Fly-Ash-Based Geopolymers Reinforced by Melamine Fibers
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
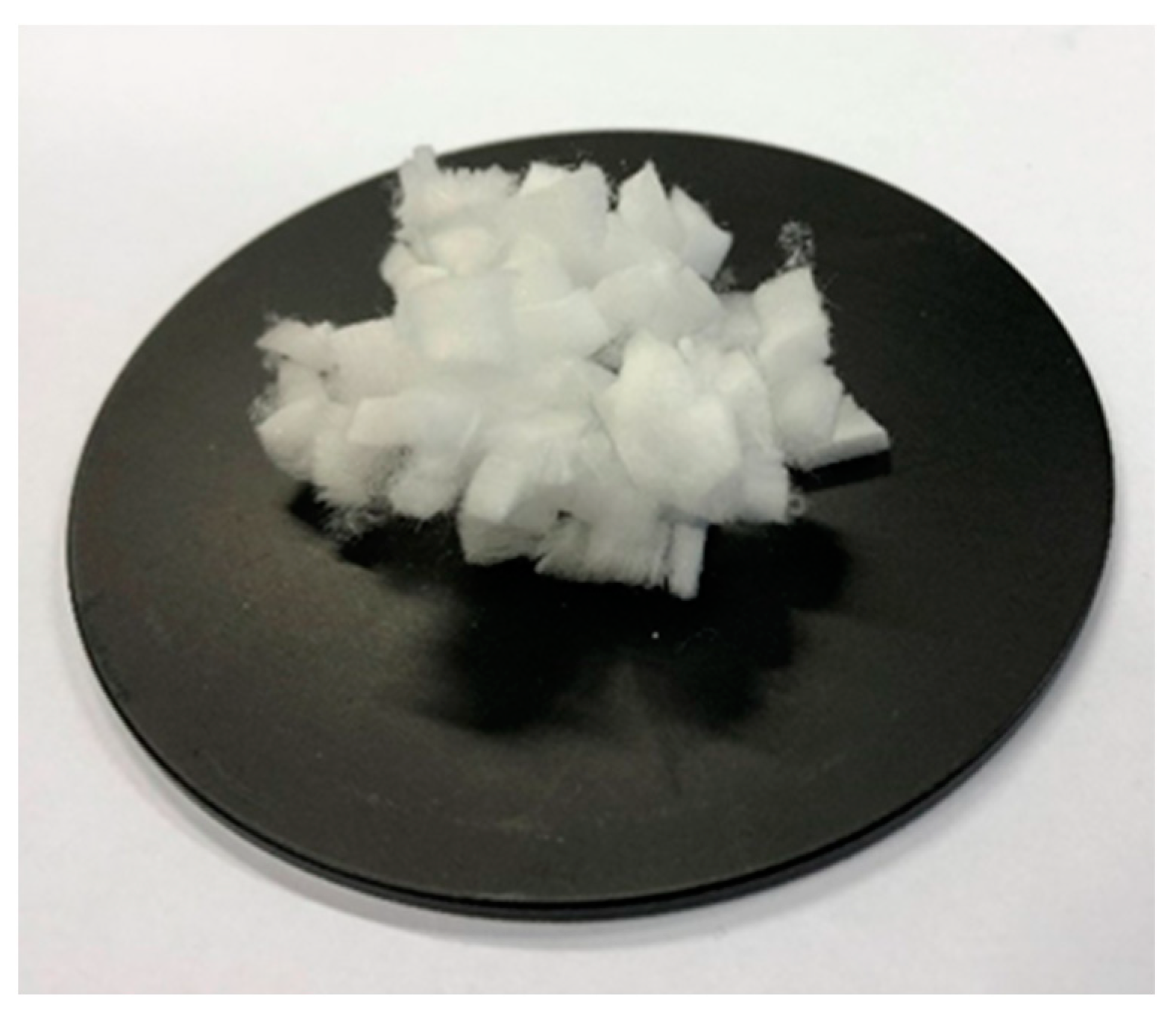
2.1. Materials and Preparation of Samples
2.2. Methodology
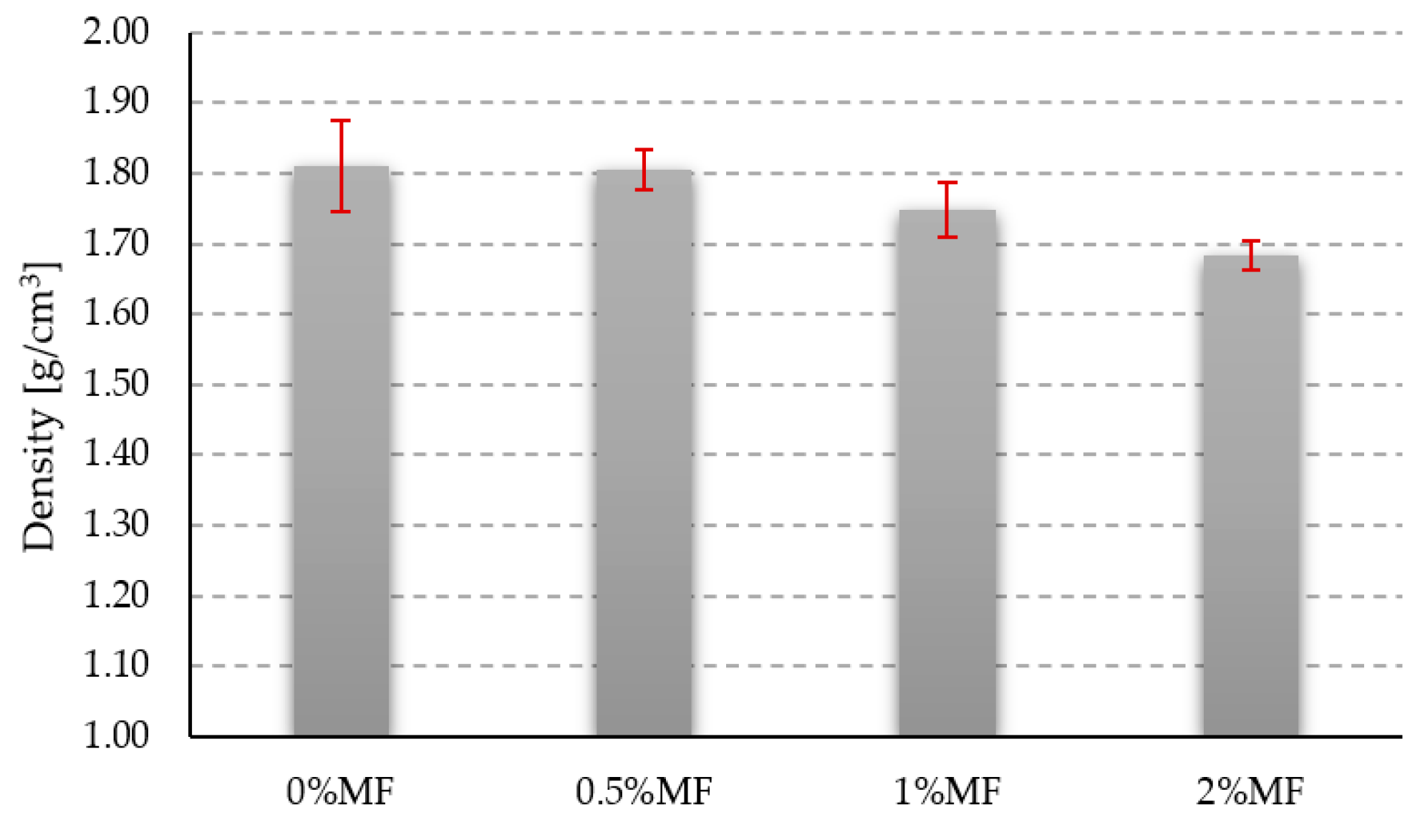
2.2.1. Density
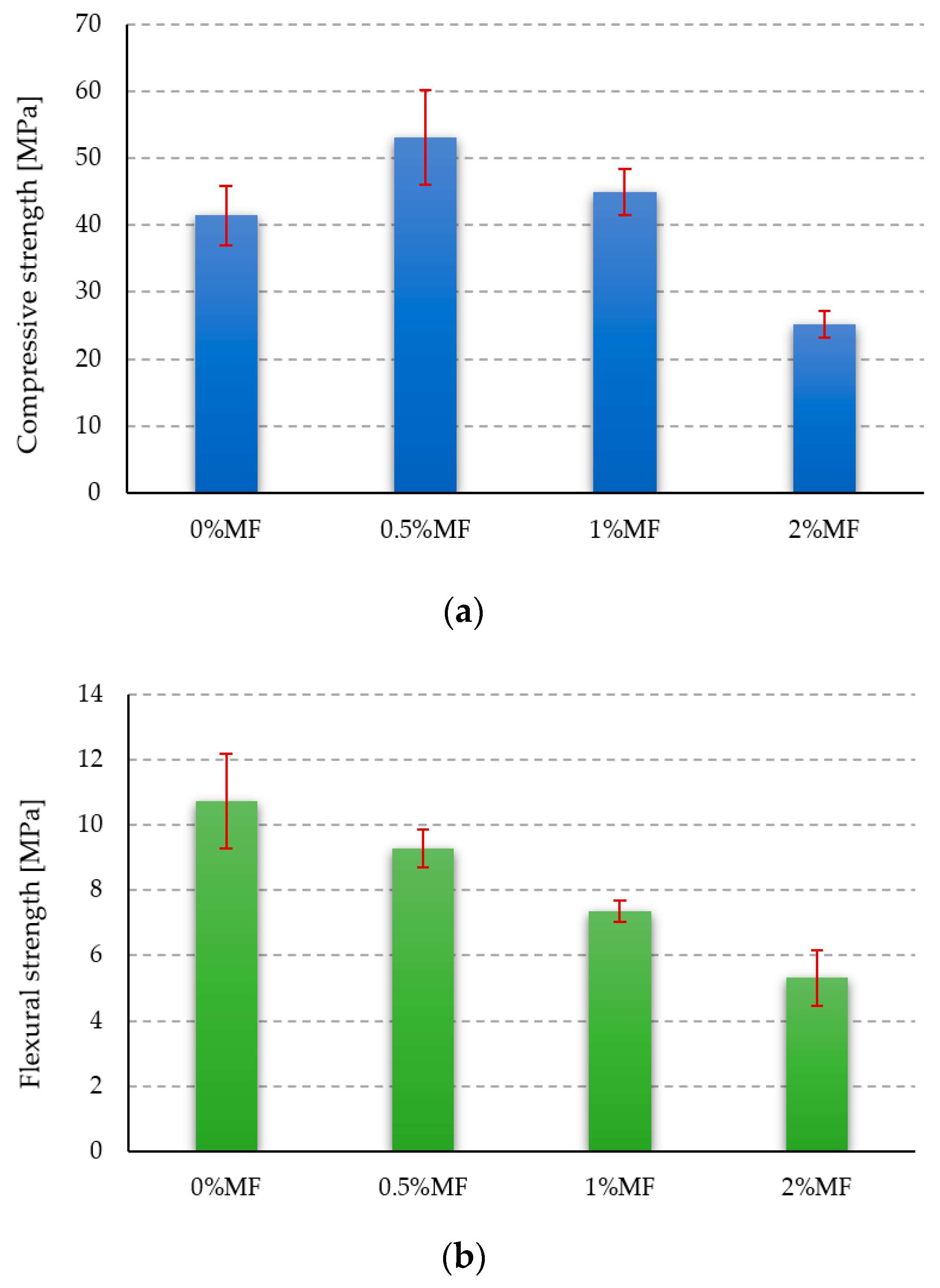
2.2.2. Strength Tests
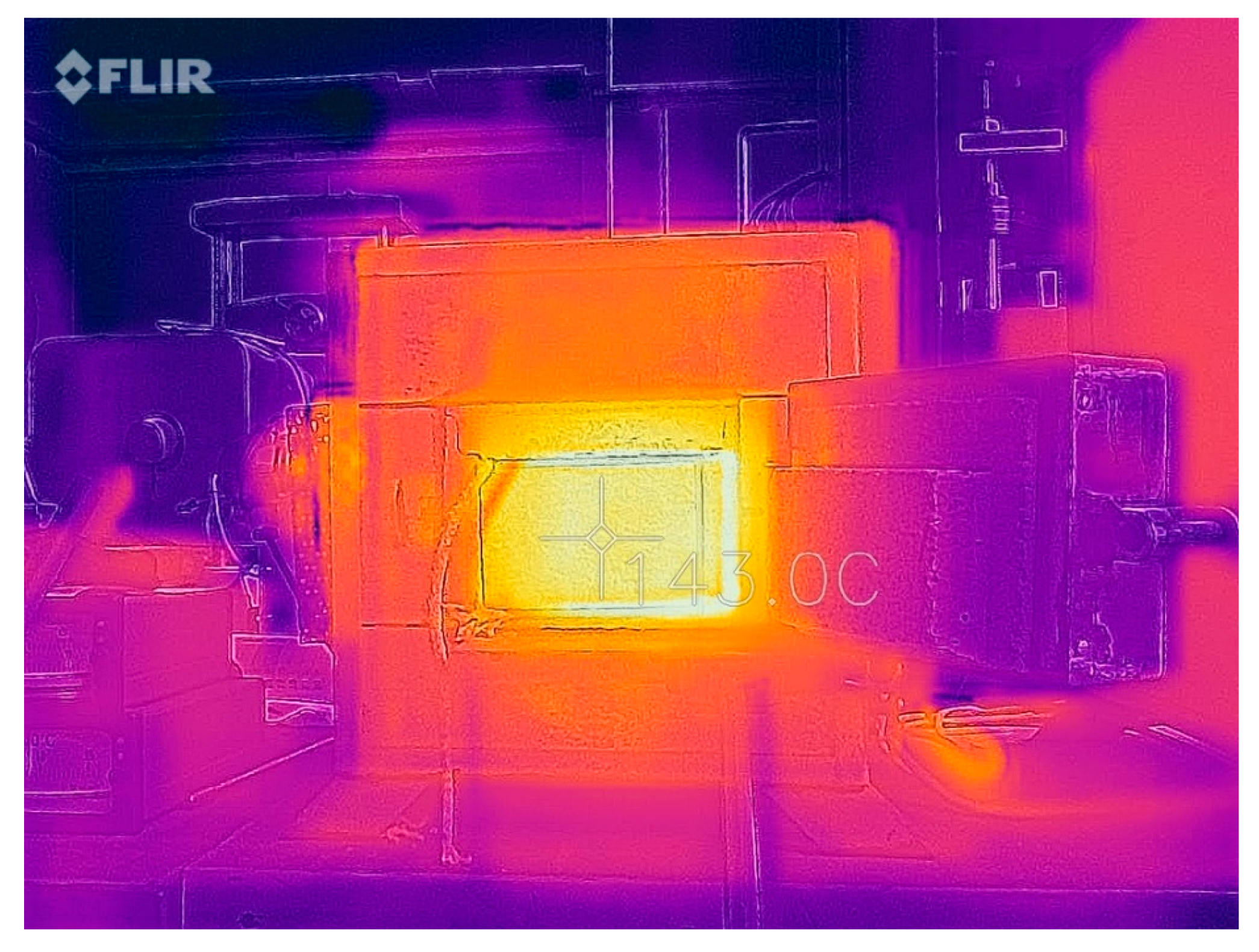
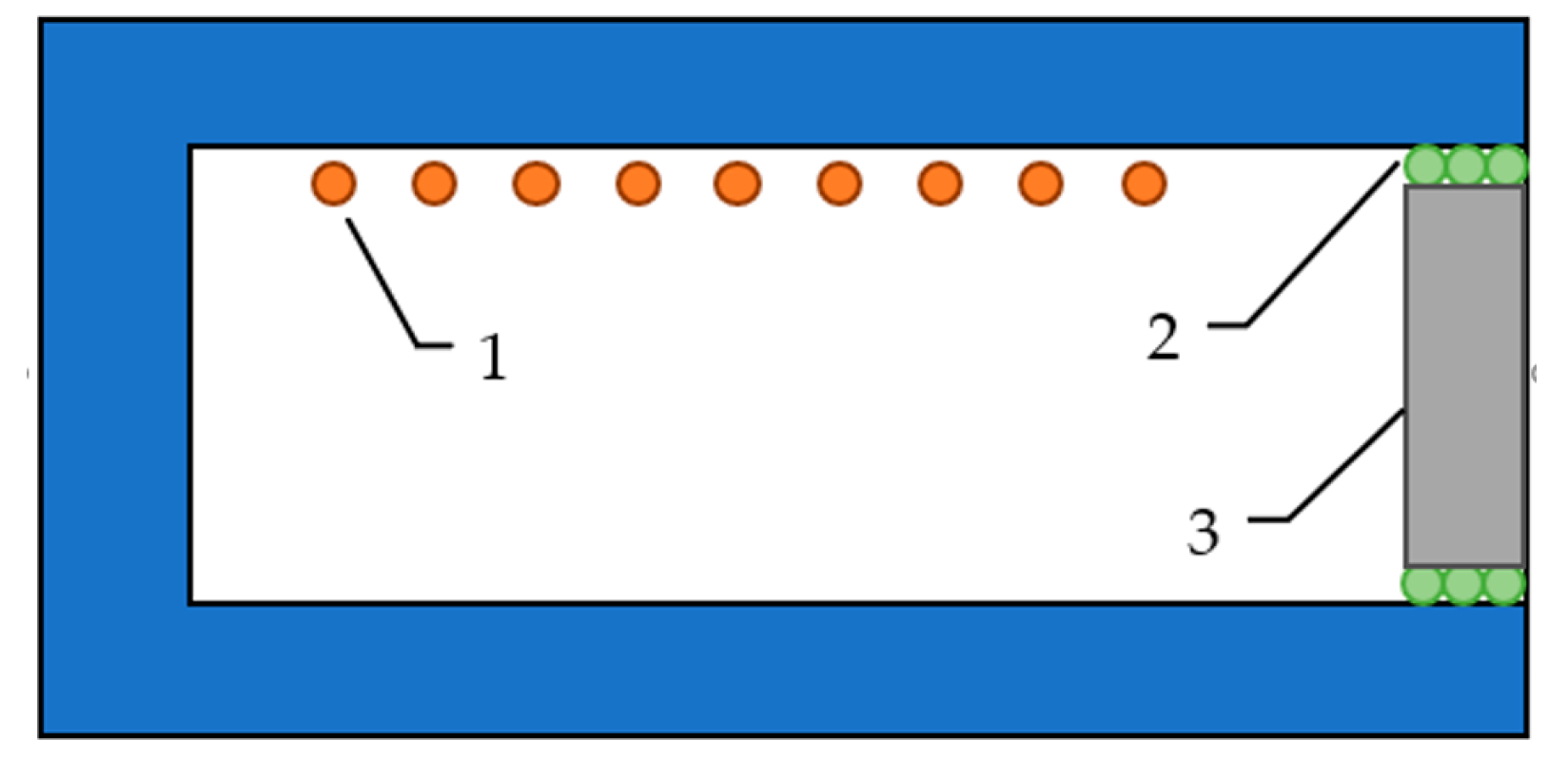
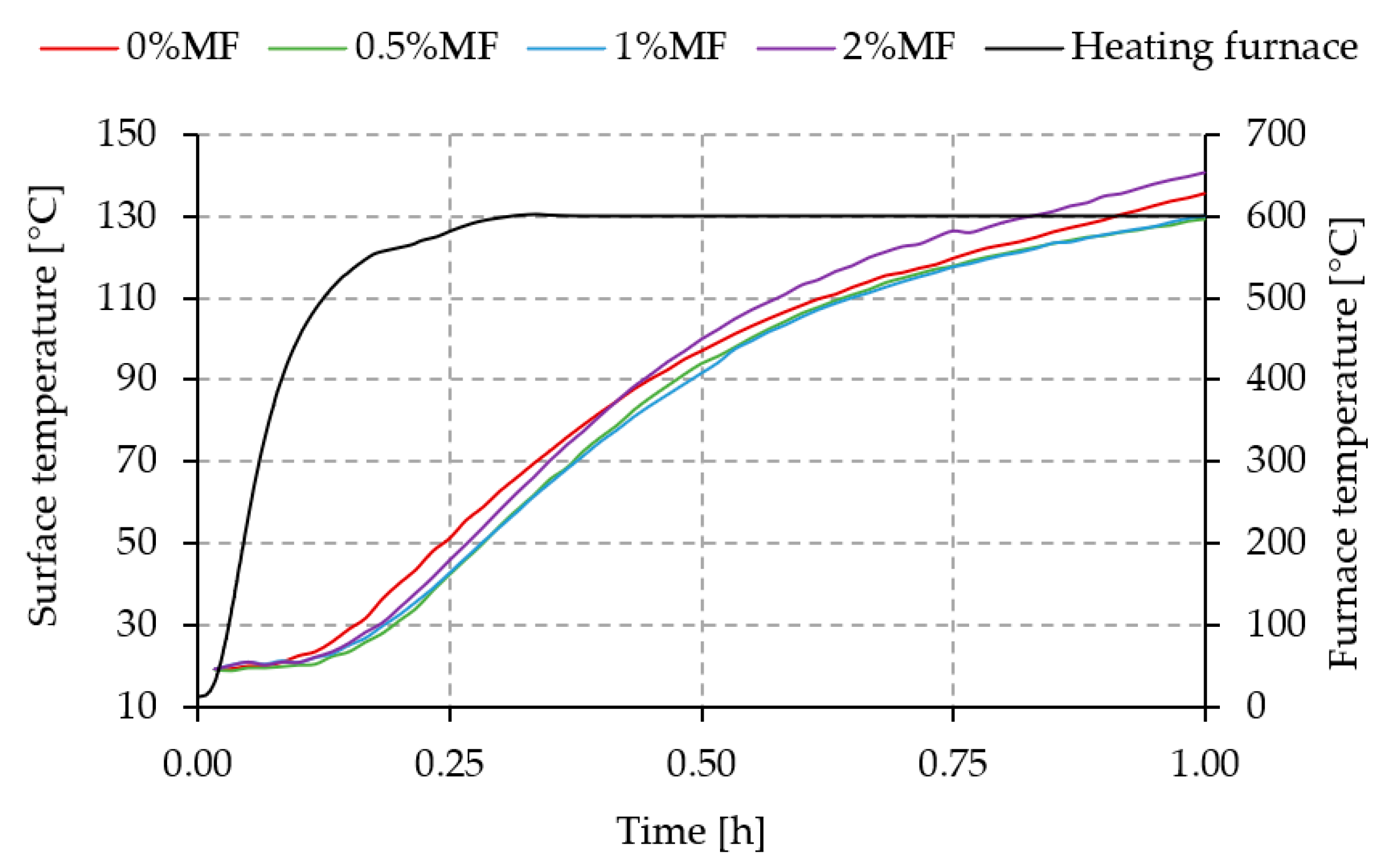
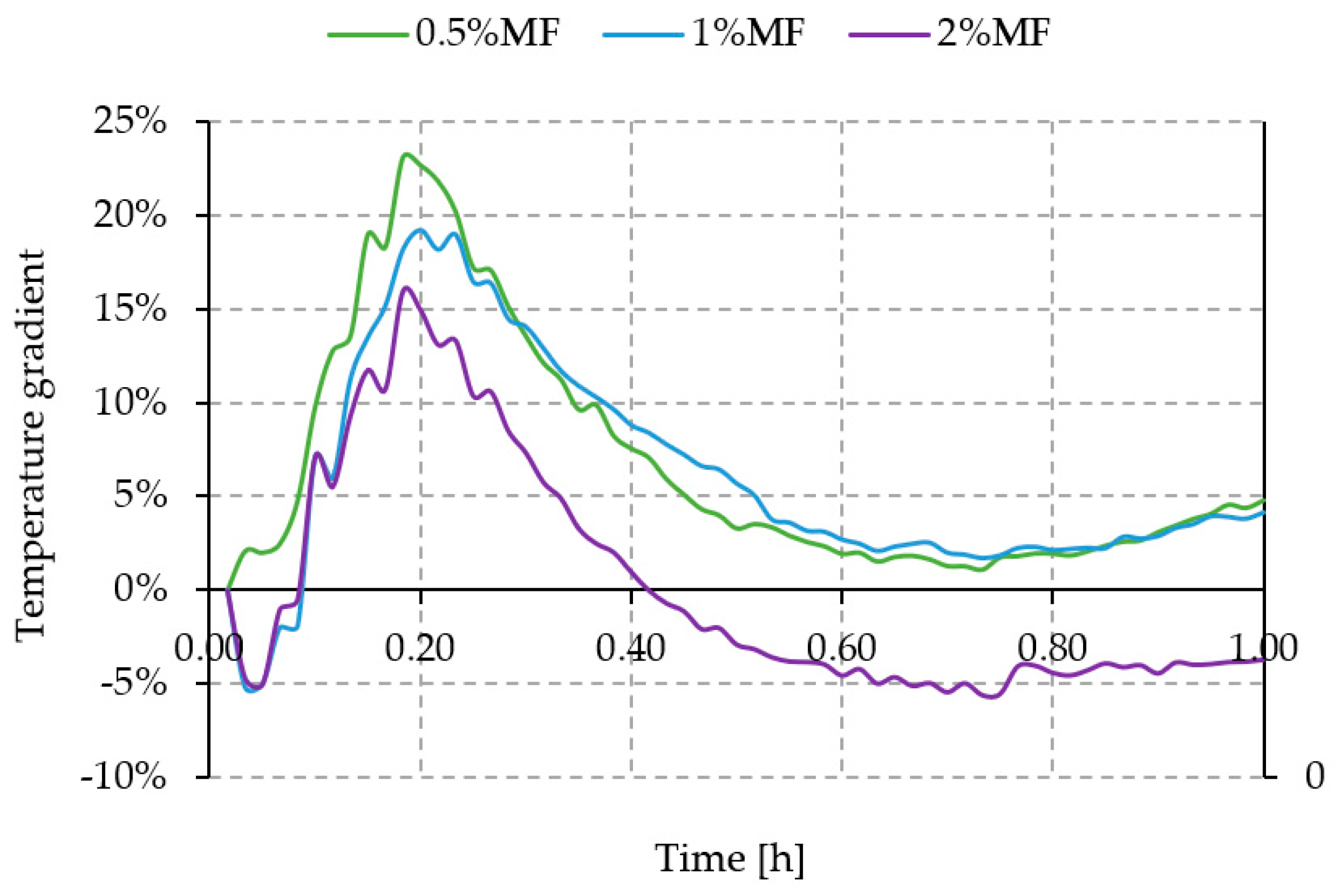
2.2.3. Thermal Radiation
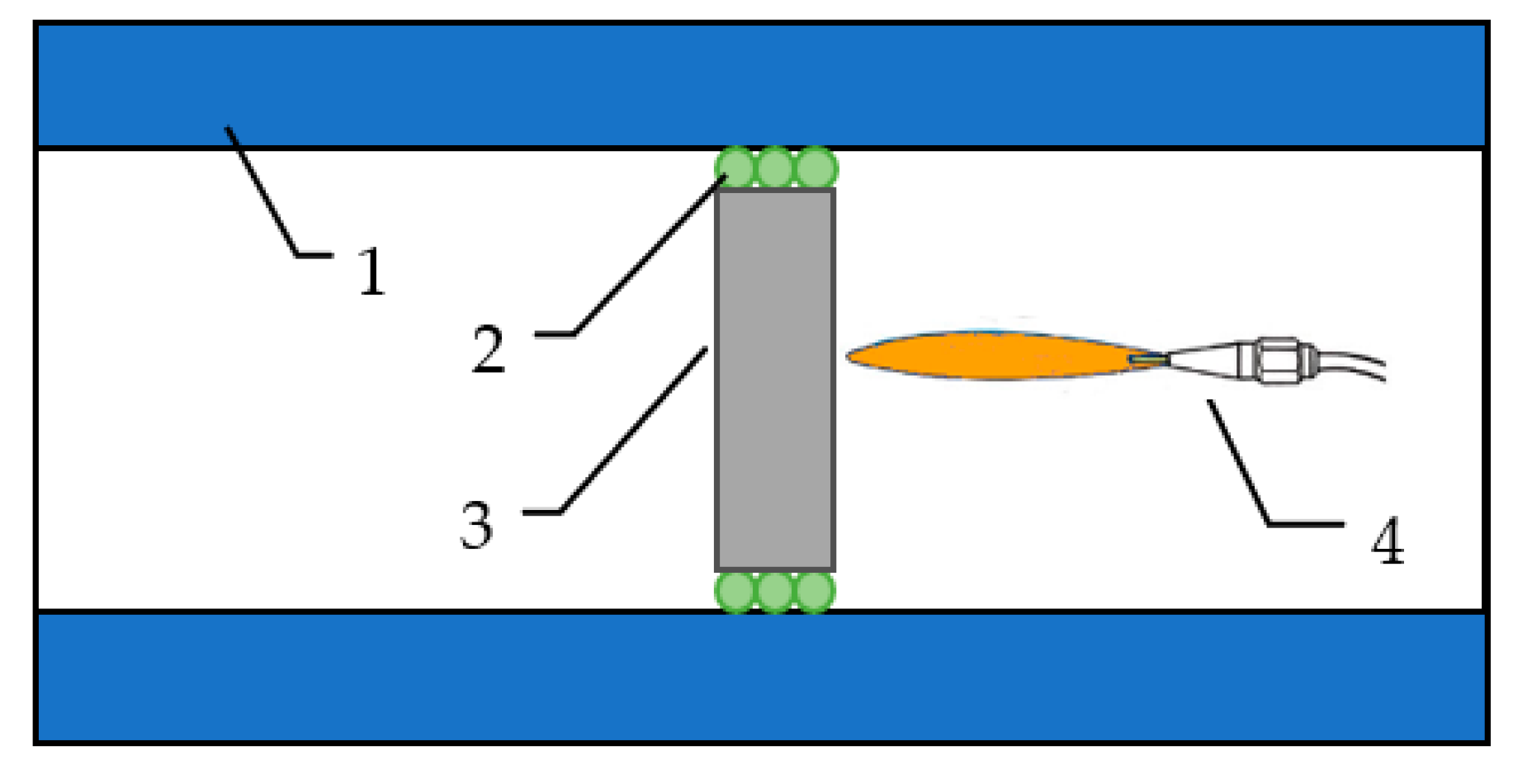
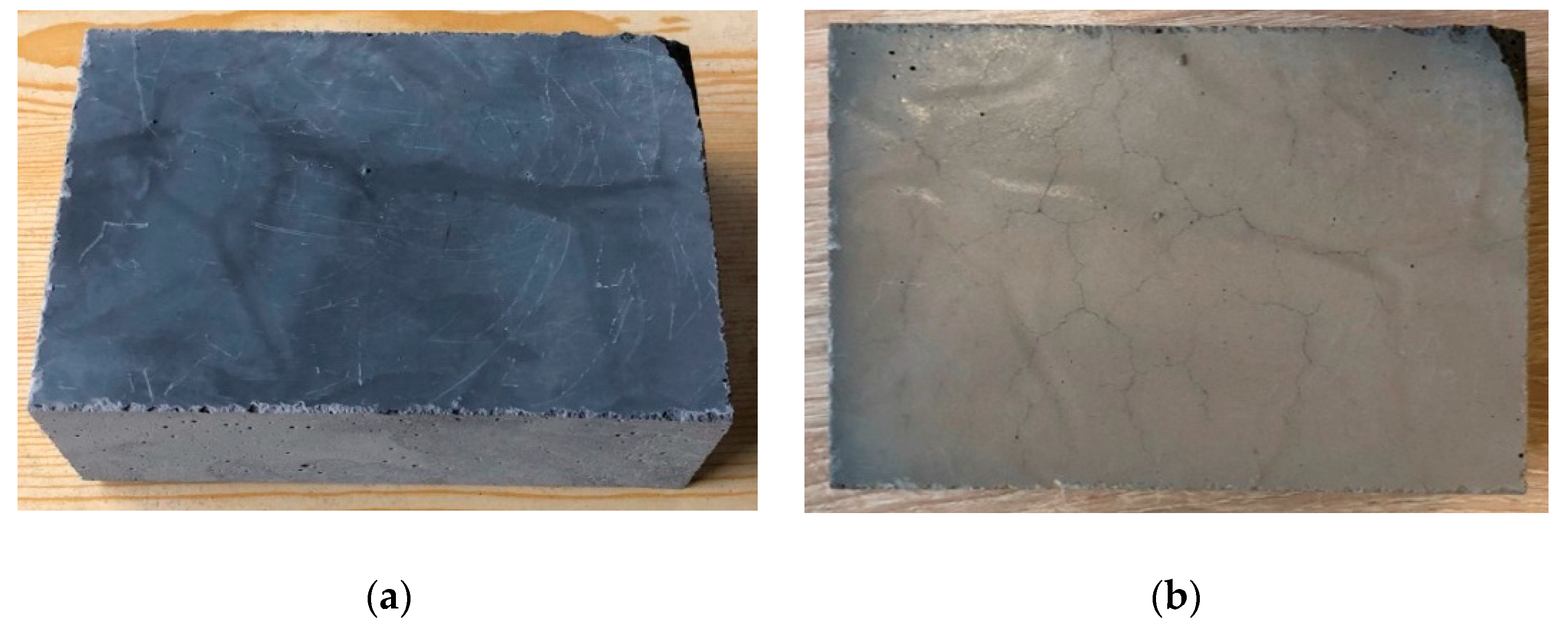
2.2.4. Fire-Jet Test
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Density
3.2. Strength Tests
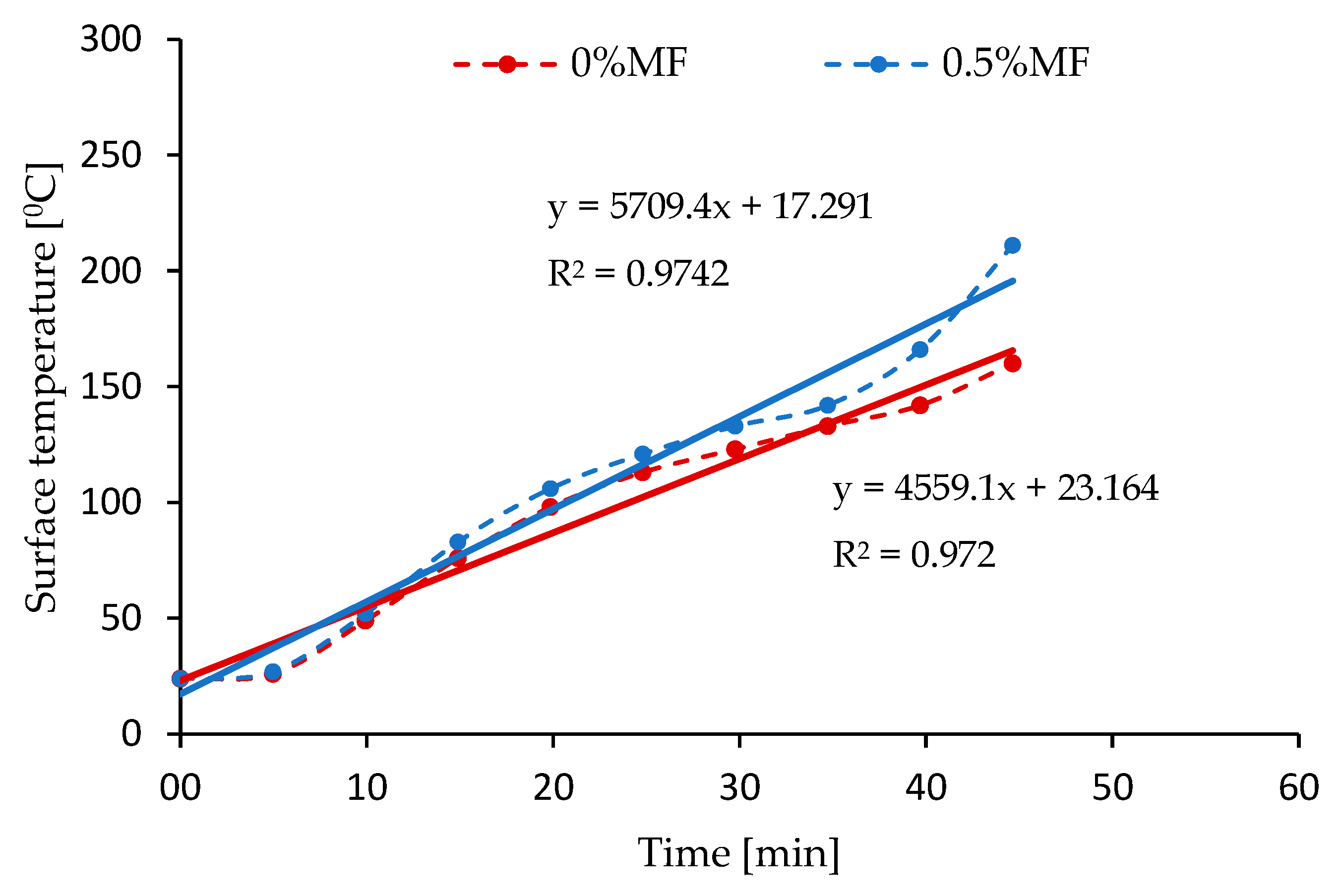
3.3. Thermal Radiation
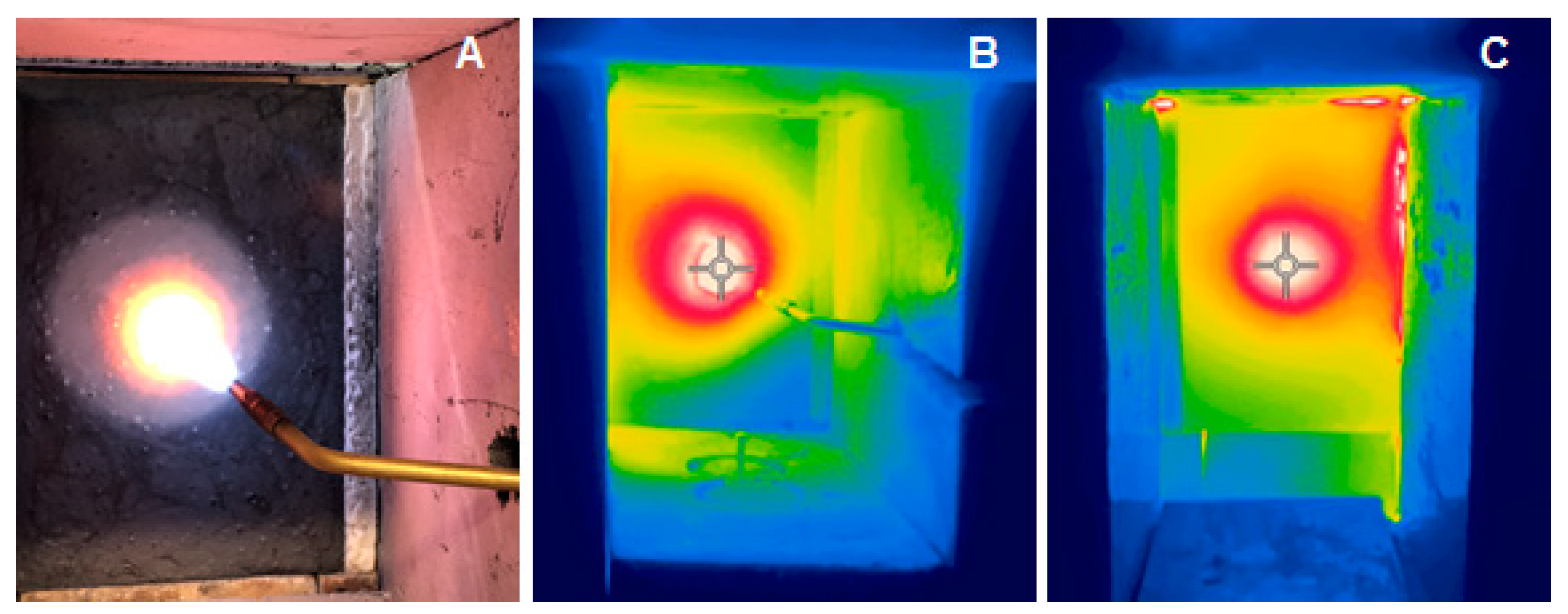
3.4. Fire-Jet Test
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pacheco-Torgal, F.; Castro-Gomes, J.; Jalali, S. Alkali-activated binders: A review Part 1. Historical background, terminology, reaction mechanisms and hydration products. Constr. Build. Mater. 2008, 22, 1305–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidovits, J. Geopolymers: Ceramic-Like Inorganic Polymers. J. Ceram. Sci. Technol. 2017, 3, 335–350. [Google Scholar]
- Provis, J.L.; Van Deventer, J.S.J. Geopolymers: Structure, Processing, Properties and Industrial Applications; Woodhead Publishing Limited: Cambridge, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Luukkonen, T.; Sarkkinen, M.; Kemppainen, K.; Rämö, J.; Lassi, U. Metakaolin geopolymer characterization and application for ammonium removal from model solutions and landfill leach-ate. Appl. Clay Sci. 2016, 119, 266–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Li, H.; Yan, F. Synthesis and mechanical properties of metakaolinite-based geopolymer. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2005, 268, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duxson, P.; Mallicoat, S.W.; Lukey, G.C.; Kriven, W.M.; Van Deventer, J.S.J. The effect of alkali and Si/Al ratio on the development of mechanical properties of metakaolin-based geopolymers. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2007, 292, 8–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sitarz, M.; Hager, I.; Choińska, M. Evolution of mechanical properties with time of fly-ash-based geopolymer mortars under the effect of granulated ground blast furnace slag addition. Energies 2020, 13, 1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Provis, J.L.; Reid, A.; Wang, H. Geopolymer foam concrete: An emerging material for sustainable construction. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 56, 113–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bumanis, G.; Vitola, L.; Pundiene, I.; Sinka, M.; Bajare, D. Gypsum, Geopolymers, and starch—Alternative binders for bio-based building materials: A review and life-cycle assessment. Sustainability 2020, 12, 5666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assi, L.N.; Ghahari, S.A.; Deaver, E.; Leaphart, D.; Ziehl, P. Improvement of the early and final compressive strength of fly ash-based geopolymer concrete at ambient conditions. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 123, 806–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, T.W.; Chiu, J.P. Fire-resistant geopolymer produce by granulated blast furnace slag. Miner. Eng. 2003, 16, 205–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.; Carvelli, V.; Adesanya, E.; Kinnunen, P.; Illikainen, M. High performance cementitious composite from alkali-activated ladle slag reinforced with polypropylene fibers. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2018, 90, 150–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cioffi, R.; Maffucci, L.; Santoro, L. Optimization of geopolymer synthesis by calcinations and polycondensation of a kaolinitic residue resources. Conserv. Recycl. 2003, 40, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyale, S.M.; Babajide, O.O.; Birch, G.D.; Böke, N.; Petrik, L.F. Synthesis and characterization of coal fly ash-based foamed geopolymer. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2013, 18, 722–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böke, N.; Birch, G.D.; Nyale, S.M.; Petrik, L.F. New synthesis method for the production of coal fly ash-based foamed geopolymers. Constr Build. Mater. 2015, 75, 189–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Łach, M.; Korniejenko, K.; Mikuła, J. Thermal Insulation and Thermally Resistant Materials Made of Geopolymer Foams. Procedia Eng. 2016, 151, 410–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shill, K.S.; Al-Deen, S.; Ashraf, M.; Hutchison, W. Resistance of fly ash based geopolymer mortar to both chemicals and high thermal cycles simultaneously. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 239, 117886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hýsek, Š.; Frydrych, M.; Herclík, M.; Louda, P.; Fridrichová, L.; Le Van, S.; Le Chi, H. Fire-Resistant Sandwich-Structured Composite Material Based on Alternative Materials and Its Physical and Mechanical Properties. Materials 2019, 12, 1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, V.S.; Louda, P.; Tran, H.N.; Nguyen, P.D.; Bakalova, T.; Ewa Buczkowska, K.; Dufkova, I. Study on Temperature-Dependent Properties and Fire Resistance of Metakaolin-Based Geopolymer Foams. Polymers 2020, 12, 2994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikuła, J.; Łach, M. Geopolymers—A new environment friendly alternative to concrete based on portland cement. Part 1—Introduction. In Pro-Ecological Solutions in the Field of Production. Modern Environmentally Friendly Composite Materials; Mikuła, J., Ed.; Cracow University of Technology: Cracow, Poland, 2007; Volume 1, pp. 13–179. [Google Scholar]
- Mehta, A.; Siddique, R. Sulfuric acid resistance of fly ash based geopolymer concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 146, 136–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sotelo-Pina, C.; Aguilera-Gonzalez, E.N.; Martinez-Luevanos, A. Geopolymers: Past, Present and Future of Low Carbon Footprint Eco-materials. In Handbook of Ecomaterials; Martinez, L.M.T., Kharissowa, O.V., Kharisov, B., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 2765–2785. [Google Scholar]
- Korniejenko, K.; Frączek, E.; Pytlak, E.; Adamski, M. Mechanical properties of geopolymer composites reinforced with natural fibers. Procedia Eng. 2016, 151, 388–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjbar, N.; Zhang, M. Fiber-Reinforced geopolymer composites: A review. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2020, 107, 103498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korniejenko, K.; Lin, W.-T.; Šimonová, H. Mechanical Properties of Short Polymer Fiber-Reinforced Geopolymer Composites. J. Compos. Sci. 2020, 4, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, F.J.; Thaumaturgo, C. Fibre reinforcement and fracture response in geopolymeric mortars. Fatigue Fract. Eng. Mater. Struct. 2003, 26, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawaz, M.; Heitor, A.; Sivakumar, M. Geopolymers in construction—Recent developments. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 260, 120472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghahari, S.; Assi, L.N.; Alsalman, A.; Alyamaç, K.E. Fracture Properties Evaluation of Cellulose Nanocrystals Cement Paste. Materials 2020, 13, 2507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazan, P.; Kozub, B.; Łach, M.; Korniejenko, K. Evaluation of Hybrid Melamine and Steel Fiber Reinforced Geopolymers Composites. Materials 2020, 13, 5548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.; Cao, Y.; Qian, L.; Chen, Y.; Qiu, Y.; Xu, B.; Xin, F. Synergistic Charring Flame-Retardant Behavior of Polyimide and Melamine Polyphosphate in Glass Fiber-Reinforced Polyamide 66. Polymers 2019, 11, 1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diniz, A.T.S.; Huth, C.; Schartel, B. Dripping and decomposition under fire: Melamine cyanurate vs. glass fibres in polyamide 6. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2020, 171, 109048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levinta, N.; Corobea, M.C.; Vuluga, Z.; Nicolae, C.-A.; Gabor, A.R.; Raditoiu, V.; Osiac, M.; Teodorescu, G.-M.; Teodorescu, M. Bio-Based Polyamide 1010 with a Halogen-Free Flame Retardant Based on Melamine–Gallic Acid Complex. Polymers 2020, 12, 1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azimi, E.A.; Al Bakri Abdullah, M.M.; Yun Ming, L.; Heah, C.Y.; Hussin, K.; Aziz, I.H. Review of Geopolymer Materials for Thermal Insulating Applications. Key Eng. 2015, 660, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Łach, M.; Mierzwiński, D.; Korniejenko, K.; Mikuła, J. Geopolymer foam as a passive fire protection. MATEC Web Conf. 2018, 247, 00031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Korniejenko, K.; Halyag, N.P.; Mucsi, G. Fly Ash as a Raw Material for Geopolymerisation—Chemical Composition and Physical Properties. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 706, 012002. [Google Scholar]
- Korniejenko, K.; Łach, M.; Marczyk, J.; Ziejewska, C.; Halyag, N.P.; Mucsi, G. Fly Ash as a Raw Material for Geopolymerisation-Mineralogical Composition and Morphology. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 706, 012006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maity, S.; Singha, K. Melamine fiber—Synthesis, features and applications. Chem. Fibers Int. 2012, 62, 183–186. [Google Scholar]
- Dias, D.P.; Thaumaturgo, C. Fracture toughness of geopolymeric concretes reinforced with basalt fibers. Cement and Concrete Composites. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2005, 27, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaikh, F.U.A. Tensile and flexural behaviour of recycled polyethylene terephthalate (PET) fibre reinforced geopolymer composites. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 245, 118438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chindaprasirt, P.; Rattanasak, U. Synthesis of polypropylene fiber/high-calcium fly ash geopolymer with outdoor heat exposure. Clean Technol. Environ. 2017, 19, 1985–1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noushini, A.; Castel, A.; Gilbert, R.I. Creep and shrinkage of synthetic fibre-reinforced geopolymer concrete. Mag. Concr. Res. 2019, 71, 1070–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baykara, H.; Cornejo, M.H.; Espinoza, A.; García, E.; Ulloa, N. Preparation, characterization, and evaluation of compressive strength of polypropylene fiber reinforced geopolymer mortars. Heliyon 2020, 6, e03755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Zhao, R.; Li, R.; Wang, Y.; Cheng, Z.; Li, F.; Ma, Z.J. Frost resistance of fiber-reinforced blended slag and Class F fly ash-based geopolymer concrete under the coupling effect of freeze-thaw cycling and axial compressive loading. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 250, 118831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashad, A.M. The effect of polypropylene, polyvinyl-alcohol, carbon and glass fibres on geopolymers properties. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2019, 35, 127–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhutta, A.; Farooq, M.; Zanotti, C.; Banthia, N. Pull-out behavior of different fibers in geopolymer mortars: Effects of alkaline solution concentration and curing. Mater. Struct. 2017, 50, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, G.; Salirrosas, J.; Ruiz, G.; Kim, S.; Nakamatsu, J.; Aguilar, R. Evaluation of fire, high-temperature and water erosion resistance of fiber-reinforced lightweight pozzolana-based geopolymer mortars. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 706, 012016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Van, S.; Hájková, P.; Kovacic, V.; Bakalova, T.; Lukáš, V.; Le Chi, H.; Ceccon Seifert, K.; Pereira Peres, A.; Louda, P. Thermal Conductivity of Reinforced Geopolymer Foams. Ceram.-Silikáty 2019, 63, 365–373. [Google Scholar]

| Precursor | Identified Phase | Percentages Content (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Name | Chemical Formula | ||
| Fly ash | Quartz | SiO2 | 42.3 |
| Mullite | Al6Si2O13 | 54.8 | |
| Hematite | Fe2O3 | 0.6 | |
| Magnetite | Fe3O4 | 0.5 | |
| Anhydrite | CaSO4 | 1.4 | |
| Rutile | TiO2 | 0.4 | |
| Designation | Mixture Proportion (% by Weight) | NaOH Solution | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fly Ash | Sand | Melamine Fiber | ||
| 0%MF | 50 | 50 | - | 10 M sodium hydroxide solution + water glass (1200 mL in total) |
| 0.5%MF | 49.75 | 49.75 | 0.5 | |
| 1%MF | 49.5 | 49.5 | 1.0 | |
| 2%MF | 49.0 | 49.0 | 2.0 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kozub, B.; Bazan, P.; Mierzwiński, D.; Korniejenko, K. Fly-Ash-Based Geopolymers Reinforced by Melamine Fibers. Materials 2021, 14, 400. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14020400
Kozub B, Bazan P, Mierzwiński D, Korniejenko K. Fly-Ash-Based Geopolymers Reinforced by Melamine Fibers. Materials. 2021; 14(2):400. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14020400
Chicago/Turabian StyleKozub, Barbara, Patrycja Bazan, Dariusz Mierzwiński, and Kinga Korniejenko. 2021. "Fly-Ash-Based Geopolymers Reinforced by Melamine Fibers" Materials 14, no. 2: 400. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14020400
APA StyleKozub, B., Bazan, P., Mierzwiński, D., & Korniejenko, K. (2021). Fly-Ash-Based Geopolymers Reinforced by Melamine Fibers. Materials, 14(2), 400. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14020400







