Therapeutic Efficacy of Artificial Skin Produced by 3D Bioprinting
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
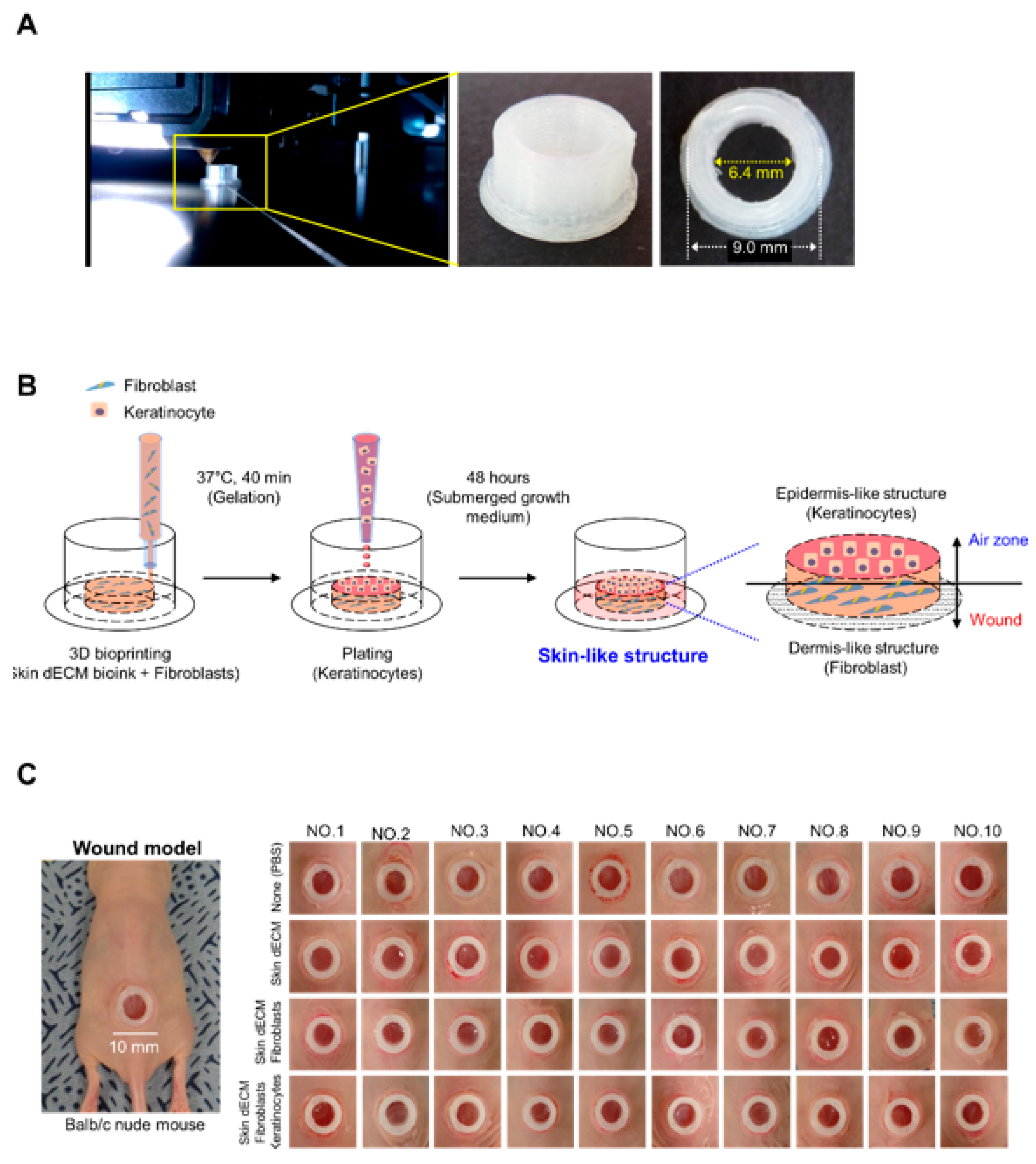
2.1. Fabrication of Chimney Structures Using a 3D Printer
2.2. Production of Artificial Skin with Skin dECM and Human Cells
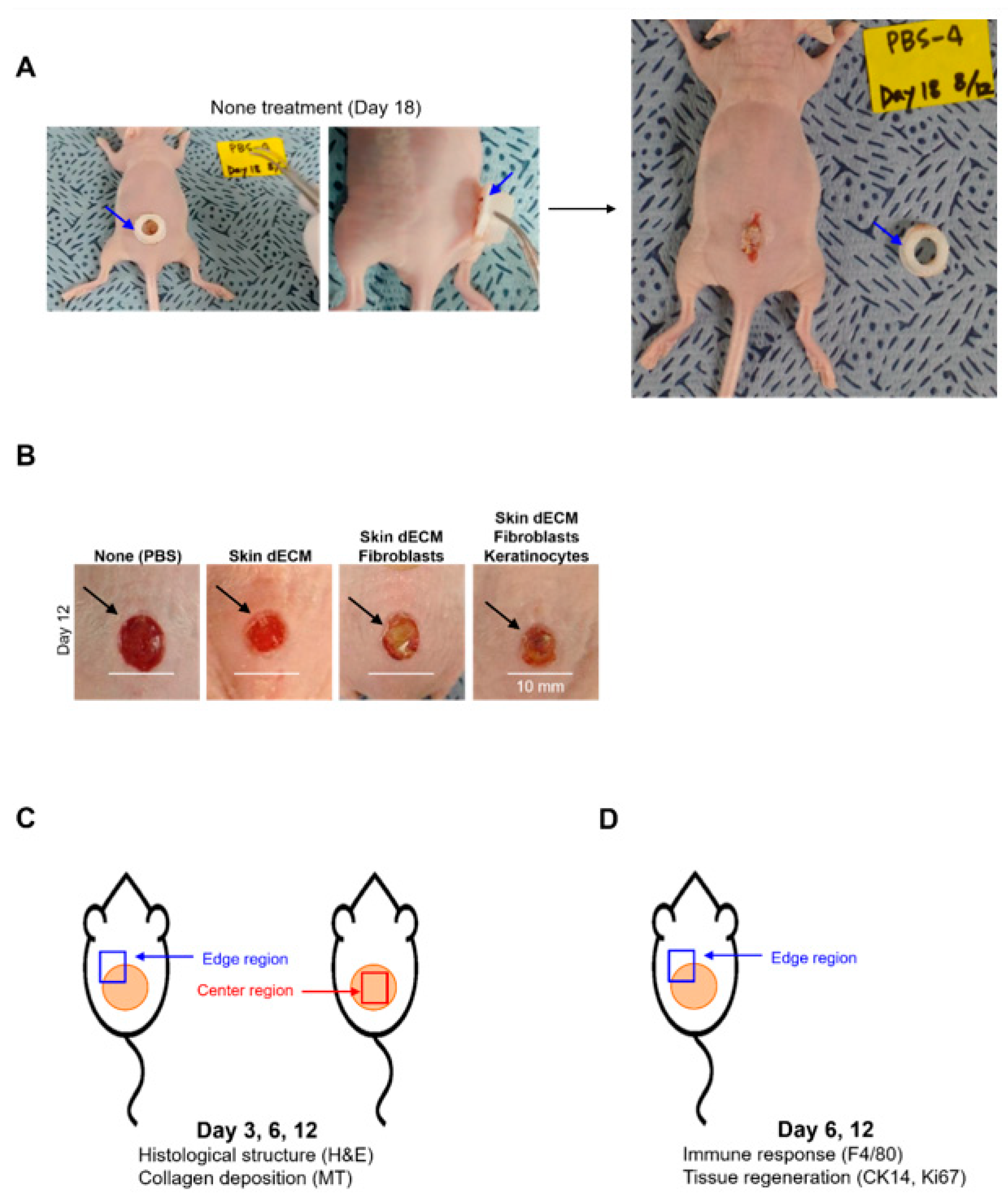
2.3. Generation of the Mouse Chimney Wound Model
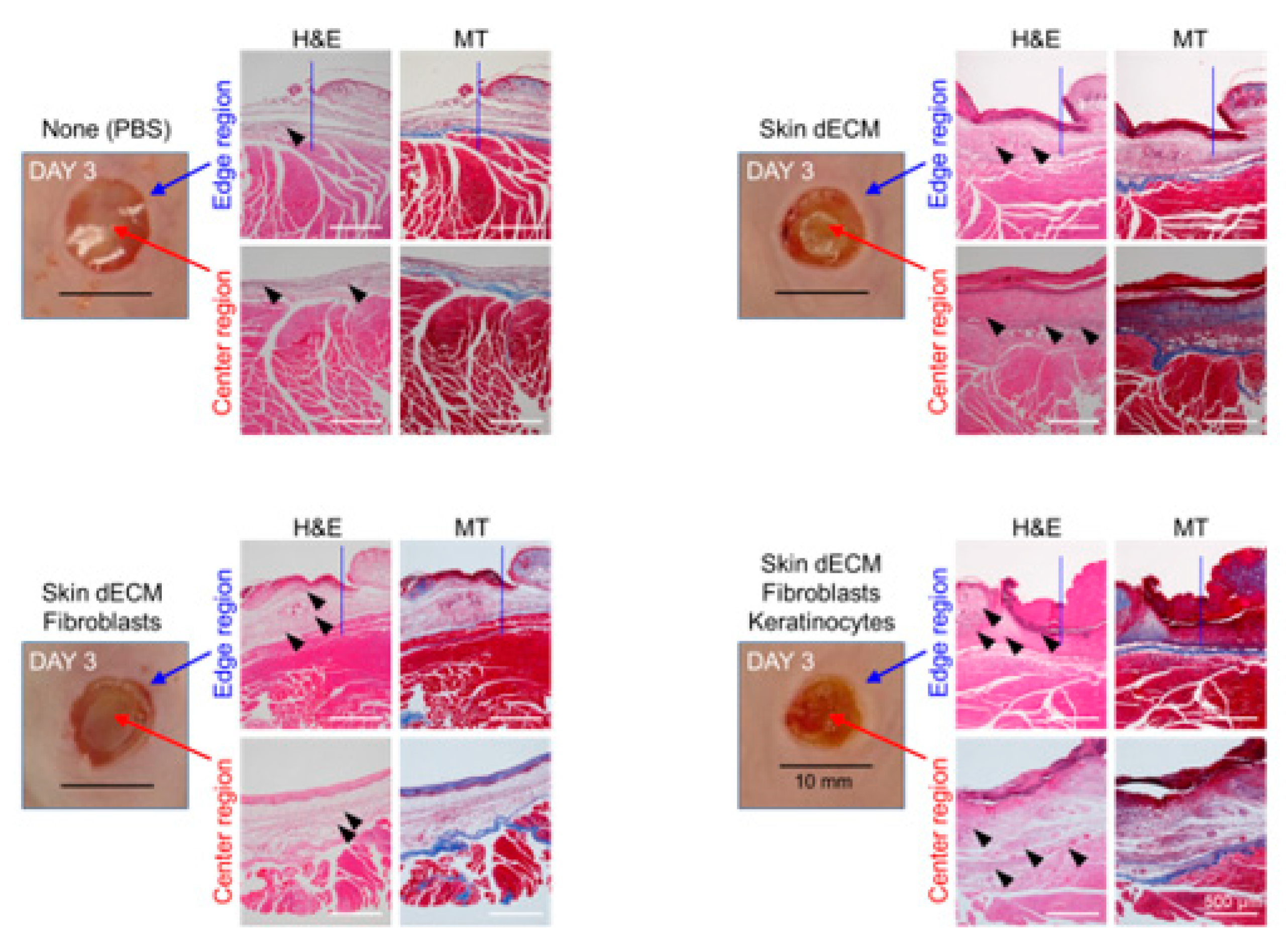
2.4. Histological Analysis (Staining Using Hematoxylin and Eosin (H&E)/Masson′s Trichrome Stain) and Immunohistochemistry Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
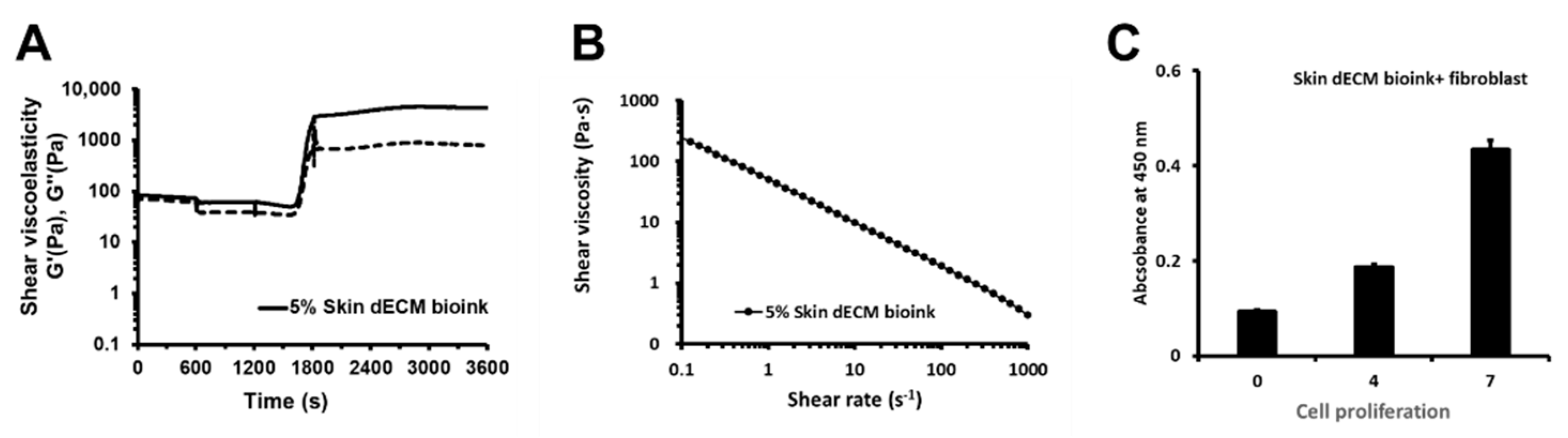
3.1. Properties of the Bioink and the Cell Proliferation of the 3D-Printed Skin Bioink
3.2. Development of a Skin-Tissue-Manufacturing Technology Using 3D Bioprinting
3.3. Optimization and Experiment Strategy of Chimney Wound Model
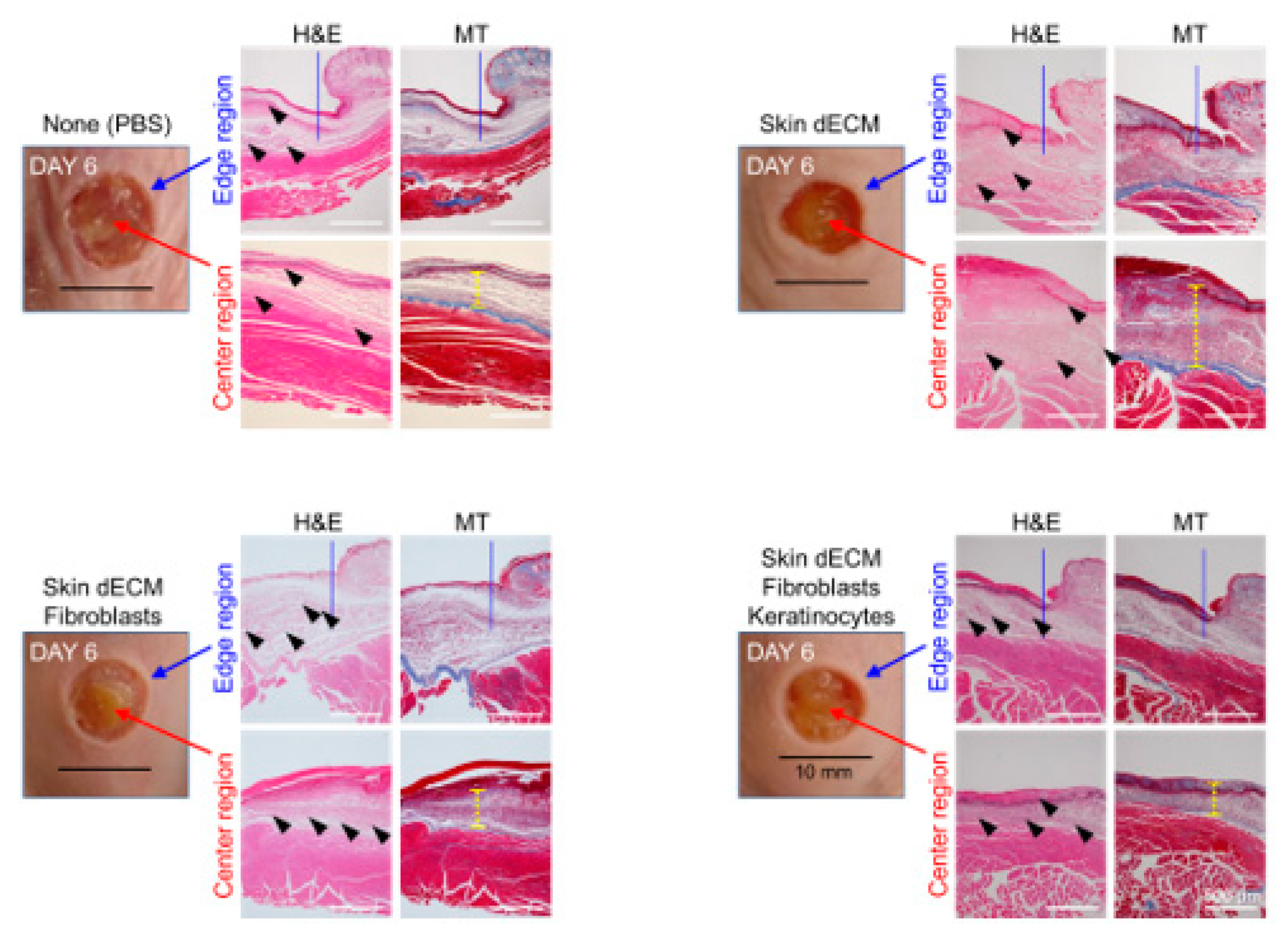
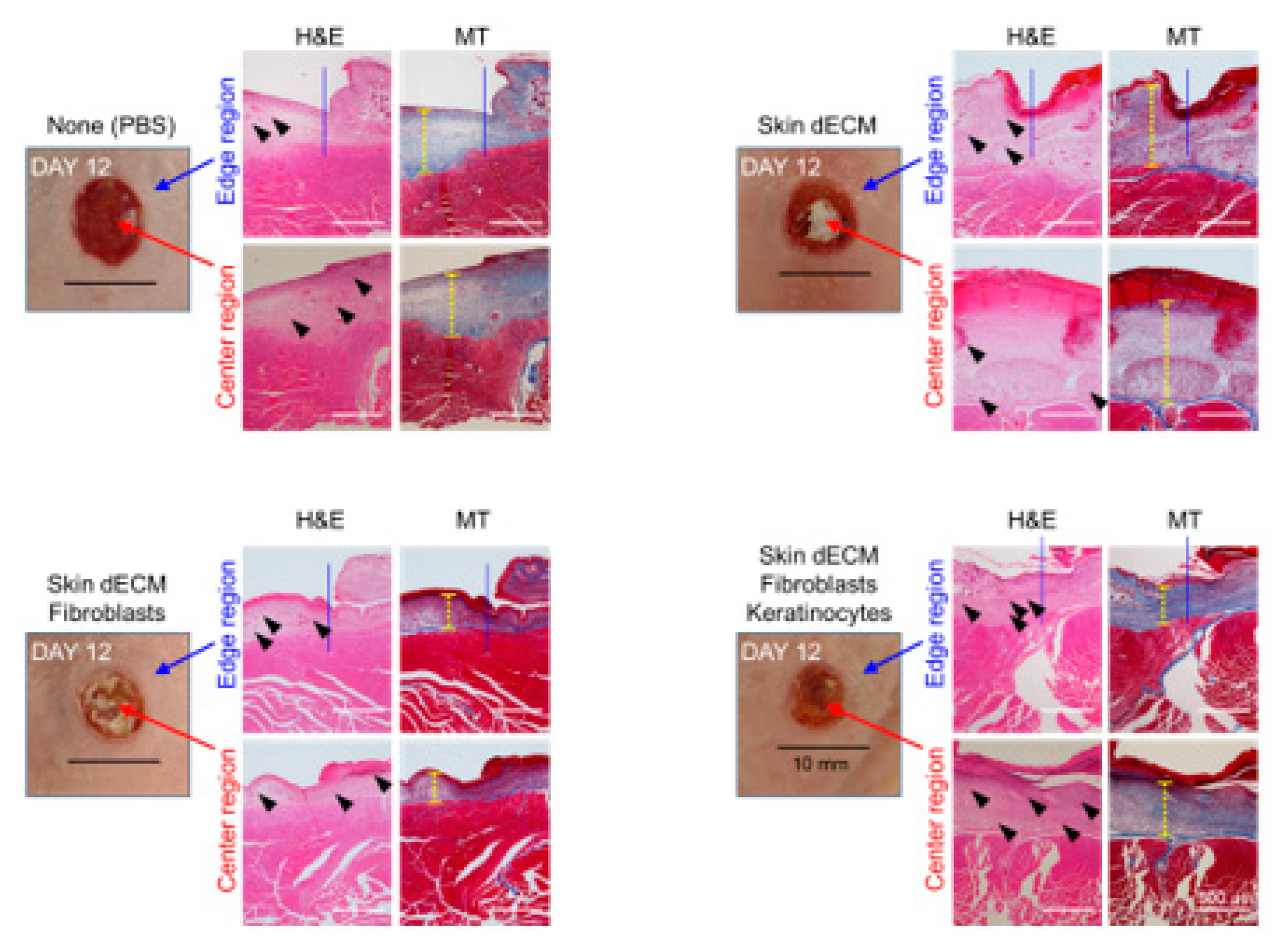
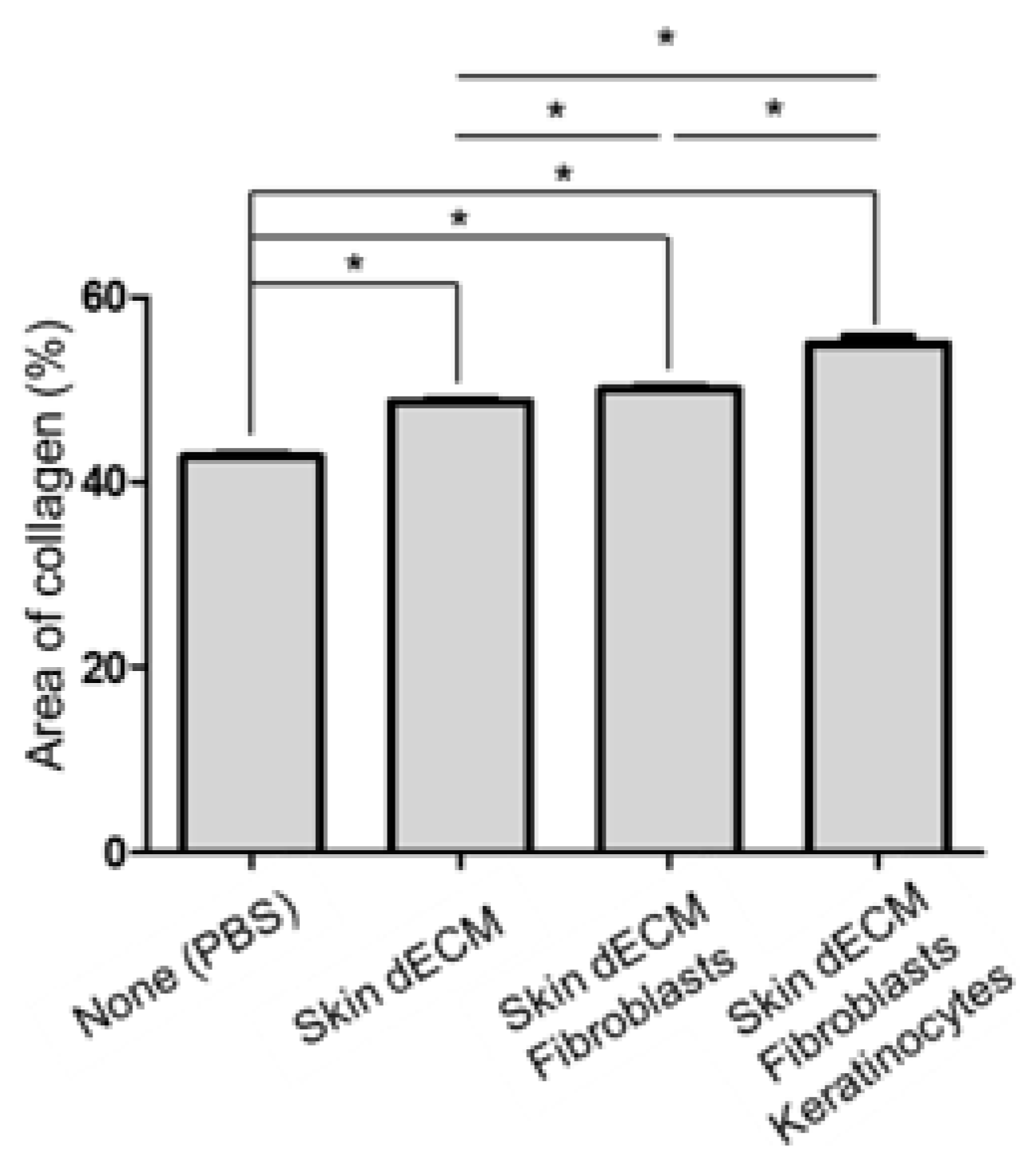
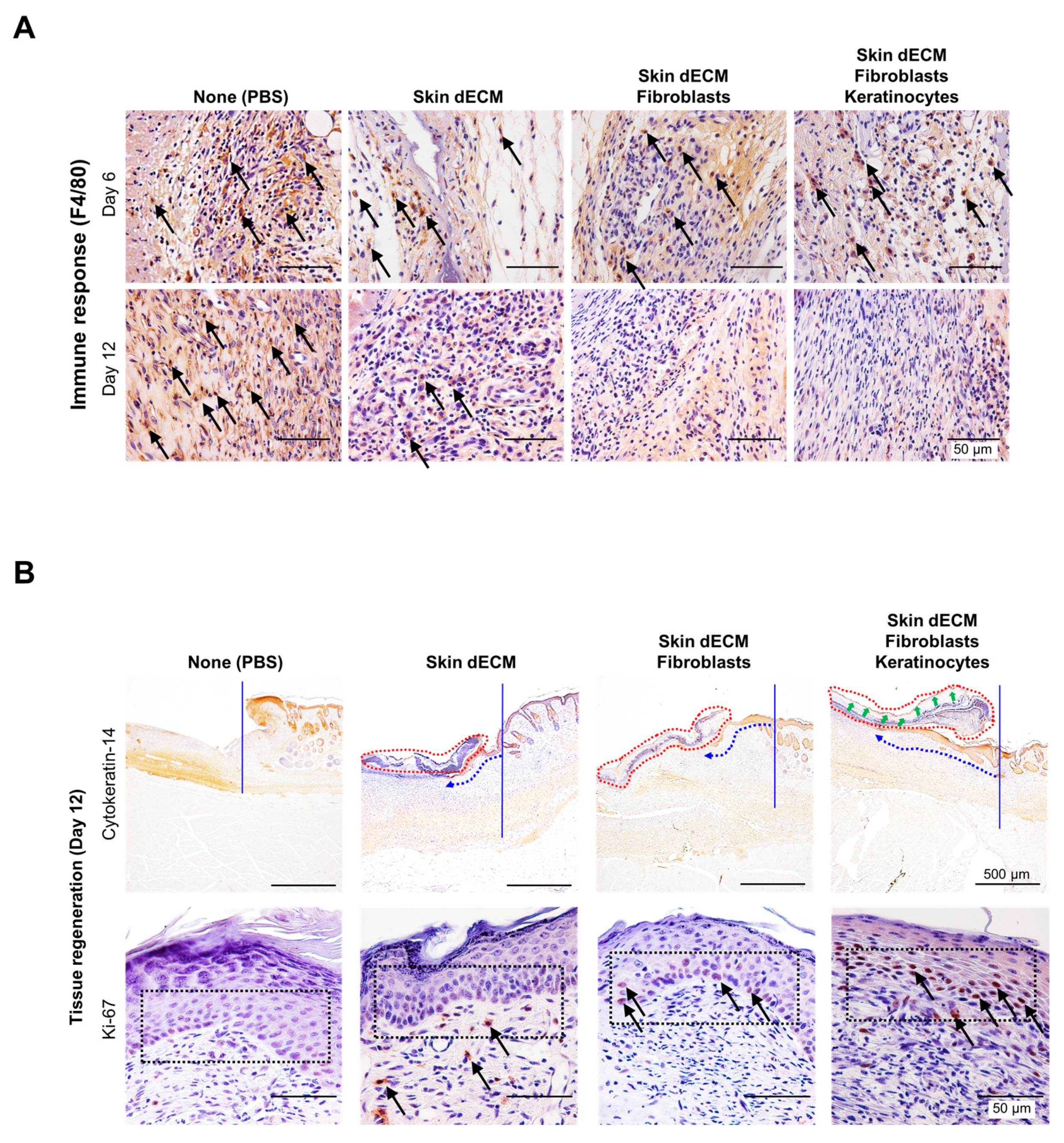
3.4. Histological Analyses of Wound Tissues in the Chimney Model
3.5. Therapeutic Effects of the 3D-Printed Artificial Skin
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Perez-Valle, A.; Amo, C.D.; Andia, I. Overview of Current Advances in Extrusion Bioprinting for Skin Applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurtner, G.C.; Werner, S.; Barrandon, Y.; Longaker, M.T. Wound repair and regeneration. Nature 2008, 453, 314–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuna, V.K.; Padma, A.M.; Håkansson, J.; Nygren, J.; Sjöback, R.; Petronis, S.; Sumitran-Holgersson, S. Significantly Accelerated Wound Healing of Full-Thickness Skin Using a Novel Composite Gel of Porcine Acellular Dermal Matrix and Human Peripheral Blood Cells. Cell Transplant. 2017, 26, 293–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, P.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, J.; Li, B.; Gou, Z.; Gou, M.; Li, X. Bioprinting of skin constructs for wound healing. Burns Trauma. 2018, 6, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- van Kogelenberg, S.; Yue, Z.; Dinoro, J.N.; Baker, C.S.; Wallace, G.G. Three-Dimensional Printing and Cell Therapy for Wound Repair. Adv. Wound Care. 2018, 7, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hrabchak, C.; Flynn, L.; Woodhouse, K.A. Biological skin substitutes for wound cover and closure. Expert. Rev. Med. Devices. 2006, 3, 373–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirchmager, D.M.; Iii, R.G.; in het Panhuis, M. An overview of the suitability of hydrogel-forming polymers for extrusion-based 3D-printing. J. Mater. Chem. B. 2015, 3, 4105–4117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Won, H.-R.; Seo, C.; Lee, H.-Y.; Roh, J.; Kim, C.-H.; Jang, J.Y.; Shin, Y.S. An Important Role of Macrophages for Wound Margin Regeneration in a Murine Flap Model. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2019, 16, 667–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzobo, K.; M Motaung, K.S.C.; Adesida, A. Recent Trends in Decellularized Extracellular Matrix Bioinks for 3D Printing: An Updated Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jorgensen, A.M.; Varkey, M.; Gorkun, A.; Clouse, C.; Xu, L.; Chou, Z.; Murphy, S.V.; Molnar, J.; Lee, S.J.; Yoo, J.J.; et al. Bioprinted Skin Recapitulates Normal Collagen Remodeling in Full-Thickness Wounds. Tissue Eng. Part. A 2020, 26, 516–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, G.; Min, K.-H.; Kim, C.; Lee, J.-S.; Kang, D.; Won, J.-Y.; Cho, D.-W.; Kim, J.-Y.; Jin, S.; Yun, W.-S.; et al. Precise stacking of decellularized extracellular matrix based 3D cell-laden constructs by a 3D cell printing system equipped with heating modules. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 8624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pati, F.; Jang, J.; Ha, D.-H.; Kim, S.W.; Rhie, J.-W.; Shim, J.-H.; Kim, D.-H.; Cho, D.-W. Printing three-dimensional tissue analogues with decellularized extracellular matrix bioink. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ouyang, L.; Yao, R.; Zhao, Y.; Sun, W. Effect of bioink properties on printability and cell viability for 3D bioplotting of embryonic stem cells. Biofabrication 2016, 8, 035020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Won, J.-Y.; Lee, M.-H.; Kim, M.-J.; Min, K.-H.; Ahn, G.; Han, J.-S.; Jin, S.; Yun, W.-S.; Shim, J.-H. A potential dermal substitute using decellularized dermis extracellular matrix derived bio-ink. Artif. Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 2019, 47, 644–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gungor-Ozkerim, P.S.; Inci, I.; Zhang, Y.S.; Khademhosseini, A.; Dokmeci, M.R. Bioinks for 3D bioprinting: An overview. Biomater. Sci. 2018, 6, 915–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yi, S.; Ding, F.; Gong, L.; Gu, X. Extracellular Matrix Scaffolds for Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine. Curr. Stem. Cell Res. Ther. 2017, 12, 233–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Z.; Guo, X.; Yu, N.; Zeng, A.; Si, L.; Long, F.; Zhang, W.; Wang, X.; Zhu, L.; Liu, Z. The Application of Decellularized Adipose Tissue Promotes Wound Healing. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2020, 17, 863–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, J.; Park, S.-J.; Choi, J.-J.; Kang, S.-W.; Lim, J.-J.; Lee, H.-J.; Kim, J.-S.; Yang, H.-M.; Kim, S.-J.; Kim, E.-Y.; et al. Examination of endothelial cell-induced epidermal regeneration in a mice-based chimney wound model. Wound Repair Regen. 2016, 24, 686–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.S.; Lee, J.-S.; Gao, G.; Cho, D.-W. Direct 3D cell-printing of human skin with functional transwell system. Biofabrication 2017, 9, 025034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, D.; Hong, G.; An, S.; Jang, I.; Yun, W.-S.; Shim, J.-H.; Jin, S. Bioprinting of Multiscaled Hepatic Lobules within a Highly Vascularized Construct. Small 2020, 16, e1905505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.-J.; Park, J.; Kim, E.M.; Choi, J.-J.; Kim, H.-N.; Chin, I.L.; Choi, Y.S.; Moon, S.-H.; Shin, H. Lotus seedpod-inspired hydrogels as an all-in-one platform for culture and delivery of stem cell spheroids. Biomaterials 2019, 225, 119534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landén, N.X.; Li, D.; Ståhle, M. Transition from inflammation to proliferation: A critical step during wound healing. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2016, 73, 3861–3885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, H.-M.; Choi, J.-J.; Kim, H.-N.; Yang, S.J.; Park, S.-J.; Kang, C.; Chung, H.-M.; Lee, M.R.; Kim, S.J.; Moon, S.-H. Reconstituting Human Cutaneous Regeneration in Humanized Mice under Endothelial Cell Therapy. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2019, 139, 692–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pastar, I.; Stojadinovic, O.; Yin, N.C.; Ramirez, H.; Nusbaum, A.G.; Sawaya, A.; Patel, S.B.; Khalid, L.; Isseroff, R.R.; Tomic-Canic, M. Epithelialization in Wound Healing: A Comprehensive Review. Adv. Wound Care (New Rochelle) 2014, 3, 445–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xue, M.; Jackson, C.J. Extracellular Matrix Reorganization During Wound Healing and Its Impact on Abnormal Scarring. Adv. Wound Care (New Rochelle) 2015, 4, 119–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Traverse, J.H.; Henry, T.D.; Dib, N.; Patel, A.N.; Pepine, C.; Schaer, G.L.; DeQuach, J.A.; Kinsey, A.M.; Chamberlin, P.; Christman, K.L. First-in-Man Study of a Cardiac Extracellular Matrix Hydrogel in Early and Late Myocardial Infarction Patients. JACC Basic Transl. Sci. 2019, 4, 659–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singelyn, J.M.; DeQuach, J.A.; Seif-Naraghi, S.B.; Littlefield, R.B.; Schup-Magoffin, P.J.; Christman, K.L. Naturally derived myocardial matrix as an injectable scaffold for cardiac tissue engineering. Biomaterials 2009, 30, 5409–5416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jang, K.-S.; Park, S.-J.; Choi, J.-J.; Kim, H.-N.; Shim, K.-M.; Kim, M.-J.; Jang, I.-H.; Jin, S.-W.; Kang, S.-S.; Kim, S.-E.; et al. Therapeutic Efficacy of Artificial Skin Produced by 3D Bioprinting. Materials 2021, 14, 5177. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14185177
Jang K-S, Park S-J, Choi J-J, Kim H-N, Shim K-M, Kim M-J, Jang I-H, Jin S-W, Kang S-S, Kim S-E, et al. Therapeutic Efficacy of Artificial Skin Produced by 3D Bioprinting. Materials. 2021; 14(18):5177. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14185177
Chicago/Turabian StyleJang, Kwang-Sik, Soon-Jung Park, Jong-Jin Choi, Ha-Na Kim, Kyung-Mi Shim, Mi-Jeong Kim, Il-Ho Jang, Song-Wan Jin, Seong-Soo Kang, Se-Eun Kim, and et al. 2021. "Therapeutic Efficacy of Artificial Skin Produced by 3D Bioprinting" Materials 14, no. 18: 5177. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14185177
APA StyleJang, K.-S., Park, S.-J., Choi, J.-J., Kim, H.-N., Shim, K.-M., Kim, M.-J., Jang, I.-H., Jin, S.-W., Kang, S.-S., Kim, S.-E., & Moon, S.-H. (2021). Therapeutic Efficacy of Artificial Skin Produced by 3D Bioprinting. Materials, 14(18), 5177. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14185177





