Poly(sodium acrylate)-Modified Magnetite Nanoparticles for Separation of Heavy Metals from Aqueous Solutions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Sorbent Synthesis
2.3. Characterization of the Adsorbent
2.3.1. XRD Analysis
2.3.2. TEM and NTA Analyzes
2.3.3. Specific Surface Area Measurement
2.3.4. FTIR Measurement
2.3.5. Magnetic Measurements
2.3.6. Zeta Potential Measurement
2.4. Batch Adsorption Tests
- -
- The pseudo-first-order model:
- -
- The pseudo-second-order model:where t—time, min; qt—adsorption capacity at time t, mg/g; kI—the pseudo-first-order kinetic constant, 1/min; kII—the pseudo-second-order kinetic constant, g/(mg min).
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characteristics of Magnetite Adsorbents
3.1.1. XRD Analysis
3.1.2. TEM and NTA Analyses
3.1.3. Specific Surface Area
3.1.4. FTIR Analysis
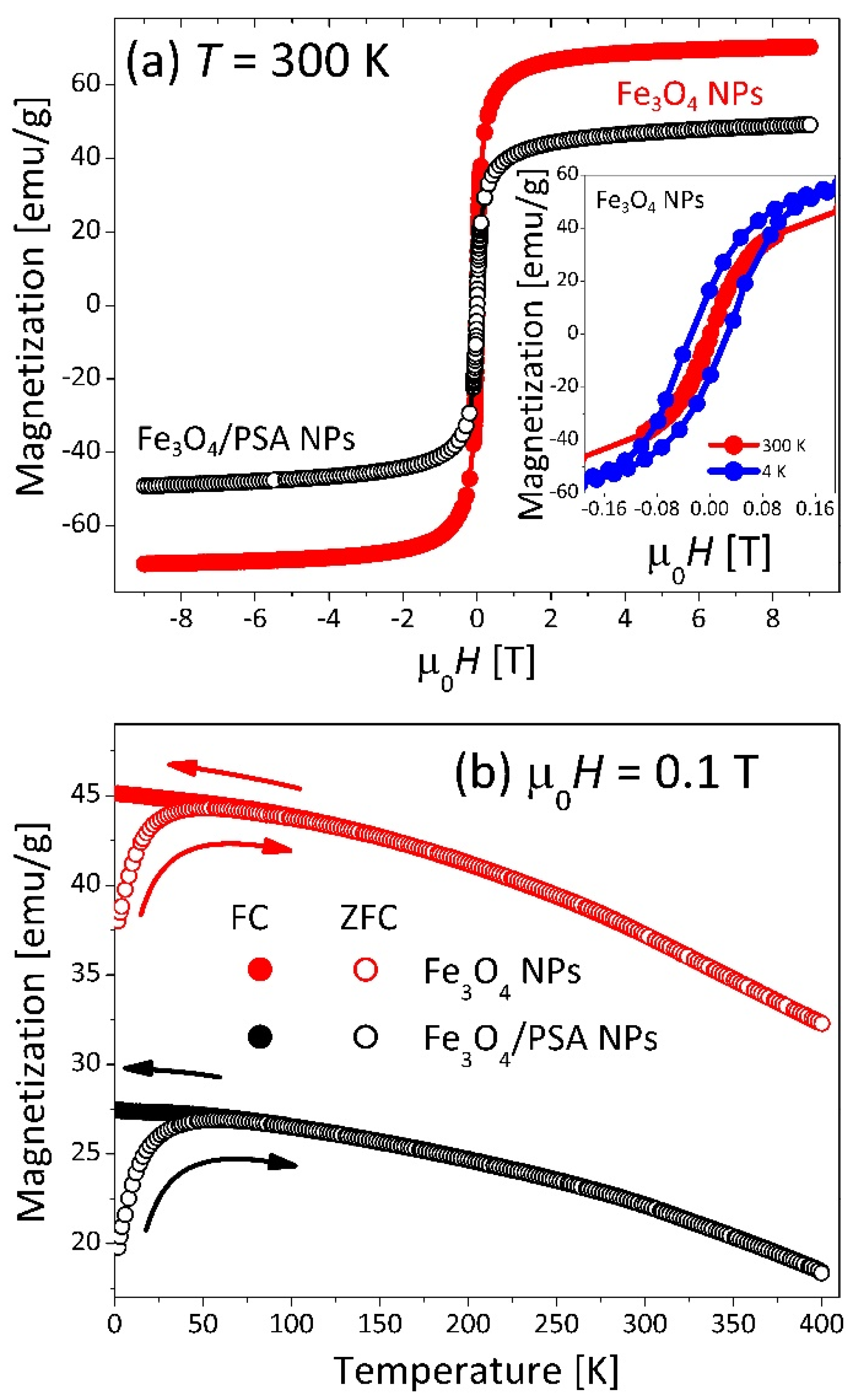
3.1.5. Magnetic Measurements
3.2. Adsorption Experiments
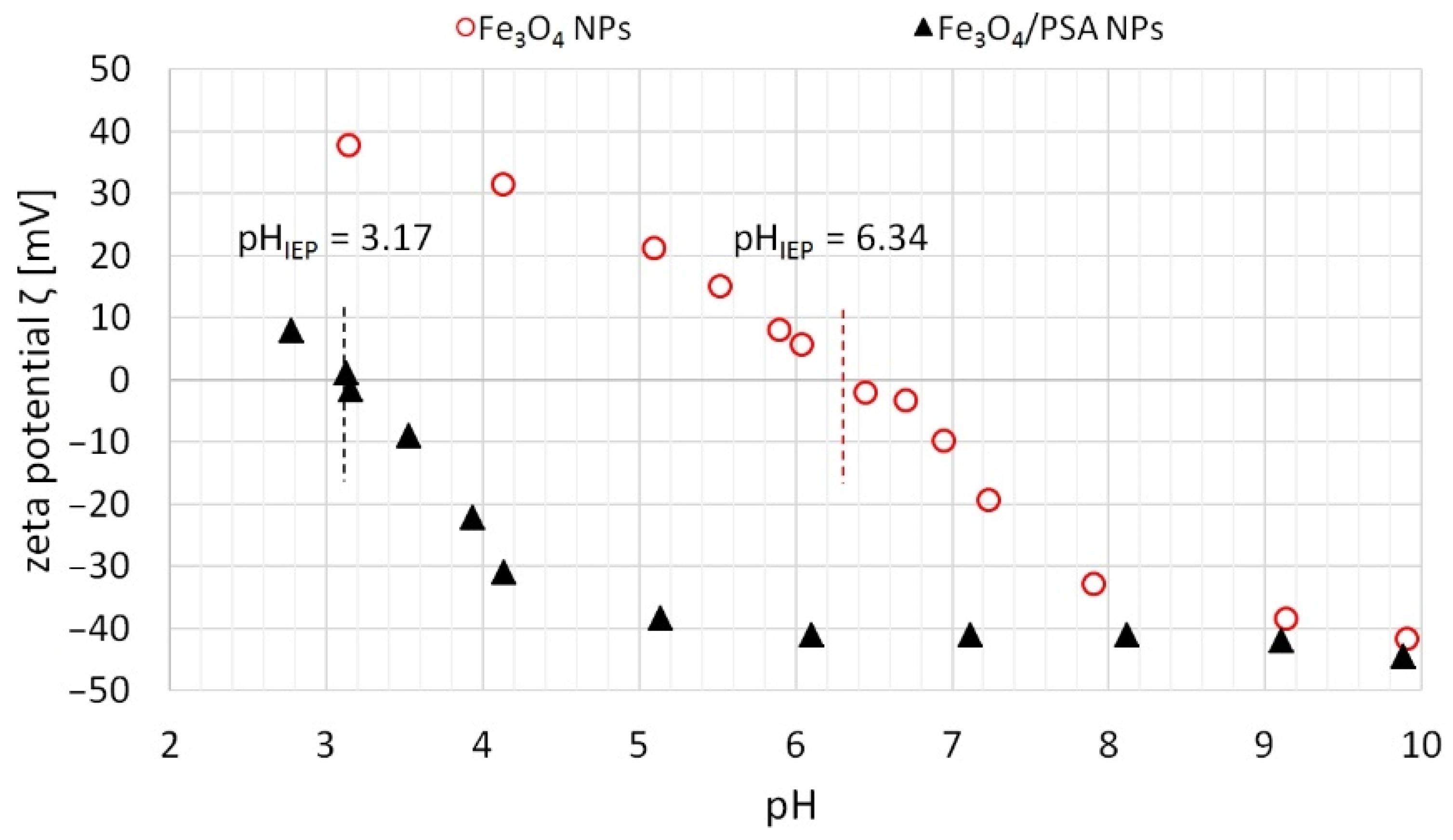
3.2.1. The Effect of pH on Sorption Effectiveness and Zeta Potential of Magnetite
3.2.2. Adsorption Isotherms
3.2.3. Adsorption Kinetics
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Carolin, C.F.; Kumar, P.S.; Saravanan, A.; Joshiba, G.J.; Naushad, M. Efficient techniques for the removal of toxic heavy metals from aquatic environment: A review. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 2782–2799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Hou, B.; Wang, J.; Tian, B.; Bi, J.; Wang, N.; Li, X.; Huang, X. Nanomaterials for the Removal of Heavy Metals from Wastewater. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, J.; Kong, H.; Jang, J. Adsorption of heavy metal ions from aqueous solution by polyrhodanine-encapsulated magnetic nanoparticles. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 359, 505–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahoon, M.A.; Siddeeg, S.M.; Salem Alsaiari, N.; Mnif, W.; Ben Rebah, F. Effective Heavy Metals Removal from Water Using Nanomaterials: A Review. Processes 2020, 8, 645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, F.S.A.; Mubarak, N.M.; Khalid, M.; Walvekar, R.; Abdullah, E.C.; Mazari, S.A.; Nizamuddin, S.; Karri, R.R. Magnetic nanoadsorbents’ potential route for heavy metals removal—A review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 24342–24356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nizamuddin, S.; Siddiqui, M.T.H.; Mubarak, N.M.; Baloch, H.A.; Abdullah, E.C.; Mazari, S.A.; Griffin, G.J.; Srinivasan, M.P.; Tanksale, A. Chapter 17—Iron Oxide Nanomaterials for the Removal of Heavy Metals and Dyes from Wastewater. In Micro and Nano Technologies. Nanoscale Materials in Water Purification; Thomas, S., Pasquini, D., Leu, S.-Y., Gopakumar, D.A., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 447–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belessiotis, G.V.; Falara, P.P.; Ibrahim, I.; Kontos, A.G. Magnetic Metal Oxide-Based Photocatalysts with Integrated Silver for Water Treatment. Materials 2022, 15, 4629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajput, S.; Singh, L.P.; Pittman, C.U.; Mohan, D. Lead (Pb2+) and copper (Cu2+) remediation from water using superparamagnetic maghemite (γ-Fe2O3) nanoparticles synthesized by Flame Spray Pyrolysis (FSP). J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 492, 176–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, A.; Bhattacharya, J. Removal of Cu(II), Zn(II) and Pb(II) from water using microwave-assisted synthesized maghemite nanotubes. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 211–212, 493–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karami, H. Heavy metal removal from water by magnetite nanorods. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 219, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.A.; Ali, S.M.; El-Dek, S.I.; Galal, A. Magnetite-hematite nanoparticles prepared by green methods for heavy metal ions removal from water. Mater. Sci. Eng. B Solid-State Mater. Adv. Technol. 2013, 178, 744–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fato, F.P.; Li, D.-W.; Zhao, L.-J.; Qiu, K.; Long, Y.-T. Simultaneous Removal of Multiple Heavy Metal Ions from River Water Using Ultrafine Mesoporous Magnetite Nanoparticles. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 7543–7549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, S.; Lian, C.; Xu, M.; Zhang, W.; Liu, L.; Lin, K. Study on competitive adsorption mechanism among oxyacid-type heavy metals in co-existing system: Removal of aqueous As(V), Cr(III) and As(III) using magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (MIONPs) as adsorbents. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 422, 675–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neyaz, N.; Siddiqui, W.A.; Nair, K.K. Application of surface functionalized iron oxide nanomaterials as a nanosorbents in extraction of toxic heavy metals from ground water: A review. Int. J. Environ. Sci. 2014, 4, 472–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Yuan, H.; Yu, J.; Lin, S. Study on the competitive adsorption and correlational mechanism for heavy metal ions using the carboxylated magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (MNPs-COOH) as efficient adsorbents. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 473, 960–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, M.; Hao, Y. Study on the adsorption of Cu(II) by EDTA functionalized Fe3O4 magnetic nano-particles. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 218, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, F.; Li, M.-M.; Ye, H.; Zhao, B.-X. Effective removal of heavy metal ions Cd2+, Zn2+, Pb2+, Cu2+ from aqueous solution by polymer-modified magnetic nanoparticles. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 211–212, 366–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, H.V.; Tran, L.D.; Nguyen, T.N. Preparation of chitosan/magnetite composite beads and their application for removal of Pb(II) and Ni(II) from aqueous solution. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2010, 30, 304–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Zhao, X.; Liu, Y.; Xu, B.; Pan, X. Highly stable and covalently functionalized magnetic nanoparticles by polyethyleneimine for Cr(vi) adsorption in aqueous solution. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 1398–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdavian, A.R.; Mirrahimi, M.A.-S. Efficient separation of heavy metal cations by anchoring polyacrylic acid on superparamagnetic magnetite nanoparticles through surface modification. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 159, 264–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korus, I. Ultrafiltration enhanced with poly(sodium acrylate) as an effective method for separation of heavy metals from multicomponent solutions. Desalin. Water Treat. 2021, 242, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massart, R. Preparation of Aqueous Magnetic Liquids in Alkaline and Acidic Media. IEEE Trans. Magn. 1981, 17, 1247–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.F.; Zhao, Z.S.; Jiang, G.B. Coating Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles with humic acid for high efficient removal of heavy metals in water. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 6949–6954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wojnarowicz, J.; Opalinska, A.; Chudoba, T.; Gierlotka, S.; Mukhovskyi, R.; Pietrzykowska, E.; Sobczak, K.; Lojkowski, W. Effect of Water Content in Ethylene Glycol Solvent on the Size of ZnO Nanoparticles Prepared Using Microwave Solvothermal Synthesis. J. Nanomater. 2016, 2016, 2789871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mascolo, M.; Pei, Y.; Ring, T. Room Temperature Co-Precipitation Synthesis of Magnetite Nanoparticles in a Large pH Window with Different Bases. Materials 2013, 6, 5549–5567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foo, K.Y.; Hameed, B.H. Insights into the modeling of adsorption isotherm systems. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 156, 2–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayawei, N.; Ebelegi, A.N.; Wankasi, D. Modelling and Interpretation of Adsorption Isotherms. J. Chem. 2017, 2017, 3039817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasheen, M.R.; El Sherif, I.; El-Wakeel, S.; Sabry, D.; El-Shahat, M.F. Heavy metals removal from aqueous solution using magnetite Dowex 50WX4 resin nanocomposite. JMES 2017, 8, 503–511. [Google Scholar]
- Giraldo, L.; Erto, A.; Moreno-Piraján, J.C. Magnetite nanoparticles for removal of heavy metals from aqueous solutions: Synthesis and characterization. Adsorption 2013, 19, 465–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; He, J.; Li, Y.; Cai, X.; Zhang, K.; Liu, T.; Hu, Y.; Lin, D.; Kong, L.; Liu, J. Removal of cadmium and lead ions from water by sulfonated magnetic nanoparticle adsorbents. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 494, 307–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kołodyńska, D.; Gęca, M.; Pylypchuk, I.V.; Hubicki, Z. Development of New Effective Sorbents Based on Nanomagnetite. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2016, 11, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coey, J.M.D. Magnetism and Magnetic Materials; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajput, S.; Pittman, C.U.; Mohan, D. Magnetic magnetite (Fe3O4) nanoparticle synthesis and applications for lead (Pb2+) and chromium (Cr6+) removal from water. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2016, 468, 334–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, C.; Zhu, D.; Wu, H.; Li, Y.; Cheng, L.; Hu, K. TEA controllable preparation of magnetite nanoparticles (Fe3O4 NPs) with excellent magnetic properties. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2016, 408, 213–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazdani, F.; Seddigh, M. Magnetite nanoparticles synthesized by co-precipitation method: The effects of various iron anions on specifications. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2016, 184, 318–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golas, P.L.; Louie, S.M.; Lowry, G.V.; Matyjaszewski, K.; Tilton, R.D. Comparative study of polymeric stabilizers for magnetite nanoparticles using ATRP. Langmuir 2010, 26, 16890–16900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Favela-Camacho, S.E.; Samaniego-Benítez, E.J.; Godínez-García, A.; Avilés-Arellano, L.M.; Pérez-Robles, J.F. How to decrease the agglomeration of magnetite nanoparticles and increase their stability using surface properties. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2019, 574, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabowska, B. Microwave crosslinking of polyacrylic compositions containing dextrin and their applications as molding sands binders. Polimery 2009, 54, 507–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, T.; Rodriguez, J.; Paez-Hernandez, M.; Guevara-Lara, A.; Barrado, E.; Hernandez, P. Chromium(VI) Removal from Aqueous Solution by Magnetite Coated by a Polymeric Ionic Liquid-Based Adsorbent. Materials 2017, 10, 502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petcharoen, K.; Sirivat, A. Synthesis and characterization of magnetite nanoparticles via the chemical co-precipitation method. Mater. Sci. Eng. B Solid-State Mater. Adv. Technol. 2012, 177, 421–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morel, M.; Martínez, F.; Mosquera, E. Synthesis and characterization of magnetite nanoparticles from mineral magnetite. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2013, 343, 76–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, M.; Kundu, S.; Ghosh, S.K.; Panigrahi, S.; Sau, T.K.; Yusuf, S.M.; Pal, T. Magnetite nanoparticles with tunable gold or silver shell. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2005, 286, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaitsev, V.S.; Filimonov, D.S.; Presnyakov, I.A.; Gambino, R.J.; Chu, B. Physical and chemical properties of magnetite and magnetite-polymer nanoparticles and their colloidal dispersions. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1999, 212, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Z.; Zhang, C.; Zheng, Z.; Hu, L.; Li, X.; Yang, Z.; Ma, C.; Zeng, G. Enhancing phosphate adsorption capacity of SDS-based magnetite by surface modification of citric acid. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 403, 413–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klapiszewski, Ł.; Zdarta, J.; Antecka, K.; Synoradzki, K.; Siwińska-Stefańska, K.; Moszyński, D.; Jesionowski, T. Magnetite nanoparticles conjugated with lignin: A physicochemical and magnetic study. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 422, 94–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachosz, K.; Synoradzki, K.; Staszak, M.; Pinelo, M.; Meyer, A.S.; Zdarta, J.; Jesionowski, T. Bioconversion of xylose to xylonic acid via co-immobilized dehydrogenases for conjunct cofactor regeneration. Bioorg. Chem. 2019, 93, 102747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitra, A.; Mohapatra, J.; Meena, S.S.; Tomy, C.V.; Aslam, M. Verwey transition in ultrasmall-sized octahedral Fe3O4 nanoparticles. J. Phys. Chem. C 2014, 118, 19356–19362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruvera, I.J.; Mendoza Zélis, P.; Pilar Calatayud, M.; Goya, G.F.; Sánchez, F.H. Determination of the blocking temperature of magnetic nanoparticles: The good, the bad, and the ugly. J. Appl. Phys. 2015, 118, 184304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zdarta, J.; Antecka, K.; Jędrzak, A.; Synoradzki, K.; Łuczak, M.; Jesionowski, T. Biopolymers conjugated with magnetite as support materials for trypsin immobilization and protein digestion. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2018, 169, 118–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadyszak, K.; Kertmen, A.; Coy, E.; Andruszkiewicz, R.; Milewski, S.; Kardava, I.; Scheibe, B.; Jurga, S.; Chybczyńska, K. Spectroscopic and magnetic studies of highly dispersible superparamagnetic silica coated magnetite nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2017, 433, 254–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lendzion-Bieluń, Z.; Wojciechowska, A.; Grzechulska-Damszel, J.; Narkiewicz, U.; Śniadecki, Z.; Idzikowski, B. Effective processes of phenol degradation on Fe3O4–TiO2 nanostructured magnetic photocatalyst. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2020, 136, 109178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Illés, E.; Tombácz, E. The effect of humic acid adsorption on pH-dependent surface charging and aggregation of magnetite nanoparticles. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2006, 295, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosmulski, M. Compilation of PZC and IEP of sparingly soluble metal oxides and hydroxides from literature. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2009, 152, 14–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ostolska, I.; Wiśniewska, M. Application of the zeta potential measurements to explanation of colloidal Cr2O3 stability mechanism in the presence of the ionic polyamino acids. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2014, 292, 2453–2464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Jin, X.; Chen, Z.; Megharaj, M.; Naidu, R. Simultaneous removal of Pb(II) and Cr(III) by magnetite nanoparticles using various synthesis conditions. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2014, 20, 3543–3549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, J.; Chen, L.; Zeng, G.; Long, F.; Deng, J.; Niu, Q.; He, X. Shellac-coated iron oxide nanoparticles for removal of cadmium(II) ions from aqueous solution. J. Environ. Sci. 2012, 24, 1165–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Langmuir Isotherm | Freundlich Isotherm | Dubinin–Radushkevich Isotherm | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Metal Ion | qmax mg/g | b dm3/g | R2 | KF (mg/g)(L/mg)1/n | n | R2 | β mol2/J2 | E kJ/mol | R2 |
| Fe3O4 NPs | |||||||||
| Zn(II) | 4.83 | 0.1608 | 0.9788 | 1.2218 | 2.941 | 0.9777 | 4.30 × 10−9 | 10.79 | 0.6822 |
| Cu(II) | 14.24 | 0.1242 | 0.9485 | 2.2213 | 2.179 | 0.9696 | 3.40 × 10−9 | 12.13 | 0.9056 |
| Ni(II) | 5.26 | 0.0166 | 0.6226 | 0.1200 | 1.284 | 0.9473 | 8.27 × 10−9 | 7.77 | 0.8713 |
| Cd(II) | 3.34 | 0.0966 | 0.9832 | 0.4088 | 1.870 | 0.8880 | 5.35 × 10−9 | 9.66 | 0.8864 |
| Pb(II) | 45.71 | 0.5823 | 0.9924 | 12.9071 | 2.184 | 0.7435 | 3.28 × 10−9 | 12.35 | 0.7685 |
| Cr(III) | 23.65 | 3.3813 | 0.9989 | 12.0458 | 3.549 | 0.7720 | 2.25 × 10−9 | 14.89 | 0.7875 |
| Cr(VI) | 35.22 | 0.4451 | 0.9545 | 12.5142 | 3.581 | 0.9054 | 2.13 × 10−9 | 15.34 | 0.9209 |
| Fe3O4/PSA NPs | |||||||||
| Zn(II) | 16.93 | 0.2794 | 0.9975 | 3.7484 | 2.187 | 0.9547 | 3.97 × 10−9 | 11.23 | 0.9736 |
| Cu(II) | 33.44 | 0.8339 | 0.9948 | 10.4807 | 2.375 | 0.9019 | 3.10 × 10−9 | 12.70 | 0.9383 |
| Ni(II) | 17.65 | 0.0947 | 0.9700 | 2.0014 | 1.774 | 0.9607 | 5.12 × 10−9 | 9.88 | 0.9588 |
| Cd(II) | 34.61 | 0.1996 | 0.9867 | 5.9572 | 1.939 | 0.9723 | 4.06 × 10−9 | 11.09 | 0.9875 |
| Pb(II) | 129.10 | 0.1616 | 0.9732 | 15.8655 | 1.665 | 0.7355 | 4.78 × 10−9 | 10.23 | 0.7833 |
| Cr(III) | 39.71 | 1.0349 | 0.9942 | 15.1007 | 2.326 | 0.8538 | 3.17 × 10−9 | 12.57 | 0.8577 |
| Cr(VI) | 39.99 | 0.1356 | 0.7535 | 10.0218 | 3.263 | 0.8433 | 2.44 × 10−9 | 14.30 | 0.8397 |
| 1st Order | 2nd Order | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Metal Ion | qe mg/g | kI min−1 | R2 | qe mg/g | kII g/(mg·min) | R2 |
| Fe3O4 NPs | ||||||
| Zn(II) | 0.895 | 0.0024 | 0.133 | 7.56 | 0.941 | 1.000 |
| Cu(II) | 2.397 | 0.0050 | 0.910 | 14.09 | 0.040 | 0.999 |
| Ni(II) | 0.896 | 0.0050 | 0.338 | 5.91 | 0.153 | 0.999 |
| Cd(II) | 1.281 | 0.0058 | 0.549 | 5.61 | 0.094 | 0.996 |
| Pb(II) | 2.404 | 0.0035 | 0.847 | 22.79 | 0.063 | 1.000 |
| Cr(III) | 2.824 | 0.0043 | 0.388 | 23.93 | 0.082 | 1.000 |
| Cr(VI) | 4.015 | 0.0026 | 0.659 | 19.07 | 0.058 | 0.999 |
| Fe3O4/PSA NPs | ||||||
| Zn(II) | 1.733 | 0.0020 | 0.469 | 17.84 | 0.117 | 1.000 |
| Cu(II) | 2.045 | 0.0019 | 0.219 | 26.48 | 0.200 | 1.000 |
| Ni(II) | 1.796 | 0.0042 | 0.731 | 14.27 | 0.060 | 1.000 |
| Cd(II) | 1.732 | 0.0025 | 0.273 | 21.75 | 0.205 | 1.000 |
| Pb(II) | 1.507 | 0.0013 | 0.160 | 24.06 | 0.830 | 1.000 |
| Cr(III) | 2.370 | 0.0034 | 0.346 | 24.47 | 0.106 | 1.000 |
| Cr(VI) | 8.032 | 0.0042 | 0.822 | 15.25 | 0.013 | 0.997 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bobik, M.; Korus, I.; Synoradzki, K.; Wojnarowicz, J.; Biniaś, D.; Biniaś, W. Poly(sodium acrylate)-Modified Magnetite Nanoparticles for Separation of Heavy Metals from Aqueous Solutions. Materials 2022, 15, 6562. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15196562
Bobik M, Korus I, Synoradzki K, Wojnarowicz J, Biniaś D, Biniaś W. Poly(sodium acrylate)-Modified Magnetite Nanoparticles for Separation of Heavy Metals from Aqueous Solutions. Materials. 2022; 15(19):6562. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15196562
Chicago/Turabian StyleBobik, Magdalena, Irena Korus, Karol Synoradzki, Jacek Wojnarowicz, Dorota Biniaś, and Włodzimierz Biniaś. 2022. "Poly(sodium acrylate)-Modified Magnetite Nanoparticles for Separation of Heavy Metals from Aqueous Solutions" Materials 15, no. 19: 6562. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15196562
APA StyleBobik, M., Korus, I., Synoradzki, K., Wojnarowicz, J., Biniaś, D., & Biniaś, W. (2022). Poly(sodium acrylate)-Modified Magnetite Nanoparticles for Separation of Heavy Metals from Aqueous Solutions. Materials, 15(19), 6562. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15196562








