AFM Characterization of Halloysite Clay Nanocomposites’ Superficial Properties: Current State-of-the-Art and Perspectives
Abstract
:1. Introduction
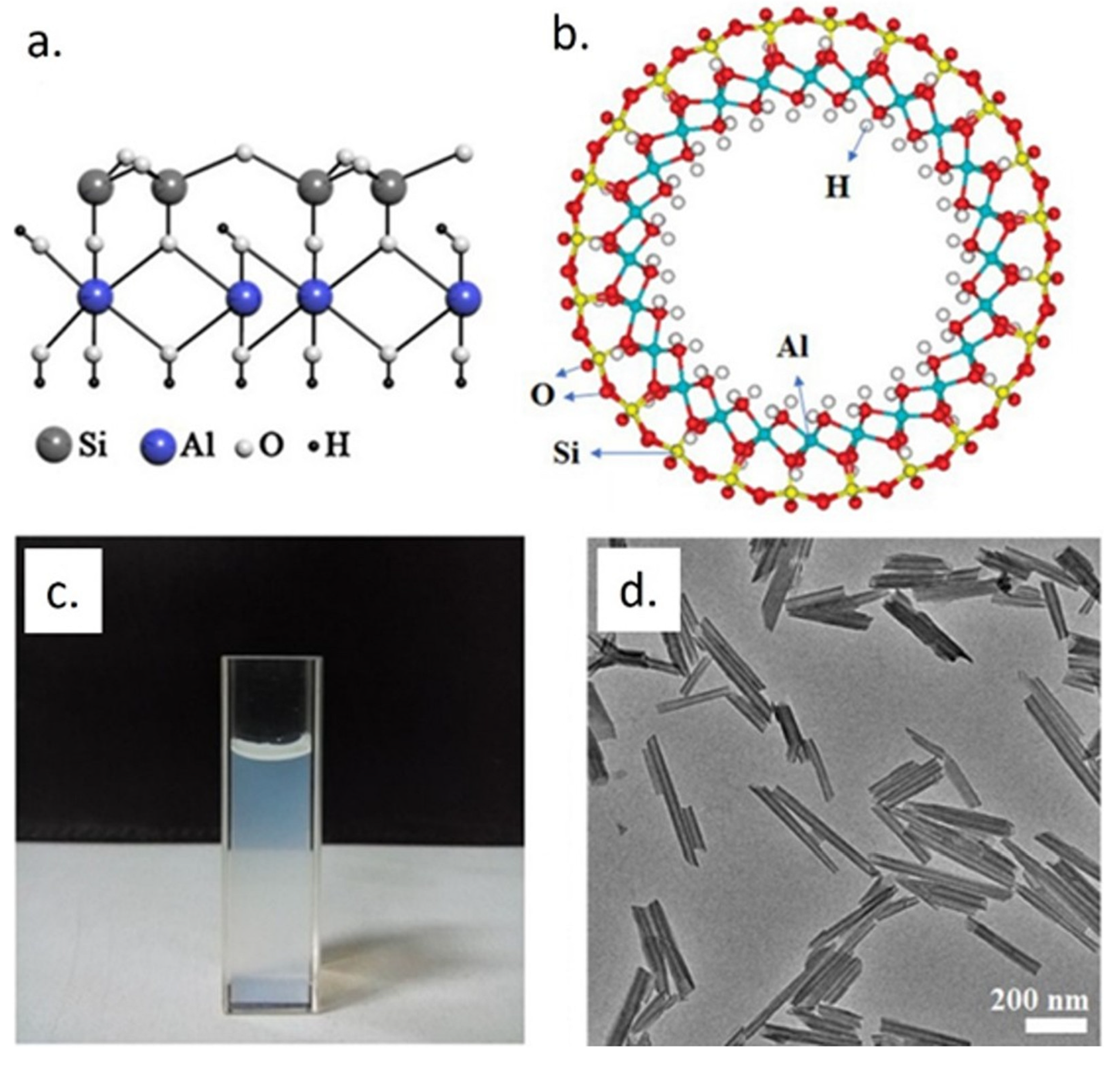
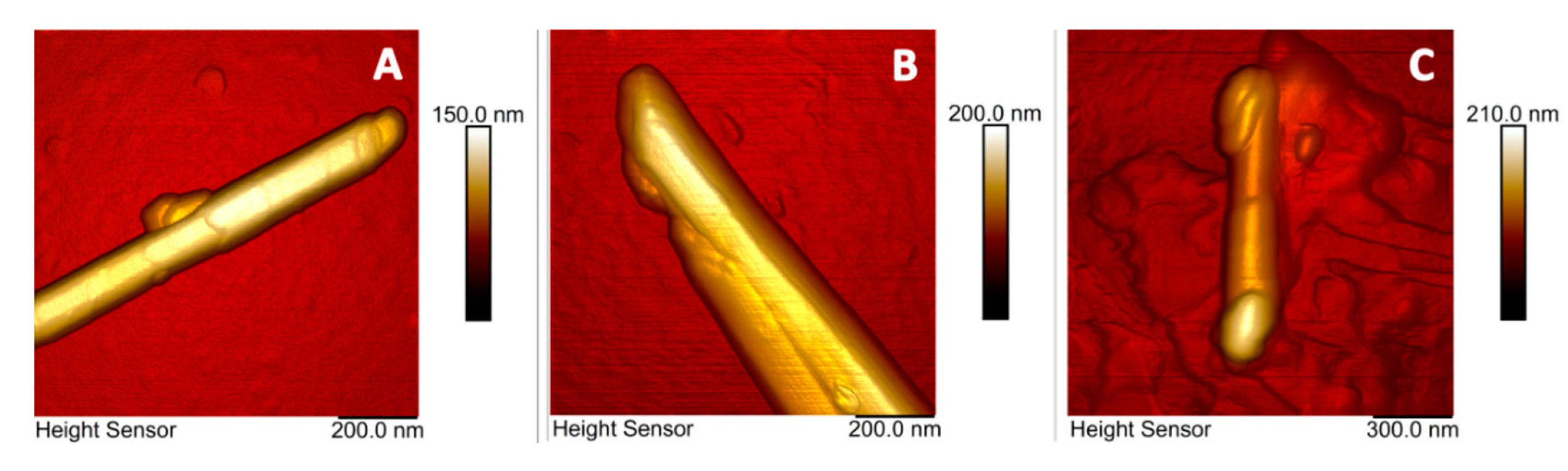
2. Halloysite Nanotubes (HNTs) and HNT Nanocomposites
3. AFM Investigations of HNT Nanocomposites
4. Conclusions and Outlook
5. Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Massaro, M.; Noto, R.; Riela, S. Past, Present and Future Perspectives on Halloysite Clay Minerals. Molecules 2020, 25, 4863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lvov, Y.; Abdullayev, E. Functional Polymer–Clay Nanotube Composites with Sustained Release of Chemical Agents. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2013, 38, 1690–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binnig, G.; Quate, C.F.; Gerber, C. Atomic Force Microscope. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1986, 56, 930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Meyer, G.; Amer, N.M. Novel Optical Approach to Atomic Force Microscopy. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1998, 53, 1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, R.; Pérez, R. Dynamic Atomic Force Microscopy Methods. Surf. Sci. Rep. 2002, 47, 197–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giessibl, F.J. Advances in Atomic Force Microscopy. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2003, 75, 949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stan, G.; King, S.W. Atomic Force Microscopy for Nanoscale Mechanical Property Characterization. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. B Nanotechnol. Microelectron. Mater. Process. Meas. Phenom. 2020, 38, 060801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, R.; Herruzo, E.T. The Emergence of Multifrequency Force Microscopy. Nat. Publ. Gr. 2012, 7, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morales-Rivas, L.; González-Orive, A.; Garcia-Mateo, C.; Hernández-Creus, A.; Caballero, F.G.; Vázquez, L. Nanomechanical Characterization of Nanostructured Bainitic Steel: Peak Force Microscopy and Nanoindentation with AFM. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 17164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leporatti, S. Halloysite Clay Nanotubes as Nano-Bazookas for Drug Delivery. Polym. Int. 2017, 66, 1111–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persano, F.; Batasheva, S.; Fakhrullina, G.; Gigli, G.; Leporatti, S.; Fakhrullin, R. Recent Advances in the Design of Inorganic and Nano-Clay Particles for the Treatment of Brain Disorders. J. Mater. Chem. B 2021, 9, 2756–2784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Persano, F.; Gigli, G.; Leporatti, S. Halloysite-Based Nanosystems for Biomedical Applications. Clays Clay Miner. 2021, 69, 501–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farzadnia, N.; Ali AA, A.; Demirboga, R.; Anwar, M.P. Effect of Halloysite Nanoclay on Mechanical Properties, Thermal Behavior and Microstructure of Cement Mortars. Cem. Concr. Res. 2013, 48, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bates, T.F.; Hildebrand, F.A.; Swineford, A. Morphology and Structure of Endellite and Halloysite. Am. Mineral. 1950, 35, 463–484. [Google Scholar]
- Lvov, Y.M.; Shchukin, D.G.; Möhwald, H.; Price, R.R. Halloysite Clay Nanotubes for Controlled Release of Protective Agents. ACS Nano 2008, 2, 814–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veerabadran, N.G.; Price, R.R.; Lvov, Y.M. Clay nanotubes for encapsulation and sustained release of drugs. Nano 2011, 2, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, S.; Fan, M. Silanization of Heat-Treated Halloysite Nanotubes Using γ-Aminopropyltriethoxysilane. Appl. Clay Sci. 2019, 180, 105204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, D.; Zhang, H.; Sun, S.; Dong, F.; Sun, H.; Li, B. Rapid Flocculation-Sedimentation of Microalgae with Organosilane-Functionalized Halloysite. Appl. Clay Sci. 2019, 177, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Bai, L.; Cheng, C.; Zhou, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, H. A Novel Surface Modification Method upon Halloysite Nanotubes: A Desirable Cross-Linking Agent to Construct Hydrogels. Appl. Clay Sci. 2019, 182, 105259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vergaro, V.; Abdullayev, E.; Lvov, Y.M.; Zeitoun, A.; Cingolani, R.; Rinaldi, R.; Leporatti, S. Cytocompatibility and Uptake of Halloysite Clay Nanotubes. Biomacromolecules 2010, 11, 820–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katana, B.; Takács, D.; Szerlauth, A.; Sáringer, S.; Varga, G.; Jamnik, A.; Bobbink, F.D.; Dyson, P.J.; Szilagyi, I. Aggregation of Halloysite Nanotubes in the Presence of Multivalent Ions and Ionic Liquids. Langmuir 2021, 37, 11869–11879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavallaro, G.; Milioto, S.; Lazzara, G. Halloysite Nanotubes: Interfacial Properties and Applications in Cultural Heritage. Langmuir 2020, 36, 3677–3689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.; Song, W.; Zhao, Q.; Zhang, H. Halloysite Nanotubes in Polymer Science: Purification, Characterization, Modification and Applications. Nanotechnol. Rev. 2020, 9, 323–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bediako, E.G.; Nyankson, E.; Dodoo-Arhin, D.; Agyei-Tuffour, B.; Łukowiec, D.; Tomiczek, B.; Yaya, A.; Efavi, J.K. Modified Halloysite Nanoclay as a Vehicle for Sustained Drug Delivery. Heliyon 2018, 4, e00689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cheng, C.; Gao, Y.; Song, W.; Zhao, Q.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, H. Halloysite Nanotube-Based H2O2-Responsive Drug Delivery System with a Turn on Effect on Fluorescence for Real-Time Monitoring. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 380, 122474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabbagh, N.; Akbari, A.; Arsalani, N.; Eftekhari-Sis, B.; Hamishekar, H. Halloysite-Based Hybrid Bionanocomposite Hydrogels as Potential Drug Delivery Systems. Appl. Clay Sci. 2017, 148, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, K.M.; Kumar, A.; Suneetha, M.; Han, S.S. PH and Near-Infrared Active; Chitosan-Coated Halloysite Nanotubes Loaded with Curcumin-Au Hybrid Nanoparticles for Cancer Drug Delivery. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 112, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharif, S.; Abbas, G.; Hanif, M.; Bernkop-Schnürch, A.; Jalil, A.; Yaqoob, M. Mucoadhesive Micro-Composites: Chitosan Coated Halloysite Nanotubes for Sustained Drug Delivery. Colloids Surf. B. 2019, 184, 110527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurczewska, J.; Cegłowski, M.; Messyasz, B.; Schroeder, G. Dendrimer-Functionalized Halloysite Nanotubes for Effective Drug Delivery. Appl. Clay Sci. 2018, 153, 134–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Liu, D.; Zhang, H.; Correia, A.; Mäkilä, E.; Salonen, J.; Hirvonen, J.; Santos, H.A. Microfluidic Assembly of a Nano-in-Micro Dual Drug Delivery Platform Composed of Halloysite Nanotubes and a PH-Responsive Polymer for Colon Cancer Therapy. Acta Biomater. 2017, 48, 238–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lvov, Y.M.; Price, R.R. Halloysite Nanotubules, a Novel Substrate for the Controlled Delivery of Bioactive Molecules. In Bio-inorganic Hybrid Nanomaterials: Strategies, Syntheses, Characterization and Applications; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2007; pp. 419–441. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, R.; Cao, X.; Shen, M.; Guo, R.; Yu, J.; Shi, X. Biocompatibility of Electrospun Halloysite Nanotube-Doped Poly(Lactic-Co-Glycolic Acid) Composite Nanofibers. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. 2012, 2012, 299–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, M.; Guo, B.; Jia, D. Newly Emerging Applications of Halloysite Nanotubes: A Review. Polym. Int. 2010, 59, 574–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.; Chen, H.; Wu, J.; Ye, L. High Impact Strength Epoxy Nanocomposites with Natural Nanotubes. Polymer 2007, 48, 6426–6433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danyliuk, N.; Tomaszewska, J.; Tatarchuk, T. Halloysite Nanotubes and Halloysite-Based Composites for Environmental and Biomedical Applications. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 309, 113077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Guo, B.; Du, M.; Jia, D. Drying Induced Aggregation of Halloysite Nanotubes in Polyvinyl Alcohol/Halloysite Nanotubes Solution and Its Effect on Properties of Composite Film. Appl. Phys. A 2007, 88, 391–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Guo, B.; Du, M.; Cai, X.; Jia, D. Properties of Halloysite Nanotube–Epoxy Resin Hybrids and the Interfacial Reactions in The. Nanotechnology 2007, 18, 455703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, B.; Zou, Q.; Lei, Y.; Du, M.; Liu, M.; Jia, D. Crystallization Behavior of Polyamide 6/Halloysite Nanotubes Nanocomposites. Thermochim. Acta 2009, 484, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Guo, B.; Zou, Q.; Du, M.; Jia, D. Interactions between Halloysite Nanotubes and 2,5-Bis(2-Benzoxazolyl) Thiophene and Their on Reinforcement of Polypropylene/Halloysite Nanocomposites. Nanotechnology 2008, 19, 205709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, M.; Guo, B.; Lei, Y.; Liu, M.; Jia, D. Carboxylated Butadiene–Styrene Rubber/Halloysite Nanotube Nanocomposites: Interfacial Interaction and Performance. Polymer 2008, 49, 4871–4876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Jia, Z.; Jia, D.; Zhou, C. Recent Advance in Research on Halloysite Nanotubes-Polymer Nanocomposite. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2014, 39, 1498–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Wang, F.; Lv, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhang, D.; Shao, Z. Halloysite Nanotubes and Fe3O4 Nanoparticles Enhanced Adsorption Removal of Heavy Metal Using Electrospun Membranes. Appl. Clay Sci. 2018, 161, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Xu, H.; Tan, D.; Fang, Y.; Roden, E.E.; Wan, Q. Adsorption of Iodate on Nanosized Tubular Halloysite. Appl. Clay Sci. 2020, 184, 105407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kausar, A.; Iqbal, M.; Javed, A.; Aftab, K.; Nazli, Z.i.H.; Bhatti, H.N.; Nouren, S. Dyes Adsorption Using Clay and Modified Clay: A Review. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 256, 395–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramadass, K.; Singh, G.; Lakhi, K.S.; Benzigar, M.R.; Yang, J.H.; Kim, S.; Almajid, A.M.; Belperio, T.; Vinu, A. Halloysite Nanotubes: Novel and Eco-Friendly Adsorbents for High-Pressure CO2 Capture. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2019, 277, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, W.; Wang, N.; Xiao, W.; Zhao, Y.; Zheng, Y. Ciprofloxacin Adsorption onto Different Micro-Structured Tourmaline, Halloysite and Biotite. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 269, 874–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandebriel, R.J.; De Jong, W.H. NSA-23932-a-Review-on-Mammalian-Toxicity-of-Zno-Nanoparticles. Sci. Appl. 2012, 5, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deng, L.; Yuan, P.; Liu, D.; Du, P.; Zhou, J.; Wei, Y.; Song, Y.; Liu, Y. Effects of Calcination and Acid Treatment on Improving Benzene Adsorption Performance of Halloysite. Appl. Clay Sci. 2019, 181, 105240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szczepanik, B.; Słomkiewicz, P.; Garnuszek, M.; Czech, K. Adsorption of Chloroanilines from Aqueous Solutions on the Modified Halloysite. Appl. Clay Sci. 2014, 101, 260–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, K.; Duan, Y.; Wang, F.; Gao, P.; Jia, H.; Ma, C.; Wang, C. Silane-Modified Halloysite/Fe3O4 Nanocomposites: Simultaneous Removal of Cr(VI) and Sb(V) and Positive Effects of Cr(VI) on Sb(V) Adsorption. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 311, 236–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Yuan, P.; Du, P.; Deng, L.; Wei, Y.; Liu, D.; Zhong, X.; Zhou, J. A Novel Halloysite–CeOx Nanohybrid for Efficient Arsenic Removal. Appl. Clay Sci. 2020, 186, 105450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, N.Y.; Yin, Q.J.; Luo, F.; Zhang, Q.; Du, R.; Fu, Q. Crystallization Behavior and Mechanical Properties of Polypropylene/Halloysite Composites. Polymer 2007, 48, 7374–7384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, T.; Jin, K.; Torkelson, J.M. Isolating the Effect of Polymer-Grafted Nanoparticle Interactions with Matrix Polymer from Dispersion on Composite Property Enhancement: The Example of Polypropylene/Halloysite Nanocomposites. Polymer 2019, 176, 38–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buruga, K.; Kalathi, J.T. A Facile Synthesis of Halloysite Nanotubes Based Polymer Nanocomposites for Glass Coating Application. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 735, 1807–1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Yan, F.; Pei, H.; Yan, K.; Cui, Z.; He, B.; Fang, K.; Li, J. Environmentally-Friendly Halloysite Nanotubes@chitosan/Polyvinyl Alcohol/Non-Woven Fabric Hybrid Membranes with a Uniform Hierarchical Porous Structure for Air Filtration. J. Memb. Sci. 2020, 594, 117445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, C.; Xiong, S.; Zhou, C. Chitosan/Halloysite Nanotubes Bionanocomposites: Structure, Mechanical Properties and Biocompatibility. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2012, 51, 566–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Dai, L.; Shi, H.; Xiong, S.; Zhou, C. In Vitro Evaluation of Alginate/Halloysite Nanotube Composite Scaffolds for Tissue Engineering. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2015, 49, 700–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, Z.W.; Dong, Y.; Han, N.; Liu, S. Water and Gas Barrier Properties of Polyvinyl Alcohol (PVA)/Starch (ST)/Glycerol (GL)/Halloysite Nanotube (HNT) Bionanocomposite Films: Experimental Characterisation and Modelling Approach. Compos. Part. B Eng. 2019, 174, 107033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouser, S.; Prabhu, A.; Prashantha, K.; Nagaraja, G.K.; D’souza, J.N.; Meghana Navada, K.; Qurashi, A.; Manasa, D.J. Modified Halloysite Nanotubes with Chitosan Incorporated PVA/PVP Bionanocomposite Films: Thermal, Mechanical Properties and Biocompatibility for Tissue Engineering. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2022, 634, 127941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatami, M.; Panah, M.Y.; Mahmoudian, M. Facile Production of HNTs\PDA\PF Nanocomposites by Unique and Environment-Friendly Method for the Removal of Phenolic Pollutants in Water as an Environmental Adsorbent. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2020, 108, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamal, N.; Ahzi, S.; Kochkodan, V. Polysulfone/Halloysite Composite Membranes with Low Fouling Properties and Enhanced Compaction Resistance. Appl. Clay Sci. 2020, 199, 105873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavallaro, G.; Milioto, S.; Konnova, S.; Fakhrullina, G.; Akhatova, F.; Lazzara, G.; Fakhrullin, R.; Lvov, Y. Halloysite/Keratin Nanocomposite for Human Hair Photoprotection Coating. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 24348–24362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batasheva, S.; Kryuchkova, M.; Fakhrullin, R.; Cavallaro, G.; Lazzara, G.; Akhatova, F.; Nigamatzyanova, L.; Evtugyn, V.; Rozhina, E.; Fakhrullin, R. Facile Fabrication of Natural Polyelectrolyte-Nanoclay Composites: Halloysite Nanotubes, Nucleotides and DNA Study. Molecules 2020, 25, 3557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cascione, M.; De Matteis, V.; Pellegrino, P.; Albanese, G.; De Giorgi, M.L.; Paladini, F.; Corsalini, M.; Rinaldi, R. Improvement of PMMA Dental Matrix Performance by Addition of Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles and Clay Nanotubes. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 2027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, X.; Nguyen, T.A.; Suo, Z.; Liu, Y.; Avci, R. Effect of Nanoparticles on the Anticorrosion and Mechanical Properties of Epoxy Coating. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2009, 204, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mozia, S.; Grylewicz, A.; Zgrzebnicki, M.; Darowna, D.; Czyzewski, A. Investigations on the Properties and Performance of Mixed-Matrix Polyethersulfone Membranes Modified with Halloysite Nanotubes. Polymer 2019, 11, 671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, R.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, X.; Cai, Y.; Li, Y.; Han, Q.; Zhang, T. A Modified, Mussel-Inspired Method to Fabricate Polyvinylidene Fluoride Membranes Filled with Halloysite Nanotubes Modified with Dopamine, Iron Oxide, and Silane for Oil–Water Separation. J. Plast. Film. Sheeting 2018, 35, 260–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, L.; Li, X.; Wang, Y.; Fu, H.; Li, Y. Effects of Surface Structure and Morphology of Nanoclays on the Properties of Jatropha Curcas Oil-Based Waterborne Polyurethane/Clay Nanocomposites. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2016, 55, 11689–11699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaaz, T.S.; Kadhum, A.A.H.; Michael, P.K.A.; Al-Amiery, A.A.; Sulong, A.B.; Nassir, M.H.; Jaaz, A.H. Unique Halloysite Nanotubes–Polyvinyl Alcohol–Polyvinylpyrrolidone Composite Complemented with Physico–Chemical Characterization. Polymers 2017, 9, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, X.; Kang, H.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, W.; Li, J.; Zhang, S. Simultaneously Toughening and Strengthening Soy Protein Isolate-Based Composites via Carboxymethylated Chitosan and Halloysite Nanotube Hybridization. Materials 2017, 10, 653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Naumenko, E.A.; Guryanov, I.D.; Yendluri, R.; Lvov, Y.M.; Fakhrullin, R.F. Clay Nanotube–Biopolymer Composite Scaffolds for Tissue Engineering. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 7257–7271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hia, I.L.; Lam, W.H.; Chai, S.P.; Chan, E.S.; Pasbakhsh, P. Surface Modified Alginate Multicore Microcapsules and Their Application in Self-Healing Epoxy Coatings for Metallic Protection. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2018, 215, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| HNT-Based Composite | AFM Modes | AFM Type | Limitations | Advantages | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chitosan/HNTs Bionanocomposites | Contact mode | Multimode Nanoscope IIIA (Bruker®, Billerica, MA, USA) | Bio nano composites Deformation upon Scanning | Analysis of Composites Roughness and Mechanical Properties | Liu et al., 2012 [56] |
| Alginate/(HNTs) composite scaffolds | Contact mode | Multimode Nanoscope IIIA (Bruker®) | Composites Deformation upon Scanning | Analysis of Topography, Surface Roughness, and Interaction Properties | Liu et al., 2015 [57] |
| Polyvinyl Alcohol (PVA)/Starch (ST)/Glycerol (GL)/HNTs Bionanocomposite Films | Tapping mode | Dimension Fast Scan (Bruker®); | Composites Aggregation | Inspection of HNTs Aspect Ratio correlated to Composites Permeability Model | Abdullah et al., 2019 [58] |
| PVA/PVP/HNTs Bionanocomposite Films | Tapping mode | FLEX-AXIOM AFM (Nano surf® Easy Scan 2, Lisstaal, Switzerland); | Bio composites dispersion aggregation | Investigation of Mechanical, Roughness and Thermal Properties | Kouser et al., 2022 [59] |
| NTs/PDA/PF Nanocomposites | Tapping Mode | Multimode Compact Frame (Bruker®); | Nanocomposite aggregation | Analysis of Nano Topography and Roughness | Hatami et al., 2020 [60] |
| Polysulfone/HNTs | Tapping QNM | Dimension Icon (Bruker®); | Sample Porosity | Inspection of Adhesion, Roughness, and HNTs Distribution in the Matrix | Kamal et al., 2020 [61] |
| Keratin/HNTs | Tapping QNM | Dimension Icon (Bruker®); | HNT Stability/Adhesion during Scanning | Investigation of Mechanical, and Adhesive Properties | Cavallaro et al., 2020 [62] |
| Mg, and Mg-DNA HNTs | Tapping QNM | Dimension Icon (Bruker®); | HNTs-DNA binding in the Lumen vs. Exterior Surface Undetectable | Analysis of Surface Adhesive and Mechanical Properties | Batasheva et al., 2020 [63] |
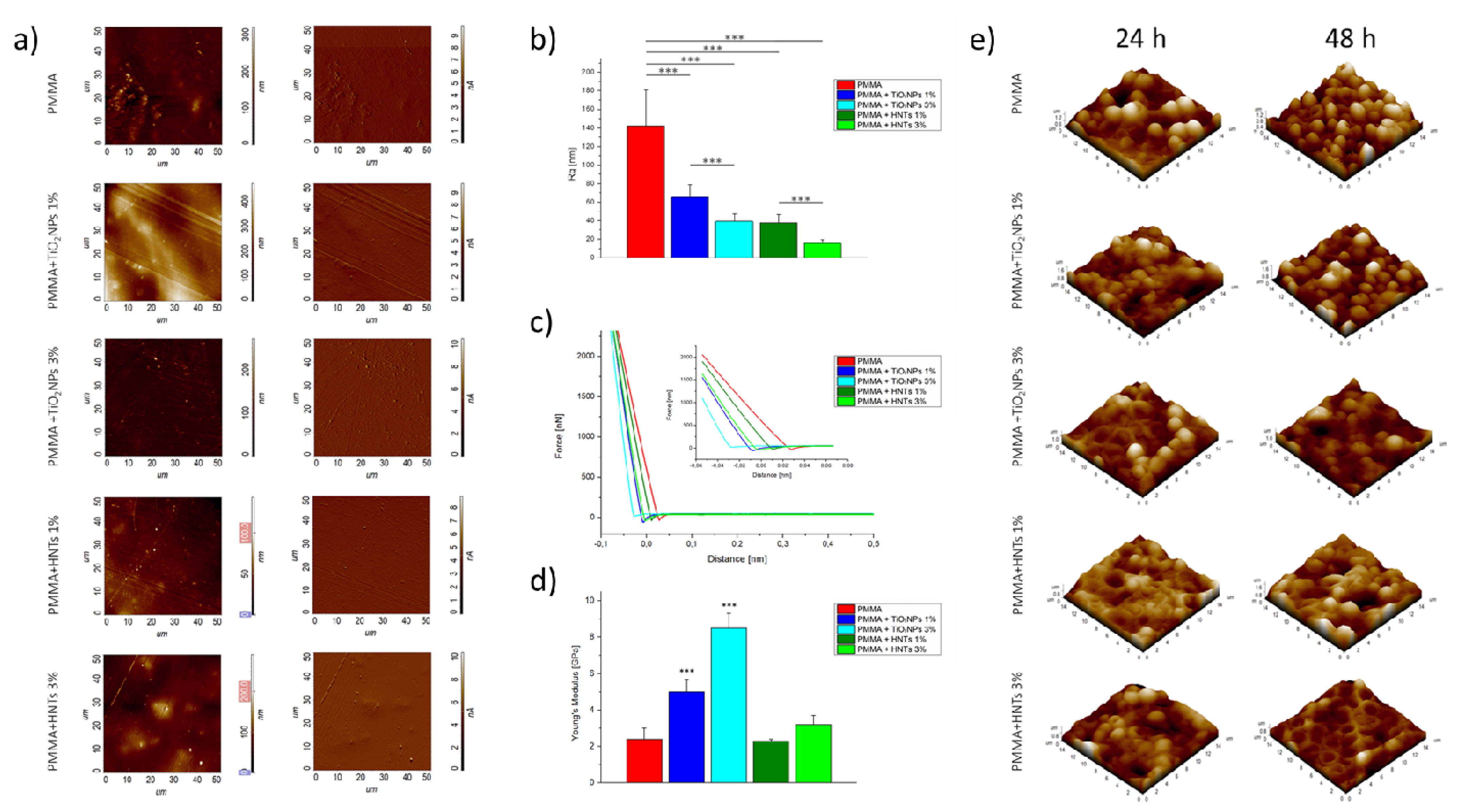
| PMMA/HNTs | Semi Contact Mode | AFM INTEGRA (NT-MDT® Spectrum Instr., Moscow, Russia) | HNTs -PMMA Adhesion/Coating | Analysis of Surface Topography, and quantification of Roughness and Young Modulus | Cascione et al., 2021 [64] |
| Epoxy/HNTs | Force vs. Distance Curves | Multimode Nanoscope IIIA (Bruker®); | Corrosion Resistance and Adhesion | Investigation of Mechanical Properties | Shi et al., 2009 [65] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cascione, M.; De Matteis, V.; Persano, F.; Leporatti, S. AFM Characterization of Halloysite Clay Nanocomposites’ Superficial Properties: Current State-of-the-Art and Perspectives. Materials 2022, 15, 3441. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15103441
Cascione M, De Matteis V, Persano F, Leporatti S. AFM Characterization of Halloysite Clay Nanocomposites’ Superficial Properties: Current State-of-the-Art and Perspectives. Materials. 2022; 15(10):3441. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15103441
Chicago/Turabian StyleCascione, Mariafrancesca, Valeria De Matteis, Francesca Persano, and Stefano Leporatti. 2022. "AFM Characterization of Halloysite Clay Nanocomposites’ Superficial Properties: Current State-of-the-Art and Perspectives" Materials 15, no. 10: 3441. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15103441
APA StyleCascione, M., De Matteis, V., Persano, F., & Leporatti, S. (2022). AFM Characterization of Halloysite Clay Nanocomposites’ Superficial Properties: Current State-of-the-Art and Perspectives. Materials, 15(10), 3441. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15103441









