Setting and Hardening Behaviour of Alkali-Activated Landfilled Fly Ash–Slag Binder at Room Temperature
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Raw Materials
2.2. Sample Preparation
2.3. Characterisation of Samples
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Setting and Hardening of the Binder
3.1.1. Influence of Alkali Solution
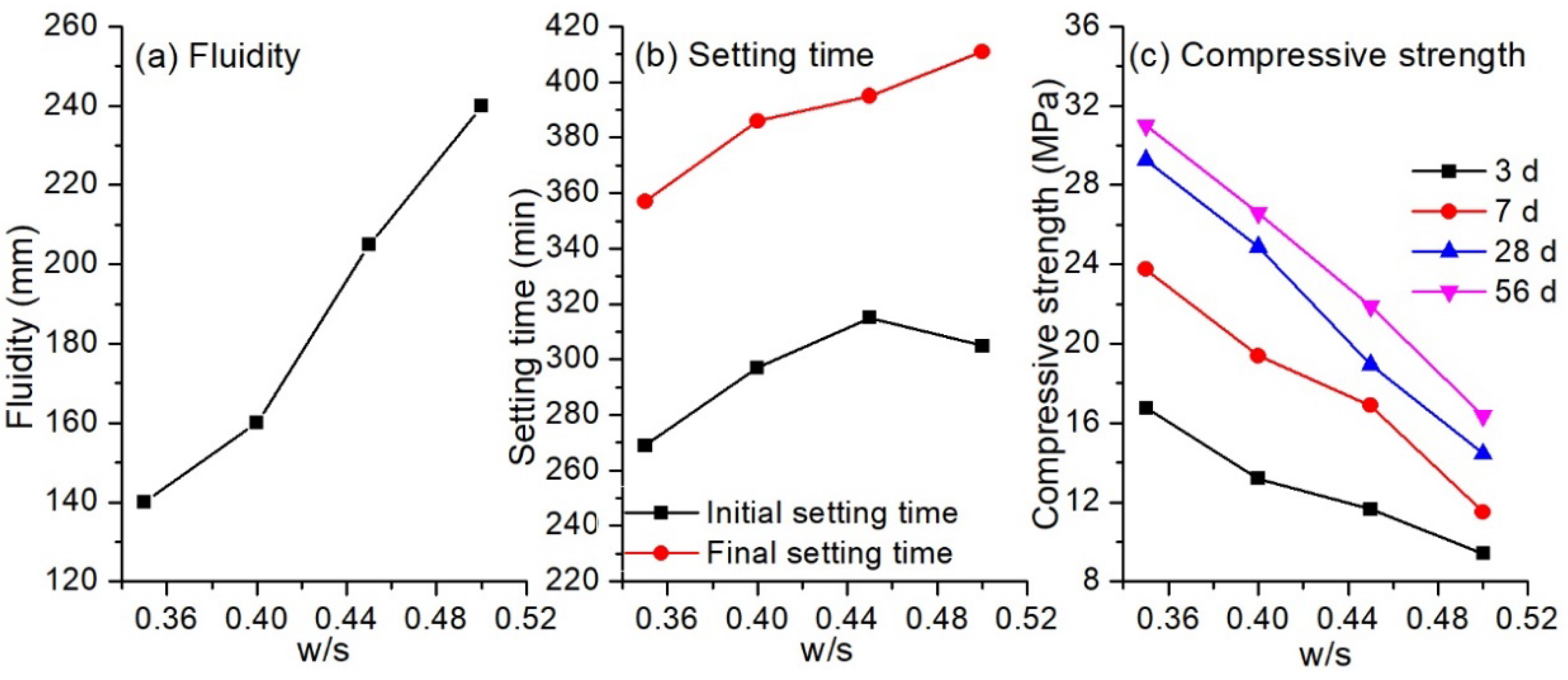
3.1.2. Influence of Water-to-Solid Ratio
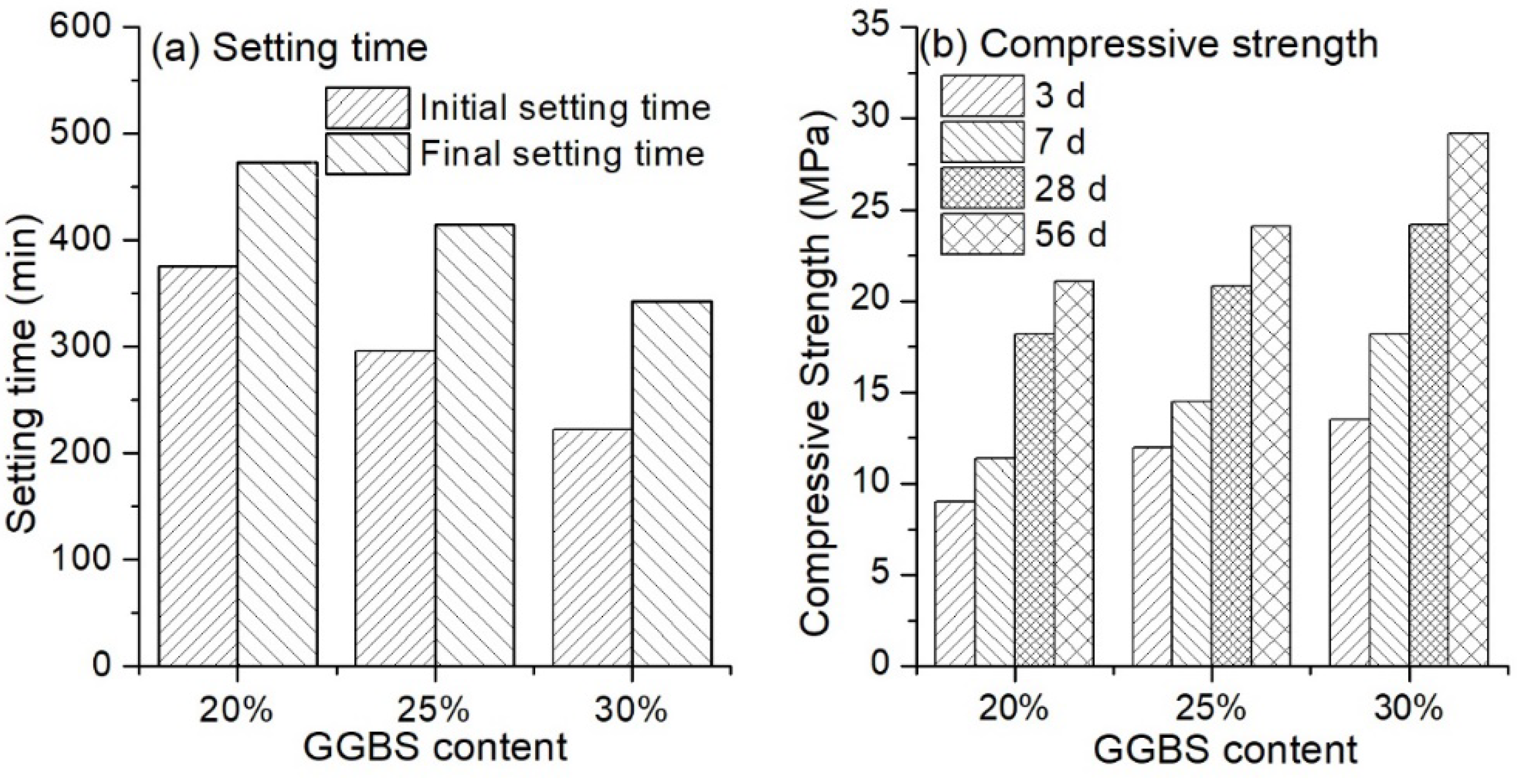
3.1.3. Influence of Ground-Granulated Blast-Furnace Slag (GGBS) Content
3.2. Reaction of the Hybrid Binder
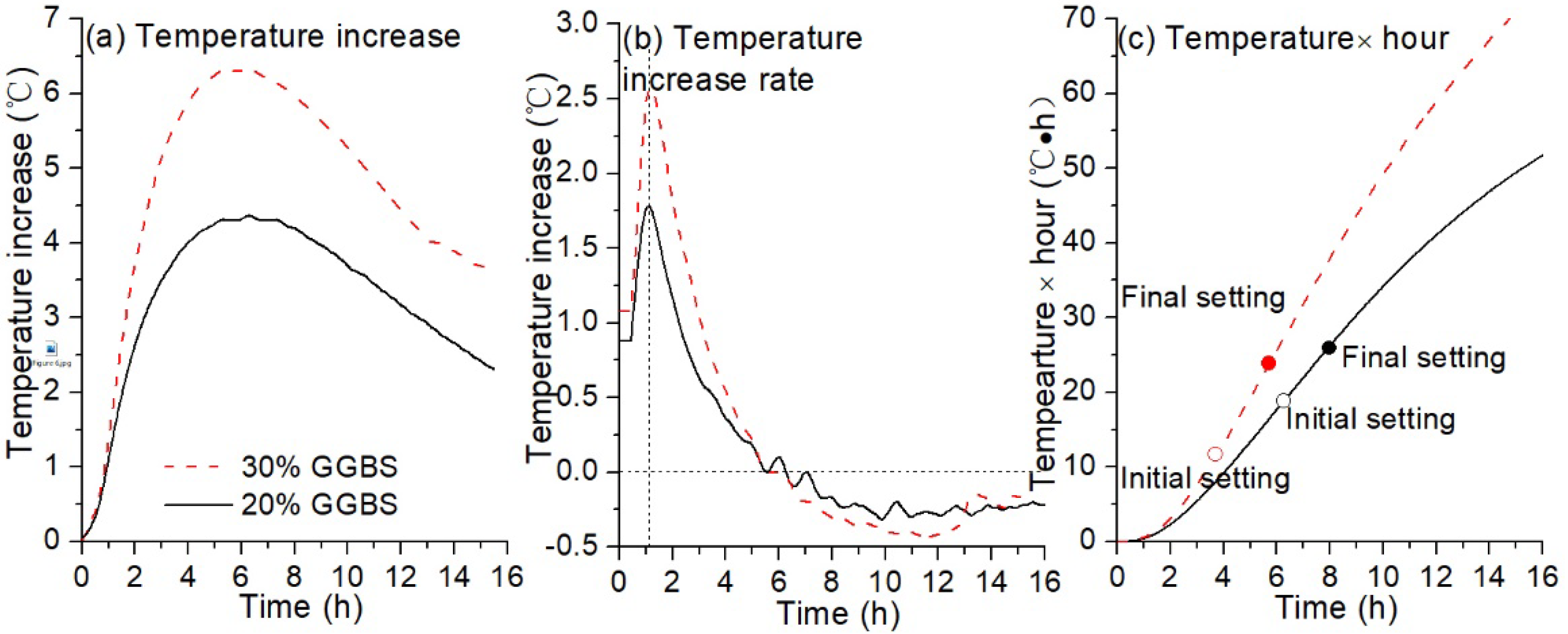
3.2.1. Isothermal Temperature Increase
3.2.2. Electrical Resistivity
3.3. Microstructure of the Hybrid Binder
3.3.1. X-ray Diffraction (XRD) Analysis
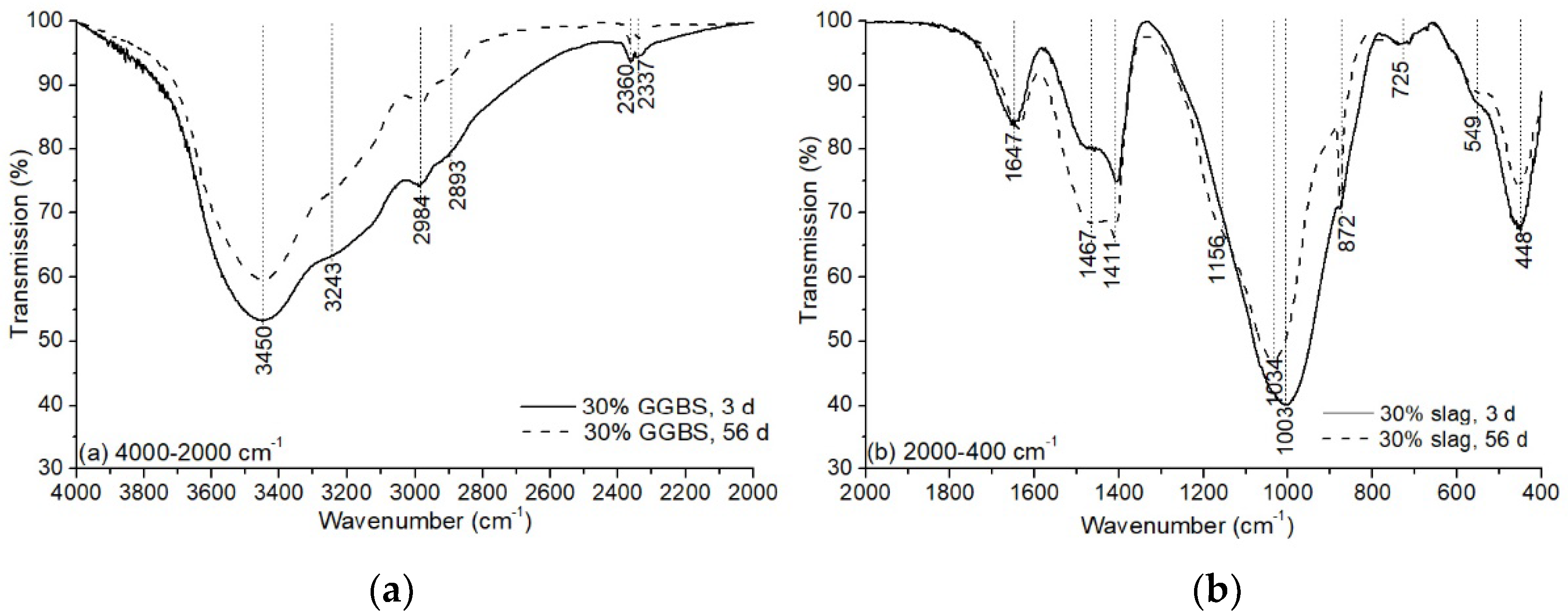
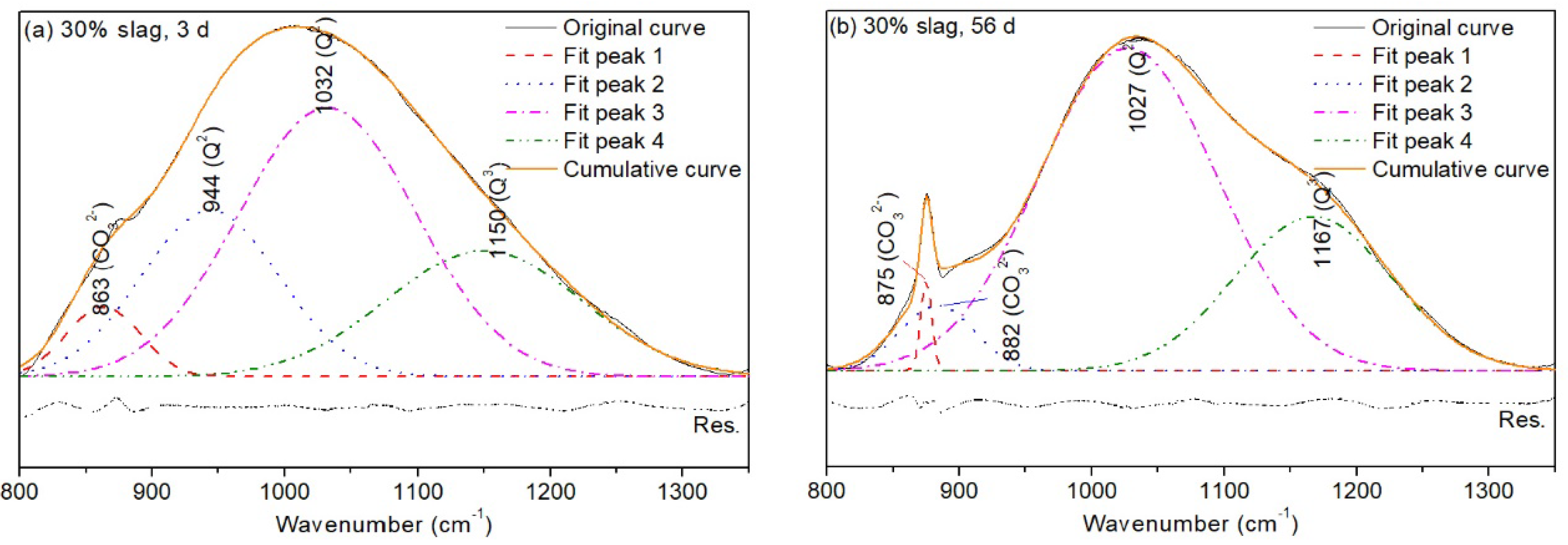
3.3.2. Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) Spectroscopy
3.3.3. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Flower, D.J.M.; Sanjayan, J.G. Greenhouse Gas Emissions Due to Concrete Manufacture. In Handbook of Low Carbon Concrete; Nazari, A., Sanjayan, J.G., Eds.; Butterworth-Heinemann: Oxford, UK, 2017; Chapter 1; pp. 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, K.H.; Song, J.K.; Song, K.I. CO2 Reduction Assessment of Alkali-Activated Concrete Based on Korean Life-Cycle Inventory Database. In Handbook of Low Carbon Concrete; Nazari, A., Sanjayan, J.G., Eds.; Butterworth-Heinemann: Oxford, UK, 2017; Chapter 7; pp. 139–157. [Google Scholar]
- Pierrehumbert, R. There is no Plan B for dealing with the climate crisis. Bull. At. Sci. 2019, 75, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmaruzzaman, M. A review on the utilization of fly ash. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 2010, 36, 327–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assi, L.N.; Carter, K.; Deaver, E.; Ziehl, P. Review of availability of source materials for geopolymer/sustainable concrete. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 263, 121477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Report on the Comprehensive Utilization of Large Emmission of Industrial Solid Wastes in China in 2017; Ni, W., Ed.; Industrial Solid Waste Network: Beijing, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Report on the Development of Fly Ash Industry in 2017. Available online: http://www.ccement.com/news/content/9301050184546.html (accessed on 27 December 2017).
- Woźniak, M.; Żygadło, M. The transformation of coal fly ash deposited on wet landfills. Energy Sources Part A Recovery Util. Environ. Eff. 2016, 38, 2734–2740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messina, F.; Ferone, C.; Colangelo, F. Alkali activated waste fly ash as sustainable composite: Influence of curing and pozzolanic admixtures on the early-age physico-mechanical properties and residual strength after exposure at elevated temperature. Compos. Part B Eng. 2018, 132, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Peng, X.; Li, S.; Wang, S.; Xu, Y.; Chen, Y. Effects of admixtures on alkali-activated low rank fly ash concrete. Concrete 2019, 353, 101–105. [Google Scholar]
- Wirth, X.; Glatstein, D.A.; Burns, S.E. Mineral phases and carbon content in weathered fly ashes. Fuel 2019, 236, 1567–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Li, S. Effects of wetting and drying on alkalinity and strength of fly ash/slag-activated materials. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 254, 119069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mobili, A.; Belli, A.; Giosuè, C.; Bellezze, T.; Tittarelli, F. Metakaolin and fly ash alkali-activated mortars compared with cementitious mortars at the same strength class. Cem. Concr. Res. 2016, 88, 198–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Provis, J.L.; Palomo, A.; Shi, C. Advances in understanding alkali-activated materials. Cem. Concr. Res. 2015, 78, 110–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia Lodeiro, I.; Cristelo, N.; Palomo, A.; Fernández-Jiménez, A. Use of industrial by-products as alkaline cement activators. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 253, 119000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elahi, M.M.A.; Hossain, M.M.; Karim, M.R.; Zain, M.F.M.; Shearer, C. A review on alkali-activated binders: Materials composition and fresh properties of concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 260, 119788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarıdemir, M.; Çelikten, S. Investigation of fire and chemical effects on the properties of alkali-activated lightweight concretes produced with basaltic pumice aggregate. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 260, 119969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Gao, Z.; Wang, J.; Guo, J.; Hu, S.; Ling, Y. Properties of fresh and hardened fly ash/slag based geopolymer concrete: A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 270, 122389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandanayake, M.; Gunasekara, C.; Law, D.; Zhang, G.; Setunge, S.; Wanijuru, D. Sustainable criterion selection framework for green building materials–An optimisation based study of fly-ash Geopolymer concrete. Sustain. Mater. Technol. 2020, 25, e00178. [Google Scholar]
- Ouellet-Plamondon, C.; Habert, G. Life cycle assessment (LCA) of alkali-activated cements and concretes. In Handbook of Alkali-Activated Cements, Mortars and Concretes; Pacheco-Torgal, F., Labrincha, J.A., Leonelli, C., Palomo, A., Chindaprasirt, P., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing: Oxford, UK, 2015; pp. 663–686. [Google Scholar]
- Assi, L.; Ghahari, S.; Deaver, E.; Leaphart, D.; Ziehl, P. Improvement of the early and final compressive strength of fly ash-based geopolymer concrete at ambient conditions. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 123, 806–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Görhan, G.; Aslaner, R.; Şinik, O. The effect of curing on the properties of metakaolin and fly ash-based geopolymer paste. Compos. Part B Eng. 2016, 97, 329–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamidi, R.M.; Man, Z.; Azizli, K.A. Concentration of NaOH and the Effect on the Properties of Fly Ash Based Geopolymer. Procedia Eng. 2016, 148, 189–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Li, X.; Tan, J.; Vandevyvere, B. Thermal and compressive behaviors of fly ash and metakaolin-based geopolymer. J. Build. Eng. 2020, 30, 101307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliabdo, A.A.; Abd Elmoaty, A.E.M.; Salem, H.A. Effect of cement addition, solution resting time and curing characteristics on fly ash based geopolymer concrete performance. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 123, 581–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Majidi, M.H.; Lampropoulos, A.; Cundy, A.; Meikle, S. Development of geopolymer mortar under ambient temperature for in situ applications. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 120, 198–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phoo-ngernkham, T.; Maegawa, A.; Mishima, N.; Hatanaka, S.; Chindaprasirt, P. Effects of sodium hydroxide and sodium silicate solutions on compressive and shear bond strengths of FA–GBFS geopolymer. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 91, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nath, P.; Sarker, P.K. Effect of GGBFS on setting, workability and early strength properties of fly ash geopolymer concrete cured in ambient condition. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 66, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puertas, F.; Martínez-Ramírez, S.; Alonso, S.; Vázquez, T. Alkali-activated fly ash/slag cements: Strength behaviour and hydration products. Cem. Concr. Res. 2000, 30, 1625–1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, J.E.; Monteiro, P.J.M.; Jun, S.S.; Choi, S.; Clark, S.M. The evolution of strength and crystalline phases for alkali-activated ground blast furnace slag and fly ash-based geopolymers. Cem. Concr. Res. 2010, 40, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, N.K.; Lee, H.K. Setting and mechanical properties of alkali-activated fly ash/slag concrete manufactured at room temperature. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 47, 1201–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Provis, J.; Van Deventer, J.S. Alkali Activated Materials: State-of-the-Art Report, RILEM TC 224-AAM; Springer: London, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, B. Research on Preparation and Performance of Alkali-Activated Low Activity Fly Ash Composite Cementitious Materials; Chongqing University: Chongqing, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, J.; Wild, S. Investigation of the temperature change and heat evolution of mortar incorporating PFA and metakaolin. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2002, 24, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komljenović, M.; Baščarević, Z.; Bradić, V. Mechanical and microstructural properties of alkali-activated fly ash geopolymers. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 181, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliabdo, A.A.; Abd Elmoaty, A.E.M.; Salem, H.A. Effect of water addition, plasticizer and alkaline solution constitution on fly ash based geopolymer concrete performance. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 121, 694–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, N. Non-Tradition Cementitious Materials Chemistry; Wuhan University of Technology Press: Wuhan, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, H.; Van Deventer, J.S.J. The geopolymerisation of alumino-silicate minerals. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2000, 59, 247–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X. Kinetics of Structure Formation and Properties of Concrete by Electrical Resistivity Mesurement; Wuhan University of Techology Press: Wuhan, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Chindaprasirt, P.; De Silva, P.; Sagoe-Crentsil, K.; Hanjitsuwan, S. Effect of SiO2 and Al2O3 on the setting and hardening of high calcium fly ash-based geopolymer systems. J. Mater. Sci. 2012, 47, 4876–4883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, M.M.A.B.; Hussin, K.; Bnhussain, M.; Ismail, K.N.; Yahya, Z.; Abdul Razak, R. Fly Ash-based Geopolymer Lightweight Concrete Using Foaming Agent. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 7186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, H.F.W. Cement Chemistry; Thomas Telford: London, UK, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Essaidi, N.; Laou, L.; Yotte, S.; Ulmet, L.; Rossignol, S. Comparative study of the various methods of preparation of silicate solution and its effect on the geopolymerization reaction. Results Phys. 2016, 6, 280–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- García-Lodeiro, I.; Fernández-Jiménez, A.; Blanco, M.T.; Palomo, A. FTIR study of the sol–gel synthesis of cementitious gels: C–S–H and N–A–S–H. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2008, 45, 63–72. [Google Scholar]
- García Lodeiro, I.; Macphee, D.E.; Palomo, A.; Fernández-Jiménez, A. Effect of alkalis on fresh C–S–H gels. FTIR analysis. Cem. Concr. Res. 2009, 39, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Björnström, J.; Martinelli, A.; Matic, A.; Börjesson, L.; Panas, I. Accelerating effects of colloidal nano-silica for beneficial calcium–silicate–hydrate formation in cement. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2004, 392, 242–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
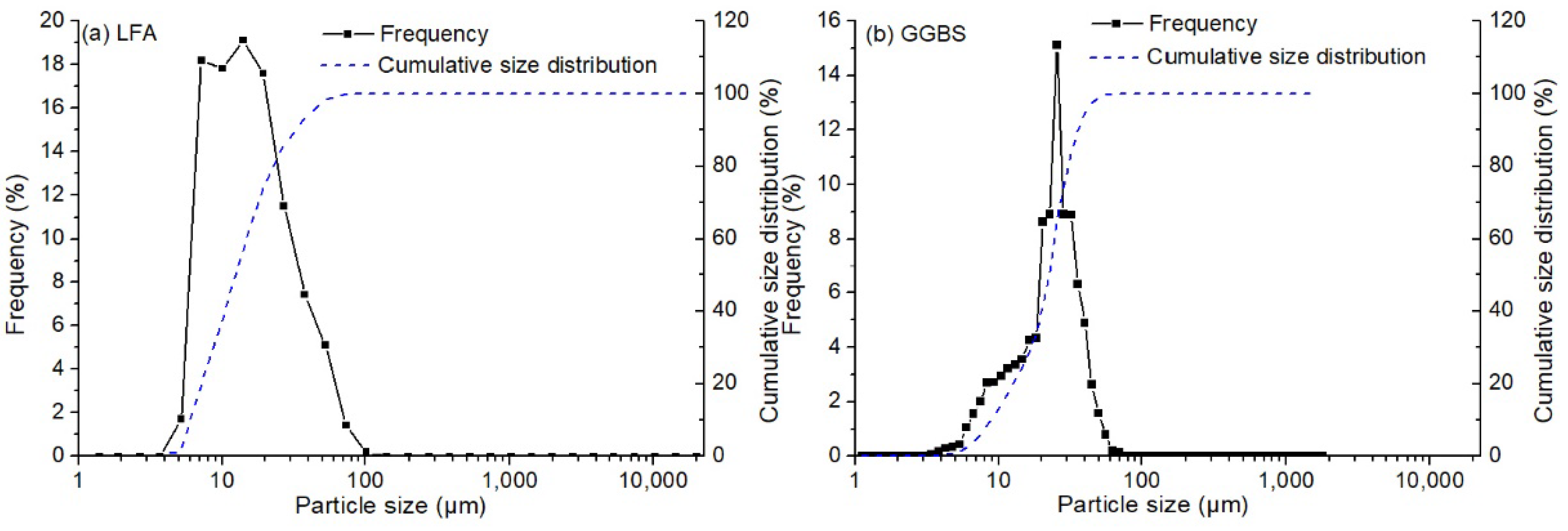
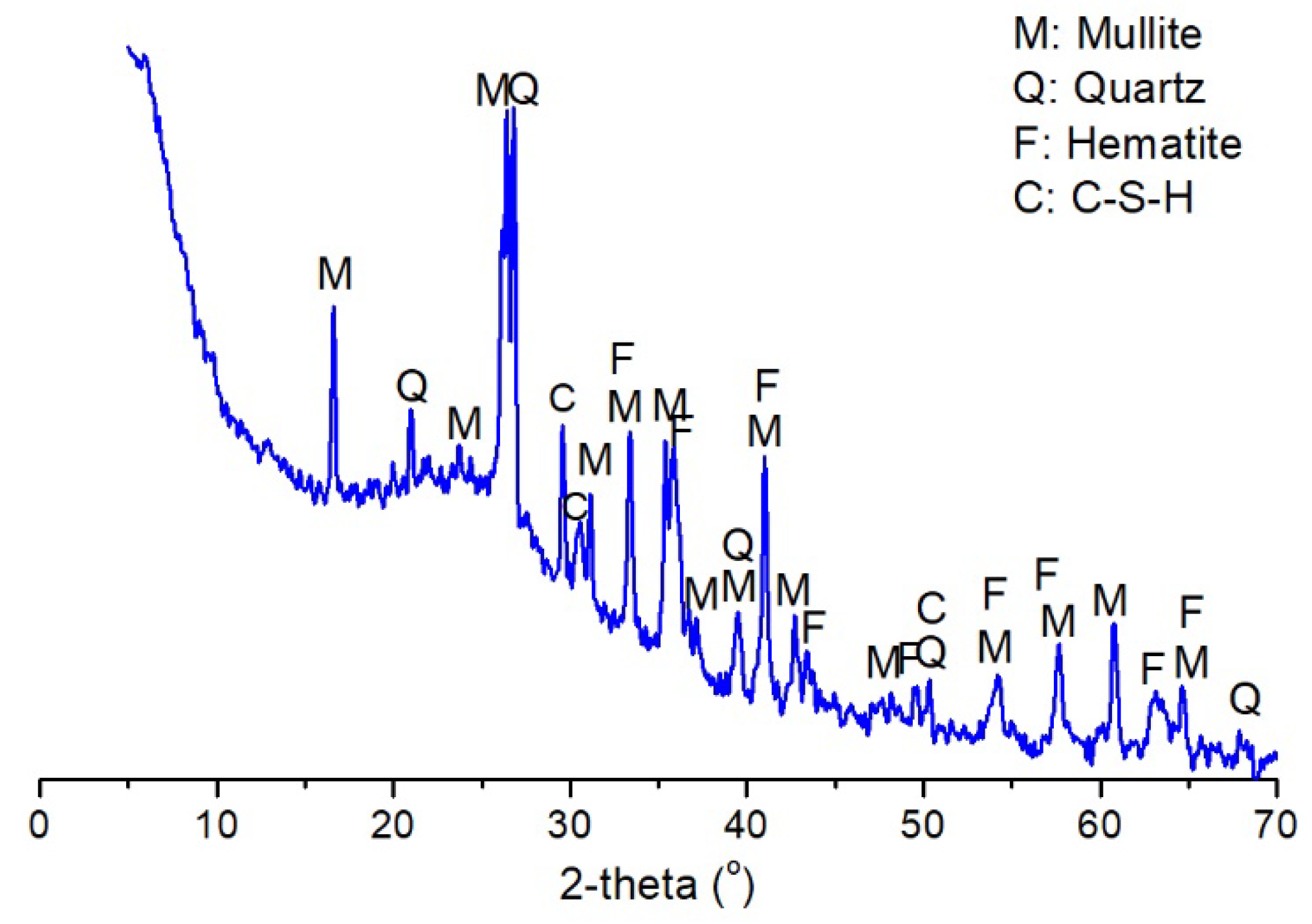
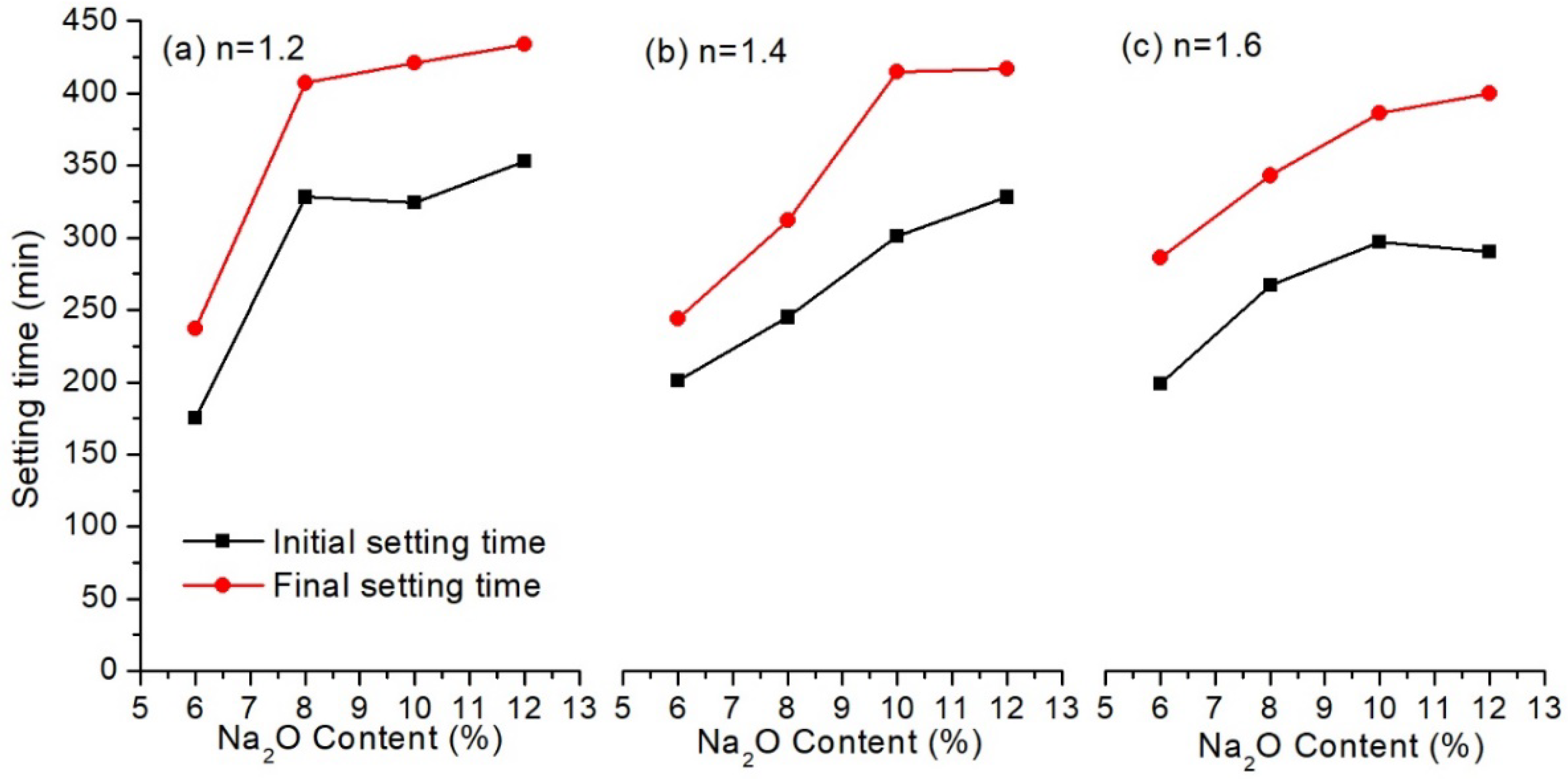
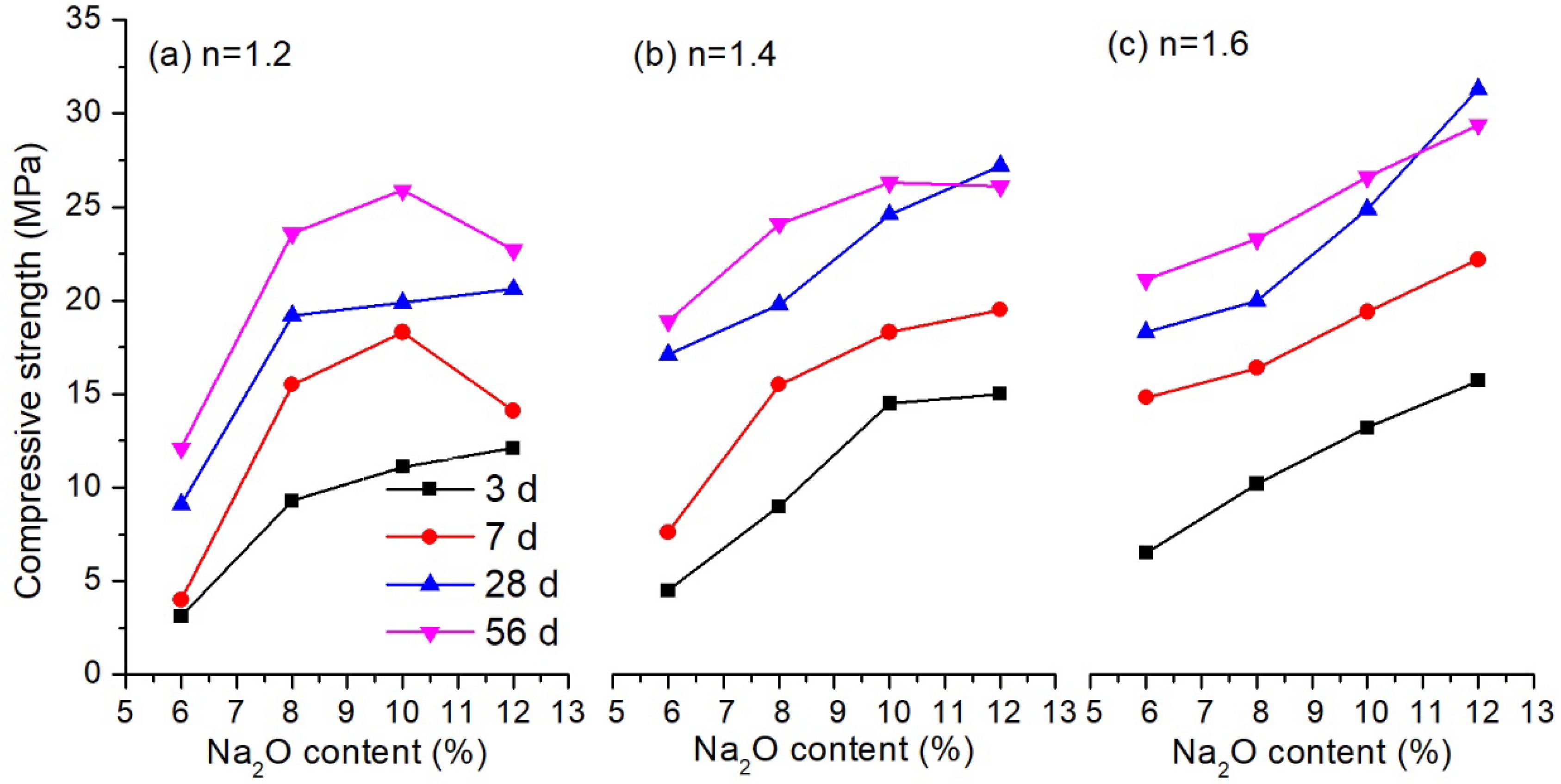



| Sample | SiO2 | Fe2O3 | Al2O3 | CaO | MgO | Ignition Loss | Others |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LFA | 40.41 | 14.65 | 24.99 | 2.49 | / | 10.56 | 6.9 |
| GGBS | 33.75 | 1.36 | 13.55 | 37.76 | 7.65 | / | 5.93 |
| Factors | Values |
|---|---|
| GGBS content | 20%, 25% and 30% |
| Modulus of alkali solution (n) | n = 1.2, 1.4 and 1.6 |
| Na2O content (mass ratio of solid materials) | 6%, 8%, 10% and 12% |
| Water to solid ratio (w/s) | 0.35, 0.40, 0.45 and 0.50 |
| Band | 3 d | 56 d | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wavenumber (cm−1) | Area Fit (%) | FWHM | Wavenumber (cm−1) | Area Fit (%) | FWHM | |
| 863 | 5.17 | 66 | 875–882 | 6.76 | 10.1, 66.9 | |
| 944 | 22.85 | 122.5 | / | / | / | |
| (Silica-rich gel) | 1032 | 47.46 | 157 | 1027 | 65.46 | 157.5 |
| 1150 | 24.52 | 172.9 | 1167 | 27.78 | 139.6 | |
| Elements | Ratio of the Element at Different Position | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |
| C | - | - | - | 4.9 | - |
| Na | 3.55 | 8.95 | 3.26 | 16.9 | 3.75 |
| Ca | 20.00 | 4.35 | 12.50 | 21.63 | 7.87 |
| O | 50.42 | 67.96 | 60.15 | 49.45 | 64.52 |
| Si | 18.55 | 15.78 | 14.05 | 10.5 | 29.01 |
| Al | 7.48 | 2.95 | 5.76 | - | 4.57 |
| Fe | 6.19 | - | - | - | - |
| Mg | - | - | 4.28 | - | - |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, W.; Lin, L.; Wang, S.; Peng, X.; Wu, B.; Sun, K.; Zeng, L. Setting and Hardening Behaviour of Alkali-Activated Landfilled Fly Ash–Slag Binder at Room Temperature. Materials 2020, 13, 3130. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13143130
Liu W, Lin L, Wang S, Peng X, Wu B, Sun K, Zeng L. Setting and Hardening Behaviour of Alkali-Activated Landfilled Fly Ash–Slag Binder at Room Temperature. Materials. 2020; 13(14):3130. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13143130
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Wei, Lin Lin, Shuping Wang, Xiaoqin Peng, Bobo Wu, Keke Sun, and Lu Zeng. 2020. "Setting and Hardening Behaviour of Alkali-Activated Landfilled Fly Ash–Slag Binder at Room Temperature" Materials 13, no. 14: 3130. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13143130
APA StyleLiu, W., Lin, L., Wang, S., Peng, X., Wu, B., Sun, K., & Zeng, L. (2020). Setting and Hardening Behaviour of Alkali-Activated Landfilled Fly Ash–Slag Binder at Room Temperature. Materials, 13(14), 3130. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13143130





