Tailoring Magnetic Properties of Fe0.65Co0.35 Nanoparticles by Compositing with RE2O3 (RE = La, Nd, and Sm)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Synthesis and Preparation of Samples
2.2. Research Methods
3. Results and Discussion
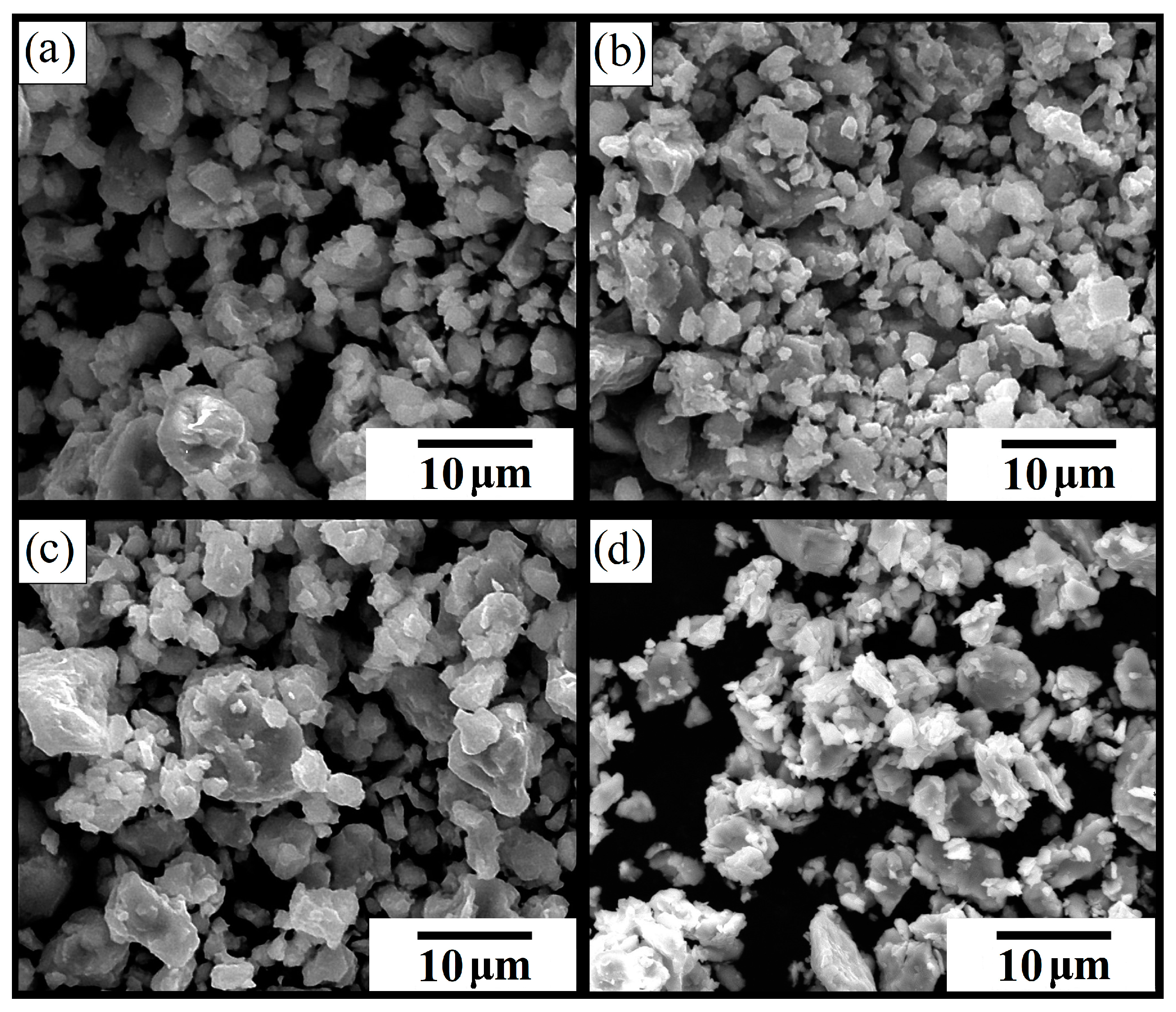
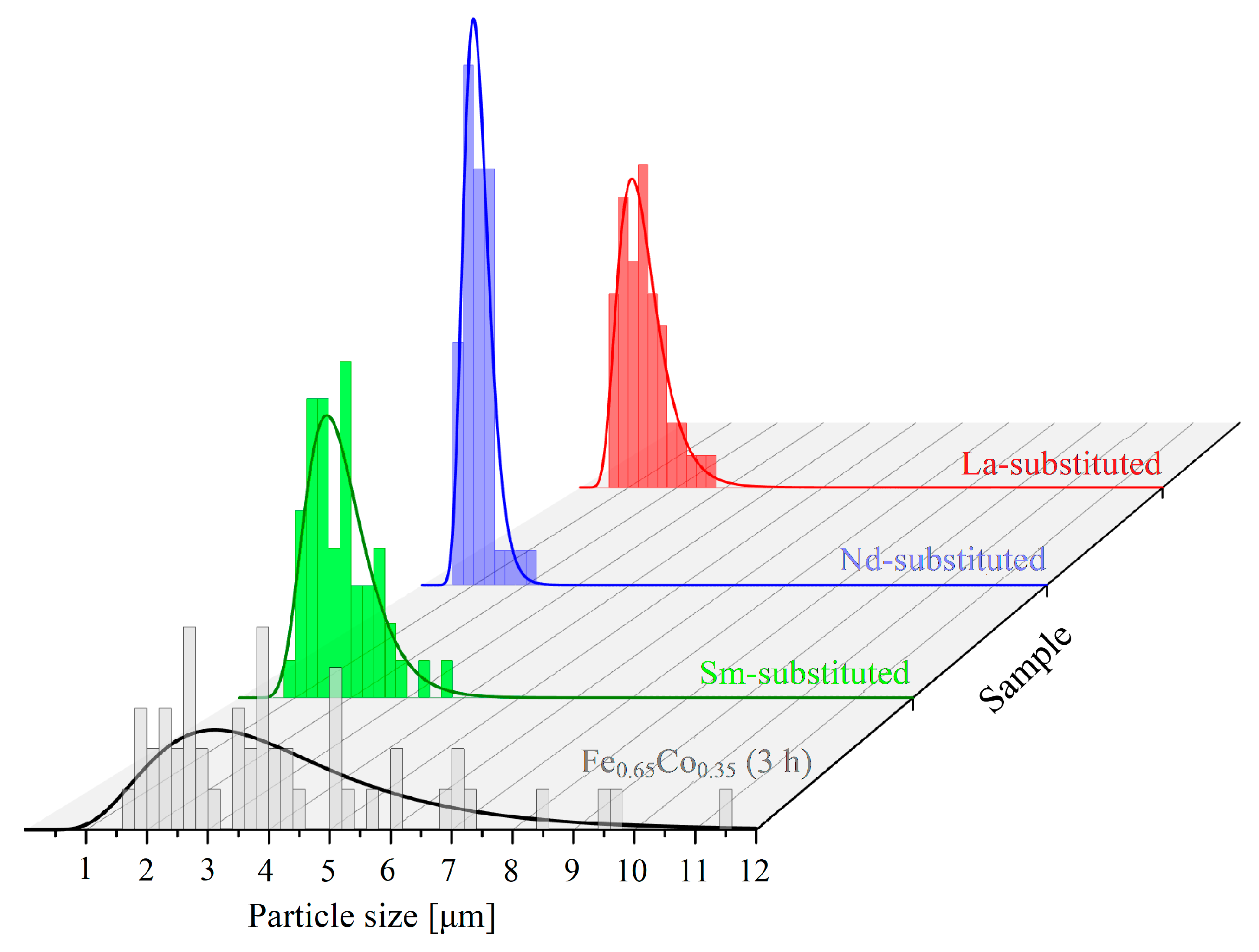
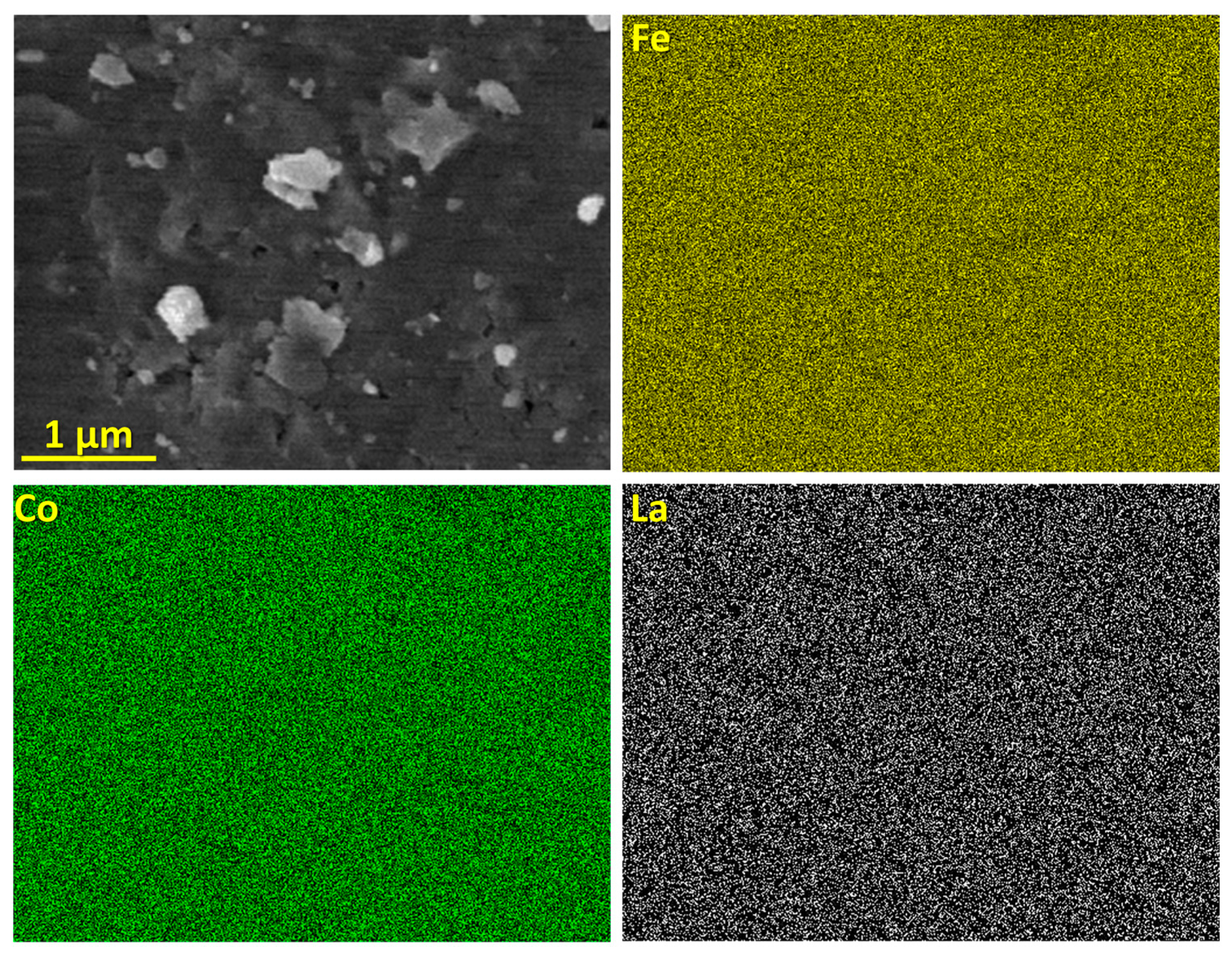
3.1. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) Analysis
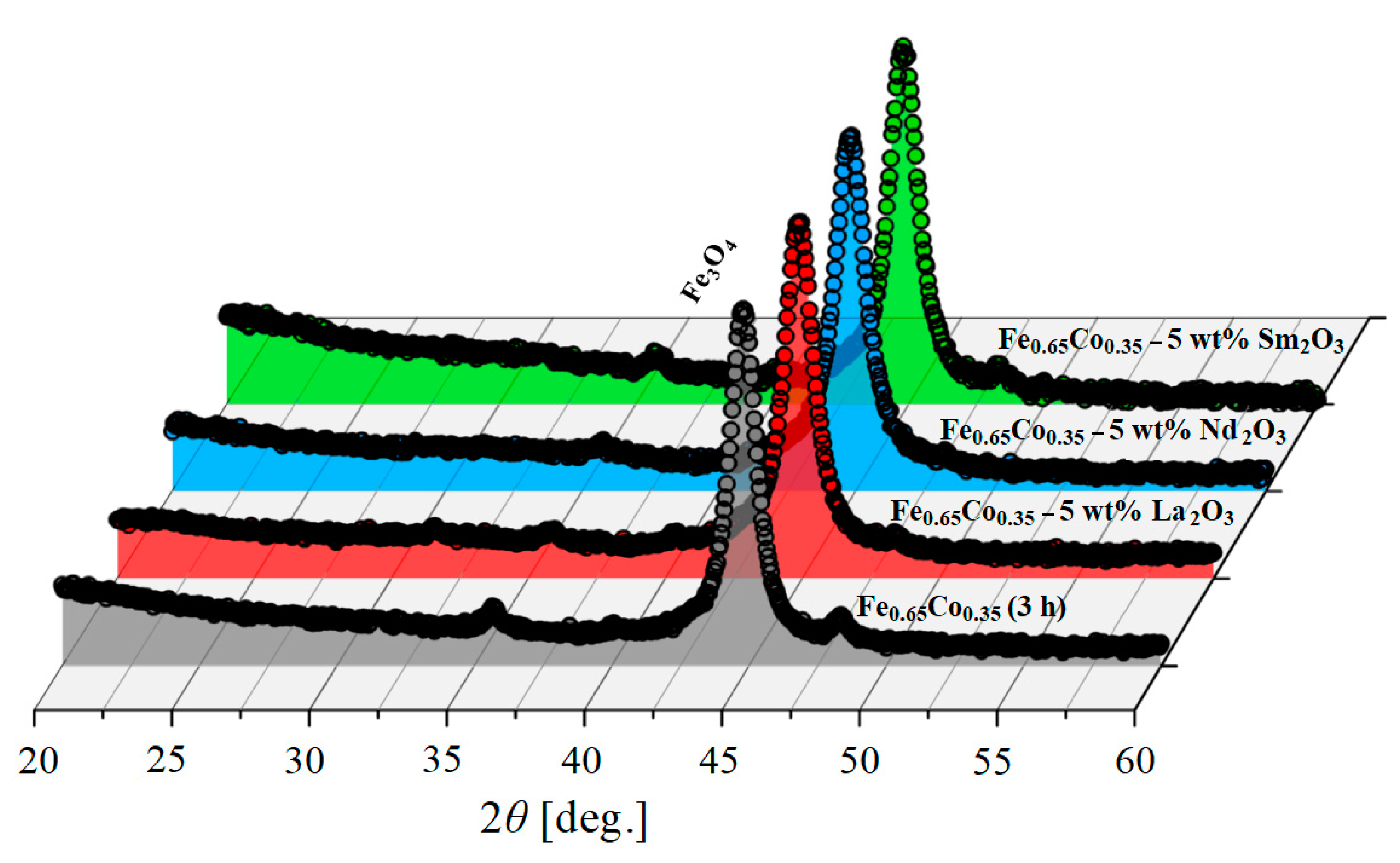
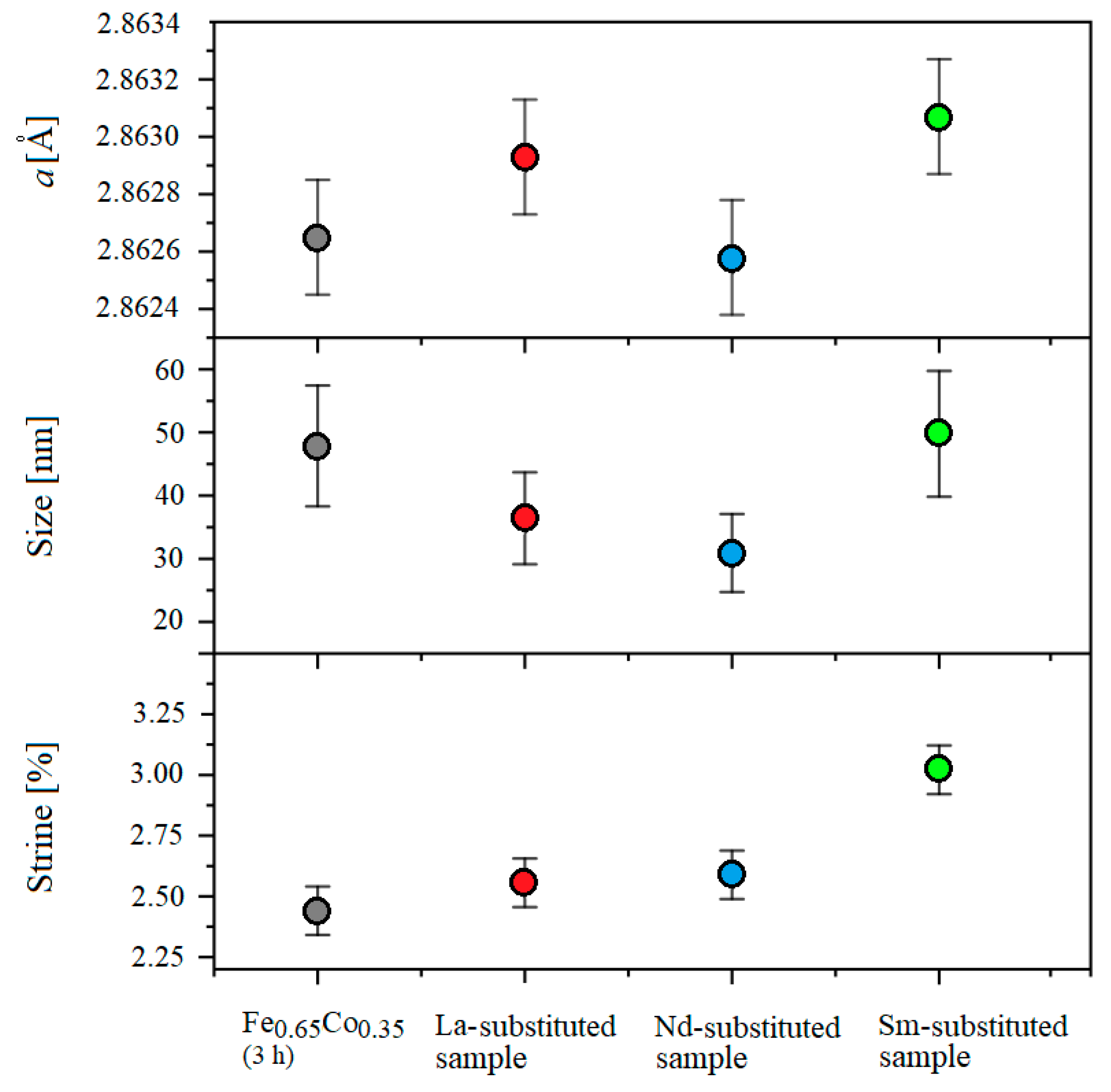
3.2. X-ray Diffraction (XRD) Analysis
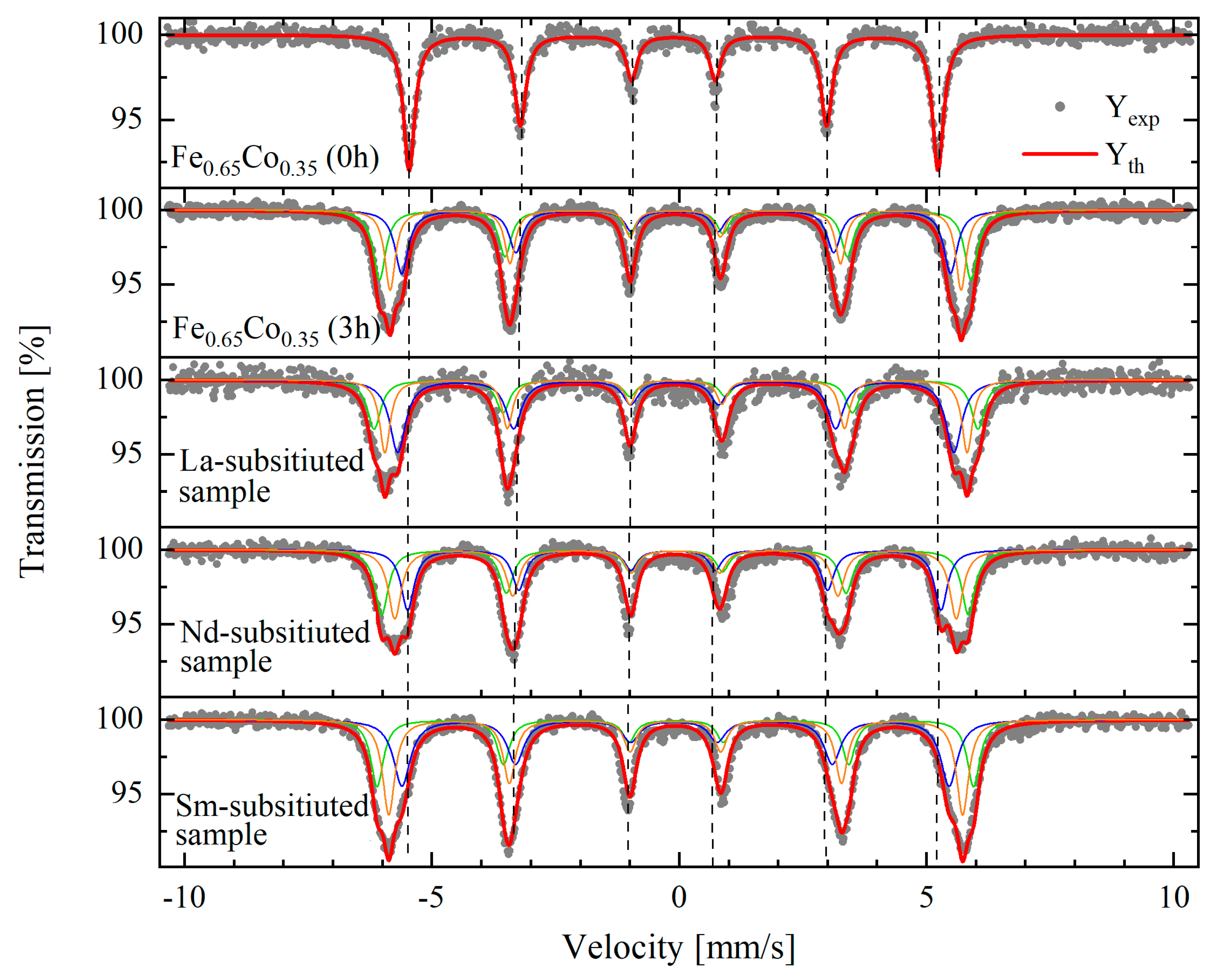
3.3. Mössbauer Spectrometry
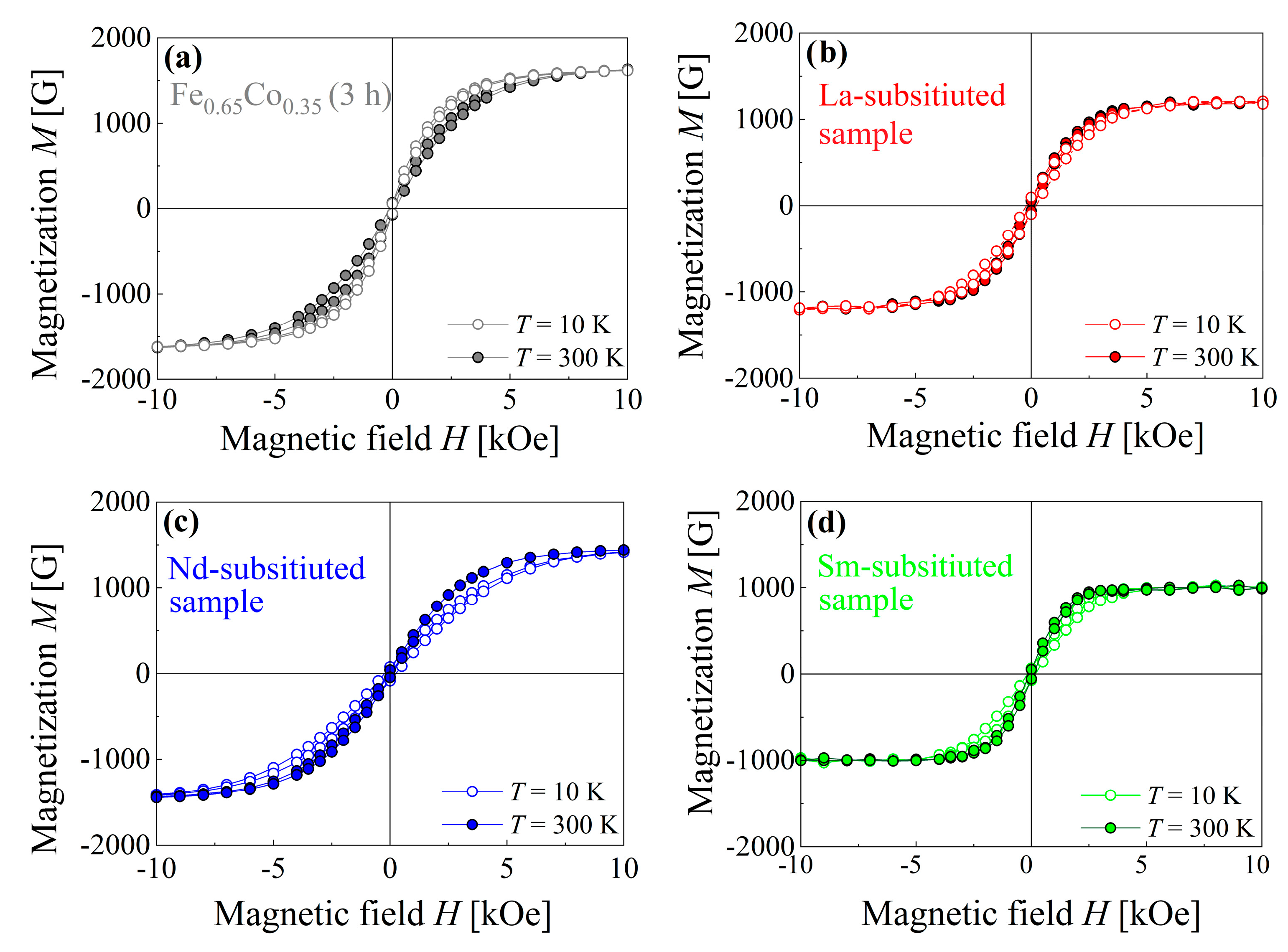
3.4. The Magnetic Properties
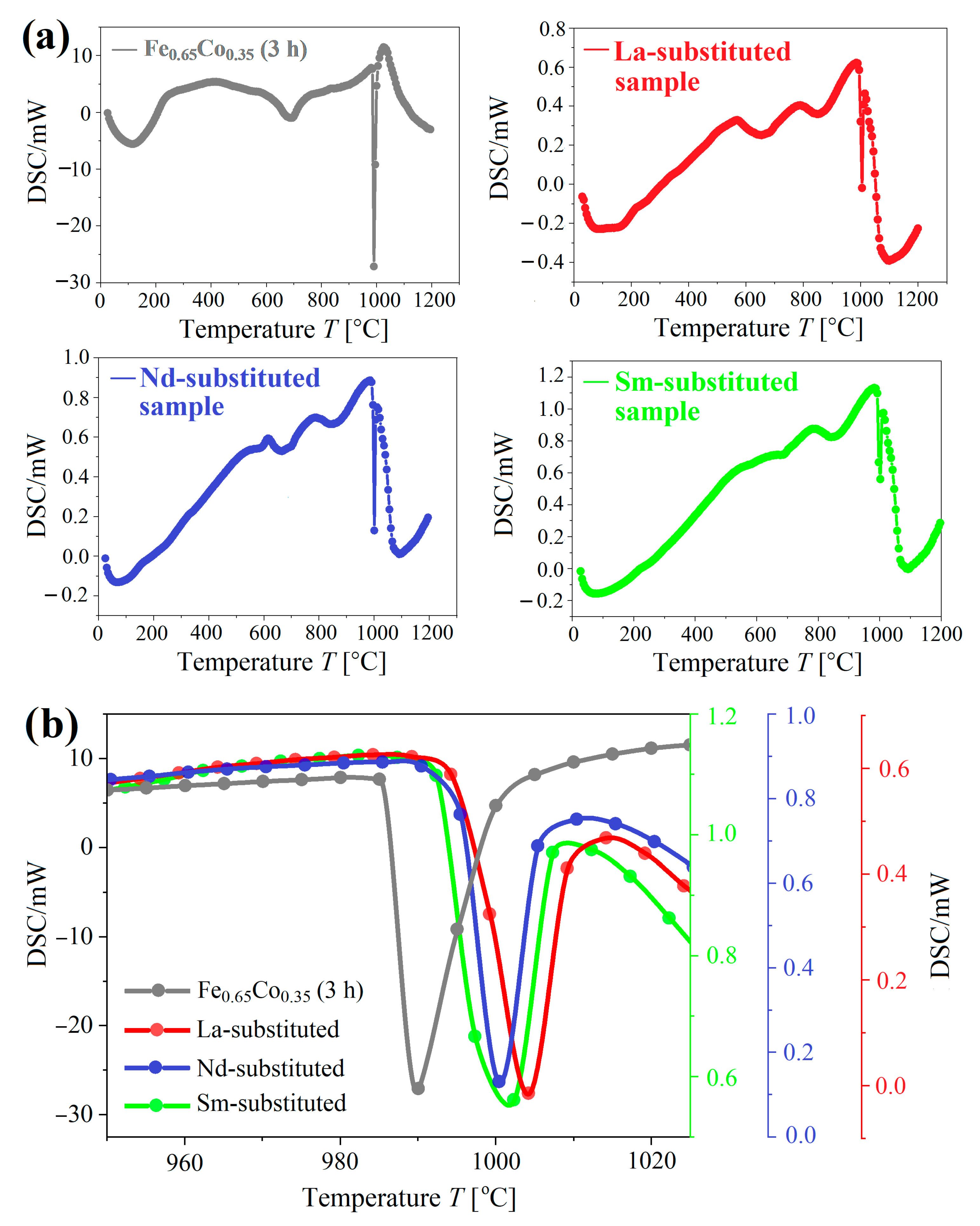
3.5. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC) Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hasegawa, T.; Kanatani, S.; Kazaana, M.; Takahashi, K.; Kumagai, K.; Hirao, M.; Ishio, S. Conversion of FeCo from soft to hard magnetic material by lattice engineering and nanopatterning. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 13215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alonso, J.; Khurshid, H.; Sankar, V.; Nemati, Z.; Phan, M.H.; Garayo, E.; García, J.A.; Srikanth, H. FeCo nanowires with enhanced heating powers and controllable dimensions for magnetic hyperthermia. J. Appl. Phys. 2015, 117, 17D113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habib, A.H.; Ondeck, C.L.; Chaudhary, P.; Bockstaller, M.R.; McHenry, M.E. Evaluation of iron-cobalt/ferrite core-shell nanoparticles for cancer thermotherapy. J. Appl. Phys. 2008, 103, 2012–2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.L.; Sherlock, S.P.; Terashima, M.; Kosuge, H.; Suzuki, Y.; Goodwin, A.P.; Robinson, J.; Seo, W.S.; Liu, Z.; Loung, R.; et al. High-contrast in vivo visualization of microvessels using novel FeCo/GC magnetic nanocrystals. Mag. Res. Med. 2009, 62, 1497–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Seo, W.S.; Lee, J.H.; Sun, X.; Suzuki, Y.; Mann, D.; Liu, Z.; Terashima, M.; Yang, P.C.; McConnell, M.V.; Nishimura, D.G.; et al. FeCo/graphitic-shell nanocrystals as advanced magnetic-resonance-imaging and near-infrared agents. Nat. Mater. 2006, 5, 971–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, X.; Jackson, E.F.; Price, R.E.; Kim, E.E.; Wu, Q.; Wallace, S.; Charnsangavej, C.; Gelovani, J.G.; Li, C. Synthesis and characterization of poly(L-glutamic acid) gadolinium chelate: A new biodegradable MRI contrast agent. Bioconjug. Chem. 2004, 15, 1408–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, B.K.; Rastogi, A.C. Thin films for secondary data storage. IETE J. Res. 1997, 43, 221–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zare, Y.; Shams, M.H.; Jazirehpour, M. Tuning microwave permittivity coefficients for enhancing electromagnetic wave absorption properties of FeCo alloy particles by means of sodium stearate surfactant. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 717, 294–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chrobak, A. High and ultra-high coercive materials in spring-exchange systems—Review, simulations and perspective. Materials 2022, 15, 6506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berasategi, J.; Gomez, A.; Bou-Ali, M.M.; Gutiérrez, J.; Barandiarán, J.M.; Beketov, I.V.; Safronov, A.P.; Kurlyandskaya, G.V. Fe nanoparticles produced by electric explosion of wire for new generation of magneto-rheological fluids. Smart Mater. Struct. 2018, 27, 045011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, C.; Shan, Y.; Wu, H.; Bi, X. Effect of a small addition of Cr on soft magnetic and mechanical properties of Fe-49Co-2V alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2013, 556, 51–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khosravi, S.; Alizadeh, M.; Sharafi, S.; Karimi-Maleh, H.; Atar, N. Structural, magnetic and electron transfer effect of Cr additive on Fe65Co35 nanopowder fabricated mechanical alloying. Powder Technol. 2015, 279, 262–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hocine, M.; Guittoum, A.; Hemmous, M.; Martínez-Blanco, D.; Gorria, P.; Rahal, B.; Blanco, J.A.; Sunol, J.J.; Laggoun, A. The role of silicon on the microstructure and magnetic behaviour of nanostructured (Fe0.7Co0.3)100−xSix powders. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2017, 422, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousefi, M.; Sharafi, S. The effect of simultaneous addition of Si and Co on microstructure and magnetic properties of nanostructured iron prepared by mechanical alloying. Mat. Design 2012, 37, 325–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhary, V.; Ping Tan, L.; Sharma, V.K.; Ramanujan, R.V. Accelerated study of magnetic Fe ̶ Co ̶ Ni alloys through compositionally graded spark plasma sintered samples. J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 869, 159318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, V.; Chandra, A.R.; Lakshmi, N.; Reddy, V.R.; Jani, S. Magnetic behaviour of 57Fe/Co/Al multilayers deposited on a glass substrate. Bull. Mater. Sci. 2019, 42, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sarkar, A.; Hembram, S.; Chatterjee, S.; Basu Mallick, A. Effect of annealing treatments on the magnetic properties of FeCo/Cu core shell nanostructures. Mater. Today Proc. 2018, 5, 745–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vadillo, V.; Gutiérrez, J.; Insausti, M.; Garitaonandia, J.S.; de Muro, I.G.; Quintana, I.; Barandiaran, J.M. Synthesis and characterization of Fe-Co-V high magnetization nanoparticles obtained by physical routes. IEEE Magn. Lett. 2019, 10, 6104805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Xu, Z.; Yin, Y. Tuning of the microwave magnetization dynamics in Dy-doped Fe65Co35-based thin films. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2015, 51, 2800904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younsi, K.; Russier, V.; Bessais, L. Structure and magnetic properties of nanocrystalline PrCo3. J. Appl. Phys. 2010, 107, 083916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younsi, K.; Crivello, J.C.; Paul-Boncour, V.; Bessais, L.; Porcher, F.; André, G. Study of the magnetic and electronic properties of nanocrystalline PrCo3 by neutron powder diffraction and density functional theory. J. Phys. Condens. Matter. 2013, 25, 116001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sirvent, P.; Berganza, E.; Aragón, A.M.; Bollero, A.; Moure Arroyo, A.; García-Hernández, M.; Marín, P.; Fernández, J.; Quesada, A. Effective high-energy ball milling in air of Fe65Co35 alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2014, 115, 17B505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chermahini, M.D.; Zandrahimi, M.; Shokrollahi, H.; Sharafi, S. The effect of milling time and composition on microstructural and magnetic properties of nanostructured Fe-Co alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2009, 477, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manh, D.H.; Tung, D.K.; Phong, L.T.H.; Phuc, N.X.; Jutimoosik, J.; Yimnirun, R. Complementary studies of phase formation during fabrication of Fe0.65Co0.35 nanoparticles by mechanical alloying. J. Elec. Mat. 2016, 45, 2501–2507. [Google Scholar]
- Hosseini, H.R.M.; Bahrami, A. Preparation of nanocrystalline Fe-Si-Ni soft magnetic powders by mechanical alloying. Mater. Sci. Eng. B Sol. Stat. Mater. Adv. Technol. 2005, 123, 74–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadkari, A.; Shinde, T.; Vasambekar, P. Influence of rare-earth ions on structural and magnetic properties of CdFe2O4 ferrites. Rare Met. 2010, 29, 168–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suo, N.; Sun, A.; Yu, L.; Zuo, Z.; Pan, X.; Zhang, W.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, Y.; Shao, L. Effect of different rare earth (RE = Y3+, Sm3+, La3+, and Yb3+) ions doped on the magnetic properties of Ni–Cu–Co ferrite nanomagnetic materials. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2021, 32, 246–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanna, R.R.; Sakthipandi, K.; Seeni Mohamed Aliar Maraikkayar, S.M.; Lenin, N.; Sivabharathy, M. Doping effect of rare-earth (lanthanum, neodymium and gadolinium) ions on structural, optical, dielectric and magnetic properties of copper nanoferrites. J. Rare Earths 2018, 36, 1299–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, R.D.; Prewitt, C.T. Effective ionic radii in oxides and fluorides. Acta Crystallogr. B 1969, 25, 925–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaubey, G.S.; Barcena, C.; Poudyal, N.; Rong, C.; Gao, J.; Sun, S.; Liu, J.P. Synthesis and stabilization of FeCo nanoparticles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 7214–7215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klencsár, Z.; Németh, P.; Sándor, Z.; Horváth, T.; Sajó, I.E.; Mészáros, S.; Mantilla, J.; Coaquira, J.A.H.; Garg, V.K.; Kuzmann, E.; et al. Structure and magnetism of Fe-Co alloy nanoparticles. J. Alloys Comp. 2016, 674, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Yan, Q.; Yang, C.; Wang, T.; Ge, C. Microstructure, mechanical properties and bonding characteristic of deformed tungsten. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2014, 43, 302–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moumeni, H.; Alleg, S.; Djebbari, C.; Bentayeb, F.Z.; Grenèche, J.M. Synthesis and characterisation of nanostructured FeCo alloys. J. Mater. Sci. 2004, 39, 5441–5443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeleňáková, A.; Olekšáková, D.; Degmová, J.; Kováč, J.; Kollár, P.; Kusý, M.; Sovák, P. Structural and magnetic properties of mechanically alloyed FeCo powders. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2007, 316, e519–e522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moumeni, H.; Alleg, S.; Greneche, J.M. Structural properties of Fe50Co50 nanostructured powder prepared by mechanical alloying. J. Alloys Compd. 2005, 386, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rincón Soler, A.I.; Rodríguez Jacobo, R.R.; Medina Barreto, M.H.; Cruz-Muñoz, B. Structural and magnetic properties of FeCoC system obtained by mechanical alloying. Hyperfine Interact. 2017, 238, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majeed, A.; Khan, M.A.; Raheem, F.; Hussain, A.; Iqbal, F.; Murtaza, G.; Akhtar, M.N.; Shakir, I.; Warsi, M.F. Structural elucidation and magnetic behavior evaluation of rare earth (La, Nd, Gd, Tb, Dy)-doped BaCoNi ̶ X hexagonal nano-sized ferrites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2016, 408, 147–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanna, R.R.; Lenin, N.; Sakthipandi, K.; Kumar, A.S. Structural, optical, dielectric, and magnetic studies of gadolinium-added Mn-Cu nanoferrites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2018, 453, 78–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padalia, D.; Johri, U.C.; Zaidi, M.G.H. Effect of cerium substitution on structural and magnetic properties of magnetite nanoparticles. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2016, 169, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prozorov, T.; Bazylinski, D.A.; Mallapragada, S.K. Novel magnetic nanomaterials inspired by magnetotactic bacteria: Topical review. Mat. Sci. Eng. 2013, R.74, 133–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalal, M. A Textbook of Physical Chemistry, 1st ed.; Dalal Institute: Rohtak, India, 2017; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, G.D.; Miao, X.S.; Cheng, W.M.; Huang, X.F.; Yang, L.; Pan, L.Q. Influence of Cu underlayer on the high-frequency magnetic properties of FeCoSiO thin films. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2015, 51, 2801504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Wu, Y.; Li, X.; Yu, R. Chemical synthesis of high-stable amorphous FeCo nanoalloys with good magnetic properties. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Almessiere, M.A.; Slimani, Y.; Baykal, A. Structural and magnetic properties of Ce-doped strontium hexaferrite. Ceram. Int. 2018, 44, 9000–9008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almessiere, M.A.; Slimani, Y.; Sertkol, M.; Gungunes, H.; Wudil, Y.S.; Demir Korkmaz, A.; Baykal, A. Impact of Gd substitution on the structure, hyperfine interactions, and magnetic properties of Sr hexaferrites. Ceram. Int. 2021, 47, 33853–33864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slimani, Y.; Güngüneş, H.; Nawaz, M.; Manikandan, A.; El Sayed, H.S.; Almessiere, M.A.; Sözeri, H.; Shirsath, S.E.; Ercan, I.; Baykal, A. Magneto-optical and microstructural properties of spinel cubic copper ferrites with Li ̶ Al co-substitution. Ceram. Int. 2018, 44, 14242–14250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, D.; Sarin, A.; Verma, V.; Venkatraman, R. Pulsed laser deposition assisted fabrication and characterization of Fe-Co nanoparticles embedded in TiN thin film matrix. Thin Solid Film. 2013, 534, 561–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poudyal, N.; Rong, C.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, D.; Kramer, M.J.; Hebert, R.J.; Ping Liu, J. Self-nanoscaling in FeCo alloys prepared via severe plastic deformation. J. Alloys Compd. 2012, 521, 55–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chitsazan, B.; Shokrollahi, H.; Behvandi, A.; Mirzaee, O. Characterization and magnetic coercivity of nanostructured (Fe50Co50)100-XVX=0,2,4 powders containing a small amount of Co 3V intermetallic obtained by mechanical alloying. Powder Technol. 2011, 214, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sourmail, T. Near equiatomic FeCo alloys: Constitution, mechanical and magnetic properties. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2005, 50, 816–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Samples | Fe [at%] | Co [at%] | RE [at%] |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fe0.65Co0.35 (3 h) | 65.2(1) | 34.8(1) | - |
| Fe0.65Co0.35 – 5 wt% La2O3 (La-substituted sample) | 64.3(1) | 34.6(1) | 1.1(1) |
| Fe0.65Co0.35 – 5 wt% Nd2O3 (Nd-substituted sample) | 64.9(1) | 34.0(1) | 1.1(1) |
| Fe0.65Co0.35 – 5 wt% Sm2O3 (Sm-substituted sample) | 64.4(1) | 33.9(1) | 1.2(1) |
| Samples | S | Rel. Contrib. [%] | IS Fe [mm/s] | H [T] | <IS> [mm/s] | <H> [T] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fe0.65Co0.35 (0 h) | S1 | 100 | 0.002(1) | 33.3(5) | --- | --- |
| Fe0.65Co0.35 (3 h) | S1 | 34.0 | 0.045(2) | 37.0(4) | 0.041 | 35.7 |
| S2 | 33.3 | 0.039(2) | 34.3(4) | |||
| S3 | 32.7 | 0.039(3) | 35.7(3) | |||
| La-substituted sample | S1 | 25.7 | 0.068(7) | 37.8(9) | 0.048 | 36.1 |
| S2 | 44.3 | 0.034(5) | 34.8(7) | |||
| S3 | 30.0 | 0.051(4) | 36.4(5) | |||
| Nd-substituted sample | S1 | 33.9 | 0.043(4) | 36.7(5) | 0.031 | 35.2 |
| S2 | 31.0 | 0.005(4) | 33.4(4) | |||
| S3 | 35.1 | 0.040(4) | 35.1(5) | |||
| Sm-substituted sample | S1 | 27.2 | 0.045(3) | 37.3(5) | 0.037 | 35.7 |
| S2 | 35.6 | 0.025(4) | 34.2(6) | |||
| S3 | 37.2 | 0.042(2) | 35.9(3) |
| Compound | Ms [G] | Mr [G] | Hc [Oe] | EM [MG.Oe] | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 [K] | 300 [K] | 10 [K] | 300 [K] | 10 [K] | 300 [K] | 10 [K] | 300 [K] | |
| Fe0.65Co0.35 (3 h) | 1690(10) | 1660(10) | 67(7) | 57(7) | 130(2) | 75(5) | 1.414 | 0.649 |
| La-substituted sample | 1205(15) | 1190(10) | 97(7) | 56(6) | 290(5) | 100(5) | 0.630 | 0.450 |
| Nd-substituted sample | 1515(15) | 1490(10) | 78(8) | 42(5) | 260(5) | 100(10) | 3.312 | 0.608 |
| Sm-substituted sample | 1025(10) | 1000(10) | 68(8) | 52(5) | 330(5) | 85(5) | 1.688 | 0.710 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Djellal, N.; Pęczkowski, P.; Mekki, D.E.; Navarro, E.; Tahraoui, T.; Piętosa, J.; Michalik, J.M.; Marín, P.; Gondek, Ł. Tailoring Magnetic Properties of Fe0.65Co0.35 Nanoparticles by Compositing with RE2O3 (RE = La, Nd, and Sm). Materials 2022, 15, 7290. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15207290
Djellal N, Pęczkowski P, Mekki DE, Navarro E, Tahraoui T, Piętosa J, Michalik JM, Marín P, Gondek Ł. Tailoring Magnetic Properties of Fe0.65Co0.35 Nanoparticles by Compositing with RE2O3 (RE = La, Nd, and Sm). Materials. 2022; 15(20):7290. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15207290
Chicago/Turabian StyleDjellal, Nacira, Paweł Pęczkowski, Djamel Eddine Mekki, Elena Navarro, Tarek Tahraoui, Jarosław Piętosa, Jan Marek Michalik, Pilar Marín, and Łukasz Gondek. 2022. "Tailoring Magnetic Properties of Fe0.65Co0.35 Nanoparticles by Compositing with RE2O3 (RE = La, Nd, and Sm)" Materials 15, no. 20: 7290. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15207290
APA StyleDjellal, N., Pęczkowski, P., Mekki, D. E., Navarro, E., Tahraoui, T., Piętosa, J., Michalik, J. M., Marín, P., & Gondek, Ł. (2022). Tailoring Magnetic Properties of Fe0.65Co0.35 Nanoparticles by Compositing with RE2O3 (RE = La, Nd, and Sm). Materials, 15(20), 7290. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15207290











