Hierarchical Nanocomposites Electrospun Carbon NanoFibers/Carbon Nanotubes as a Structural Element of Potentiometric Sensors
Abstract
:1. Introduction
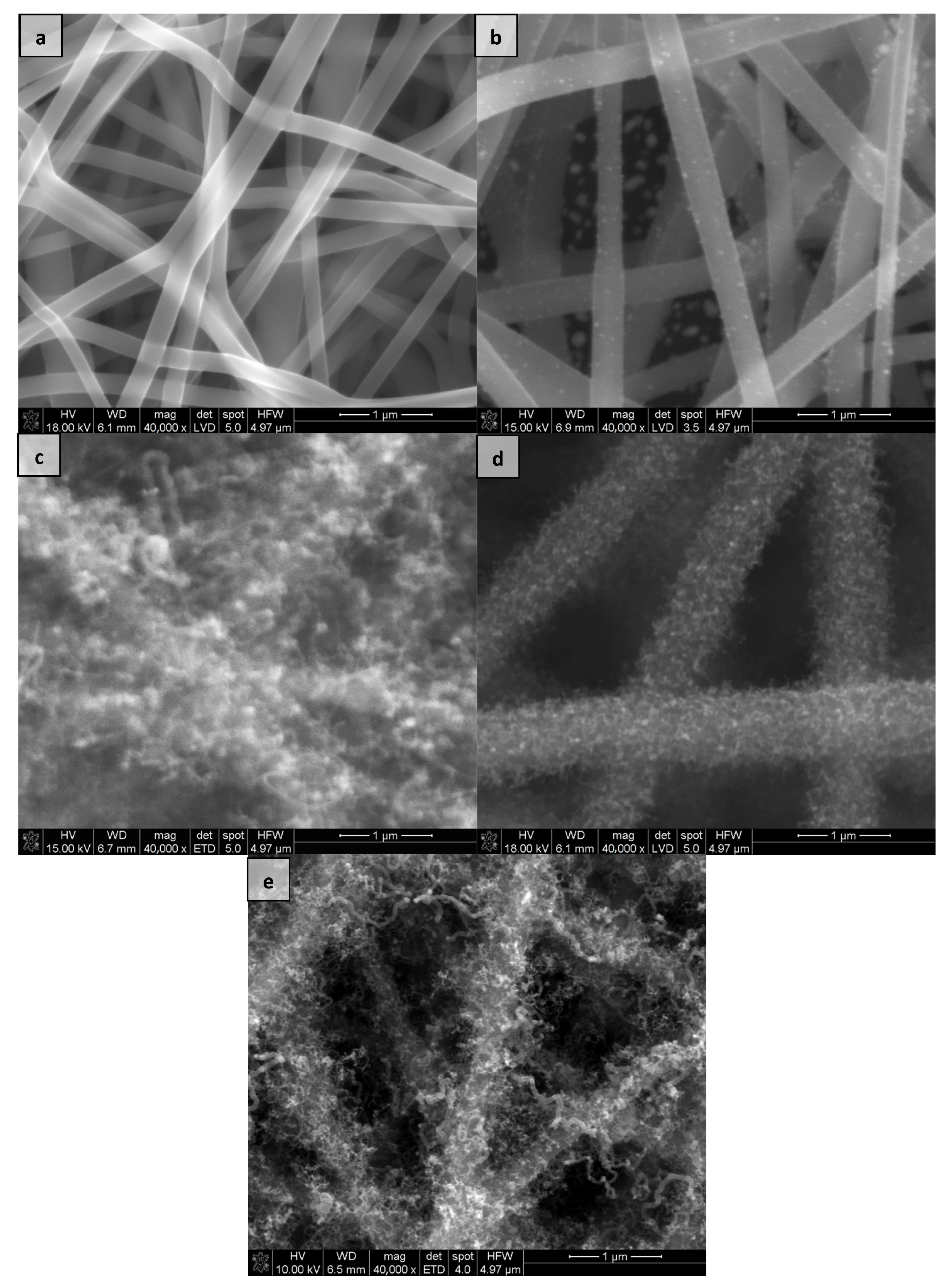
- electrospun carbon nanofibers (eCNF),
- eCNF with Co nanoparticles deposited on the surface (eCNF-Co),
- hierarchical nanocomposite with Co nanoparticles as a CNT growth catalyst (eCNF/CNT[HD]-Co),
- two hierarchical nanocomposites eCNF/CNT with NiCo nanoparticles as growth catalysts differing in the surface density of CNT:
- -
- with high density eCNF/CNT[HD]-NiCo
- -
- with low density eCNF/CNT[LD]-NiCo.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Electrode Preparation
2.3. Apparatus and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Microstructure Analysis by Scanning Electron Microscopy
3.2. Wettability
3.3. Potentiometric Measurements
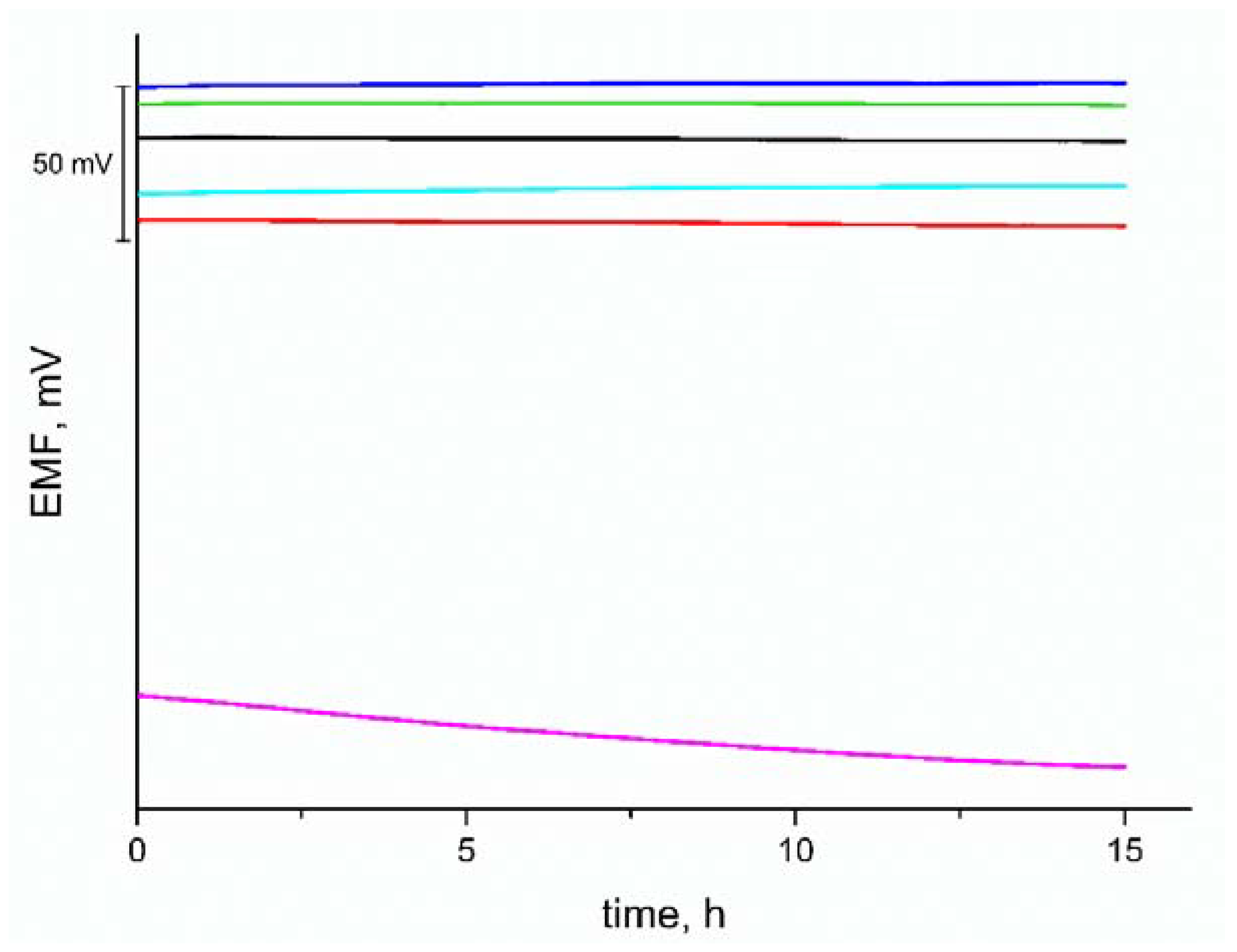
3.4. Stability of the Response
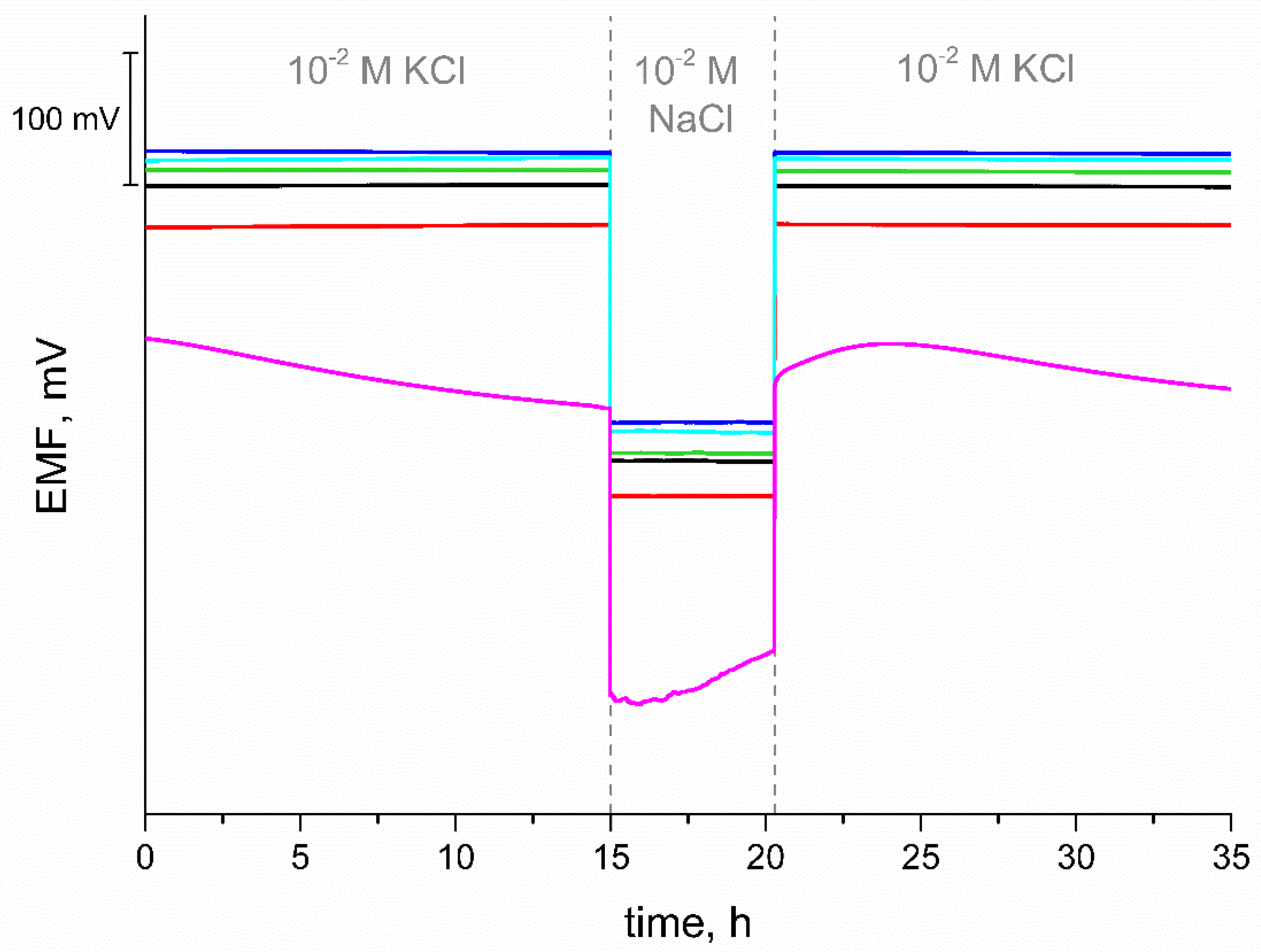
3.5. Reversibility Test
3.6. Water Layer Test
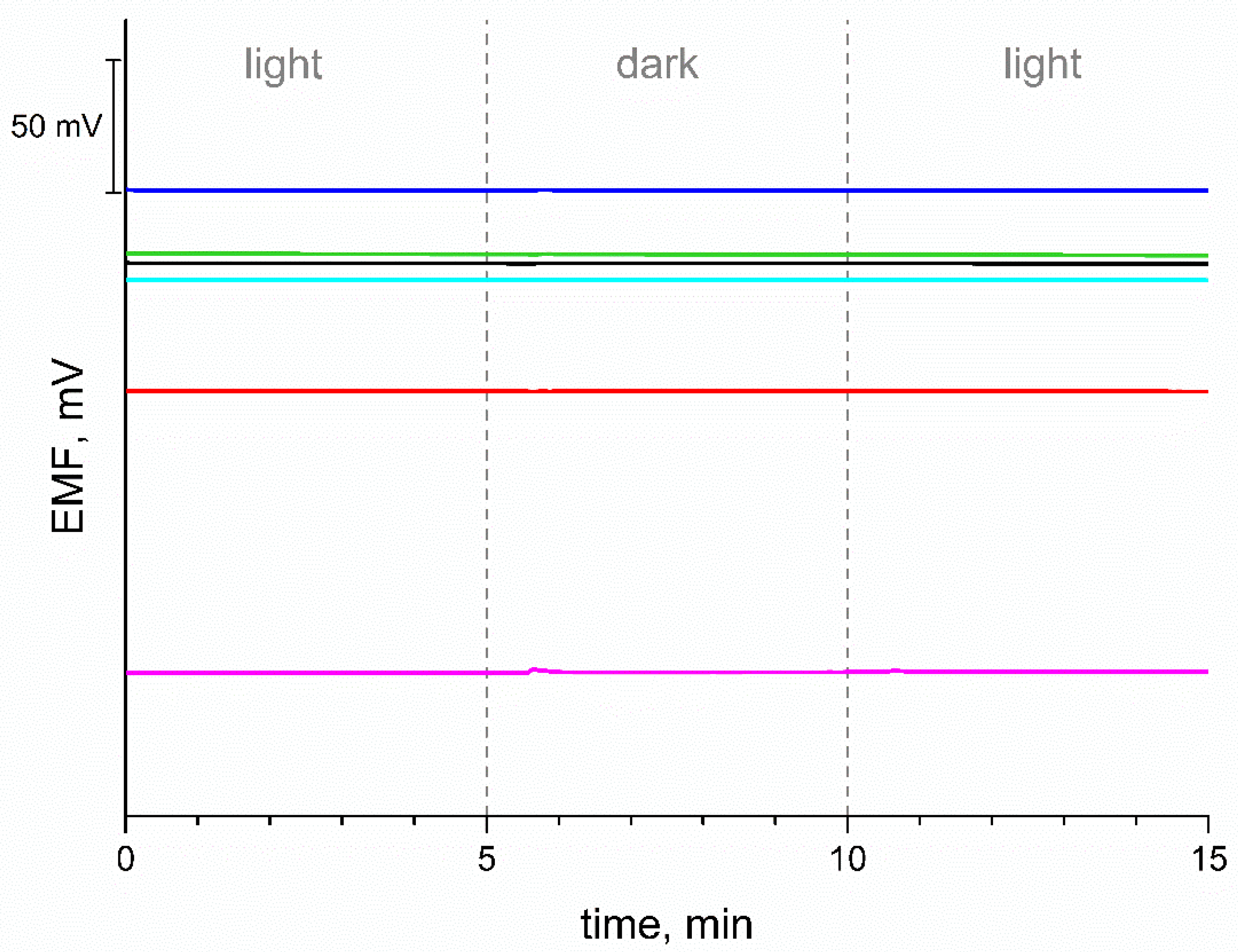
3.7. Light Sensitivity Test
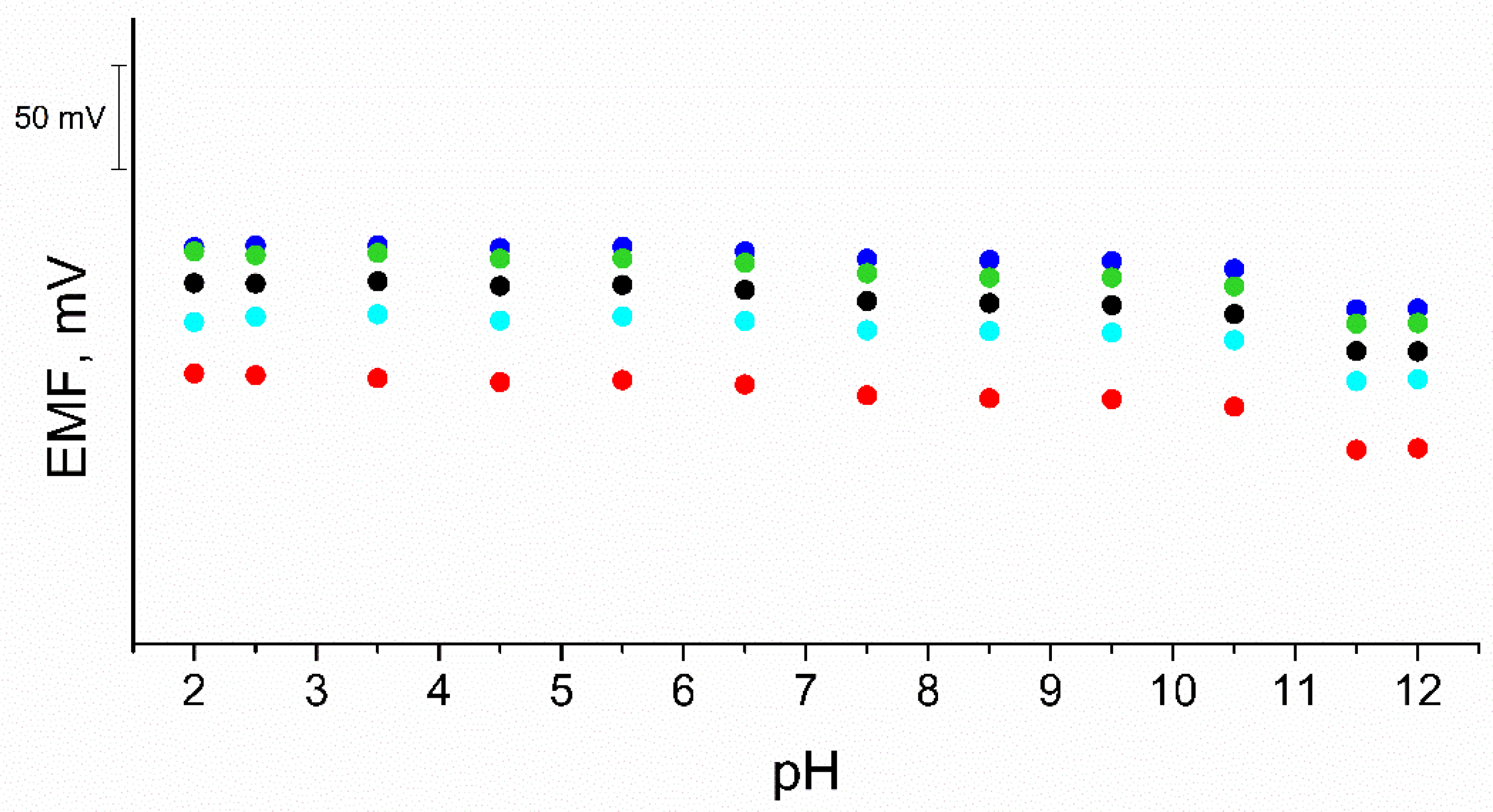
3.8. pH Sensitivity
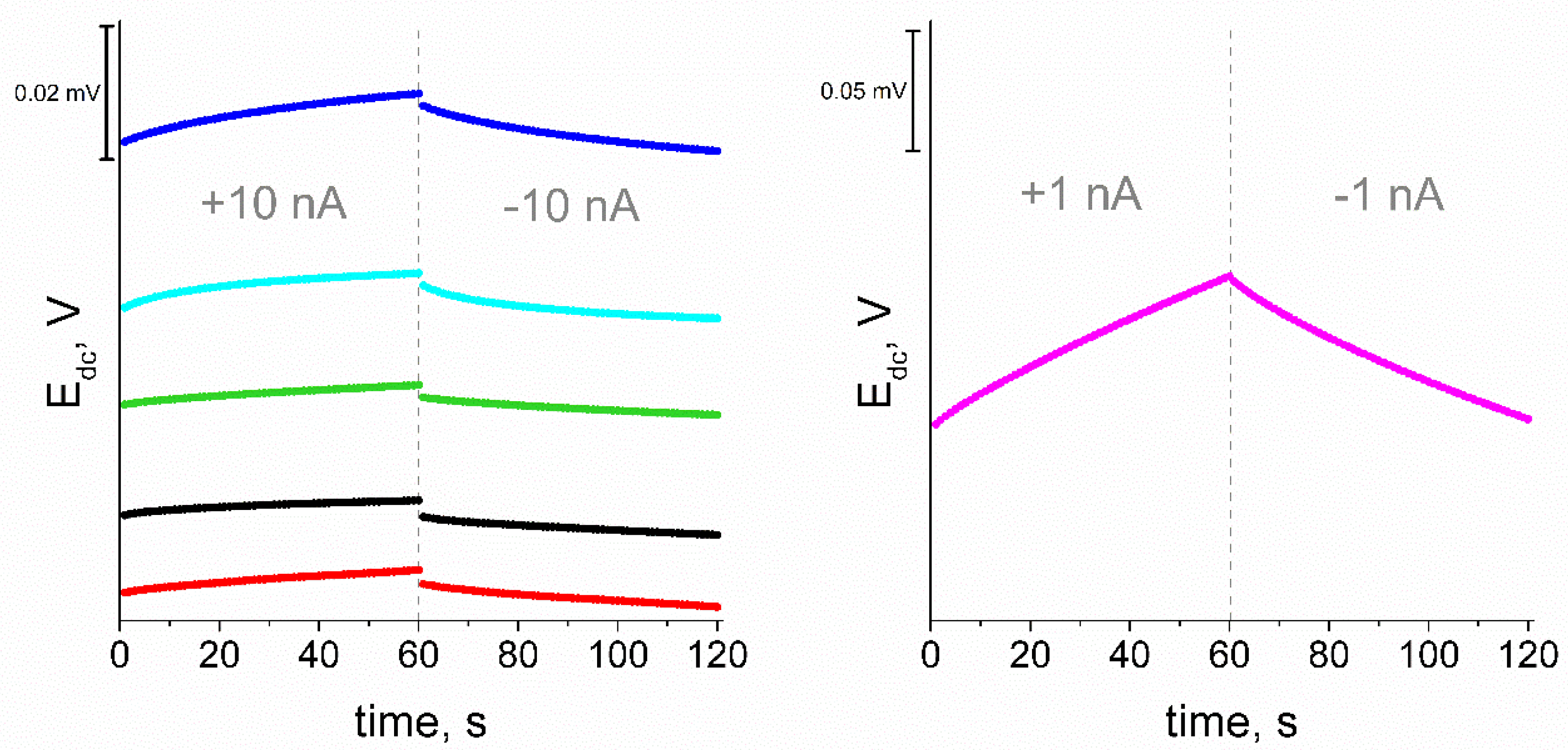
3.9. Chronopotentiometric Measurements
3.10. Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy Measurements
4. Application
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bakker, E. Ion-Selective Electrodes, 3rd ed.; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; ISBN 9780124095472. [Google Scholar]
- Janata, J. Principles of Chemical Sensors, 2nd ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2009; ISBN 9780387699301. [Google Scholar]
- Shao, Y.; Ying, Y.; Ping, J. Recent Advances in Solid-Contact Ion-Selective Electrodes: Functional Materials, Transduction Mechanisms, and Development Trends. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2020, 49, 4405–4465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, T.; Qin, W. Applications of Nanomaterials in Potentiometric Sensors. TrAC-Trends Anal. Chem. 2013, 51, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crespo, G.A.; Macho, S.; Rius, F.X. Ion-Selective Electrodes Using Carbon Nanotubes as Ion-to-Electron Transducers. Anal. Chem. 2008, 80, 1316–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crespo, G.A.; Gugsa, D.; Macho, S.; Rius, F.X. Solid-Contact PH-Selective Electrode Using Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2009, 395, 2371–2376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, Q.; Gan, S.; Xu, J.; Bao, Y.; Wu, T.; Kong, H.; Zhong, L.; Ma, Y.; Song, Z.; Niu, L. A Multichannel Electrochemical All-Solid-State Wearable Potentiometric Sensor for Real-Time Sweat Ion Monitoring. Electrochem. Commun. 2019, 107, 106553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ping, J.; Wang, Y.; Wu, J.; Ying, Y. Development of an All-Solid-State Potassium Ion-Selective Electrode Using Grapheme as the Solid-Contact Transducer. Electrochem. Commun. 2011, 13, 1529–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paczosa-Bator, B. All-Solid-State Selective Electrodes Using Carbon Black. Talanta 2012, 93, 424–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Cui, Z.; Li, D.; Yue, G.; Liu, J.; Ding, H.; Gao, S.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, N.; Zhao, Y. Hierarchically Structured Electrospinning Nanofibers for Catalysis and Energy Storage. Compos. Commun. 2019, 13, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zambrzycki, M.; Fraczek-Szczypta, A. Study on the Synthesis and Properties of Hierarchically Structured Electrospun/Vapour-Grown Carbon Nanofibres Nanocomposites. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2020, 86, 100–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Mel, A.A.; Achour, A.; Xu, W.; Choi, C.H.; Gautron, E.; Angleraud, B.; Granier, A.; Le Brizoual, L.; Djouadi, M.A.; Tessier, P.Y. Hierarchical Carbon Nanostructure Design: Ultra-Long Carbon Nanofibers Decorated with Carbon Nanotubes. Nanotechnology 2011, 22, 435302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zander, N.E. Hierarchically Structured Electrospun Fibers. Polymers 2013, 5, 19–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hou, H.; Reneker, D.H. Carbon Nanotubes on Carbon Nanofibers: A Novel Structure Based on Electrospun Polymer Nanofibers. Adv. Mater. 2004, 16, 69–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zambrzycki, M.; Łoś, S.; Fraczek-Szczypta, A. Structure and Electrical Transport Properties of Carbon Nanofibres/Carbon Nanotubes 3D Hierarchical Nanocomposites: Impact of the Concentration of Acetylacetonate Catalyst. Ceram. Int. 2021, 47, 4020–4033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadhari, N.S.; Gholave, J.V.; Patil, S.S.; Patil, V.R.; Upadhyay, S.S. Enantioselective High Performance New Solid Contact Ion-Selective Electrode Potentiometric Sensor Based on Sulphated γ-Cyclodextrin-carbon Nanofiber Composite for Determination of Multichiral Drug Moxifloxacin. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2021, 882, 114981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Górska, A.; Zambrzycki, M.; Paczosa-Bator, B.; Piech, R. New Electrochemical Sensor Based on Hierarchical Carbon Nanofibers with NiCo Nanoparticles and Its Application for Cetirizine Hydrochloride Determination. Materials 2022, 15, 3648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bobacka, J. Potential Stability of All-Solid-State Ion-Selective Electrodes Using Conducting Polymers as Ion-to-Electron Transducers. Anal. Chem. 1999, 71, 4932–4937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Marco, R.; Veder, J.P.; Clarke, G.; Nelson, A.; Prince, K.; Pretsch, E.; Bakker, E. Evidence of a Water Layer in Solid-Contact Polymeric Ion Sensors. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2008, 10, 73–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lrving, H.M.N.H.; Zettler, H.; Baudin, G.; Freiser, H.; Guilbault, G.G.; Menis, O.; Rice, N.M.; Robertson, A.J.B.; Docherty, A.C.; Fischer, W.; et al. Recommendations for Nomenclature of Ion-Selective Electrodes (Recommendations 1975). Pure Appl. Chem. 1976, 48, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rius-Ruiz, F.X.; Crespo, G.A.; Bejarano-Nosas, D.; Blondeau, P.; Riu, J.; Rius, F.X. Potentiometric Strip Cell Based on Carbon Nanotubes as Transducer Layer: Toward Low-Cost Decentralized Measurements. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 8810–8815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Ye, J.; Zhou, M.; Gan, S.; Zhang, Q.; Han, D.; Niu, L. All-Solid-State Potassium-Selective Electrode Using Graphene as the Solid Contact. Analyst 2012, 137, 618–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; Li, F.; Gan, S.; Jiang, Y.; An, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Niu, L. Using Sp2-C Dominant Porous Carbon Sub-Micrometer Spheres as Solid Transducers in Ion-Selective Electrodes. Electrochem. Commun. 2015, 50, 60–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Zou, X.U.; Stein, A.; Bühlmann, P. Ion-Selective Electrodes with Colloid-Imprinted Mesoporous Carbon as Solid Contact. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 7111–7118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paczosa-Bator, B. Ion-Selective Electrodes with Superhydrophobic Polymer/Carbon Nanocomposites as Solid Contact. Carbon 2015, 95, 879–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szigeti, Z.; Vigassy, T.; Bakker, E.; Pretsch, E. Approaches to Improving the Lower Detection Limit of Polymeric Membrane Ion-Selective Electrodes. Electroanalysis 2006, 18, 1254–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novell, M.; Parrilla, M.; Crespo, A.; Rius, F.X.; Andrade, F.J. Paper-Based Ion-Selective Potentiometric Sensors. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 4695–4702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ping, J.; Wang, Y.; Fan, K.; Tang, W.; Wu, J.; Ying, Y. High-Performance Flexible Potentiometric Sensing Devices Using Free-Standing Graphene Paper. J. Mater. Chem. B 2013, 1, 4781–4791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fibbioli, M.; Morf, W.E.; Badertscher, M.; De Rooij, N.F.; Pretsch, E. Potential Drifts of Solid-Contacted Ion-Selective Electrodes Due to Zero-Current Ion Fluxes through the Sensor Membrane. Electroanalysis 2000, 12, 1286–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cha, G.S.; Liu, D.; Meyerhoff, M.E.; Cantor, H.C.; Rees, A.M.; Goldberg, H.D.; Brown, R.B. Electrochemical Performance, Biocompatibility, and Adhesion of New Polymer Matrices for Solid-State Ion Sensors. Anal. Chem. 1991, 63, 1666–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

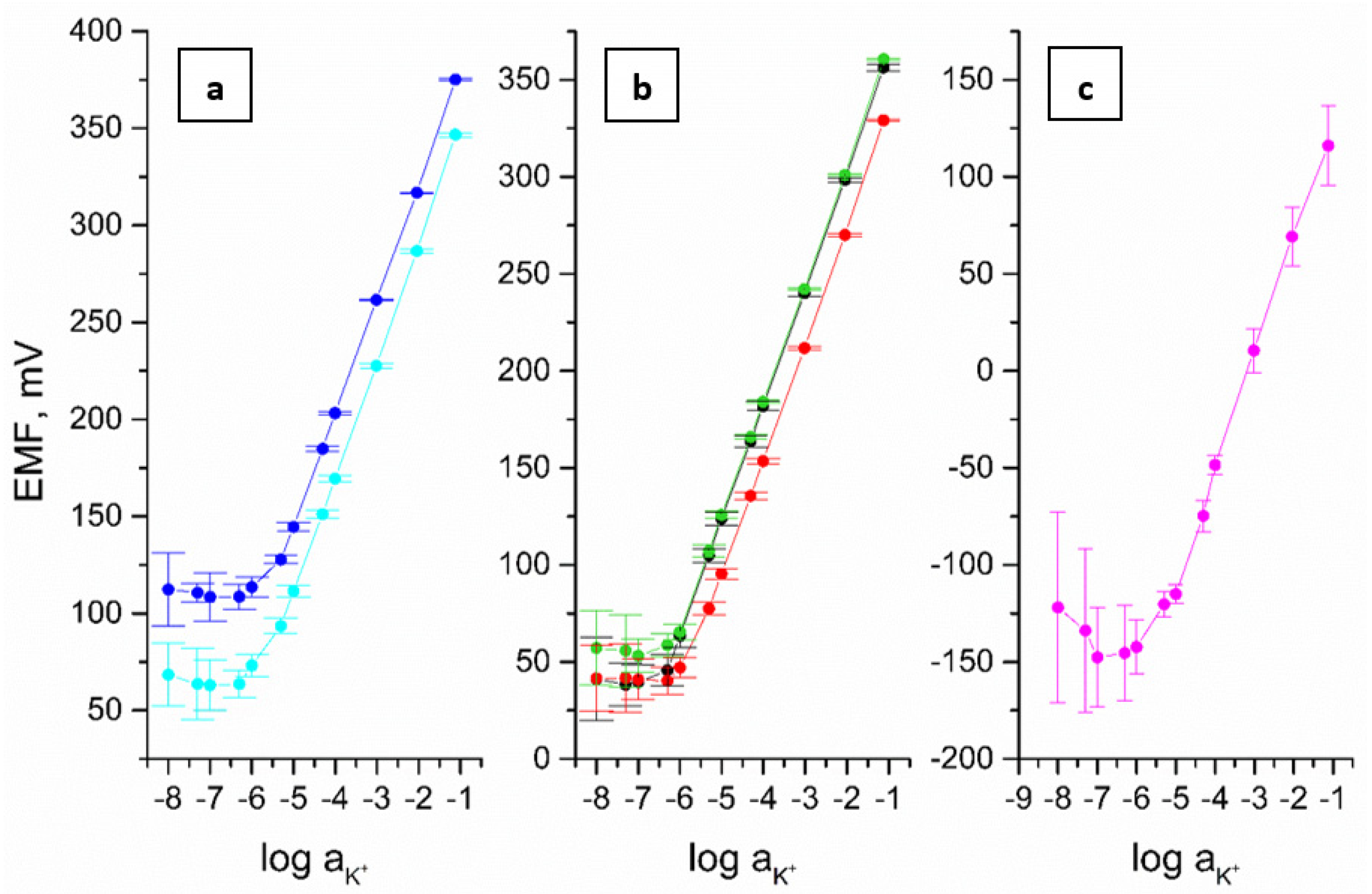


| Electrode | Parameter | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Slope (mV/dec) | E0 (mV) | LOD (M) | Linear Range (M) | |
| GC/eCNF/K+-ISM | 59.45 ± 0.70 | 435.3 ± 1.7 | 10−5.5 ± 0.1 | 10−5–10−1 |
| GC/eCNF-Co/K+-ISM | 59.32 ± 0.80 | 401.0 ± 1.7 | 10−5.7 ± 0.1 | 10−5–10−1 |
| GC/eCNF/CNT[HD]-Co/K+-ISM | 59.41 ± 0.54 | 416.0 ± 1.1 | 10−6.1 ± 0.1 | 10−5.3–10−1 |
| GC/eCNF/CNT[HD]-NiCo/K+-ISM | 59.39 ± 0.80 | 413.7 ± 0.9 | 10−6.3 ± 0.1 | 10−6–10−1 |
| GC/eCNF/CNT[LD]-NiCo/K+-ISM | 59.40 ± 0.65 | 385.5 ± 1.1 | 10−5.8 ± 0.1 | 10−5–10−1 |
| GC/K+-ISM | 62.00 ± 4.52 | 192.3 ± 20.6 | 10−5.4 ± 0.2 | 10−5–10−1 |
| C/SWCNT/ K+-ISM [19] | 57.4 | - | 10−6.5 | 10−5–10−2 |
| GC/CRGO/K+-ISM [20] | 59.2 | - | 10−5 | 10−4.5–10−2 |
| CNT paper/K+-ISM [21] | 56.4 | - | 7.2 × 10−6 | 10−5–10−1 |
| GNP/GNP/K+-ISM [22] | 59 | 403 | - | 10−5.8–10−1 |
| Electrode GC/: | R ± SD [kΩ] | ΔEdc/Δt ± SD [μV/s] | C ± SD [μF] (CP Method) | C [μF] (EIS Method) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| eCNF/K+-ISM | 91.3 ± 0.7 | 88.4 ± 1.3 | 113.1 ± 1.7 | 89.5 |
| eCNF-Co/K+-ISM | 93.1 ± 0.1 | 53.5 ± 0.5 | 186.8 ± 1.8 | 125 |
| eCNF/CNT[HD]-Co/K+-ISM | 94.0 ± 0.8 | 38.3 ± 1.4 | 260 ± 10 | 220 |
| eCNF/CNT[HD]-NiCo/K+-ISM | 122.4 ± 0.7 | 31 ± 1.5 | 330 ± 10 | 266 |
| eCNF/CNT[LD]-NiCo/K+-ISM | 105.3 ± 0.2 | 46.2 ± 1.3 | 220 ± 10 | 185 |
| K+-ISM | 1065 ± 13 | 1007 ± 70 | 1.0 ± 0.1 | 1.18 |
| Electrode | K+ Concentration [mg/L] | Recovery [%] | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fresh Juice | Commercial Juice 1 | Commercial Juice 2 | ||
| GC/eCNF/K+-ISM | 1980 ± 50 | 1980 ± 60 | 2300 ± 70 | 97 |
| GC/eCNF-Co/K+-ISM | 2100 ± 50 | 2030 ± 70 | 2220 ± 80 | 102 |
| GC/eCNF/CNT[HD]-Co/K+-ISM | 1980 ± 40 | 2090 ± 50 | 2250 ± 50 | 101 |
| GC/eCNF/CNT[HD]-NiCo/K+-ISM | 1940 ± 40 | 2040 ± 60 | 2180 ± 70 | 97 |
| GC/eCNF/CNT[LD]-NiCo/K+-ISM | 1890 ± 50 | 2020 ± 60 | 2150 ± 60 | 99 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Niemiec, B.; Zambrzycki, M.; Piech, R.; Wardak, C.; Paczosa-Bator, B. Hierarchical Nanocomposites Electrospun Carbon NanoFibers/Carbon Nanotubes as a Structural Element of Potentiometric Sensors. Materials 2022, 15, 4803. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15144803
Niemiec B, Zambrzycki M, Piech R, Wardak C, Paczosa-Bator B. Hierarchical Nanocomposites Electrospun Carbon NanoFibers/Carbon Nanotubes as a Structural Element of Potentiometric Sensors. Materials. 2022; 15(14):4803. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15144803
Chicago/Turabian StyleNiemiec, Barbara, Marcel Zambrzycki, Robert Piech, Cecylia Wardak, and Beata Paczosa-Bator. 2022. "Hierarchical Nanocomposites Electrospun Carbon NanoFibers/Carbon Nanotubes as a Structural Element of Potentiometric Sensors" Materials 15, no. 14: 4803. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15144803
APA StyleNiemiec, B., Zambrzycki, M., Piech, R., Wardak, C., & Paczosa-Bator, B. (2022). Hierarchical Nanocomposites Electrospun Carbon NanoFibers/Carbon Nanotubes as a Structural Element of Potentiometric Sensors. Materials, 15(14), 4803. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15144803








