Microstructures and Mechanical Properties of an AlCoCrNiFe HEA/WC Reinforcing Particle Composite Coating Prepared by Laser Cladding
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Methods
3. Results and Discussions
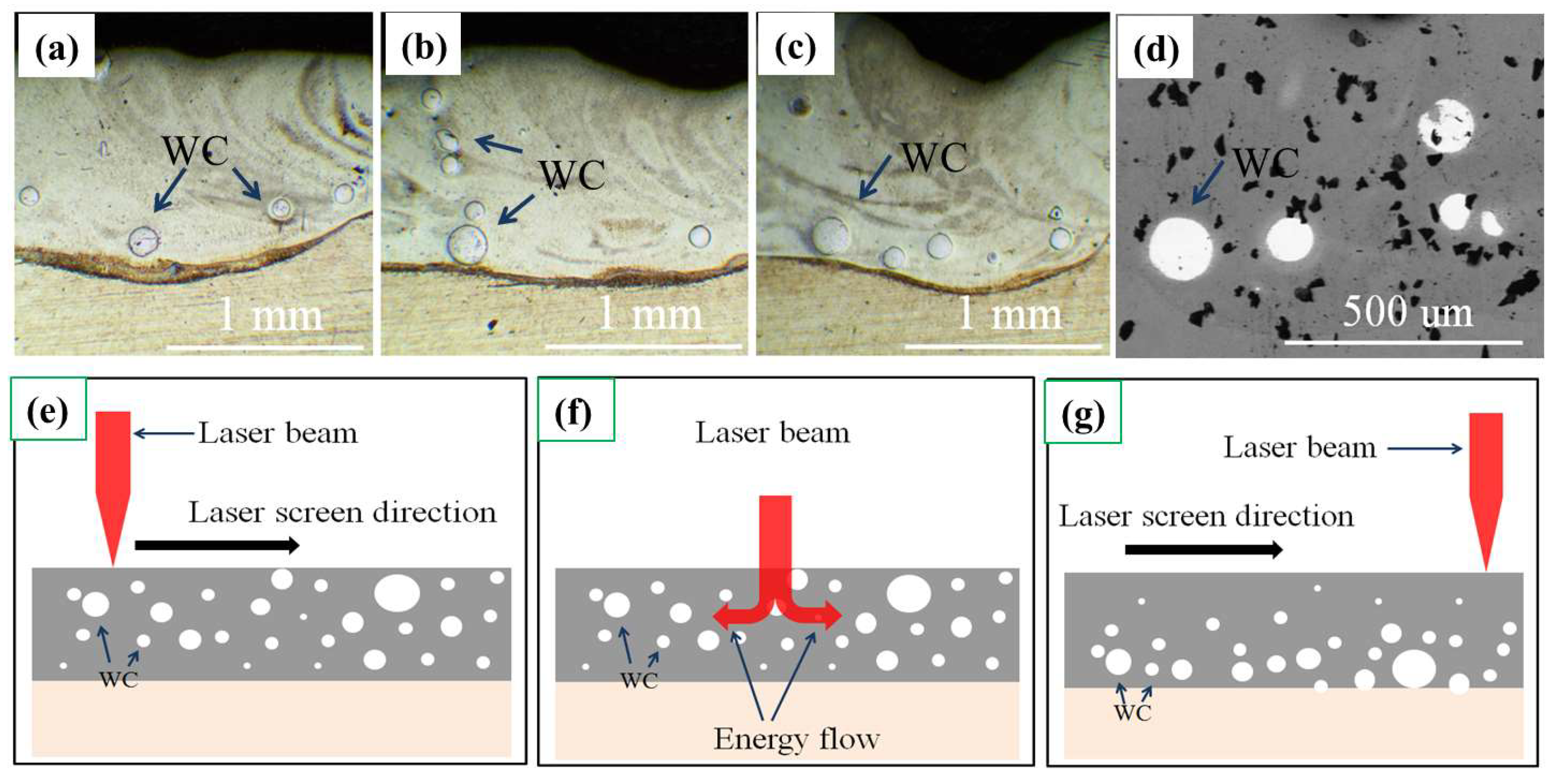
3.1. Morphology of the AlCoCrFeNi HEA Composite Coatings
3.2. Phase Composition
3.3. Mechanical Properties of the Cladded Coating
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- The morphology of the HEA composite coating was observed and explained by the differences in the flow and density of matrix in the molten pool and constitutional undercooling criterion.
- (2)
- The diffraction peaks with the highest intensity were identified as the solid solution, with a BCC phase as the major constituent, while the remaining diffraction peaks were identified as some metal carbides and WC.
- (3)
- The microhardnesses of the HAZ and HEA/WC coating were 1.5 times and 3 times that of the 316Lss substrate, respectively. The main reasons for this are the grain refinement strengthening and solid solution hardening.
- (4)
- In the electrochemical experiments, compared with the 316Lss substrate (Ecorr = −0.705 V and Icorr = 8.184 × 10−7), the HEA/WC coating had a higher positive corrosion potential (Ecorr = −0.633 V) and a lower corrosion current density (Icorr = 5.921 × 10−8), which indicates that the corrosion resistance of the 316Lss was enhanced by the HEA/WC composite cladded coating.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yeh, J.W.; Chen, S.K.; Lin, S.J.; Gan, J.Y.; Chin, T.S.; Shun, T.T. Nanostructured high-entropy alloys with multiple principal elements: Novel alloy design concepts and Outcomes. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2004, 6, 299–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantor, B.; Chang, I.T.; Knight, H.P.; Vincent, A.J.B. Microstructural development in equiatomic multicomponent alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2004, 375–377, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; He, Y.Z.; Pan, Y.; Guo, S. Thermally stable laser cladded CoCrCuFeNi high-entropy alloy coating with low stacking fault energy. J. Alloys Compd. 2014, 600, 210–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, J.; Haghdadi, N.; Shamlaye, K.; Hodgson, P.; Barnett, M.; Fabijanic, D. The sliding wear behaviour of CoCrFeMnNi and AlxCoCrFeNi high entropy alloys at elevated temperatures. Wear 2019, 428–429, 32–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Li, T.; Liao, Y.; Li, C.; Jang, J.S.; Hsueh, C. Hardness and strength enhancements of CoCrFeMnNi high-entropy alloy with Nd doping. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 764, 138192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, T.M.; Weaver, M.L. Oxidation behavior of arc melted AlCoCrFeNi multi- component high-entropy alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2016, 674, 229–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, T.M.; Zhang, H. Laser cladding of FeCoNiCrAlCuxSi0.5 high entropy alloys on AZ31 Mg alloy substrates. Mater. Res. Innovat. 2014, 18, 624–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Q.W.; Zhang, G.J.; Yin, K.X.; Wang, W.W.; Cheng, W.L.; Wang, Y.N. The strengthening effects of relatively lightweight AlCoCrFeNi high entropy alloy. Mater. Charact. 2019, 151, 302–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Wu, C.L.; Zhang, C.H.; Guan, M.; Tan, J.Z. Laser surface alloying of FeCoCrAlNi high-entropy alloy on 304 stainless steel to enhance corrosion and cavitation erosion resistance. Opt. Laser Technol. 2016, 84, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Z.; Cui, X.; Liu, Z.; Li, Y.; Dong, M.; Jin, G. Microstructure and wear resistance of laser cladded Ni-Cr-Co-Ti-V high-entropy alloy coating after laser remelting processing. Opt. Laser Technol. 2018, 99, 276–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunen, A.; Lindner, T.; Karakas, M.S. Effect of the boriding environment on the wear response of laser-clad AlCoCrFeNi HEA coatings. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2022, 29, 128830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.M.; Ding, N.; Liu, G.Q. Microstructure evolution of a multi-track AlCoCrFeNi HEA coatings fabricated by laser cladding. Mater. Charact. 2022, 184, 111660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, Z.Z.; Sun, Y.N.; Cheng, W.J. Laser remelting induces grain refinement and properties enhancement in high-speed laser cladding AlCoCrFeNi HEA coatings. Intermetallics 2022, 150, 107686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.T.; Wang, K.M.; Fu, H.G. Microstructure and wear resistance of in-situ TiC reinforced AlCoCrFeNi-based coatings by laser cladding. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2022, 585, 152703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.F.; Feng, Y.H. Influence of NbC particles on microstructure and mechanical properties of AlCoCrFeNi HEA coatings prepared by laser cladding. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 788, 485–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, J.P.; Wu, Y.P.; Hong, S. Effects of WC addition on the erosion behavior of high-velocity oxygen fuel sprayed AlCoCrFeNi HEA coatings. Ceram. Int. 2022, 48, 18502–18512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurizi Enrici, T.; Dedry, O.; Boschini, F.; Tchuindjang, J.T.; Mertens, A. Microstructural and Thermal Characterization of 316L+WC Composite Coatings obtained by Laser Cladding. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2020, 22, 2000291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, Z.; Yong, X.; Bang, L. Effect of laser remelting on microstructure and properties of WC reinforced Fe-based amorphous composite coatings by laser cladding. Opt. Laser Technol. 2018, 103, 8–16. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, L.; Xiao, S.H.; Yang, Z. Multi-objective optimization of coating properties and cladding efficiency in 316L/WC composite laser cladding based on grey relational analysis. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2021, 112, 1449–1459. [Google Scholar]
- Mohammad, E.; Hassan, A.-P.; Hamidreza, M.-S. Kinetics and oxidation behavior of laser clad WC-Co and Ni/WC-Co coatings. Ceram. Int. 2018, 44, 12805–12814. [Google Scholar]
- Rutter, J.W.; Chalmers, B. A prismatic substructure formed during solidification of metals. Can. J. Phys. 1953, 31, 15–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.B.; Zhang, W.; Li, T.C. Microstructures and mechanical properties of FeCoCrNi high entropy alloy/WC reinforcing particles composite coatings prepared by laser cladding and plasma cladding. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2019, 84, 105044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.L.; Chen, J.L.; Cheng, Q.Q. Microstructure and sliding wear behavior of AlCoCrFeNi1-xWCx. Ceram. Int. 2022, 48, 19399–19411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toyserkani, E.; Khajepour, A.; Corbin., S.F. Laser Cladding; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Yeh, J.W. Alloy design strategies and future trends in high entropy alloy. Met. Mater. Soc. 2013, 65, 1759–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zuo, T.T.; Tang, Z. Microstructures and properties of high entropy alloys. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2014, 61, 1–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, J.Y.; Yu, G.; He, X.; Li, S.X.; Chen, R.; Zhao, Y. Grain size evolution under different cooling rate in laser additive manufacturing of superalloy. Opt. Laser. Technol. 2019, 119, 105662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, D.; Chao, W.; Chai, L.J. Mechanical and chemical properties of CoCrFeNiMo0.2 high entropy alloy coating fabricated on Ti6Al4V by laser cladding. Intermetallics 2022, 144, 107504. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.J.; Han, D.; Li, X.W. Impact of short range ordering on the anomalous four-stage strain hardening behavior of low solid-solution hardening Ni-Cr alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2021, 814, 141193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sha, M.H.; Jia, C.T.; Qiao, J.; Feng, W.Q.; Ai, X.G.; Jing, Y.A.; Shen, M.G.; Li, S.L. Microstructure and properties of high-entropy AlxCoCrFe2.7MoNi alloy coatings prepared by laser cladding. Metals 2019, 9, 1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Hu, S.W.; Li, W.H. Corrosion monitoring for prestressed concrete cylinder pipe spigot with combined use of Tafel extrapolation and surface acoustic wave methods. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 337, 127572. [Google Scholar]
- Hao, Z.W.; Cheng, Y.H.; Yang, J.Y. Microstructure and properties of laser clad Fe-based amorphous alloy coatings containing Nb powder. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2020, 550, 120351. [Google Scholar]
- Lei, J.B.; Shi, C.; Zhou, S.F. Enhanced corrosion and wear resistance properties of carbon fiber reinforced Ni-based composite coating by laser cladding. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2018, 334, 274–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Cr | Ni | Mn | Mo | Si | Fe |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 17 | 12 | 2 | 2.5 | 1.5 | 65 |
| Materials | Ecorr (V/SCE) | Icorr (A/cm2) |
|---|---|---|
| WC-10% | −0.633 | 5.921 × 10−8 |
| WC-0% | −0.660 | 1.763 × 10−7 |
| 316Lss | −0.705 | 8.184 × 10−7 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, J.; Zhu, Z.; Li, K.; Shi, W.; Zhao, Y.; He, M. Microstructures and Mechanical Properties of an AlCoCrNiFe HEA/WC Reinforcing Particle Composite Coating Prepared by Laser Cladding. Materials 2022, 15, 8020. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15228020
Huang J, Zhu Z, Li K, Shi W, Zhao Y, He M. Microstructures and Mechanical Properties of an AlCoCrNiFe HEA/WC Reinforcing Particle Composite Coating Prepared by Laser Cladding. Materials. 2022; 15(22):8020. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15228020
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Jiang, Zhikai Zhu, Kaiyue Li, Wenqing Shi, Yang Zhao, and Minyi He. 2022. "Microstructures and Mechanical Properties of an AlCoCrNiFe HEA/WC Reinforcing Particle Composite Coating Prepared by Laser Cladding" Materials 15, no. 22: 8020. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15228020
APA StyleHuang, J., Zhu, Z., Li, K., Shi, W., Zhao, Y., & He, M. (2022). Microstructures and Mechanical Properties of an AlCoCrNiFe HEA/WC Reinforcing Particle Composite Coating Prepared by Laser Cladding. Materials, 15(22), 8020. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15228020






