Application of Mössbauer Spectroscopy for Identification of Iron-Containing Components in Upper Silesian Topsoil Being under Industrial Anthropopressure
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
4. Summary
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References and Note
- Sims, I.; Crane, M.; Johonson, I.; Credland, P. Biomonitoring the environmental impact of atmospheric emission from the Avonmouth zinc smelter, United Kingdon. Ecotoxicology 2009, 18, 961–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, C.F.; Allen, D.T. Hydrocarbon emissions from industrial release events in the Houston-Galveston area and their impact on ozone formation. Atmos. Environ. 2005, 39, 3785–3789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szumiata, T.; Rachwał, M.; Magiera, T.; Brzózka, K.; Gzik-Szumiata, M.; Gawroński, M.; Górka, B.; Kyzioł-Komisińska, J. Iron-containing phases in metallurgical and coke dust as well as in bog iron ore. Nukleonika 2017, 62, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kierlik, P.; Hanc-Kuczkowska, A.; Męczyński, R.; Matuła, I.; Dercz, G. Phase composition of urban soils by x-ray diffraction and mössbauer spectroscopy analysis. Arch. Metall. Mater. 2019, 64, 1029–1032. [Google Scholar]
- Rachwał, M.; Magiera, T.; Wawer, M. Coke industry and steel metallurgy as the source of sil contamination by technogenic magnetic particles, heavy metals and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Chemosphere 2015, 138, 863–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koukouzas, N.; Hämäläinen, J.; Papanikolaou, A.; Tourunen, T.; Jäntii, T. Mineralogical and elemental composition of fly ash from pilot scale fluidized bed combustion of lignite, bituminous coal, wood chips and their blends. Fuel 2007, 86, 2186–2193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lourenco, A.; Gomes, C. Integration of magnetic measurements, chemical and statistical analysis in characterizing agricultural soils (central Portugal). Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bućko, M.; Magiera, T.; Johanson, B.; Petrovsky, E.; Pesonen, L. Identification of magnetic particulates in road dust accumulated on roadside snow using magnetic, geochemical and micro-morphological analyses. Environ. Pollut. 2011, 159, 1266–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeleńska, M.; Górka-Kostrubiec, B.; Werner, T.; Kądziałko-Hofmokl, M.; Szczepaniak-Wnuk, I.; Gonet, T.; Szwarczewski, P. Evaluatin of indoor/outdoor urban air pollution by magnetic, chemical and microscopic studies. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2017, 8, 754–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magiera, T.; Parzentny, H.; Róg, L.; Chybiorz, R.; Wawer, M. Spatial variation of soil magnetic susceptibility in relation to different emission sources in southern Poland. Geoderma 2015, 255, 94–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaparro, M.; Lavornia, J.; Chaparro, M.; Sinito, A. Biomonitors of urban air pollution: Magnetic studies and SEM observations of corticolous foliose and microfoliose lichens and their suitability for magnetic monitoring. Environ. Pollut. 2013, 172, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ewing, S.; Christensen, J.; Brown, S.; Vancuren, R.; Cliff, S.; Depaolo, D. Pb isotopes as ndicator of the Asian contribution to particulate air pollution in ueban California. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 891–9816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunindi, M.; Tasdemir, Y. Atmospheric polychlorinated biphentyl (pcb) inputs to coastal city near the marmara sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2011, 215, 427–439. [Google Scholar]
- Jordanova, D.; Goddu, S.; Kotsev, T.; Jordanova, N. Industrial contaminaion of alluvial soils near Fe-Pb mining site revealed by magnetic and geochemical studies. Geoderma 2013, 192, 237–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Dubikova, M.; French, D.; Sahajwalla, V. Characterization of the origin and distribution of the minerals and phases in metallurgical cokes. Energy Fuels 2007, 21, 303–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dziubanek, G.; Spychała, A.; Marchwińska-Wyrwał, E.; Rusin, M.; Hajok, I.; Ćwieląg-Drabek, M.; Piekut, A. Long-term exposure to urban air pollution and the relationship with life expectancy in cohort of 3.5 million people in Silesia. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 580, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zawadzki, J.; Fabijańczyk, P.; Magiera, T.; Rachwał, M. Micro-scale spatial correlation of magnetic susceptibility in soil profile in forest located in an industrial area. Geoderma 2015, 249–250, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Łukasik, A.; Gruba, P.; Magiera, T. Application of magnetometry to assess distribution of dust pollution in topsoil of under-crown area of Norway spruce (Picea abies Karst.) and European beech (Fagus sylvatica L.). Catena 2017, 150, 246–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rachwał, M.; Wawer, M.; Magiera, T.; Steinnes, E. Integration of soil magnetometry and geochemistry for assessment of human health risk from metallurgical slag dumps. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 26410–26423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wawer, M.; Rachwał, M.; Kowalska, J. Impact of noise barriers on the dispersal of solid pollutants from car emissions and their deposition in soil. Soil Sci. Annu. 2017, 68, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lecoanet, H.; Leveque, F.; Segura, S. Magnetic susceptibility in environmental applications: Comparison of field probes. Phys. Earth Planet. Inter. 1999, 115, 191–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 21226:2019—International ISO Standard: Soil Quality—Guideline for the Screening of Soil Polluted with Toxic Elements Using Soil Magnetometry, 1st ed.; International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2019.
- McAndrew, J. Calibration of a Frantz isodynamic separator and its application to mineral separation. Proc. Aust. Inst. Min. Metall. 1957, 181, 59–73. [Google Scholar]
- PMOS—The specialized program for experimental Mössbauer spectra analysis designed by J. Żukrowski for the needs of University of Silesia employees.
- Stevens, J.G.; Khansanov, A.M.; Miller, J.W.; Pollak, H.; Li, Z. Mössbauer Mineral Handbook, Mössbauer Effect Data Center, 3rd ed.; The University of North Carolina: Asheville, NC, USA, 2005; pp. 1–636. [Google Scholar]
- Hatfield, R.; Maher, B. Fingerprinting upland sediment sources: Particle size specific magnetic linkages between soils, lake sediments and suspended sediments. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2009, 34, 1359–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oldfield, F.; Hao, Q.; Bloemendal, J.; Gibbs-Eggar, Z.; Patil, S.; Guo, Z. Links between particle size and magnetic grain size: General observations and some implications for Chinese loess studies. Sedimentology 2009, 56, 2091–2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razik, S.; Dekkers, M.; Dobeneck, T. How environmental magnetism can enhance the interpretational value of grain-size analysis: A time-slice study on sediment export to the NW African margin in Heinrich Stadial and Mid Holocene. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2014, 406, 33–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, G.; Brindley, G.W. X-ray Diffraction Procedures for Clay Mineral Identification. In Crystal Structures of Clay Minerals and their X-Ray Identification; Brindley, G.W., Brown, G., Eds.; Mineralogical Society of Great Britain and Ireland: London, UK, 1980; pp. 305–360. [Google Scholar]
- Kalinowski, B.; Schweda, P. Kinetics of muscovite, phlogopite, and biotite dissolution and alteration at pH 1,4, room temperaturę. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1996, 60, 367–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, S.W. Structures of Layer Silicates. In Crystal Structures of Clay Minerals and their X-Ray Identification; Brindley, G.W., Brown, G., Eds.; Mineralogical Society of Great Britain and Ireland: London, UK, 1980; pp. 1–124. [Google Scholar]
- Kopcewicz, B.; Kopcewicz, M.; Jelenska, M.; Hasso-Agopsowicz, A. Mössbauer study of chemical transformations in soil samples during thermomagnetic measurements. Hyperfine Interact. 2005, 166, 631–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, M.; Verma, N.; Prasad, R. Structural and catalytic properties of Zn1–xCuxFe2O4 nanoparticles. J. Mater. Sci. 2007, 42, 1833–1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kądziołka-Gaweł, M.; Smolka-Danielowska, D. 57Fe Mössbauer spectroscopy investigations of iron phase cmposition in fluidized beds from the ELCHO power plant in Chorzów, Poland. Nukleonika 2017, 62, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Waanders, F.; Vinken, E.; Mans, A.; Mulaba-Bafubiandi, A. Iron minerals in coal, weathered coal and coal ash—SEM and Mössbauer results. Hyperfine Interact. 2003, 148–149, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szumiata, T.; Gawroński, M.; Górka, B.; Brzózka, K.; Świetlik, R.; Trojanowska, M.; Strzelecka, M. Chemical, magnetic and Mössbauer effect analysis of road dust from expressway. Nukleonika 2013, 58, 109–122. [Google Scholar]
- Silva, G.; Almeida, F.; Ferreira, A.; Ciminelli, V. Preparation and Application of a Magnetic Composite (Mn3O4/Fe3O4) for Removal of As(III) from Aqueous Solutions. Mater. Res. 2012, 15, 403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omer, M.; Elbadawi, A.; Yassin, O. Synthesis and structural properties of MgFe2O4 ferrite nano-particles. J. Appl. Ind. Sci. 2013, 1, 20–23. [Google Scholar]
- Doriguetto, A.; Fernandes, N.; Persiano, A.; Nunes Filho, E.; Greneche, J.; Fabris, J. Characterization of natural magnetite. Phys. Chem. Miner. 2003, 30, 249–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
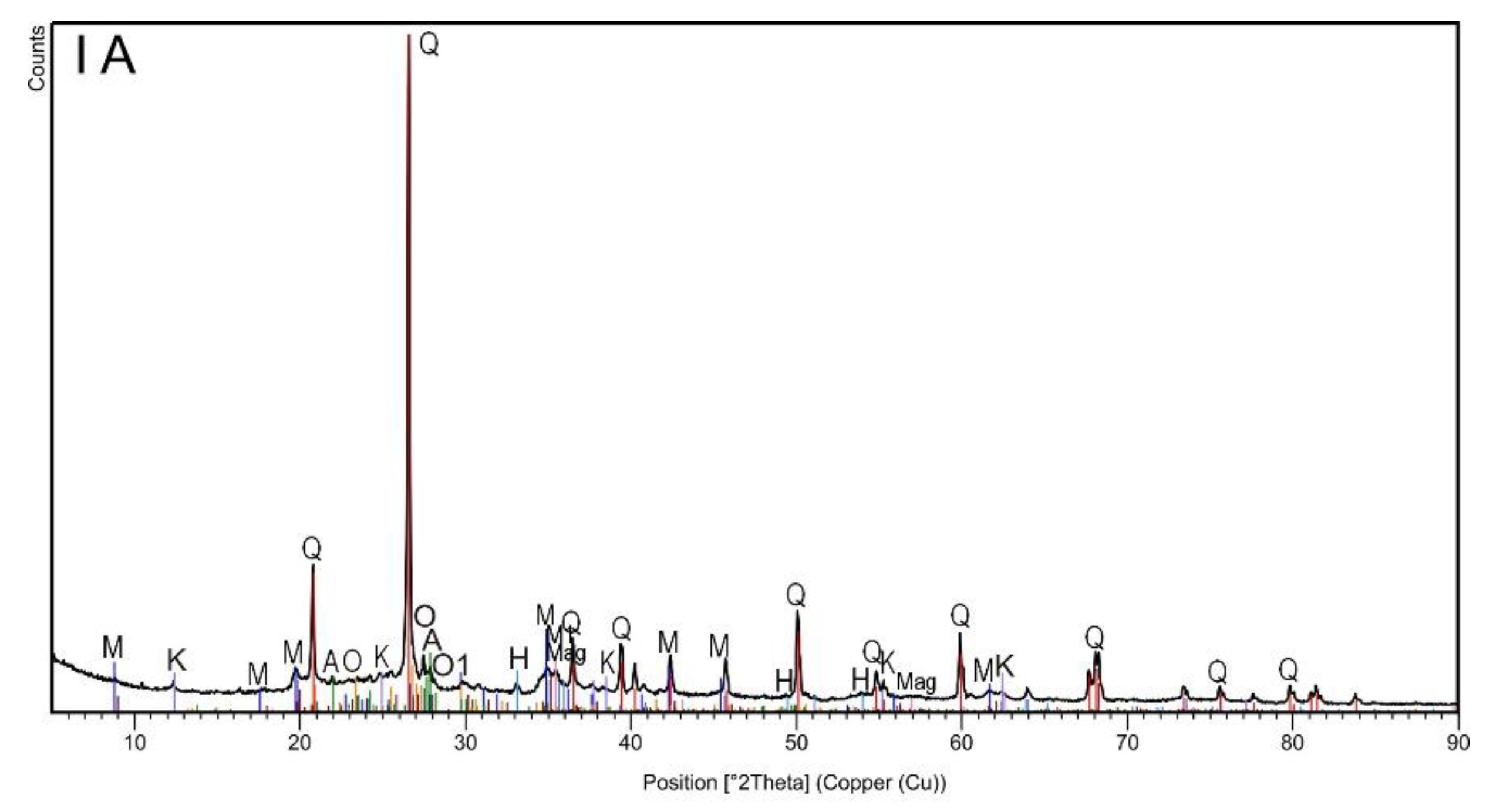
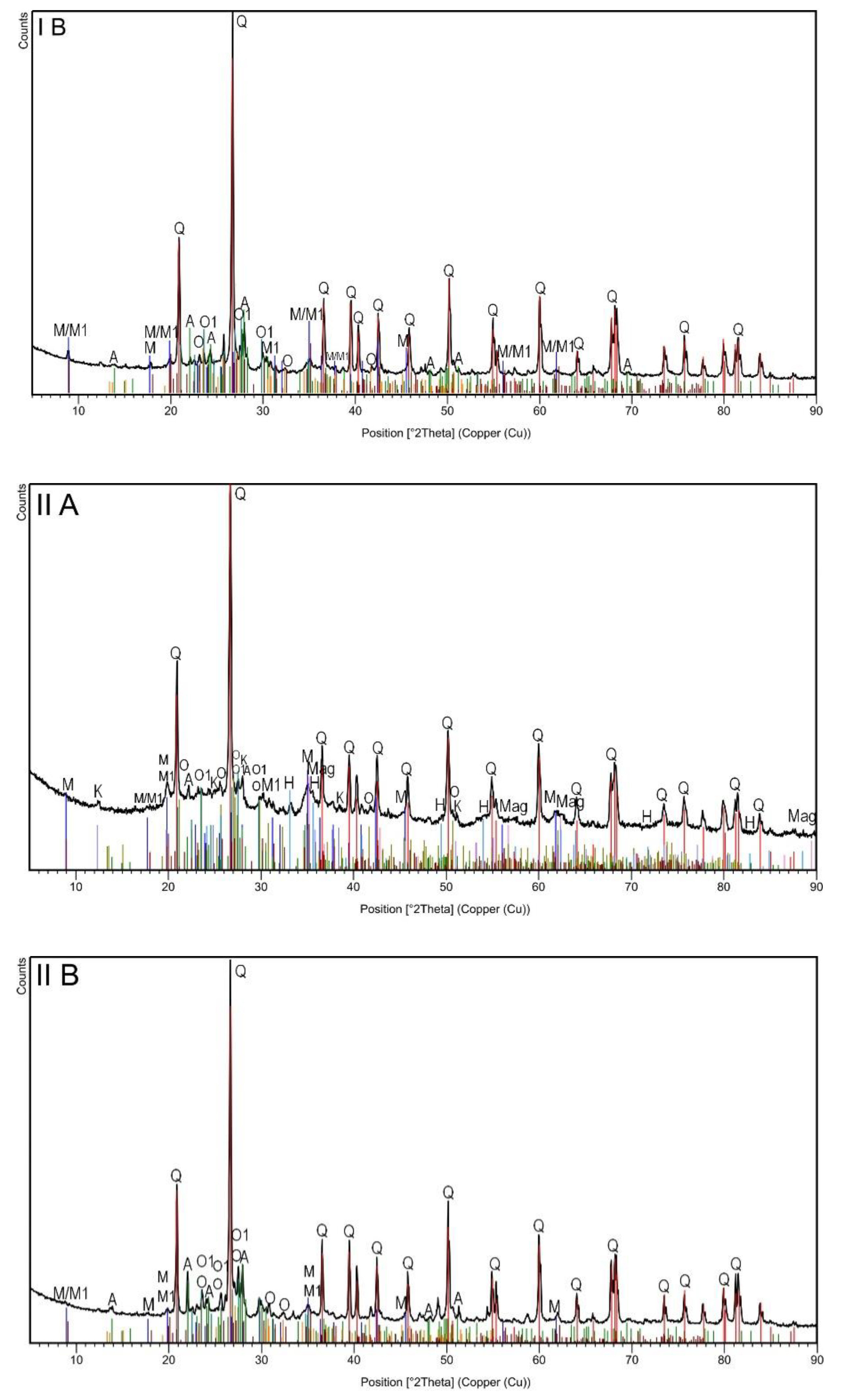

| Topsoil Subsample | Grain Size (mm) | Current Intensity (A) | χ (×10−8 m3/kg) |
|---|---|---|---|
| IA (strongly magnetic) | 0.05–0.1 | 0.2 | 247.6 |
| IIA (strongly magnetic) | 0.25–0.5 | 0.2 | 139.4 |
| IB (weakly magnetic) | 0.05–0.1 | 1.6 | 3.6 |
| IIB (weakly magnetic) | 0.25–0.5 | 1.6 | 4.0 |
| Identified Phase | Topsoil Subsample | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chemical Formula | Mineral (Symbol) | IA | IIA | IB | IIB |
| SiO2 | Quartz (Q) | x | x | x | x |
| H2KAl3(Si04)3 | Muscovite (M) | x | x | x | x |
| K0.60Na0.37Mg0.06Ti0.02Fe0.10Al2.81Si3.03O10(OH)2 | Muscovite -2M1 (M1) | x | x | x | x |
| NaAlSi2O8 | Albite (A) | x | x | x | x |
| Si2 Al2O5(OH)4 | Kaolinite (K) | x | x | ||
| KAlSi3O8 | Orthoclase (O) | x | x | x | x |
| K(Al,Fe)Si2O8 | Orthoclase (O1) | x | x | x | x |
| Fe3O4 | Magnetite (Mag) | x | x | ||
| Fe2O3 | Hematite (H) | x | x | ||
| Subsample | IA | IIA | Iron-Containing Phase | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Component | IS | QS | H | A | IS | QS | H | A | |
| [mm/s] | [mm/s] | [T] | [%] | [mm/s] | [mm/s] | [T] | [%] | ||
| D1 | 0.35 | 0.64 | 0 | 51 | 0.33 | 0.67 | 0 | 51 | Aluminosilicates with Fe3+ |
| D2 | 0.86 | 2.47 | 0 | 8 | 1.24 | 2.4 | 0 | 14 | Aluminosilicates with Fe2+ |
| Z1 | 0.36 | −0.18 | 51 | 17 | 0.36 | −0.16 | 51 | 19 | Hematite |
| Z2 | 0.61 | −0.08 | 46 | 20 | 0.5 | 0.05 | 46 | 16 | Magnetite |
| Z3 | 0.27 | −0.02 | 49 | 4 | - | - | - | - | |
| Subsample | IB | IIB | Iron-Containing Phase | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Component | IS | QS | A | IS | QS | A | |
| [mm/s] | [mm/s] | [%] | [mm/s] | [mm/s] | [%] | ||
| D1 | 0.34 | 0.65 | 93 | 0.34 | 0.62 | 85 | Aluminosilicates with Fe3+ |
| D2 | 1.22 | 2.32 | 7 | 1.24 | 2.29 | 15 | Aluminosilicates with Fe2+ |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kierlik, P.; Hanc-Kuczkowska, A.; Rachwał, M.; Męczyński, R.; Matuła, I. Application of Mössbauer Spectroscopy for Identification of Iron-Containing Components in Upper Silesian Topsoil Being under Industrial Anthropopressure. Materials 2020, 13, 5206. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13225206
Kierlik P, Hanc-Kuczkowska A, Rachwał M, Męczyński R, Matuła I. Application of Mössbauer Spectroscopy for Identification of Iron-Containing Components in Upper Silesian Topsoil Being under Industrial Anthropopressure. Materials. 2020; 13(22):5206. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13225206
Chicago/Turabian StyleKierlik, Patrycja, Aneta Hanc-Kuczkowska, Marzena Rachwał, Ryszard Męczyński, and Izabela Matuła. 2020. "Application of Mössbauer Spectroscopy for Identification of Iron-Containing Components in Upper Silesian Topsoil Being under Industrial Anthropopressure" Materials 13, no. 22: 5206. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13225206
APA StyleKierlik, P., Hanc-Kuczkowska, A., Rachwał, M., Męczyński, R., & Matuła, I. (2020). Application of Mössbauer Spectroscopy for Identification of Iron-Containing Components in Upper Silesian Topsoil Being under Industrial Anthropopressure. Materials, 13(22), 5206. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13225206





