The Essential Role of 1-Butyl-3-Methylimidazolium-Based Ionic Liquids in the Development of Transparent Silica-Filled Elastomer Systems
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
3. Results
3.1. Rheometric Measurements, Crosslink Density, and Transparency Effect
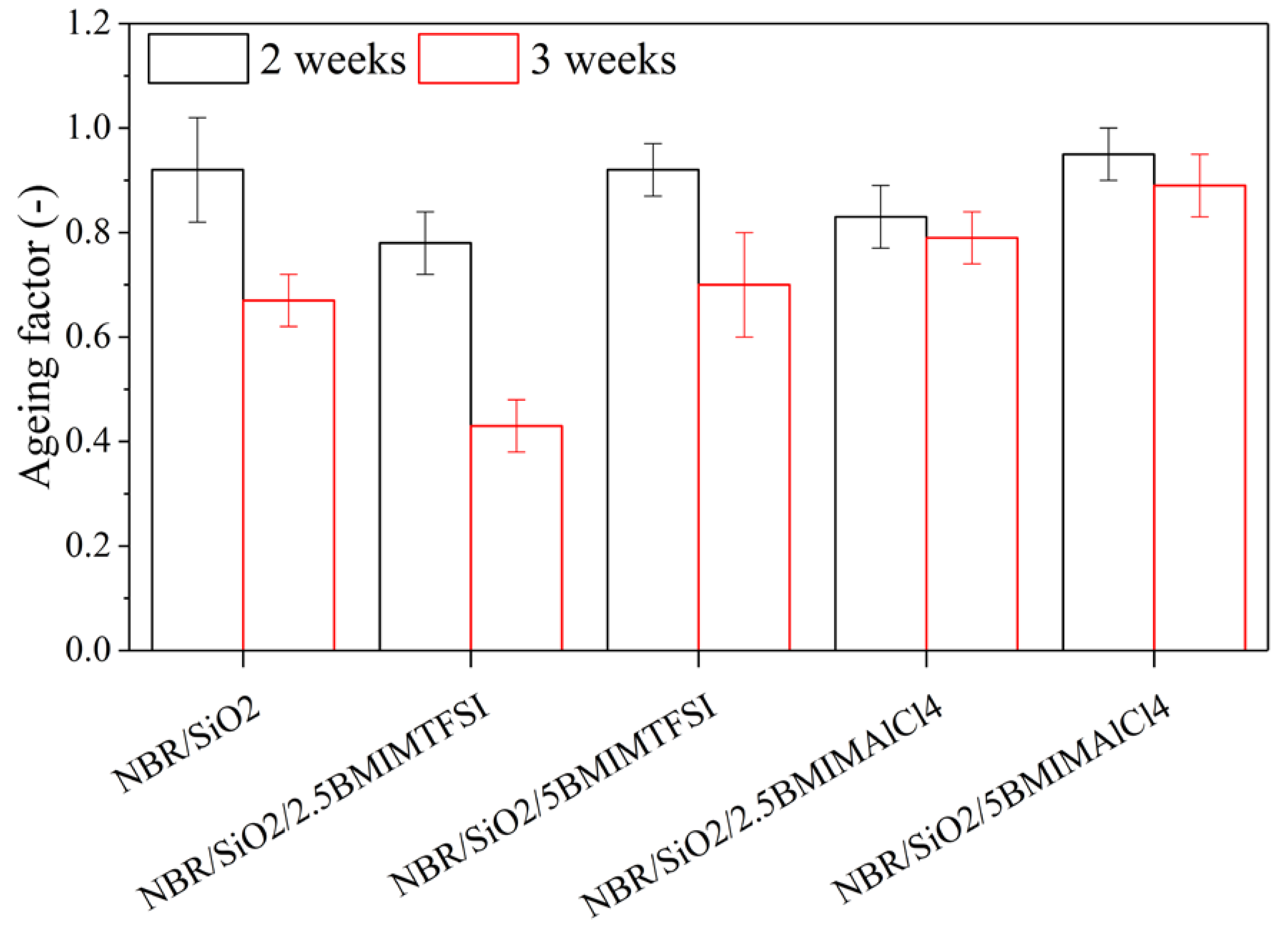
3.2. Mechanical Properties, Morphology, Ionic Conductivity, and Thermooxidative Ageing
3.3. Dynamic-Mechanical Properties (DMA)
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bauer, S.; Bauer-Gogonea, S.; Graz, I.; Kaltenbrunner, M.; Keplinger, C.; Schwödiauer, R. 25th anniversary article: A soft future: From robots and sensor skin to energy harvesters. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 149–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, D.K.; Sakhaei, A.H.; Layani, M.; Zhang, B.; Ge, Q.; Magdassi, S. Highly stretchable and UV curable elastomers for digital light processing based 3D printing. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1606000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frogley, M.D.; Ravich, D.; Wagner, H.D. Mechanical properties of carbon nanoparticle-reinforced elastomers. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2003, 63, 1647–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcés, J.M.; Moll, D.J.; Bicerano, J.; Fibiger, R.; McLeod, D.G. Polymeric nanocomposites for automotive applications. Adv. Mater. 2000, 12, 1835–1839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bokobza, L. The reinforcement of elastomeric networks by fillers. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2004, 289, 607–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gotoh, H.; Liu, C.; Imran, A.B.; Hara, M.; Seki, T.; Mayumi, K.; Ito, K.; Takeoka, Y. Optically transparent, high-toughness elastomer using a polyrotaxane cross-linker as a molecular pulley. Sci. Adv. 2018, 4, 7629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahapatra, S.S.; Yadav, S.K.; Yoo, H.J.; Cho, J.W. Highly stretchable, transparent and scalable elastomers with tunable dielectric permittivity. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 7686–7691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacLaren, D.C.; White, M.A. Dye–developer interactions in the crystal violet lactone–lauryl gallate binary system: Implications for thermochromism. J. Mater. Chem. 2003, 13, 1695–1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Xu, J.H.; Chen, J.Y.; Hu, P.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, W.; Fu, J.J. Transparent, Mechanically Strong, Extremely Tough, Self-Recoverable, Healable Supramolecular Elastomers Facilely Fabricated via Dynamic Hard Domains Design for Multifunctional Applications. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 1907109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, A.; George, J.J.; Kutlu, B.; Leuteritz, A.; Wang, D.Y.; Rooj, S.; Jurk, R.; Rajeshbabu, R.; Stöckelhuber, K.W.; Galiatsatos, V.; et al. A Novel Thermotropic Elastomer based on Highly-filled LDH-SSB Composites. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2012, 33, 337–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laskowska, A.; Zaborski, M.; Boiteux, G.; Gain, O.; Marzec, A.; Maniukiewicz, W. Ionic elastomers based on carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) and magnesium aluminum layered double hydroxide (hydrotalcite). EXPRESS Polym. Lett. 2014, 8, 374–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laskowska, A.; Marzec, A.; Zaborski, M.; Boiteux, G. Reinforcement of carboxylated acrylonitrile-butadiene rubber (XNBR) with graphene nanoplatelets with varying surface area. J. Polym. Eng. 2014, 34, 883–893. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Li, X.; Xu, L.; Zhang, P. Investigation of aging behavior and mechanism of nitrile-butadiene rubber (NBR) in the accelerated thermal aging environment. Polym. Test. 2016, 54, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, A.; Wang, D.W.; Leuteritz, A.; Subramaniam, K.; Greenwell, H.C.; Wagenknecht, U.; Heinrich, G. Preparation of zinc oxide free, transparent rubber nanocomposites using a layered double hydroxide filler. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 7194–7200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogihara, W.; Kosukegawa, H.; Ohno, H. Proton-conducting ionic liquids based upon multivalent anions and alkylimidazolium cations. Chem. Commun. 2006, 34, 3637–3639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huddleston, J.G.; Visser, A.E.; Reichert, W.M.; Willauer, H.D.; Broker, G.A.; Rogers, R.D. Characterization and Comparison of Hydrophilic and Hydrophobic Room Temperature Ionic Liquids Incorporating the Imidazolium Cation. Green Chem. 2001, 3, 156–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plechkova, N.V.; Seddona, K.R. Applications of ionic liquids in the chemical industry. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2008, 37, 123–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Likozar, B. The effect of ionic liquid type on the properties of hydrogenated nitrile elastomer/hydroxy-functionalized multi-walled carbon nanotube/ionic liquid composites. Soft. Matter. 2011, 7, 970–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramaniam, K.; Das, A.; Heinrich, G. Development of conducting polychloroprene rubber using imidazolium based ionic liquid modified multi-walled carbon nanotubes. Comp. Sci. Technol. 2011, 71, 1441–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramaniam, K.; Das, A.; Haussler, L.; Harnish, C.; Stockelhuber, K.W.; Heinrich, G. Enhanced thermal stability of polychloroprene rubber composites with ionic liquid modified MWCNTs. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2012, 97, 776–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laskowska, A.; Marzec, A.; Boiteux, G.; Zaborski, M.; Gain, O.; Serghei, A. Investigations of Nitrile Rubber Composites Containing Imidazolium Ionic Liquids. Macromol. Symp. 2014, 314, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzec, A.; Laskowska, A.; Boiteux, G.; Zaborski, M.; Gain, O.; Serghei, A. Study on Weather Aging of Nitrile Rubber Composites Containing Imidazolium Ionic Liquids. Macromol. Symp. 2014, 342, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bains, D.; Singh, G.; Kaur, N.; Singh, N. Development of Ionic Liquid@Metal Based Nanocomposites-Loaded Hierarchical Hydrophobic Surface to the Aluminium Substrate for Antibacterial Properties. ACS Appl. Biol. Mater. 2020, 3, 4962–4973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flory, P.J.; Rehner, J. Statistical Mechanics of Cross-Linked Polymer Networks I. Rubberlike Elasticity. J. Chem. Phys. 1943, 11, 512–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzec, A.; Laskowska, A.; Boiteux, G.; Zaborski, M.; Gain, O.; Serghei, A. Properties of carboxylated nitrile rubber/hydrotalcite composites containing imidazolium ionic liquids. Macromol. Symp. 2014, 341, 7–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Li, Y.; Cao, X.; You, J.; Dong, W. Multifunctional role of an ionic liquid in melt-blended poly (methyl methacrylate)/multi-walled carbon nanotube nanocomposites. Nanotechnology 2012, 23, 255702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maciejewska, M.; Walkiewicz, F.; Zaborski, M. Novel ionic liquids as accelerators for the sulfur vulcanization of butadiene–styrene elastomer composites. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2013, 52, 8410–8415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laskowska, A.; Marzec, A.; Boiteux, G.; Zaborski, M.; Gain, O.; Serghei, A. Effect of imidazolium ionic liquid type on the properties of nitrile rubber composites. Polym. Int. 2013, 62, 1575–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maciejewska, M.; Zaborski, M. Effect of ionic liquids on the dispersion of zinc oxide and silica nanoparticles, vulcanisation behaviour and properties of NBR composites. Express Polym. Lett. 2014, 8, 932–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szadkowski, B.; Marzec, A.; Rybiński, P.; Żukowski, W.; Zaborski, M. Characterization of Ethylene–propylene Composites Filled with Perlite and Vermiculite Minerals: Mechanical, Barrier, and Flammability Properties. Materials 2020, 13, 585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szadkowski, B.; Marzec, A.; Zaborski, M. Use of carbon black as a reinforcing nano-filler in conductivity-reversible elastomer composites. Polym. Test. 2020, 81, 106222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, A.P.; Capper, G.; Davies, D.L.; Rasheed, R.K.; Shikotra, P. Selective extraction of metals from mixed oxide matrixes using choline-based ionic liquids. Inorg. Chem. 2005, 44, 6497–6499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadilohar, B.L.; Shankarling, G.S. Choline based ionic liquids and their applications in organic transformation. J. Mol. Liq. 2017, 227, 234–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armand, M.; Endres, F.; MacFarlane, D.R.; Ohno, H.; Scrosati, B. Ionic-liquid materials for the electrochemical challenges of the future. In Materials for Sustainable Energy: A Collection of Peer-Reviewed Research and Review Articles from Nature Publishing Group, 1st ed.; Dusastre, V., Ed.; Nature Publishing Group: London, UK, 2011; Volume 8, pp. 129–137. [Google Scholar]
- Scott, M.; Rahman, M.; Brazel, C. Application of ionic liquids as low-volatility plasticizers for PMMA. Eur. Polym. J. 2003, 39, 1947–1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, M.P.; Brazel, C.S.; Benton, M.G.; Mays, J.W.; Holbrey, J.; Rogers, R.D. Application of ionic liquids as plasticizers for poly(methyl methacrylate). ChemComm 2002, 13, 1370–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
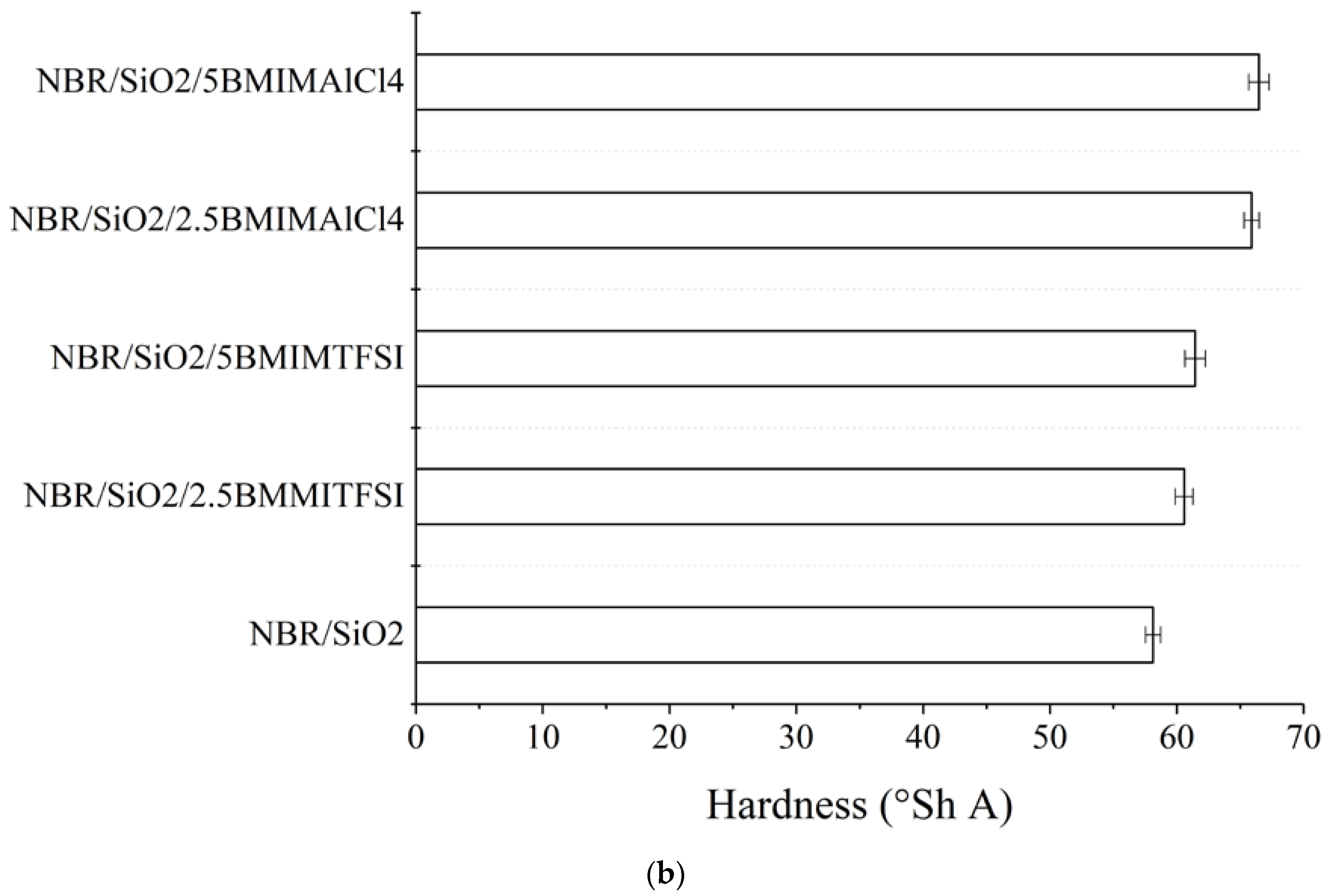
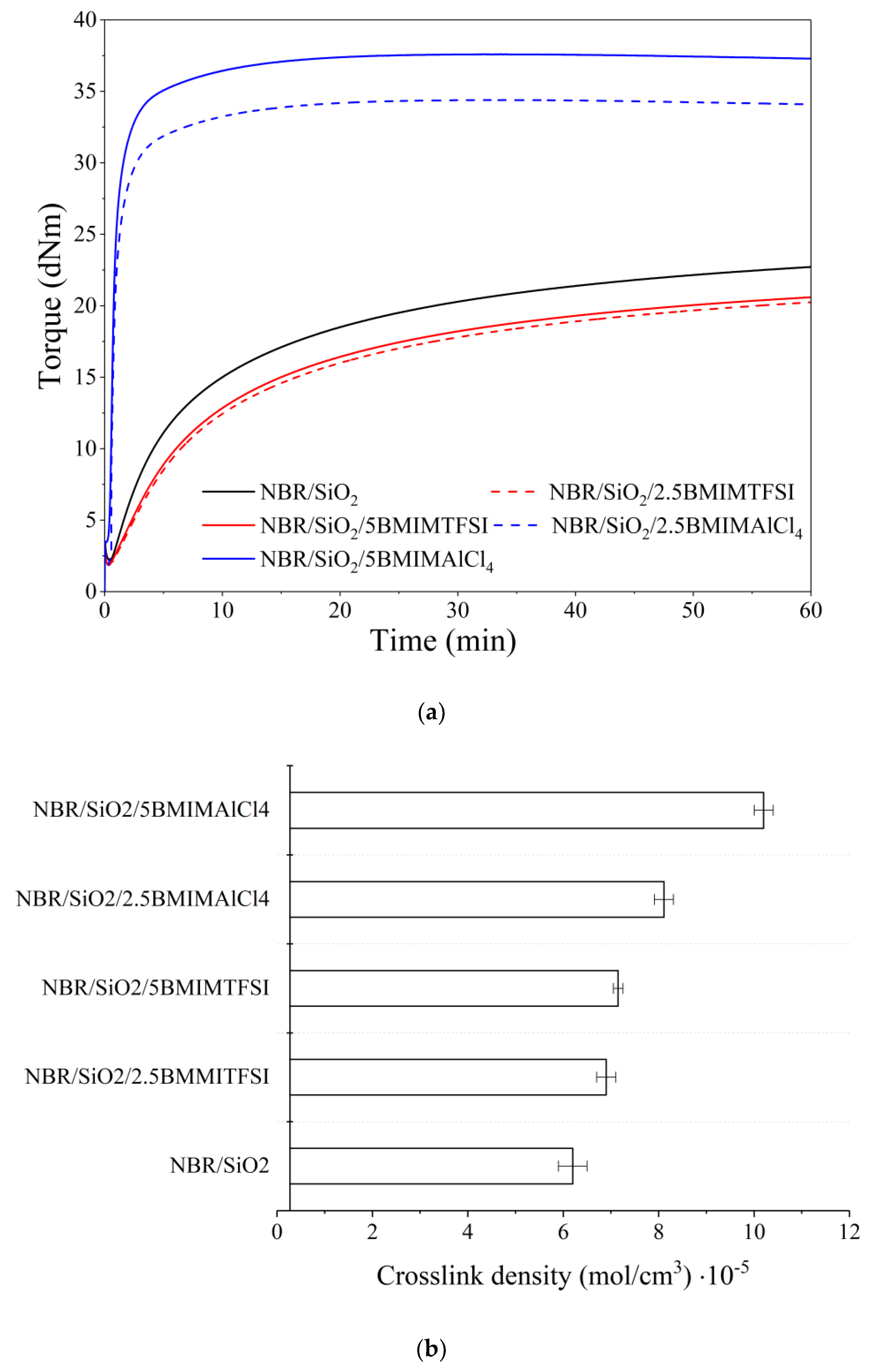

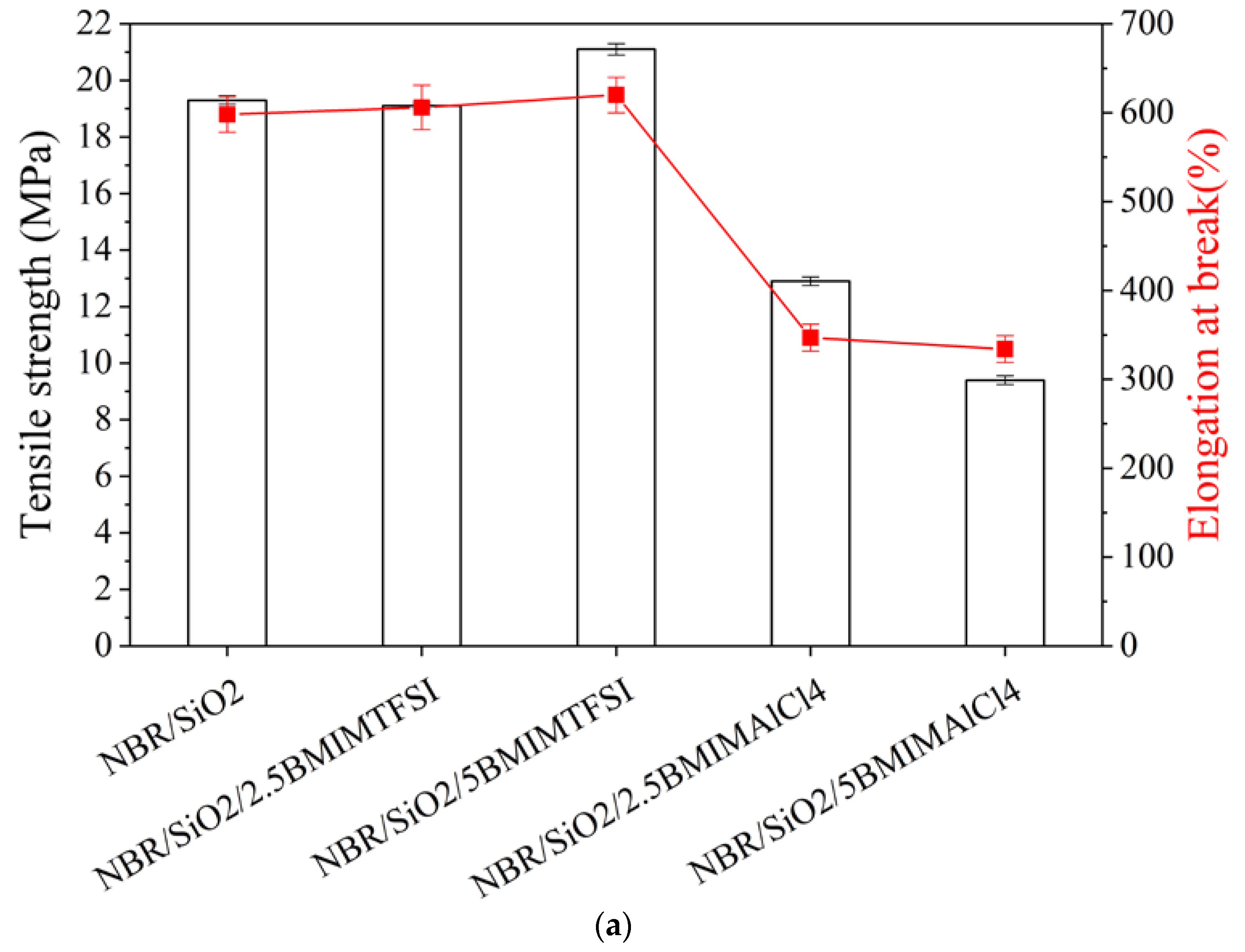


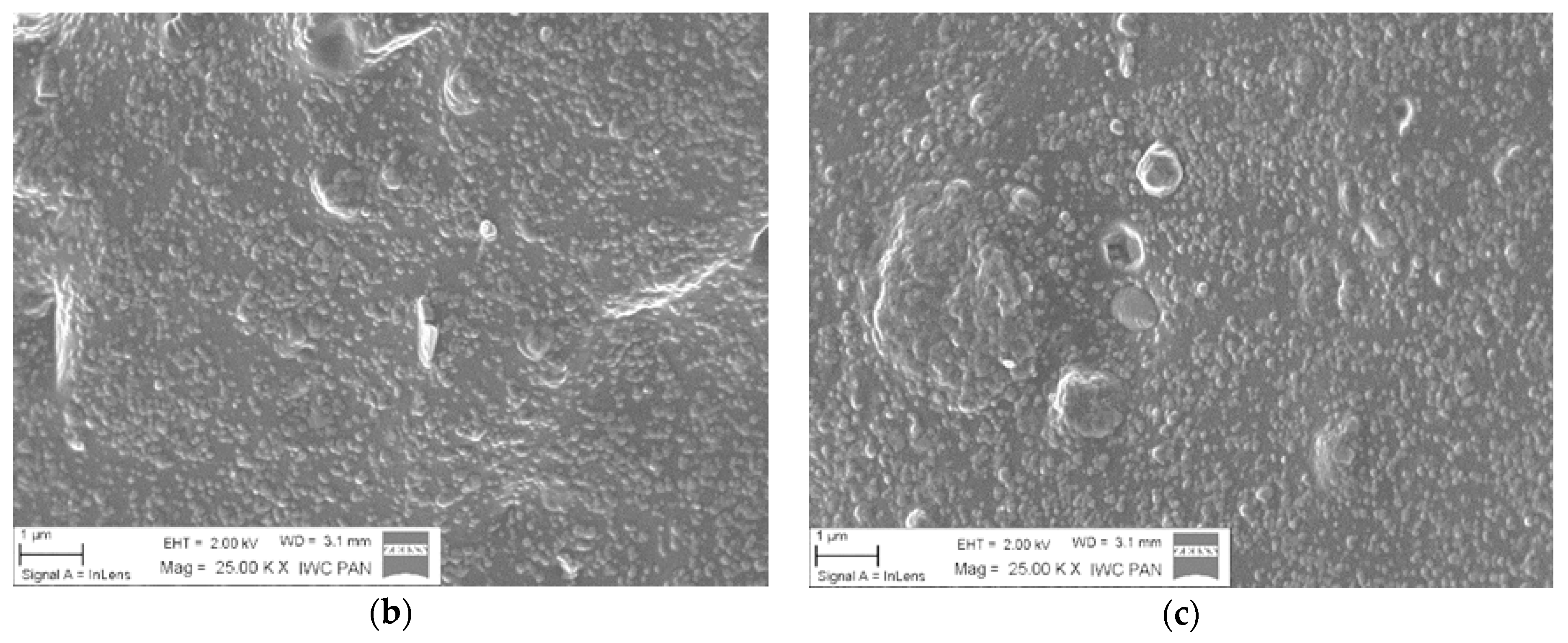
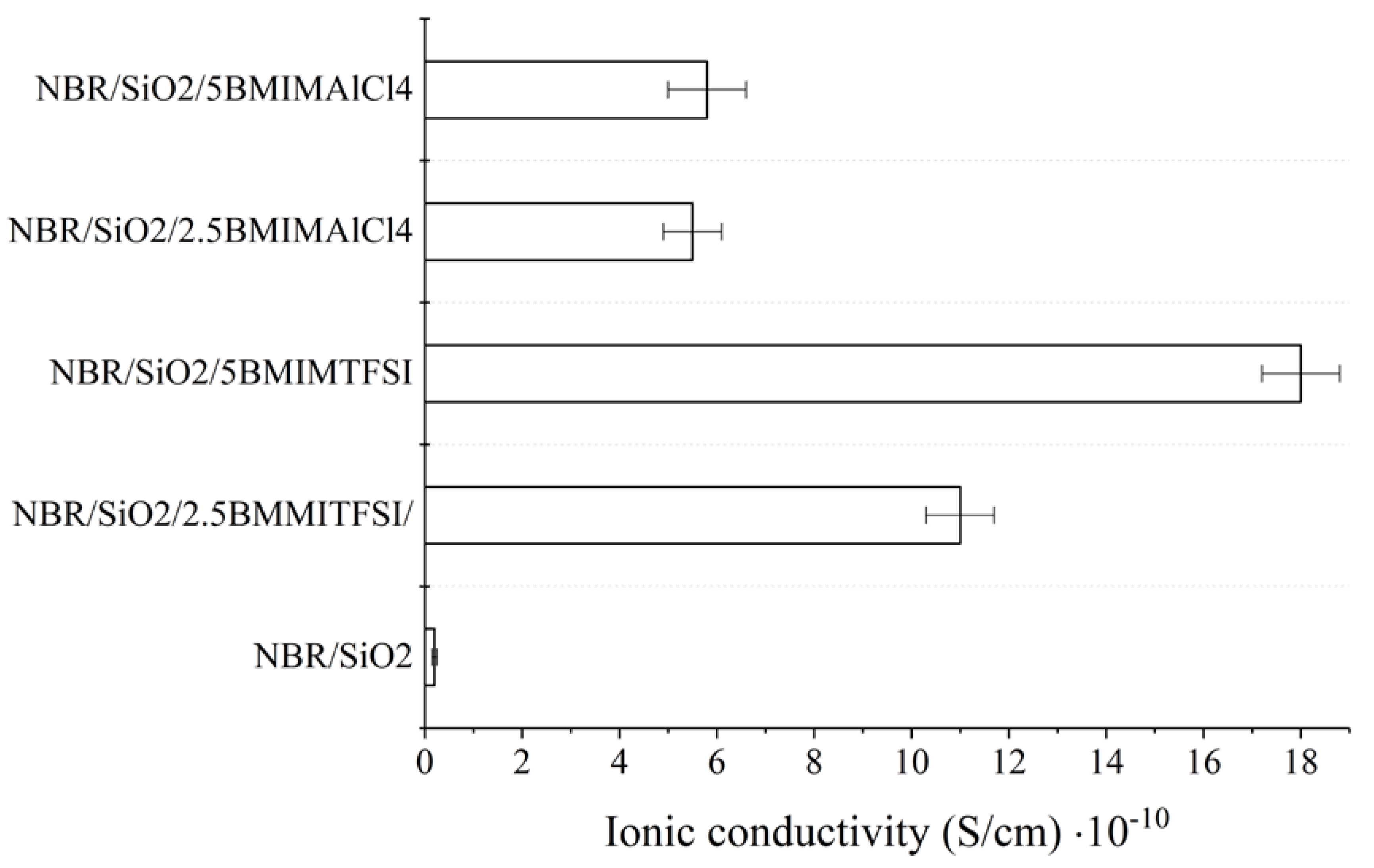

| Composite Name | Mmin (dNm) | ΔM (dNm) | τ02 (min) | τ90 (min) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NBR | 2.17 | 20.55 | 1.31 | 32.96 |
| NBR/SiO2/2.5BMIMTFSI | 2.04 | 19.42 | 1.87 | 33.14 |
| NBR/SiO2/5BMIMTFSI | 1.87 | 18.38 | 1.79 | 34.98 |
| NBR/SiO2/2.5BMIMAlCl4 | 1.94 | 27.09 | 0.57 | 6.97 |
| NBR/SiO2/5BMIMAlCl4 | 3.25 | 34.15 | 0.42 | 3.49 |
| Composite Name | L | a* | b* | ΔE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NBR/SiO2 | 69.5 | 6.9 | 24.4 | - |
| NBR/SiO2/2.5BMIMTFSI | 69.6 | 6.8 | 26.1 | 1.9 |
| NBR/SiO2/5BMIMTFSI | 71.5 | 4.8 | 19.4 | 4.8 |
| NBR/SiO2/2.5BMIMAlCl4 | 53.7 | 13.9 | 35.6 | 20.4 |
| NBR/SiO2/5BMIMAlCl4 | 65.6 | 16.5 | 55.5 | 32.8 |
| Composite Name | Tg (°C) | tanδmax (–) |
|---|---|---|
| NBR/SiO2 | −25.5 | 1.2 |
| NBR/SiO2/2.5BMIMTFSI | −21.4 | 1.2 |
| NBR/SiO2/5BMIMTFSI | −21.1 | 1.1 |
| NBR/SiO2/2.5BMIMAlCl4 | −19.1 | 0.9 |
| NBR/SiO2/5BMIMAlCl4 | −14.5 | 0.6 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kuśmierek, M.; Szadkowski, B.; Marzec, A. The Essential Role of 1-Butyl-3-Methylimidazolium-Based Ionic Liquids in the Development of Transparent Silica-Filled Elastomer Systems. Materials 2020, 13, 4337. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13194337
Kuśmierek M, Szadkowski B, Marzec A. The Essential Role of 1-Butyl-3-Methylimidazolium-Based Ionic Liquids in the Development of Transparent Silica-Filled Elastomer Systems. Materials. 2020; 13(19):4337. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13194337
Chicago/Turabian StyleKuśmierek, Małgorzata, Bolesław Szadkowski, and Anna Marzec. 2020. "The Essential Role of 1-Butyl-3-Methylimidazolium-Based Ionic Liquids in the Development of Transparent Silica-Filled Elastomer Systems" Materials 13, no. 19: 4337. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13194337
APA StyleKuśmierek, M., Szadkowski, B., & Marzec, A. (2020). The Essential Role of 1-Butyl-3-Methylimidazolium-Based Ionic Liquids in the Development of Transparent Silica-Filled Elastomer Systems. Materials, 13(19), 4337. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13194337





