Abstract
Grain refinement using oxide additions is commercially feasible and ecofriendly. MgAl2O4 has a lattice structure similar to Al and small lattice misfits with Al, and it can be an effective nucleation core when it meets certain conditions. In this paper, the influencing factor of MgAl2O4 on heterogeneous nucleation and grain refinement in Al alloys was reviewed in terms of physical force, mass percent, particle size and distribution, heating temperature and duration, interface matching, lattice distortion, and chemical reactions at the liquid/solid interfaces. The existence of in situ MgAl2O4 was necessary for heterogeneous nucleation and grain refinement, and the content of MgAl2O4 was a crucial factor in grain refinement. Physical force highly enhanced heterogeneous nucleation and grain refinement through tuning of the wetting, size, and distribution of MgAl2O4 particles with little content. The heterogeneous nucleation of MgAl2O4 played a vital role in grain size reduction when the content was at a critical value. A single crystal of exogenous MgAl2O4 could also be a potent heterogeneous nucleation substrate for Al and Al–Mg alloys under a casting temperature or a high heating temperature with a short holding time for the small lattice misfits between nucleated-phase Al and the MgAl2O4 substrate, with limited lattice distortion.
1. Introduction
It is inevitable that oxidation occurs on the surface of Al or Al–Mg alloy melts, especially at high temperatures, due to the high affinity between oxygen and lively elements such as Mg and Al [1]. Oxide particles are generally considered to be responsible for the performance degradation of the casting; however, with preferential solidification performance, the oxides in the melt could possibly act as inoculants during the solidification process, which results in grain refinement under certain conditions [2]. An inoculation phenomenon is considered to occur when there is a decrease in the interfacial free energy between crystal nuclei and inoculants, which is believed to be the controlling factor in the inoculation process [3]. The “linear” disregistry and “planar” disregistry theories proposed by Turnbull–Vonnegut and Bramfitt can be combined to reach the minimum criterion for interfacial free energy, when crystal nuclei and inoculant lattices match each other [4,5]. The best match can be achieved under circumstances where low-index crystallographic planes and directions of crystal nuclei and inoculants are parallel and the lattice parameters in these planes are either similar or integral–multiple.
Because MgAl2O4 has a similar crystal structure to and nearly twice the multiple lattice parameters as aluminum, in addition to a natural formation tendency on the Al alloy surface [6], it is more likely to form low-energy interfaces between Al and MgAl2O4 in their cube-on-cube orientations [7]. MgAl2O4 is a potentially vital nucleation agent for Al alloys, and closer attention has been paid to endogenous (in situ) and exogenous MgAl2O4 oxides in terms of their nucleation and grain refinement effectiveness. Endogenous (in situ) oxides can be formed through in situ reactions through the addition of oxide particles or oxygen sources external to the melt, which are usually under some physical fields and mechanical forces during the solidification. For example, in situ MgAl2O4 particles can be formed through the addition of various oxides or acids, such as SiO2 [6], TiO2, and H3BO3 [7], upon the reduction of oxides and the consumption of Al and Mg in the matrix alloy. They can also occur through oxygen introduced by a ceramic tube into the Al–Mg melts above the liquid temperature. Unfortunately, endogenous MgAl2O4 oxides that naturally form in the Al–Mg alloys always adsorb onto the surface of the alloy melt in the form of liquid-like films or clusters consisting of numerous individual micron-sized particles, which make it difficult to initiate heterogeneous nucleation [1]. As a result, physical fields and mechanical forces (including mechanical stirring using impeller-intensive shearing in a special unit with a 500-rpm screw rotation speed) and ultrasonic cavitation have been introduced into the alloy melt in order to break films or clusters into fine pieces, which can improve the heterogeneous nucleation potency of MgAl2O4 [8,9]. Li et al. [10] investigated the heterogeneous nucleation effect of MgAl2O4 particles in Al–Mg alloys with different Mg contents through intensive melt-shearing treatment and provided MgAl2O4, which acted as a potent site for the nucleation of α-Al grains from their cube-on-cube orientation relationship (OR). Wang et al. [2] and Kim [11] studied the characterization of MgAl2O4 formed in Al–Mg alloys with mechanical stirring or different oxidation times at 750 °C and discussed the nucleation possibility of endogenous MgAl2O4 particles acting as a nucleated substrate in terms of their lattice mismatch. Cube-on-cube ORs, {111} <110>Al||{111} <110>MgAl2O4, and {010} <001>Al||{010} <001>MgAl2O4 were experimentally observed while under continuous stirring. The lattice misfits of the two ORs were both calculated to be ~0.19%, which proved the potent nucleation ability of MgAl2O4 for Al. Recently, ultrasonic treatment (UT) and ultrasonic cavitation were found to facilitate the deagglomeration and disintegration of MgAl2O4 clusters into fine particles and nanoparticles, providing bulk nucleation sites for Al in Al–Mg alloys. An in situ Al–MgAl2O4 master alloy was synthesized through the reaction of an oxide precursor or through H3BO3 acid addition assisted by ultrasonic treatment. The grain refinement effects of in situ MgAl2O4 particles on Al and Al–Mg alloys were researched by R.S. Harini et al. [12,13] and R. Raghu et al. [7]. It was found that Al and Al–Mg alloys benefited from a 7–8-fold and even up to an 11–12-fold reduction in grain size due to ultrasonic cavitation and acoustic streaming because they provided wetting and the uniform dispersion of MgAl2O4 particles for nucleation. R. Haghayeghi and M. Qian [14] observed (in situ) a near-atomic resolution nucleation process in a liquid Al–10Mg (wt %) alloy with in situ MgAl2O4 seeds dispersed into the melt through ultrasonic vibration as a nucleated agent from a superheated temperature to approximately the liquid temperature of the alloy. The nucleation process started from three ordered layers of Al atoms that formed and remelted alternately at a superheat of 73 °C to three similar and more stable ordered layers of Al atoms formed at an approximate liquid temperature of 607 °C, which entailed subsequent crystallization.
The cube-on-cube OR of {010} <001>Al||{010} <001>MgAl2O4 was also observed in the heterogeneous nucleation of pure Al on a complete or part-MgAl2O4 reaction layer with a different morphology and thickness formed at a different heating temperature between the Al and MgO single-crystal substrate [15,16]. Small nucleation undercooling, good cube-on-cube ORs, an estimated negative Gibbs free energy for the reaction, and a calculated low lattice misfit all indicated that the new MgAl2O4 reaction product acted as a new nucleated agent instead of the original MgO substrate.
The heterogeneous nucleation effect of exogenous MgAl2O4 oxides acting as direct nucleated substrates has been investigated at a high heating temperature in Al/MgAl2O4 systems by Zhang et al. [17]. It was noted that there was an Al2O3 dendritic reaction from the Al melt and MgAl2O4 substrate, and meanwhile, part of the MgAl2O4 substrate (which had a new crystal plane) was exposed to the Al melt. Differently from the above cube-on-cube ORs, a new OR between Al and freshly exposed MgAl2O4 substrate was observed ({111} <011>Al||{200} <013>MgAl2O4 with a large misfit of about 8.36%), as was a distorted layer that was about 1 nm thick that relieved the strain between the matching planes. Both the microreaction layer and the bulk nucleated substrate of MgAl2O4 were exogenous oxides that were retained outside of the Al melt during the nucleation process.
Though various industrial grain refiners that have been discovered have been successfully used to refine aluminum, including Al–Ti–B, Al–Ti–C master alloys, and even some novel refiners with significant grain refinement effects, the release of fluoride and chloride gases and the formation of slag for the preparation of master alloys have serious adverse effects on the environment. Therefore, research to find a suitable nucleated agent and grain refiner for Al and Al–Mg alloys is still necessary [18]. Exploration of the use of in situ or exogenous MgAl2O4 particles as heterogeneous nucleating sites for Al and Al–Mg alloys is a broad task, and it has attracted more interest since MgAl2O4 particles themselves are commercially viable and environmentally friendly. The present study explores and summarizes the influencing factors of MgAl2O4 in heterogeneous nucleation and grain refinement on Al alloy melts.
2. Interactions between Melt and MgAl2O4 Particles
2.1. In Situ MgAl2O4 Particles
The similar crystal structure between Al and MgAl2O4 provides an opportunity to form a low-energy interface between them and any of their orientations. Meanwhile, MgAl2O4 displays nice wettability with Al alloys, and there are no chemical reactions between Al and MgAl2O4 at low temperatures. All of these characteristics probably make MgAl2O4 particles act as potential heterogeneous nucleation sites and further enhance the grain refinement of alloys. MgAl2O4 particles can be synthesized in situ in Al–Mg melts through the addition of oxides or other oxygen sources, such as SiO2, TiO2, B2O3, and H3BO3 [7,19,20]. Negative Gibbs free energy in the reactions between oxides and Al–Mg melts at processing temperatures of 650–900 °C suggests that the formation of an MgAl2O4 phase is thermodynamically stable. However, it is difficult to obtain a complete reaction of parent oxides and to disperse the in situ MgAl2O4 particles into the alloy melt, thus leading to the poor nucleation ability of MgAl2O4. In order to resolve this question, physical fields such as mechanical stirring, ultrasonic treatment, and intensive melt shearing have been introduced, which has resulted in in situ MgAl2O4 forming with, on average, small particle sizes and a diffuse distribution in the melt.
Using ultrasonic treatment, one reaction resulted in the massive growth of MgAl2O4 particles from an Al–Mg melt, and the oxides could be attributed to the constant removal of MgAl2O4 particles on the oxides’ surface and to the pushing of MgAl2O4 particles into the melt, thus exposing fresh oxide surfaces and allowing for the advancement of the bulk oxide reaction [13]. Ultrasonic treatment is used as an effective physical tool to enhance the heterogeneous nucleation of an Al–Mg melt from three fields. Firstly, ultrasonic treatment introduces ultrasonic cavitation, producing intense local hotspots of temperature (5000 °C), high pressure (100 MPa), and microjets (100 m/s) [21]. A high local temperature and pressure assist with the reaction of Al and Mg atoms on the surfaces of oxides, leading to the in situ formation of MgAl2O4 crystals. Secondly, microjets aid in the fragmentation of oxides as well as in the removal of MgAl2O4 crystals, exposing fresh oxide surfaces for further reactions. Lastly, acoustic streaming and ultrasonic treatment aid in the dispersion of small MgAl2O4 crystals, which are bonded by a van der Waals force. These in situ MgAl2O4 crystals grow with low index faces, such as {220}, {311}, and {400}, and have low interfacial energy with Al [12,13].
The experimental parameters, including the melting and solidification methods, the alloy compositions and melt treatments, the compositions of the Al–MgAl2O4 master, the addition contents and modes of the master, and the ultrasonic treatment processes, can affect the size of the microstructural components. Therefore, studies with similar experimental methods and parameters were selected to assess the grain refinement effects of MgAl2O4 on Al alloys. The refinement degrees of the average alloy grain sizes in References [7,12,13,18] (with different contents of MgAl2O4 and different ultrasonic treatment (UT) processes) are summarized in Table 1.

Table 1.
The refinement degree of alloy grain sizes with different contents of MgAl2O4 and different ultrasonic treatment (UT) processes.
In the table, it can be seen that a significant grain size reduction was observed in pure Al and Al–Mg alloys with in situ MgAl2O4 and ultrasonic treatment, while few grain refinements (a reduction of 2–3-fold) were obtained with just in situ MgAl2O4 and hardly any grain refinements were obtained (a reduction of ~1.1-fold) with just ultrasonic treatment. This implies that the combination of in situ MgAl2O4 and ultrasonic treatment contributes to a significant grain size reduction in alloys. The presence of MgAl2O4 particles acting as nucleated sites is critical, and ultrasonic treatment results in the in-situ-formed MgAl2O4 being nanoscale-sized, with a uniform dispersion and a 2–4-fold increased number density when compared to previous formulations. The mean grain size of MgAl2O4 was almost equivalent with different UT times and temperatures. It is worth noting that the grain refinement effects with the above melting and solidification methods, UT temperatures and times, and mean grain sizes of MgAl2O4 in the different experiments were similar except for the larger grain refinement effect obtained with a short UT time (30 s) with pure Al compared to more UT time (5 min) with the Al–Mg alloy. This suggests that UT time and temperature do not play decisive roles in grain refinement. The same refinement degree for average alloy grain sizes of the Al–4Mg alloy with different mass percents of MgAl2O4 (0.58 wt % and 3 wt %) was achieved due to the different lengths of the samples (Φ 20 × 80 mm and Φ 20 × 120 mm ) in the experiment. Therefore, the effect of the mass percent of MgAl2O4 on grain refinement was then mainly studied and discussed in terms of another physical force, intensive melt shearing.
Intensive melt shearing is another approach used in grain refinement treatments of Al and Al–Mg alloys. When given enough oxidation time, porous MgO initially forms on the surface of the Al–4Mg alloy, and MgAl2O4 particles later form, covered with a thin layer composed of Al2O3 from the reaction of liquid aluminum and oxygen, which is introduced from the air through the porous MgO. Therefore, it seems that MgAl2O4 generated naturally during oxidation has difficulty serving as a direct substrate for the nucleation of Al due to the separation of Al2O3 [11]. Due to the similar crystal structure of Al and MgAl2O4 and due to the MgAl2O4 solid phase forming in the melt prior to the solidification of Al, it has been proven that intensive melt shearing breaks up the MgAl2O4 oxide films and disperses the potent oxide particles, which leads to potent heterogeneous nucleation and a grain refinement effect in Al–Mg alloys. Detailed research has been carried out on the effect of the Mg content and intensive melt shearing on grain refinement in Al–Mg alloys [10]. Al–Mg alloys were prepared in an electric resistance furnace using commercial purity Al and Mg. After Mg was dissolved under the protection of Ar gas, the melt was held at a constant temperature of 700 °C for 4 h to assist in the natural reaction of MgAl2O4, with an average grain size of hundreds of nanoscales. The sheared samples were prepared through sheared melting for 60 s at 700 °C and then poured into a copper mold at a consistent cooling rate of 3.5 K s−1 in the central region. The dimensions of the mold were about 25 mm in diameter at the bottom, 60 mm in diameter at the top, and 65 mm in length. The nonsheared samples were treated in the same way without the melting and shearing. Significant grain refinement was achieved with intensive melt shearing or by increasing the content of Mg when it was less than 1 wt %. When comparing the grain sizes, there was a critical Mg content observed, around 2 wt %, regardless of whether the Al–Mg alloys sheared or not, as they were nearly equivalent and almost constant. A similar result was observed in the Al–5Mg alloy with the addition of Ti. Intensive melt shearing introduced further grain refinement when the content of Ti was less than 0.05 wt %, while the grain sizes of the nonsheared and sheared Al–5Mg alloys were constant with more than a critical content of 0.05 wt %. The effect of the mass percent of MgAl2O4 or Mg with UT or an intensive melt shearing process on grain refinement is comprehensively considered and illustrated in Figure 1 with data from References [7,10,12,13,18].
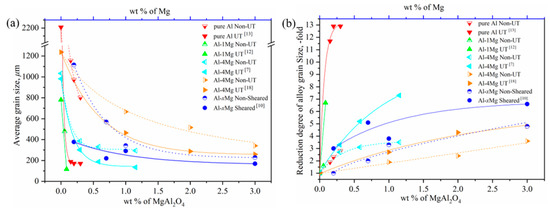
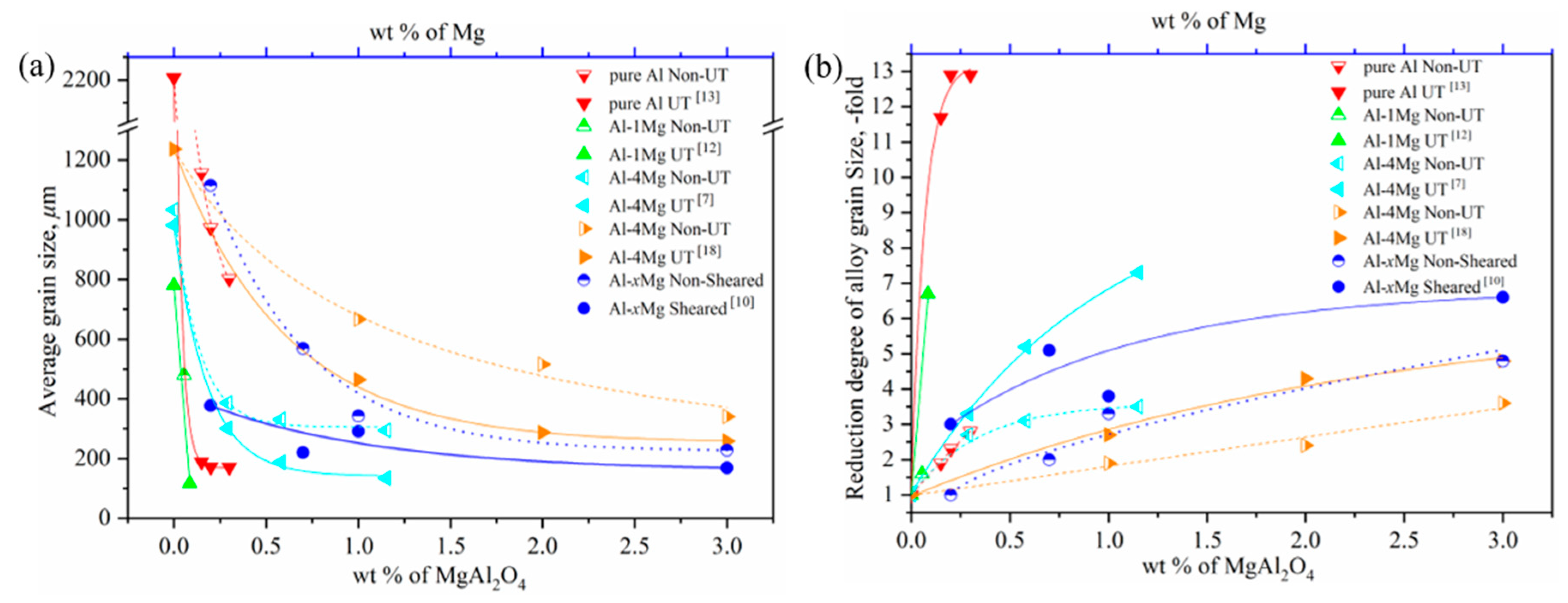
Figure 1.
(a) The average grain size with respect to the mass percent of MgAl2O4 or Mg with UT or an intensive melt shearing process; (b) the reduction degree of the grain size relative to the mass percent of MgAl2O4 or Mg with UT or an intensive melt shearing process, with data from References [7,10,12,13,18].
It is interesting to note that in Figure 1a, the average grain sizes of the pure Al and Al–Mg alloys obviously decrease with an increase in the content of MgAl2O4 or Mg, which is in the low range of 0 to 1 wt %. At the same time, UT and intensive melt shearing further highly strengthen the grain size reduction in the low content range of MgAl2O4 or Mg, which suggests that physical force is an effective method in breaking up the MgAl2O4 film into nanoparticles, dispersing MgAl2O4 particles into melts, and then enhancing the heterogeneous nucleation effect of MgAl2O4 particles. However, with a continuing increase in the content of MgAl2O4 or Mg, the average grain size decreases slowly and has a gradual leveling tendency: meanwhile, the effect of the size reduction is small under physical force when the content of MgAl2O4 or Mg is more than the critical value of around 2 wt %. In order to understand the respective contributions of endogenous MgAl2O4 particles and the physical force of UT or shearing, the reduction degree of grain size with respect to the mass percent of MgAl2O4 or Mg with UT or a shearing process was converted into Figure 1b from Figure 1a. It can be seen that the contribution of endogenous MgAl2O4 to grain size reduction is 2–3-fold, while that of physical force is about 5–8 and up to 11–12-fold when the content of MgAl2O4 or Mg is in the low range, less than 1 wt %. The contribution of physical force to grain size reduction becomes stable after reaching the critical content of MgAl2O4 or Mg.
Combining the above experimental results and analysis, it is clear that physical force plays a more important role when there is an assured existence of endogenous MgAl2O4 in a low content range. This implies that physical force enhances the heterogeneous nucleation and grain refinement of Al by tuning the wetting and distribution of MgAl2O4 particles. In addition, and more importantly, it is clear that the MgAl2O4 content is a critical factor in the grain refinement of Al and Al–Mg alloys, since similar grain sizes are obtained with or without physical force when the content of MgAl2O4 or Mg exceeds 2 wt %. This also proves that the endogenous MgAl2O4 phase is a potent heterogeneous core for the nucleation of Al and Al–Mg alloys and plays a vital role in grain size reduction under the following conditions: a uniform distribution, hundreds of nanoscale-sized to several microscale-sized particles, and a mass percent of about 2 wt % (whether there is physical force or not).
2.2. Exogenous MgAl2O4
Both MgO and MgAl2O4 are common oxides formed during the preparation and remelting processes of Al–Mg alloys and are regarded as being effective heterogeneous nucleating agents for Al-based alloys due to their similar lattice structures and small lattice misfits. However, some researchers have reported that liquid Al reacts with MgO substrates in various exposed crystal planes over a wide temperature span [16,17,22,23]. In these research results, Sun [16] found MgAl2O4 is a final product at a normal casting temperature between 700 °C and 800 °C with a holding time of 3 min. MgAl2O4 products are straight, and distinct layers or small islands with thicknesses of 10–40 nm form between Al and MgO. This can be referred to as exogenous MgAl2O4 in this case due to the reaction product MgAl2O4 always being retained outside of the Al melt during the nucleation process. The cube-on-cube ORs between Al, MgAl2O4, and MgO have also been confirmed by Sun, such as {200} <001>Al||{200} <001>MgAl2O4||{200} <001>MgO, {220} <001>Al||{220} <001>MgAl2O4||{220} <001>MgO, and {111} <110>Al||{111} <110> MgAl2O4||{111} <110>MgO. Both the cube-on-cube ORs and small nucleated undercooling (3–8 °C) suggest that MgAl2O4 is a perfect catalyzer for the nucleation of liquid Al.
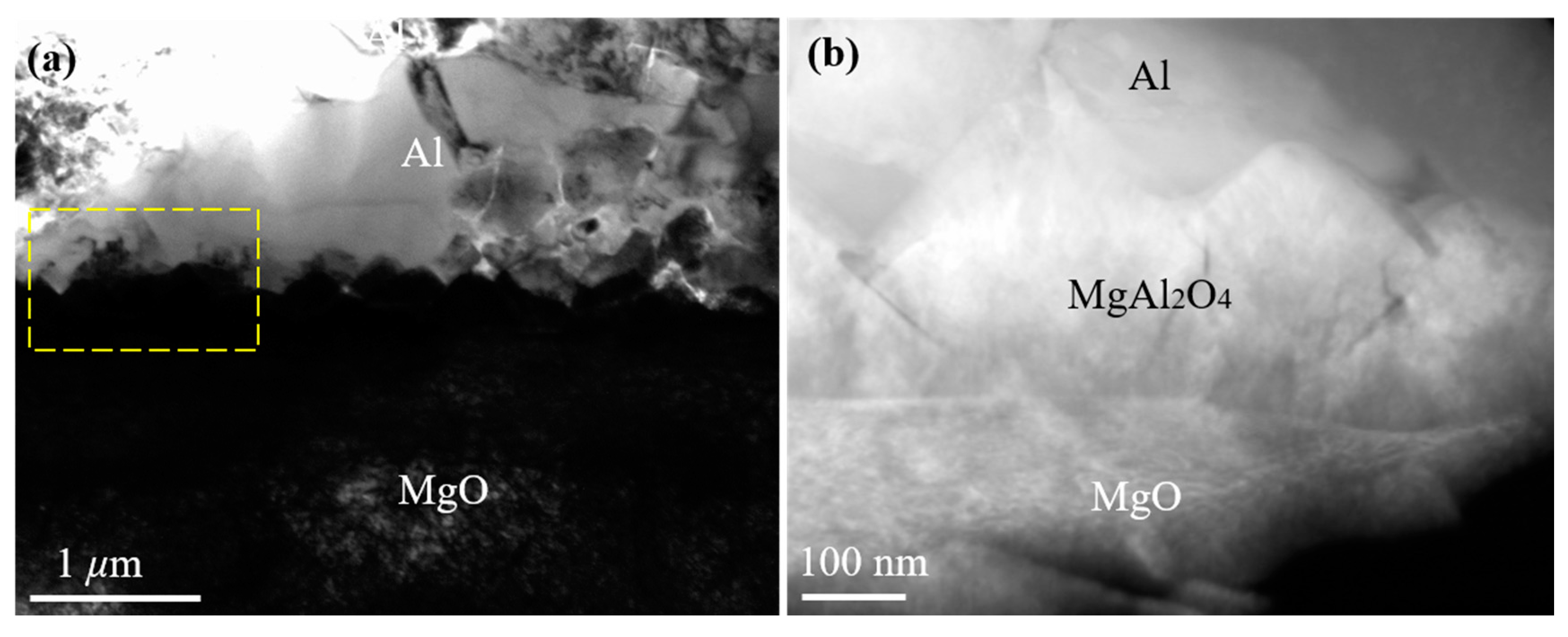
J. Morgile et al. [22,23] have clarified that MgAl2O4 is an intermediate product and Al2O3 is a final product of the reaction at a high temperature between the Al melt and MgO substrate. Similarly to Morgile’s results, the reaction product MgAl2O4 (with a thickness between 100 and 300 nm) was also seen at the Al/MgO interface in our research. High-purity Al (>99.999%) was melted at 1027 °C with a holding time of 5–10 s and then cooled on the selected terminated planes of the MgO substrate from 1027 °C, with a cooling rate of 20 K/s in a high-vacuum chamber. The interface between MgAl2O4 and MgO was approximately straight, while the interface between MgAl2O4 and Al was a zigzag, as seen in Figure 2. To further confirm the morphology of MgAl2O4, a high-angle annular dark-field (HAADF) Z-contrast image of the Al/MgO interface was obtained (Figure 2b, corresponding to the frame of Figure 2a). Because the image contrast is proportional to the atomic mass, the contrast of the Al area is bright, while that of the MgO area is dark. The contrast of MgAl2O4 is distinct from Al and MgO, with a straight interface with MgO and a zigzag interface with Al.
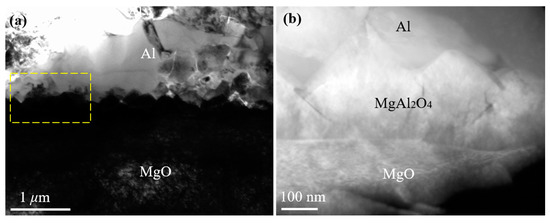
Figure 2.
(a) A typical cross-sectional transmission electron microscope (TEM) image of the Al/ {001} MgO interface. (b) A high-angle annular dark-field (HAADF) Z-contrast image of the Al/MgO interface, which corresponds to the frame of (a).
The morphology and thickness of MgAl2O4 at the Al/MgO interface were different from the straight and distinct layer or small islands of MgAl2O4 formed at a normal casting temperature (between 700 and 800 °C). This suggests that the different reactions of Al and MgO occur at different heating temperatures, leading to a different morphology and thickness of the MgAl2O4 product. It can be concluded that the exogenous MgAl2O4 layer formed at the interface of pure Al and MgO can act as a new heterogeneous nucleation substrate for Al when the heating temperature is at a normal casting temperature or at a higher temperature with a holding time of a few seconds.
The heterogeneous nucleation effect of exogenous MgAl2O4 oxides acting as direct nucleated substrates was investigated at a high heating temperature by Zhang et al. [17] in an Al/MgAl2O4 system at 1027 °C with a holding time of 30 s. An Al2O3 dendritic reaction from the Al melt and MgAl2O4 substrate was noted, and meanwhile, part of the MgAl2O4 substrate (with a new crystal plane) was exposed to the Al melt. As a result, differently from the above three cube-on-cube ORs, the OR between the Al and freshly exposed MgAl2O4 substrate was {111} <011>Al||{200} <013>MgAl2O4 with a large misfit of about 8.36% and a distorted layer about 1 nm thick, which relieved the strain between the matching planes. This indicates that MgAl2O4 substrates easily form alumina and are not potent nucleation substrates for Al alloys at a high heating temperature and long holding time.
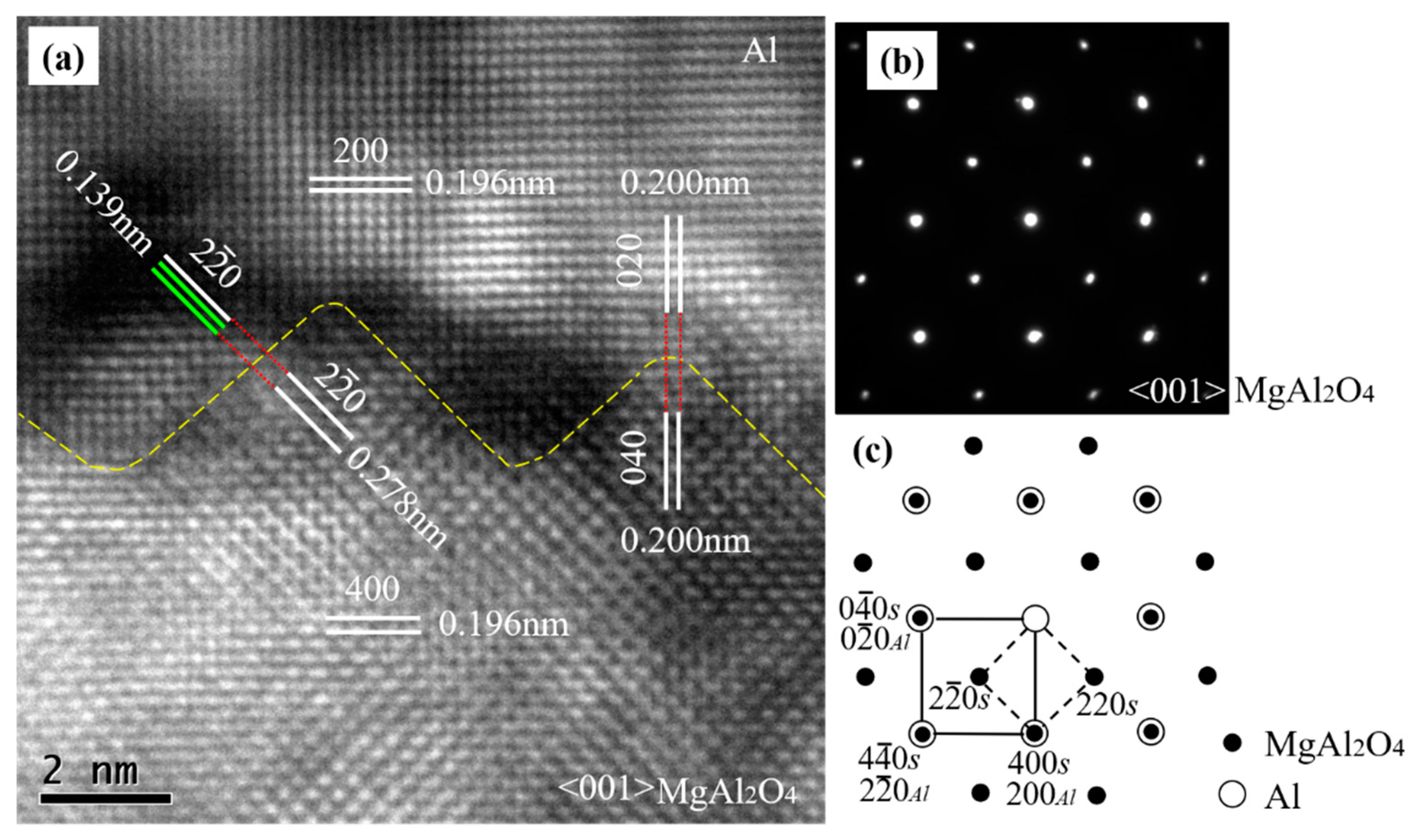
To understand the direct effect of the exogenous MgAl2O4 substrate on the heterogeneous nucleation of Al at 1027 °C with a short holding time of 3–5 s, high-resolution transmission electron microscopy (TEM) was carried out at the Al/MgAl2O4 nucleation interface in the <001> MgAl2O4-zone direction. Figure 3b is a selected area electron diffraction (SAED) pattern taken from both MgAl2O4 and the adjacent Al matrix along their <001> zone axes across the MgAl2O4/Al interface in Figure 3a. The SAED pattern on the MgAl2O4/Al interface shows overlapped spots. Through an analysis of the SAED pattern, we found two sets of diffraction patterns. One set was a face-centered cubic (FCC) structure with a d-spacing of 0.196 nm and 0.278 nm, which corresponded to {400} and {20} planes of MgAl2O4 (as indexed with small solid circles in Figure 3c). The other set was also an FCC structure, with d-spacing of about 0.196 nm and 0.139 nm, which corresponded to {200} and {20} planes of Al (as indexed with large open circles). Figure 3c gives a schematic indexing of the SAED pattern, indicating that the same crystal planes and the same crystal directions were parallel to each other in the MgAl2O4 and Al crystals. From the evidence of the SAED, it is clear that there was a cube-on-cube OR between the MgAl2O4 and Al matrices, which was {200} <001>Al||{400} <001>MgAl2O4.
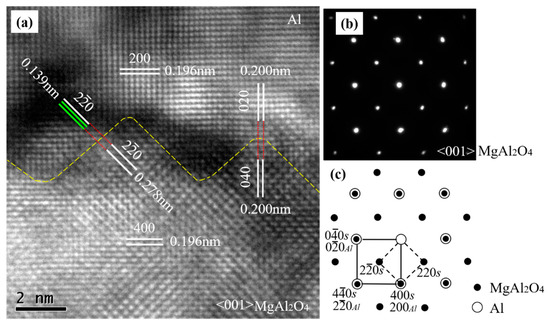
Figure 3.
(a) High-resolution TEM image of Al/MgAl2O4 taken in the <001> MgAl2O4-zone direction; (b) selected area electron diffraction (SAED) pattern taken from both the MgAl2O4 (spinel, S) particle and the adjacent Al; and (c) the schematic of the pattern indexed along the <001> axis for both the MgAl2O4 and Al crystals, showing the cube-on-cube crystallographic orientation relationship (OR) between the two phases.
It is worth noting that both MgAl2O4 and Al had an FCC crystal structure and that the lattice parameter for MgAl2O4 was 0.80831 nm, about double that of Al (0.40494 nm) [2]. The theoretical crystal plane spacings of {400} MgAl2O4 and {200} Al were 0.2021 nm and 0.2025 nm, respectively. Theoretically, the lattice misfits for the parallel crystal planes between Al and MgAl2O4 in Figure 3a were small, and the calculation results can be seen in Table 2.

Table 2.
The theoretical lattice misfits (f) for the parallel crystal planes between Al and MgAl2O4 in Figure 3a.
The calculated lattice misfits of the different parallel planes between Al and MgAl2O4 were near those (0.09%) of the Al and Al3Ti monolayer between the Al and TiB2 substrate [24], suggesting that MgAl2O4 acts as a potent heterogeneous substrate that can be considered for actual industrial applications. Actually, well-defined atomic rows and lattice planes can be identified in Figure 3a. As can be seen in Figure 3, the {200} Al plane was parallel to the {400} MgAl2O4 plane, and the plane spacing of {200} Al was the same as that of {400} MgAl2O4. Meanwhile, {020} Al was parallel to {040} MgAl2O4, and their d-spacings were also equal to each other. The {20} Al was parallel to the {20} MgAl2O4, while the d-spacing (0.278 nm) of the {20} MgAl2O4 was double that of (0.139 nm) {20} Al. The parallel crystal planes, the crystal directions, and the same or integral multiple-crystal-plane spacing indicated that the cube-on-cube OR {200} <001>Al||{400} <001>MgAl2O4 was the expected value.
According to theoretical lattice misfit calculations, there should be small lattice misfits in Al/MgAl2O4 along three sets of parallel crystal planes. However, the crystal plane spacings between the three sets of parallel crystal planes were the same or double. This means that there was lattice distortion at the interface, which was consistent with our previous study, where the nucleated-phase Al fit the substrate with limited lattice distortion within a small lattice misfit (f < 3.1%) [25]. These studies prove that both in situ MgAl2O4 (using physical force) and endogenous MgAl2O4 (controlling for the heating temperature) are possibly potent heterogeneous nucleation substrates in the heterogeneous nucleation of Al alloys.
3. Conclusions
Both in situ MgAl2O4 (using a physical tool in the melt) and the exogenous MgAl2O4 crystal (controlling for the heating temperature and holding time outside of the melt) are possible candidates for use as potent heterogeneous nucleation substrates for Al alloys because of their similar crystal structures and small lattice misfits.
- The existence of in situ MgAl2O4 means a potent heterogeneous core, and it is the premise for heterogeneous nucleation and grain refinement in Al and Al–Mg alloys. Physical force highly enhances heterogeneous nucleation and grain refinement through tuning of the wetting, size, and distribution of MgAl2O4 particles. The content of MgAl2O4 is a crucial factor in grain refinement. The heterogeneous nucleation of MgAl2O4 plays a vital role in grain size reduction when the content of MgAl2O4 arrives at a critical value. The optimal addition of in situ MgAl2O4 has the following conditions: a uniform distribution, hundreds of nanoscale-sized to several microscale-sized particles, and a mass percent of about 2 wt %.
- MgAl2O4 reactions (from Al and MgO substrates) are retained outside the Al melt during the nucleation process and can act as potent nucleation substrates for Al alloys. Different heating temperatures control the extent of the reaction of the Al and MgO and lead to different morphologies and thicknesses of the MgAl2O4 product.
- The exogenous MgAl2O4 single crystal is also a potent heterogeneous nucleation substrate for Al and Al–Mg alloys under a casting temperature or a high heating temperature with a short holding time. The cube-on-cube OR of {200} <001>Al||{400} <001>MgAl2O4and the same or integral multiple-crystal-plane spacing indicate that nucleated-phase Al fits the substrate with limited lattice distortion for small lattice misfits between Al and MgAl2O4.
Author Contributions
Investigation, M.Y.; writing—original draft preparation, L.Y.; writing—review and editing, L.W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province in China, grant number BK20181047; the Natural Science General Program of Jiangsu Higher Education Institution in China, grant number 18KJB430012; and the National Natural Science Foundation of China, grant number 51601078.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Wang, Y.; Li, H.T.; Fan, Z. Oxidation of Aluminium Alloy Melts and Inoculation by Oxide Particles. Trans. Indian Inst. Met. 2012, 65, 653–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, H.T.; Fan, Z.; Scamans, G. Characterisation of Oxide Films in Al–Mg Alloy Melts. Mater. Sci. Forum 2013, 765, 220–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, V.Y.; Novikov, V.Y. Heterogeneous nucleation in crystallization: Impact of impurities and local melt inhomogeneity. Mater. Lett. 2018, 229, 164–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turnbull, D.; Vonnegut, B. Nucleation catalysis. Ind. Eng. Chem. 1952, 44, 1292–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bramfitt, B.L. The effect of carbide and nitride additions on the heterogeneous nucleation behavior of liquid iron. Metall. Trans. 1970, 1, 1987–1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sreekumar, V.M.; Babu, N.H.; Eskin, D.G.; Fan, Z. Structure-property analysis of in-situ Al–MgAl2O4 metal matrix composites synthesized using ultrasonic cavitation. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2015, 628, 30–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghu, R.; Nampoothiri, J.; Kumar, T.S. In-situ generation of MgAl2O4 particles in Al–Mg alloy using H3BO3 addition for grain refinement under ultrasonic treatment. Measurement 2018, 129, 389–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, T.; Zhou, Y.J. Effects of Ultrasonic Introduced by L-Shaped Ceramic Sonotrodes on Microstructure and Macro-Segregation of 15t AA2219 Aluminum Alloy Ingot. Materials 2019, 12, 3162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pericleous, K.; Bojarevics, V.; Djambazov, G.; Dybalska, A.; Griffiths, W.D.; Tonry, C. Contactless Ultrasonic Cavitation in Alloy Melts. Materials 2019, 12, 3610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.T.; Wang, Y.; Fan, Z. Mechanisms of enhanced heterogeneous nucleation during solidification in binary Al–Mg alloys. Acta Mater. 2012, 60, 1528–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.H. Formation of endogenous MgO and MgAl2O4 particles and their possibility of acting as substrate for heterogeneous nucleation of aluminum grains. Surf. Interface Anal. 2015, 47, 429–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harini, R.S.; Nampoothiri, J.; Nagasivamuni, B.; Raj, B.; Ravi, K.R. Ultrasonic assisted grain refinement of Al–Mg alloy using in-situ MgAl2O4 particles. Mater. Lett. 2015, 145, 328–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harini, R.S.; Raj, B.; Ravi, K.R. Synthesis of Al- MgAl2O4 Master Alloy and its Grain Refinement Studies in Pure Aluminium. Trans. Indian Inst. Met. 2015, 68, 1059–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haghayeghi, R.; Qian, M. Initial crystallisation or nucleation in a liquid aluminium alloy containing spinel seeds. Mater. Lett. 2017, 196, 358–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Xia, M.; Babu, N.H.; Li, J.G. Formation of MgAl2O4 at Al/MgO interface. Mater. Trans. 2015, 56, 277–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Wang, D.; Zhang, Y.; Sheng, C.; Dargusch, M.; Wang, G.; John, D.S.; Zhai, Q. Heterogeneous nucleation of pure Al on MgO single crystal substrate accompanied by a MgAl2O4 buffer layer. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 753, 543–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Wang, L.; Xia, M.; Babu, N.H.; Li, J.G. Misfit paradox on nucleation potency of MgO and MgAl2O4 for Al. Mater. Charact. 2016, 119, 92–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghu, R.; Nampoothiri, J.; Kumar, T.S.; Subramanian, R. Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Al/ MgAl2O4 In Situ Composites Synthesized by Ultrasonic Cavitation. Trans. Indian Inst. Met. 2019, 72, 1013–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horvitz, D.; Gotman, I.; Gutmanas, E.Y.; Claussen, N. In Situ Processing of Dense Al2O3-Ti Aluminide Interpenetrating Phase Composites. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2002, 22, 947–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Zhao, N.; Liu, E.; Shi, C.; Du, X.; Wang, J. Fabrication of aluminum matrix composites with enhanced mechanical properties reinforced by in situ generated MgAl2O4 whiskers. Compos. Part A 2012, 43, 631–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suslick, K.S.; Price, G.J. Applications of ultrasound to materials chemistry. Annu. Rev. Mater. Sci. 1999, 29, 295–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak, R.; Sobczak, N.; Sienicki, E.; Morgiel, J. Structural characterization of reaction product region in Al/MgO and Al/MgAl2O4 systems. Solid State Phenom. 2011, 172–174, 1273–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgiel, J.; Sobczak, N.; Pomorska, M.; Nowak, R. First stage of reaction of molten Al with MgO substrate. Mater. Charact. 2015, 103, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Qin, T.; Zhou, X.R.; Thompson, G.E.; Pennycook, T.; Hashimoto, T. Grain refining mechanism in the Al/Al-Ti-B system. Acta Mater. 2015, 84, 292–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Yang, L.; Zhang, D.; Xia, M.; Wang, Y.; Li, J.G. The Role of Lattice Misfit on heterogeneous nucleation of pure aluminum. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2016, 47, 5012–5022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).