Effect of Loading Methods on the Fatigue Properties of Dissimilar Al/Steel Keyhole-Free FSSW Joints
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Procedures
2.1. Experimental Materials
2.2. Welding Methods
2.3. Tensile-Shear Test
2.4. Fatigue Test
3. Results and Discussion
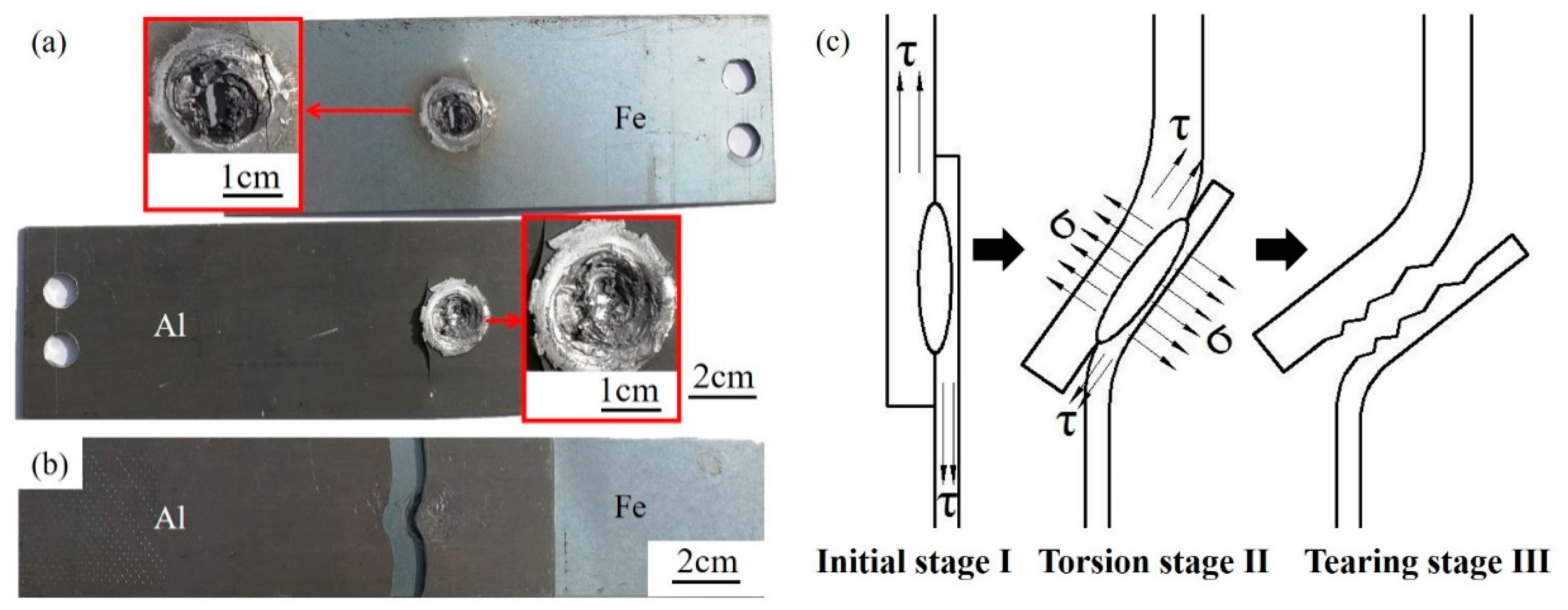
3.1. Formation of the Joint
3.2. F-N Curve of Fatigue Loading
3.3. Research on the Energy Evolution of the Fatigue Damage Process
3.3.1. Energy Evolution under Low-Frequency Asymmetric Fatigue Cyclic Loading
3.3.2. Energy Evolution under High-Frequency Asymmetric Fatigue Cyclic Loading
3.3.3. Energy Evolution under Low-Frequency Symmetrical Fatigue Cyclic Loading
3.3.4. Comparative Study on the Fatigue Properties under Different Fatigue Loads
3.4. Analysis of the Fatigue Failure Mode and Fracture Mechanism
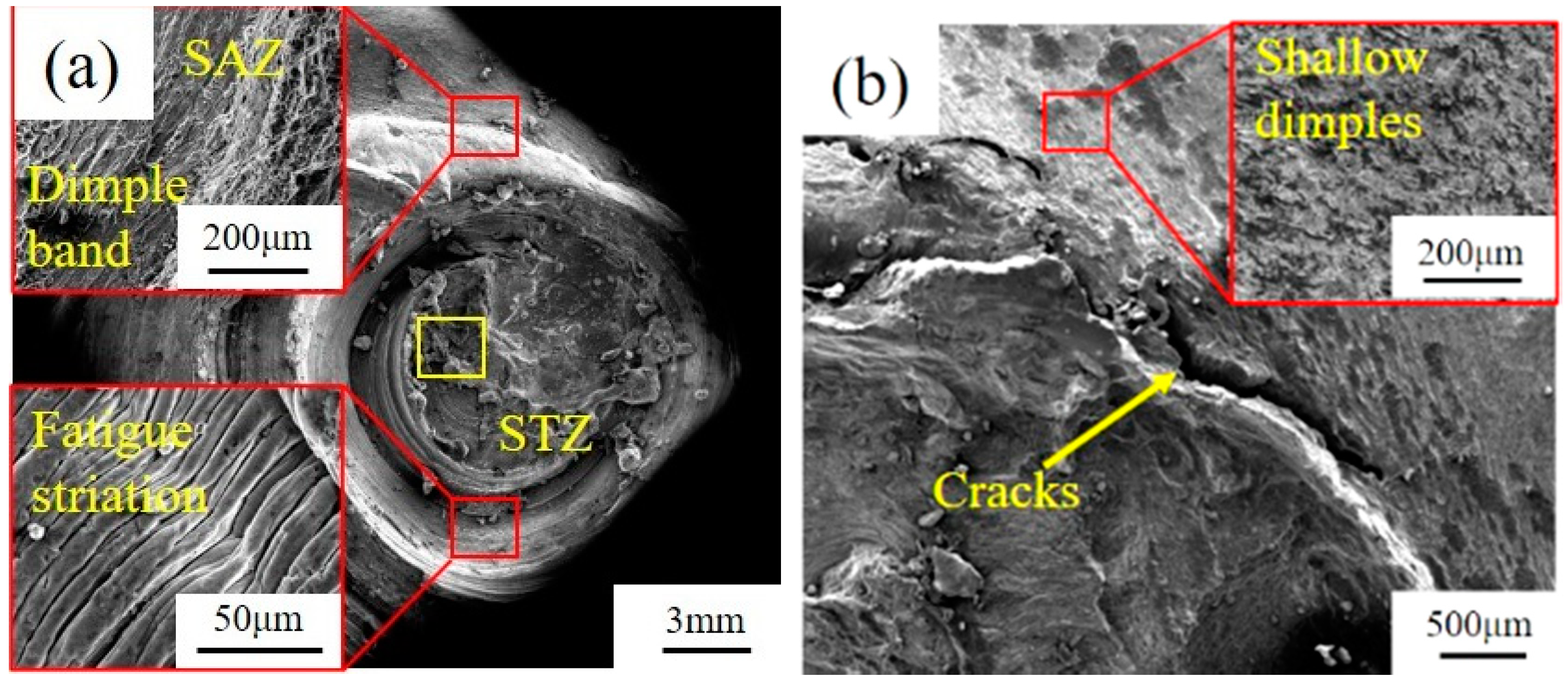
3.4.1. Macro Fatigue Fracture
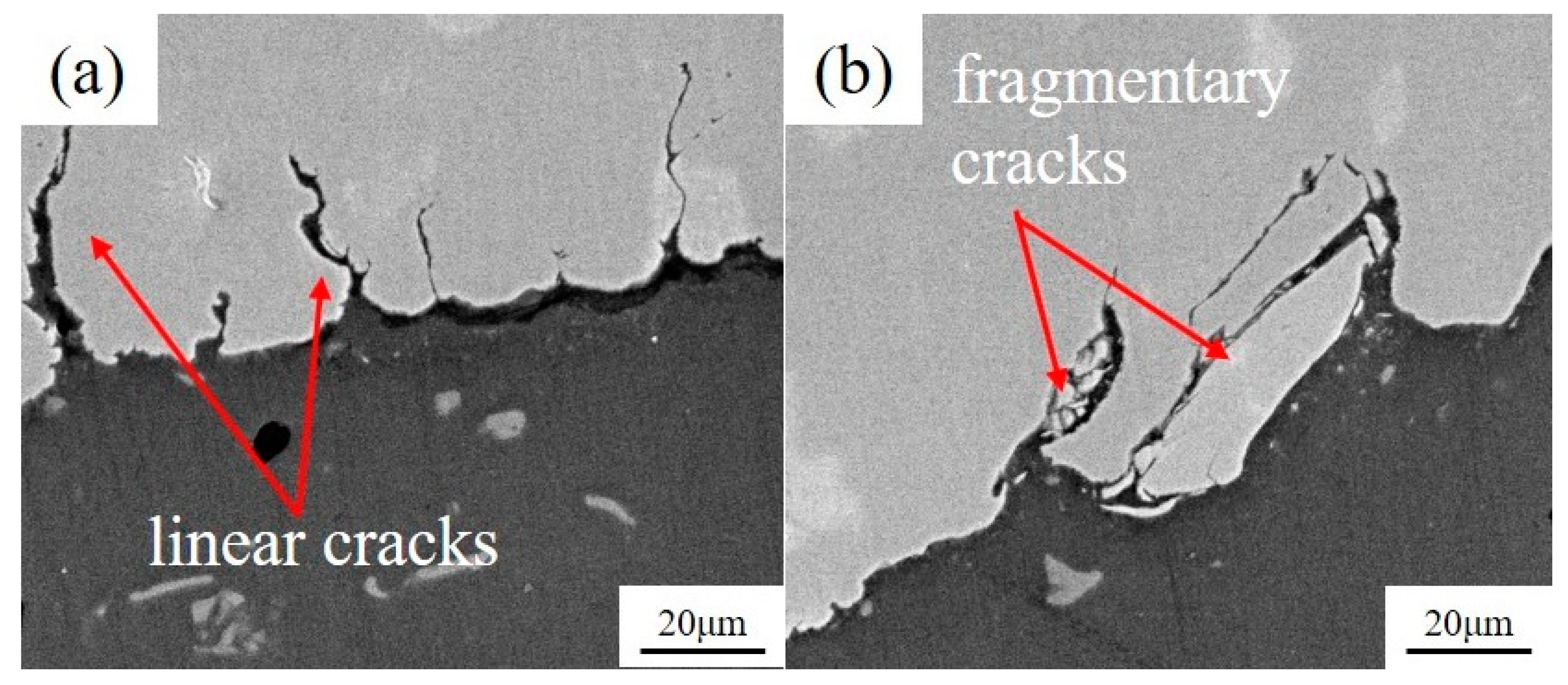
3.4.2. Micro Fatigue Fracture
3.4.3. Analysis of Fatigue Failure
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- When the loading frequency is constant, the fatigue limit F−1 ≈ 1.47 kN of the spot-welded joint under the symmetric load is less than the fatigue limit Ff ≈ 2.24 kN under the asymmetric load. When the stress ratio R is constant, the fatigue limit FfH under high-frequency loading is almost the same as the fatigue limit FfL under low-frequency loading, but the speed of reaching the fatigue limit Ff is different. The higher the frequency is, the faster the speed of approaching the fatigue limit. Therefore, the loading mode, that is, the stress ratio R, determines the fatigue limit Ff, while the fatigue limit Ff is not sensitive to the loading frequency.
- (2)
- The symmetrical fatigue load can form the steady-state hysteresis loop, while asymmetric fatigue loading cannot, but asymmetric fatigue loading can form the displacement increment μ of fatigue softening. At the same time, the high-frequency fatigue load can increase the displacement deformation μ and fatigue fracture absorption energy Ea of the spot-welded joint, which are larger under asymmetric fatigue loading than those under symmetrical fatigue loading.
- (3)
- Under the low-stress symmetric fatigue load, the spot welded joint fractures on the Al plate at the edge of the joint, while it fractures on the STZ of the joint under asymmetric fatigue loading. The fracture failure of spot-welded joints is a multiple crack source and the mixed-mode of ductile and brittle fracture mechanism, which has typical fatigue striations on fatigue fractures.
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shahani, A.R.; Farrahi, A. Experimental investigation and numerical modeling of the fatigue crack growth in friction stir spot welding of lap-shear specimen. Int. J. Fatigue 2019, 125, 520–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiraly, M.; Shamanian, M.; Toroghinejad, M.R.; Jazani, M.A. Effect of Tool Rotation Rate on Microstructure and Mechanical Behavior of Friction Stir Spot-Welded Al/Cu Composite. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2014, 23, 413–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, J.Y.; Kim, C.; Hun, R.S. Effect of Circumferential Tool Path Control on Friction Stir Spot Welding of Al/Fe Dissimilar Metal Joint. J. Weld. Join. 2016, 34, 6–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.J.; Li, W.H.; Zhao, G. Connection mechanism research on friction stir spot welding without keyhole between magnesium and steel dissimilar alloys. Mater. Res. Innov. 2014, 18, 1063–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Yu, Y.; Zhao, H.; Wang, X. Interface Behavior and Impact Properties of Dissimilar Al/Steel Keyhole-Free FSSW Joints. Metals 2019, 9, 691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; Chen, S.; Song, Y.; Guo, X.; Zhang, X.; Sun, Z. Refilled friction stir spotwelding of aluminum alloy to galvanized steel sheets. Mater. Des. 2016, 94, 457–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Su, W.; Zhang, J.; Wei, Z. Friction Stir Brazing: A Novel Process for Fabricating Al/Steel Layered Composite and for Dissimilar Joining of Al to Steel. Met. Mater. Trans. A 2011, 42A, 2850–2861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.F.; Fujii, H.; Takaki, N.; Okitsu, Y. Microstructure and mechanical properties of dissimilar Al alloy/steel joints prepared by a flat spot friction stir welding technique. Mater. Des. 2013, 47, 350–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, M.; Gupta, R.K.; Husain, M.M. Friction Stir Welding of Stainless Steel to Al Alloy: Effect of Thermal Condition on Weld Nugget Microstructure. Met. Mater. Trans. A 2014, 45A, 854–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozzi, S.; Helbert-Etter, A.L.; Baudin, T.; Criqui, B.; Kerbiguet, J.G. Intermetallic compounds in Al 6016/IF-steel friction stir spot welds. Mat. Sci. Eng. A-Struct 2010, 527, 4505–4509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, M.; Yoon, J.; Kim, C. Hook formation and joint strength in friction stir spot welding of Al alloy and Al-Si-coated hot-press forming steel. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2020, 106, 1671–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, A.; Bhattacharya, A. Strength and failure analysis of similar and dissimilar friction stir spot welds: Influence of different tools and pin geometries. Mater. Des. 2017, 127, 272–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakavos, D.; Prangnell, P.B. Effect of reduced or zero pin length and anvil insulation on friction stir spot welding thin gauge 6111 automotive sheet. Sci. Technol. Weld. Join. 2009, 14, 443–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathak, N.; Bandyopadhyay, K.; Sarangi, M.; Panda, S.K. Microstructure and Mechanical Performance of Friction Stir Spot-Welded Aluminum-5754 Sheets. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2013, 22, 131–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fereiduni, E.; Movahedi, M.; Kokabi, A.H. Dissimilar Al/steel friction stir spot welding: To penetrate into the lower steel sheet or not? Sci. Technol. Weld. Join. 2016, 21, 466–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figner, G.; Vallant, R.; Weinberger, T.; Schroettner, H.; Pasic, H.; Enzinger, N. Friction stir spot welds between aluminium and steel automotive sheets: Influence of welding parameters on mechanical properties and microstructure. Weld. World 2009, 53, R13–R23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitlin, D.; Radmilovic, V.; Pan, T.; Chen, J.; Feng, Z.; Santella, M.L. Structure-properties relations in spot friction welded (also known as friction stir spot welded) 6111 aluminum. Mat. Sci. Eng. A-Struct. 2006, 441, 9–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajed, M.; Bisadi, H. Experimental failure study of friction stir spot welded similar and dissimilar aluminum alloys. Weld. World 2016, 60, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.Z.; Yang, X.Q.; Luan, G.H. Fatigue properties of friction stir welds in Al 5083 alloy. Scr. Mater. 2005, 53, 1187–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uematsu, Y.; Tokaji, K.; Tozaki, Y.; Kurita, T.; Murata, S. Effect of re-filling probe hole on tensile failure and fatigue behaviour of friction stir spot welded joints in Al-Mg-Si alloy. Int. J. Fatigue 2008, 30, 1956–1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uematsu, Y.; Tokaji, K. Comparison of fatigue behaviour between resistance spot and friction stir spot welded aluminium alloy sheets. Sci. Technol. Weld. Join. 2009, 14, 62–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malafaia, A.M.S.; Milan, M.T.; Oliveira, M.F.; Spinelli, D. Evaluation of dynamic defect detection in FSSW welded joints under fatigue tests. Procedia Eng. 2010, 2, 1823–1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joy-A-Ka, S.; Ogawa, Y.; Akebono, H.; Kato, M.; Sugeta, A.; Sun, Y.; Fujii, H. Fatigue Damage Evaluation of Friction Stir Spot Welded Cross-Tension Joints Under Repeated Two-Step Force Amplitudes. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2015, 24, 2494–2502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grujicic, M.; Arakere, G.; Pandurangan, B.; Hariharan, A.; Yen, C.F.; Cheeseman, B.A.; Fountzoulas, C. Statistical Analysis of High-Cycle Fatigue Behavior of Friction Stir Welded AA5083-H321. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2011, 20, 855–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, H.M.; Jordon, J.B.; Barkey, M.E.; Guo, Y.B.; Su, X.; Badarinarayan, H. Influence of structural integrity on fatigue behavior of friction stir spot welded AZ31 Mg alloy. Mat. Sci. Eng. A-Struct. 2013, 564, 369–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, H.; Pal, T.K. High Cycle Fatigue Behaviour of Friction Stir Lap Welded 6061 Aluminium Alloy to Coated Steel Sheet Joint. Trans. Indian Inst. Met. 2015, 68, 959–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Ni, D.R.; Xiao, B.L.; Ma, Z.Y. Non-uniform deformation in a friction stir welded Mg-Al-Zn joint during stress fatigue. Int. J. Fatigue 2014, 59, 9–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Z.M.; He, R.Y.; Lin, P.C.; Dong, K. Fatigue analyses for swept friction stir spot welds in lap-shear specimens of alclad 2024-T3 aluminum sheets. Int. J. Fatigue 2014, 61, 129–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, S.H.; Chen, D.L.; Bhole, S.D.; Cao, X.; Wanjara, P. Lap shear strength and fatigue behavior of friction stir spot welded dissimilar magnesium-to-aluminum joints with adhesive. Mat. Sci. Eng. A-Struct. 2013, 562, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venukumar, S.; Muthukumaran, S.; Yalagi, S.G.; Kailas, S.V. Failure modes and fatigue behavior of conventional and refilled friction stir spot welds in AA 6061-T6 sheets. Int. J. Fatigue 2014, 61, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, G.-Q.; Xu, G.-S.; Shang, D.-G.; Chen, S.-J. Welding parameter selection and short fatigue crack growth of dissimilar aluminum alloy friction stir welded joint. Weld. World 2019, 63, 1761–1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, T.J.; Shi, B.L.; Duan, Q.Q.; Fu, J.W.; Yang, Y.S. Fatigue behavior of friction stir spot welded AZ31 Mg alloy sheet joints. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2013, 23, 1949–1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakiuchi, T.; Uematsu, Y.; Suzuki, K. Evaluation of fatigue crack propagation in dissimilar Al/steel friction stir welds. In Proceedings of the 21st European Conference on Fracture, ECF 21, Catania, Italy, 20–24 June 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Zhong, H.; Li, S.; Zhao, H.; Chen, J.; Qi, L. Microstructure, mechanical properties and fatigue crack growth behavior of friction stir welded joint of 6061-T6 aluminum alloy. Int. J. Fatigue 2020, 135, 105556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassanifard, S.; Mohammadpour, M.; Rashid, H.A. A novel method for improving fatigue life of friction stir spot welded joints using localized plasticity. Mater. Des. 2014, 53, 962–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, H.; Wu, C.S.; Bachmann, M.; Rethmeier, M. Numerical modeling for the effect of pin profiles on thermal and material flow characteristics in friction stir welding. Mater. Des. 2015, 77, 114–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Liu, X.; Ni, J. Keyhole refilled friction stir spot welding of aluminum alloy to advanced high strength steel. J. Mater. Proc. Technol. 2017, 249, 452–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boucherit, A.; Avettand-Fènoël, M.N.; Taillard, R. Effect of a Zn interlayer on dissimilar FSSW of Al and Cu. Mater. Des. 2017, 124, 87–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.D.; Ding, Z.M.; Shen, C.B.; Chen, Y. Interfacial microstructure and properties of aluminum–magnesium AZ31B multi-pass friction stir processed composite plate. Mater. Des. 2016, 94, 240–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
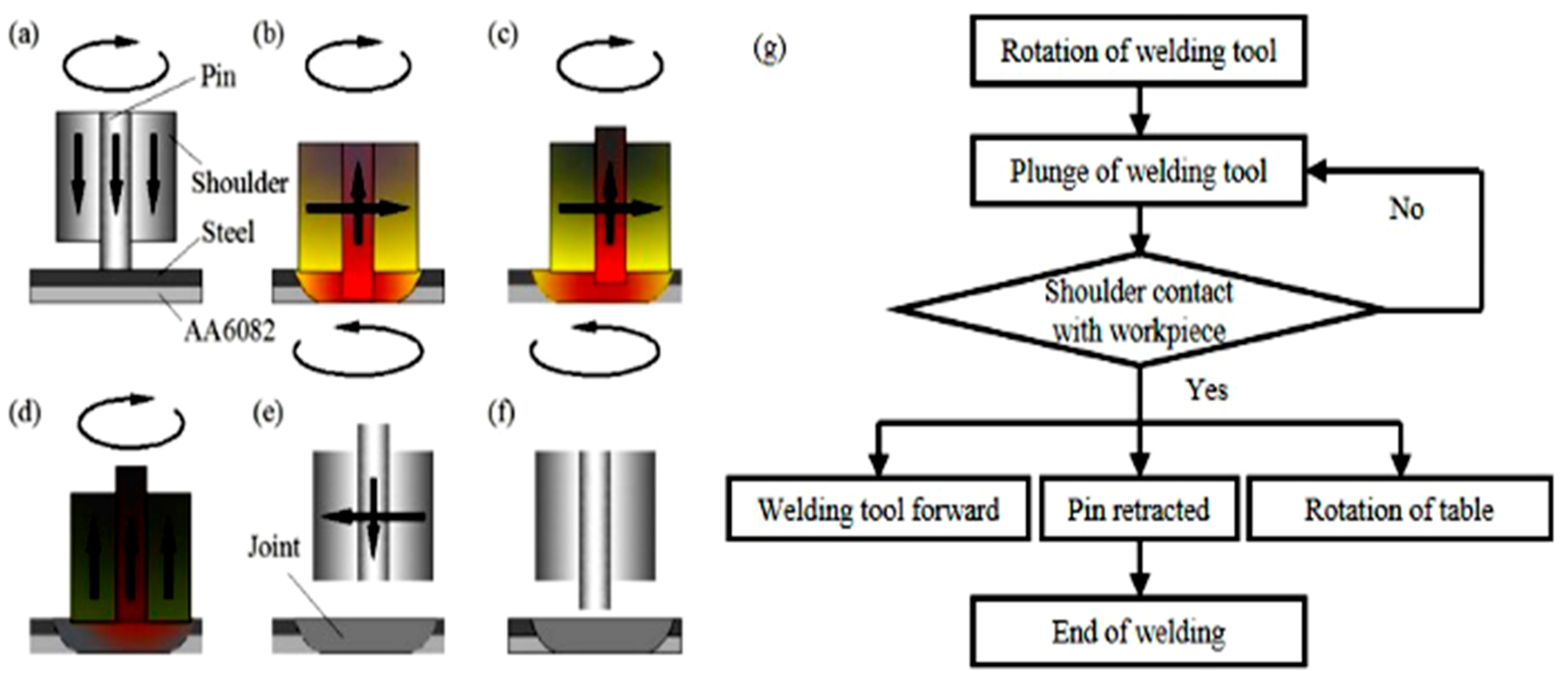

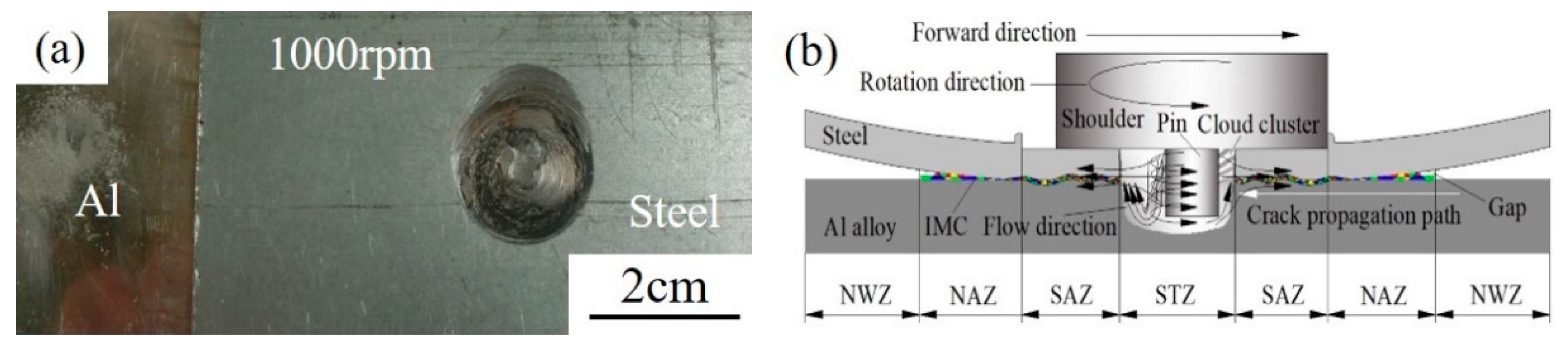

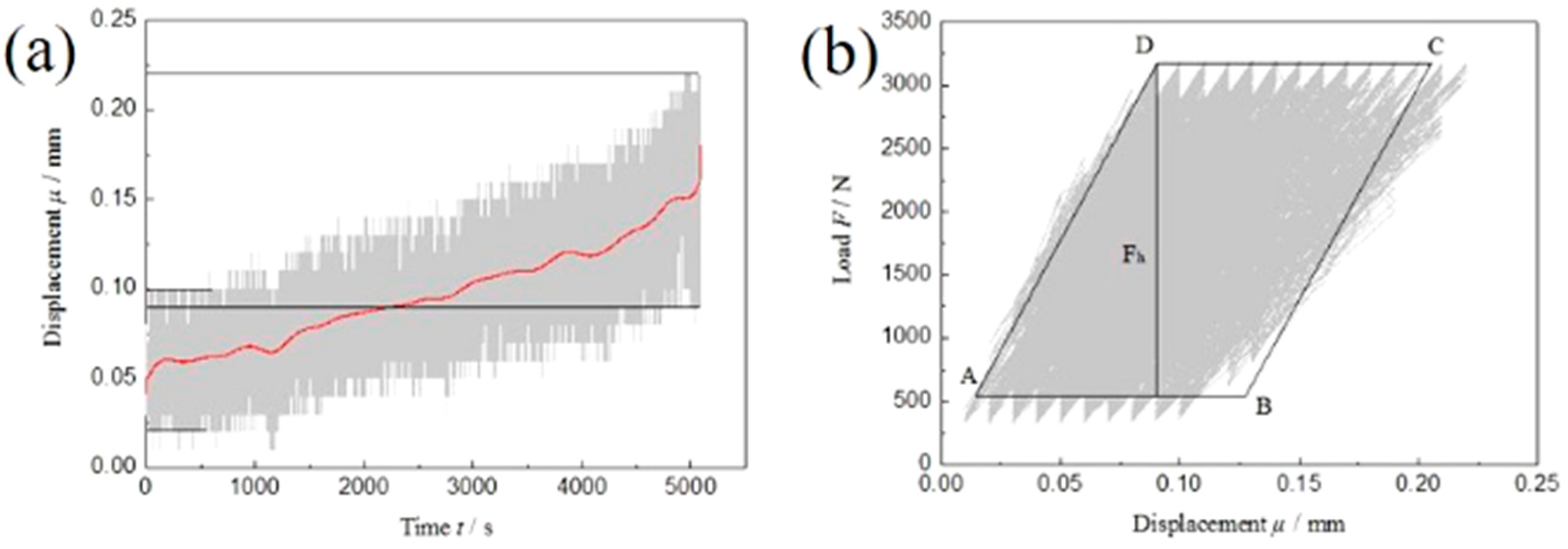


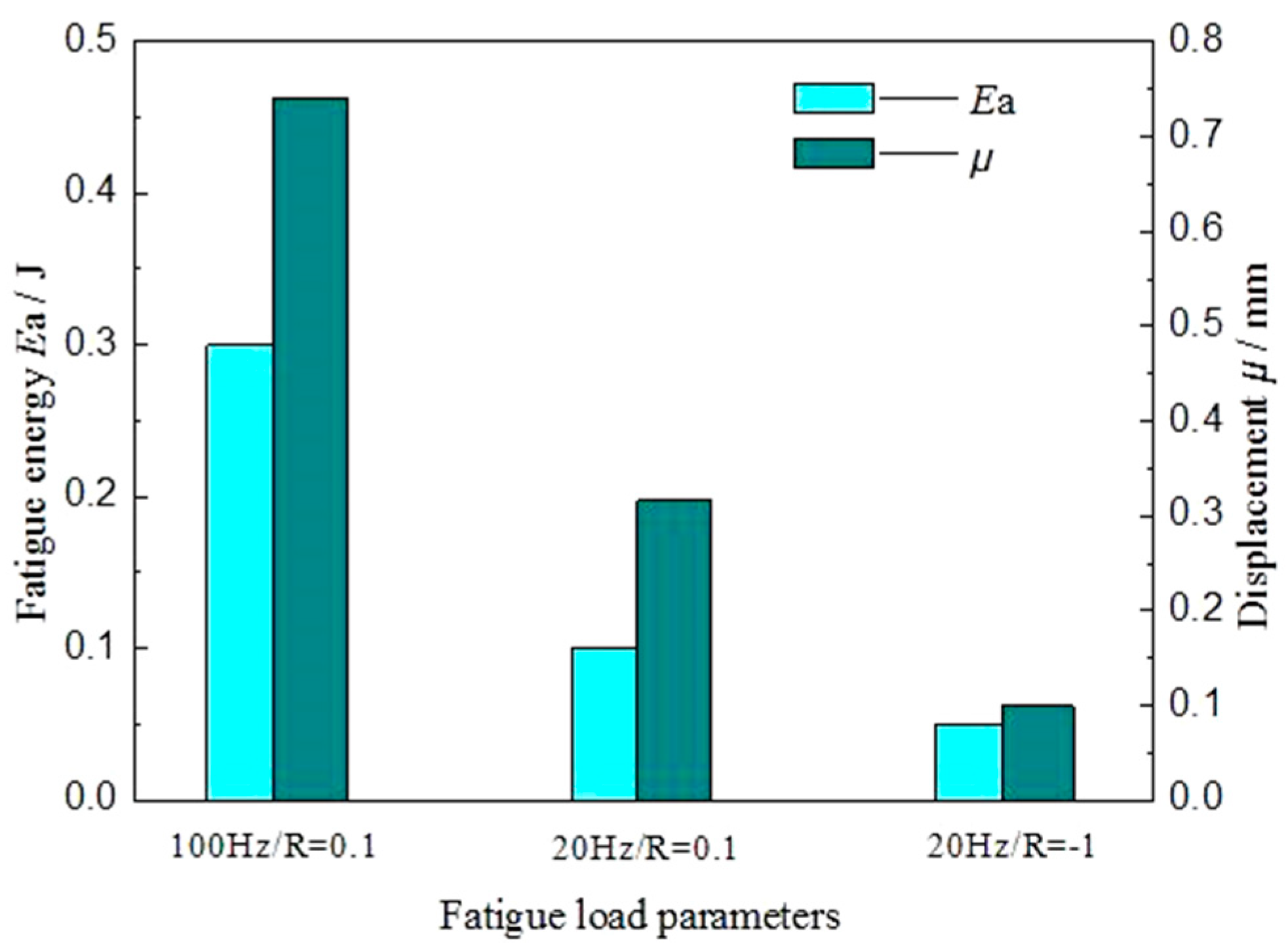

| AA6082 | Si | Fe | Cu | Mn | Mg | Cr | Zn | Ti | Other |
| Content | 0.7–1.3 | 0.50 | 0.10 | 0.4–1.0 | 0.6–1.2 | 0.25 | 0.20 | 0.10 | 0.15 |
| DP600 | C | Mn | Si | Al | Mo | Cr | Cu | S | P |
| Content | 0.09 | 1.84 | 0.36 | 0.05 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.03 | 0.005 | 0.005 |
| Pin LengthL (mm) | Plunging Depthlp (mm) | Shoulder DiameterDs (mm) | Retracting Speedvb (mm/min) | Rotation Rate of Welding ω (rpm) |
| 2.0 | 0.3 | 22.0 | 5.0 | 800/1000/1200 |
| Pin DiameterDp (mm) | Plunging Speedvp (mm/min) | Welding Speedv (mm/min) | Forward DistanceD (mm) | Rotation Rate of Table ωt (rpm) |
| 5.0 | 5.0 | 3.0 | 1.5 | 3.0 |
| R = 0.1 | 80% Fb | 70% Fb | 60% Fb | 50% Fb | 40% Fb | 35% Fb | 30% Fb |
| Fmaz (kN) | 6.40 | 5.60 | 4.80 | 4.00 | 3.20 | 2.8 | 2.40 |
| Fmin (kN) | 0.64 | 0.56 | 0.48 | 0.40 | 0.32 | 0.28 | 0.24 |
| R = −1 | 50% Fb | 40% Fb | 30% Fb | 25% Fb | 20% Fb | ||
| Fmaz (kN) | 4.00 | 3.20 | 2.40 | 2.00 | 1.60 | ||
| Fmin (kN) | −4.00 | −3.20 | −2.40 | −2.00 | −1.60 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Z.; Yu, Y.; Zhao, H.; Tong, H. Effect of Loading Methods on the Fatigue Properties of Dissimilar Al/Steel Keyhole-Free FSSW Joints. Materials 2020, 13, 4247. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13194247
Zhang Z, Yu Y, Zhao H, Tong H. Effect of Loading Methods on the Fatigue Properties of Dissimilar Al/Steel Keyhole-Free FSSW Joints. Materials. 2020; 13(19):4247. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13194247
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Zhongke, Yang Yu, Huaxia Zhao, and Hui Tong. 2020. "Effect of Loading Methods on the Fatigue Properties of Dissimilar Al/Steel Keyhole-Free FSSW Joints" Materials 13, no. 19: 4247. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13194247
APA StyleZhang, Z., Yu, Y., Zhao, H., & Tong, H. (2020). Effect of Loading Methods on the Fatigue Properties of Dissimilar Al/Steel Keyhole-Free FSSW Joints. Materials, 13(19), 4247. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13194247





