–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Xing, J.; Guo, C. Improving fracture toughness and hardness of Fe2B in high boron white cast iron by chromium addition. Mater. Des. 2010, 31, 3084–3089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Xing, J.; Lv, L. Effect of tungsten addition on the toughness and hardness of Fe2B in wear-resistant Fe–B–C cast alloy. Mater. Charact. 2013, 75, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian, Y.; Huang, Z.; Xing, J.; Guo, X.; Wang, Y.; Lv, Z. Effects of Mn addition on the two-body abrasive wear behavior of Fe-3.0 wt% B alloy. Tribol. Int. 2016, 103, 243–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, H.; Xiao, Q.; Kuang, J.; Jiang, Z.; Xing, J.D. Effect of rare earth and titanium additions on the microstructures and properties of low carbon Fe-B cast steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2007, 466, 160–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Xing, J.; Fu, H.; Yi, D.; Zhang, J.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zhu, B.; Ma, S. Interfacial morphology and corrosion resistance of Fe–B cast steel containing chromium and nickel in liquid zinc. Corros. Sci. 2011, 53, 2826–2834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Xing, J.; Yi, D.; Fu, H.; Zhang, J.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, G.; Zhu, B. Effects of chromium addition on corrosion resistance of Fe-3.5B alloy in liquid zinc. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2011, 205, 4902–4909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wang, M.; Yin, F.; Ouyang, X.; Li, Z. Effects of Tungsten Addition on the Microstructure and Corrosion Resistance of Fe-3.5B Alloy in Liquid Zinc. Materials 2017, 10, 399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yin, F.; Ouyang, X.; Chen, G.; Zhao, M.; Liu, Y. Effect of Molybdenum on the Microstructures of As-Cast Fe-B Alloys and Their Corrosion Resistance in Molten Zinc. Corrosion 2017, 73, 942–952. [Google Scholar]
- Kato, T.; Nunome, K.; Kaneko, K.; Saka, H. Formation of the ζ phase at an interface between an Fe substrate and a molten 0.2 mass% Al–Zn during galvannealing. Acta Mater. 2000, 48, 2257–2262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akdeniz, M.V.; Mekhrabov, A.O. The effect of substitutional impurities on the evolution of Fe-Al diffusion layer. Acta Mater. 1998, 46, 1185–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Chen, W. Microstructure, mechanical properties and corrosion behavior of an Fe-10Cr-2.7B-5.5Al-13Mn alloy prepared by spark plasma sintering. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 741, 348–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.J.; Ohnuma, I.; Kainuma, R.; Ishida, K. Thermodynamic assessment of the Aluminum-Manganese (Al-Mn) binary phase diagram. J. Phase Equilibria 1999, 20, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hetzner, D. Microindentation Hardness Testing of Materials Using ASTM E384. Microsc. Microanal. 2003, 9, 708–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, K.; Tang, N.-Y.; Goodwin, F.E.; Sexton, S. Reaction of 316L stainless steel with a galvanizing bath. J. Mater. Sci. 2007, 42, 9736–9745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, J.; Li, C.; Liu, Y. Reactive synthesis of FeWB powders and preparation of bulk materials. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2014, 46, 80–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, K.; Wang, R.-c.; Peng, C.-q.; Wang, N.-g.; Cai, Z.-y.; Zhang, C. Effects of Mn and Sn on microstructure of Al–7Si–Mg alloy modified by Sr and Al–5Ti–B. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2015, 25, 3546–3552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Xing, J.; Fu, H.; He, Y.; Bai, Y.; Li, Y.; Bai, Y. Interface characteristics and corrosion behaviour of oriented bulk Fe2B alloy in liquid zinc. Corros. Sci. 2014, 78, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, G.; Lu, J.-t.; Xu, Q.-y. Dissolution mechanism of solid nickel in liquid zinc saturated with Fe. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2007, 17, 564–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esmaily, H.; Habibolahzadeh, A.; Tajally, M. Improving pulsed laser weldability of duplex stainless steel to 5456 aluminum alloy via friction stir process reinforcing of aluminum by BNi-2 brazing alloy. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2019, 29, 1401–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xing, J.; Ma, S.; Liu, G.; He, Y.; Yang, D.; Bai, Y. Effect of Fe2B orientation on erosion–corrosion behavior of Fe–3.5 wt.% B steel in flowing zinc. Corros. Sci. 2015, 98, 240–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Xing, J.; He, Y.; Fu, H.; Li, Y.; Liu, G. Effect of orientation and lamellar spacing of Fe2B on interfaces and corrosion behavior of Fe-B alloy in hot-dip galvanization. Acta Mater. 2016, 115, 392–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]




| Specimens | W | Mn | B | Al | Balance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fe-3.5B-11W | 11 | 0 | 3.5 | 0 | Fe |
| Fe-3.5B-11W-7Mn-1Al | 11 | 7 | 3.5 | 1 | Fe |
| Fe-3.5B-11W-7Mn-4Al | 11 | 7 | 3.5 | 4 | Fe |
| Fe-3.5B-11W-7Mn-6Al | 11 | 7 | 3.5 | 6 | Fe |
| Fe-4.2B-11W-7Mn-4Al | 11 | 7 | 4.2 | 4 | Fe |
| Alloy | Phase | Fe | W | B | Mn | Al | Calculated Phase Fraction |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fe-3.5B-11W | α-(Fe, W) | 98.7 | 1.3 | - | - | - | 64.8% |
| (Fe, W)3B | 75.3 | 3.0 | 21.7 | - | - | 31.4% | |
| FeWB | 34.1 | 32.3 | 33.6 | - | - | 3.8% | |
| Fe-3.5B-11W-7Mn-1Al | α-(Fe, W, Mn, Al) | 87.8 | 0.8 | - | 5.2 | 6.2 | 60.0% |
| (Fe, W, Mn)2B | 52.4 | 2.6 | 32.4 | 12.2 | 0.4 | 36.0% | |
| FeWB | 32.2 | 35.2 | 32.6 | - | - | 4.0% | |
| Fe-3.5B-11W-7Mn-4Al | α-(Fe, W, Mn, Al) | 82.0 | 0.7 | - | 5.5 | 11.8 | 28.7% |
| (Fe, W, Mn)2B | 50.7 | 3.8 | 32.4 | 11.6 | 1.5 | 71.3% | |
| Fe-3.5B-11W-7Mn-6Al | α-(Fe, W, Mn, Al) | 80.2 | 0.6 | - | 5.3 | 13.9 | 56.6% |
| (Fe, W, Mn)2B | 56.3 | 3.5 | 25.7 | 11.8 | 2.7 | 43.4% |
| Position | Fe | Al | Zn | W | Mn | Phase | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| wt.% | at.% | wt.% | at.% | wt.% | at.% | wt.% | at.% | wt.% | at.% | ||
| +1 in Fe-3.5B-11W | 10.9 | 13.1 | - | - | 81.4 | 84.0 | 7.7 | 2.5 | - | - | δ-FeZn10 |
| +2 in Fe-3.5B-11W-7Mn-1Al | 11.7 | 13.7 | 0.4 | 1.0 | 84.1 | 83.7 | 3.3 | 1.2 | 0.5 | 0.4 | δ-FeZn10 |
| +3 in Fe-3.5B-11W-7Mn-4Al | 7.1 | 8.2 | - | - | 92.9 | 91.8 | - | - | - | - | ζ-FeZn13 |
| +4 in Fe-3.5B-11W-7Mn-6Al | 31.6 | 24.1 | 38.7 | 61.2 | 17.7 | 11.6 | 11.6 | 2.7 | 0.4 | 0.4 | Fe3AlZnx |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Luo, Z.; Liu, K.; Cui, Z.; Ouyang, X.; Zhang, C.; Yin, F. The Microstructure and Corrosion Resistance of Fe-B-W-Mn-Al Alloy in Liquid Zinc. Materials 2022, 15, 1092. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15031092
Luo Z, Liu K, Cui Z, Ouyang X, Zhang C, Yin F. The Microstructure and Corrosion Resistance of Fe-B-W-Mn-Al Alloy in Liquid Zinc. Materials. 2022; 15(3):1092. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15031092
Chicago/Turabian StyleLuo, Zixiang, Ke Liu, Zizhen Cui, Xuemei Ouyang, Chen Zhang, and Fucheng Yin. 2022. "The Microstructure and Corrosion Resistance of Fe-B-W-Mn-Al Alloy in Liquid Zinc" Materials 15, no. 3: 1092. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15031092
APA StyleLuo, Z., Liu, K., Cui, Z., Ouyang, X., Zhang, C., & Yin, F. (2022). The Microstructure and Corrosion Resistance of Fe-B-W-Mn-Al Alloy in Liquid Zinc. Materials, 15(3), 1092. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15031092







