Mechanical Simulation of Thermoplastic Composite Fiber Variable-Angle Laminates
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Mathematical Model of Variable-Angle Trajectory Planning Based on the Quadratic Bezier Curve Method
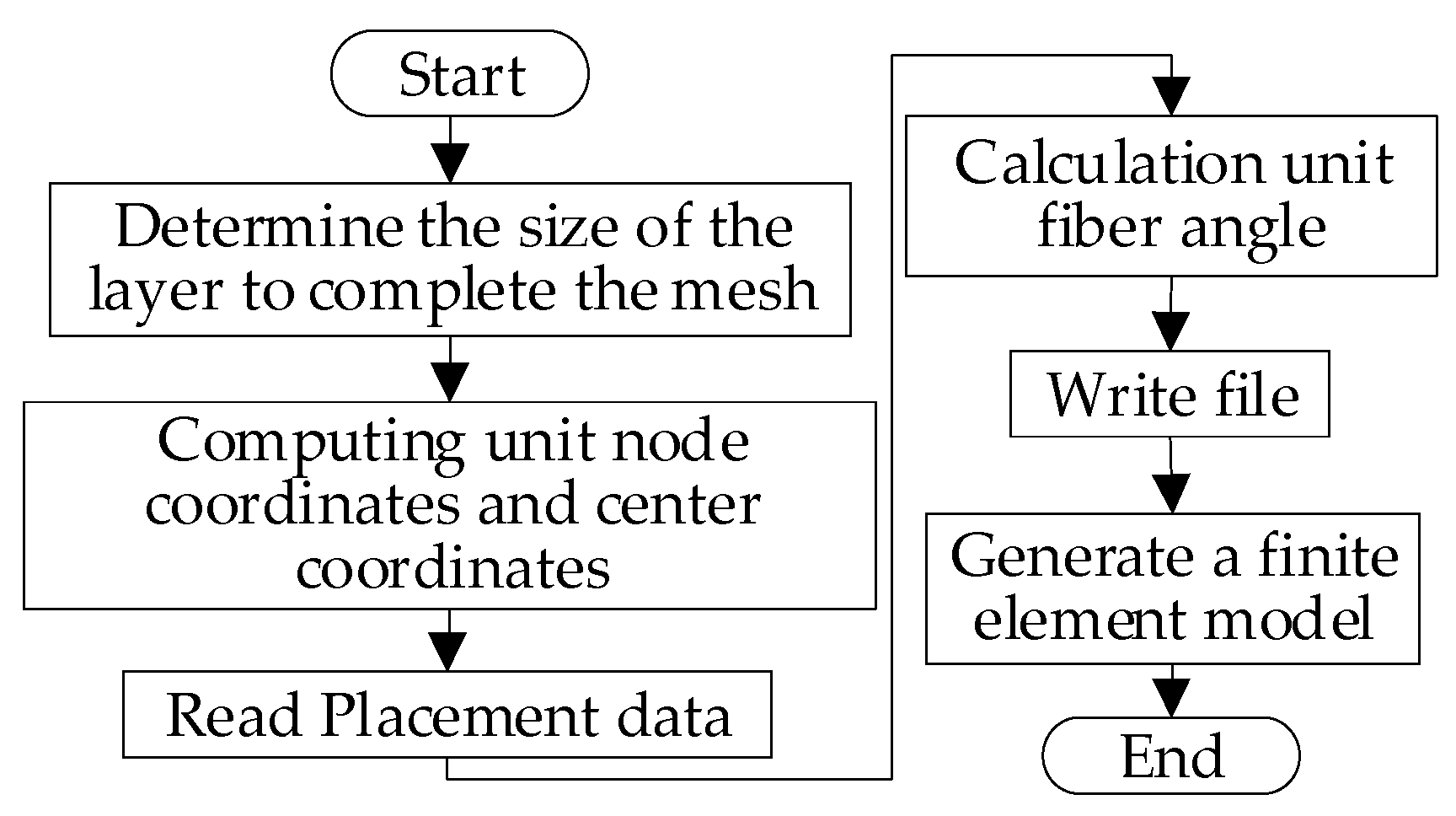
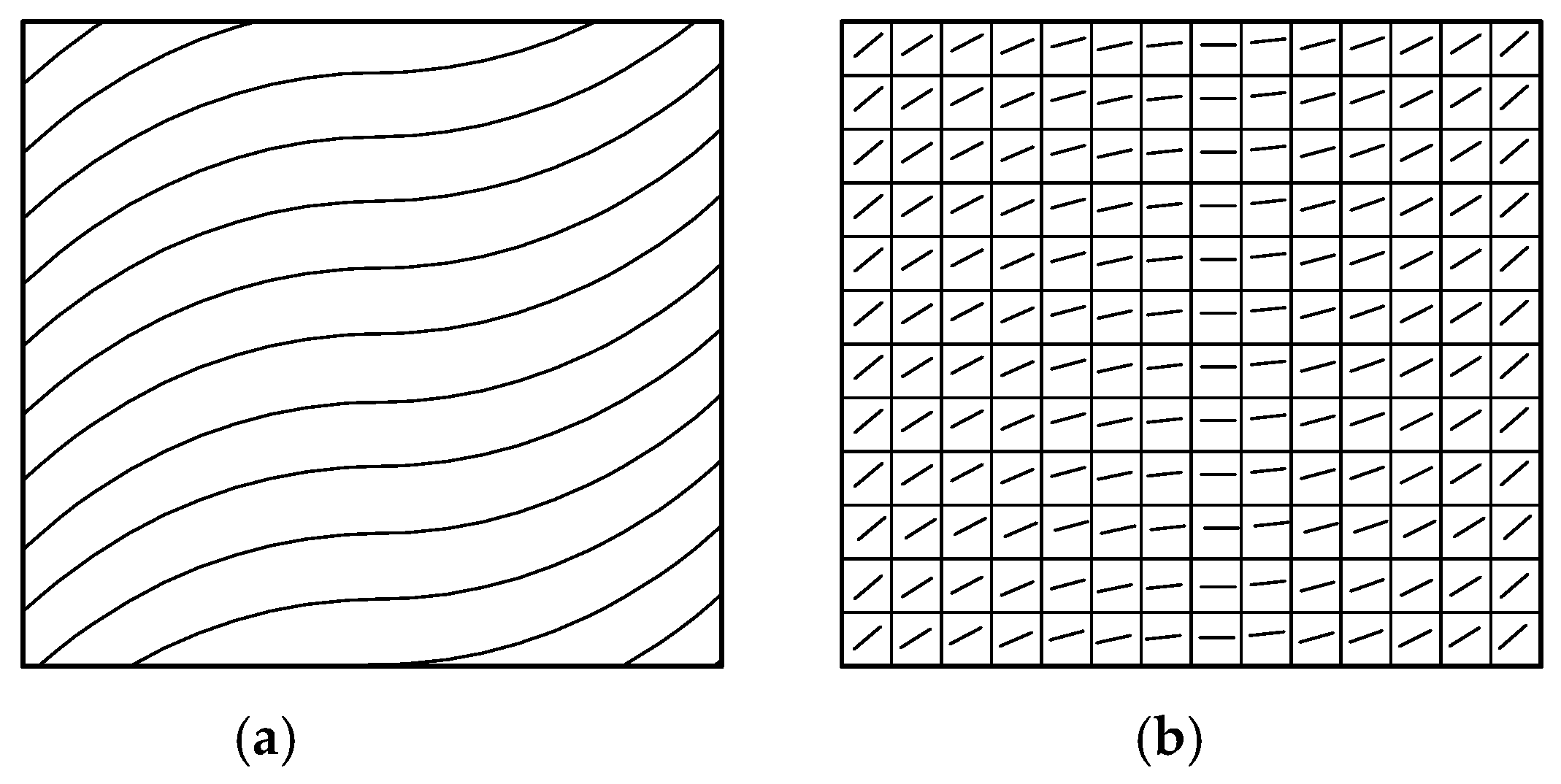
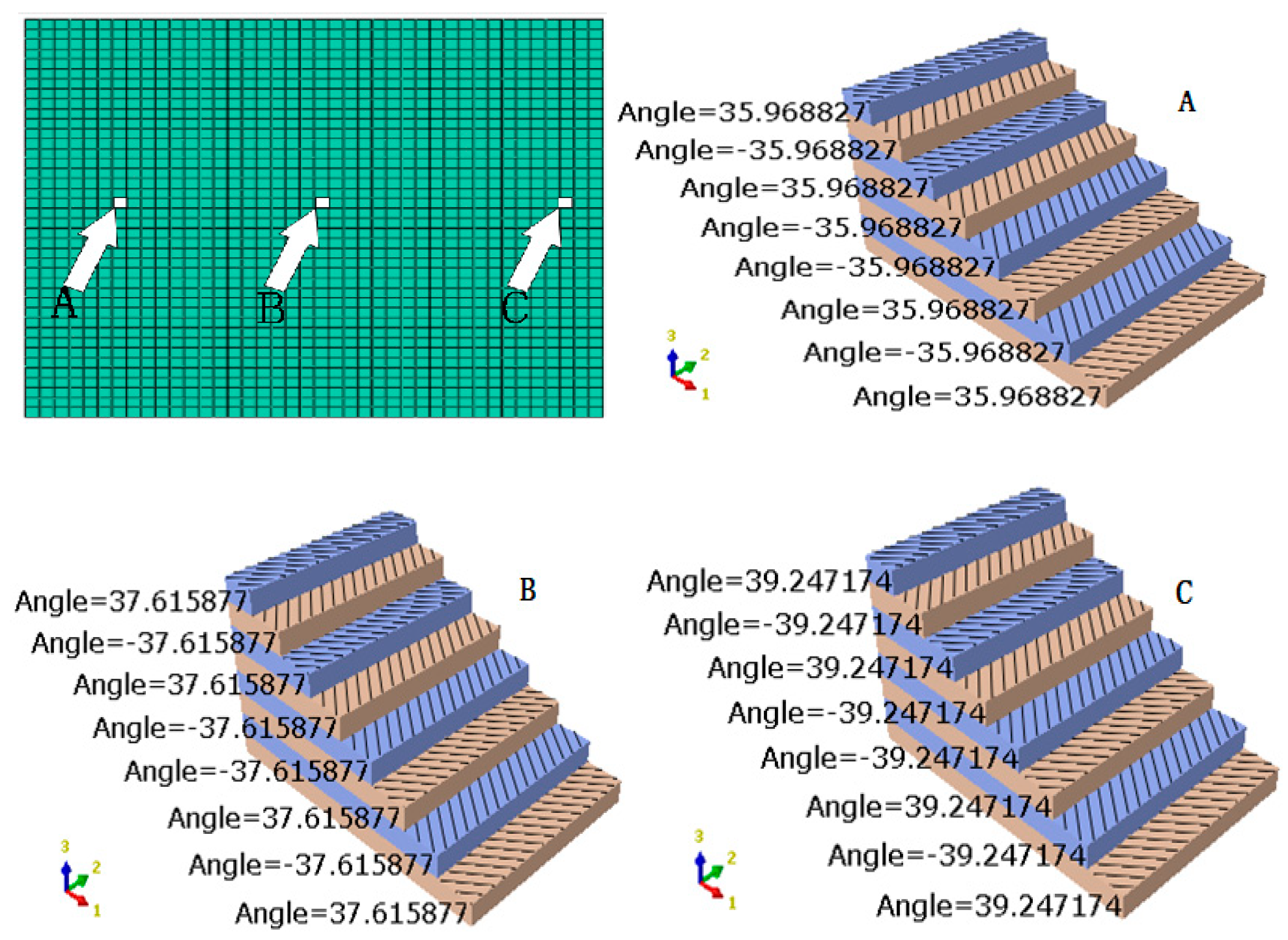
3. Finite Element Analysis Model of the Variable-Angle Layer
4. Study on Statics of Thermoplastic Fiber Variable-Angle Laminates
4.1. Constitutive Equation of Variable-Angle Laminates
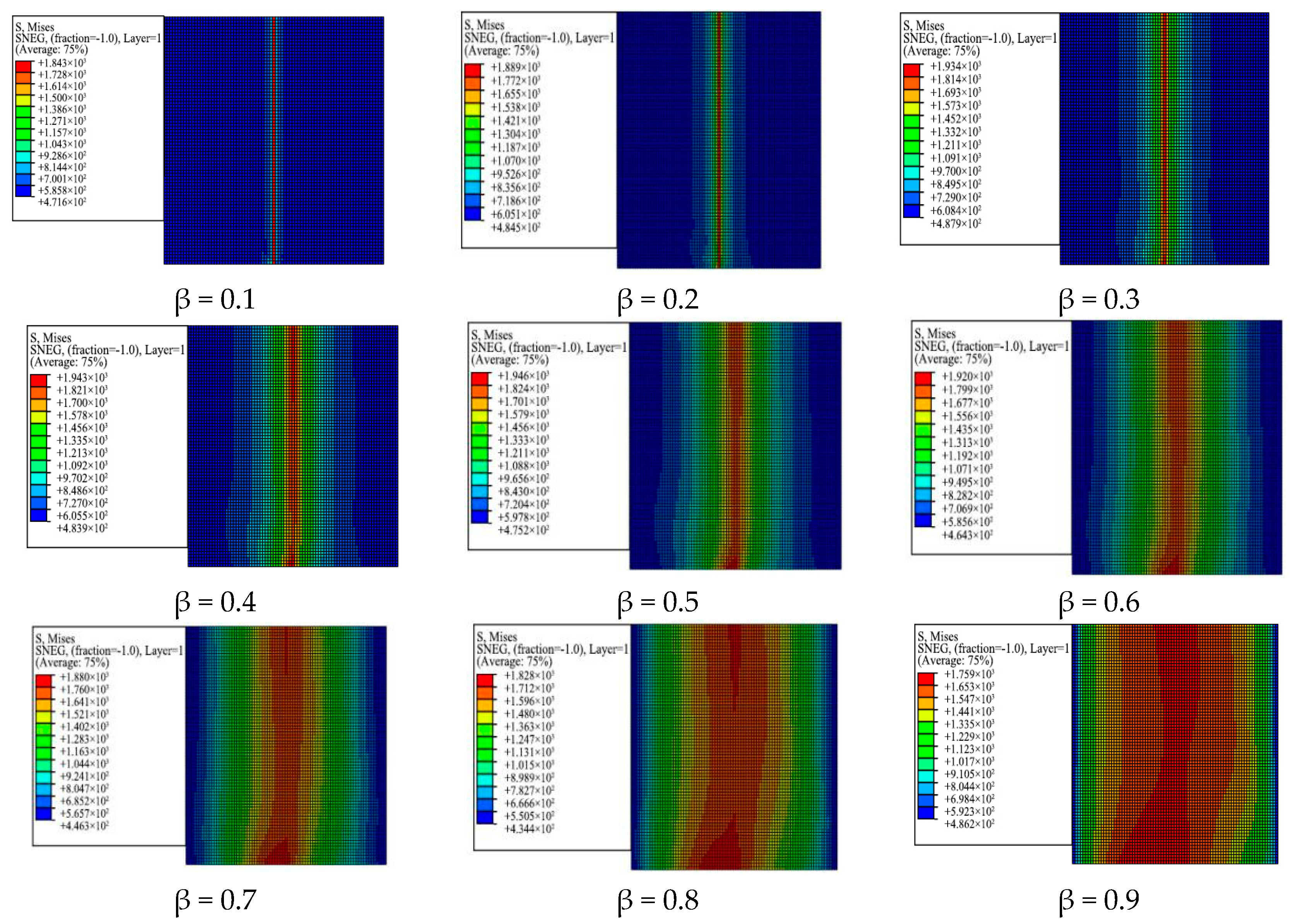
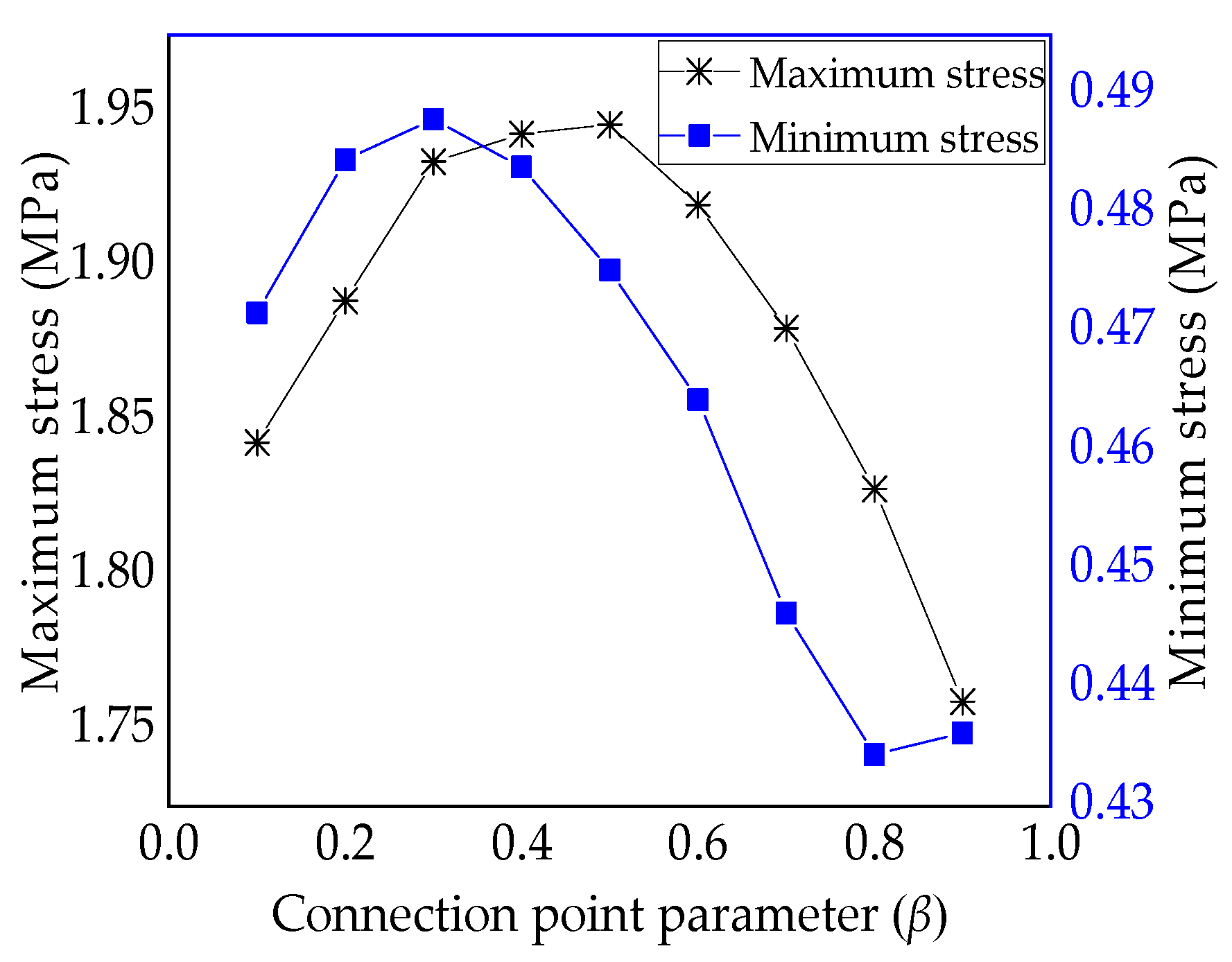
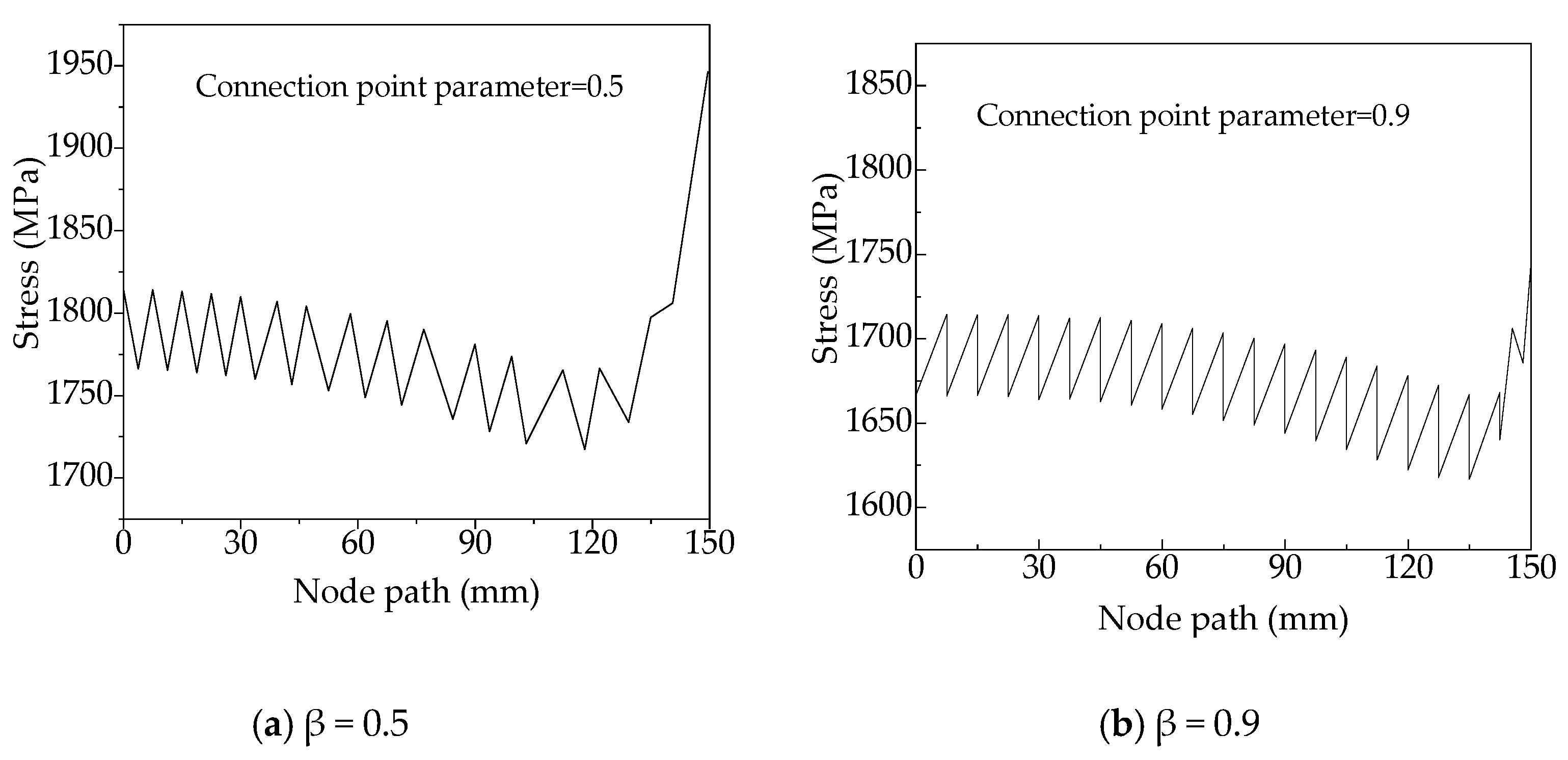
4.2. Stress Analysis of the Variable-Angle Laminate
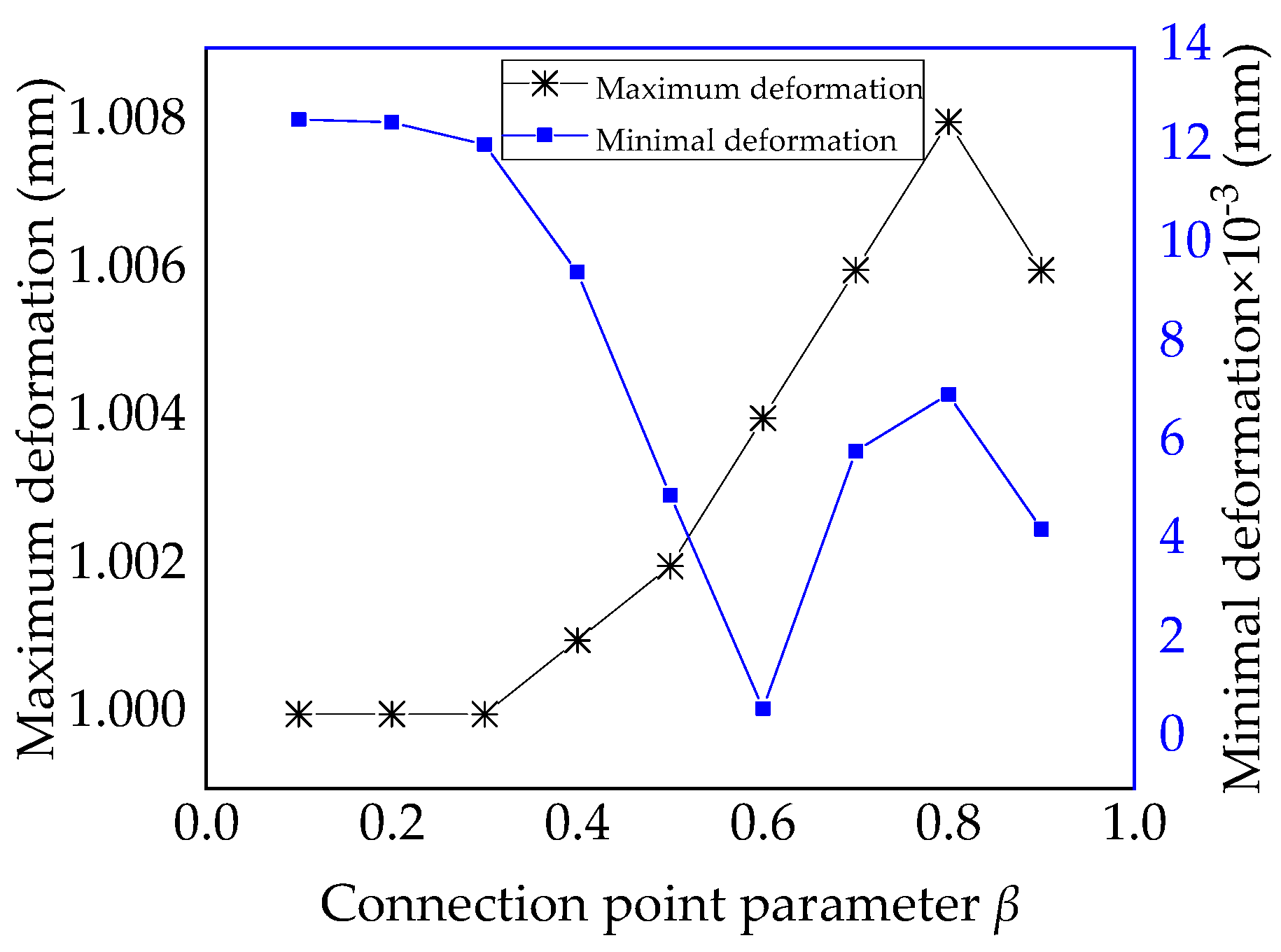
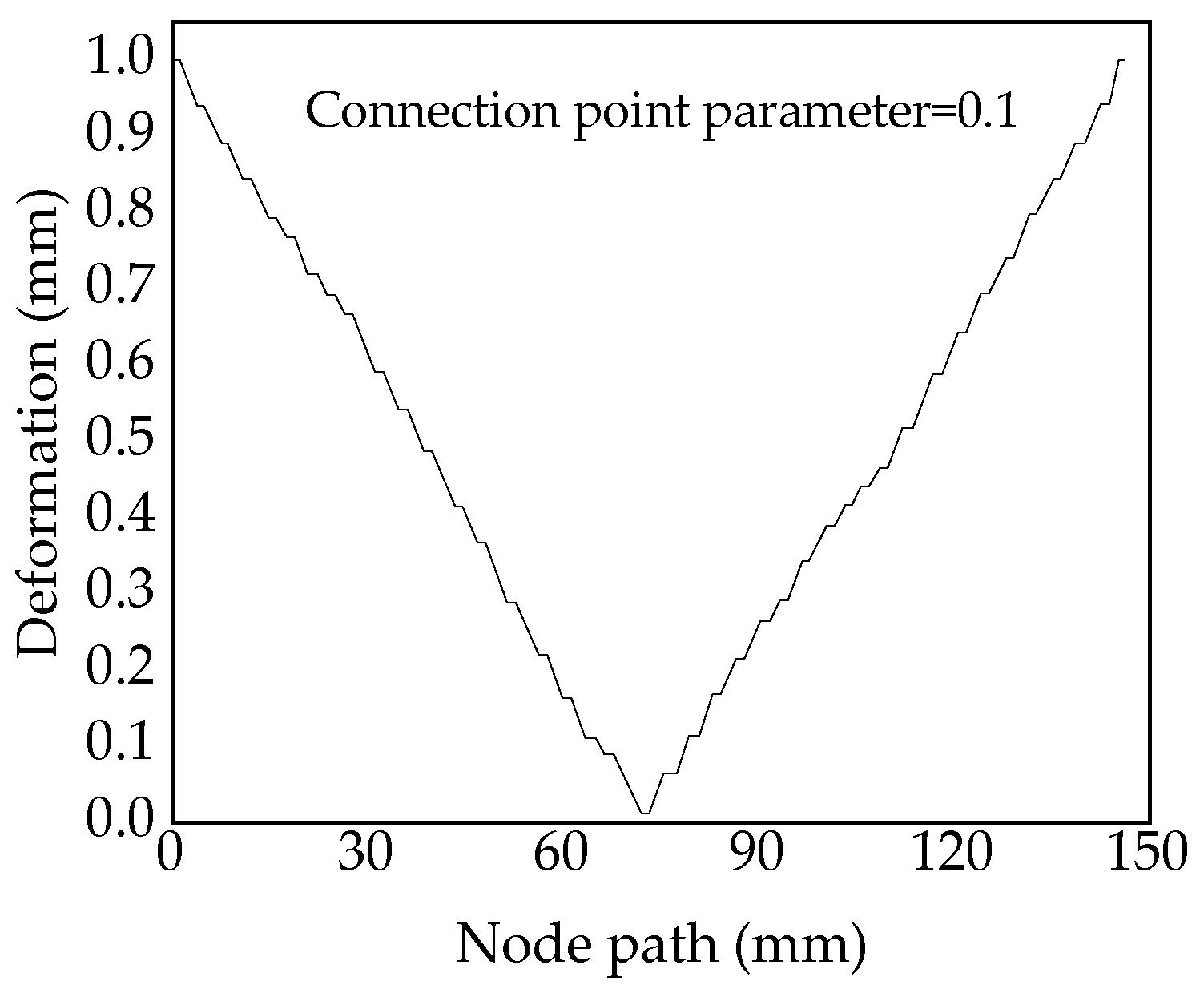
4.3. Deformation Analysis of Variable-Angle Laminates
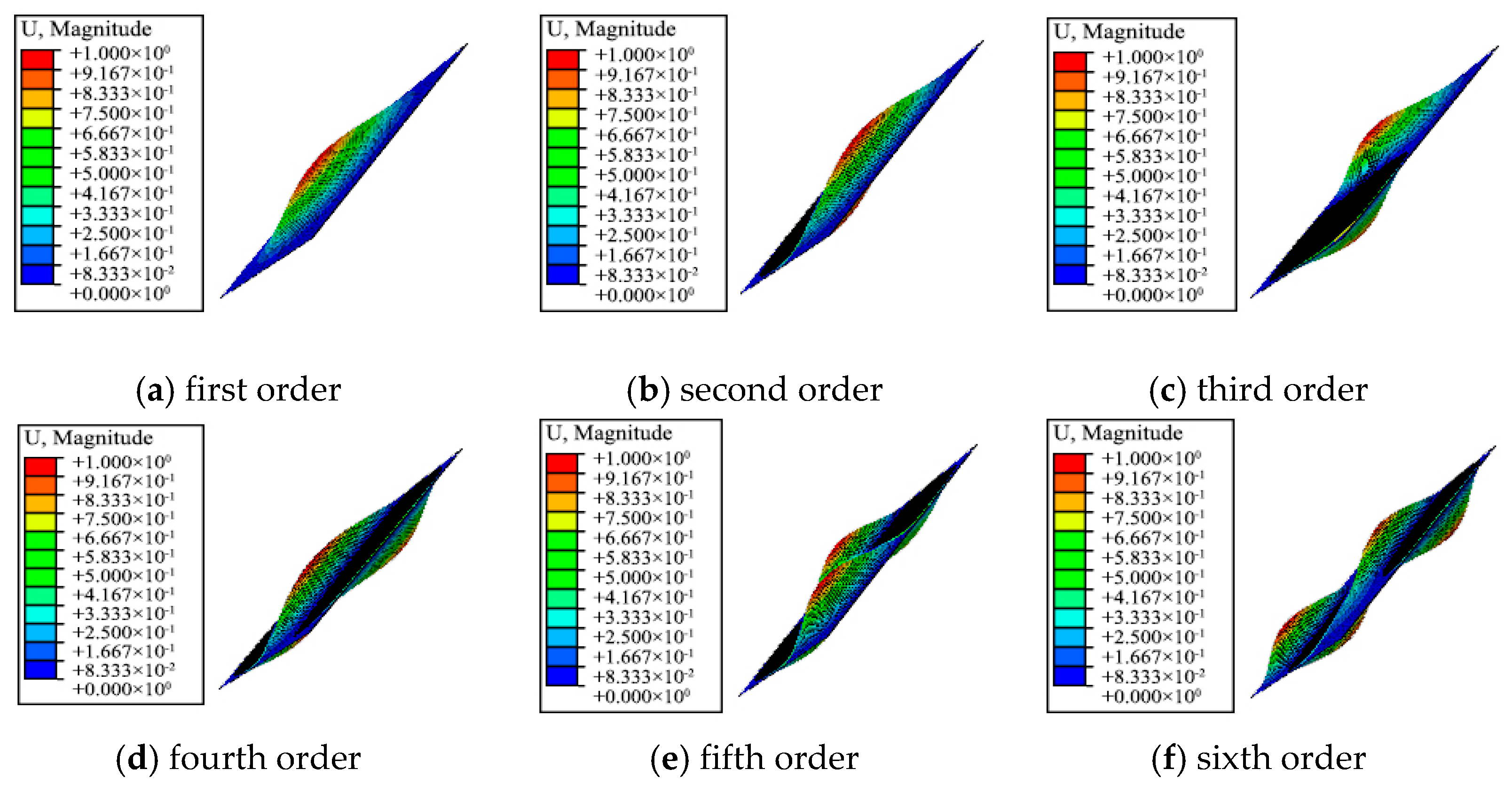
4.4. Modal Analysis of Variable-Angle Laminates
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Broderick, H.C.; Paul, M.W. Buckling analysis, design and optimization of variable-stiffness sandwich panels. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2016, 96, 217–228. [Google Scholar]
- Schinner, G.; Brandt, J.; Richter, H. Recycling carbon-fiber-reinforced thermoplastic composites. J. Thermoplast Compos. Mater. 1996, 3, 239–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouritz, A.P.; Leong, K.H.; Herszberg, I. A review of the effect of stitching on the inplane mechanical properties of fibre-reinforced polymer composites. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 1997, 12, 979–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morey, B. Automating composites fabrication. Manuf. Eng. 2008, 4, 12–16. [Google Scholar]
- Lukaszewicz, D.H.; Ward, C.; Potter, K.D. The engineering aspects of automated prepreg layup History present and future. Compos. Part B Eng. 2012, 3, 997–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattia, D.F.; Laura, V.; Giuseppe, D.A.; Kevin, P. Heater power control for multi-material, variable speed Automated Fibre Placement. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2017, 101, 408–421. [Google Scholar]
- Stokes, C.; Kollmannsbergerb, A.; Compstona, P.; Drechsler, K. The effect of processing temperature on wedge peel strength of CF/PA6 laminates manufactured in a laser tape placement process. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2019, 121, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gearóid, C.; Daniël, P.; Vincenzo, O.; David, J.; Ronan, H.; Paul, W. A study of the influence of processing parameters on steering of carbon Fibre/PEEK tapes using laser-assisted tape placement. Compos. Part B Eng. 2019, 163, 243–251. [Google Scholar]
- Daniël, P.; Gearóid, C.; Vincenzo, O.; Ronan, H.; David, J.; Paul, W. Concurrent design and manufacture of a thermoplastic composite stiffener. Compos. Struct. 2019, 212, 271–280. [Google Scholar]
- Tatsuno, D.; Yoneyama, T.; Kawamoto, K.; Okamoto, M. Production system to form, cut, and join by using a press machine for continuous carbon fiber-reinforced thermoplastic sheets. Polym. Compos. 2016, 45, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redman, C.; McClain, M.; Timoschchuk, N.; Bayraktar, H. Curved beam test behavior of 3D composites. Sampe J. 2014, 45, 36–37. [Google Scholar]
- Aswani, K.B.; Gearóid, C.; Daniël, P.B.; Ronan, M.O. Properties of a thermoplastic composite skin-stiffener interface in a stiffened structure manufactured by laser-assisted tape placement with in situ consolidation. Compos. Struct. 2019, 214, 123–131. [Google Scholar]
- Frketic, J.; Dickens, T.; Ramakrishnan, S. Automated manufacturing and processing of fibre-reinforced polymer (FRP) composites: An additive review of contemporary and modern techniques for advanced materials manufacturing. Addit. Manuf. 2017, 14, 69–86. [Google Scholar]
- Clément, H.; Lionel, B.; Wen, F.X. Feasibility study of robotic fibre placement on intersecting multi-axial revolution surfaces. Robot. Comput. Integr. Manuf. 2017, 48, 73–79. [Google Scholar]
- Gürdal, Z.; Olmedo, R. In-plane response of laminates with spatially varying fiber orientations: Variable stiffness concept. AIAA J. 1993, 4, 751–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tom, W.; Thomas, B.; Alicia, B.; Avinash, P.M.; Manuel, S. Tailored fibre placement of carbon fibre rovings for reinforced polypropylene composite part 1: PP infusion of carbon reinforcement. Compos. Part B Eng. 2019, 16, 703–711. [Google Scholar]
- Marouene, A.; Boukhili, R.; Chen, J.; Yousefpour, A. Buckling behavior of variable-stiffness composite laminates manufactured by the tow-drop method. Compos. Struct. 2016, 139, 243–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabido, A.; Bahamonde, L.; Harik, R.; Tooren, M.J. Maturity assessment of the laminate variable stiffness design process. Compos. Struct. 2017, 16, 804–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milazzo, A.; Oliveri, V. Buckling and Postbuckling of Stiffened Composite Panels with Cracks and Delaminations by Ritz Approach. AIAA J. 2017, 3, 965–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madeoa, A.; Grohb, R.M.; Zuccoa, G.; Weaverb, P.M.; Zagaria, G.; Zinnoa, R. Post-buckling analysis of variable-angle tow composite plates using Koiter’s approach and the finite element method. Thin-Walled Struct. 2017, 110, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhajahmad, A.; Abdalla, M.; Gürdal, Z. Optimal design of tow-placed fuselage panels for maximum strength with buckling considerations. J. Aircr. 2010, 3, 775–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, C.; Gürdal, Z.; Camanho, P.; Gürdal, Z. Tailoring for Strength of Composite Steered-fiber Panels with Cutouts. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2010, 8, 1760–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samukham, S.; Gangadharan, R.; Vyasarayani, C.P. Parametric instability of variable angle tow composite laminate under axial compression. Compos. Struct. 2017, 7, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazem, F.; Mahdi, A.; Damiano, P.; Lessard, L. Defect layer method to capture effect of gaps and overlaps in variable stiffness laminates made by Automated Fiber Placement. Compos. Struct. 2013, 7, 245–251. [Google Scholar]
- Pedro, R.; Hamed, A.; Andrzej, T. A review on the mechanical behaviour of curvilinear fiber composite laminates panels. J. Compos. Mater. 2013, 1, 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, Z.L.; Fu, H.Y.; Han, Z.Y. Comparative Study on Bezier Curve and Linear Variable Angle Method for Variable Stiffness Laminates. Polym. Compos. 2019, 3, 952–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waldhart, C.; Gürdal, Z.; Ribbens, C. Analysis of Tow Placed, Parallel Fiber, Variable Stiffness Laminates. AIAA J. 1996, 4, 2210–2221. [Google Scholar]
- Wan, Z.Q.; Li, S.R.; Ma, H.W. Coupling vibration and its control of duplex-bearing car and bridge. Int. J. Appl. Mech. 2018, 5, 983–989. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, K.Q.; Liu, J.Y. Geometric nonlinear formulation for curved beams with varying curvature. Theor. Appl. Mech. Lett. 2012, 6, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wei, T.; Brian, G.; Falzon, Y. Modelling the crush behaviour of thermoplastic composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2016, 6, 57–71. [Google Scholar]






| Parameter | Unit | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Elastic Modulus E1 | GPa | 139 |
| Elastic Modulus E2 | GPa | 10.3 |
| Shear modulus G12 | GPa | 5.2 |
| Shear modulus G13 | GPa | 5.2 |
| Shear modulus G23 | GPa | 3.96 |
| Poisson’s ratio μ12 | 0.3 |
| β | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.4 | 0.5 | 0.6 | 0.7 | 0.8 | 0.9 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Maximum × 103 (MPa) | 1.843 | 1.889 | 1.934 | 1.943 | 1.946 | 1.92 | 1.88 | 1.828 | 1.759 |
| Minimum × 102 (MPa) | 0.472 | 0.485 | 0.488 | 0.484 | 0.475 | 0.464 | 0.446 | 0.434 | 0.486 |
| β | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.4 | 0.5 | 0.6 | 0.7 | 0.8 | 0.9 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Maximum (mm) | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1.001 | 1.002 | 1.004 | 1.006 | 1.008 | 1.006 |
| Minimum (mm × 10−3) | 12.55 | 12.49 | 12.04 | 9.457 | 4.937 | 0.615 | 5.83 | 6.979 | 4.249 |
| Orders | Frequency | Mode of Vibration |
|---|---|---|
| (Hz) | ||
| 1 | 49.07 | The plate center vibrates along the Z direction |
| 2 | 83.53 | The left and right sides of the plate center vibrate in the Z direction |
| 3 | 107.77 | The upper and lower sides of the plate center vibrate along the Z direction |
| 4 | 133.38 | The two diagonals of the plate vibrate in the Z direction |
| 5 | 144.61 | The center and diagonal of the plate vibrate in the Z direction |
| 6 | 192.51 | The upper, middle, and lower parts of the plate vibrate in the Z direction |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cao, Z.; Guo, D.; Fu, H.; Han, Z. Mechanical Simulation of Thermoplastic Composite Fiber Variable-Angle Laminates. Materials 2020, 13, 3374. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13153374
Cao Z, Guo D, Fu H, Han Z. Mechanical Simulation of Thermoplastic Composite Fiber Variable-Angle Laminates. Materials. 2020; 13(15):3374. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13153374
Chicago/Turabian StyleCao, Zhongliang, Dengke Guo, Hongya Fu, and Zhenyu Han. 2020. "Mechanical Simulation of Thermoplastic Composite Fiber Variable-Angle Laminates" Materials 13, no. 15: 3374. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13153374
APA StyleCao, Z., Guo, D., Fu, H., & Han, Z. (2020). Mechanical Simulation of Thermoplastic Composite Fiber Variable-Angle Laminates. Materials, 13(15), 3374. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13153374






