Structure and Properties of Biodegradable PLLA/ZnO Composite Membrane Produced via Electrospinning
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of PLLA/ZnO Composite Membranes
2.2. Characterization of PLLA/ZnO Composite Membranes
2.3. Antibacterial Activity of PLLA/ZnO Composite Membranes
3. Results
3.1. Physico-Chemical Properties of PLLA/ZnO Composite Membranes
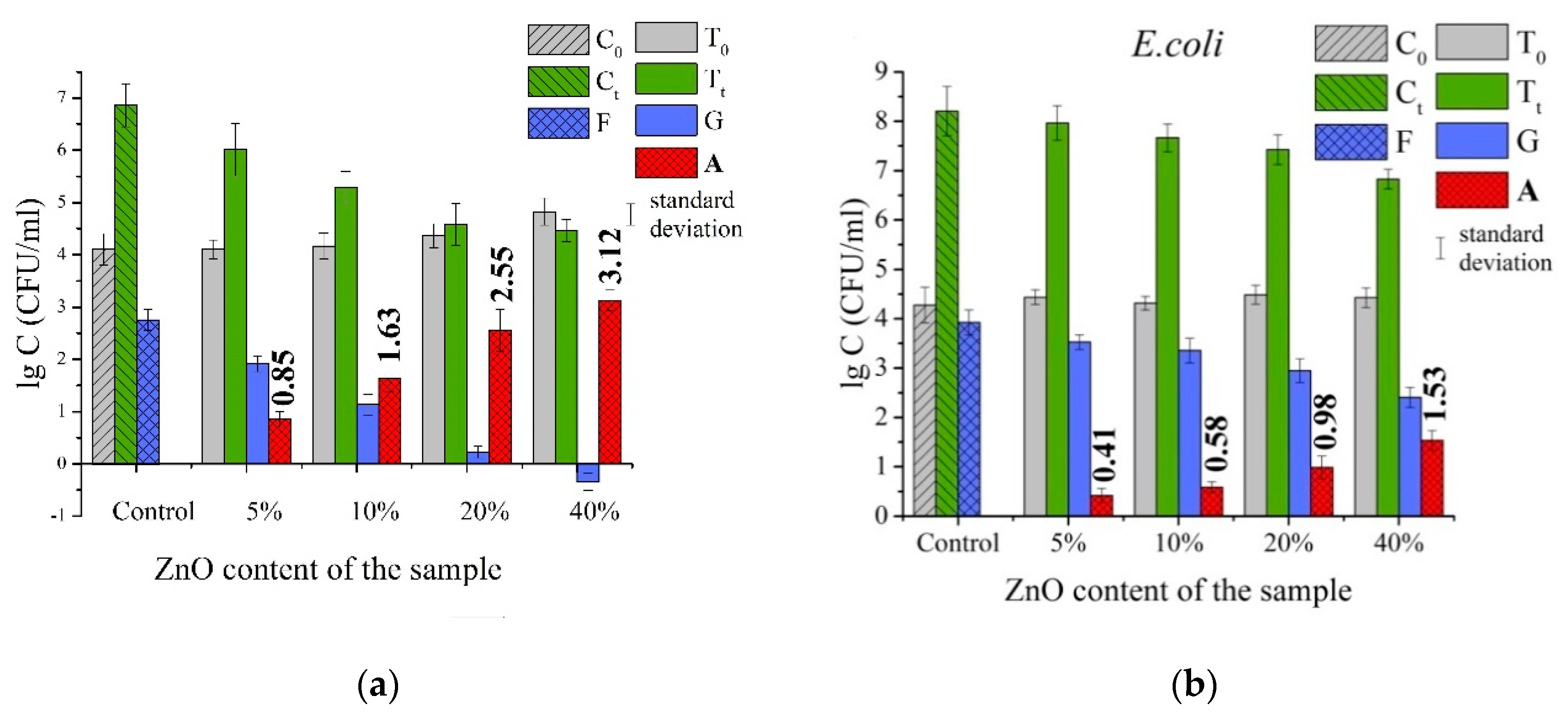
3.2. Antibacterial Properties of PLLA/ZnO Composite Membranes
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Armentano, I.; Bitinis, N.; Fortunati, E.; Mattioli, S.; Rescignano, N.; Verdejo, R.; Lopez-Manchado, M.A.; Kenny, J.M. Multifunctional nanostructured PLA materials for packaging and tissue engineering. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2013, 38, 1720–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murariu, M.; Dubois, P. PLA composites: From production to properties. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2016, 107, 17–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raquez, J.-M.; Habibi, Y.; Murariu, M.; Dubois, P. Polylactide (PLA)-based nanocomposites. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2013, 38, 1504–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Pi, J.; Cai, J. The advancing of zinc oxide nanoparticles for biomedical applications. Bioinorg. Chem. Appl. 2018, 2018, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abebe, B.; Zereffa, E.A.; Tadesse, A.; Murthy, H.C.A. A review on enhancing the antibacterial activity of ZnO: Mechanisms and microscopic investigation. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2020, 15, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiedot-Tobola, M.; Ciesielska, M.; Maliszewska, I.; Rac-Rumijowska, O.; Suchorska-Wozniak, P.; Teterycz, H.; Bryjak, M. Deposition of zinc oxide on different polymer textiles and their antibacterial properties. Materials 2018, 11, 707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svetlichnyi, V.; Shabalina, A.; Lapin, I.; Goncharova, D.; Nemoykina, A. ZnO nanoparticles obtained by pulsed laser ablation and their composite with cotton fabric: Preparation and study of antibacterial activity. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 372, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, A.S.; Bao, B. Molecular mechanisms of zinc as a pro-antioxidant mediator: Clinical therapeutic implications. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiBaise, M.; Tarleton, S.M. Hair, nails, and skin: Differentiating cutaneous manifestations of micronutrient deficiency. Nutr. Clin. Pract. 2019, 34, 490–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, J.; Tinkov, A.; Strand, T.A.; Alehagen, U.; Skalny, A.; Aaseth, J. Early nutritional interventions with zinc, selenium and vitamin D for raising anti-viral resistance against progressive COVID-19. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hackenberg, S.; Scherzed, A.; Kessler, M.; Froelich, K.; Ginzkey, C.; Koehler, C.; Burghartz, M.; Hagen, R.; Kleinsasser, N. Zinc oxide nanoparticles induce photocatalytic cell death in human head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cell lines in vitro. Int. J. Oncol. 2010, 37, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cross, S.E.; Innes, B.; Roberts, M.S.; Tsuzuki, T.; Robertson, T.A.; McCormick, P. Human skin penetration of sunscreen nanoparticles: In-vitro assessment of a novel micronized zinc oxide formulation. Skin Pharmacol. Physiol. 2007, 20, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osmond, M.J.; Mccall, M.J. Zinc oxide nanoparticles in modern sunscreens: An analysis of potential exposure and hazard. Nanotoxicology 2010, 4, 15–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valerini, D.; Tammaro, L.; Di Benedetto, F.; Vigliotta, G.; Capodieci, L.; Terzi, R.; Rizzo, A. Aluminum-doped zinc oxide coatings on polylactic acid films for antimicrobial food packaging. Thin Solid Films 2018, 645, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bumbudsanpharoke, N.; Choi, J.; Park, H.J.; Ko, S. Zinc migration and its effect on the functionality of a low density polyethylene-ZnO nanocomposite film. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2019, 20, 100301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Kumar, R. Investigations on rare earth activated ZnO nanoparticles reinforcement in polymer matrix for 3D printing application. In Reference Module in Materials Science and Materials Engineering; Elsevier: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2020; pp. 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamburova, K.; Boshkova, N.; Boshkov, N.; Radeva, T. Composite coatings with polymeric modified ZnO nanoparticles and nanocontainers with inhibitor for corrosion protection of low carbon steel. Colloids Surf. A 2021, 609, 125741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, P.; Zhang, D.; Wu, Y.; Yu, J.; Russell, T.P. Polymer-modified ZnO nanoparticles as electron transport layer for polymer-based solar cells. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 2002932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavrilenko, E.A.; Goncharova, D.A.; Lapin, I.N.; Nemoykina, A.L.; Svetlichnyi, V.A.; Aljulaih, A.A.; Mintcheva, N.; Kulinich, S.A. Comparative study of physicochemical and antibacterial properties of ZnO nanoparticles prepared by laser ablation of Zn target in water and air. Materials 2019, 12, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Tobías, H.; Morales, G.; Ledezma, A.; Romero, J.; Grande, D. Novel antibacterial electrospun mats based on poly(d,l-lactide) nanofibers and zinc oxide nanoparticles. J. Mater. Sci. 2014, 49, 8373–8385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, D.; Wang, R.; Tang, G.; Mou, Z.; Lei, J.; Han, J.; De Smedt, S.; Xiong, R.; Huang, C. Ecofriendly electrospun membranes loaded with visible-light-responding nanoparticles for multifunctional usages: Highly efficient air filtration, dye scavenging, and bactericidal activity. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 12880–12889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Duan, X.-P.; Li, Y.-M.; Yang, D.-P.; Long, Y.-Z. Electrospun nanofibers for wound healing. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 76, 1413–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Y.; Thomas, N.L.; Lu, X. Electrospun dual-layer mats with covalently bonded ZnO nanoparticles for moisture wicking and antibacterial textiles. Mater. Des. 2017, 134, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virovska, D.; Paneva, D.; Manolova, N.; Rashkov, I.; Karashanova, D. Electrospinning/electrospraying vs. electrospinning: A comparative study on the design of poly(l-lactide)/zinc oxide non-woven textile. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 311, 842–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trujillo, S.; Lizundia, E.; Vilas, J.L.; Salmeron-Sanchez, M. PLLA/ZnO nanocomposites: Dynamic surfaces to harness cell differentiation. Colloids Surf. B 2016, 144, 152–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GOST 3811-72. Textile materials. Textile fabrics, nonwonen fabrics and piece-articles. In Methods for Determination of Linear Dimensions, Linear and Surface Density, 4th ed.; GOST: Moscow, Russia, 1991. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Tauc, J.; Grigorovici, R.; Vancu, A. Optical properties and electronic structure of amorphous germanium. Phys. Status Solidi 1966, 15, 627–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 20743:2013. Textiles—Determination of Antibacterial Activity of Textile Products, 2nd ed.; ISO: Geneva, Swizerland, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Z.-M.; Zhang, Y.-Z.; Kotaki, M.; Ramakrishna, S. A review on polymer nanofibers by electrospinning and their applications in nanocomposites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2003, 63, 2223–2253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Augustine, R.; Kalarikkal, N.; Thomas, S. Effect of zinc oxide nanoparticles on the in vitro degradation of electrospun polycaprolactone membranes in simulated body fluid. Int. J. Polym. Mater. Polym. Biomater. 2016, 65, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassie, A.B.D.; Baxter, S. Wettability of porous surfaces. Trans. Faraday Soc. 1944, 40, 546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tjong, S.C. Structural and mechanical properties of polymer nanocomposites. Mater. Sci. Eng. R 2006, 53, 73–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kister, G.; Cassanas, G.; Vert, M. Effects of morphology, conformation and configuration on the IR and Raman spectra of various poly(lactic acid)s. Polymer 1998, 39, 267–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, A.; Ahuja, R.; Bhati, P.; Singh, S.; Chauhan, P.; Vashisth, P.; Kumar, A.; Bhatnagar, N. Fabrication and characterization of PLLA/Mg composite tube as the potential bioresorbable/biodegradable stent (BRS). Materials 2020, 10, 100661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gondal, M.A.; Drmosh, Q.A.; Yamani, Z.H.; Saleh, T.A. Synthesis of ZnO2 nanoparticles by laser ablation in liquid and their annealing transformation into ZnO nanoparticles. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2009, 25, 298–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Duan, Y.; Sato, H.; Tsuji, H.; Noda, I.; Yan, S.; Ozaki, Y. Crystal modifications and thermal behavior of poly(-l-lactic acid) revealed by infrared spectroscopy. Macromolecules 2005, 38, 8012–8021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srikant, V.; Clarke, D.R. Optical absorption edge of ZnO thin films: The effect of substrate. J. Appl. Phys. 1997, 81, 6357–6364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zeng, F.; Lin, Y.; Wang, G.; Pan, F. Correlation of oxygen vacancy variations to band gap changes in epitaxial ZnO thin films. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2013, 102, 181908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tachikawa, S.; Noguchi, A.; Tsuge, T.; Hara, M.; Odawara, O.; Wada, H. Optical properties of ZnO nanoparticles capped with polymers. Materials 2011, 4, 1132–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honda, M.; Goto, T.; Owashi, T.; Rozhin, A.G.; Yamaguchi, S.; Ito, T.; Kulinich, S.A. ZnO nanorods prepared via ablation of Zn with millisecond lase in liquid media. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2016, 18, 23628–23637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goto, T.; Honda, M.; Kulinich, S.A.; Shimizu, Y.; Ito, T. Defects in ZnO nanoparticles laser-ablated in water-ethanol mixtures at different pressures. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2015, 54, 070305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, X.; Shao, C.; Liu, Y. Photoluminescence of polyethylene oxide–ZnO composite electrospun fibers. Polymer 2007, 48, 1459–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonohara, R.; Muramatsu, N.; Ohshima, H.; Kondo, T. Difference in surface properties between Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus as revealed by electrophoretic mobility measurements. Biophys. Chem. 1995, 55, 273–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirelkhatim, A.; Mahmud, S.; Seeni, A.; Kaus, N.H.M.; Ann, L.C.; Bakhori, S.K.M.; Hasan, H.; Mohamad, D. Review on zinc oxide nanoparticles: Antibacterial activity and toxicity mechanism. Nano Micro Lett. 2015, 7, 219–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Silva, B.L.; Caetano, B.L.; Chiari-Andreo, B.G.; Pietro, R.C.L.R.; Chiavacci, L.A. Increased antibacterial activity of ZnO nanoparticles: Influence of size and surface modification. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2019, 177, 440–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zarrindokht, E.-K. Antibacterial activity of ZnO nanoparticle on gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria. Afr. J. Microbiol. Res. 2012, 5, 440–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padmavathy, N.; Vijayaraghavan, R. Enhanced bioactivity of ZnO nanoparticles—An antimicrobial study. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2008, 9, 035004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohira, T.; Yamamoto, O.; Iida, Y.; Nakagawa, Z. Antibacterial activity of ZnO powder with crystallographic orientation. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2008, 19, 1407–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
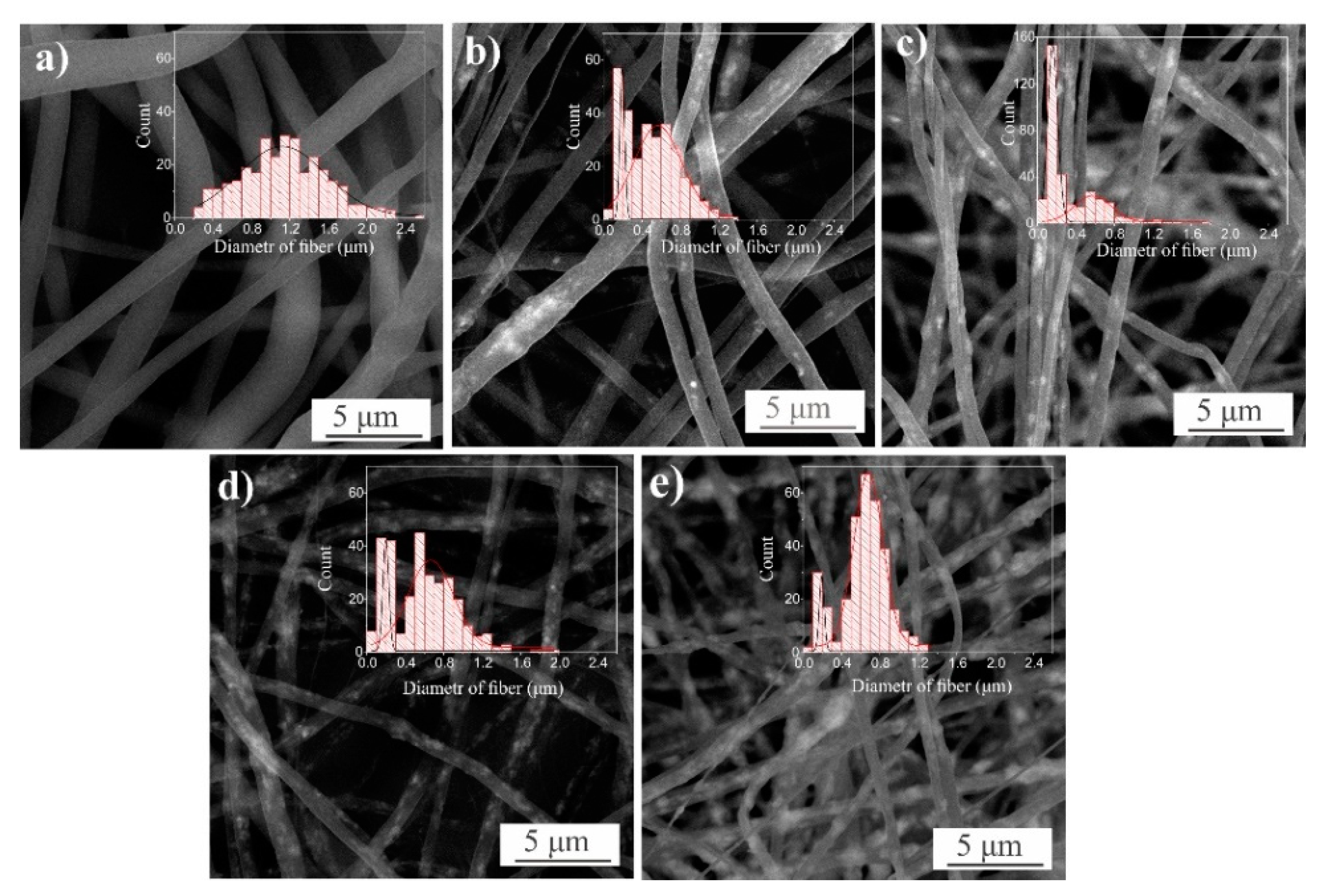
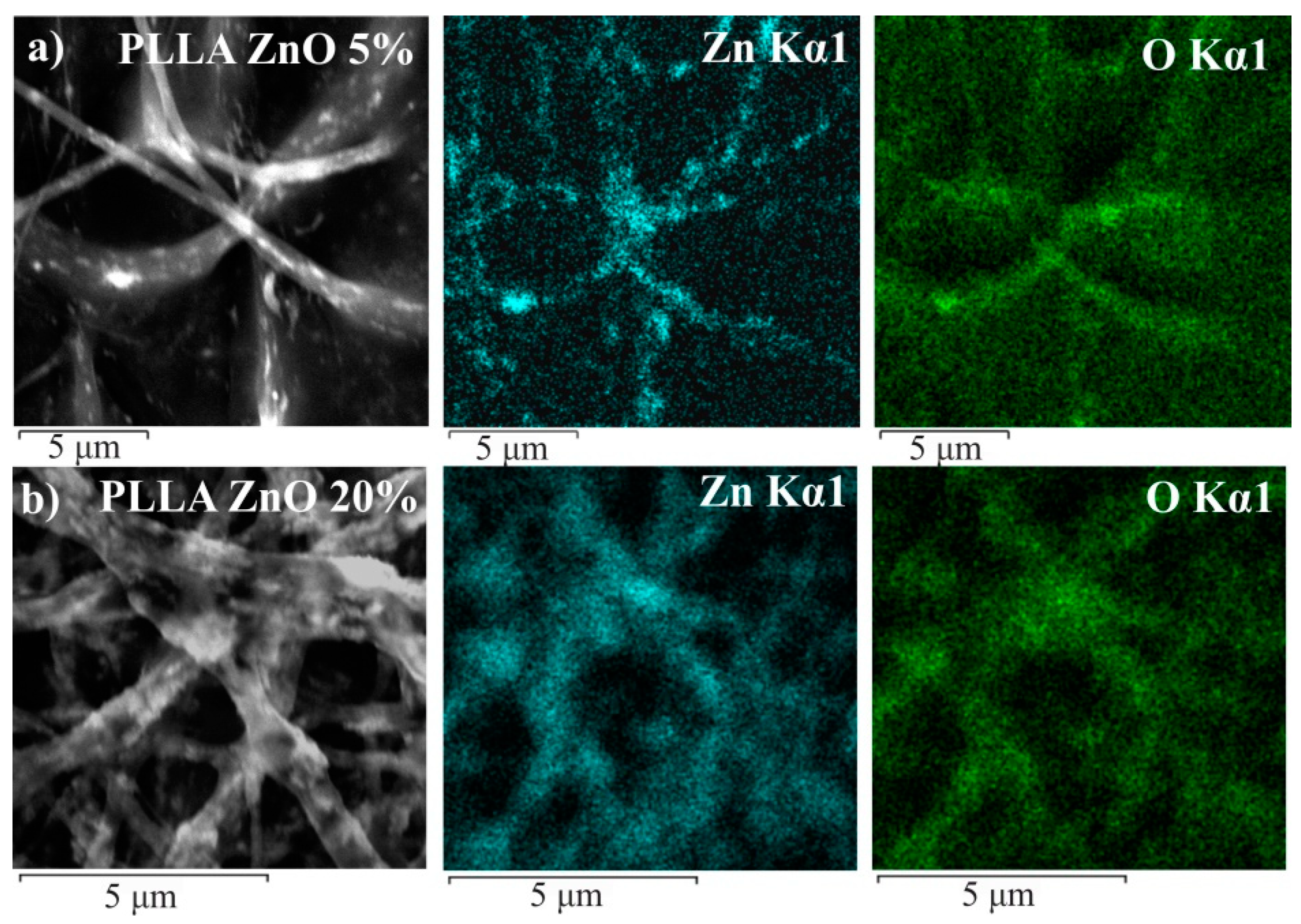
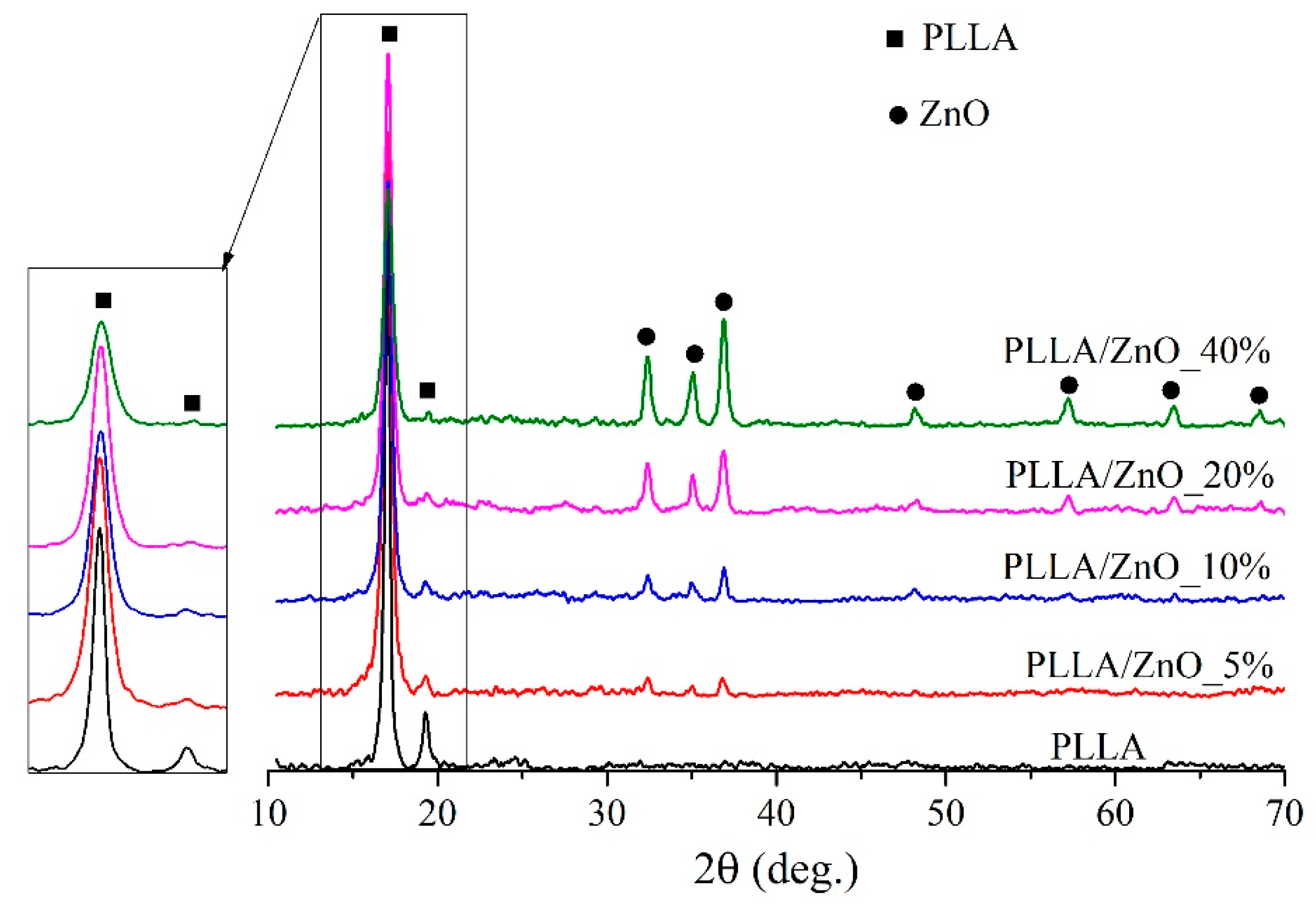
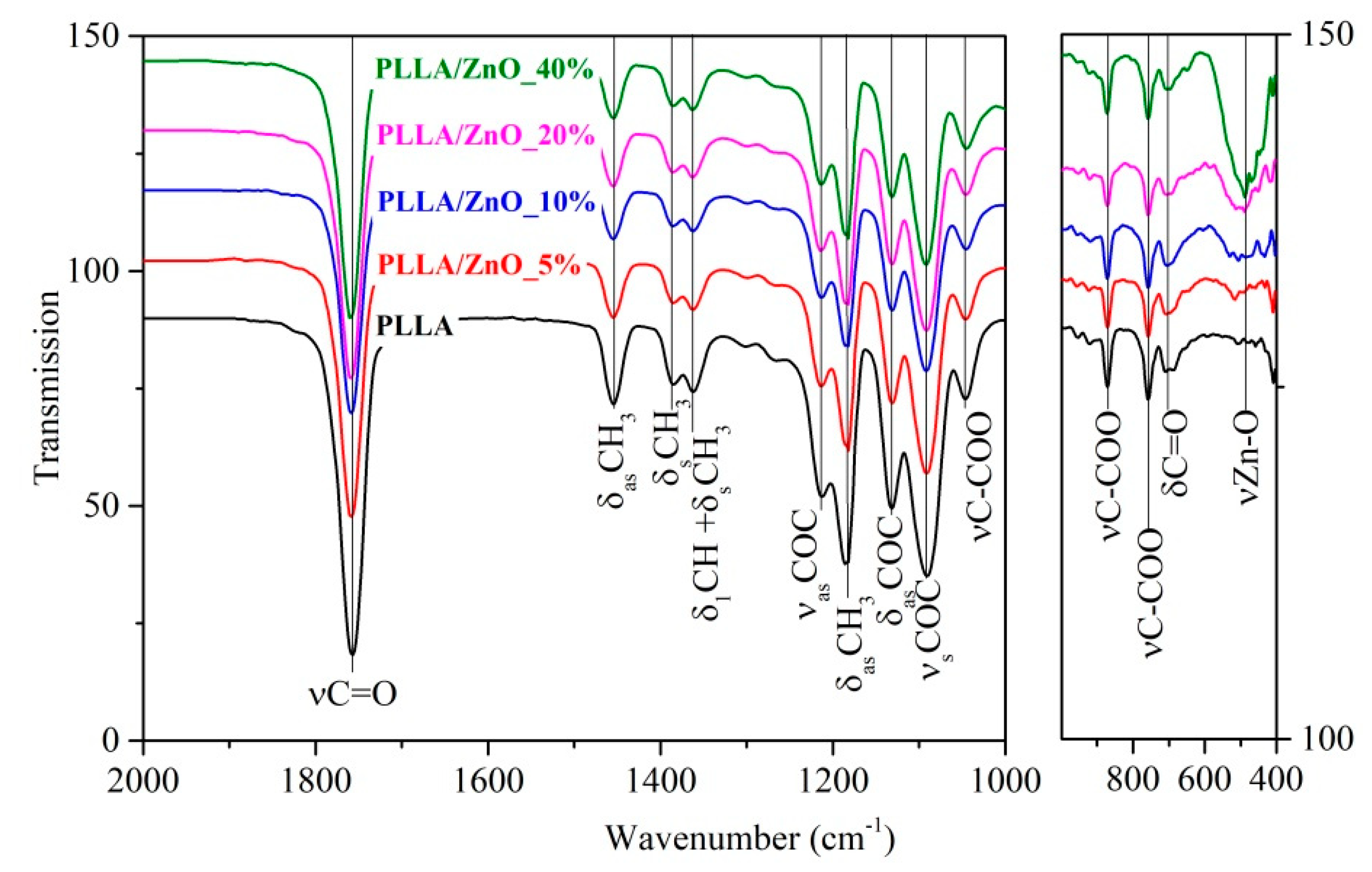
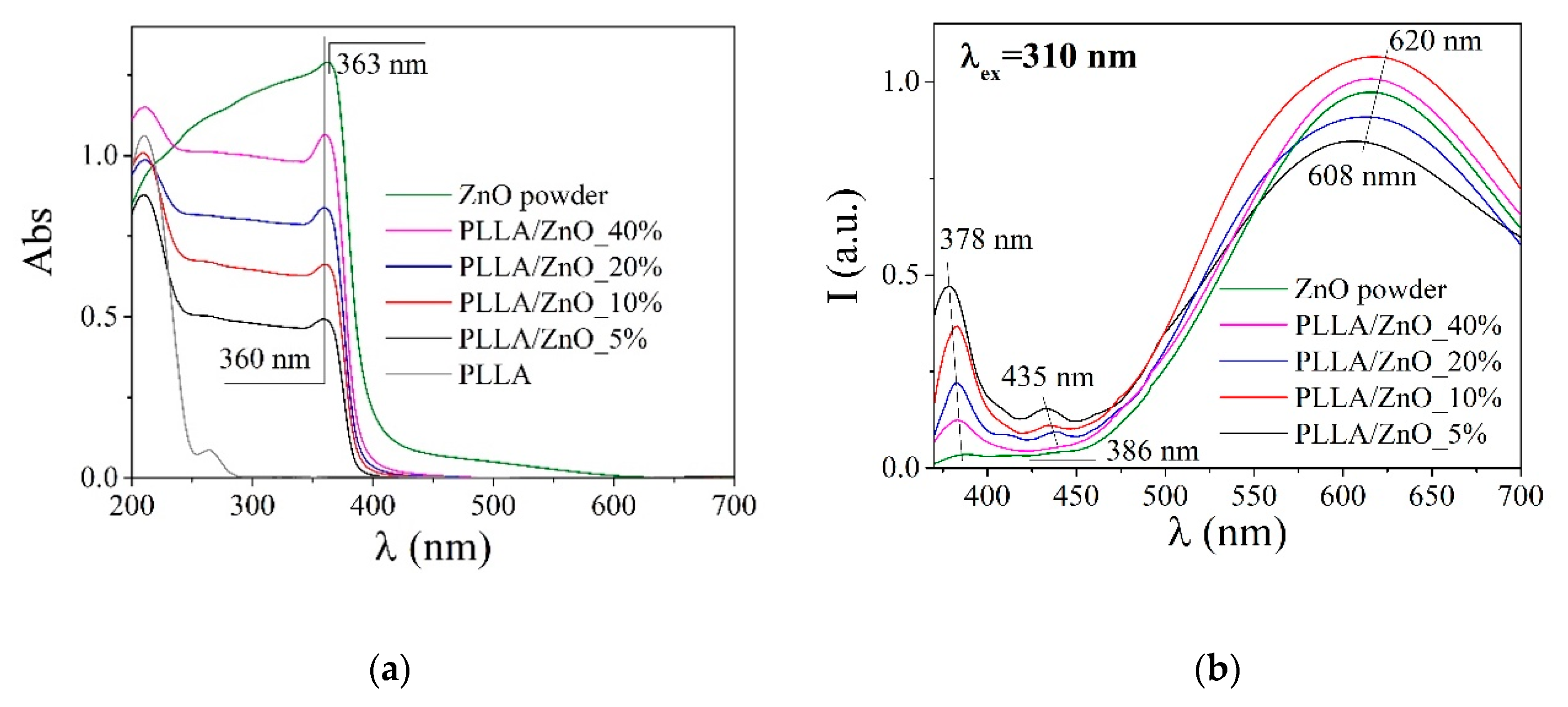

| Sample | Density, g/cm3 | Average Fiber Diameter, μm (Peak Intensity) | Water Contact Angle H2O, ° | Stretch, % | Strength Limit, MPa | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PLLA | 0.15 | 1.1 (30) | 122 ± 1 | 62 ± 5 | 2.7 ± 0.1 | |
| PLLA/ZnO_5% | 0.16 | 0.2 (40) | 0.6 (40) | 124 ± 2 | 35 ± 1 | 3.7 ± 0.2 |
| PLLA/ZnO_10% | 0.17 | 0.2 (150) | 0.6 (30) | 126 ± 2 | 30 ± 4 | 3.9 ± 0.2 |
| PLLA/ZnO_20% | 0.16 | 0.2 (30) | 0.7 (70) | 127 ± 1 | 44 ± 2 | 3.1 ± 0.2 |
| PLLA/ZnO_40% | 0.19 | 0.2 (60) | 0.5 (35) | 117 ± 1 | 48 ± 7 | 2.5 ± 0.2 |
| Sample | Luminescence | ΔE, eV | |
|---|---|---|---|
| λmax, nm | Iinter-band/Idefect 1 | ||
| PLLA | 431 | - | - |
| PLLA/ZnO_5% | 379/435/612 | 0.5 | 3.27 |
| PLLA/ZnO_10% | 382/431/612 | 0.3 | 3.27 |
| PLLA/ZnO_20% | 382/439/608 | 0.2 | 3.27 |
| PLLA/ZnO_40% | 382/607 | 0.08 | 3.27 |
| ZnO powder | 387/608 | 0.04 | 3.22 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Goncharova, D.A.; Bolbasov, E.N.; Nemoykina, A.L.; Aljulaih, A.A.; Tverdokhlebova, T.S.; Kulinich, S.A.; Svetlichnyi, V.A. Structure and Properties of Biodegradable PLLA/ZnO Composite Membrane Produced via Electrospinning. Materials 2021, 14, 2. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14010002
Goncharova DA, Bolbasov EN, Nemoykina AL, Aljulaih AA, Tverdokhlebova TS, Kulinich SA, Svetlichnyi VA. Structure and Properties of Biodegradable PLLA/ZnO Composite Membrane Produced via Electrospinning. Materials. 2021; 14(1):2. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14010002
Chicago/Turabian StyleGoncharova, Daria A., Evgeny N. Bolbasov, Anna L. Nemoykina, Ali A. Aljulaih, Tamara S. Tverdokhlebova, Sergei A. Kulinich, and Valery A. Svetlichnyi. 2021. "Structure and Properties of Biodegradable PLLA/ZnO Composite Membrane Produced via Electrospinning" Materials 14, no. 1: 2. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14010002
APA StyleGoncharova, D. A., Bolbasov, E. N., Nemoykina, A. L., Aljulaih, A. A., Tverdokhlebova, T. S., Kulinich, S. A., & Svetlichnyi, V. A. (2021). Structure and Properties of Biodegradable PLLA/ZnO Composite Membrane Produced via Electrospinning. Materials, 14(1), 2. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14010002








