Influence of Oxide Glass Modifiers on the Structural and Spectroscopic Properties of Phosphate Glasses for Visible and Near-Infrared Photonic Applications
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Structural Properties of Phosphate Glasses
3.2. Spectroscopic Properties of Phosphate Glasses
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liao, X.; Jiang, X.; Yang, Q.; Wang, L.; Chen, D. Spectral Properties of Er3+/Tm3+ Co-Doped ZBLAN Glasses and Fibers. Materials 2017, 10, 486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Wen, H.; Pan, X.; Yu, J.; Shao, H.; Ai, F.; Yu, H.; Tang, M.; Gai, L. Study on Upconversion and Thermal Properties of Tm3+/Yb3+ Co-Doped La2O3-Nb2O5-Ta2O5 Glasses. Materials 2018, 11, 1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ragin, T.; Baranowska, A.; Kochanowicz, M.; Zmojda, J.; Miluski, P.; Dorosz, D. Study of Mid-Infrared Emission and Structural Properties of Heavy Metal Oxide Glass and Optical Fibre Co-Doped with Ho3+/Yb3+ Ions. Materials 2019, 12, 1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, Y.; Wang, S.; An, H. White-light emission and chromaticity characterization of Dy3+ doped fluoride glass for standard white light source. J. Non Cryst. Solids 2019, 526, 119697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Li, D.; Pun, E.Y.B.; Lin, H. Dy3+ doped tellurium-borate glass phosphors for laser-driven white illumination. J. Lumin. 2019, 206, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balaji Rao, R.; Gerhardt, R.A. Effect of alkaline earth modifier ion on the optical, magnetic and electrical properties of lithium nickel borate glasses. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2008, 112, 186–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavić, L.; Fazinić, S.; Ertap, H.; Karabulut, M.; Moguš-Milanković, A.; Šantić, A. Polaronic Conductivity in Iron Phosphate Glasses Containing B2O3. Materials 2020, 13, 2505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balakrishna, A.; Rajesh, D.; Ratnakaram, Y.C. Spectroscopic analysis of Ho3+ transitions in different modifier oxide based lithium-fluoro-borate glasses. Physica B 2014, 450, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naga Raju, G.; Venkateswara Rao, P.; Ravi Kumar, V.; Chandrakala, C.; Ashok, J. Study on the influence of TiO2 on the characteristics of multi component modifier oxide based B2O3 glass system. J. Non Cryst. Solids 2018, 498, 309–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, R.N.A.; Siva, B.V.; Neeraja, K.; Krishna Mohan, N.; Rojas, J.I. Influence of modifier oxides on spectroscopic features of Nd2O3 doped PbO-Ro2O3–WO3–B2O3 glasses (with Ro2O3 = Sb2O3, Al2O3, and Bi2O3). J. Lumin. 2020, 223, 117171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Zhuang, Y.; Han, J.; Ruan, J.; Liu, C.; Zhao, X. Multi-band near-infrared emission in low concentration bismuth doped alkaline earth alumino-boro-germanate glass. Ceram. Int. 2020, 46, 15544–15553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, K.S.R.K.; Swapna, K.; Mahamuda, S.; Venkateswarlu, M.; Rao, A.S.; Vijaya Prakash, G. Investigation on structural and luminescence features of Dy3+ ions doped alkaline-earth boro tellurite glasses for optoelectronic devices. Opt. Mater. 2018, 85, 200–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griebenow, K.; Bragatto, C.B.; Kamitsos, E.I.; Wondraczek, L. Mixed-modifier effect in alkaline earth metaphosphate glasses. J. Non Cryst. Solids 2018, 481, 447–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaky, K.M.; Lakshminarayana, G.; Baki, S.O.; Taufiq-Yap, Y.H.; Kityk, I.V.; Mahdi, M.A. Structural, thermal, and optical analysis of zinc boro-aluminosilicate glasses containing different alkali and alkaline modifier ions. J. Non Cryst. Solids 2017, 456, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leśniak, M.; Szal, R.; Starzyk, B.; Gajek, M.; Kochanowicz, K.; Żmojda, J.; Miluski, P.; Dorosz, J.; Sitarz, M.; Dorosz, D. Influence of barium oxide on glass-forming ability and glass stability of the tellurite-phosphate oxide glasses. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2019, 138, 4295–4302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavić, L.; Moguš-Milanković, A.; Raghava Rao, P.; Šantić, A.; Ravi Kumar, V.; Veeraiah, N. Effect of alkali-earth modifier ion on electrical, dielectric and spectroscopic properties of Fe2O3 doped Na2SO4-MO-P2O5 glass system. J. Alloys Compd. 2014, 604, 352–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratnakaram, Y.C.; Balakrishna, A.; Rajesh, D. Effect of modifier oxides on absorption and emission properties of Eu3+ doped different lithium fluoroborate glass matrices. Physica B 2012, 407, 4303–4307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, K.S.R.K.; Swapna, K.; Venkateswarlu, M.; Mahamuda, S.; Rao, A.S. Thermal, Up-Conversion and Near-Infrared Luminescence studies of Erbium ions doped Alkaline-Earth Boro Tellurite glasses. Solid State Sci. 2019, 97, 106016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luewarasirikul, N.; Kaewkhao, J. The effect of alkaline earth on luminescence properties of A-Na-B glasses (A = Mg, Ca, Sr and Ba) doped with Dy2O3. Mater. Today Proc. 2018, 5, 15098–15103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudhakar, K.S.V.; Srinivasa Reddy, M.; Srinivasa Rao, L.; Veeraiah, N. Influence of modifier oxide on spectroscopic and thermoluminescence characteristics of Sm3+ ion in antimony borate glass system. J. Lumin. 2008, 128, 1791–1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashirvadam, A.; Ravi Kumar, V.; Naga Raju, G. Influence of modifier oxide on emission features of Sm3+ ion in lithium antimonate glasses. Mater. Today Proc. 2018, 5, 26191–26198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravi Kumar, V.; Giridhar, G.; Veeraiah, N. Influence of modifier oxide on emission features of Dy3+ ion in Pb3O4-ZnO-P2O5 glasses. Opt. Mater. 2016, 60, 594–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balakrishna, A.; Rajesh, D.; Ratnakaram, Y.C. Structural and optical properties of Nd3+ in lithium fluoro-borate glass with relevant modifier oxides. Opt. Mater. 2013, 35, 2670–2676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petit, L. Radiation effects on phosphate glasses: Review. Int. J. Appl. Glass Sci. 2020, 11, 511–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojha, N.; Tuomisto, M.; Lastusaari, M.; Petit, L. Phosphate glasses with blue persistent luminescence prepared using the direct doping method. Opt. Mater. 2019, 87, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boetti, N.G.; Scarpignato, G.C.; Lousteau, J.; Pugliese, D.; Bastard, L.; Broquin, J.-E.; Milanese, D. High concentration Yb-Er co-doped phosphate glass for optical fiber amplification. J. Opt. 2015, 17, 065705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stępień, R.; Franczyk, M.; Pysz, D.; Kujawa, I.; Klimczak, M.; Buczyński, R. Ytterbium-Phosphate Glass for Microstructured Fiber Laser. Materials 2014, 7, 4723–4738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filho, J.C.; Messias, D.N.; Pilla, V.; Silva, A.C.; Dantas, N.O.; Andrade, A.A. Temperature-dependence on the lifetime of Nd3+-doped phosphate glass. J. Lumin. 2020, 219, 116901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damodaraiah, S.; Reddy Prasad, V.; Ratnakaram, Y.C. Structural and luminescence properties of Sm3+-doped bismuth phosphate glass for orange-red photonic applications. Luminescence 2018, 33, 594–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Félix-Quintero, H.; Mejía-Uriarte, E.V.; Falcony, C.; Acosta, D.; Hernández A, J.; Flores J, C.; Camarillo G, E.; Murrieta S, H. Tunable white light emission through energy transfer processes between silver species in Ag-doped zinc phosphate glass. J. Lumin. 2020, 222, 117122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcondes, L.M.; Santagneli, S.H.; Manzani, D.; Cassanjes, F.C.; Batista, G.; Mendoza, V.G.; da Cunha, C.R.; Poirier, G.Y.; Nalin, M. High tantalum oxide content in Eu3+-doped phosphate glass and glass-ceramics for photonic applications. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 842, 155853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dousti, M.R.; Poirier, G.Y.; de Camargo, A.S.S. Tungsten sodium phosphate glasses doped with trivalent rare earth ions (Eu3+, Tb3+, Nd3+ and Er3+) for visible and near-infrared applications. J. Non Cryst. Solids 2020, 530, 119838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, Y.; Mingming, L.; Li, J.; Tang, J.; Cao, W.; Wu, Z. Optical properties of Er3+/Yb3+ co-doped phosphate glass system for NIR lasers and fiber amplifiers. Ceram. Int. 2018, 44, 22467–22472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kummara, V.K.; Neelima, G.; Ravi, N.; Nallabala, N.K.R.; Reddy, H.S.K.; Dwaraka Viswanath, C.S.; Lenine, D.; Surekha, G.; Padma Suvarna, R.; Yuvaraj, C.; et al. Near infrared broadband and visible upconversion emissions of erbium ions in oxyfluoride glasses for optical amplifier applications. Opt. Laser Technol. 2020, 127, 106167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morassuti, C.Y.; Nunes, L.A.O.; Lima, S.M.; Andrade, L.H.C. Eu3+-doped alumino-phosphate glass for ratiometric thermometer based on the excited state absorption. J. Lumin. 2018, 193, 39–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.B.; Ji, Y.; Liu, J.L.; Wang, W.C. Nd3+-doped mixed-anion fluoro-sulfo-phosphate glass for 1.06 μm solid-state laser. J. Non Cryst. Solids 2019, 522, 119586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boetti, N.G.; Pugliese, D.; Ceci-Ginistrelli, E.; Lousteau, J.; Janner, D.; Milanese, D. Highly Doped Phosphate Glass Fibers for Compact Lasers and Amplifiers: A Review. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, C.C.; Guedes, I.; Loong, C.-K.; Boatner, L.A.; Moura, A.L.; de Araujo, M.T.; Jacinto, C.; Vermelho, M.V.D. Spectroscopic properties of Er3+-doped lead phosphate glasses for photonic application. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2010, 43, 025102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Chen, G.; Liu, X.; Xu, J.; Zhou, X.; Yang, T.; Yuan, C.; Zhou, C. Upconversion luminescence, optical thermometric properties and energy transfer in Yb3+/Tm3+ co-doped phosphate glass. Opt. Mater. 2018, 81, 78–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aryal, P.; Kim, H.J.; Khan, A.; Saha, S.; Kang, S.J.; Kothan, S.; Yamsuk, Y.; Kaewkhao, J. Development of Eu3+-doped phosphate glass for red luminescent solid-state optical devices. J. Lumin. 2020, 227, 117564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huerta, E.F.; Meza-Rocha, A.N.; Lozada-Morales, R.; Speghini, A.; Bordignon, S.; Caldiño, U. White, yellow and reddish-orange light generation in lithium-aluminum-zinc phosphate glasses co-doped with Dy3+/Tb3+ and tri-doped with Dy3+/Tb3+/Eu3+. J. Lumin. 2020, 219, 116882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huerta, E.F.; Soriano-Romero, O.; Meza-Rocha, A.N.; Bordignon, S.; Speghini, A.; Caldiño, U. Lithium-aluminum-zinc phosphate glasses activated with Sm3+, Sm3+/Eu3+ and Sm3+/Tb3+ for reddish-orange and white light generation. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 846, 156332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Faber, A.J.; de Waal, H. Luminescence quenching by OH groups in highly Er-doped phosphate glasses. J. Non Cryst. Solids 1995, 181, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.C.; Faber, A.J.; de Waal, H.; Kik, P.G.; Polman, A. Erbium-doped phosphate glass waveguide on silicon with 4.1 dB/cm gain at 1.535 μm. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1997, 71, 2922–2924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Iscoa, P.; Salminen, T.; Hakkarainen, T.; Petit, L.; Janner, D.; Boetti, N.G.; Lastusaari, M.; Pugliese, D.; Paturi, P.; Milanese, D. Effect of partial crystallization on the structural and luminescence properties of Er3+-doped phosphate glasses. Materials 2017, 10, 473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Iscoa, P.; Ojha, N.; Aryal, U.; Pugliese, D.; Boetti, N.G.; Milanese, D.; Petit, L. Spectroscopic properties of Er3+-doped particles-containing phosphate glasses fabricated using the direct doping method. Materials 2019, 12, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Iscoa, P.; Petit, L.; Massera, J.; Janner, D.; Boetti, N.G.; Pugliese, D.; Fiorilli, S.; Novara, C.; Giorgis, F.; Milanese, D. Effect of the addition of Al2O3, TiO2 and ZnO on the thermal, structural and luminescence properties of Er3+-doped phosphate glasses. J. Non Cryst. Solids 2017, 460, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Eckert, H. Intermediate role of gallium in oxidic glasses: Solid state NMR structural studies of the Ga2O3-NaPO3 system. J. Phys. Chem. 2014, 118, 15386–15403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshimoto, K.; Masuno, A.; Ueda, M.; Inoue, H.; Yamamoto, H.; Kawashima, T. Low phonon energies and wideband optical windows of La2O3-Ga2O3 glasses prepared using an aerodynamic levitation techniques. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 45600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, Z.; Ya-Xun, Z.; Shi-Xun, D.; Tie-Feng, X.; Qiu-Hua, N.; Xiang, S. Effect of Ga2O3 on the spectroscopic properties of erbium-doped boro-bismuth glasses. Spectrochim. Acta A 2007, 68, 548–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatramu, V.; Vijaya, R.; León-Luis, S.F.; Babu, P.; Jayasankar, C.K.; Lavín, V.; Dhareshwar, L.J. Optical properties of Yb3+-doped phosphate laser glasses. J. Alloys Compd. 2011, 509, 5084–5089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, K.; Vishwakarma, A.K.; Jayasimhadri, M.; Haranath, D. Multicolor and white light emitting Tb3+/Sm3+ co-doped zinc phosphate barium titanate glasses via energy transfer for optoelectronic device applications. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 719, 116–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisarska, J.; Sołtys, M.; Żur, L.; Pisarski, W.A.; Jayasankar, C.K. Excitation and luminescence of rare earth-doped lead phosphate glasses. Appl. Phys. B 2014, 116, 837–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terra, I.A.A.; de Camargo, A.S.S.; Nunes, L.A.D.O.; Carvalho, R.A.; Li, M.S. Evaluation of the OH- influence on visible and near-infrared quantum efficiencies of Tm3+ and Yb3+ codoped sodium aluminophoshate glasses. J. Appl. Phys. 2006, 100, 123103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoch, P.; Stoch, A.; Ciecinska, M.; Krakowiak, I.; Sitarz, M. Structure of phosphate and iron-phosphate glasses by DFT calculations and FTIR/Raman spectroscopy. J. Non Cryst. Solids 2016, 450, 48–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moustafa, Y.M.; El-Egili, K. Infrared spectra of sodium phosphate glasses. J. Non Cryst. Solids 1998, 240, 144–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascuta, P.; Borodi, G.; Jumate, N.; Vida-Simiti, I.; Viorel, D.; Culea, E. The structural role of manganese ions in some zinc phosphate glasses and glass ceramics. J. Alloys Compd. 2010, 504, 479–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, P.K.; Pandey, O.P.; Singh, K. FTIR spectral analysis and mechanical properties of sodium phosphate glass-ceramics. J. Mol. Struct. 2015, 1083, 278–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Y.; Liang, X.; Yang, S.; Liu, P.; Zeng, Y.; Hu, C. Raman and FTIR spectra of CeO2 and Gd2O3 in iron phosphate glasses. J. Alloys Compd. 2014, 617, 597–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Little Flower, G.; Srinivasa Reddy, M.; Sahaya Baskaran, G.; Veeraiah, N. The structural influence of chromium ions in lead gallium phosphate glasses by means of spectroscopic studies. Opt. Mater. 2007, 30, 357–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilieva, D.; Jivov, B.; Bogachev, G.; Petkov, C.; Penkov, I.; Dimitriev, Y. Infrared and Raman spectra of Ga2O3-P2O5 glasses. J. Non Cryst. Solids 2011, 283, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vedeanu, N.; Magdas, D.A.; Stefan, R. Structural modifications induced by addition of copper oxide to lead-phosphate glasses. J. Non Cryst. Solids 2012, 358, 3170–3174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reza Dousti, M.; Amjad, R.J. Spectroscopic properties of Tb3+-doped lead zinc phosphate glass for green solid state laser. J. Non Cryst. Solids 2015, 420, 21–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakshmikantha, R.; Rajaramakrishna, R.; Anavekar, R.V.; Ayachit, N.H. Characterization and structural studies of lithium doped lead zinc phosphate glass system. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2012, 133, 249–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.S.; Chin, T.S.; Yung, S.W. FTIR and XPS studies of low-melting PbO-ZnO-P2O5 glasses. Mater. Chem. Phys. 1997, 50, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magdas, D.A.; Cozar, O.; Chis, V.; Ardelean, I.; Vedeanu, N. The structural dual role of Fe2O3 in some lead-phosphate glasses. Vib. Spectrosc. 2008, 48, 251–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, B.; Liang, X.; Wang, C.; Yang, S. Structure and properties of calcium iron phosphate glasses. J. Nucl. Mater. 2013, 443, 140–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suneel Kumar, A.; Narendrudu, T.; Suresh, S.; Sambasiva Rao, M.V.; Chinna Ram, G.; Krishna Rao, D. Role of titanium ions on the physical and structural properties of calcium zinc bismuth phosphate glass ceramics. J. Non Cryst. Solids 2016, 434, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, A.K.; Singh, P. A review of the structures of oxide glasses by Raman spectroscopy. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 67583–67609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Liang, X.; Li, H.; Yu, H.; Li, Z.; Yang, S. Structure and properties of gadolinium loaded calcium phosphate glasses. J. Nucl. Mater. 2014, 453, 220–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuczek, J.; Jeleń, P.; Stoch, P.; Błachowski, A.; Wacławska, I.; Szumera, M. Raman and Mössbauer studies of iron phosphate-silicate glasses. J. Mol. Struct. 2018, 1170, 82–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivascu, C.; Timar Gabor, A.; Cozar, O.; Daraban, L.; Ardelean, I. FT-IR, Raman and thermoluminescence investigation of P2O5–BaO–Li2O glass system. J. Mol. Struct. 2011, 993, 249–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deopa, N.; Sumandeep, K.; Prasad, A.; Joshi, B.; Rao, A.S. Spectral studies of Eu3+ doped lithium lead alumino borate glasses for visible photonic applications. Opt. Laser Technol. 2018, 108, 434–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Żmojda, J.; Kochanowicz, M.; Miluski, P.; Golonko, P.; Baranowska, A.; Ragiń, T.; Dorosz, J.; Kuwik, M.; Pisarski, W.; Pisarska, J.; et al. Luminescent Studies on Germanate Glasses Doped with Europium Ions for Photonic Applications. Materials 2020, 13, 2817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pawlik, N.; Szpikowska-Sroka, B.; Sołtys, M.; Pisarski, W.A. Optical properties of silica sol-gel materials singly- and doubly-doped with Eu3+ and Gd3+ ions. J. Rare Earths 2016, 34, 786–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, K.; Jayasimhadri, X.; Haranath, D.; Jang, K. Influence of modifier oxides on spectroscopic properties of Eu3+ doped oxy-fluoro tellurophosphate glasses for visible photonic applications. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 789, 622–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirdsiri, K.; Rajaramakrishna, R.; Damdee, B.; Kim, H.J.; Nuntawong, N.; Horphathum, M.; Kaewkhao, J. Influence of alkaline earth oxides on Eu3+ doped lithium borate glasses for photonic, laser and radiation detection material applications. Solid State Sci. 2019, 89, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrmann, A.; Kuhn, S.; Tiegel, M.; Rüssel, C. Fluorescence properties of Eu3+-doped alumino silicate glasses. Opt. Mater. 2014, 37, 293–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pugliese, D.; Boetii, N.G.; Lousteau, J.; Ceci-Genistrelli, E.; Bertone, E.; Geobaldo, F.; Milanese, D. Concentration quenching in an Er-doped phosphate glass for compact optical lasers and amplifiers. J. Alloys Compd. 2016, 657, 678–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera-López, F.; Babu, P.; Jyothi, L.; Rodríguez-Mendoza, U.R.; Martín, I.R.; Jayasankar, C.K.; Lavín, V. Er3+–Yb3+ codoped phosphate glasses used for an efficient 1.5 μm broadband gain medium. Opt. Mater. 2012, 34, 1235–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Zhou, D.; Zhao, Z.; Yang, Z.; Song, Z.; Zhu, K.; Xu, Y.; Qiu, J. Effect of optical basicity on broadband infrared fluorescence in erbium-doped germanate glasses. J. Alloys Compd. 2012, 513, 339–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janek, J.; Sołtys, M.; Żur, L.; Pietrasik, E.; Pisarska, J.; Pisarski, W.A. Luminescence investigations of rare earth doped lead-free borate glasses modified by MO (M = Ca, Sr, Ba). Mater. Chem. Phys. 2016, 180, 237–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zur, L.; Janek, J.; Pietrasik, E.; Sołtys, M.; Pisarska, J.; Pisarski, W.A. Influence of MO/MF2 modifiers (M = Ca, Sr, Ba) on spectroscopic properties of Eu3+ ions in germanate and borate glasses. Opt. Mater. 2016, 61, 59–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherbib, M.A.; Kapoor, S.; Bockowski, M.; Smedskjaer, M.M.; Wondraczek, L. Luminescence behavior of Eu3+ in hot-compressed silicate glasses. J. Non Cryst. Solids X 2019, 4, 100041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stambouli, W.; Elhouichet, H.; Gelloz, B.; Férid, M. Optical and spectroscopic properties of Eu-doped tellurite glasses and glass ceramics. J. Lumin. 2013, 138, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisarski, W.A.; Żur, L.; Goryczka, T.; Sołtys, M.; Pisarska, J. Structure and spectroscopy of rare earth—Doped lead phosphate glasses. J. Alloys Compd. 2014, 587, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Żur, L.; Janek, J.; Sołtys, M.; Pisarska, J.; Pisarski, W.A. Spectroscopic properties of Eu3+, Dy3+ and Tb3+ ions in lead silicate glasses obtained by the conventional high-temperature melt-quenching technique. Phys. Scr. 2013, 2013, 014035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramesh, P.; Hegde, V.; Pramod, A.G.; Eraiah, B.; Agarkov, D.A.; Eliseeve, G.M.; Pandey, M.K.; Annapurna, K.; Jagannath, G.; Kokila, M.K. Compositional dependence of red photoluminescence of Eu3+ ions in lead and bismuth containing borate glasses. Solid State Sci. 2020, 107, 106360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gökçe, M. Development of Eu3+ doped bismuth germanate glasses for red laser applications. J. Non Cryst. Solids 2019, 505, 272–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, T.; Chen, F.; Tian, Y.; Xu, S. Broadband 1.53 μm emission property in Er3+ doped germa-silicate glass for potential optical amplifier. Opt. Commun. 2014, 315, 199–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; He, D.; Wang, G.; Zhang, J.; Hu, L. Influence of cationic field strength of modifiers on the 1.53 μm spectroscopic properties of Er3+-doped tellurite glasses. J. Non Cryst. Solids 2009, 355, 2250–2253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sołtys, M.; Żur, L.; Pisarska, J.; Goryczka, T.; Pisarski, W.A. Selective oxide modifiers M2O3 (M = Al, Ga) as crystallizing agents in Er3+-doped lead phosphate glass host. Ceram. Int. 2015, 41, 4334–4339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
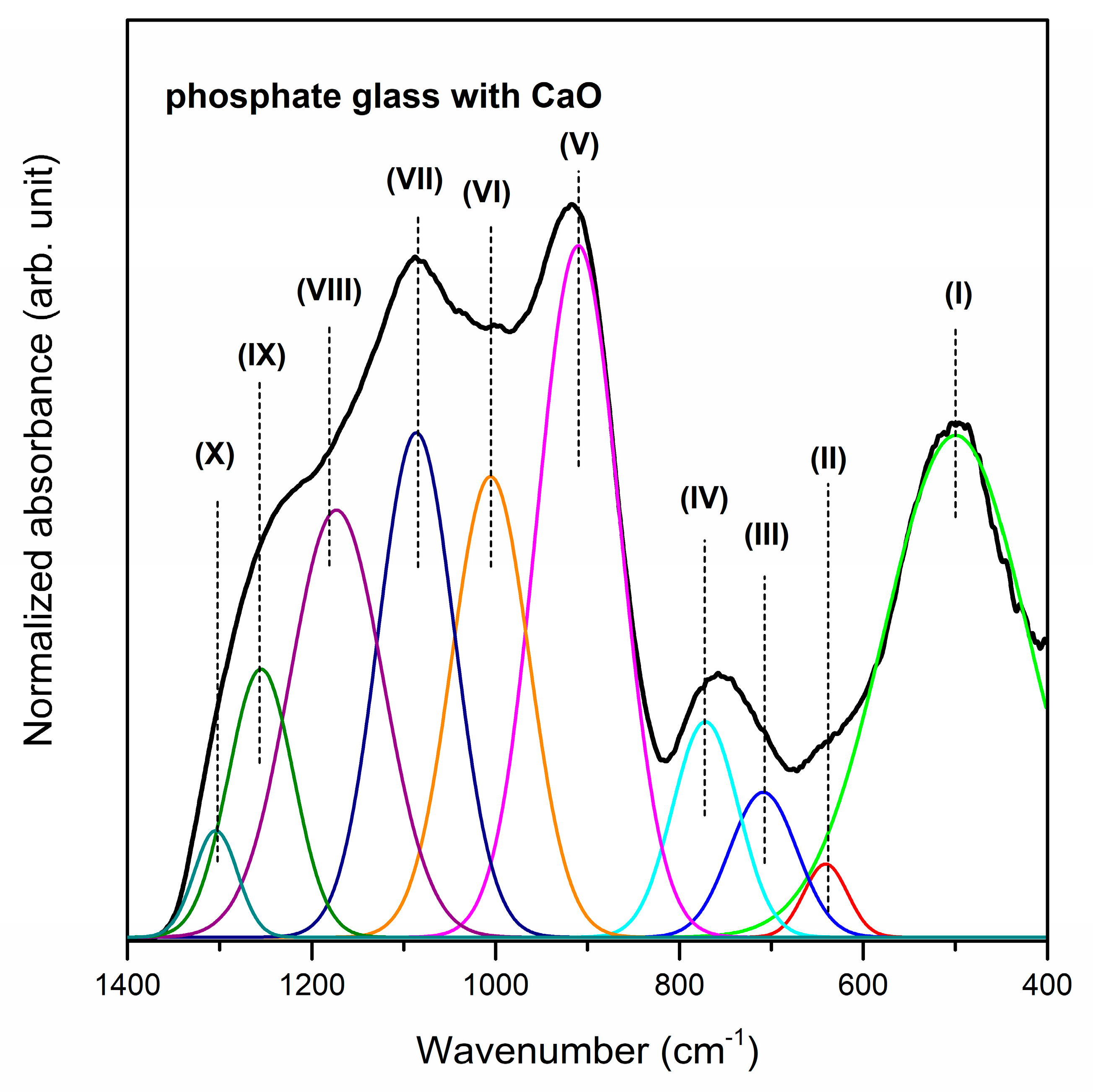
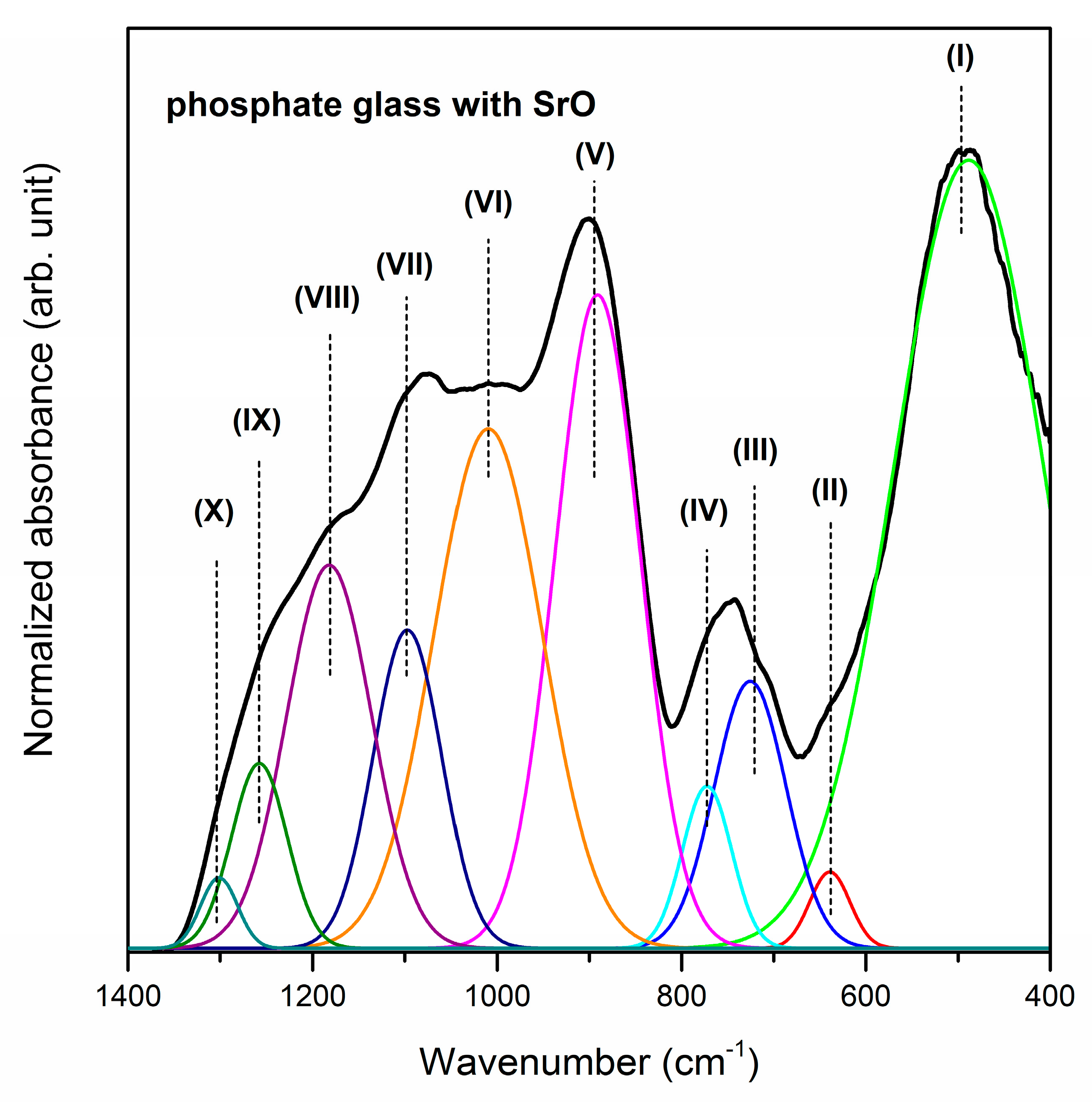
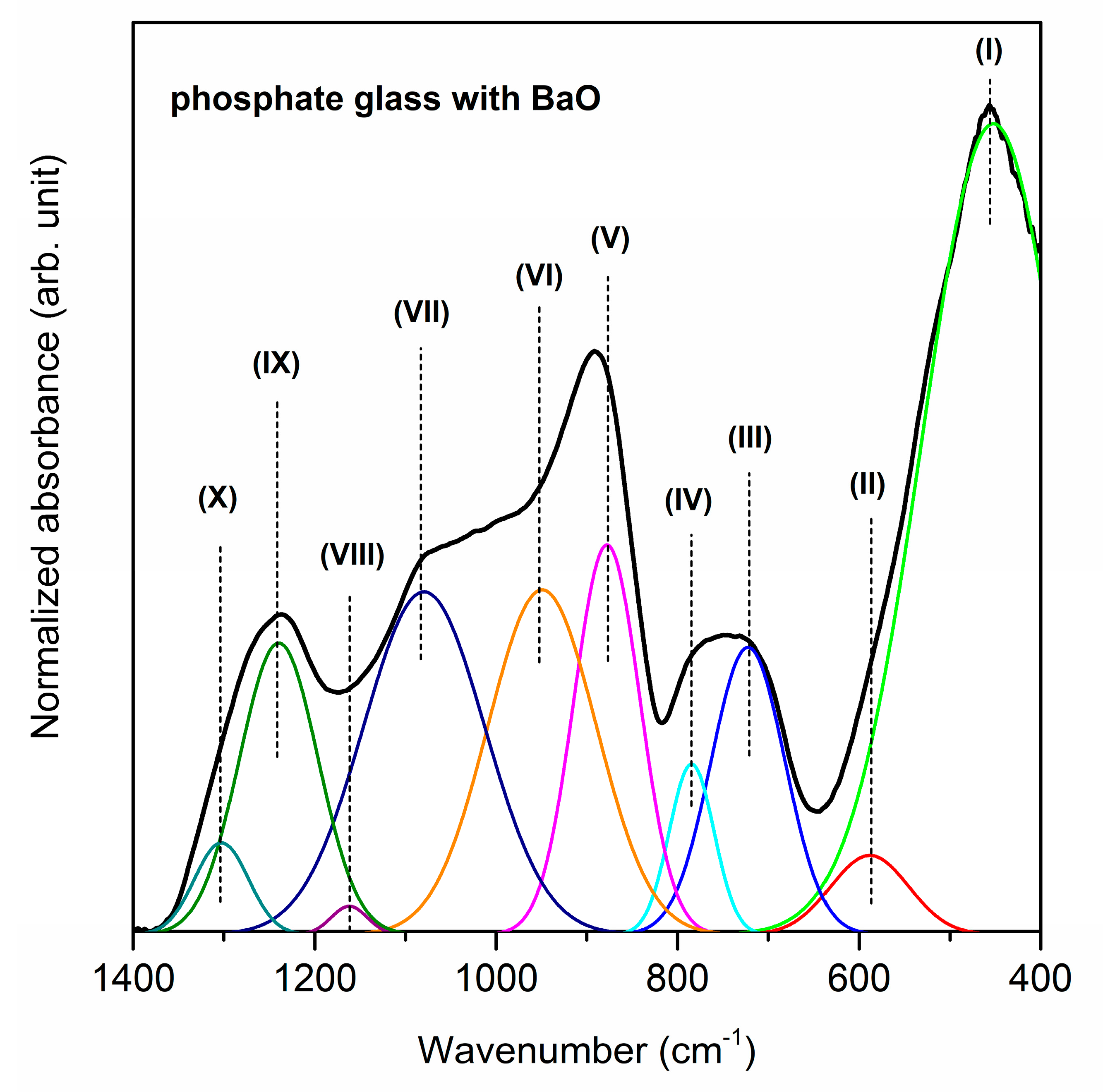
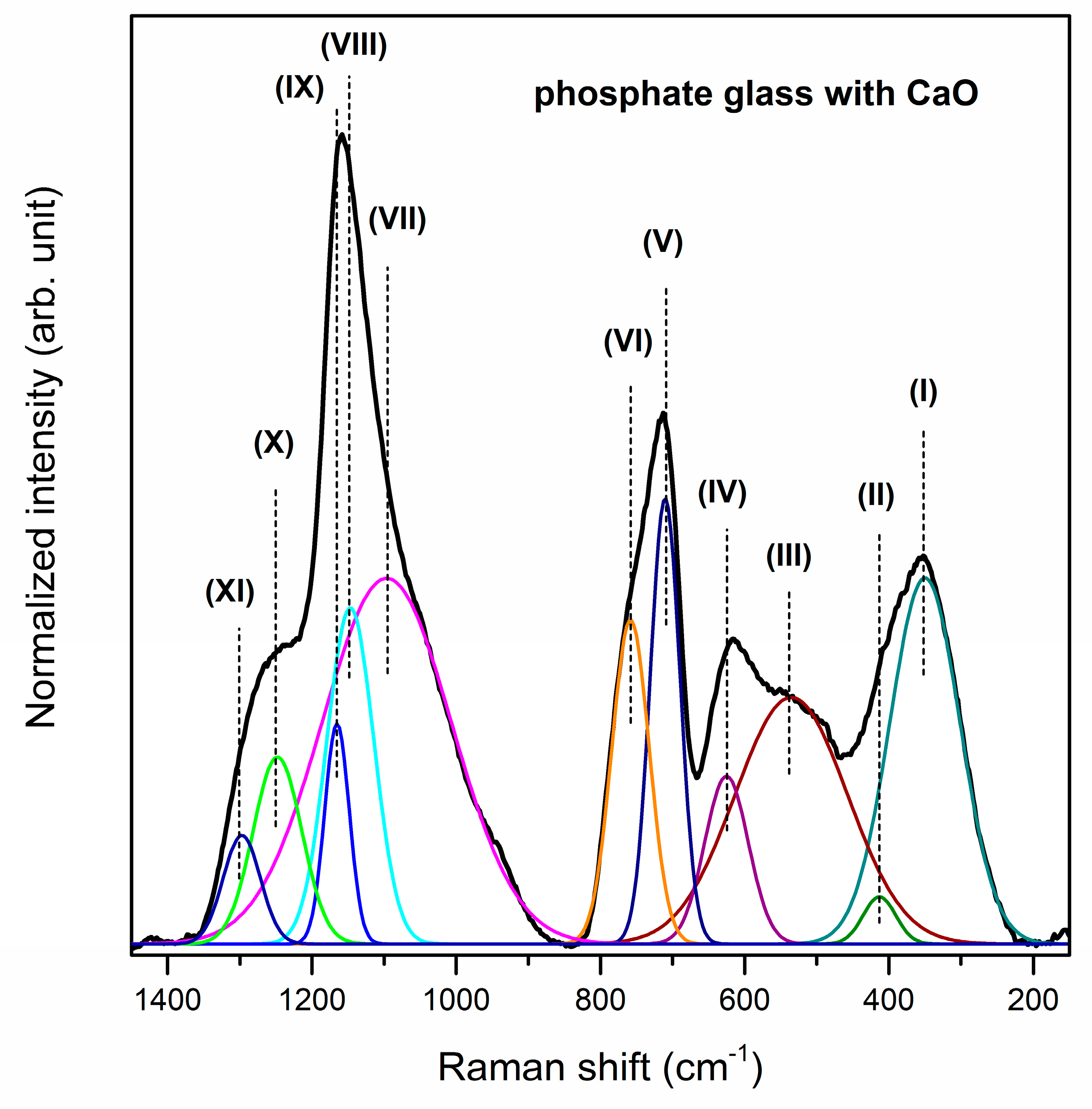
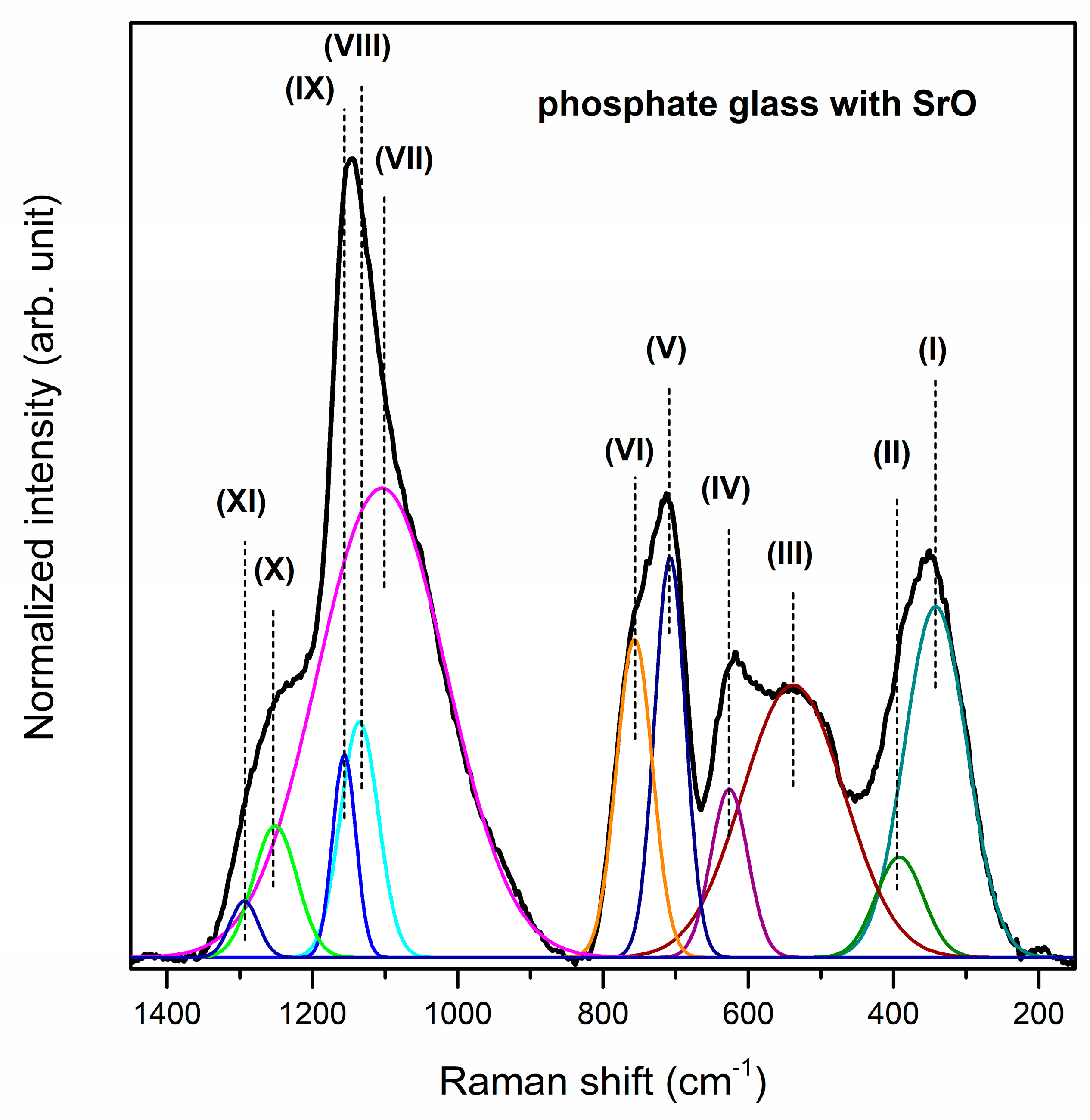
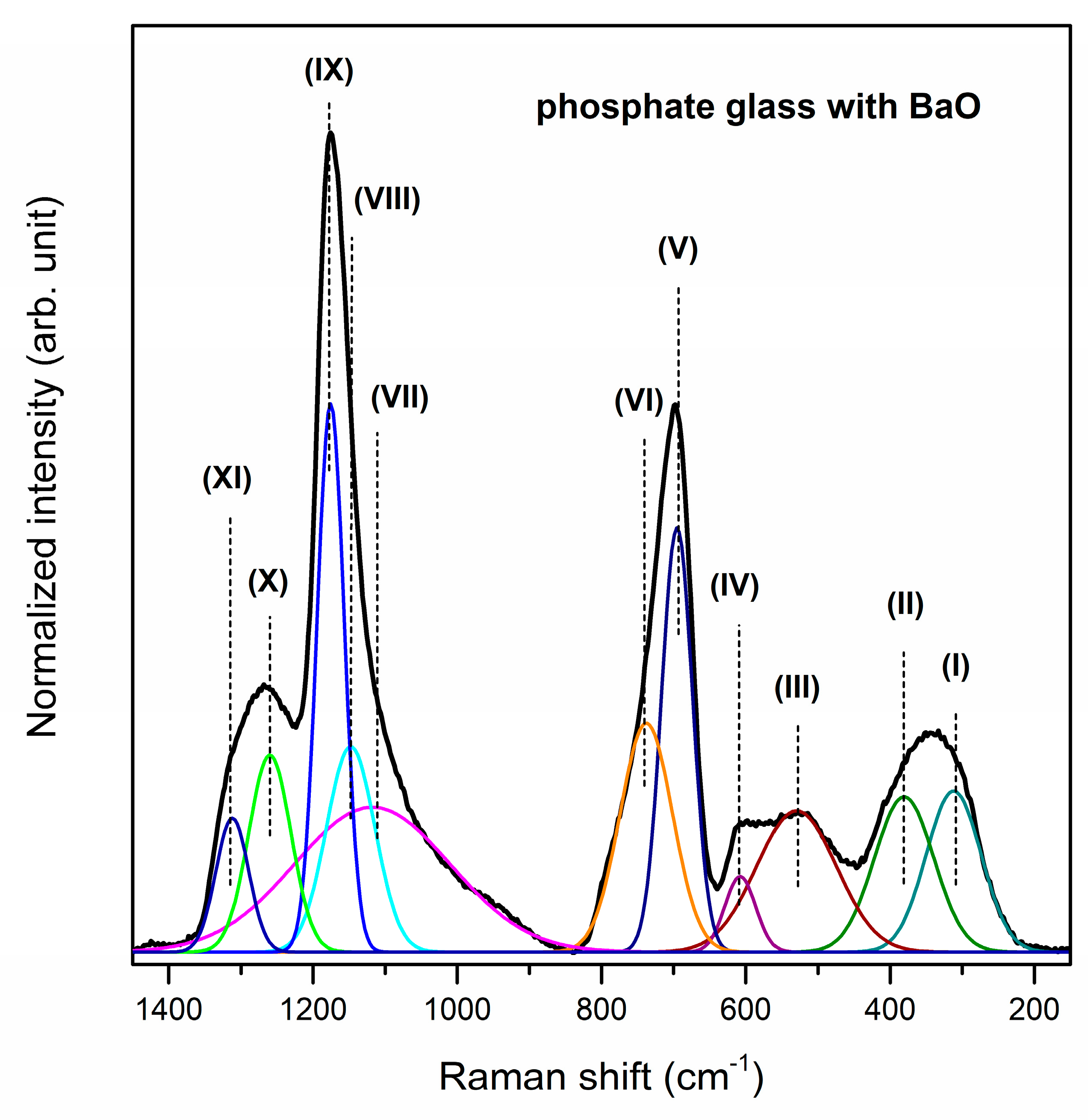
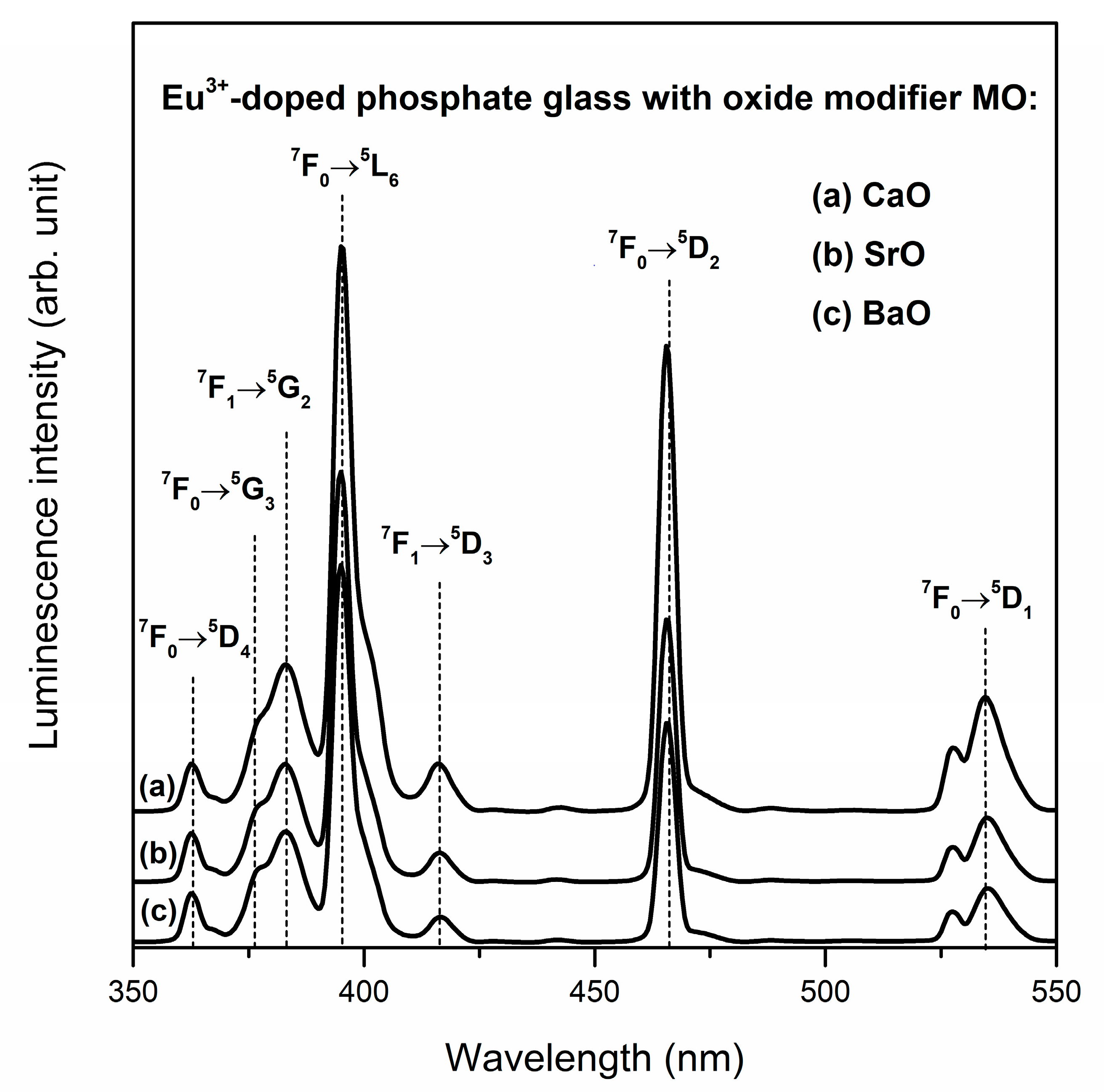
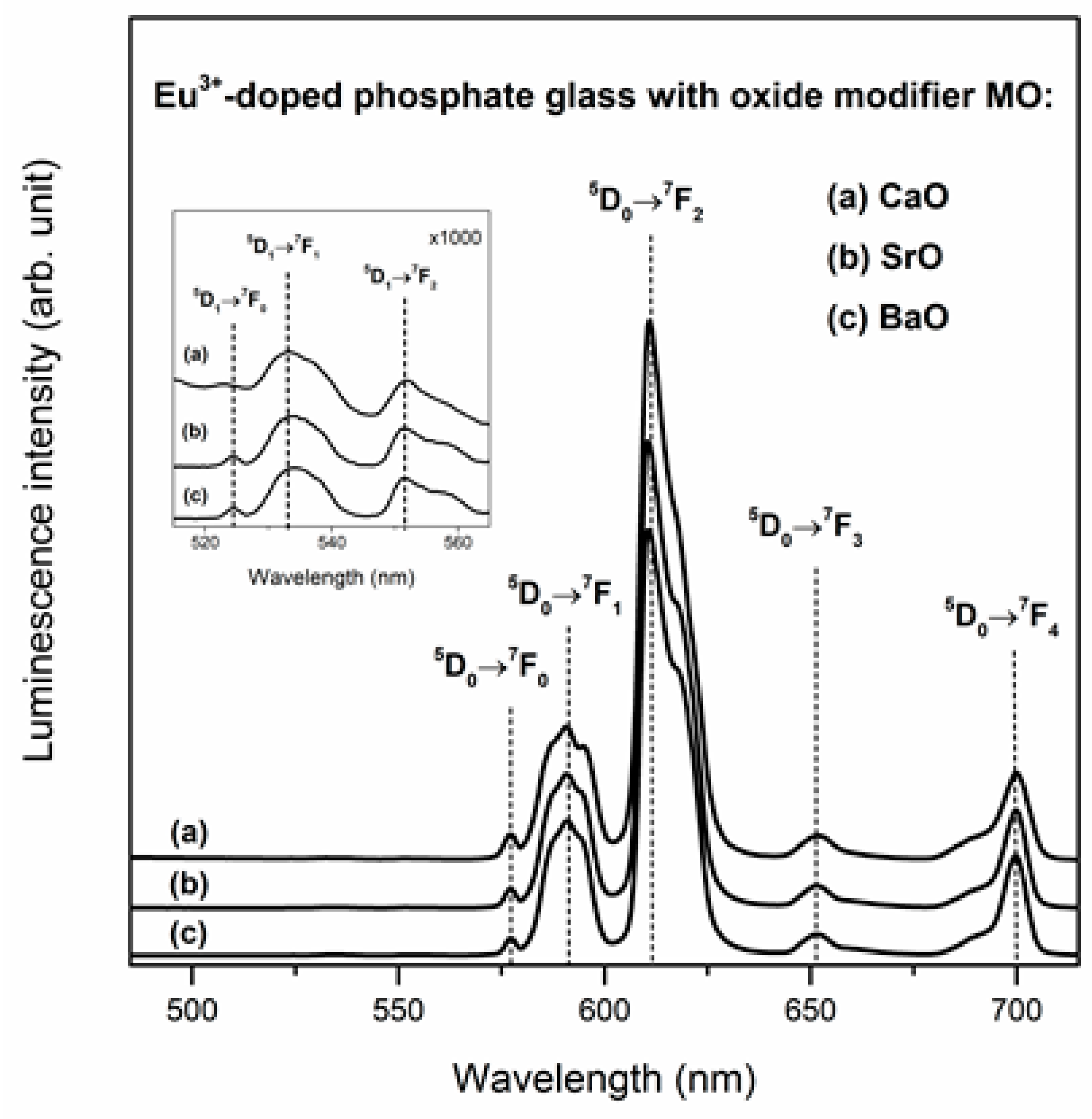
| Band | Frequency (cm−1) | Band Assignment | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| (I) | 499/488/452 cm−1 | harmonics of bending vibrations of O=P–O linkages | [57] |
| (II) | 640/639/588 cm−1 | stretching vibrations the M–O–P bonds stretching vibrations of P–O–P mode bending vibrations of O–P–O modes | [58,59] |
| (III) | 708/725/722 cm−1 | symmetric stretching vibrations of P–O–P linkages in between Q1 and Q2 | [58] |
| (IV) | 772/772/784 cm−1 | symmetric stretching mode of P–O–P bonds | [62] |
| (V) | 910/891/877 cm−1 | asymmetric stretching vibrations of bridging oxygen atoms in P–O–P bonds asymmetric stretching vibrations of the P–O–P linkage of Q1 and Q2 tetrahedra with non-bridging oxygen | [63,64] |
| (VI) | 1006/1009/949 cm−1 | asymmetric stretching vibrations of PO43− structural group | [66] |
| (VII) | 1086/1087/1079 cm−1 | symmetric stretching vibrations of PO43− tetrahedral (PO− ionic group) symmetric stretching vibrations of PO32− in the Q1 tetrahedra | [66,67] |
| (VIII) | 1173/1182/1161 cm−1 | asymmetric stretching vibrations of PO2− in the Q2 tetrahedra | [67] |
| (IX) | 1255/1258/1240 cm−1 | P=O stretching vibration of PO2− groups | [68] |
| (X) | 1304/1301/1303 cm−1 | harmonic of the doubly bonded oxygen vibration | [58] |
| Band | Frequency (cm−1) | Band Assignment | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| (I) | 350/342/312 cm−1 | GaO6 vibrational groups | [69] |
| (II) | 413/392/381 cm−1 | Ga-O-P linkages bending vibrations of PO4 units | [68,69] |
| (III) | 535/538/530 cm−1 | bending vibrations of P2O74− groups | [58] |
| (IV) | 625/626/607 cm−1 | symmetric stretching vibrations of P–O– terminal bonds | [70] |
| (V) | 710/708/695 cm−1 | symmetric stretching vibrations of P–O–P bonds in Q2 metaphosphate tetrahedra | [70] |
| (VI) | 758/757/738 cm−1 | symmetric stretching vibrations of P–O–P bonds associated with Q1 tetrahedra | [55,70] |
| (VII) | 1096/1104/1117 cm−1 | ||
| (VIII) | 1147/1135/1148 cm−1 | symmetric stretching modes of non-bridging atoms on Q2 tetrahedra | [72] |
| (IX) | 1165/1156/1176 cm−1 | ||
| (X) | 1248/1251/1260 cm−1 | symmetric stretching of P–O bonds | [69] |
| (XI) | 1297/1284/1312 cm−1 | stretching vibrations of non-bridging bonds PO2− of Q2 metaphosphate tetrahedra P=O stretching of terminal oxygen | [71] |
| Ln3+ | Spectroscopic Parameter | Oxide Glass Modifier | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CaO | SrO | BaO | ||
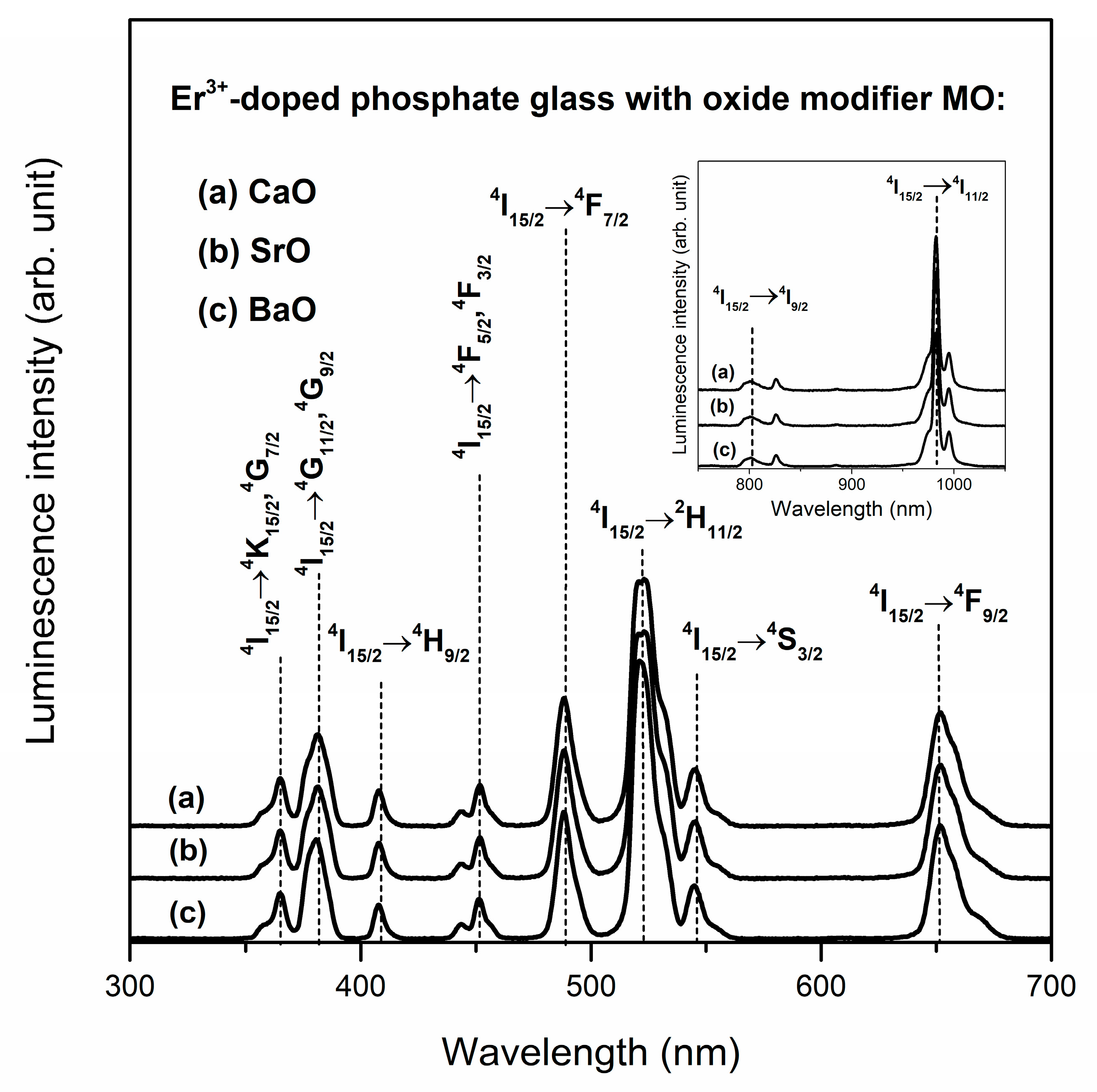
| Eu3+ | λmax 5D0→7F1 (nm) | 590.5 | 590.5 | 591.0 |
| λmax 5D0→7F2 (nm) | 611.0 | 610.5 | 611.0 | |
| R/O | 3.77 | 3.29 | 3.09 | |
| τm (ms) | 2.06 ± 0.0013 | 2.15 ± 0.0015 | 2.20 ± 0.0013 | |
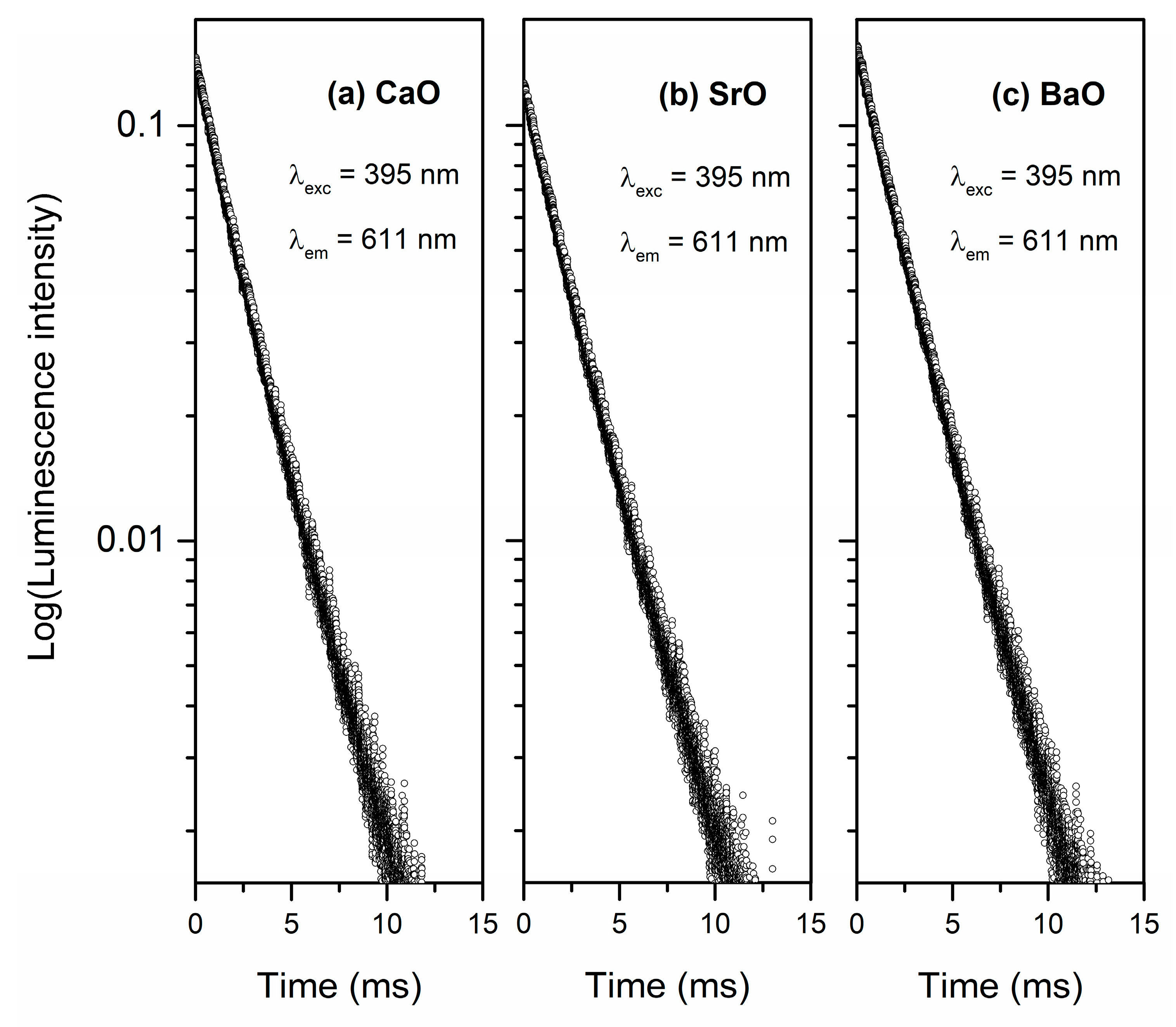
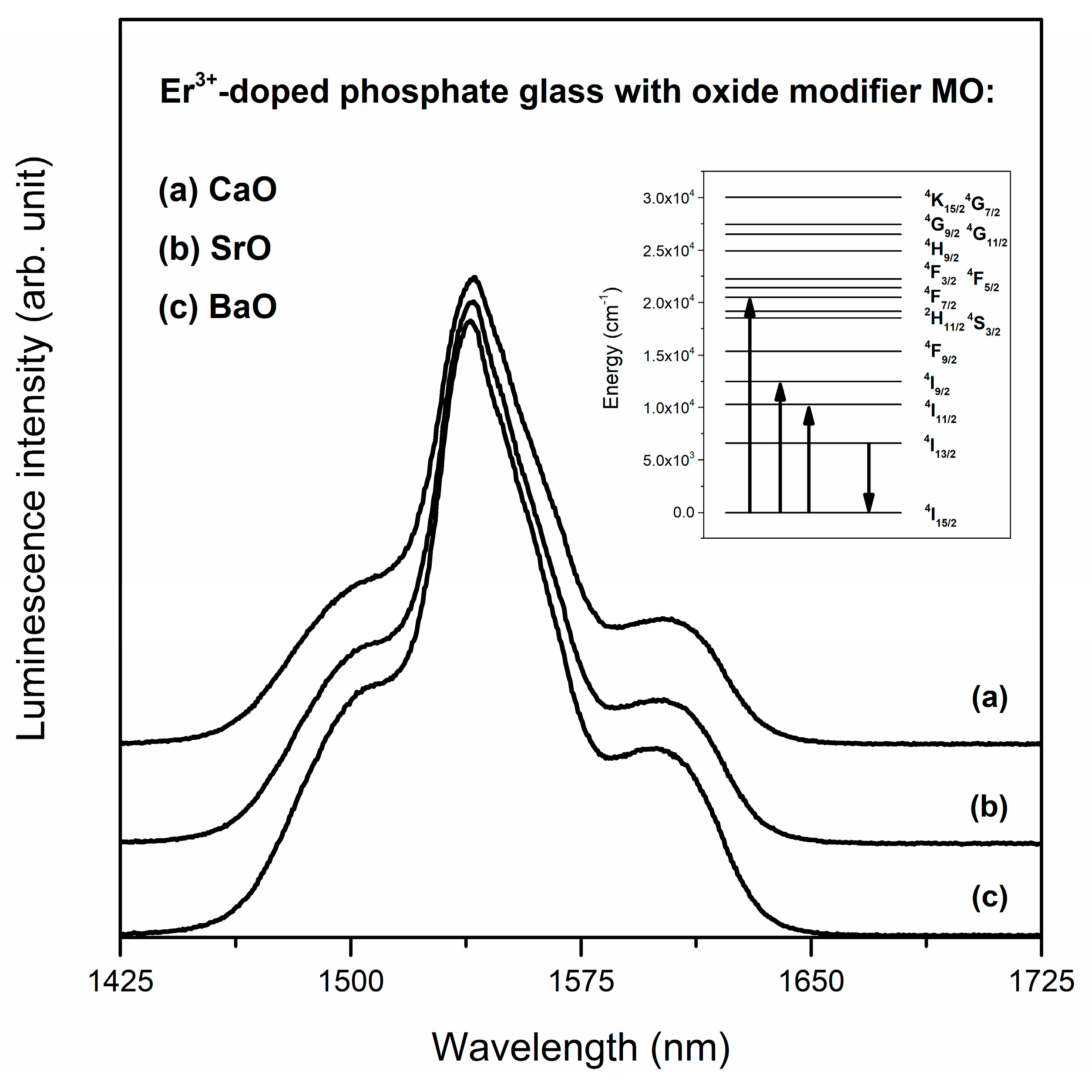
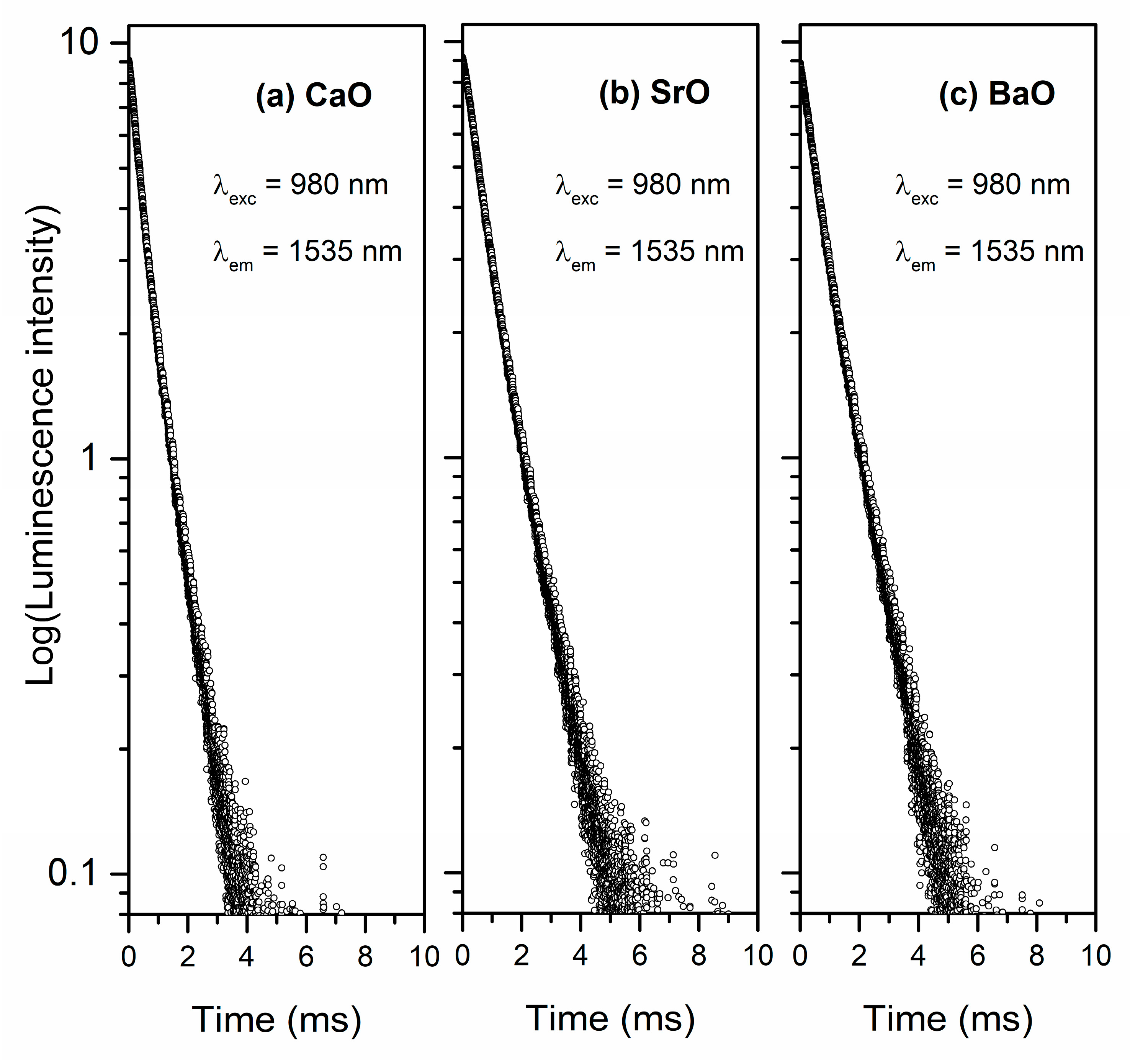
| Er3+ | λmax 4I13/2→4I15/2 (nm) | 1540 | 1540 | 1539 |
| FWHM (nm) | 44 | 43 | 44 | |
| τm (μs) | 640 ± 0.66 | 888 ± 0.65 | 920 ± 0.71 | |
| Glass Composition | τm for 5D0 State of Eu3+ (ms) | References |
|---|---|---|
| P2O5-Ga2O3-BaO-Eu2O3 | 2.20 ± 0.0013 | present work |
| B2O3-Ga2O3-BaO-Eu2O3 | 1.60 | [82] |
| GeO2-Ga2O3-BaO-Eu2O3 | 1.22 | [83] |
| Li2O-BaO-B2O3-Eu2O3 | 1.81 | [77] |
| SiO2-Al2O3-BaO-Eu2O3 | 2.17 | [78] |
| SiO2-MgO-CaO-Na2O-K2O-Eu2O3 | 2.55 | [84] |
| TeO2-La2O3-TiO2-Eu2O3 | 0.82 | [85] |
| PbO-P2O5-Ga2O3-Eu2O3 | 2.02 | [86] |
| PbO-SiO2-Ga2O3-Eu2O3 | 1.27 | [87] |
| La2O3-Bi2O3-B2O3-Eu2O3 | 1.01 | [88] |
| La2O3-PbO-B2O3-Eu2O3 | 1.29 | [88] |
| Bi2O3-GeO2-Eu2O3 | 1.03 | [89] |
| Glass Composition | FWHM (nm) | τm for 4I13/2 State of Er3+ (ms) | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| P2O5-Ga2O3-BaO-Er2O3 | 44 | 0.92 ± 0.0071 | present work |
| B2O3-Ga2O3-BaO-Er2O3 | 98 | 0.42 | [82] |
| GeO2-Ga2O3-BaO-Er2O3 | 50 | 5.35 | [83] |
| P2O5-Li2O-Al2O3-BaO-MgO-Gd2O3-Er2O3 | 30 | 7.01 | [79] |
| P2O5-K2O-BaO-Al2O3-Yb2O3-Er2O3 | 37 | 0.78 | [80] |
| SiO2-GeO2-CaO-BaO-Nb2O-Li2O-Er2O3 | 77 | 0.78 | [90] |
| TeO2-ZnO-BaO-Er2O3 | 46 | 4.70 | [91] |
| PbO-P2O5-Ga2O3-Er2O3 | 52 | 2.50 | [92] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kuwik, M.; Pisarska, J.; Pisarski, W.A. Influence of Oxide Glass Modifiers on the Structural and Spectroscopic Properties of Phosphate Glasses for Visible and Near-Infrared Photonic Applications. Materials 2020, 13, 4746. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13214746
Kuwik M, Pisarska J, Pisarski WA. Influence of Oxide Glass Modifiers on the Structural and Spectroscopic Properties of Phosphate Glasses for Visible and Near-Infrared Photonic Applications. Materials. 2020; 13(21):4746. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13214746
Chicago/Turabian StyleKuwik, Marta, Joanna Pisarska, and Wojciech A. Pisarski. 2020. "Influence of Oxide Glass Modifiers on the Structural and Spectroscopic Properties of Phosphate Glasses for Visible and Near-Infrared Photonic Applications" Materials 13, no. 21: 4746. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13214746
APA StyleKuwik, M., Pisarska, J., & Pisarski, W. A. (2020). Influence of Oxide Glass Modifiers on the Structural and Spectroscopic Properties of Phosphate Glasses for Visible and Near-Infrared Photonic Applications. Materials, 13(21), 4746. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13214746





