Effects of Forging and Heat Treatment on Martensite Lath, Recrystallization and Mechanical Properties Evolution of 18Ni(250) Maraging Steel
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experiments
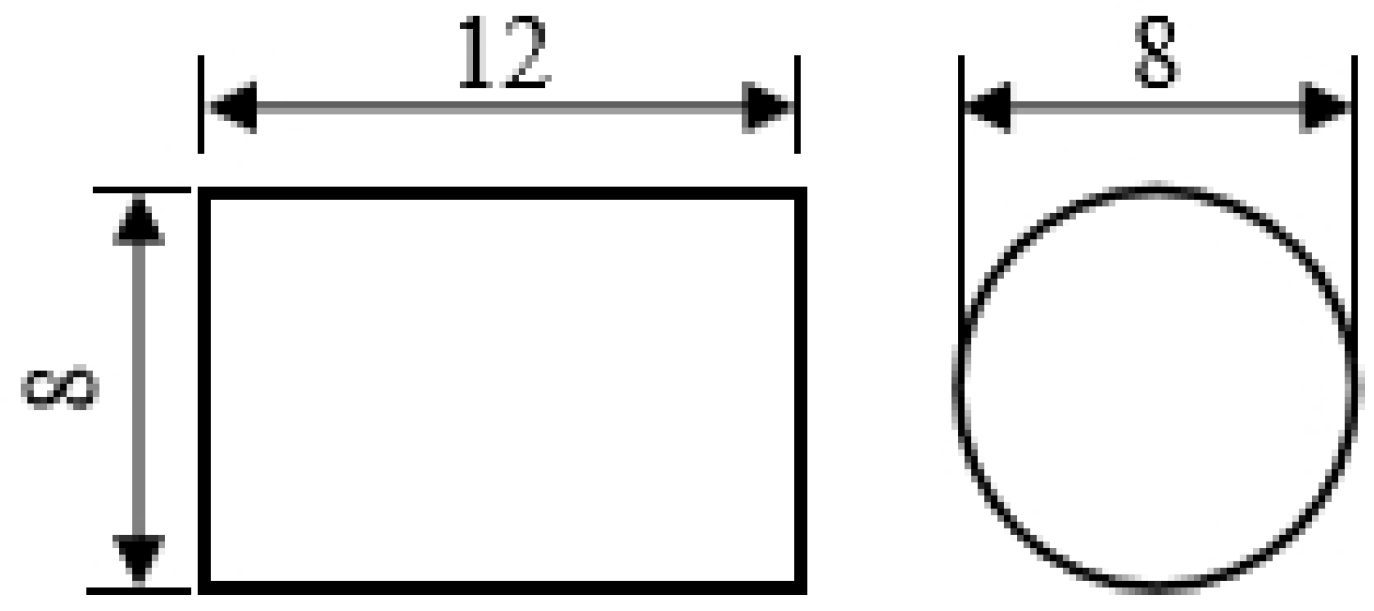
2.1. Thermal Compression Experiment of Small Samples
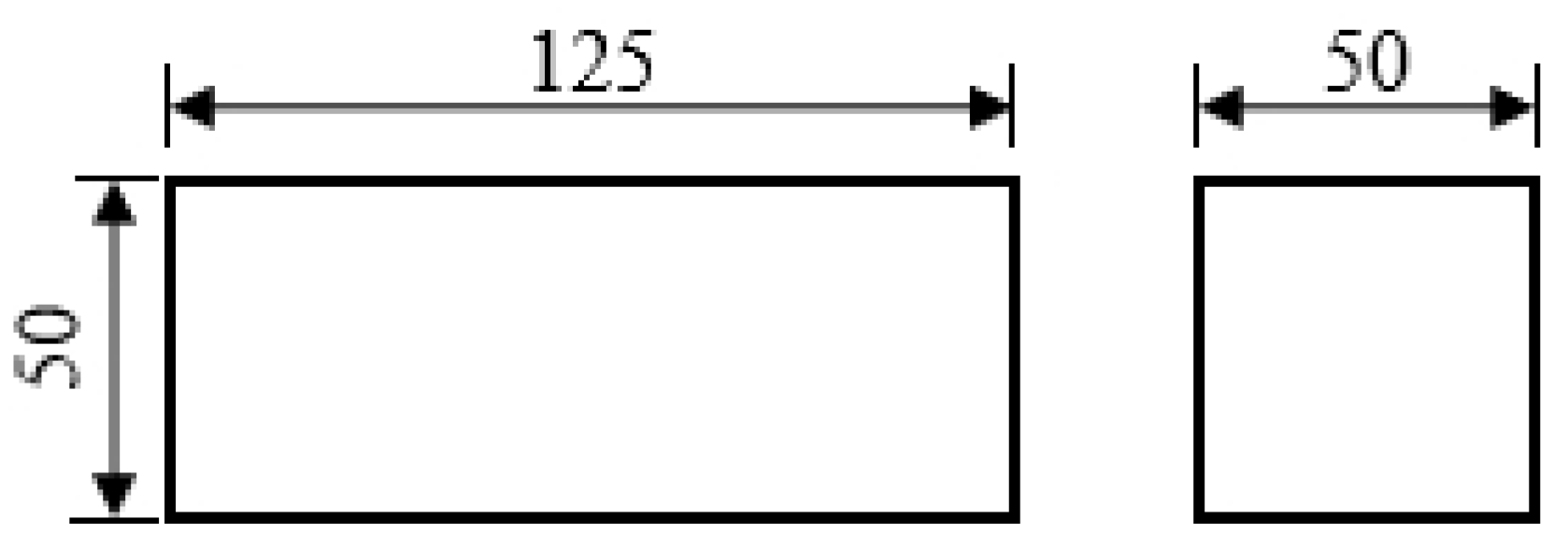
2.2. Upsetting Experiment of Large Samples
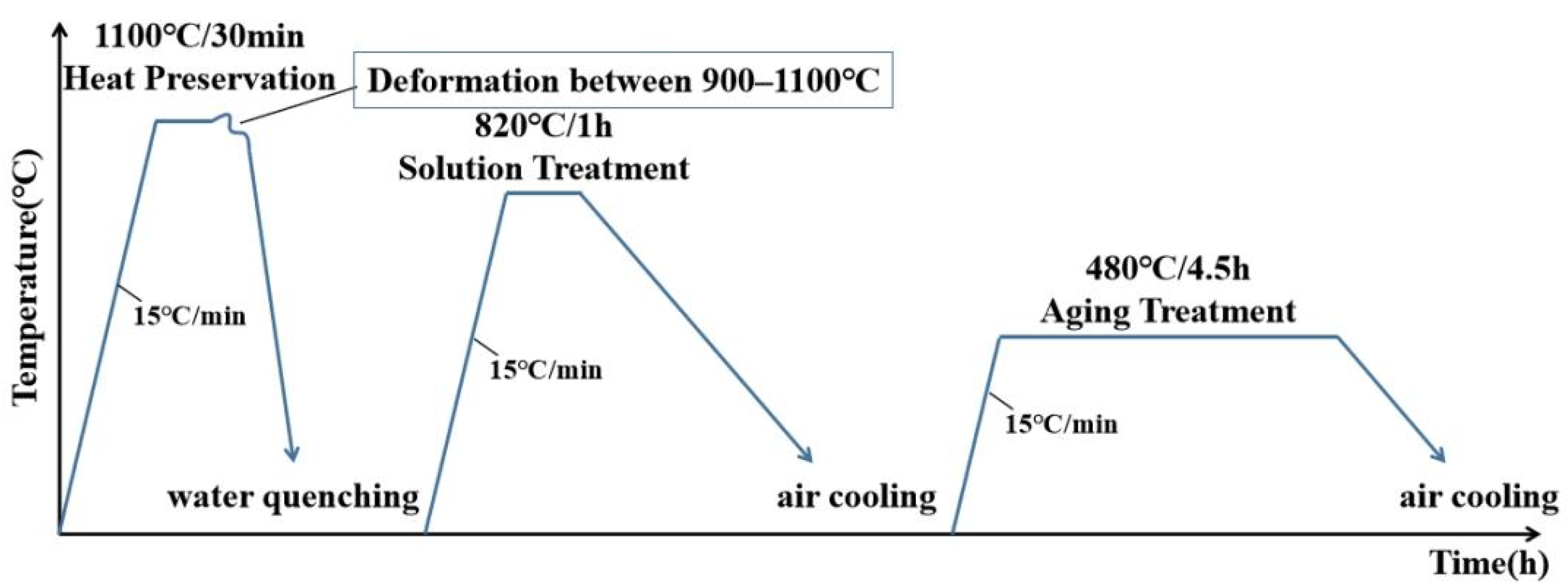
2.3. Heat Treatment Experiment
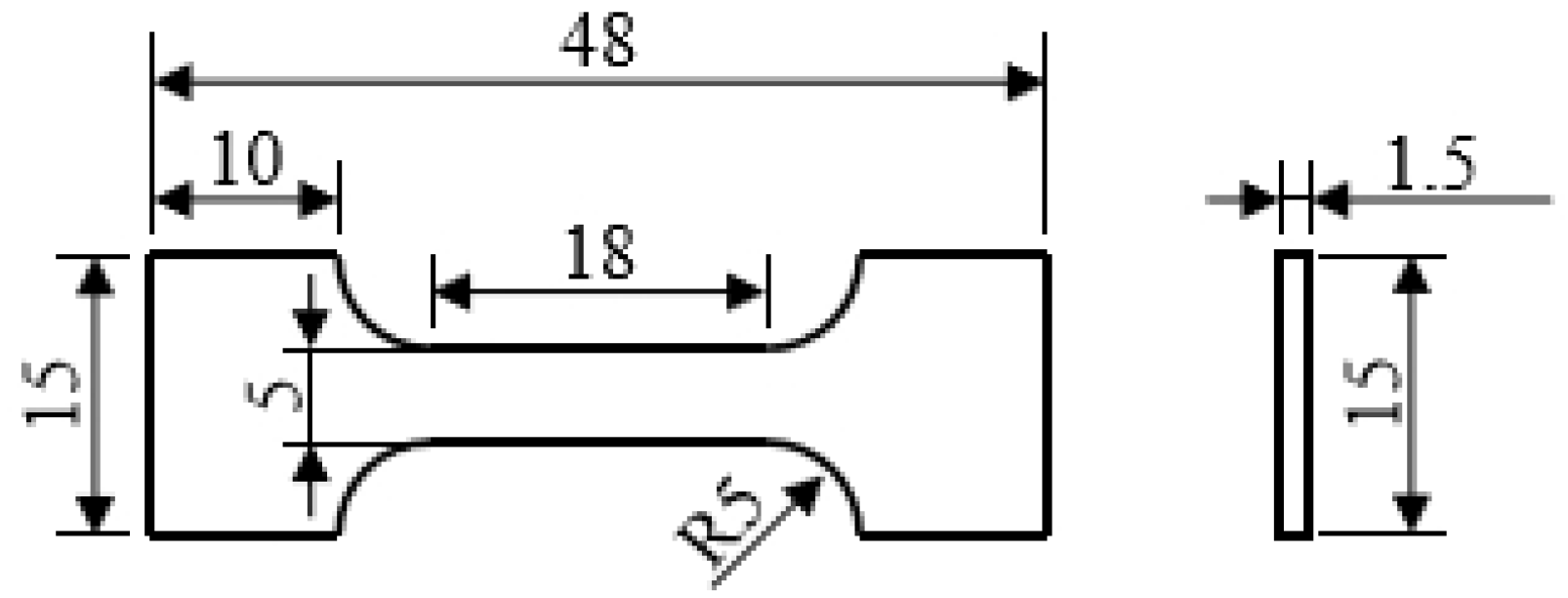
2.4. Tensile Experiment
3. Results
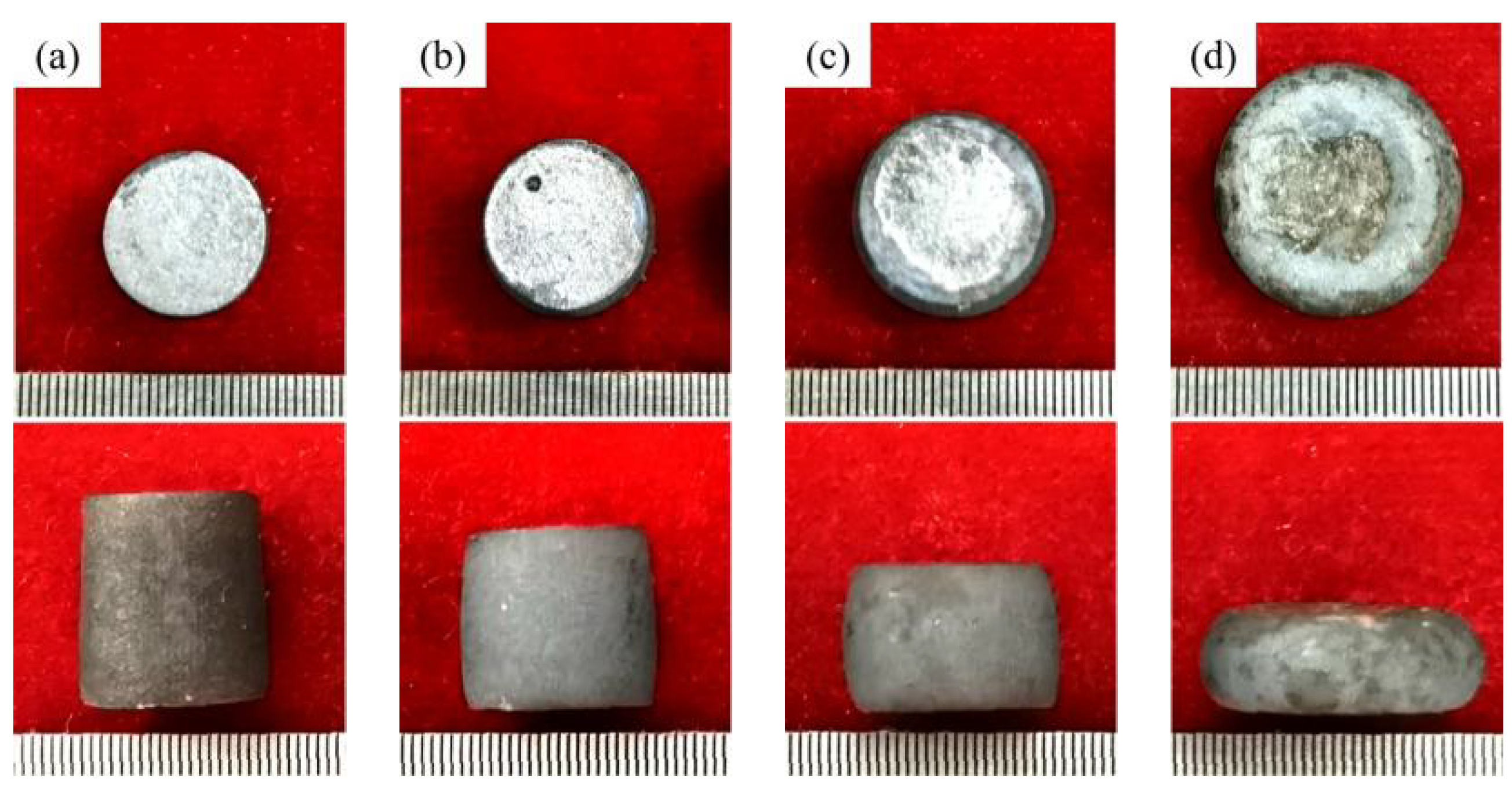
3.1. The Morphology of Thermal Compression Samples
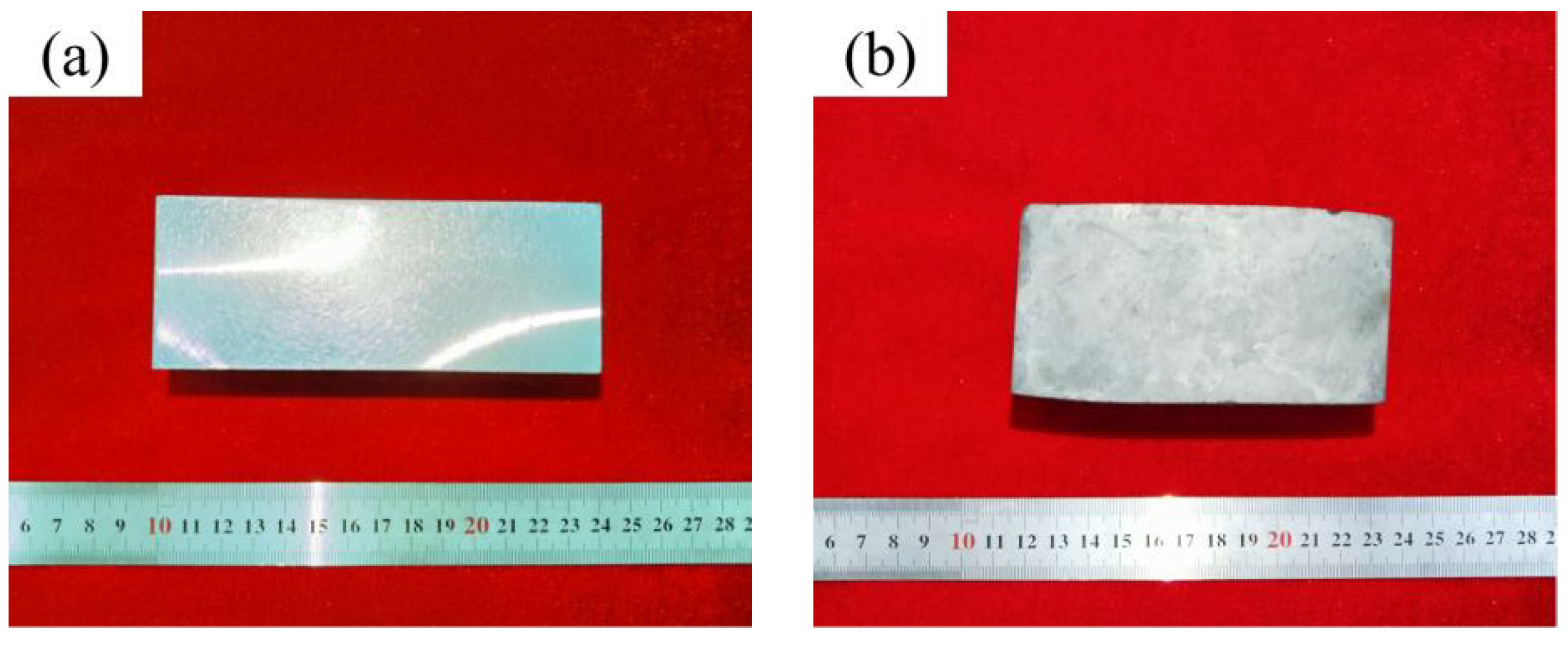
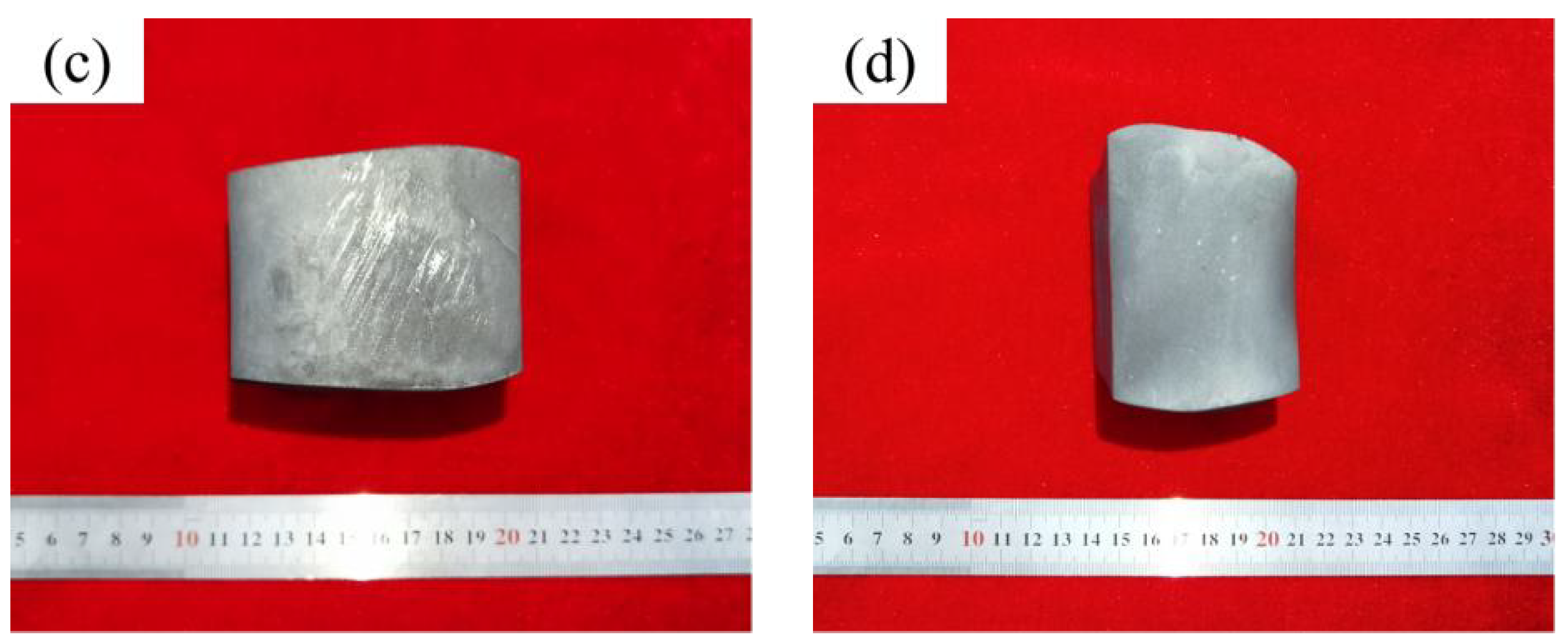
3.2. The Morphology of Upsetting Samples
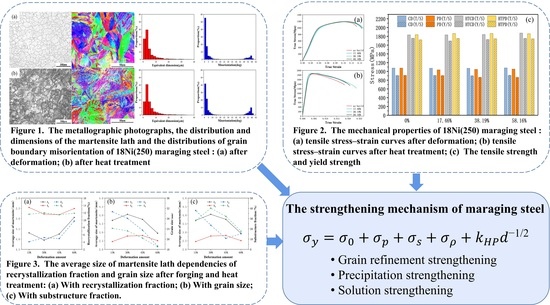
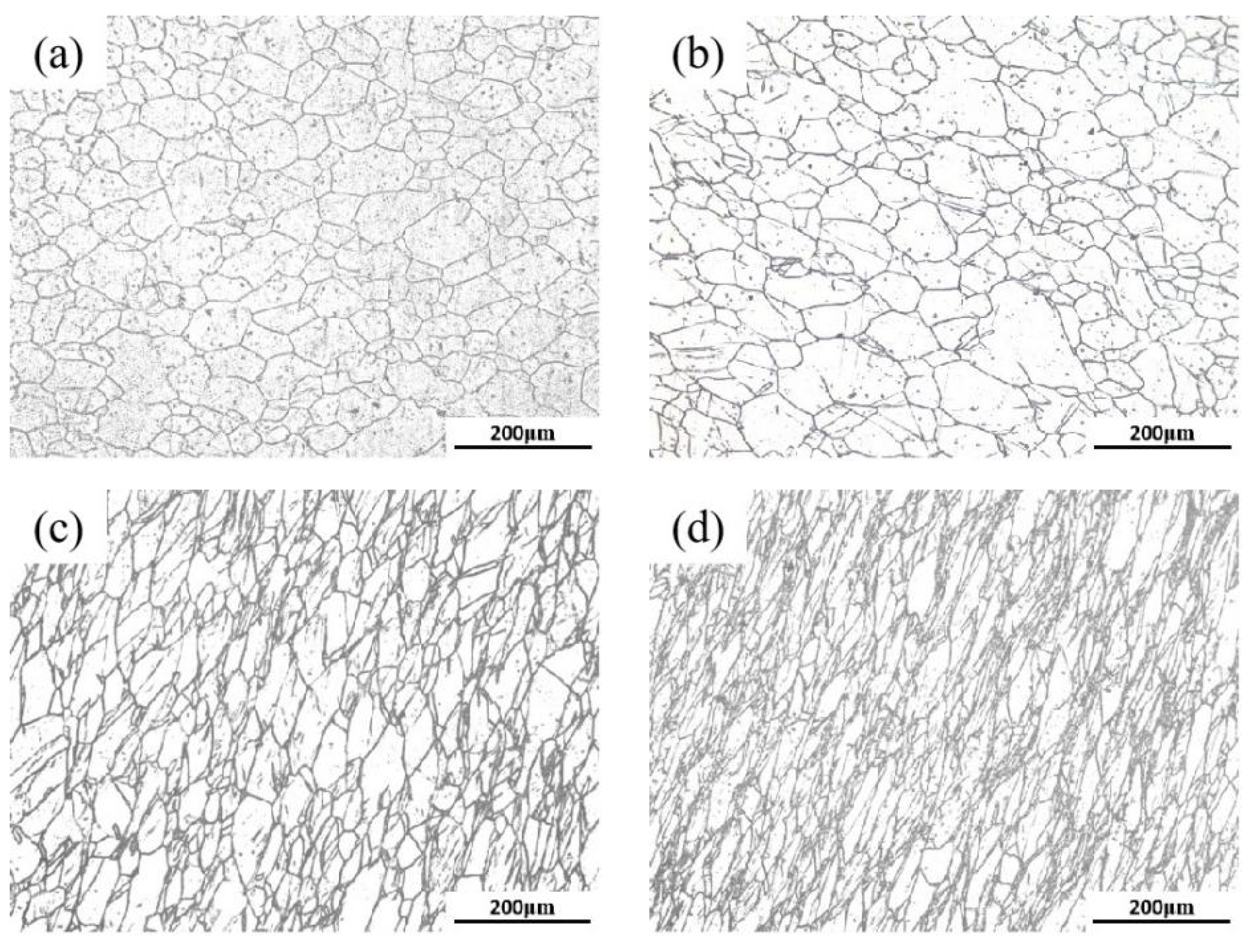
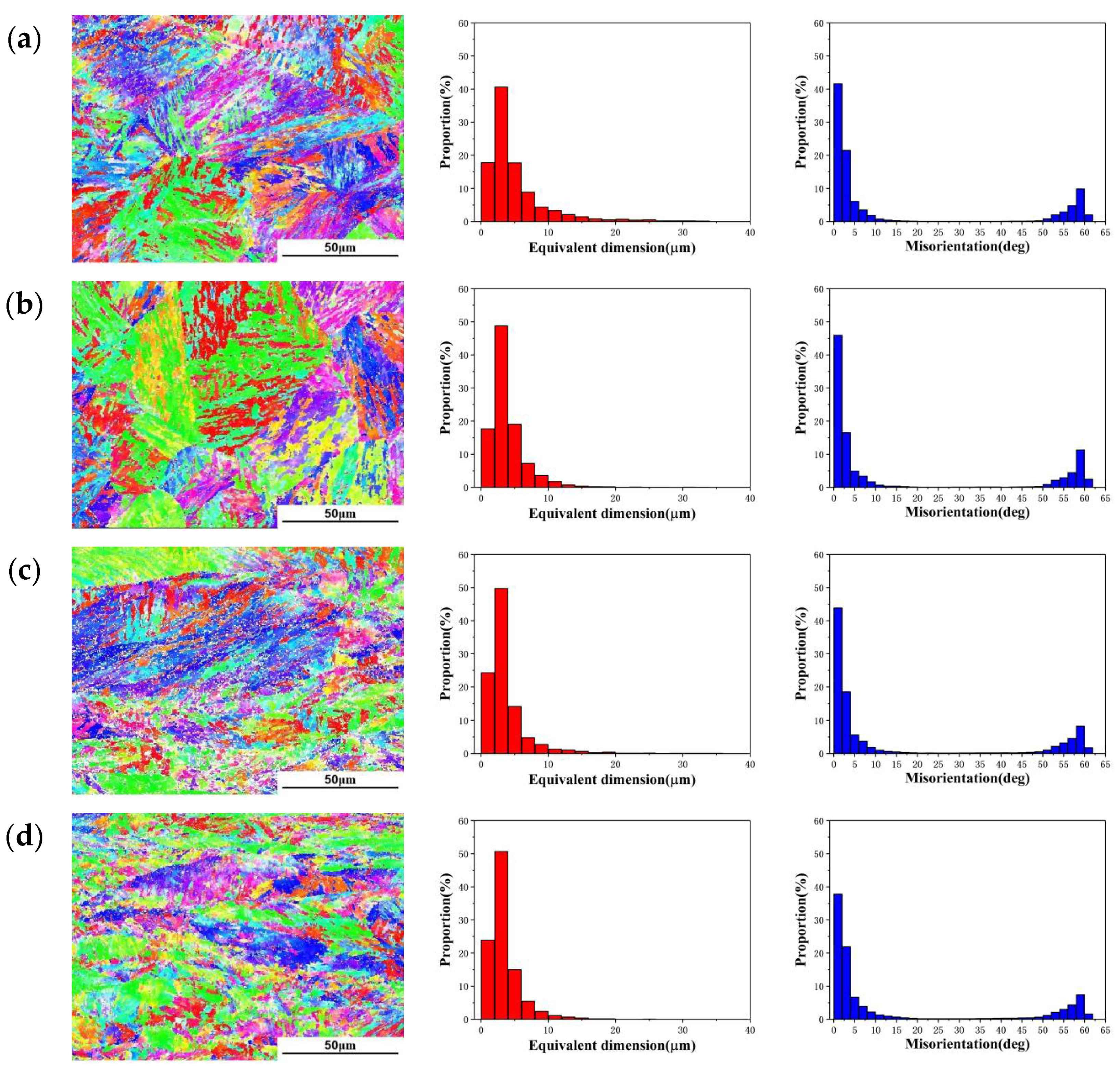
3.3. Microstructure Evolution of 18Ni(250) Steel after Deformation
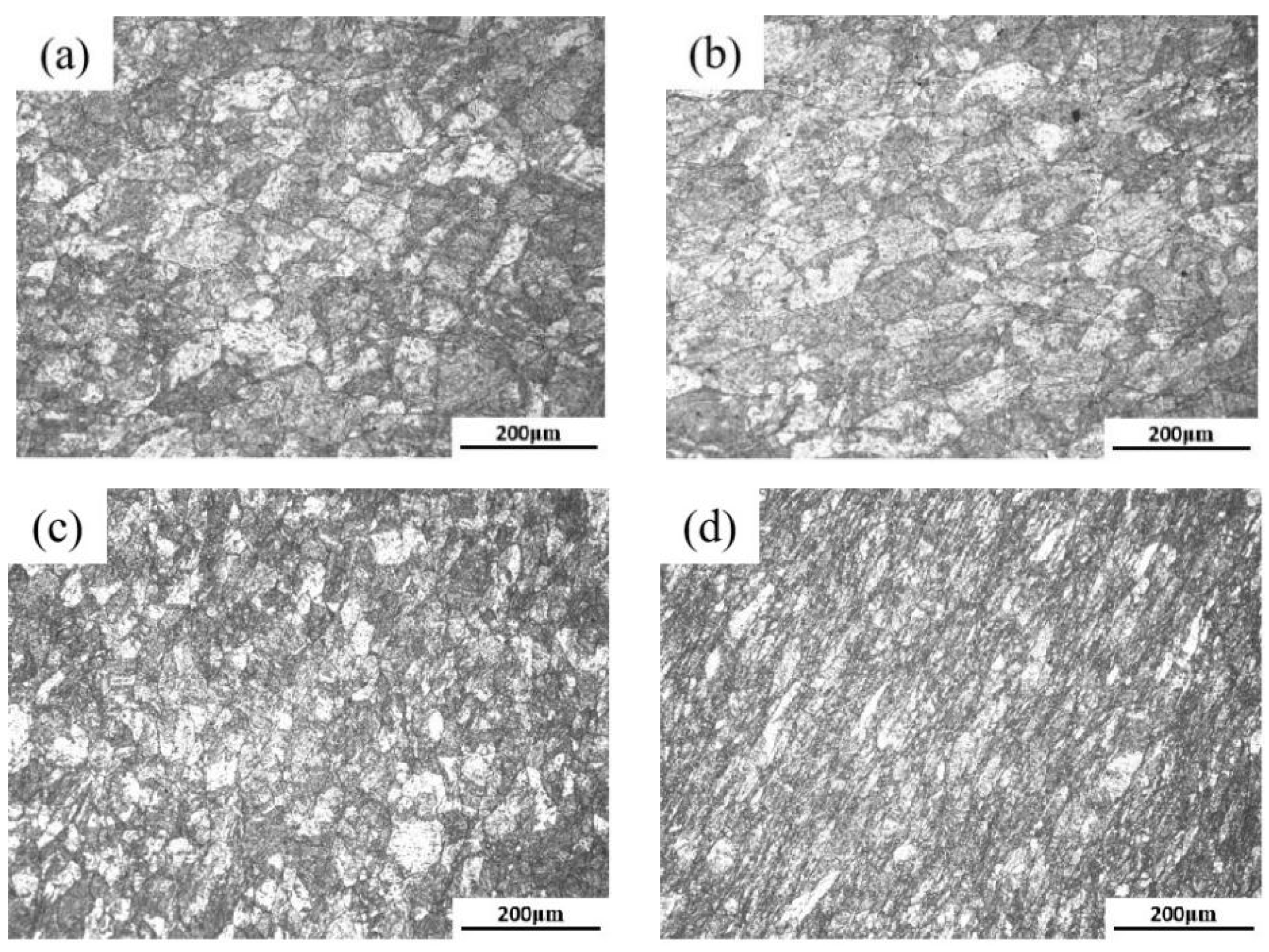
3.4. Microstructure Evolution of 18Ni(250) Steel after Heat Treatment
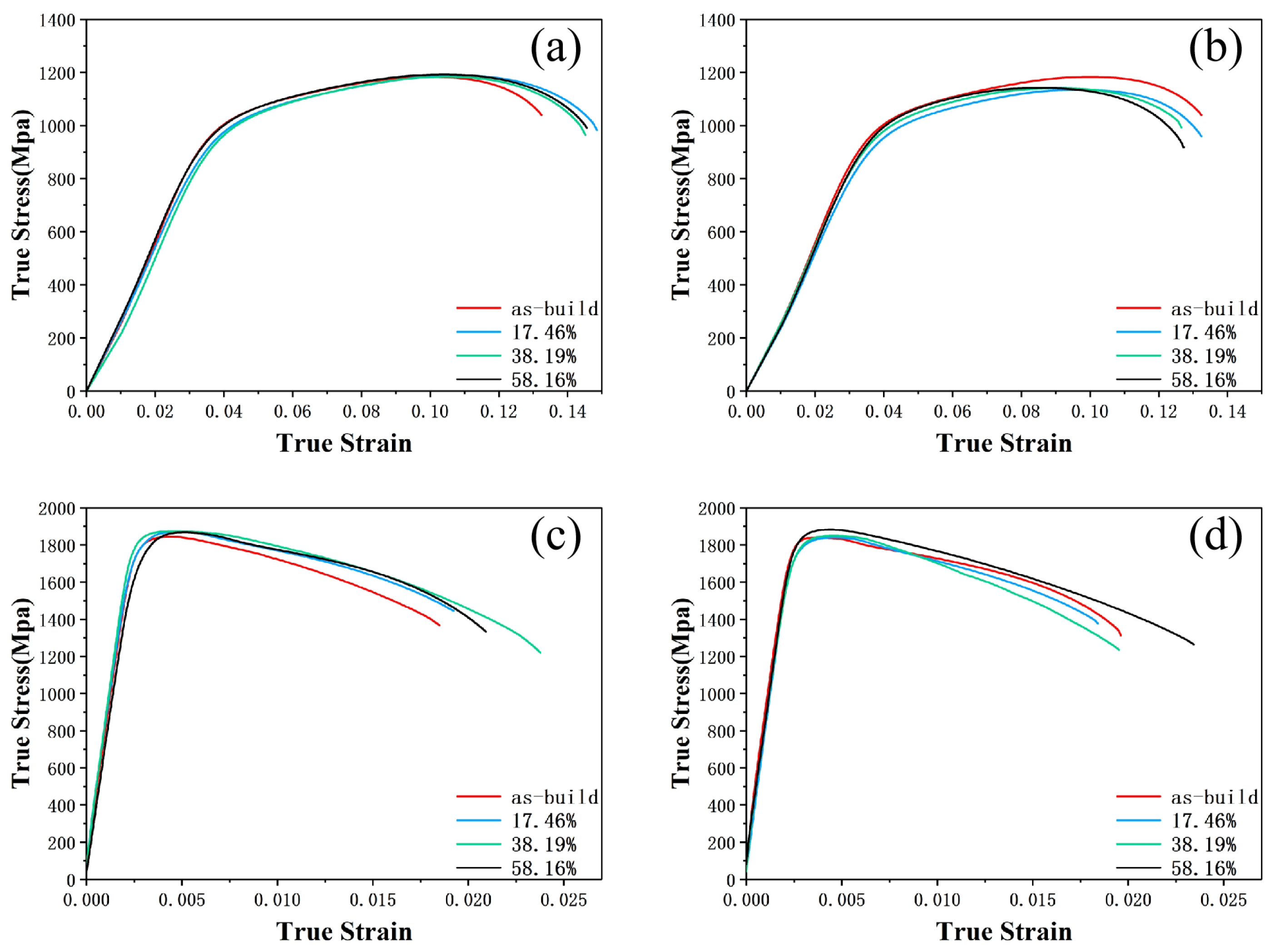
3.5. The Mechanical Properties of 18Ni(250) Steel after Forging and Heat Treatment
4. Discussion
4.1. The Average Size of Martensite Lath Dependencies of Recrystallization and Grain Size
4.2. The Strengthening Mechanism of 18Ni(250) Maraging Steel
5. Conclusions
- The change of the martensite lath size is opposite to the recrystallization fraction, and the change trend is approximately negatively correlated. The influence of recrystallization on martensite transformation is also related to the martensite substructure and grain size, since with the increase of martensite substructure fraction and grain size, the martensite transformation is first promoted and then inhibited.
- The strength of 18Ni(250) steel is affected by multiple strengthening mechanisms. Grain refinement strengthening is the main strengthening mechanism during forging, precipitation strengthening and solution strengthening are the most important strengthening mechanisms during heat treatment.
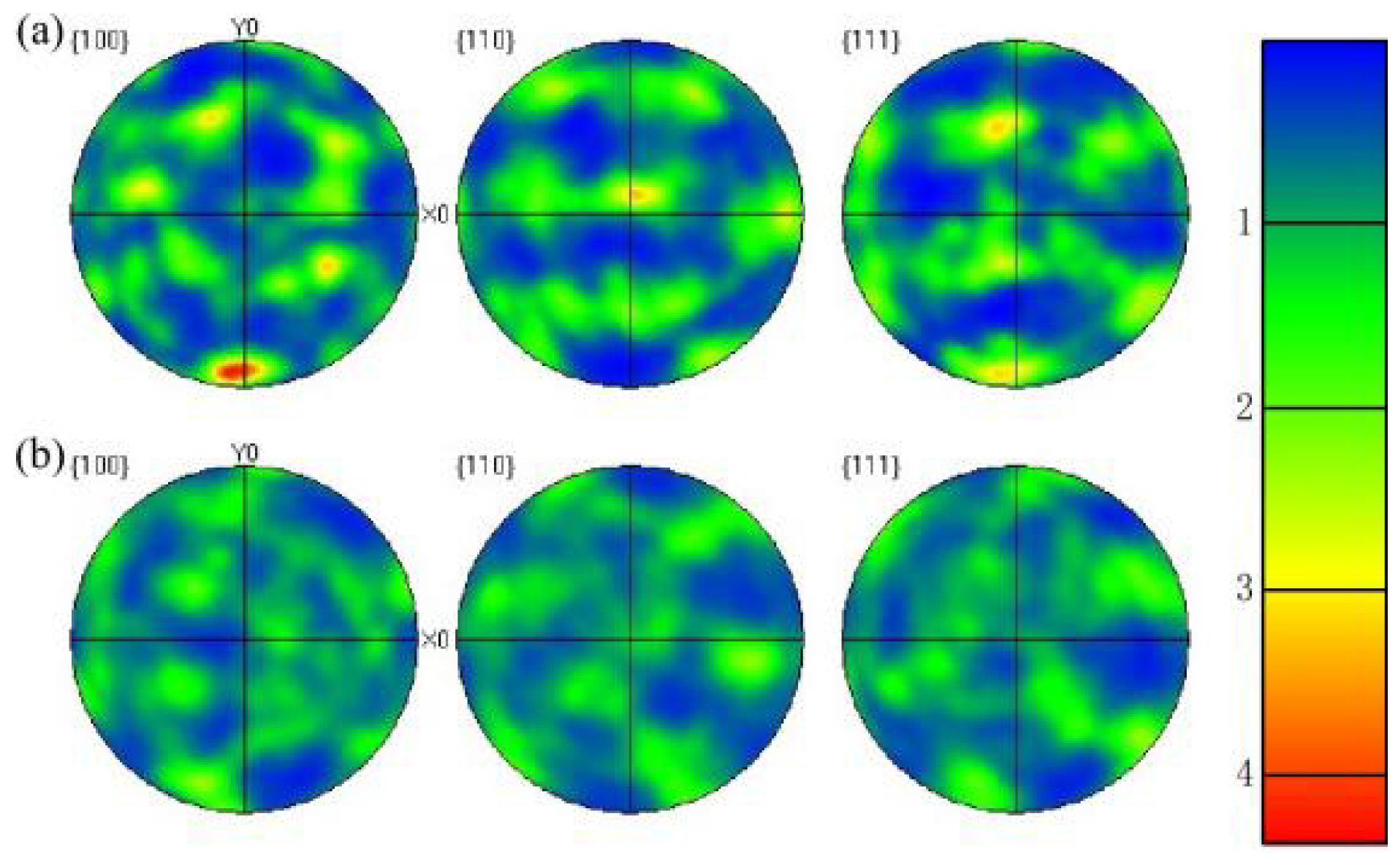
- After solution and aging heat treatment, the 18Ni(250) maraging steel is recrystallized and the texture generated by uniaxial compression deformation is significantly weakened, so that it does not show obvious anisotropy after heat treatment.
- Forging combined with heat treatment can refine grains and the martensite lath, and the internal defects of the original material can be better eliminated; thermal deformation can better play the role of grain refinement compared with cyclic phase transformation, which can improve the plasticity of 18Ni(250) maraging steel.
- The strengthening mechanism of forging and heat treatment are investigated, which can be applied to the design of forgings with high performance requirements in the future, which is helpful for developing a robotic free forging process and improving the intelligent manufacturing level of key aviation forgings of maraging steel.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fu, H.G.; Xie, L.J.; Wang, X.B.; Hu, X.; Gao, F.N. Fracture mechanism and model of 18Ni maraging steel. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2020, 36, 894–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chadha, K.; Tian, Y.; Bocher, P.; Spray, J.G.; Aranas, C. Microstructure Evolution, Mechanical Properties and Deformation Behavior of an Additively Manufactured Maraging Steel. Materials 2020, 13, 2380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sha, W.; Guo, Z. Maraging Steels: Modelling of Microstructure, Properties and Applications; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Lu, Q.D.; Zhang, D.W.; Huang, S.Z. Study on Hot Deformation Behavior and Applications in Aerospace of Ultra-high Strength and High-Toughness Steel. Aerosp. Shanghai 2019, 36, 111–117. [Google Scholar]
- Naim, M.; Bahadur, S. Effect of microstructure and mechanical properties on the erosion of 18 Ni(250) maraging steel. Wear 1986, 112, 217–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casati, R.; Lemke, J.; Vedani, M. Microstructural and Mechanical Properties of as Built, Solution Treated and Aged 18 Ni (300 grade) Maraging Steel Produced by Selective Laser Melting. Metall. Ital. 2017, 109, 11–20. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, X.T.; Ren, W.B.; Zhao, J.L.; Zhao, G.J. Effect of Solution Temperature on Mechanical Properties of 18NiC250 Material. Hot Work. Technol. 2018, 47, 198–200. [Google Scholar]
- Schnitzer, R.; Schober, M.; Zinnerc, S.; Leitner, H. Effect of Cu on the evolution of precipitation in an Fe-Cr-Ni-Al-Ti maraging steel. Acta Mater. 2010, 58, 3733–3741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casati, R.; Lemke, J.N.; Tuissi, A.; Vedani, M. Aging Behaviour and Mechanical Performance of 18-Ni300 Steel Processed by Selective Laser Melting. Metals 2016, 6, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Kim, T.; Ha, K.; Oak, J.J.; Jeon, J.B.; Park, Y.; Lee, W. Effect of Heat Treatment Condition on Microstructural and Mechanical Anisotropies of Selective Laser Melted Maraging 18Ni-300 Steel. Metals 2020, 10, 410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bodziak, S.; Al-Rubaie, K.S.; Dalla Valentina, L.; Lafratta, F.H.; Santos, E.C.; Zanatta, A.M.; Chen, Y.M. Precipitation in 300 grade maraging steel built by selective laser melting: Aging at 510 °C for 2 h. Mater. Charact. 2019, 151, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohit, B.; Muktinutalapati, N.R. Fatigue Behavior of 18% Ni Maraging Steels: A Review. Performance 2021, 30, 2341–2354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Rivera-Diaz-del-Castillo, P.E.J.; van der Zwaag, S. Computational design of UHS maraging stainless steels incorporating composition as well as austenitisation and ageing temperatures as optimisation parameters. Philos. Mag. 2009, 89, 1647–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Galindo-Nava, E.I.; Rainforth, W.M.; Rivera-Díaz-del-Castillo, P.E.J. Predicting microstructure and strength of maraging steels: Elemental optimisation. Acta Mater. 2016, 117, 270–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.C.; Wang, D.; Yang, Y.Q.; Wang, H. Effect of heat treatment on the microstructure and mechanical properties of maraging steel by selective laser melting. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2019, 760, 105–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereloma, E.V.; Shekhter, A.; Miller, M.K.; Ringer, S.P. Ageing behaviour of an Fe-20Ni-1.8Mn-1.6Ti-0.59Al (wt%) maraging alloy: Clustering, precipitation and hardening. Acta Mater. 2004, 52, 5589–5602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.P.; Wang, X. Microstructure and mechanical properties of maraging 18Ni-300 steel obtained by powder bed based selective laser melting process. Rapid Prototyp. J. 2020, 26, 1379–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Duan, Q.Q.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, Z.J.; Li, X.W.; Zhang, Z.F. Investigation on the cracking resistances of different ageing treated 18Ni maraging steels. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2020, 771, 138553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.M.; Zhang, J.W.; Hu, J.P.; Ouyang, M.N.; Qiu, C.J. Effects of aging time on the microstructure and mechanical properties of laser-cladded 18Ni300 maraging steel. J. Mater. Sci. 2021, 56, 8835–8847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagle, E.A.; Choi, P.P.; Van Humbeeck, J.; Raabe, D. Precipitation and austenite reversion behavior of a maraging steel produced by selective laser melting. J. Mater. Res. 2014, 29, 2072–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nedjad, S.H.; Ahmadabadi, M.N.; Furuhara, T. Correlation between the intergranular brittleness and precipitation reactions during isothermal aging of an Fe-Ni-Mn maraging steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2008, 490, 105–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tariq, F.; Shifa, M.; Baloch, R.A. Effect of Overaging Conditions on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Maraging Steel. Metal Sci. Heat Treat. 2020, 62, 188–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dos Santos, L.P.M.; Béreš, M.; de Castro, M.O.; Sarvezuk, P.W.C.; Wu, L.; Herculano, L.F.G.; Paesano, A.; Silva, C.C.; Masoumi, M.; de Abreu, H.F.G. Kinetics of Reverted Austenite in 18 wt.% Ni Grade 300 Maraging Steel: An In-Situ Synchrotron X-ray Diffraction and Texture Study. JOM 2020, 72, 3502–3512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohit, B.; Muktinutalapati, N.R. Austenite reversion in 18% Ni maraging steel and its weldments. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2018, 34, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soleimani, M.; Kalhor, A.; Mirzadeh, H. Transformation-induced plasticity (TRIP) in advanced steels: A review. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2020, 795, 140023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnitzer, R.; Zickler, G.A.; Lach, E.; Clemens, H.; Zinner, S.; Lippmann, T.; Leitner, H. Influence of reverted austenite on static and dynamic mechanical properties of a PH 13-8 Mo maraging steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2010, 527, 2065–2070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnitzer, R.; Radis, R.; Nohrer, M.; Schober, M.; Hochfellner, R.; Zinner, S.; Povoden-Karadeniz, E.; Kozeschnik, E.; Leitner, H. Reverted austenite in PH 13-8 Mo maraging steels. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2010, 122, 138–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raabe, D.; Ponge, D.; Dmitrieva, O. Designing Ultrahigh Strength Steels with Good Ductility by Combining Transformation Induced Plasticity and Martensite Aging. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2009, 11, 547–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leitner, H.; Schober, M.; Schnitzer, R.; Zinner, S. Strengthening behavior of Fe-Cr-Ni-Al-(Ti) maraging steels. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2011, 528, 5264–5270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kucerova, L.; Zetkova, I.; Jenicek, S.; Burdova, K. Hybrid parts produced by deposition of 18Ni300 maraging steel via selective laser melting on forged and heat treated advanced high strength steel. Addit. Manuf. 2020, 32, 101108. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, P.; Wynne, B.P.; Knowles, A.J.; Turk, A.; Ma, L.; I Galindo-Nava, E.; Rainforth, W.M. Effect of ageing on the microstructural evolution in a new design of maraging steels with carbon. Acta Mater. 2020, 196, 101–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.G.; Lu, F.S.; Zhang, J.L.; Zhang, J.S.; Zhang, J.F. Influence of Gradient Cyclic Heat Treatment on Microstructure and Properties of 3J33 (C) Maraging Steel. Metallic Funct. Mater. 2010, 17, 16–19. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, W.Y.; Jiang, J.; Liu, X.M.; Wang, C.X. Study on Grain Refinement of 18Ni Maraging Steel by Cyclic Transformation. Mater. Heat Treat. 2012, 41, 194–199. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J. Effect of Cyclic Transformation Process on Properties and Grain Size of 0018Ni Steel. Spec. Steel Technol. 2014, 20, 32–35, 57. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, W.; Shahzad, M.B.; Shan, Y.Y.; Yang, K. Hot Deformation Behavior of an Ultra-High-Strength Fe-Ni-Co-Based Maraging Steel. Acta Metall. Sin. (Engl. Lett.) 2019, 32, 1161–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chakravarthi, K.V.A.; Koundinya, N.T.B.N.; Murty, S.V.S.N.; Rao, B.N. Microstructure, properties and hot workability of M300 grade maraging steel. Def. Technol. 2017, 14, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakravarthi, K.V.A.; Koundinya, N.T.B.N.; Murty, S.V.S.N.; Rao, B.N. Microstructural Evolution and Constitutive Relationship of M350 Grade Maraging Steel during Hot Deformation. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2016, 26, 1174–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Jeong, H.W.; Seo, S.M.; Yun, D.W.; Park, K.; Yim, K.H.; Yoo, Y.S. Influence of Segregation on Microstructure and Hot Workability of Grade 250 Maraging Steel. Metals Mater. Int. 2020, 27, 691–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.H.; Zhao, F.; Yan, Y.; Zhang, Z.L. Hot deformation behaviour of 18Ni maraging steel. Ordnance Mater. Sci. Eng. 2013, 36, 114–117. [Google Scholar]
- Han, S.; Wang, C.X.; Li, Y.; Lye, Z.Q.; Wan, W.Z.; Yang, C. Effect of forging ratio on microstructure and properties of 18Ni(250) maraging steel. Forg. Stamp. Technol. 2020, 45, 192–197. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, P.; Gu, C.Q. Elastic Energy Releasing Wave Stimulating the Nucleation Mechanism of Martensitic Transformation in the Austenite. J. Xi’an Univ. Technol. 2002, 18, 62–66. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Z.; Taku, S.; Yao, Z. Effect of Dynamically Recrystallized Austenite on Martensitic Transformation. Mater. Sci. Technol. 1997, 5, 124–128. [Google Scholar]
- Du, P.J.; Wu, D. Effect of prior austenite grain size on martensitic transformation in medium manganese steel. Heat Treat. Metals 2021, 46, 21–27. [Google Scholar]
- Morito, S.; Yoshida, H.; Maki, T.; Huang, X. Effect of block size on the strength of lath martensite in low carbon steels. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2005, 438, 237–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
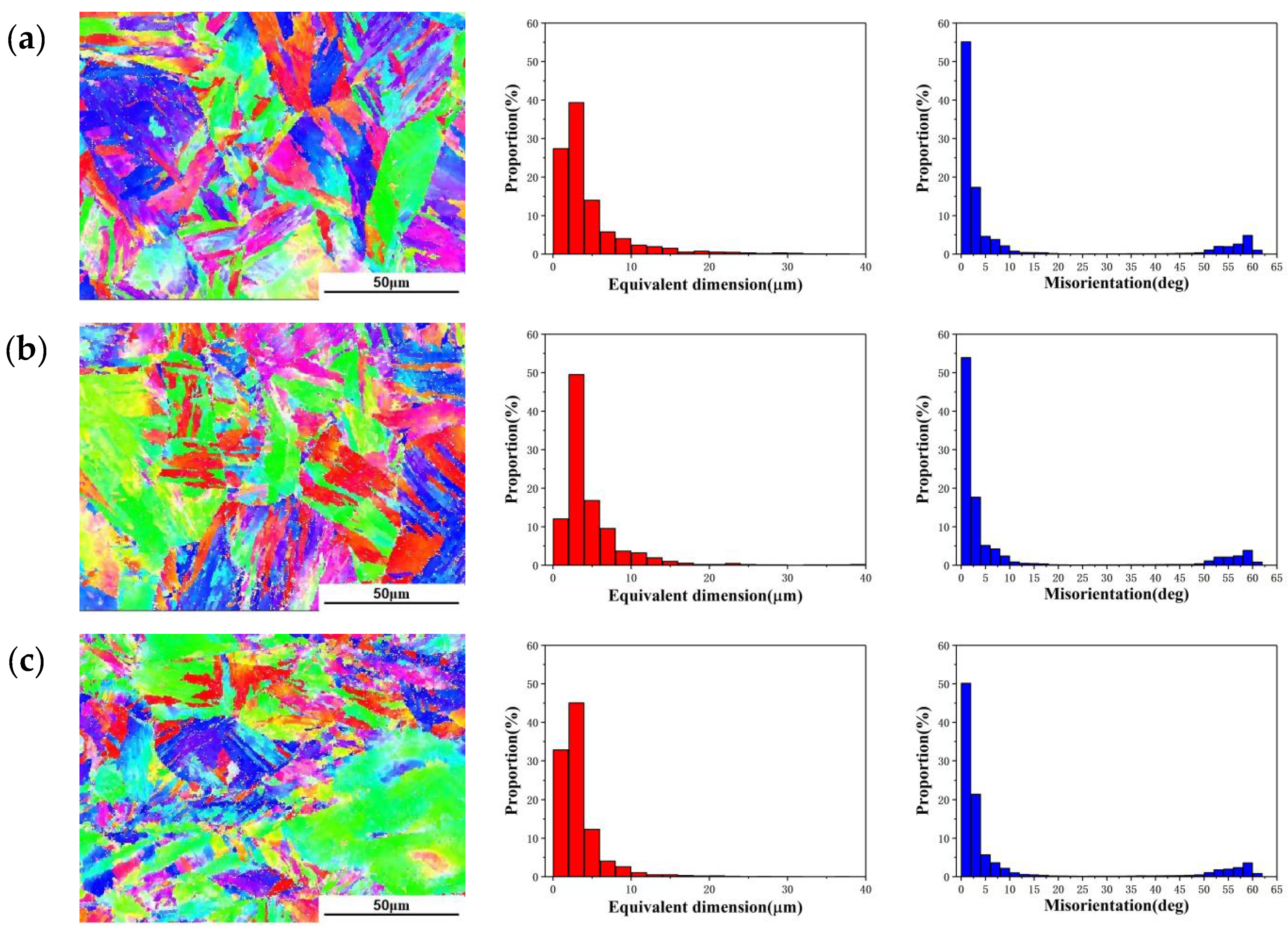
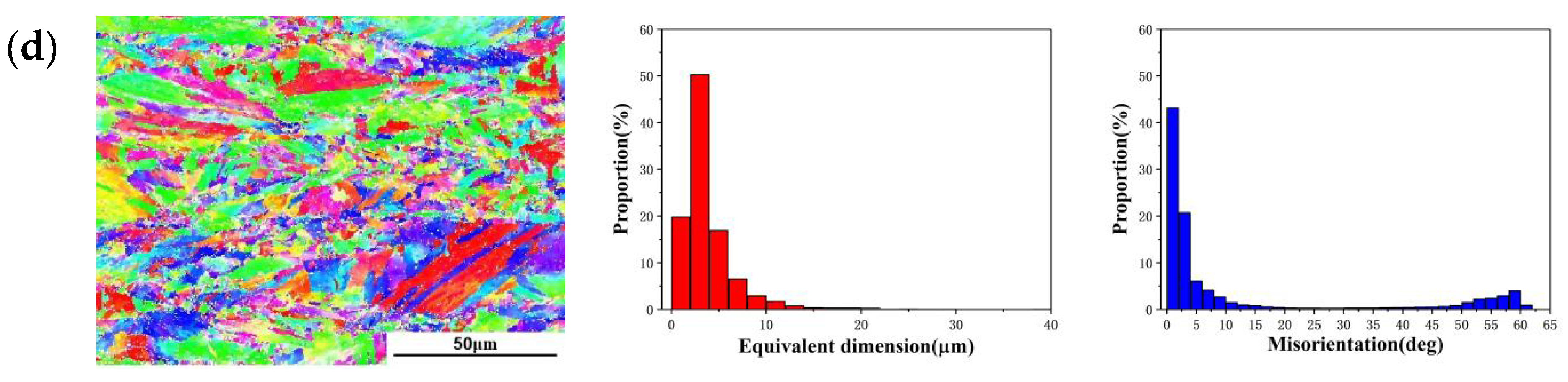
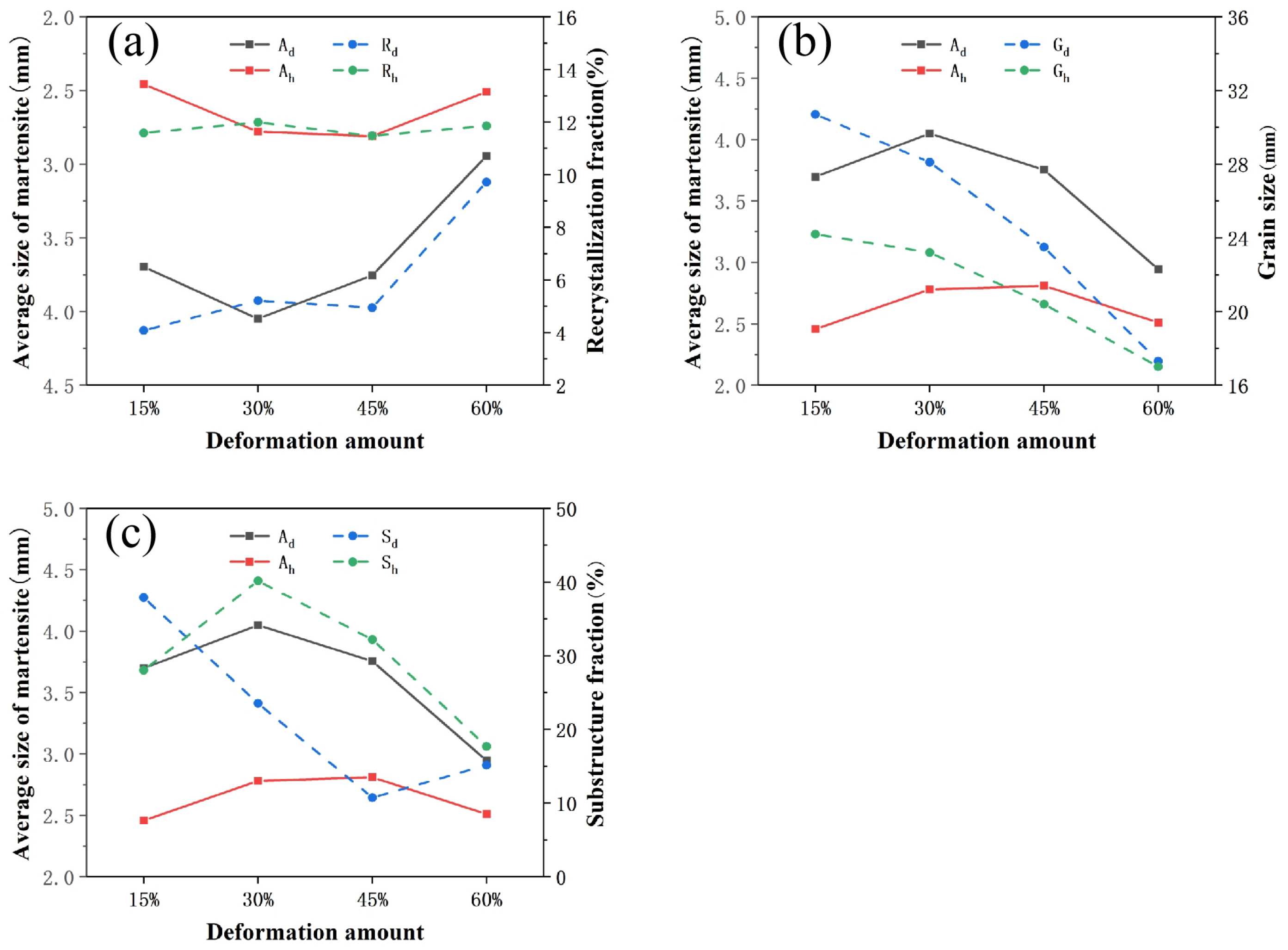

| Deformation Amount | The Grain Size | The Average Size of the Martensite Lath | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Deformation | Heat Treatment | Deformation | Heat Treatment | |
| 15% | 30.7 μm | 24.2 μm | 3.70 μm | 2.46 μm |
| 30% | 28.1 μm | 23.2 μm | 4.05 μm | 2.78 μm |
| 45% | 23.5 μm | 20.4 μm | 3.757 μm | 2.81 μm |
| 60% | 17.3 μm | 17.0 μm | 2.947 μm | 2.51 μm |
| No. | Deformation Amount | Rh/% | Sh/% | Gh/μm | Ah/μm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 15% | 11.5883 | 28.0148 | 30.7 | 2.46 |
| 2 | 30% | 11.9901 | 40.1456 | 28.1 | 2.78 |
| 3 | 45% | 11.4710 | 32.1939 | 23.5 | 2.81 |
| 4 | 60% | 11.8554 | 17.6714 | 17.3 | 2.51 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, S.; Yuan, L.; Xu, W.; Shan, D.; Guo, B. Effects of Forging and Heat Treatment on Martensite Lath, Recrystallization and Mechanical Properties Evolution of 18Ni(250) Maraging Steel. Materials 2022, 15, 4600. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15134600
Xu S, Yuan L, Xu W, Shan D, Guo B. Effects of Forging and Heat Treatment on Martensite Lath, Recrystallization and Mechanical Properties Evolution of 18Ni(250) Maraging Steel. Materials. 2022; 15(13):4600. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15134600
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Shucong, Lin Yuan, Wenchen Xu, Debin Shan, and Bin Guo. 2022. "Effects of Forging and Heat Treatment on Martensite Lath, Recrystallization and Mechanical Properties Evolution of 18Ni(250) Maraging Steel" Materials 15, no. 13: 4600. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15134600
APA StyleXu, S., Yuan, L., Xu, W., Shan, D., & Guo, B. (2022). Effects of Forging and Heat Treatment on Martensite Lath, Recrystallization and Mechanical Properties Evolution of 18Ni(250) Maraging Steel. Materials, 15(13), 4600. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15134600