Microstructures and Electrical Conduction Behaviors of Gd/Cr Codoped Bi3TiNbO9 Aurivillius Phase Ceramic
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Sample Preparation
2.2. Sample Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
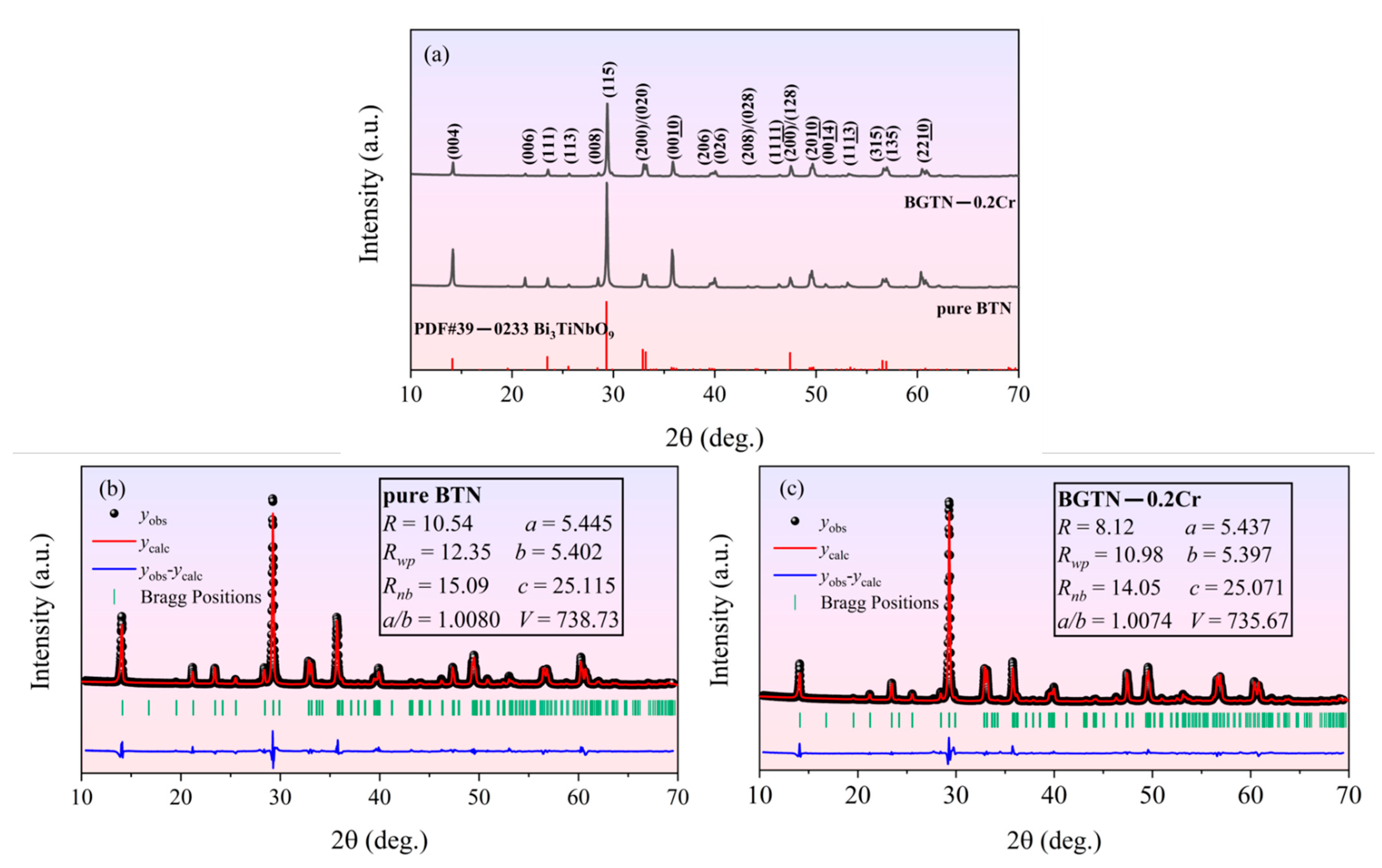
3.1. Phase Structure of Ceramics
3.2. Grain Morphology and Chemical Composition of Ceramics
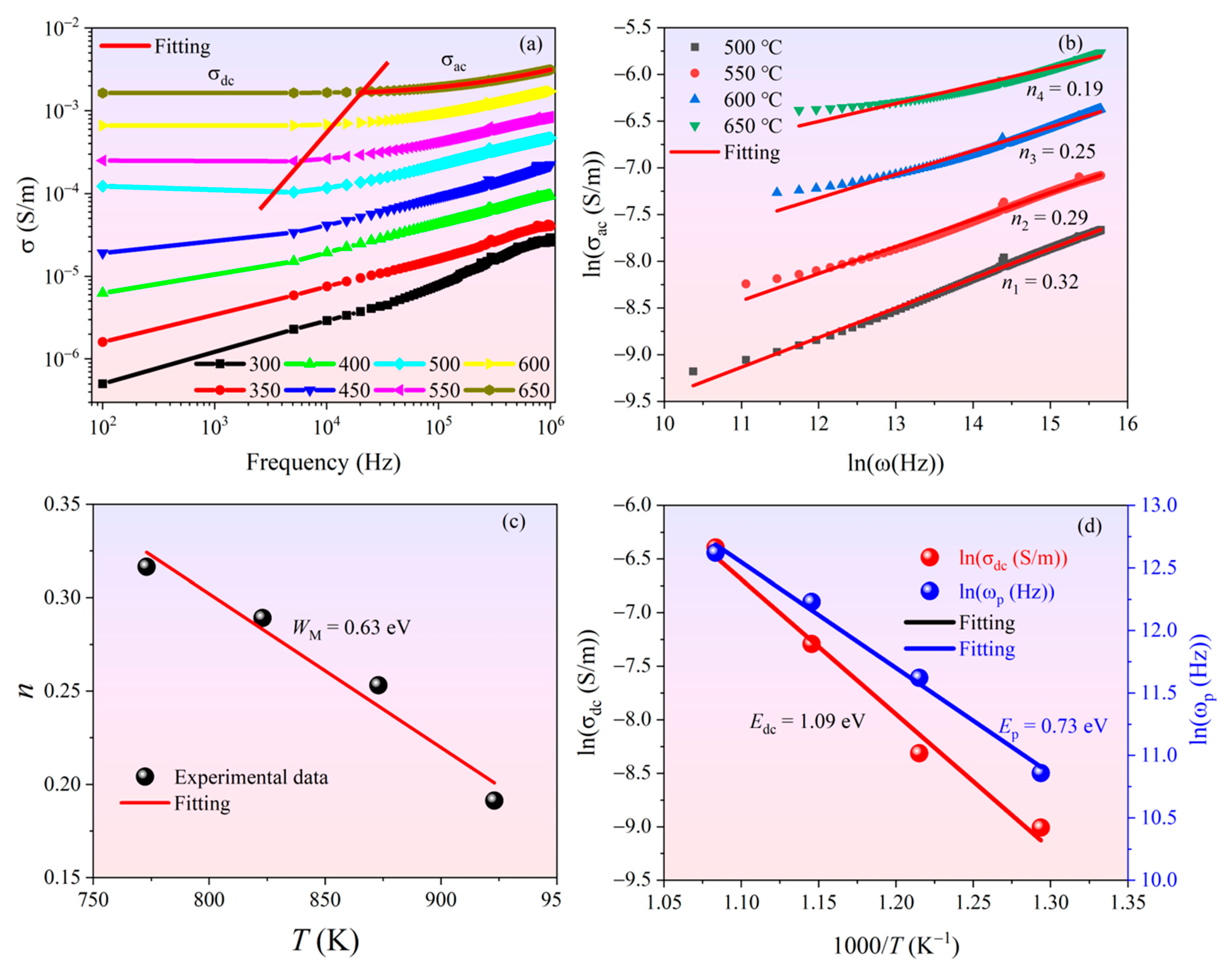
3.3. Electrical Conduction Behaviors of Ceramics
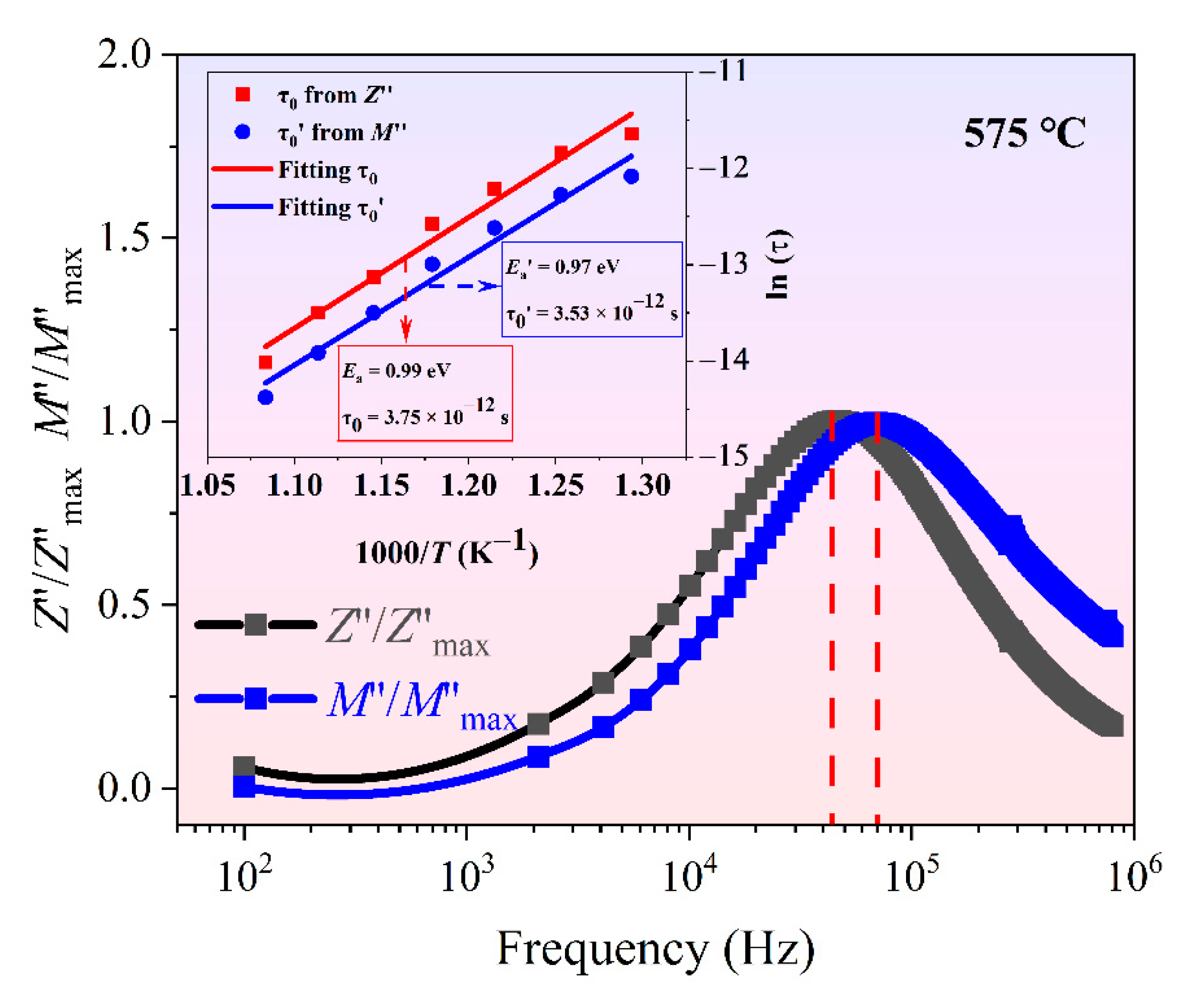
3.4. Electrical Impedance Spectroscopy of Ceramics
3.5. Electrical Modulus Spectroscopy of Ceramics
3.6. Electromechanical Resonance Spectroscopy of Ceramics
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Subbarao, E.C. Crystal Chemistry of Mixed Bismuth Oxides with Layer-Type Structure. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1962, 45, 166–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aurivillius, B. Mixed Bismuth Oxides with Layer Lattices: I. Arkiv Kemi 1949, 1, 463–480. [Google Scholar]
- Newnham, R.E.; Wolfe, R.W.; Dorrian, J.F. Structural basis of ferroelectricity in the bismuth titanate family. Pergamon 1971, 6, 1029–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardo, L.; Castro, A.; Millan, P.; Alemany, C.; Jimenez, R.; Jimenez, B. (Bi3TiNbO9)x(SrBi2Nb2O9)1−x aurivillius type structure piezoelectric ceramics obtained from mechanochemically activated oxides. Acta Mater. 2000, 48, 2421–2428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.H.; Trolier-McKinstry, S.; Messing, G.L. Dielectric and Electromechanical Properties of Textured Niobium—Doped Bismuth Titanate Ceramics. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2000, 83, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Araujo, C.P.; Cuchiaro, J.D.; McMillan, L.D.; Scott, M.C.; Scott, J.F. Fatigue−free ferroelectric capacitors with platinum electrodes. Nature 1995, 374, 627–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shulman, H.S.; Testorf, M.; Damjanovic, D.; Setter, N. Microstructure, Electrical Conductivity, and Piezoelectric Properties of Bismuth Titanate. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1996, 79, 3124–3128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, J.G.; Rae, A.D.; Withers, R.L.; Craig, D.C. Revised structure of Bi3TiNbO9. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. B 1991, 47, 174–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Yan, H.X.; Dong, X.L.; Wang, Y.L. Preparation and electrical properties of bismuth layer−structured ceramic Bi3NbTiO9 solid solution. Mater. Res. Bull. 2003, 38, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moure, A.; Pardo, L.; Alemany, C.; Millán, P.; Castro, A. Piezoelectric ceramics based on Bi3 TiNbO9 from mechanochemically activated precursors. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2001, 21, 1399–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolfe, R.W.; Newnham, R.E.; Smith, D. Crystal structure of Bi3TiNbO9. Ferroelectrics 1972, 3, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Withers, R.L.; Thompson, J.G.; Rae, A.D. The crystal chemistry underlying ferroelectricity in Bi4Ti3O12, Bi3TiNbO9, and Bi2WO6. J. Solid. State. Chem. 1991, 94, 404–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Nie, R.; Chen, Q.; Xiao, D.; Zhu, J. Structural distortion, piezoelectric properties, and electric resistivity of A-site substituted Bi3TiNbO9-based high-temperature piezoceramics. Mater. Res. Bull. 2019, 115, 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricote, J.; Pardo, L.; Moure, A.; Castro, A.; Millán, P.; Chateigner, D. Microcharacterisation of grain-oriented ceramics based on Bi3TiNbO9 obtained from mechanochemically activated precursors. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2001, 21, 1403–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Yan, H.X.; Dong, X.L.; Wang, Y.L. Structural and electrical properties of Bi3NbTiO9 solid solution. J. Inorg. Mater. 2003, 18, 1377–1380. [Google Scholar]
- Lisiñska-Czekaj, A.; Czekaj, D.; Gomes, M.J.M.; Kuprianov, M.F. Investigations on the synthesis of Bi3NbTiO9 ceramics. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 1999, 19, 969–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Yan, H.X.; Dong, X.L.; Xiang, P. Grain orientation effects on the properties of a bismuth layer-structured ferroelectric (BLSF) Bi3NbTiO9 solid solution. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2004, 87, 602–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moure, A.; Pardo, L. Microstructure and texture dependence of the dielectric anomalies and dc conductivity of Bi3TiNbO9 ferroelectric ceramics. J. Appl. Phys. 2005, 97, 084103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peng, Z.H.; Yan, D.X.; Chen, Q.; Xin, D. Crystal structure, dielectric and piezoelectric properties of Ta/W codoped Bi3TiNbO9 Aurivillius phase ceramics. Curr. Appl. Phys. 2014, 14, 1861–1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekhtin, M.A.; Bush, A.A.; Kamentsev, K.E.; Segalla, A.G. Preparation and Dielectric and Piezoelectric Properties of Bi3TiNbO9, Bi2CaNb2O9, and Bi2.5Na0.5Nb2O9 Ceramics Doped with Various Elements. Neorg. Mater. 2016, 52, 557–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.Q.; Wahyudi, O.; Liu, Z.F.; Gu, H. Preparation and electrical properties of a new−type intergrowth bismuth layer−structured (Bi3TiNbO9)1(Bi4Ti3O12)2 ceramics. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 753, 54–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zubkov, S.V. Crystal structure and dielectric properties of layered perovskite−like solid solutions Bi3−xGdxTiNbO9 (x = 0, 0.1, 0.2, 0.3) with high Curie temperature. J. Adv. Dielectr. 2020, 10, 2060002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Groń, T.; Maciejkowicz, M.; Tomaszewicz, E.; Guzik, M.; Oboz, M.; Sawicki, B.; Pawlus, S.; Nowok, A.; Kukuła, Z. Combustion synthesis, structural, magnetic and dielectric properties of Gd3+−doped lead molybdato-tungstates. J.Adv. Ceram. 2020, 9, 255–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, Y.; Peng, Z.H.; Wang, Q.Y.; Zhu, J. Crystalline structure, ferroelectric properties, and electrical conduction characteristics of W/Cr co−doped Bi4Ti3O12 ceramics. J. Alloys Compd. 2014, 612, 120–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Liang, D.Y.; Wang, Q.Y.; Zhu, J. Microstructures, dielectric, and piezoelectric properties of W/Cr co−doped Bi4Ti3O12 ceramics. J. Appl. Phys. 2014, 116, 074108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.N.; Zhang, Y.H.; Huang, P.M.; Li, X. Enhanced piezoelectric properties and thermal stability in Mo/Cr co−doped CaBi2Nb2O9 high-temperature piezoelectric ceramics. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2020, 136, 109195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onoe, M.; Jumonji, H. Useful formulas for piezoelectric ceramic resonators and their application to measurement of parameters. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1967, 41, 974–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.F.; Chen, I.W. Ferroelectric thin films of bismuth-containing layered perovskites: Part II, PbBi2Nb2O9. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1998, 81, 3260–3264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Yang, M.J.; Park, J.S.; Wei, S.-H.; Berry, J.J.; Zhu, K. Stabilizing Perovskite Structures by Tuning Tolerance Factor: Formation of Formamidinium and Cesium Lead Iodide Solid−State Alloys. Chem. Mater. 2016, 28, 284–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.M.; Wang, J.F.; Zhang, S.J.; Shrout, T.R. Electromechanical properties of A−site (LiCe)−modified sodium bismuth titanate (Na0.5Bi4.5Ti4O15) piezoelectric ceramics at elevated temperature. J. Appl. Phys. 2009, 105, 094110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Z.H.; Chen, Q.; Chen, Y.; Xiao, D. Microstructure and electrical properties in W/Nb co−doped Aurivillius phase Bi4Ti3O12 piezoelectric ceramics. Mater. Res. Bull. 2014, 59, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonscher, A.K. Dielectric relaxation in solids. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 1999, 32, R57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonscher, A.K. The ‘universal’ dielectric response. Nature 1977, 267, 673–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, S.R. Temperature dependence of ac conductivity of chalcogenide glasses. Philos. Mag. B 1978, 37, 553–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, C.B.; Karoui, K.; Saidi, S.; Guidara, K.; Rhaiem, A.B. Electrical properties, phase transitions and conduction mechanisms of the [(C2H5)NH3]2CdCl4 compound. Phys. B Condens. Matter. 2014, 451, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, G.; Tiwari, V.S.; Gupta, P.K. Role of oxygen vacancies on relaxation and conduction behavior of KNbO3 ceramic. J. Appl. Phys. 2010, 107, 064103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, P.; Badapanda, T.; Singh, A.K.; Panigrahi, S. Possible relaxation and conduction mechanism in W6+ doped SrBi4Ti4O15 ceramic. Ceram. Int. 2017, 43, 4527–4535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.T.; Yan, H.X.; Reece, M.J. The effect of Nd substitution on the electrical properties of Bi3NbTiO9 Aurivillius phase ceramics. J. Appl. Phys. 2009, 106, 044106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almond, D.P.; Duncan, G.K.; West, A.R. The determination of hopping rates and carrier concentrations in ionic conductors by a new analysis of ac conductivity. Solid State Ion. 1983, 8, 159–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, R.C.; Fuierer, P.A.; Newnham, R.E.; Shrout, T.R. Materials for high temperature acoustic and vibration sensors: A review. Appl. Acoust. 1994, 41, 299–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Hao, J.; Du, J.; Fu, P.; Sun, W.; Chen, C.; Xu, Z.; Chu, R. Electrical properties and luminescence properties of 0.96(K0.48Na0.52)(Nb0.95Sb0.05)–0.04Bi0.5(Na0.82K0.18)0.5ZrO3–xSm lead−free ceramics. J. Adv. Ceram. 2020, 9, 72–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sumi, S.; Raon, P.P.; Koshy, P. Impedance spectroscopic investigation on electrical conduction and relaxation in manganese substituted pyrochlore type semicon−ducting oxides. Ceram. Int. 2015, 41, 5992–5998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, F.; Li, J.B.; Dou, Y.K.; Zhang, J.S.; Zhao, Y.J.; Rizwan, M.; Khalid, S.; Jin, H.B. Dielectric relaxations and electrical properties of Aurivillius Bi3.5La0.5Ti2Fe0.5Nb0.5O12 Ceramics. J. Alloys Compd. 2016, 654, 315–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, Y.J.; Hassan, J.; Hashim, M. Dielectric properties, impedance analysis and modulus behavior of CaTiO3 ceramics prepared by solid state reaction. J. Alloys Compd. 2013, 571, 138–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrison, F.D.; Sinclair, D.C.; West, A.R. Characterization of Lanthanum-doped barium titanate ceramics using impedance spectroscopy. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2001, 84, 531–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahamoud, H.; Louati, B.; Hlel, F.; Guidara, K. Impedance and modulus analysis of the (Na0.6Ag0.4)2PbP2O7 compound. J. Alloys Compd. 2011, 509, 6083–6089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, S.K.; Dey, P.; Nath, T.K. Structural, electrical and dielectric properties of La0.7Sr0.3MnO3–ErMnO3 multiferroic composites. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2014, 181, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanty, V.; Cheruku, R.; Vijayan, L.; Govindaraj, G. Ce-substituted lithium ferrite: Preparation and electrical relaxation studies. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2014, 30, 335–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zurbuchen, M.A.; Sherman, V.O.; Tagantsev, A.K.; Schubert, J.; Hawley, M.E.; Fong, D.D.; Streiffer, S.K.; Jia, Y.; Tian, W.; Schlom, G. Synthesis, structure, and electrical behavior of Sr4Bi4Ti7O24. J. Appl. Phys. 2010, 107, 024106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]






Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, H.; Wang, S.; Wu, D.; Chen, Q.; Chen, Y. Microstructures and Electrical Conduction Behaviors of Gd/Cr Codoped Bi3TiNbO9 Aurivillius Phase Ceramic. Materials 2021, 14, 5598. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14195598
Zhou H, Wang S, Wu D, Chen Q, Chen Y. Microstructures and Electrical Conduction Behaviors of Gd/Cr Codoped Bi3TiNbO9 Aurivillius Phase Ceramic. Materials. 2021; 14(19):5598. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14195598
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Huajiang, Shaozhao Wang, Daowen Wu, Qiang Chen, and Yu Chen. 2021. "Microstructures and Electrical Conduction Behaviors of Gd/Cr Codoped Bi3TiNbO9 Aurivillius Phase Ceramic" Materials 14, no. 19: 5598. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14195598
APA StyleZhou, H., Wang, S., Wu, D., Chen, Q., & Chen, Y. (2021). Microstructures and Electrical Conduction Behaviors of Gd/Cr Codoped Bi3TiNbO9 Aurivillius Phase Ceramic. Materials, 14(19), 5598. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14195598







