Histological and Histomorphometric Evaluation of New Bone Formation after Maxillary Sinus Augmentation with Two Different Osteoconductive Materials: A Randomized, Parallel, Double-Blind Clinical Trial
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Patient Selection
2.3. Surgical Procedure
2.4. Post-Operative Care
2.5. Histological Procedure
2.6. Statistical Analysis
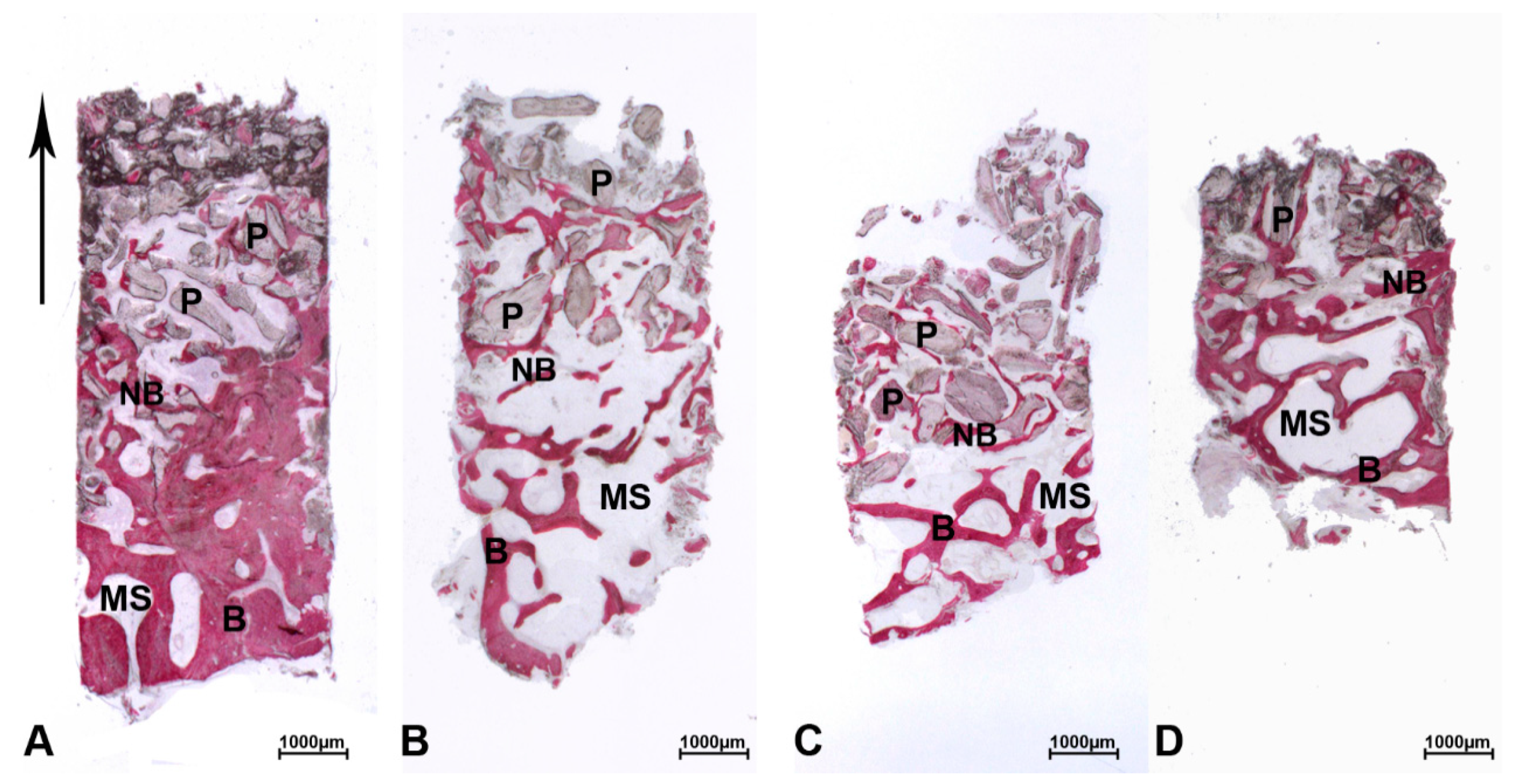
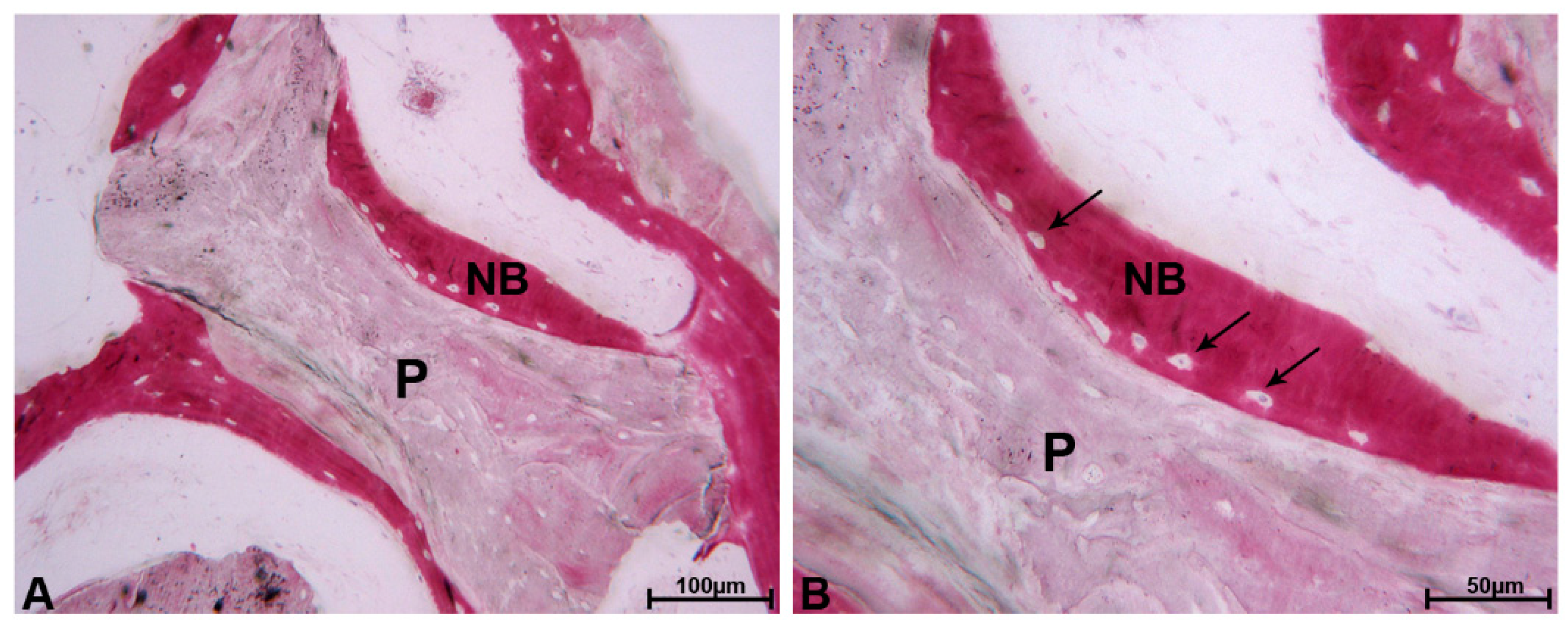
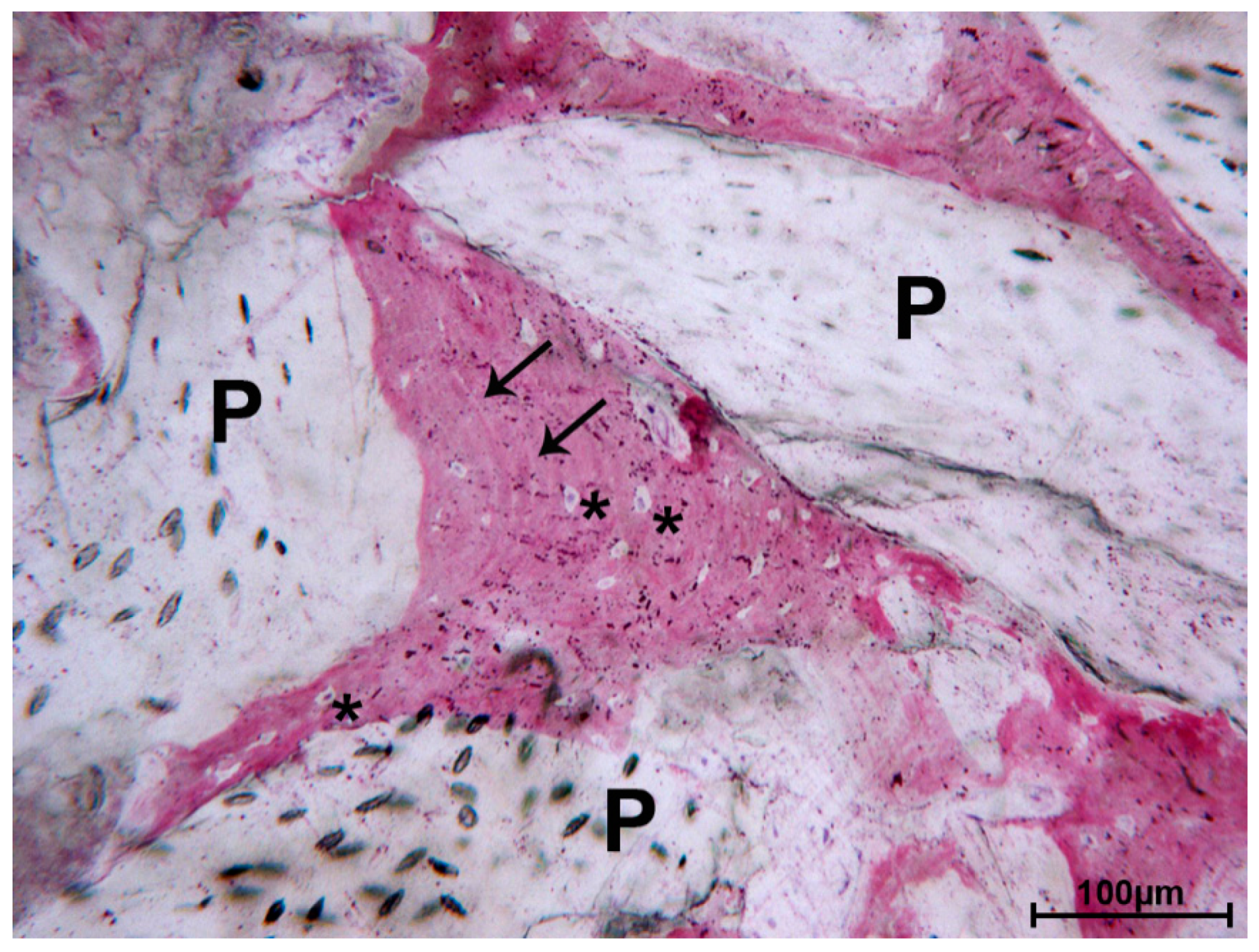
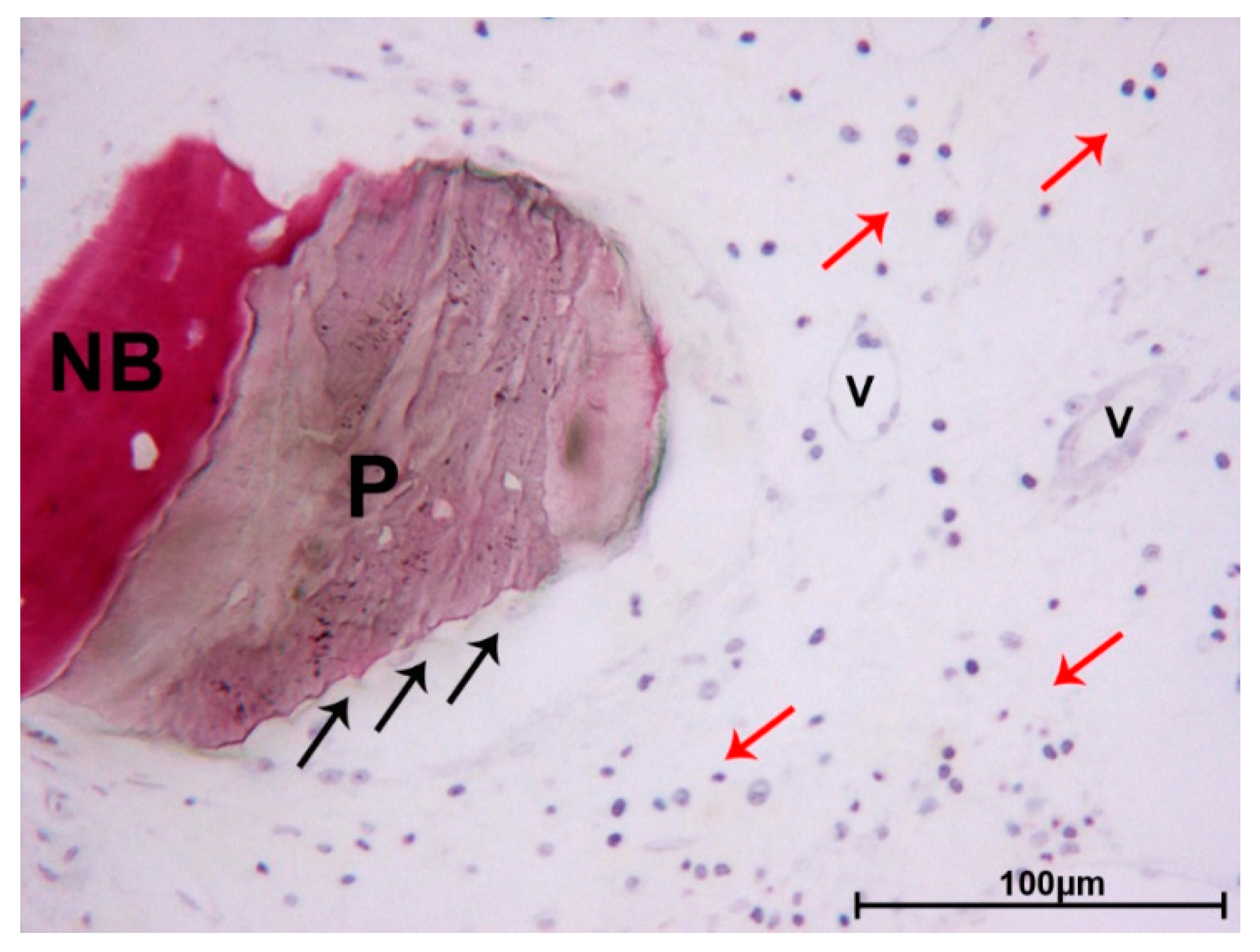
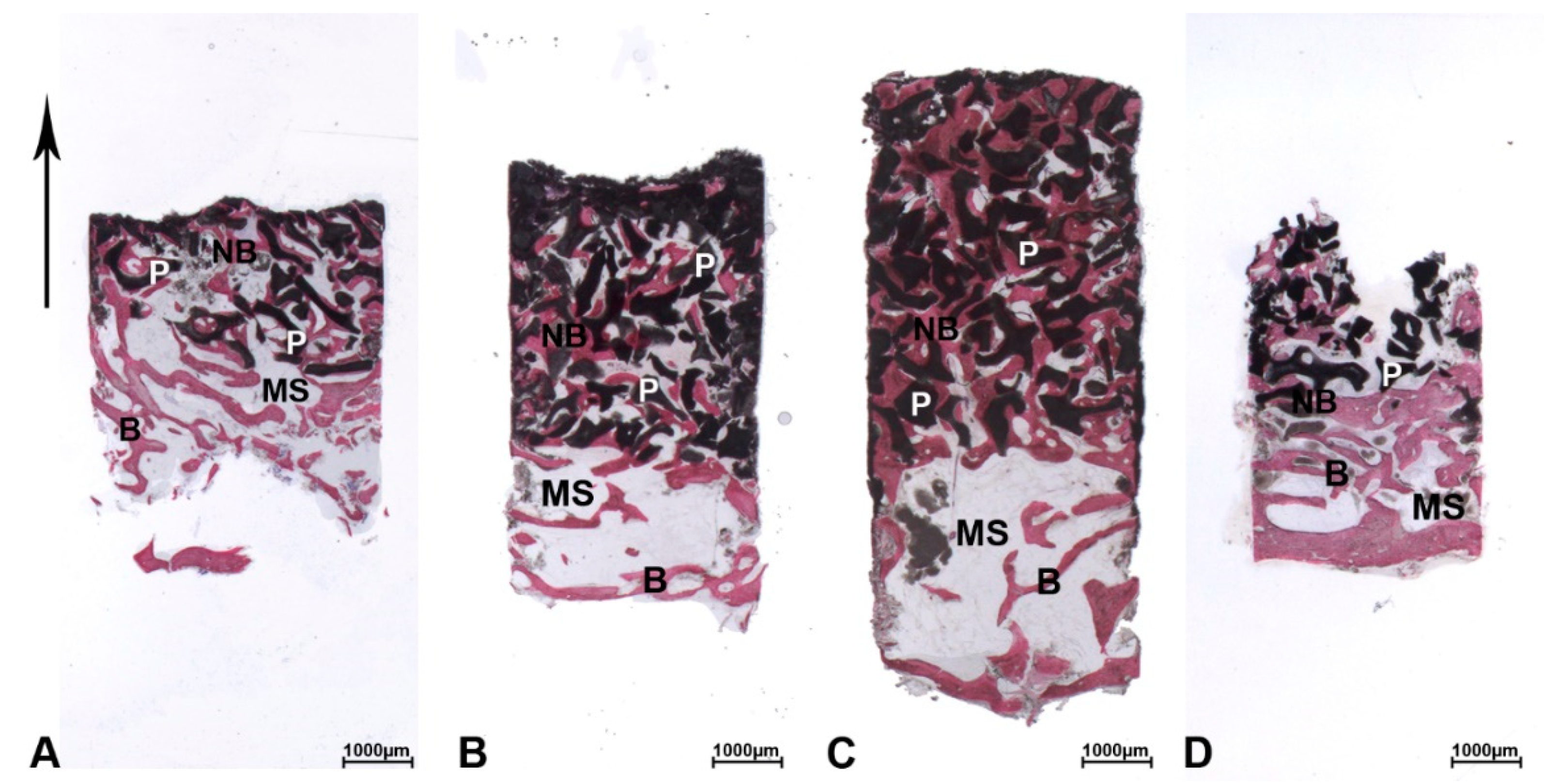
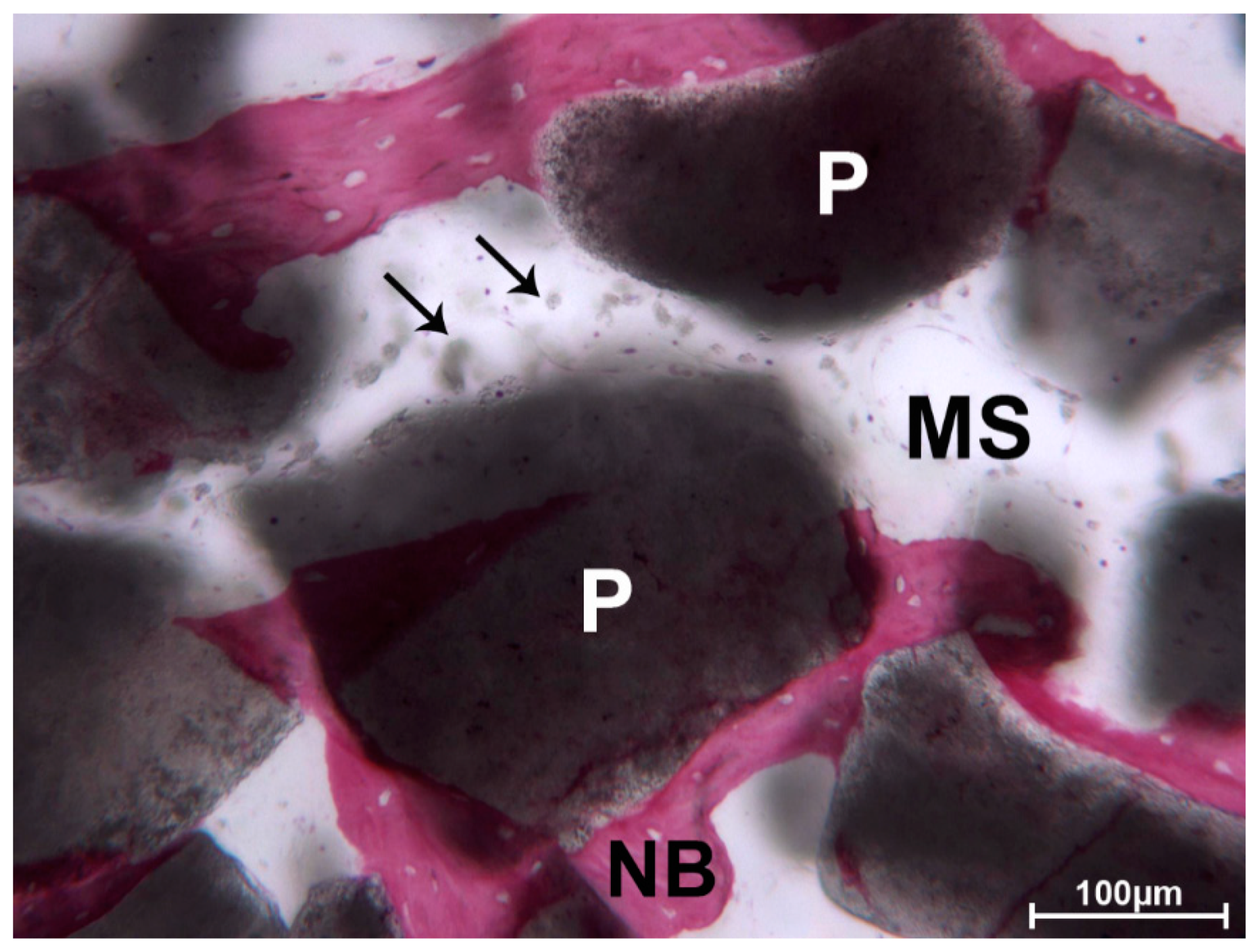
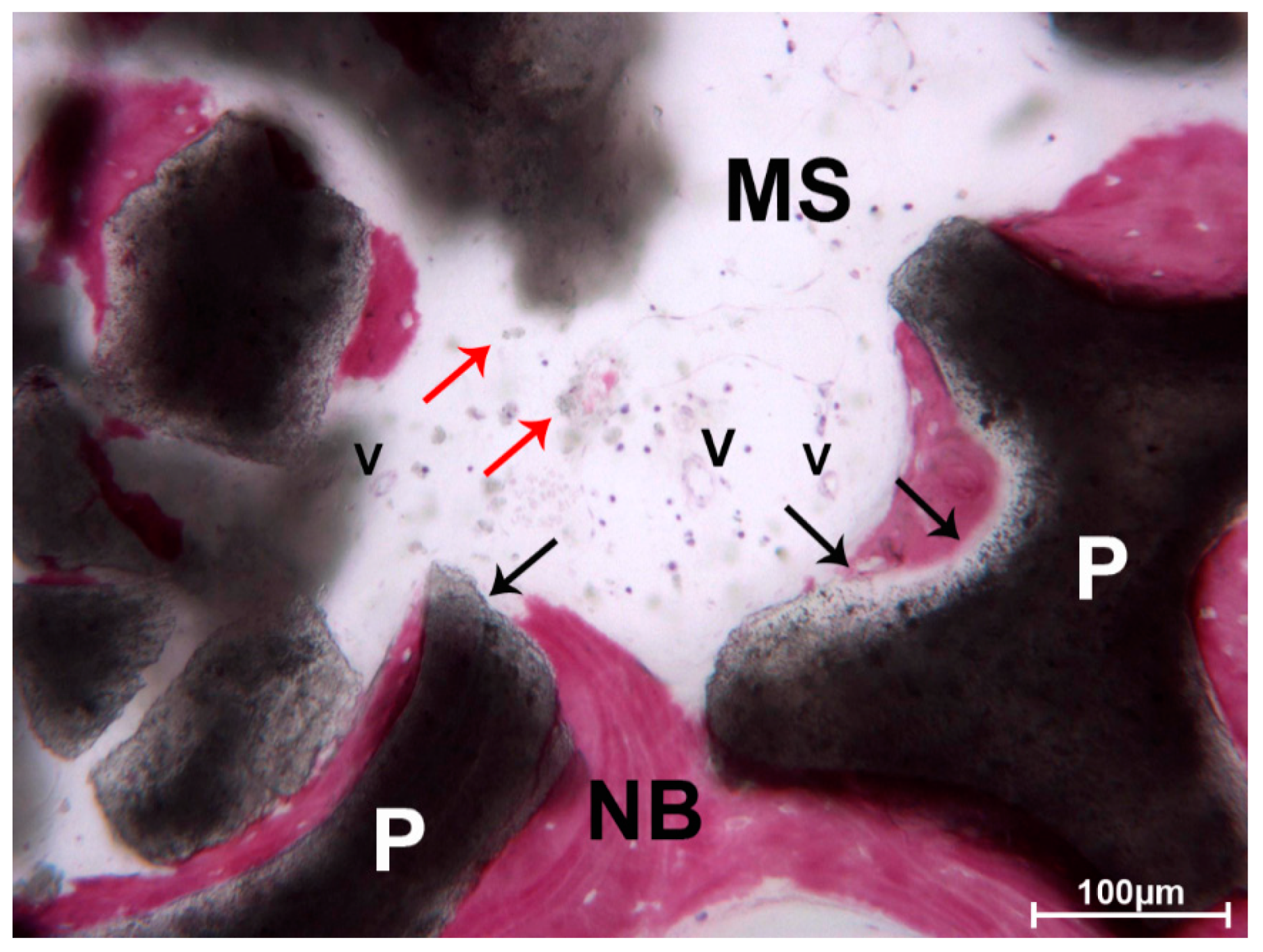
3. Results
3.1. DEBM
3.2. ABB
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Aimetti, M.; Romagnoli, R.; Ricci, G.; Massei, G. Maxillary sinus elevation: The effect of macrolacerations and microlacerations of the sinus membrane as determined by endoscopy. Int. J. Periodontics Restor. Dent. 2001, 21, 581–589. [Google Scholar]
- Jensen, O.T.; Shulman, L.B.; Block, M.S.; Iacono, V.J. Report of the Sinus Consensus Conference of 1996. Int. J. Oral. Maxillofac. Implant. 1998, 13, 11–45. [Google Scholar]
- Froum, S.J.; Khouly, I.; Favero, G.; Cho, S.C. Effect of maxillary sinus membrane perforation on vital bone formation and implant survival: A retrospective study. J. Periodontol. 2013, 84, 1094–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiapasco, M.; Zaniboni, M.; Boisco, M. Augmentation procedures for the rehabilitation of deficient edentulous ridges with oral implants. Clin. Oral. Implant. Res. 2006, 17, 136–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchetti, E.; Lopez, M.A.; Confalone, L.; Mummolo, S.; Marzo, G. Maxillary sinus augmentation by crestal approach and ultrasound. J. Osseointegration 2010, 3, 79–83. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, T.W.; Chang, H.S.; Leung, K.W.; Lai, Y.L.; Kao, S.Y. Implant placement immediately after the lateral approach of the trap door window procedure to create a maxillary sinus lift without bone grafting: A 2-year retrospective evaluation of 47 implants in 33 patients. J. Oral. Maxillofac. Surg. 2007, 65, 2324–2328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, L.D.; de Lima, V.N.; Faverani, L.P.; de Mendonça, M.R.; Okamoto, R.; Pellizzer, E.P. Maxillary sinus lift surgery-with or without graft material? A systematic review. Int. J. Oral. Maxillofac. Surg. 2016, 45, 1570–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, C.M.; O’Brien, F.J.; Little, D.G.; Schindeler, A. Cell-scaffold interactions in the bone tissue engineering triad. Eur. Cells Mater. 2013, 26, 120–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Fabbro, M.; Testori, T.; Francetti, L.; Weinstein, R. Systematic review of survival rates for implants placed in the grafted maxillary sinus. Int. J. Periodontics Restor. Dent. 2004, 24, 565–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peleg, M.; Mazor, Z.; Chaushu, G.; Garg, A.K. Sinus Floor Augmentation With Simultaneous Implant Placement in the Severely Atrophic Maxilla. J. Periodontol. 1998, 69, 1397–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Fabbro, M.; Rosano, G.; Taschieri, S. Implant survival rates after maxillary sinus augmentation. Eur. J. Oral. Sci. 2008, 116, 497–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moussa, N.T.; Dym, H. Maxillofacial Bone Grafting Materials. Dent. Clin. N. Am. 2020, 64, 473–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handschel, J.; Simonowska, M.; Naujoks, C.; Depprich, R.A.; Ommerborn, M.A.; Meyer, U.; Kübler, N.R. A histomorphometric meta-analysis of sinus elevation with various grafting materials. Head Face Med. 2009, 5, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esposito, M.; Felice, P.; Worthington, H.V. Interventions for replacing missing teeth: Augmentation procedures of the maxillary sinus. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2014, CD008397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mummolo, S.; Nota, A.; Marchetti, E.; Capuano, S.; Tecco, S.; Marzo, G.; Campanella, V. Histologic and histomorphometric analysis of maxillary sinus augmentation with different biomaterials. A pilot split-mouth human study. Oral Implantol. 2018, 11, 249–256. [Google Scholar]
- Marchetti, E.; Mancini, L.; Bernardi, S.; Bianchi, S.; Cristiano, L.; Torge, D.; Marzo, G.; Macchiarelli, G. Evaluation of Different Autologous Platelet Concentrate Biomaterials: Morphological and Biological Comparisons and Considerations. Materials 2020, 13, 2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernardi, S.; Mummolo, S.; Varvara, G.; Marchetti, E.; Continenza, M.A.; Marzo, G.; Macchiarelli, G. Bio-morphological evaluation of periodontal ligament fibroblasts on mineralized dentin graft: An in vitro study. J. Biol. Regul. Homeost. Agents 2019, 33, 275–280. [Google Scholar]
- Burchardt, H. The biology of bone graft repair. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 1983, 174, 28–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nkenke, E.; Schultze-Mosgau, S.; Radespiel-Tröger, M.; Kloss, F.; Neukam, F.W. Morbidity of harvesting of chin grafts: A prospective study. Clin. Oral. Implants Res. 2001, 12, 495–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nkenke, E.; Weisbach, V.; Winckler, E.; Kessler, P.; Schultze-Mosgau, S.; Wiltfang, J.; Neukam, F.W. Morbidity of harvesting of bone grafts from the iliac crest for preprosthetic augmentation procedures: A prospective study. Int. J. Oral. Maxillofac. Surg. 2004, 33, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nkenke, E.; Stelzle, F. Clinical outcomes of sinus floor augmentation for implant placement using autogenous bone or bone substitutes: A systematic review. Clin. Oral. Implants Res. 2009, 20, 124–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klijn, R.J.; Meijer, G.J.; Bronkhorst, E.M.; Jansen, J.A. A meta-analysis of histomorphometric results and graft healing time of various biomaterials compared to autologous bone used as sinus floor augmentation material in humans. Tissue Eng. Part B Rev. 2010, 16, 493–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klijn, R.J.; Meijer, G.J.; Bronkhorst, E.M.; Jansen, J.A. Sinus Floor Augmentation Surgery Using Autologous Bone Grafts from Various Donor Sites: A Meta-Analysis of the Total Bone Volume. Tissue Eng. Part. B Rev. 2010, 16, 295–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Froum, S.J.; Wallace, S.S.; Elian, N.; Cho, S.C.; Tarnow, D.P. Comparison of mineralized cancellous bone allograft (Puros) and anorganic bovine bone matrix (Bio-Oss) for sinus augmentation: Histomorphometry at 26 to 32 weeks after grafting. Int. J. Periodontics Restor. Dent. 2006, 26, 543–551. [Google Scholar]
- Chackartchi, T.; Iezzi, G.; Goldstein, M.; Klinger, A.; Soskolne, A.; Piattelli, A.; Shapira, L. Sinus floor augmentation using large (1–2 mm) or small (0.25–1 mm) bovine bone mineral particles: A prospective, intra-individual controlled clinical, micro-computerized tomography and histomorphometric study. Clin. Oral. Implants Res. 2011, 22, 473–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Li, B.; Lin, X. Histological outcomes of sinus augmentation for dental implants with calcium phosphate or deproteinized bovine bone: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Oral. Maxillofac. Surg. 2016, 45, 1471–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nevins, M.; Heinemann, F.; Janke, U.W.; Lombardi, T.; Nisand, D.; Rocchietta, I.; Santoro, G.; Shupbach, P.; Kim, D.M. Equine-derived bone mineral matrix for maxillary sinus floor augmentation: A clinical, radiographic, histologic, and histomorphometric case series. Int. J. Periodontics Restor. Dent. 2013, 33, 483–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tetè, S.; Vinci, R.; Zizzari, V.L.; Zara, S.; La Scala, V.; Cataldi, A.; Gherlone, E.; Piattelli, A. Maxillary sinus augmentation procedures through equine-derived biomaterial or calvaria autologous bone: Immunohistochemical evaluation of OPG/RANKL in humans. Eur. J. Histochem. 2013, 57, e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Stefano, D.A.; Gastaldi, G.; Vinci, R.; Polizzi, E.M.; Cinci, L.; Pieri, L.; Gherlone, E. Bone Formation Following Sinus Augmentation with an Equine-Derived Bone Graft: A Retrospective Histologic and Histomorphometric Study with 36-Month Follow-up. Int. J. Oral. Maxillofac. Implants 2016, 31, 406–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivara, F.; Negri, M.; Lumetti, S.; Parisi, L.; Toffoli, A.; Calciolari, E.; Manfredi, E.; Macaluso, G.M. Maxillary Sinus Floor Augmentation Using an Equine-Derived Graft Material: Preliminary Results in 17 Patients. Biomed. Res. Int. 2017, 9164156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artzi, Z.; Tal, H.; Dayan, D. Porous bovine bone mineral in healing of human extraction sockets. Part 1: Histomorphometric evaluations at 9 months. J. Periodontol. 2000, 71, 1015–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sogal, A.; Tofe, A.J. Risk assessment of bovine spongiform encephalopathy transmission through bone graft material derived from bovine bone used for dental applications. J. Periodontol. 1999, 70, 1053–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.Y.; Koo, K.T.; Kim, T.I.; Seol, Y.J.; Lee, Y.M.; Ku, Y.; Rhyu, I.C.; Chung, C.P. Socket preservation using deproteinized horse-derived bone mineral. J. Periodontal Implant Sci. 2010, 40, 227–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Stefano, D.A.; Gastaldi, G.; Vinci, R.; Cinci, L.; Pieri, L.; Gherlone, E. Histomorphometric Comparison of Enzyme-Deantigenic Equine Bone and Anorganic Bovine Bone in Sinus Augmentation: A Randomized Clinical Trial with 3-Year Follow-Up. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implants 2015, 30, 1161–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Monaca, G.; Iezzi, G.; Cristalli, M.P.; Pranno, N.; Sfasciotti, G.L.; Vozza, I. Comparative Histological and Histomorphometric Results of Six Biomaterials Used in Two-Stage Maxillary Sinus Augmentation Model after 6-Month Healing. Biomed. Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 9430989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivolella, S.; Meggiorin, S.; Ferrarese, N.; Lupi, A.; Cavallin, F.; Fiorino, A.; Giraudo, C. CT-based dentulous mandibular alveolar ridge measurements as predictors of crown-to-implant ratio for short and extra short dental implants. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 16229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staderini, E.; Guglielmi, F.; Cornelis, M.A.; Cattaneo, P.M. Three-dimensional prediction of roots position through cone-beam computed tomography scans-digital model superimposition: A novel method. Orthod. Craniofac. Res. 2019, 22, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sankar, A.; Johnson, S.R.; Beattie, W.S.; Tait, G.; Wijeysundera, D.N. Reliability of the American Society of Anesthesiologists physical status scale in clinical practice. Br. J. Anaesth. 2014, 113, 424–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fugazzotto, P.A.; Vlassis, J. A Simplified Classification and Repair System for Sinus Membrane Perforations. J. Periodontol. 2003, 74, 1534–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piattelli, A.; Scarano, A.; Quaranta, M. High-precision, cost-effective cutting system for producing thin sections of oral tissues containing dental implants. Biomaterials 1997, 18, 577–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nevins, M.; Camelo, M.; De Angelis, N.; Hanratty, J.J.; Khang, W.G.; Kwon, J.-J.; Rasperini, G.; Rocchietta, I.; Schupbach, P.; Kim, D.M. The clinical and histologic efficacy of xenograft granules for maxillary sinus floor augmentation. Int. J. Periodontics Restor. Dent. 2011, 31, 226–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stievano, D.; Di Stefano, D.A.; Ludovichetti, M.; Pagnutti, S.; Gazzola, F.; Boato, C.; Stellini, E. Maxillary sinus lift through heterologous bone grafts and simultaneous acid-etched implants placement: Five year follow-up. Minerva Chir 2008, 63, 79–91. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Traxler, H.; Windisch, A.; Geyerhofer, U.; Surd, R.; Solar, P.; Firbas, W. Arterial blood supply of the maxillary sinus. Clin. Anat. 1999, 12, 417–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardi, S.; Mummolo, S.; Ciavarelli, L.M.; Li Vigni, M.; Continenza, M.A.; Marzo, G. Cone beam computed tomography investigation of the antral artery anastomosis in a population of Central Italy. Folia Morphol. 2016, 75, 149–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staderini, E.; De Luca, M.; Candida, E.; Rizzo, M.I.; Rajabtork Zadeh, O.; Bucci, D.; Zama, M.; Lajolo, C.; Cordaro, M.; Gallenzi, P. Lay People Esthetic Evaluation of Primary Surgical Repair on Three-Dimensional Images of Cleft Lip and Palate Patients. Medicina 2019, 55, 576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| DEBM (Biogen) (Mean ± SD) | AAB (Endobon) (Mean ± SD) | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| New bone | 22.20 ± 7.18 | 22.84 ± 7.34 | 0.6058 |
| Residual biomaterial | 27 ± 6.75 | 30.94 ± 10.20 | 0.4807 |
| Marrow spaces | 50.77 ± 7.59 | 46.20 ± 14.30 | 0.2359 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Grasso, G.; Mummolo, S.; Bernardi, S.; Pietropaoli, D.; D’Ambrosio, G.; Iezzi, G.; Piattelli, A.; Bianchi, S.; Marchetti, E. Histological and Histomorphometric Evaluation of New Bone Formation after Maxillary Sinus Augmentation with Two Different Osteoconductive Materials: A Randomized, Parallel, Double-Blind Clinical Trial. Materials 2020, 13, 5520. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13235520
Grasso G, Mummolo S, Bernardi S, Pietropaoli D, D’Ambrosio G, Iezzi G, Piattelli A, Bianchi S, Marchetti E. Histological and Histomorphometric Evaluation of New Bone Formation after Maxillary Sinus Augmentation with Two Different Osteoconductive Materials: A Randomized, Parallel, Double-Blind Clinical Trial. Materials. 2020; 13(23):5520. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13235520
Chicago/Turabian StyleGrasso, Giuseppe, Stefano Mummolo, Sara Bernardi, Davide Pietropaoli, Giuseppe D’Ambrosio, Giovanna Iezzi, Adriano Piattelli, Serena Bianchi, and Enrico Marchetti. 2020. "Histological and Histomorphometric Evaluation of New Bone Formation after Maxillary Sinus Augmentation with Two Different Osteoconductive Materials: A Randomized, Parallel, Double-Blind Clinical Trial" Materials 13, no. 23: 5520. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13235520
APA StyleGrasso, G., Mummolo, S., Bernardi, S., Pietropaoli, D., D’Ambrosio, G., Iezzi, G., Piattelli, A., Bianchi, S., & Marchetti, E. (2020). Histological and Histomorphometric Evaluation of New Bone Formation after Maxillary Sinus Augmentation with Two Different Osteoconductive Materials: A Randomized, Parallel, Double-Blind Clinical Trial. Materials, 13(23), 5520. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13235520








