Effects of SiC Fibers and Laminated Structure on Mechanical Properties of Ti–Al Laminated Composites
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Procedures
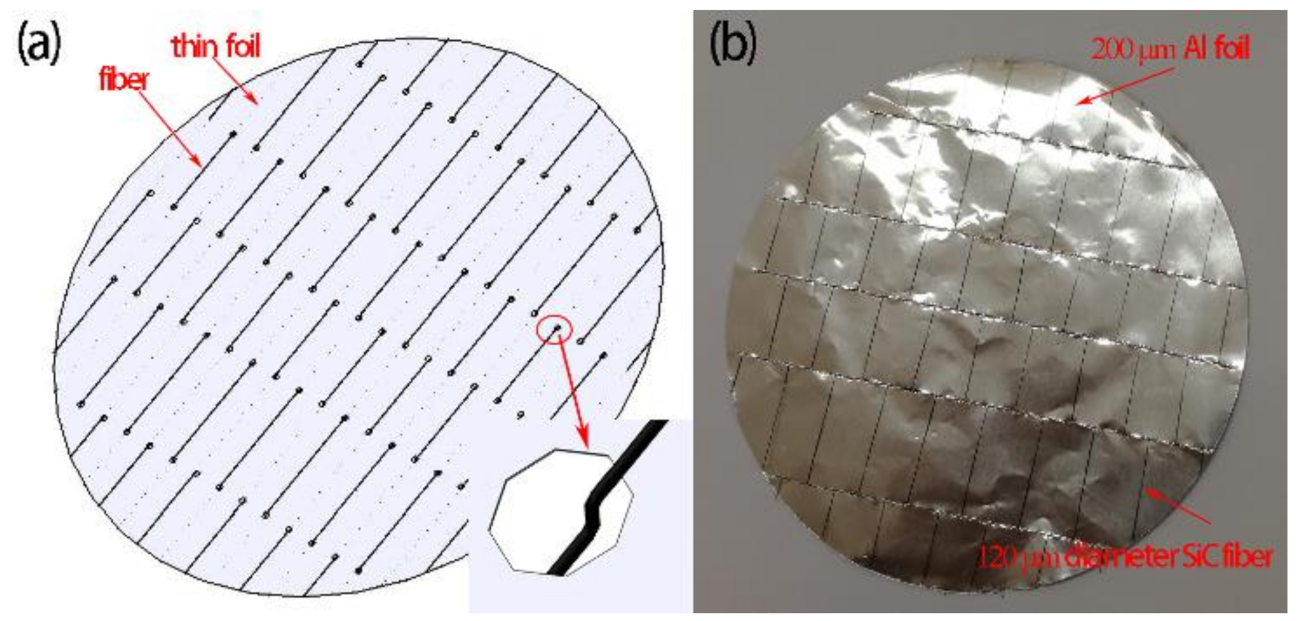
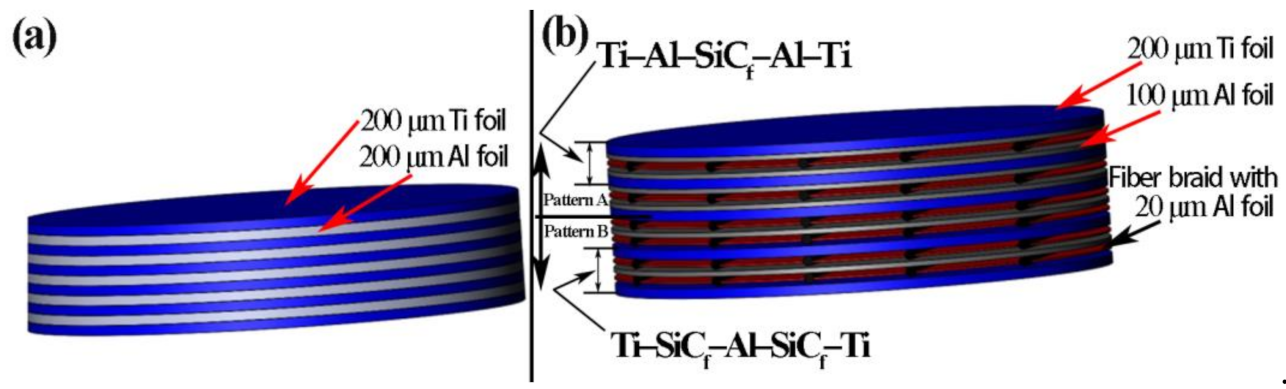
2.1. Structure Design
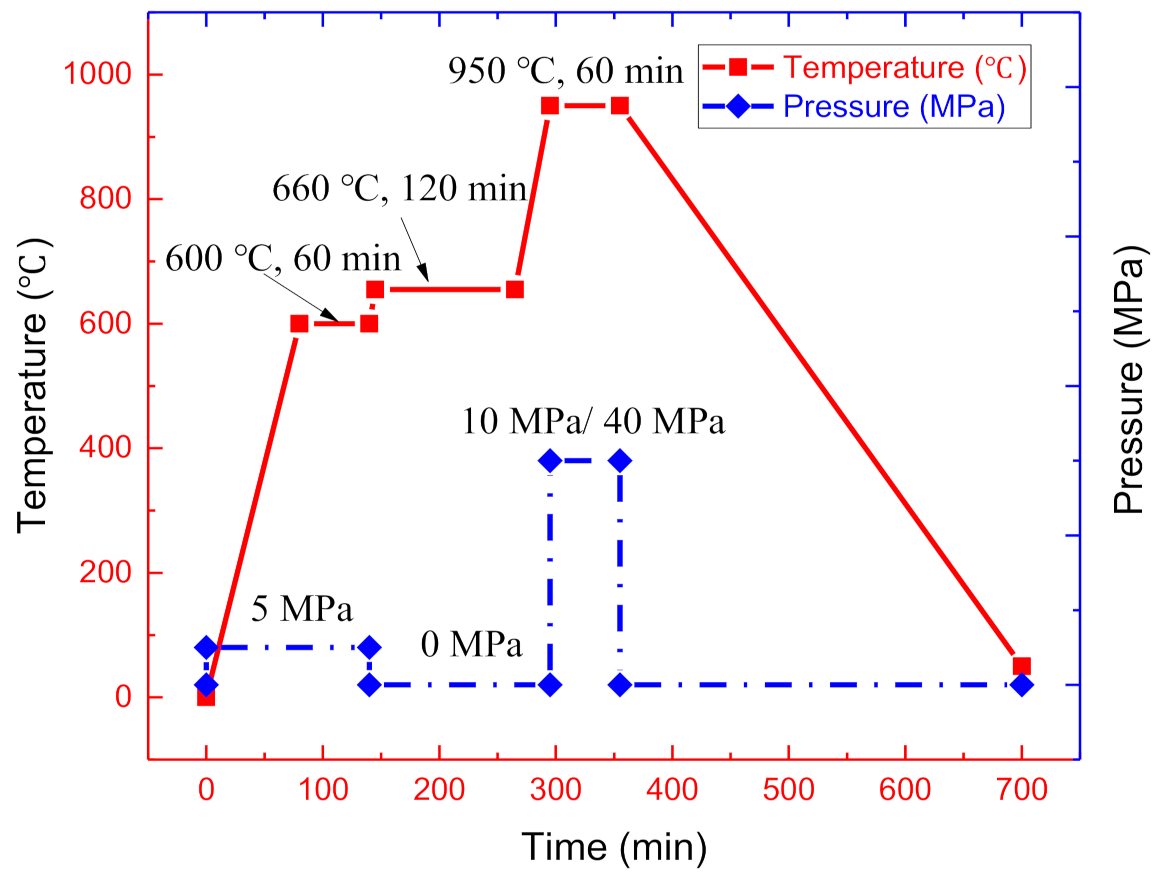
2.2. Sintering Process
2.3. Materials Characterization
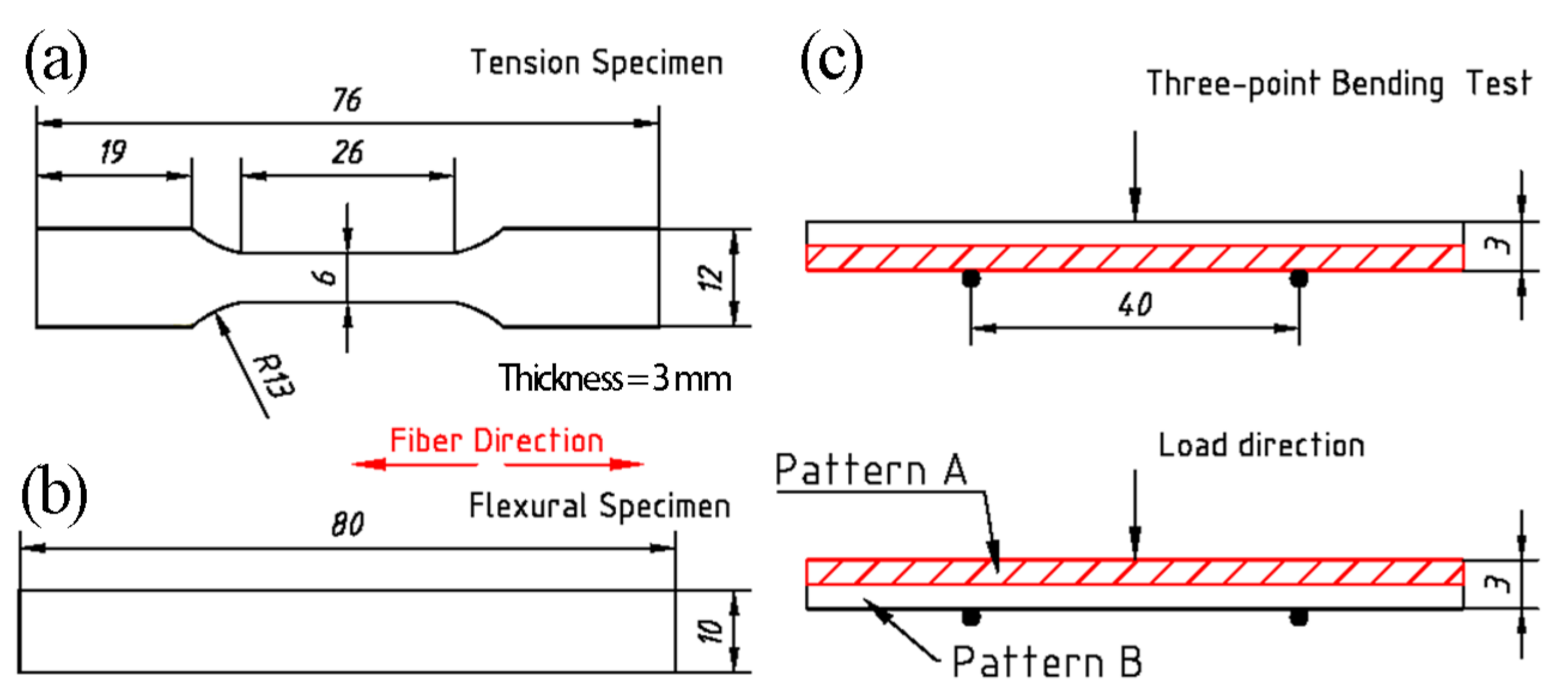
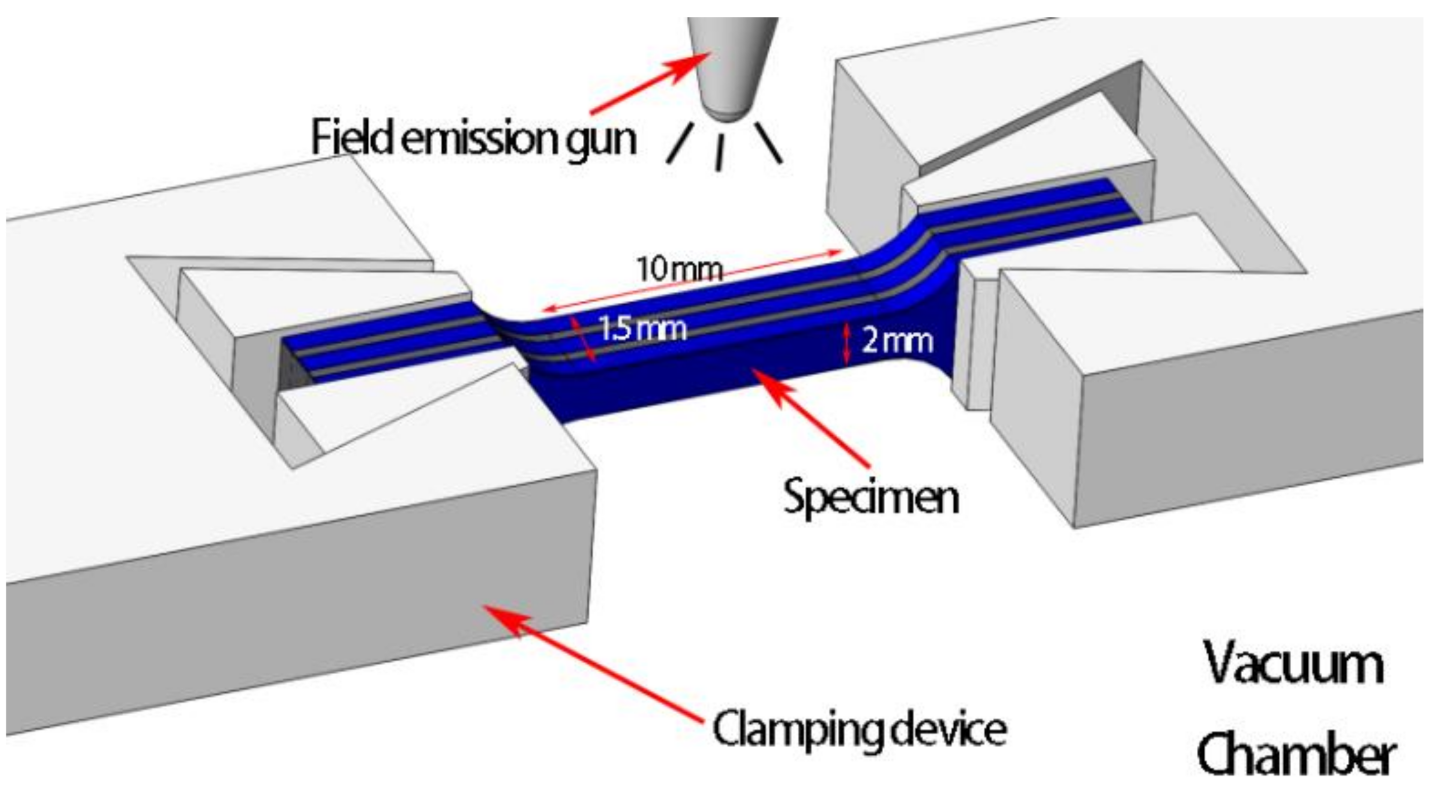
2.4. Mechanical Properties Measurements
3. Results and Discussion
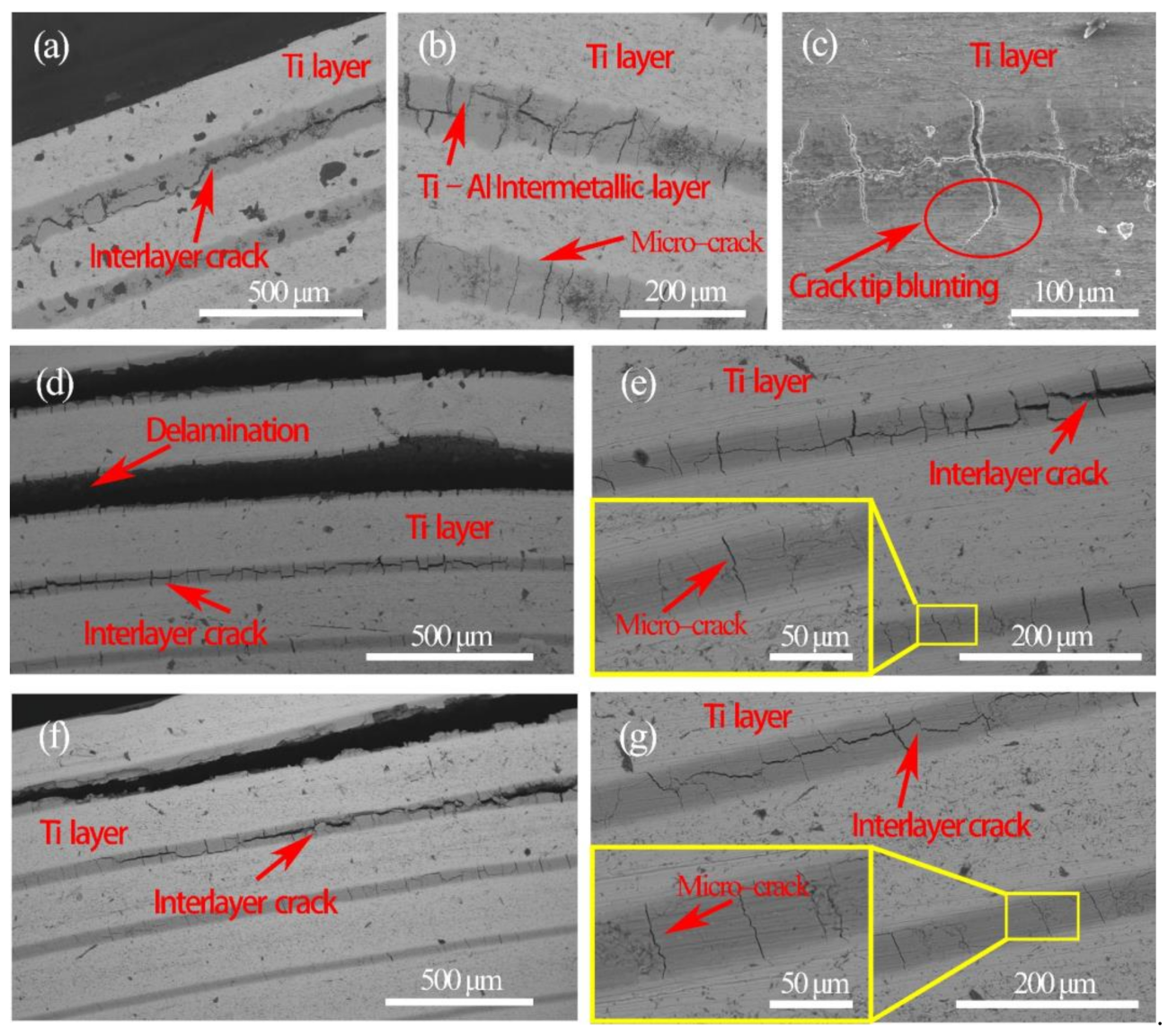
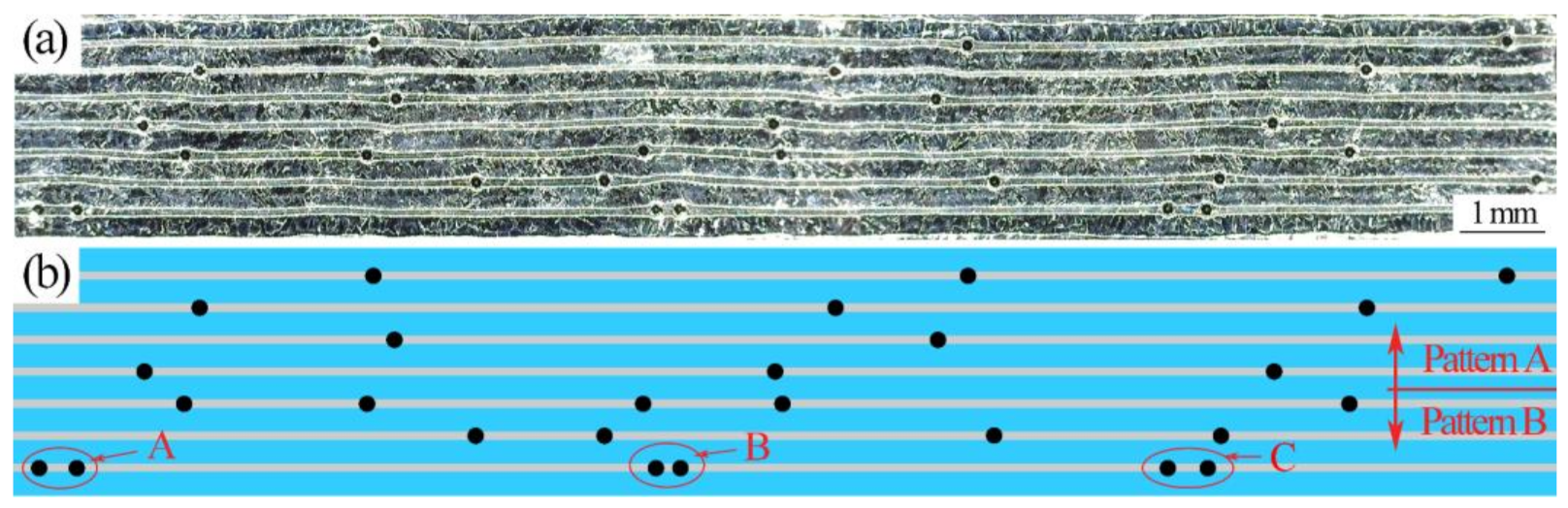
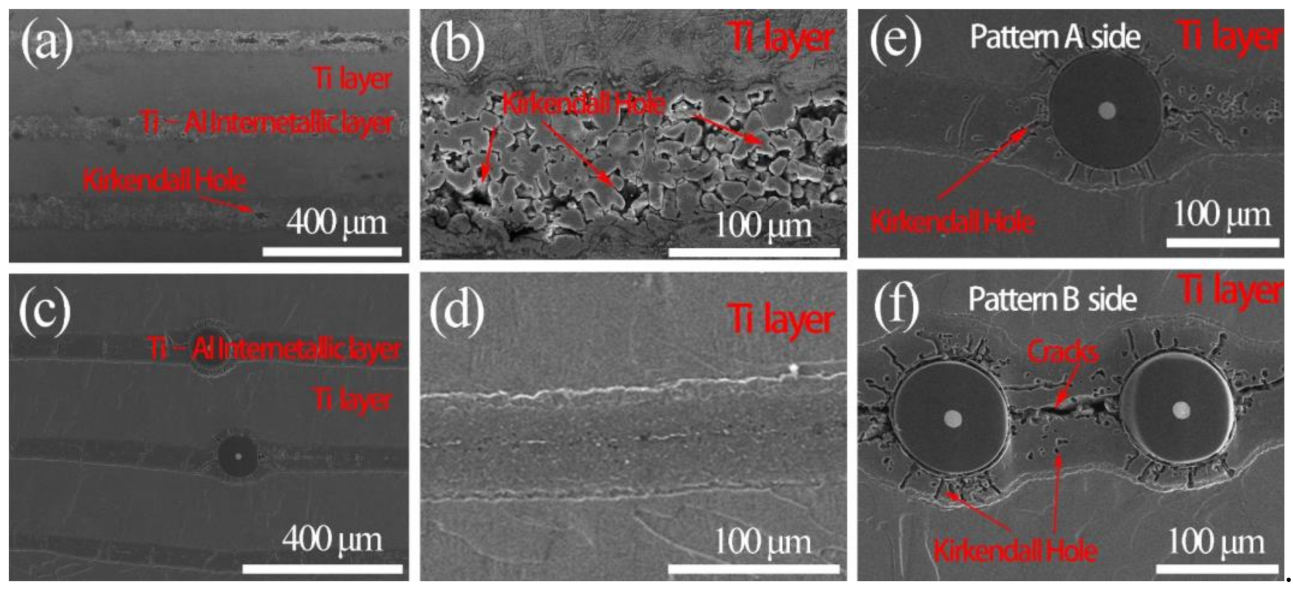
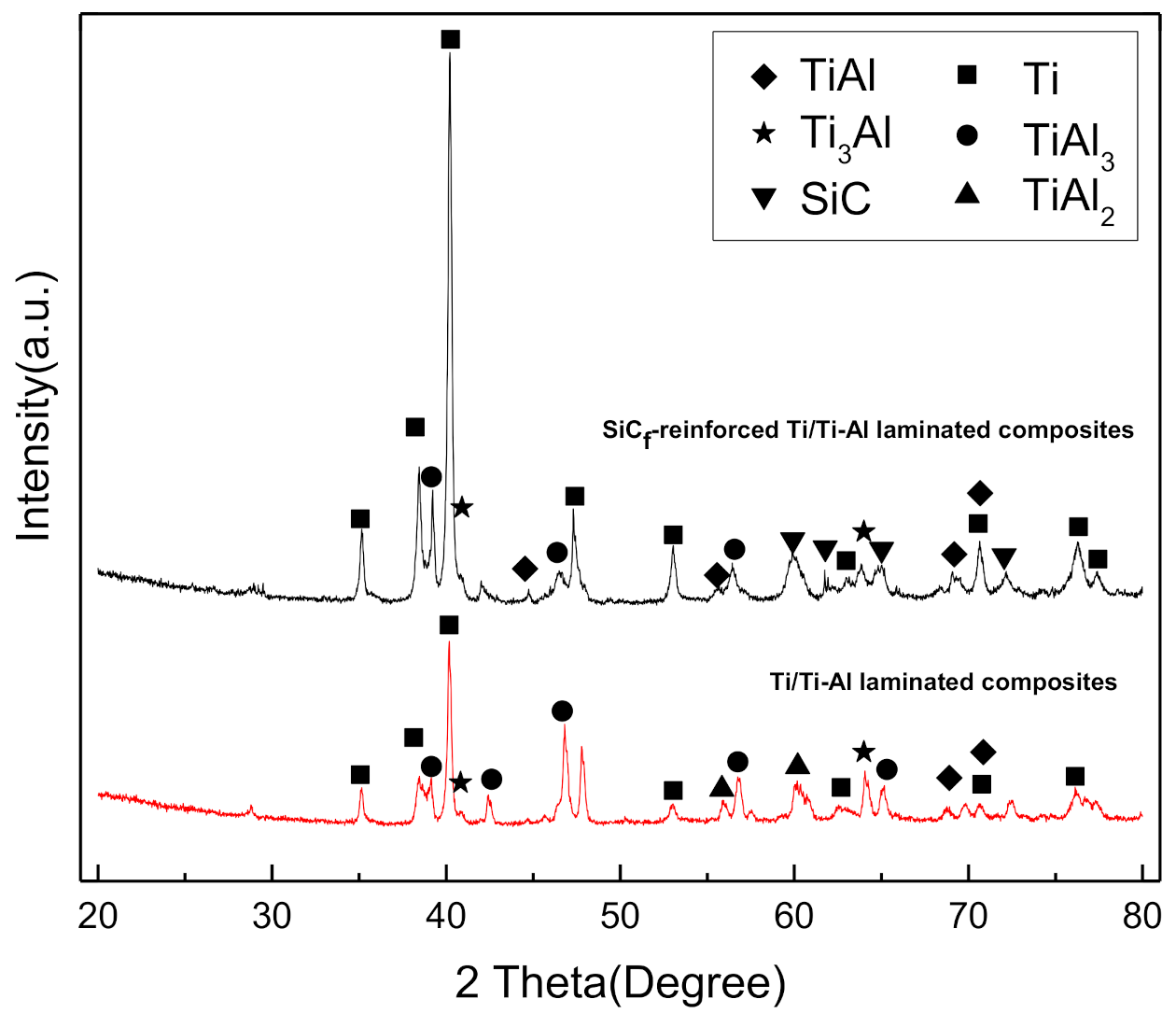
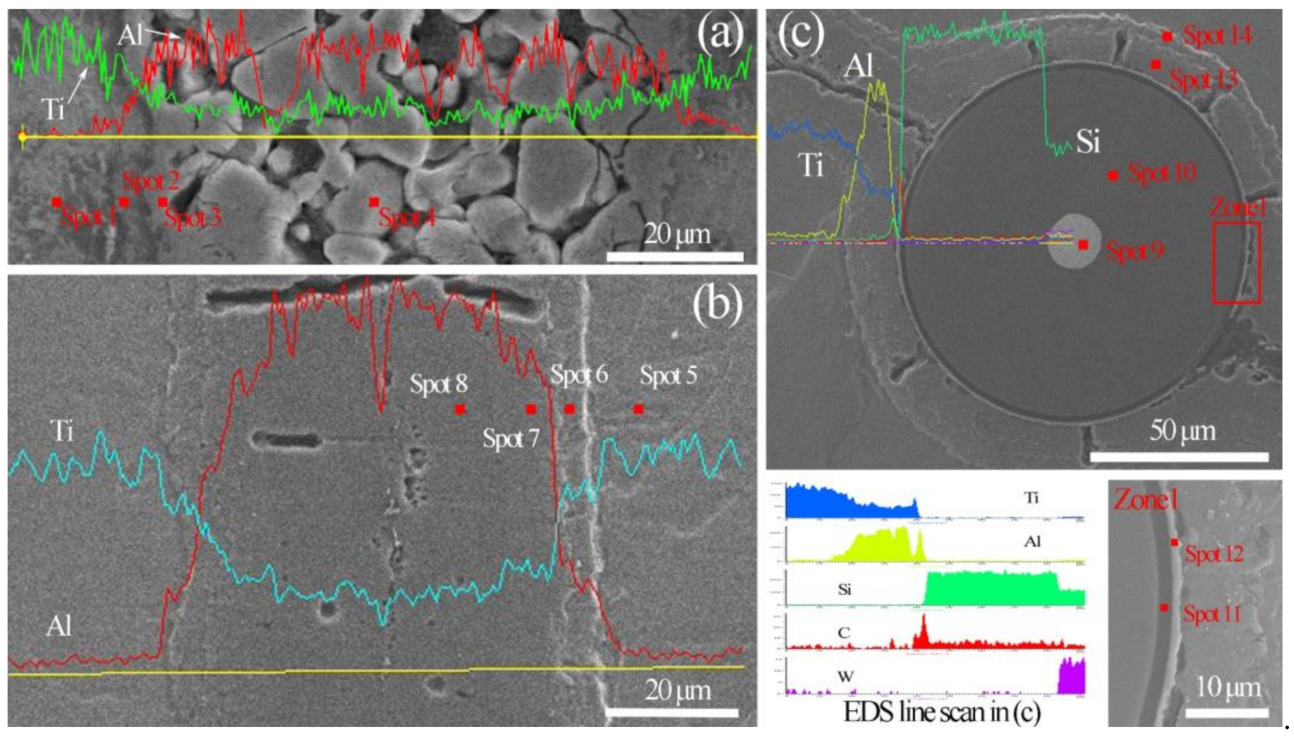
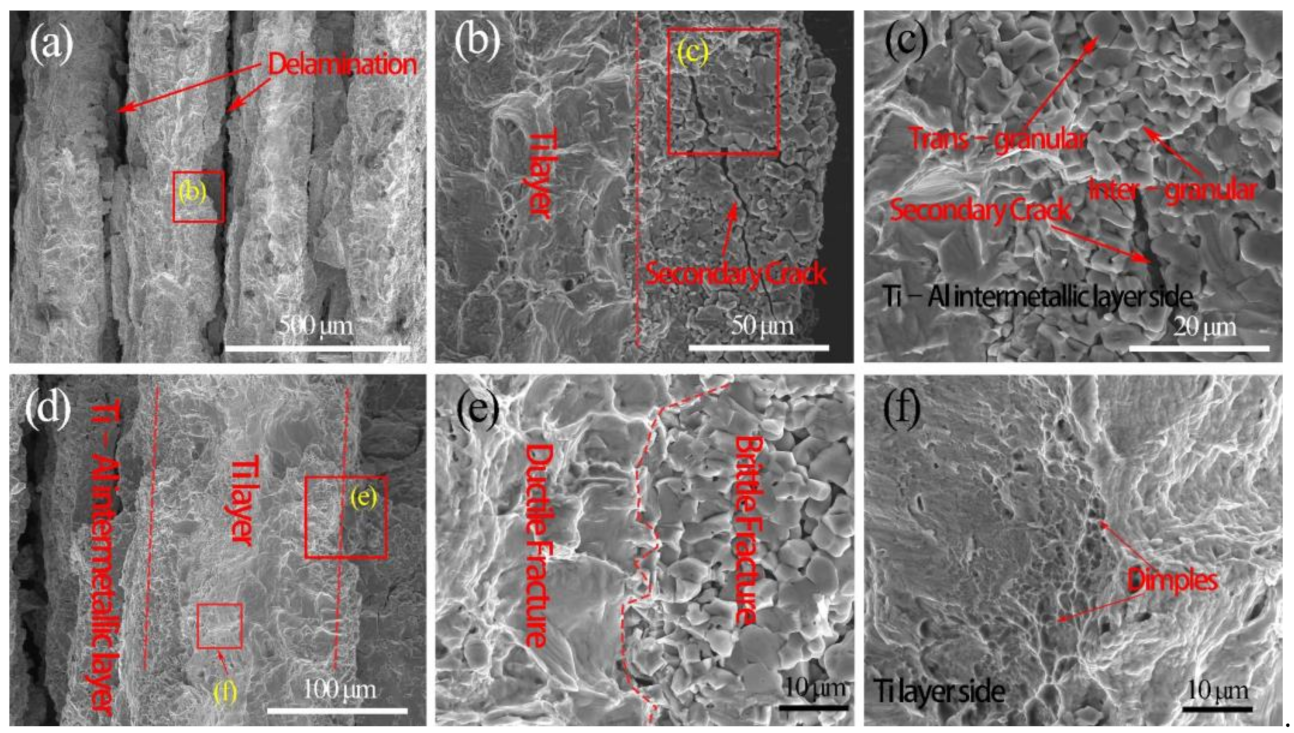
3.1. Microstructure Characterization
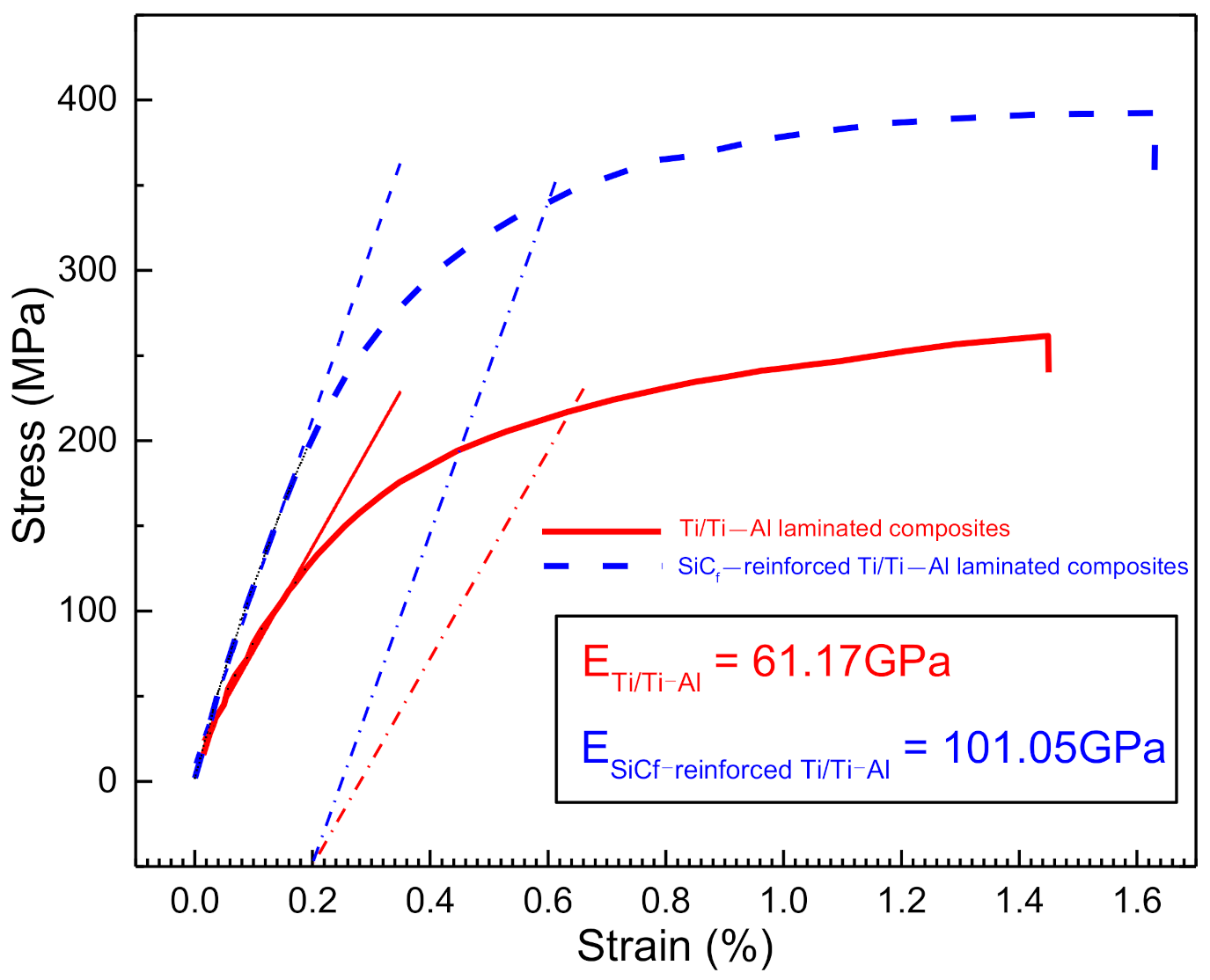
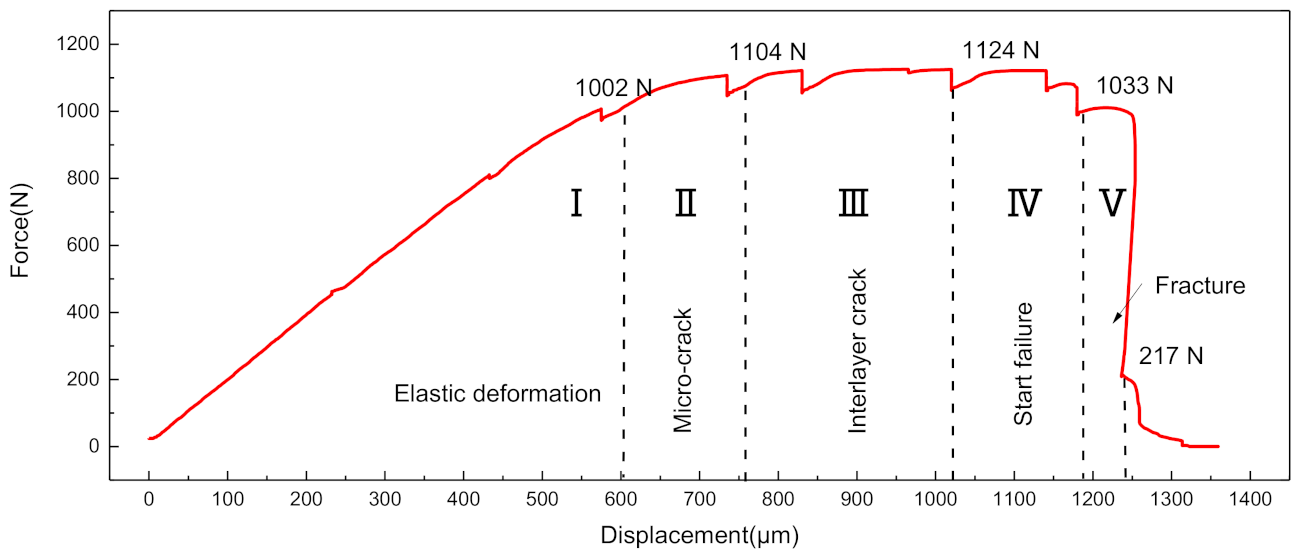
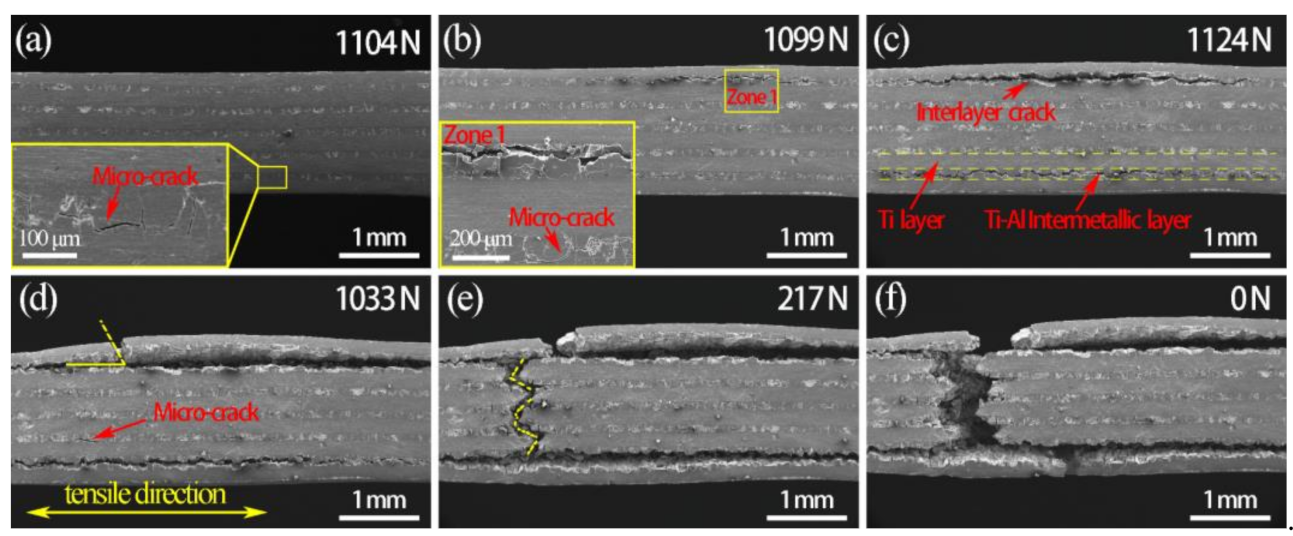
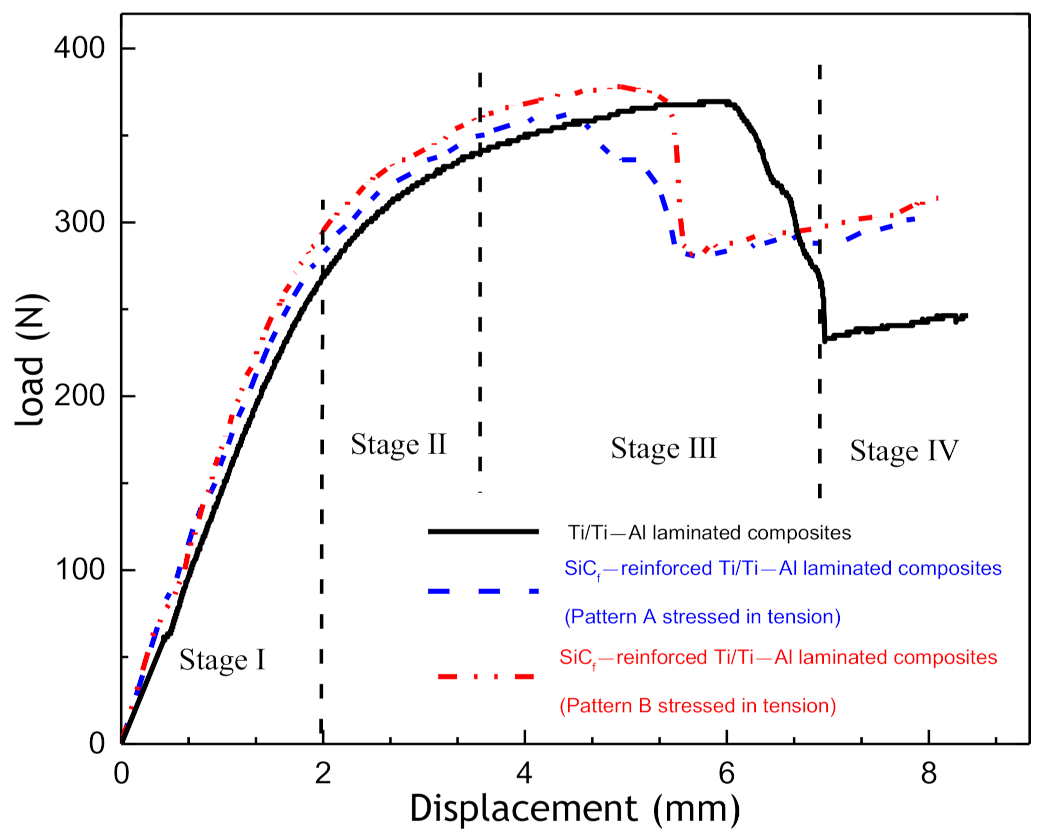
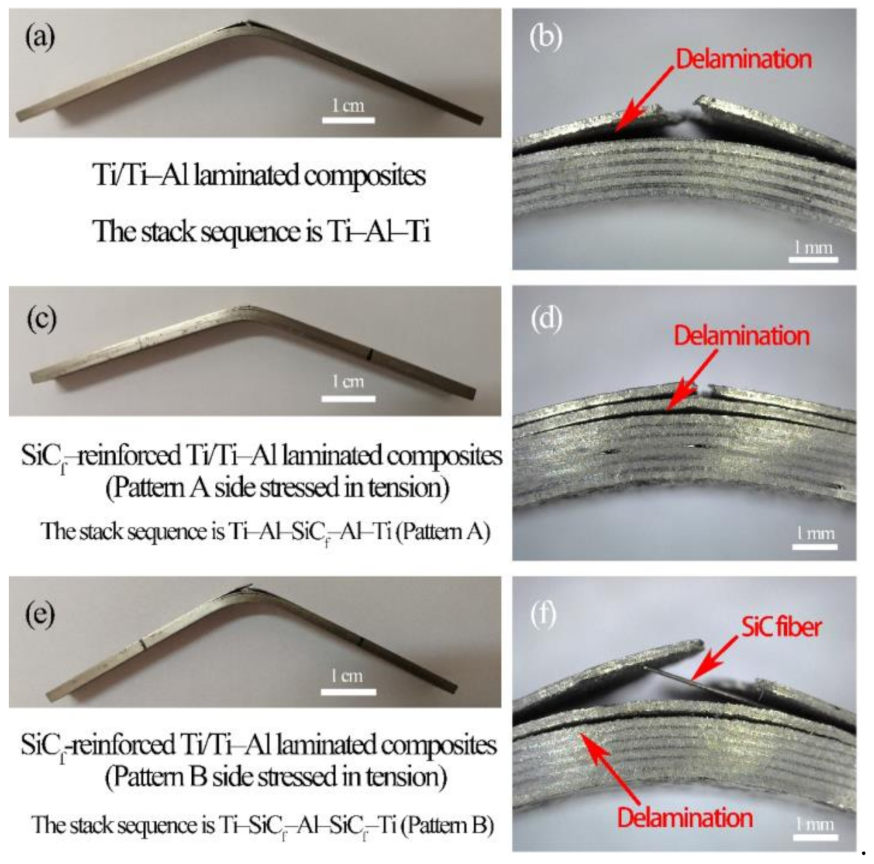
3.2. Mechanical Properties
4. Conclusions
- Equal spacing of the fibers could be guaranteed for SiCf-reinforced Ti/Ti–Al laminated composites prepared by a novel method of fiber weaving. No other elements would be introduced to contaminate the composites.
- With the higher exerted pressure, more compact structure with fewer Kirkendall holes could be obtained in SiCf-reinforced Ti/Ti–Al laminated composites.
- SiCf-reinforced Ti/Ti–Al laminated composites had a tensile strength of 400 ± 10 MPa and flexural strength of 900 ~ 950 MPa. Compared to Ti/Ti–Al laminates, the tensile strength increased by 60%, while the ultimate elongation reached 1.6% (increased by about 14%). The flexural strength did not change much (Ti/Ti–Al laminate composites had a flexural strength of 923 ± 10 MPa). The tensile properties of the laminated composites could be effectively improved by introducing the SiC fibers, while the bending properties were not obviously influenced due to the small volume fraction of fibers.
- The deformation behavior and fracture mechanisms of SiCf-reinforced Ti/Ti–Al laminated composites were obtained through in situ tensile tests. Microcracks first occurred in the Ti–Al intermetallic layer. With the growth and merging of microcracks, interlayer cracks formed in the Ti–Al intermetallic layer along the load direction.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Djanarthany, S.; Viala, J.C.; Bouix, J. An overview of monolithic titanium aluminides based on Ti3Al and TiAl. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2001, 72, 301–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bewlay, B.P.; Nag, S.; Suzuki, A.; Weimer, M.J. TiAl alloys in commercial aircraft engines. Mater. High Temp. 2016, 33, 549–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward-Close, C.M.; Minor, R.; Doorbar, P.J. Intermetallic-matrix composites—A review. Intermetallics 1996, 4, 217–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, K.; Yu, W.B.; Aman, Y.; Jing, T. Synthesis, microstructure and mechanical properties of a bio-inspired Ti-intermetallic multi-layered/SiCf-reinforced Ti-matrix hybrid composite. J. Mater. Sci. 2016, 51, 8747–8760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, T.T.; Niu, Q.F.; Deng, Z.F.; Li, W.H.; Dong, H.F.; Jing, R.; Zou, X.Y. Nature-inspired nacre-like Ti6Al4V-(Ti2AlC/TiAl) laminate composites combining appropriate strength and toughness with synergy effects. Intermetallics 2020, 121, 106774. [Google Scholar]
- Lyu, S.Y.; Sun, Y.B.; Ren, L.; Xiao, W.L.; Ma, C.L. Simultaneously achieving high tensile strength and fracture toughness of Ti/Ti-Al multilayered composites. Intermetallics 2017, 90, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, K.; Zhang, X.; Liu, B.; He, J.; Feng, J.; Ji, P.; Fang, W.; Yin, F. The Deformation Characteristics, Fracture Behavior and Strengthening-Toughening Mechanisms of Laminated Metal Composites: A Review. Metals 2020, 10, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.Z.; Al Olevsky, E.; Meyers, M.A. The development of residual stresses in Ti6Al4V-Al3Ti metal-intermetallic laminate (MIL) composites. Mater. Sci. Eng. Struct. Mater. Prop. Microstruct. Process. 2008, 473, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhari, G.P.; Acoff, V.L. Titanium aluminide sheets made using roll bonding and reaction annealing. Intermetallics 2010, 18, 472–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazurenko, D.V.; Mali, V.I.; Bataev, I.A.; Thoemmes, A.; Bataev, A.A.; Popelukh, A.I.; Anisimov, A.G.; Belousova, N.S. Metal-Intermetallic Laminate Ti-Al3Ti Composites Produced by Spark Plasma Sintering of Titanium and Aluminum Foils Enclosed in Titanium Shells. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2015, 46, 4326–4334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vecchio, K.S. Synthetic multifunctional metallic-intermetallic laminate composites. JOM 2005, 57, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Yang, Y.Q.; Zhao, G.M.; Feng, Z.Q.; Huang, B.; Luo, X.; Li, M.H.; Chen, Y.X. Interfacial reaction studies of B4C-coated and C-coated SiC fiber reinforced Ti–43Al–9V composites. Intermetallics 2014, 50, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Zhu, K.; Aman, Y.; Guo, Z.; Xiong, S. Bio-inspired design of SiCf-reinforced multi-layered Ti-intermetallic composite. Mater. Des. 2016, 101, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.C.; Her, Y.C.; Yang, J.M. Fatigue behavior and damage modeling of SCS-6/titanium/titanium aluminide hybrid laminated composite. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 1998, 245, 100–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zhang, G.; Yuan, M.; Li, S.; Hou, H.; Qu, H.; Zhao, B. Fabrication and Interface Reaction of SiC Fiber Reinforced Ti/Ti2AlNb Laminated Composite. Chin. J. Rare Metals 2017, 41, 1093–1098. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, C.F.; Wang, S.Y.; Yan, H.R.; Han, Y.Q.; Zhu, J.Y.; Shi, H. Optimization Mechanisms of Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of SiC Fiber Reinforced Ti/Al3Ti Laminated Composite Synthesized Using Titanium Barrier. Met. Mater. Int. 2021, 306–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoshhal, R.; Soltanieh, M.; Mirjalili, M. Formation and growth of titanium aluminide layer at the surface of titanium sheets immersed in molten aluminum. Iran. J. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2010, 7, 24–31. [Google Scholar]
- Tavoosi, M. The Kirkendall void formation in Al/Ti interface during solid-state reactive diffusion between Al and Ti. Surf. Interfaces 2017, 9, 196–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Cui, Y.Y.; Hao, Y.L.; Yang, R. Growth of intermetallic layer in multi-laminated Ti/Al diffusion couples. Mater. Sci. Eng. Struct. Mater. Prop. Microstruct. Process. 2006, 435, 638–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.Q.; Jiang, F.C.; Lin, C.F.; Yuan, D.; Huang, H.; Wang, E.H.; Wang, Z.Q.; Guo, C.H. Microstructure and mechanical properties of continuous ceramic SiC and shape memory alloy NiTi hybrid fibers reinforced Ti-Al metal-intermetallic laminated composite. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 729, 1145–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.F.; Han, Y.Q.; Guo, C.H.; Chang, Y.P.; Han, X.X.; Lan, L.; Jiang, F.C. Synthesis and mechanical properties of novel Ti-(SiCf/Al3Ti) ceramic-fiber-reinforced metal-intermetallic-laminated (CFR-MIL) composites. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 722, 427–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baik, K.H. Tensile Failure Behavior of SiC/Ti-6Al-4V Composites Manufactured by Plasma Spraying Route. Mater. Trans. 2006, 47, 2815–2820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]



| Materials | Composition (%) |
|---|---|
| TA1 | Ti: Margin Fe < 0.13, C < 0.012, N < 0.003, O < 0.11, H < 0.003 |
| 1060Al | Al: Margin Si0.25, Fe0.35, Cu0.05, Mn0.3, Mg0.03, Zn0.05, Ti0.03 |
| Point No. | Ti | Al | Point No. | Ti | Al | Phase |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Spot 1 | 95 | 5 | Spot 5 | 96 | 4 | Ti |
| Spot 2 | 70 | 30 | Spot 6 | 71 | 29 | Ti3Al |
| Spot 3 | 35 | 65 | Spot 7 | 34 | 66 | TiAl2 |
| Spot 4 | 24 | 76 | Spot 8 | 25 | 75 | TiAl3 |
| Point No. | Ti | Al | Si | C | W |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Spot 9 | – | – | – | – | 100 |
| Spot 10 | – | – | 36 | 64 | – |
| Spot 11 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 95 | – |
| Spot 12 | 28 | 8 | 3 | 61 | – |
| Spot 13 | 34 | 66 | – | – | – |
| Spot 14 | 72 | 28 | – | – | – |
| Composites | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Flexural Strength (MPa) |
|---|---|---|
| SiCf-reinforced Ti/Ti–Al laminated composites | 400 ± 10 | 910 ± 30 Pattern A stressed in tension |
| 950 ± 30 Pattern B stressed in tension | ||
| Ti/Ti–Al laminated composites | 250 ± 30 | 923 ± 10 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hou, C.; Zhang, S.; Ma, Z.; Lu, B.; Wang, Z. Effects of SiC Fibers and Laminated Structure on Mechanical Properties of Ti–Al Laminated Composites. Materials 2021, 14, 1323. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14061323
Hou C, Zhang S, Ma Z, Lu B, Wang Z. Effects of SiC Fibers and Laminated Structure on Mechanical Properties of Ti–Al Laminated Composites. Materials. 2021; 14(6):1323. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14061323
Chicago/Turabian StyleHou, Chenyang, Shouyin Zhang, Zhijian Ma, Baiping Lu, and Zhenjun Wang. 2021. "Effects of SiC Fibers and Laminated Structure on Mechanical Properties of Ti–Al Laminated Composites" Materials 14, no. 6: 1323. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14061323
APA StyleHou, C., Zhang, S., Ma, Z., Lu, B., & Wang, Z. (2021). Effects of SiC Fibers and Laminated Structure on Mechanical Properties of Ti–Al Laminated Composites. Materials, 14(6), 1323. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14061323





