Study on the Melting Temperature of CaF2-CaO-MgO-Al2O3-TiO2 Slag under the Condition of a Fixed Ratio of Titanium and Aluminum in the Steel during the Electroslag Remelting Process
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Slag-Metal Reaction Experiments in Resistance Furnace
2.2. Slag Melting Temperature Tests
3. Results and Discussion
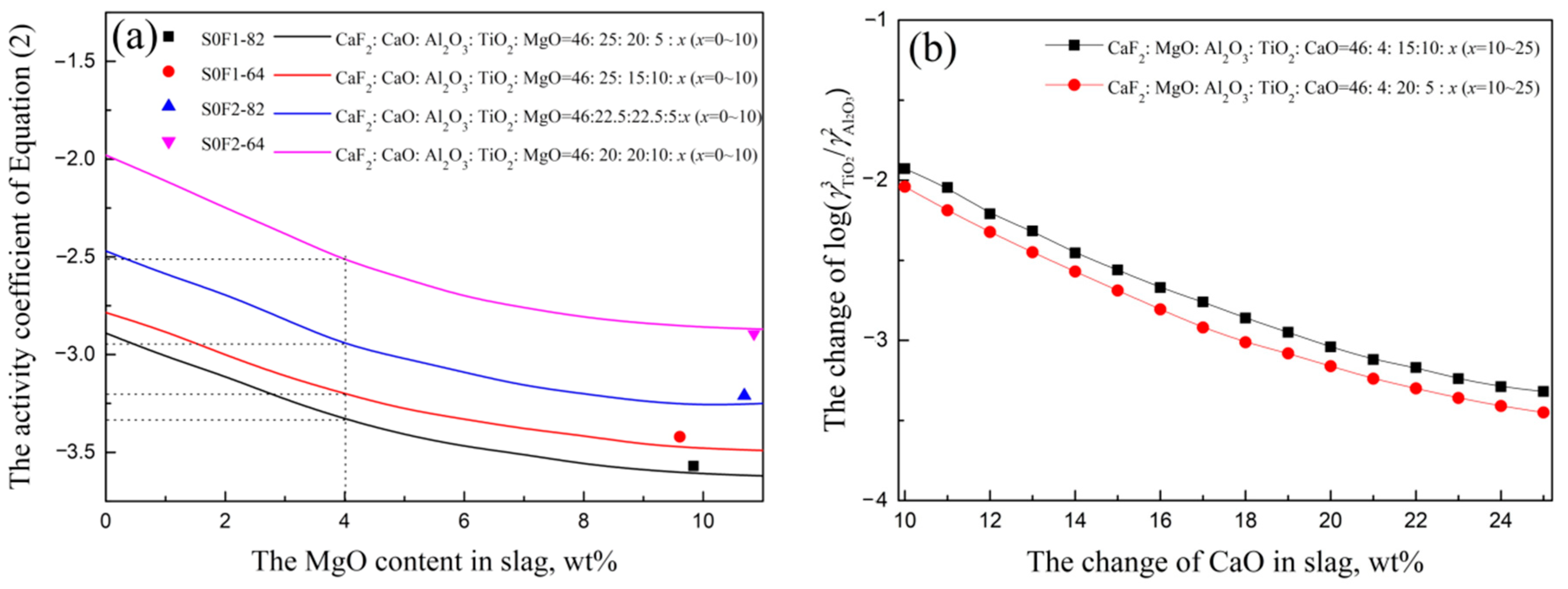
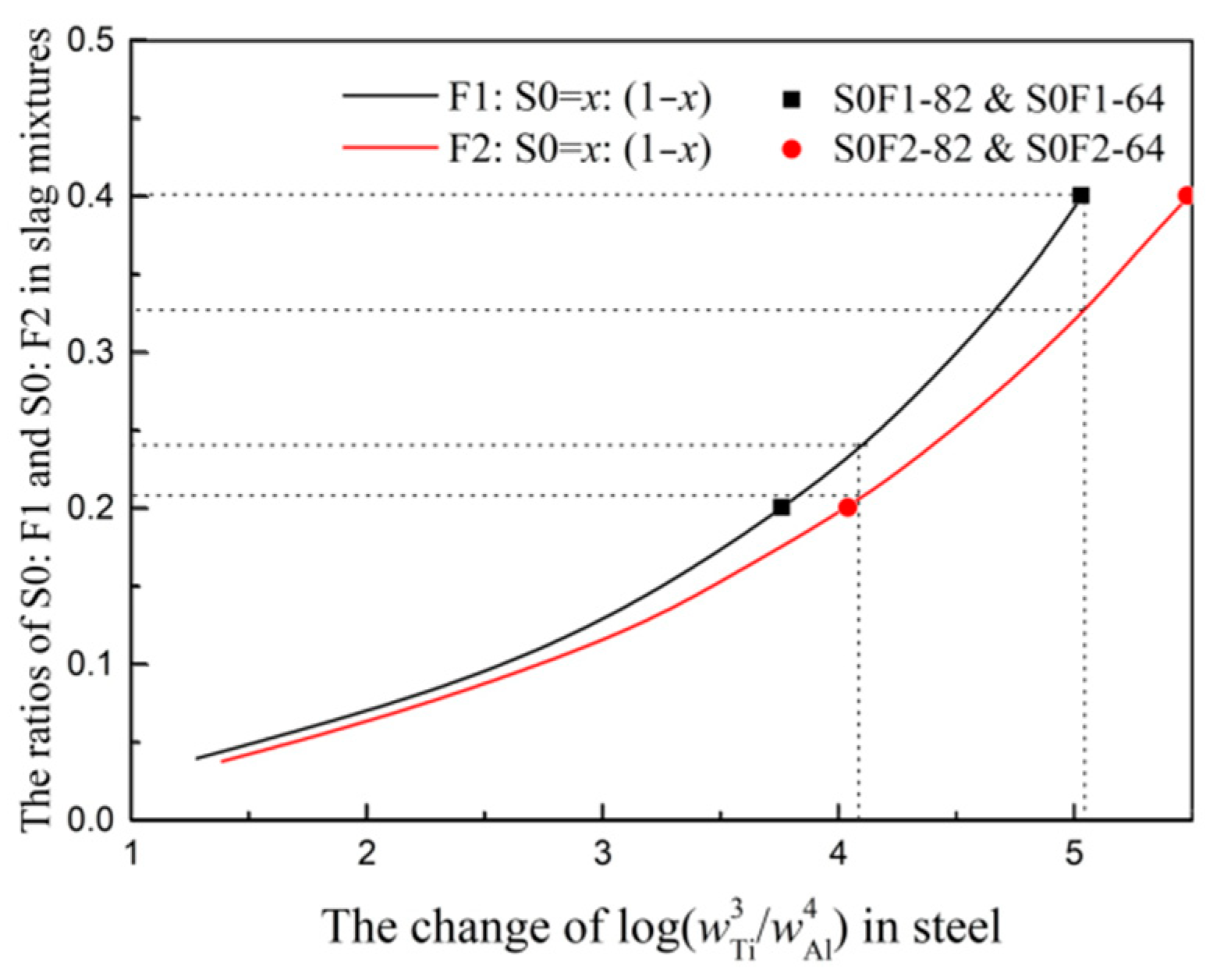
3.1. Slag-Metal Reaction Experiments Results
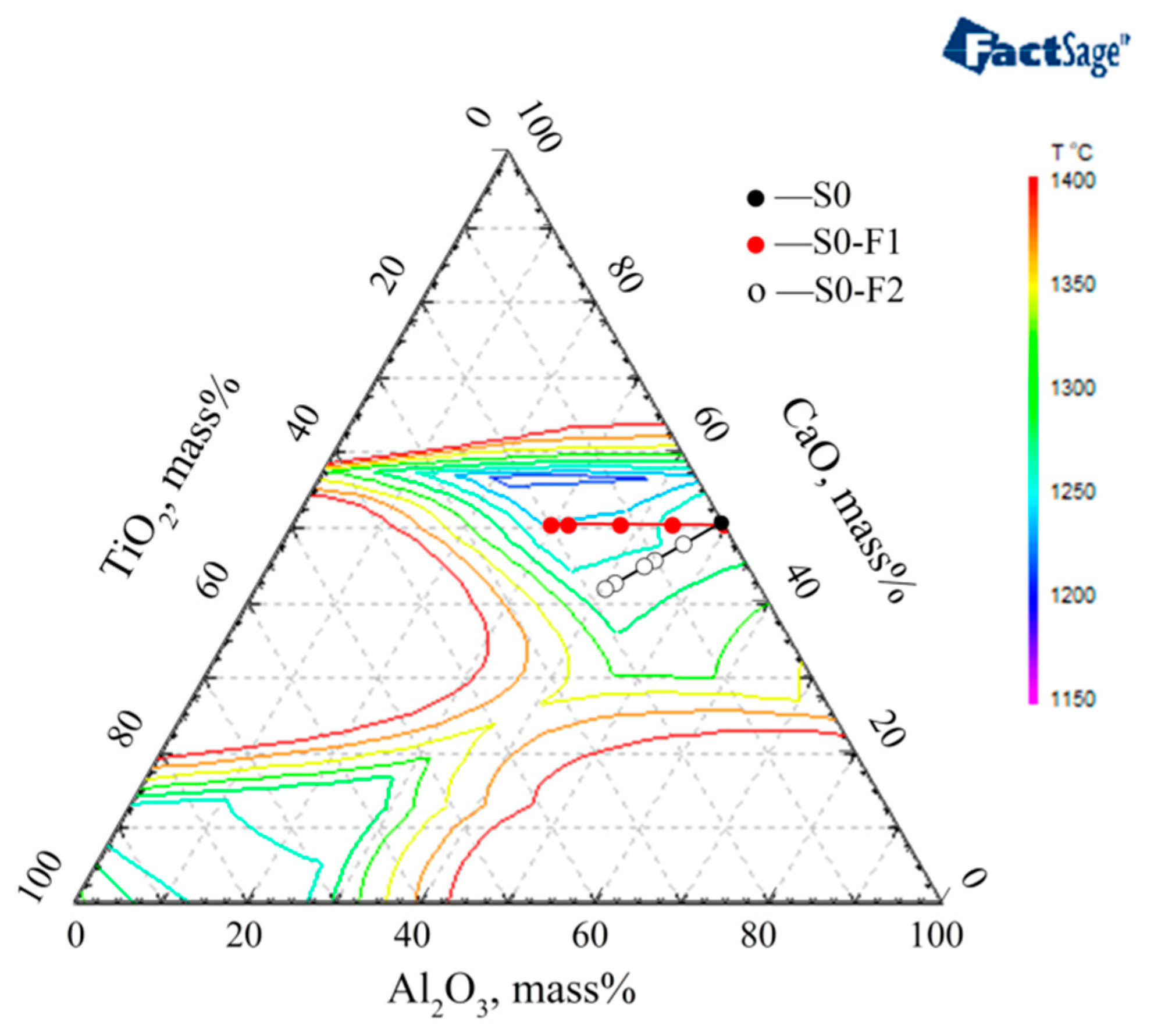
3.2. Slag Melting Temperature Results
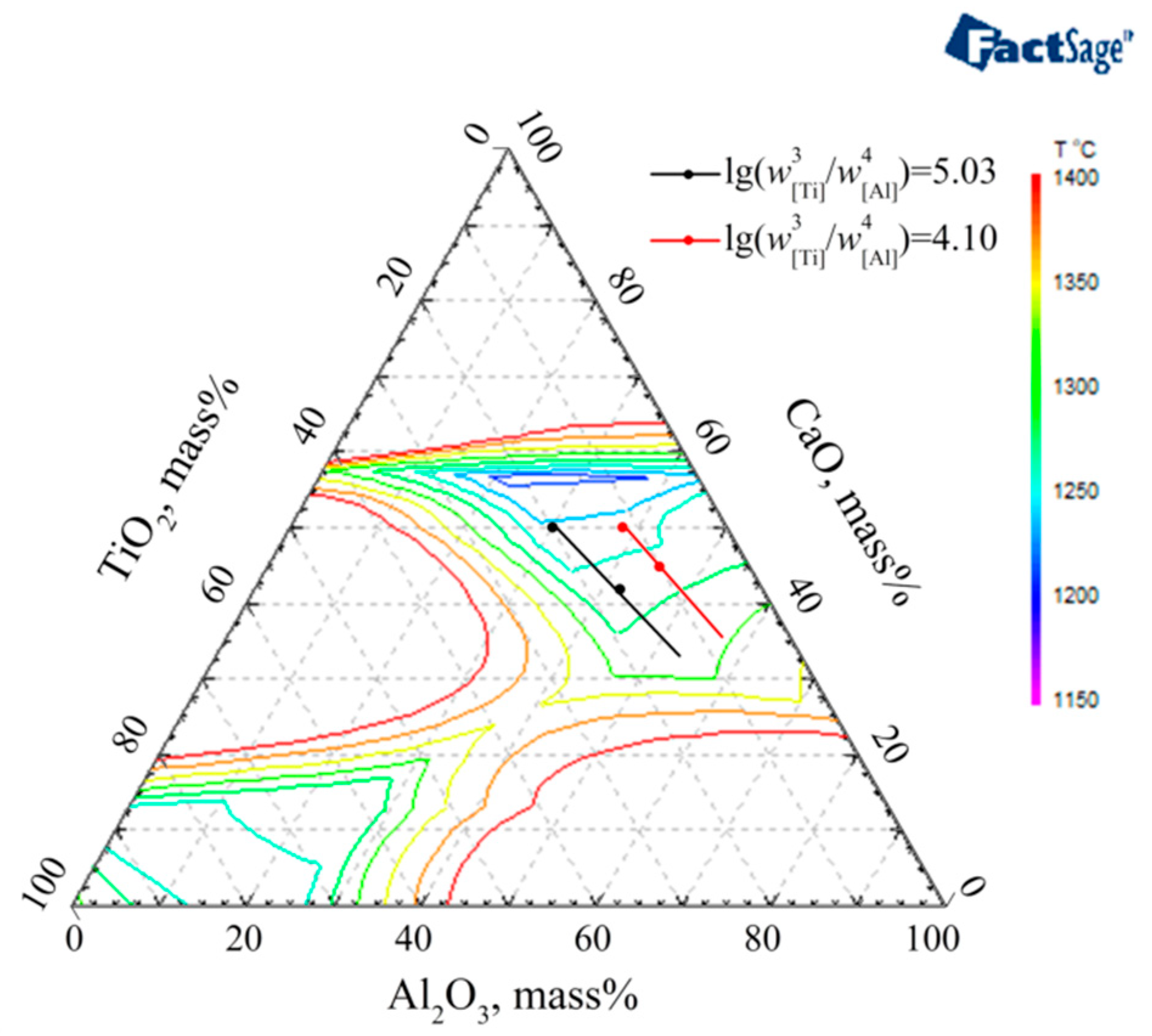
3.3. The Optimized Low Melting Temperature Slag Used for Steel Containing Ti and Al
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- The calculated results of thermodynamic analysis based on Factsage are in good agreement with the slag-metal reaction experimental results in resistance furnace. The changes of S0:F1 and S0:F2 ratios in slag mixtures with different titanium and aluminum contents in steel are determined. The slag S0-F1 containing high CaO needs large ratio of TiO2/Al2O3 to guarantee the thermodynamic equilibrium of 3[Ti] + 2(Al2O3) = 4[Al] + 3(TiO2) and the ratio of Ti/Al in steel.
- (2)
- The melting temperature of slag S0-F1 with a CaO/(Al2O3 + TiO2) ratio = 1 is lower than that of slag S0-F2 with a CaO/Al2O3 ratio = 1. Especially for thermodynamic equilibrium slag containing high TiO2, the melting temperature of S0-F1 slag CaF2:CaO:MgO:Al2O3:TiO2 = 46:25:4:15:10 is much lower than that of S0-F2 slag CaF2:CaO:MgO:Al2O3:TiO2 = 46:20.875:4:20.875:8.25.
- (3)
- The slag mixtures consisting of pre-melted slag S0 (CaF2:MgO:CaO:Al2O3 = 46:4:25:25) and pre-melted slag F1 (CaF2:MgO:CaO:TiO2 = 46:4:25:25), which component is CaF2:CaO:MgO:Al2O3:TiO2 = 46:25:4:(25 − x):x, have the desired low melting temperature property while satisfying the concentrations of Ti and Al in steel.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, Z.Y.; Yang, S.F.; Qu, J.L.; Li, J.S.; Dong, A.P.; Gu, Y. Effects of different melting technologies on the purity of superalloy GH4738. Materials 2018, 11, 1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zeng, T.Y.; Zhang, S.Z.; Shi, X.B.; Wang, W.; Yan, W.; Tian, Y.; Zhao, M.C.; Yang, K. Effects of the primary NbC elimination on the SSCC resistance of a HSLA steel for oil country tubular goods. Materials 2021, 14, 5301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, D.L.; Li, J.; Shi, C.B.; Ju, T. Effect of TiO2 on the crystallisation behavior of CaF2-CaO-MgO-Al2O3 slag for electroslag remelting of Ti-containing tool steel. Ironmak. Steelmak. 2018, 45, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.B.; Cho, J.W.; Zheng, D.L.; Li, J. Fluoride evaporation and crystallization behavior of CaF2-CaO-Al2O3-(TiO2) slag for electroslag remelting of Ti-containing steels. Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater. 2016, 23, 627–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.B.; Li, J.; Cho, J.W.; Jiang, F.; Jung, I.H. Effect of SiO2 on the crystallization behaviors and in-mold performance of CaF2-CaO-Al2O3 slags for drawing-ingot-type electroslag remelting. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2015, 46, 2110–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Duan, S.C.; Shi, X.; Wang, F.; Zhang, M.C.; Sun, Y.; Guo, H.J.; Guo, J. A review of methodology development for controlling loss of alloying elements during the electroslag remelting process. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2019, 50, 3055–3071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, S.C.; Shi, X.; Zhang, M.C.; Li, B.; Yang, W.S.; Wang, F.; Guo, H.J.; Guo, J. Effect of slag composition on the deoxidation and desulfurization of Inconel 718 superalloy by ESR type slag without deoxidizer addition. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2020, 51, 353–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.H.; Hou, D.; Dong, Y.W.; Cao, Y.L.; Cao, H.B.; Gong, W. Effect of slag on titanium, silicon and aluminum content in superalloy during electroslag remelting. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2016, 47, 1465–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, D.; Jiang, Z.H.; Dong, Y.W.; Cao, Y.L.; Cao, H.B.; Gong, W. Thermodynamic design of electroslag remelting slag for high titanium and low aluminium stainless steel based on IMCT. Ironmak. Steelmak. 2016, 43, 517–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, D.; Jiang, Z.H.; Dong, Y.W.; Gong, W.; Cao, Y.L.; Cao, H.B. Effect of slag composition on the oxidation kinetics of alloying elements during electroslag remelting of stainless steel: Part-1 mass-transfer model. ISIJ Int. 2017, 57, 1400–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hou, D.; Jiang, Z.H.; Dong, Y.W.; Gong, W.; Cao, Y.L.; Cao, H.B. Effect of slag composition on the oxidation kinetics of alloying elements during electroslag remelting of stainless steel: Part-2 control of titanium and aluminum content. ISIJ Int. 2017, 57, 1410–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hou, D.; Jiang, Z.H.; Qu, T.P.; Wang, D.Y.; Liu, F.B. Aluminum, titanium and oxygen control during electroslag remelting of stainless steel based on thermodynamic analysis. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 2019, 26, 20–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, D.; Wang, D.Y.; Qu, T.P.; Tian, J.; Wang, H.H. Kinetic study on alloying element transfer during an electroslag remelting process. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2019, 50, 3088–3102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, D.; Wang, D.Y.; Jiang, Z.H.; Qu, T.P.; Wang, H.H.; Dong, J.W. Investigation on slag-metal-inclusion multiphase reactions during electroslag remelting of die Steel. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2021, 52, 478–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; He, Z.; Li, G.Q.; Li, B.K.; Zhu, C.Y.; Chen, P.J. Numerical investigation of desulfurization behavior in electroslag remelting process. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2017, 104, 943–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, L.; Chen, W.P.; Hou, D. Kinetic analysis of spinel formation from powder compaction of magnesia and alumina. Ceram. Int. 2020, 46, 2853–2861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.L.; Pang, Z.G.; Xing, X.D.; Xu, R.S. Thermodynamic properties, viscosity, and structure of CaO-SiO2-MgO-Al2O3-TiO2-based slag. Materials 2021, 14, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Min, D.J. A novel electrochemical process for desulfurization in the CaO-SiO2-Al2O3 system. Materials 2020, 13, 2478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.X.; Leng, M.; Chen, Y.F.; Chen, Z.C.; Li, J.L. Crystallization products and structural characterization of CaO-SiO2-based mold fluxes with varying Al2O3/SiO2 ratios. Materials 2019, 12, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leng, M.; Lai, F.F.; Li, J.L. Effect of cooling rate on phase and crystal morphology transitions of CaO-SiO2-based systems and CaO-Al2O3-based systems. Materials 2019, 12, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gu, S.P.; Wen, G.H.; Ding, Z.Q.; Tang, P.; Liu, Q. Effect of shear stress on isothermal crystallization behavior of CaO-Al2O3-SiO2-Na2O-CaF2 slags. Materials 2018, 11, 1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- The Japan Society for the Promotion of Science. The 19th Committee on Steelmaking: Steelmaking Data Sourcebook; Gordon and Breach Science Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, D.; Jiang, Z.H.; Dong, Y.W.; Li, Y.; Gong, W.; Liu, F.B. Mass transfer model of desulfurization in the electroslag remelting process. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2017, 48, 1885–1897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.H.; Li, H.; Zhu, H.M.; Xu, P.J. Effects of steel-slag components on interfacial-reaction characteristics of permeable steel-slag-bitumen mixture. Materials 2020, 13, 3885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Long, X.; Wang, L.Z.; Tong, S.H.; Wang, X.T.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.T. Inclusion Characteristics in 95CrMo Steels with Different Calcium and Sulfur Contents. Materials 2020, 13, 619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, B.; Shi, X.; Guo, H.J.; Guo, J. Study on Precipitation and Growth of TiN in GCr15 Bearing Steel during Solidification. Materials 2019, 12, 1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, J.X.; Chen, Y.M.; Li, X.M.; Cui, Y.R.; Lu, X.T. Mechanism of slag composition change during electroslag remelting process. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 2011, 18, 24–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| C | Si | Mn | Cr | Ni | Ti | Al | P | S |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.09 | 0.64 | 1.06 | 18.32 | 9.76 | 0.47 | 0.068 | 0.021 | 0.0017 |
| Exp. | Slag | CaF2 | CaO | MgO | Al2O3 | TiO2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S0F1-82 | S0:F1 = 8:2 | 46 | 25 | 4 | 20 | 5 |
| S0F2-82 | S0:F2 = 8:2 | 46 | 22.5 | 4 | 22.5 | 5 |
| S0F1-64 | S0:F1 = 6:4 | 46 | 25 | 4 | 15 | 10 |
| S0F2-64 | S0:F2 = 6:4 | 46 | 20 | 4 | 20 | 10 |
| Slag | Slag ratio | CaF2 | CaO | Al2O3 | MgO | TiO2 | Halfsphere Temperature, K | Flowing Temperature, K |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S0 | -- | 46 | 25 | 25 | 4 | 0 | 1560 | 1570 |
| F1 | -- | 46 | 25 | 0 | 4 | 25 | 1605 | 1614 |
| F2 | -- | 46 | 12.5 | 12.5 | 4 | 25 | 1618 | 1629 |
| S0F1-1 | S0:F1 = 88:12 | 46 | 25 | 22 | 4 | 3 | 1543 | 1554 |
| S0F1-2 | S0:F1 = 76:24 | 46 | 25 | 19 | 4 | 6 | 1534 | 1546 |
| S0F1-3 | S0:F1 = 64:36 | 46 | 25 | 16 | 4 | 9 | 1533 | 1539 |
| S0F1-4 | S0:F1 = 60:40 | 46 | 25 | 15 | 4 | 10 | 1535 | 1542 |
| S0F2-1 | S0:F2 = 88:12 | 46 | 23.5 | 23.5 | 4 | 3 | 1548 | 1559 |
| S0F2-2 | S0:F2 = 79:21 | 46 | 22.375 | 22.375 | 4 | 5.25 | 1550 | 1559 |
| S0F2-3 | S0:F2 = 76:24 | 46 | 22 | 22 | 4 | 6 | 1549 | 1560 |
| S0F2-4 | S0:F2 = 67:33 | 46 | 20.875 | 20.875 | 4 | 8.25 | 1566 | 1576 |
| S0F2-5 | S0:F2 = 64:36 | 46 | 20.5 | 20.5 | 4 | 9 | 1572 | 1581 |
| Exp. | Si | Ti | Al | Al2O3 | TiO2 | MgO | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S0F1-82 | 0.68 | 0.33 | 0.058 | 18.91 | 4.75 | 9.84 | −3.57 |
| S0F2-82 | 0.69 | 0.35 | 0.053 | 21.28 | 4.64 | 10.69 | −3.21 |
| S0F1-64 | 0.66 | 0.40 | 0.032 | 14.39 | 9.51 | 9.61 | −3.42 |
| S0F2-64 | 0.68 | 0.42 | 0.028 | 18.91 | 9.37 | 10.93 | −2.89 |
| C | Si | Mn | P | S | Al | Ti | Cr | Ni | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Al | 0.091 | 0.056 | 0.035 | 0.033 | 0.035 | 0.08 | 0.004 | 0.03 | - |
| Ti | −0.19 | −0.025 | −0.043 | −0.0064 | −0.27 | 0.0037 | 0.013 | 0.055 | 0.009 |
| Slag | CaF2 | CaO | MgO | Al2O3 | TiO2 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S0:F1 = 8:2 | 46 | 25 | 4 | 20 | 5 | −3.33 | 3.76 |
| S0:F2 = 8:2 | 46 | 22.5 | 4 | 22.5 | 5 | −2.95 | 4.04 |
| S0:F1 = 6:4 | 46 | 25 | 4 | 15 | 10 | −3.20 | 5.03 |
| S0:F2 = 6:4 | 46 | 20 | 4 | 20 | 10 | −2.52 | 5.49 |
| Slag | Slag Ratio | CaF2 | CaO | MgO | Al2O3 | TiO2 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5.03 | −4.51 | S0F1-4 | S0:F1 = 60:40 | 46 | 25 | 4 | 15 | 10 |
| 5.03 | −4.51 | S0F2-4 | S0:F2 = 67:33 | 46 | 20.875 | 4 | 20.875 | 8.25 |
| 4.10 | −5.44 | S0F1-2 | S0:F1 = 76:24 | 46 | 25 | 4 | 19 | 6 |
| 4.10 | −5.44 | S0F2-2 | S0:F2 = 79:21 | 46 | 22.375 | 4 | 22.375 | 5.25 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hou, D.; Pan, P.; Wang, D.; Hu, S.; Wang, H.; Zhang, G. Study on the Melting Temperature of CaF2-CaO-MgO-Al2O3-TiO2 Slag under the Condition of a Fixed Ratio of Titanium and Aluminum in the Steel during the Electroslag Remelting Process. Materials 2021, 14, 6047. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14206047
Hou D, Pan P, Wang D, Hu S, Wang H, Zhang G. Study on the Melting Temperature of CaF2-CaO-MgO-Al2O3-TiO2 Slag under the Condition of a Fixed Ratio of Titanium and Aluminum in the Steel during the Electroslag Remelting Process. Materials. 2021; 14(20):6047. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14206047
Chicago/Turabian StyleHou, Dong, Peng Pan, Deyong Wang, Shaoyan Hu, Huihua Wang, and Ganggang Zhang. 2021. "Study on the Melting Temperature of CaF2-CaO-MgO-Al2O3-TiO2 Slag under the Condition of a Fixed Ratio of Titanium and Aluminum in the Steel during the Electroslag Remelting Process" Materials 14, no. 20: 6047. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14206047
APA StyleHou, D., Pan, P., Wang, D., Hu, S., Wang, H., & Zhang, G. (2021). Study on the Melting Temperature of CaF2-CaO-MgO-Al2O3-TiO2 Slag under the Condition of a Fixed Ratio of Titanium and Aluminum in the Steel during the Electroslag Remelting Process. Materials, 14(20), 6047. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14206047








