Characterization of Microstructure, Chemical, and Physical Properties of Delignified and Densified Poplar Wood
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Materials
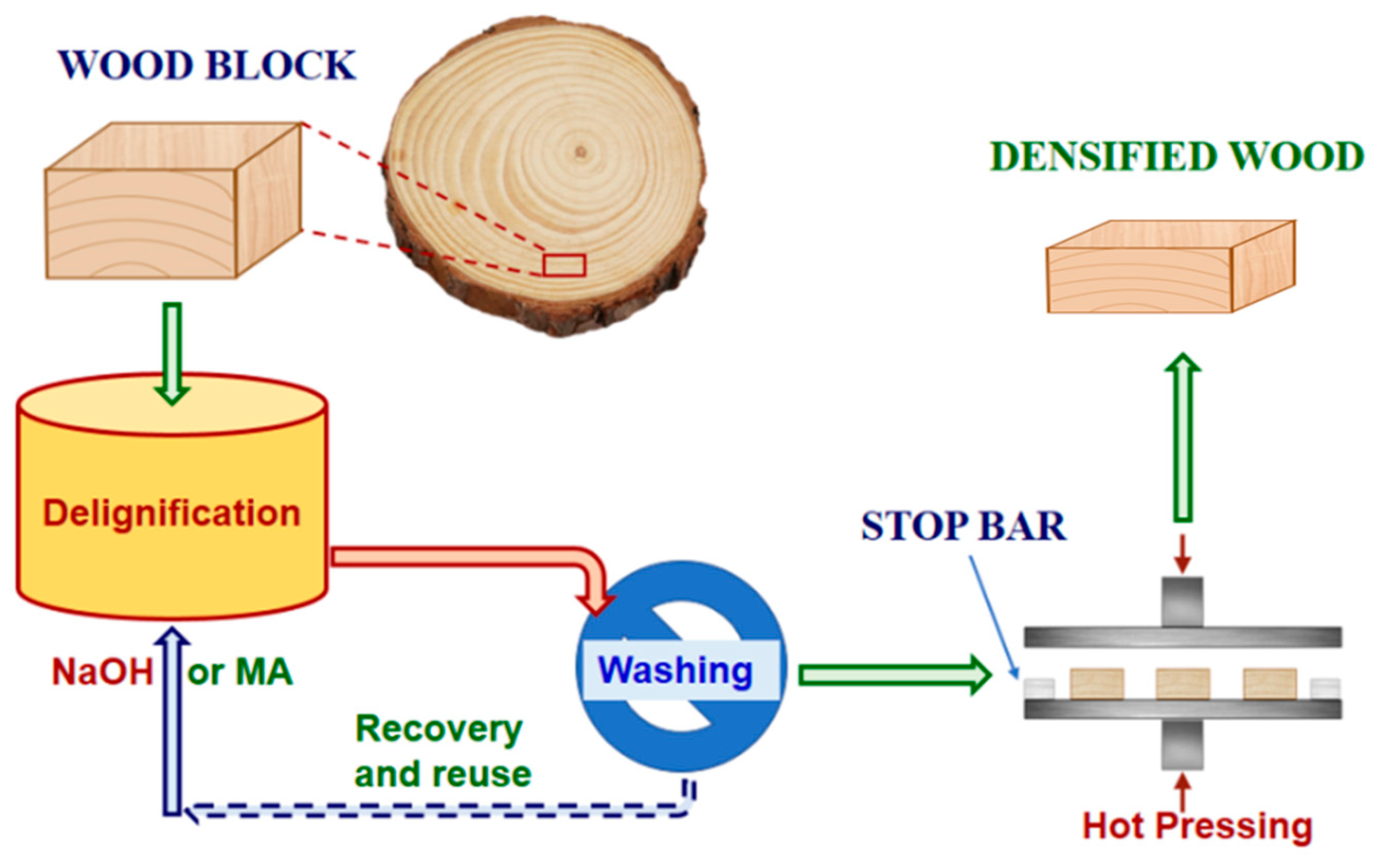
2.2. Delignification
2.3. Wood Densification
2.4. Post-Densification Hydrothermal Treatment
2.5. Analysis of Microstructure, Chemical Composition and Physical Properties
3. Results and Discussion
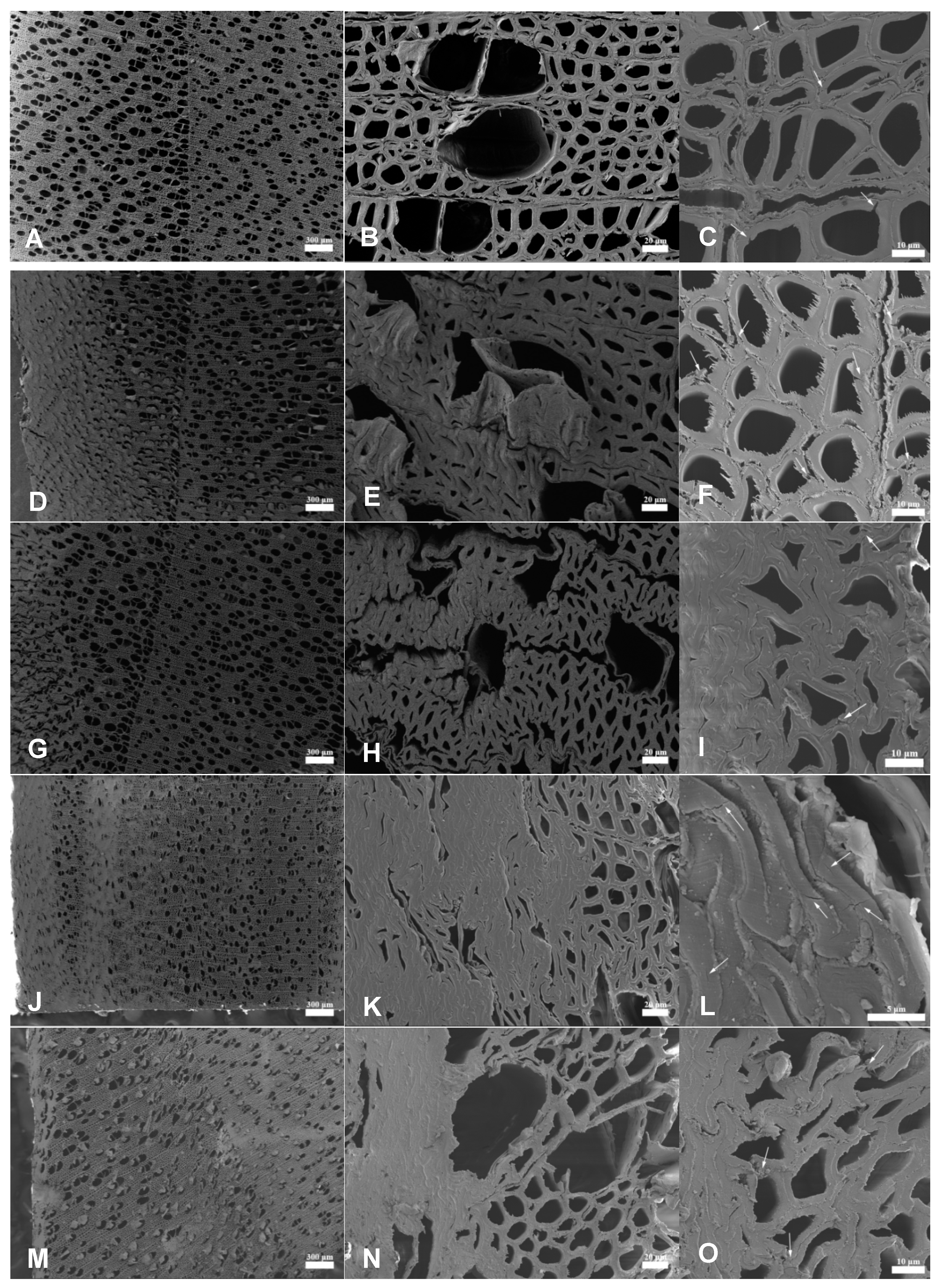
3.1. Microstructure of Densified Wood
3.2. Chemical Properties of Densified Wood
3.3. Physical Properties of Densified Wood
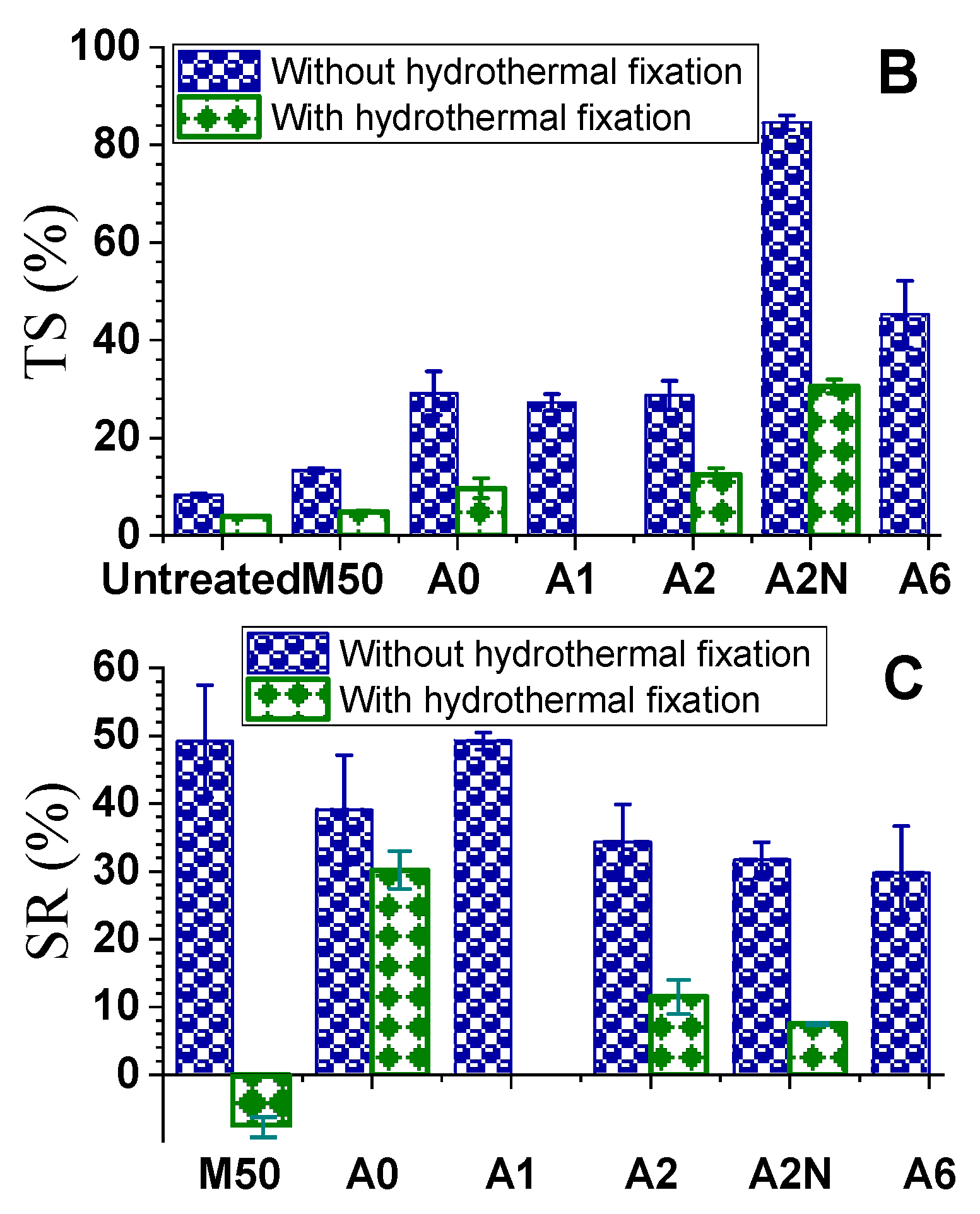
3.3.1. Dimensional Stability
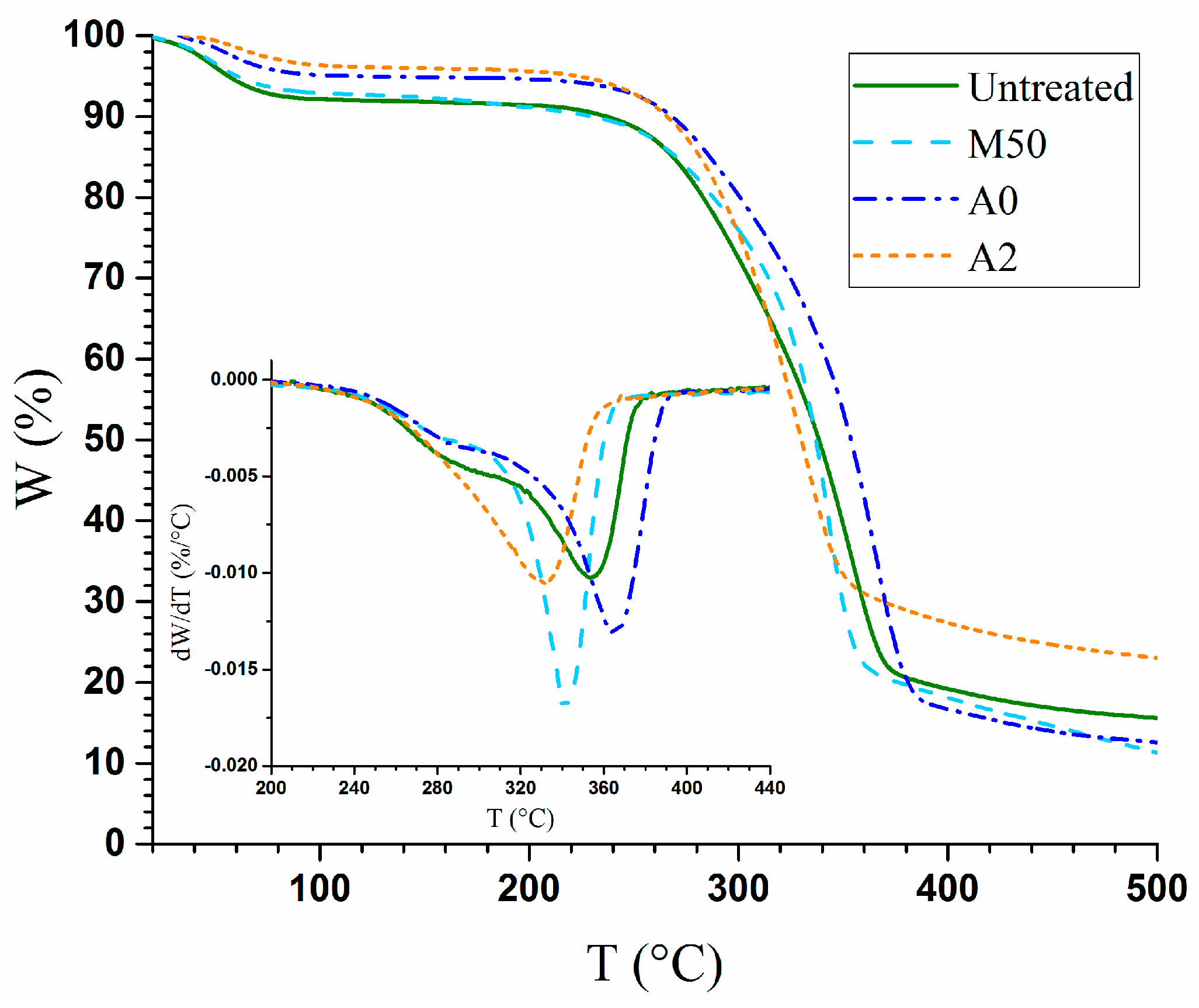
3.3.2. Thermal Stability
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Qiu, H.; Yang, S.; Han, Y.; Shen, X.; Fan, D.; Li, G.; Chu, F. Improvement of the performance of plantation wood by grafting water-soluble vinyl monomers onto cell walls. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 14450–14459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourgois, J.; Bartholin, M.C.; Guyonnet, R. Thermal treatment of wood: Analysis of the obtained product. Wood Sci. Technol. 1989, 23, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Wang, K.; Li, J.; Zhang, S.; Shi, S.Q. Environmentally benign wood modifications: A review. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 3532–3540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Song, J.; Cheng, J.; Pang, Z.; Gan, W.; Chen, G.; Kuang, Y.; Huang, H.; Ray, U.; Li, T.; et al. Highly Elastic Hydrated Cellulosic Materials with Durable Compressibility and Tunable Conductivity. ACS Nano 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tullo, A.H. Making wood last forever with acetylation. CEn 2012, 90, 22–23. [Google Scholar]
- Song, J.; Chen, C.; Zhu, S.; Zhu, M.; Dai, J.; Ray, U.; Li, Y.; Kuang, Y.; Li, Y.; Quispe, N.; et al. Processing bulk natural wood into a high-performance structural material. Nature 2018, 554, 224–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frey, M.; Widner, D.; Segmehl, J.S.; Casdorff, K.; Keplinger, T.; Burgert, I. Delignified and Densified Cellulose Bulk Materials with Excellent Tensile Properties for Sustainable Engineering. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 5030–5037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Kuang, Y.; Zhu, S.; Burgert, I.; Keplinger, T.; Gong, A.; Li, T.; Berglund, L.; Eichhorn, S.J.; Hu, L. Structure–property–function relationships of natural and engineered wood. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2020, 5, 642–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Jyske, T.; Petrič, M. Delignified Wood from Understanding the Hierarchically Aligned Cellulosic Structures to Creating Novel Functional Materials: A Review. Adv. Sustain. Syst. 2021, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donaldson, L.; Hague, J.; Snell, R. Lignin Distribution in Coppice Poplar, Linseed and Wheat Straw. Holzforschung 2001, 55, 379–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, M.; Huang, X.; Jiang, M.; Yu, W.; Yu, Y. Effect of thermo-hydro-mechanical densification on microstructure and properties of poplar wood (Populus tomentosa). J. Wood Sci. 2017, 63, 591–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navi, P.; Heger, F. Combined densification and thermo-hydro-mechanical processing of wood. MRS Bull. 2004, 29, 332–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navi, P.; Girardet, F. Effects of thermo-hydro-mechanical treatment on the structure and properties of wood. Holzforschung 2000, 54, 287–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabrielli, C.P.; Kamke, F.A. Phenol–formaldehyde impregnation of densified wood for improved dimensional stability. Wood Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchelt, B.; Dietrich, T.; Wagenführ, A. Testing of set recovery of unmodified and furfurylated densified wood by means of water storage and alternating climate tests. Holzforschung 2014, 68, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laine, K.; Segerholm, K.; Wålinder, M.; Rautkari, L.; Hughes, M. Wood densification and thermal modification: Hardness, set-recovery and micromorphology. Wood Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 883–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocaefe, D.; Huang, X.; Kocaefe, Y. Dimensional Stabilization of Wood. Curr. For. Rep. 2015, 1, 151–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, E.; Feng, S.; Yang, S.; Huang, R. Sandwich compression of wood: Effect of superheated steam treatment on sandwich compression fixation and its mechanisms. Wood Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Fishwild, S.J.; Begel, M.; Zhu, J.Y. Properties of densified poplar wood through partial delignification with alkali and acid pretreatment. J. Mater. Sci. 2020, 55, 14664–14676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, S.; Zhu, W.; Gleisner, R.; Pan, X.; Zhu, J. Comparisons of SPORL and dilute acid pretreatments for sugar and ethanol productions from aspen. Biotechnol. Prog. 2011, 27, 419–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, C.; Hirth, K.; Gleisner, R.; Lou, H.; Qiu, X.; Zhu, J.Y. Maleic acid as a dicarboxylic acid hydrotrope for sustainable fractionation of wood at atmospheric pressure and ≤100 °C: Mode and utility of lignin esterification. Green Chem. 2020, 22, 1605–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Xu, K.; Peng, H.; Jiang, J.; Zhao, R.; Lu, J. Effect of Heat Treatment on Water Absorption of Chinese fir Using TD-NMR. Appl. Sci. 2018, 9, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Laine, K.; Segerholm, K.; Walinder, M.; Rautkari, L.; Ormondroyd, G.; Hughes, M.; Jones, D. Micromorphological studies of surface densified wood. J. Mater. Sci. 2014, 49, 2027–2034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Dou, J.; Ma, Q.; Li, N.; Wu, R.; Bian, H.; Yelle, D.J.; Vuorinen, T.; Fu, S.; Pan, X.; et al. Rapid and near-complete dissolution of wood lignin at ≤ 80 °C by a recyclable acid hydrotrope. Sci. Adv. 2017, 3, e1701735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kutnar, A.; Kamke, F.A.; Sernek, M. Density profile and morphology of viscoelastic thermal compressed wood. Wood Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekhta, P.; Proszyk, S.; Krystofiak, T.; Sedliacik, J.; Novak, I.; Mamonova, M. Effects of short-term thermomechanical densification on the structure and properties of wood veneers. Wood Mater. Sci. Eng. 2015, 12, 40–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wålinder, M.; Omidvar, A.; Seltman, J.; Segerholm, K. Micromorphological studies of modified wood using a surface preparation technique based on ultraviolet laser ablation. Wood Mater. Sci. Eng. 2009, 4, 46–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, S.; Steiner, P. The Behaviour of Five Wood Species in Compression. IAWA J. 2002, 23, 201–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, M. Permanent fixation of compressive deformation by hygro-thermal treatment using moisture in wood. Wood Res Bull 1993, 29, 54–61. [Google Scholar]
- Pelit, H.; Budakçı, M.; Sönmez, A. Effects of heat post-treatment on dimensional stability and water absorption behaviours of mechanically densified Uludağ fir and black poplar woods. BioResources 2016, 11, 3215–3229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khalil, H.A.; Yusra, A.I.; Bhat, A.; Jawaid, M. Cell wall ultrastructure, anatomy, lignin distribution, and chemical composition of Malaysian cultivated kenaf fiber. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2010, 31, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delmotte, L.; Ganne-Chedeville, C.; Leban, J.-M.; Pizzi, A.; Pichelin, F. CP-MAS 13C NMR and FT-IR investigation of the degradation reactions of polymer constituents in wood welding. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2008, 93, 406–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Song, K.; Salmén, L.; Yin, Y. Changes of wood cell walls in response to hygro-mechanical steam treatment. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 115, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Yan, R.; Chen, H.; Lee, D.H.; Zheng, C. Characteristics of hemicellulose, cellulose and lignin pyrolysis. Fuel 2007, 86, 1781–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Zhu, J.Y.; Gleisner, R.; Zhan, H.Y. Effect of wet pressing-induced fiber hornification on enzymatic saccharification of lignocelluloses. Cellulose 2011, 18, 1339–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higashihara, T. Permanent fixation of transversely compressed wood by steaming and its mechanism. J. Jpn. Wood Res. Soc. 2000, 46, 291–297. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, Y.; Yan, Y.; Ma, H.; Zhang, S.; Li, J.; Xia, C.; Shi, S.Q.; Cai, L. In-situ chemosynthesis of ZnO nanoparticles to endow wood 568 with antibacterial and UV-resistance properties. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2017, 33, 266–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, U.P.; Ralph, S.A.; Reiner, R.S.; Baez, C. New cellulose crystallinity estimation method that differentiates between 570 organized and crystalline phases. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 190, 262–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamm, A.J. Thermal degradation of wood and cellulose. Ind Eng. Chem. 1956, 48, 413–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramiah, M.V. Thermogravimetric and differential thermal analysis of cellulose, hemicellulose, and lignin. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1970, 14, 1323–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popescu, M.-C.; Lisa, G.; Froidevaux, J.; Navi, P.; Popescu, C.-M. Evaluation of the thermal stability and set recovery of thermo-hydro-mechanically treated lime (Tilia cordata) wood. Wood Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 85–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Chen, C.; Pei, Y.; He, S.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, B.; Jiao, M.; Gan, W.; Liu, D.; Yang, B.; et al. A strong, flame-retardant, and thermally insulating wood laminate. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 383, 123109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Sample | Delignification, Densification | Chemical Composition | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T (°C) | Time (min) | Stop bar | Density (g/cm3) | Solids Yield (%) | K Lignin (%) | Glucan (%) | Xylan (%) | Mannan (%) | |
| Untreated | — | — | — | 0.463 | 100 | 23.6 (100) | 45.2 (100) | 18.4 (100) | 3.2 (100) |
| A0 | 155 | 30 | Yes | 0.554 | 95.2 | 25.9 (101) | 47.0 (99) | 17.9 (92) | 3.3 (91) |
| A1 | 155 | 30 | Yes | 0.511 | 90.4 | 22.3 (86) | 51.5 (103) | 18.8 (92) | 2.7 (85) |
| A2 | 155 | 30 | Yes | 0.536 | 86.7 | 24.6 (90) | 48.7 (94) | 17.9 (84) | 2.3 (79) |
| A2N | 155 | 30 | No | 0.811 | — | — | — | — | — |
| A6 | 155 | 30 | Yes | 0.569 | 74.3 | 19.9 (63) | 56.1 (92) | 16.2 (65) | 1.3 (57) |
| M50 | 100 | 60 | Yes | 0.507 | 98.0 | 24.5 (102) | 50.5 (110) | 18.2 (97) | 3.6 (96) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, J.; Liu, J.; Li, J.; Zhu, J.Y. Characterization of Microstructure, Chemical, and Physical Properties of Delignified and Densified Poplar Wood. Materials 2021, 14, 5709. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14195709
Wang J, Liu J, Li J, Zhu JY. Characterization of Microstructure, Chemical, and Physical Properties of Delignified and Densified Poplar Wood. Materials. 2021; 14(19):5709. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14195709
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Jiajun, Junliang Liu, Jianzhang Li, and J. Y. Zhu. 2021. "Characterization of Microstructure, Chemical, and Physical Properties of Delignified and Densified Poplar Wood" Materials 14, no. 19: 5709. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14195709
APA StyleWang, J., Liu, J., Li, J., & Zhu, J. Y. (2021). Characterization of Microstructure, Chemical, and Physical Properties of Delignified and Densified Poplar Wood. Materials, 14(19), 5709. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14195709






