Microstructure Evolution and Mechanical Properties of PM-Ti43Al9V0.3Y Alloy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Procedures
2.1. Fabrication of Powder
2.2. Hot Isostatic Pressing
2.3. Microstructural Characterizations
2.4. Mechanical Property Tests
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterizations of Powder
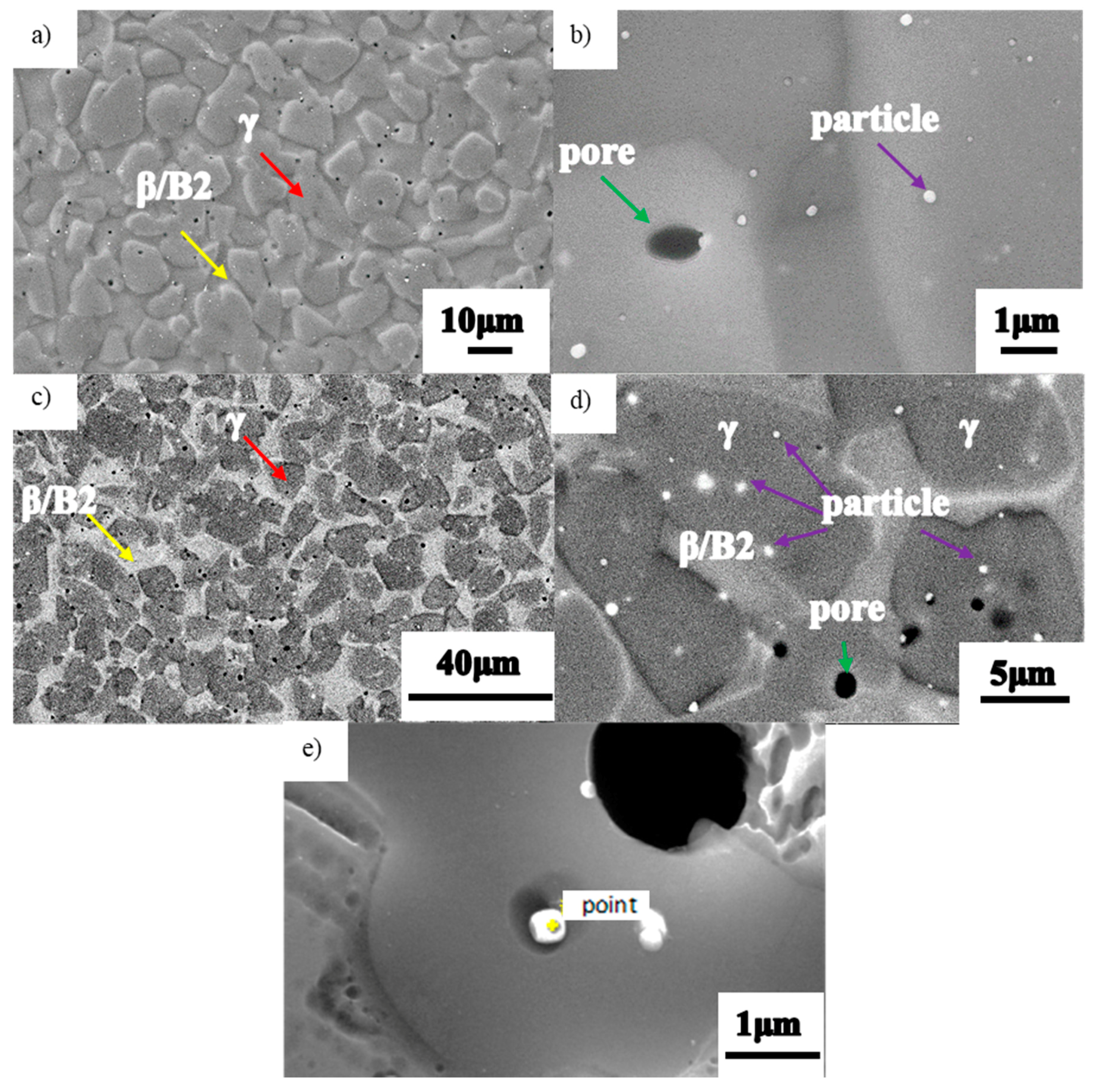
3.2. As-HIPed Microstructures
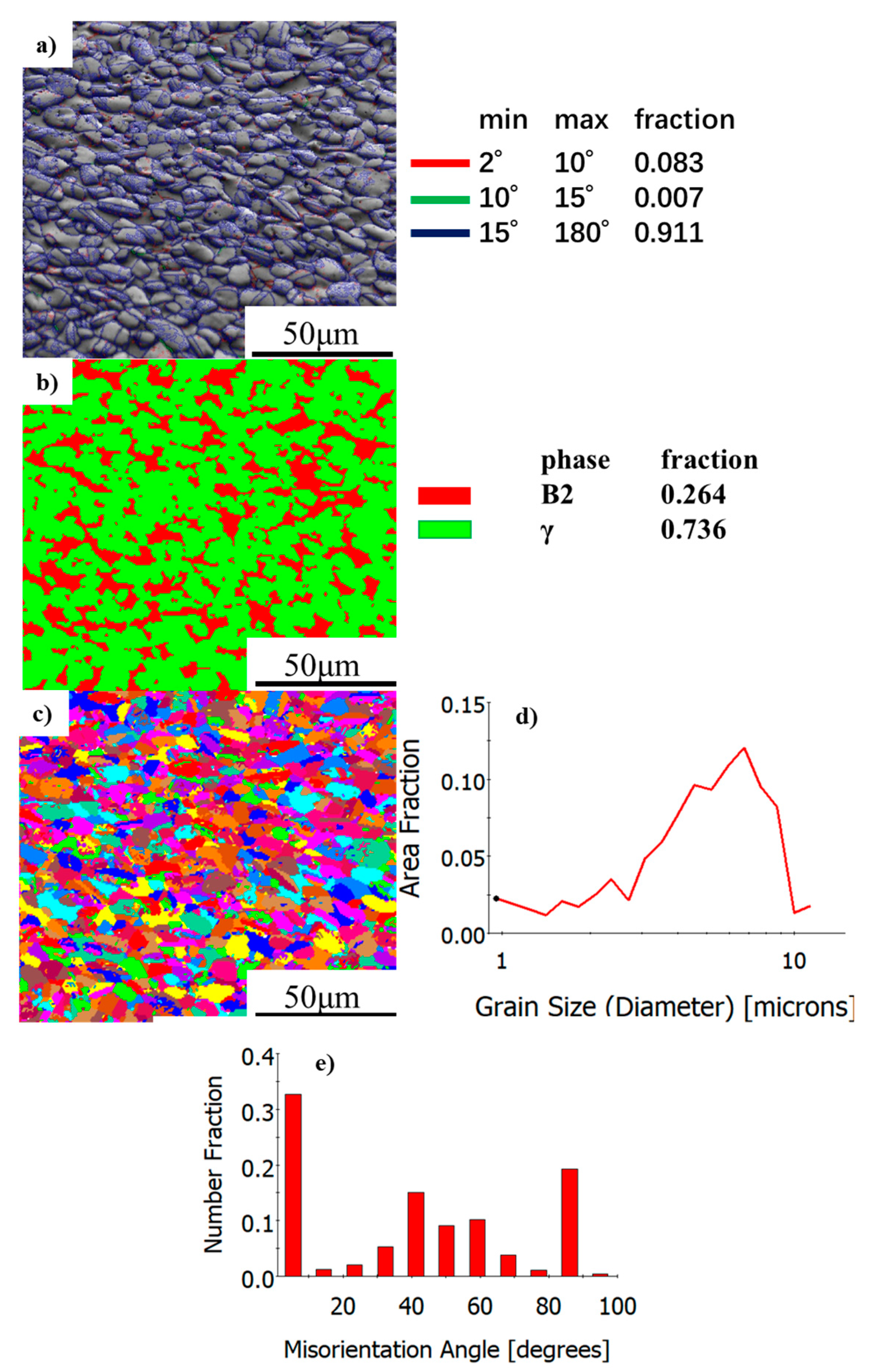
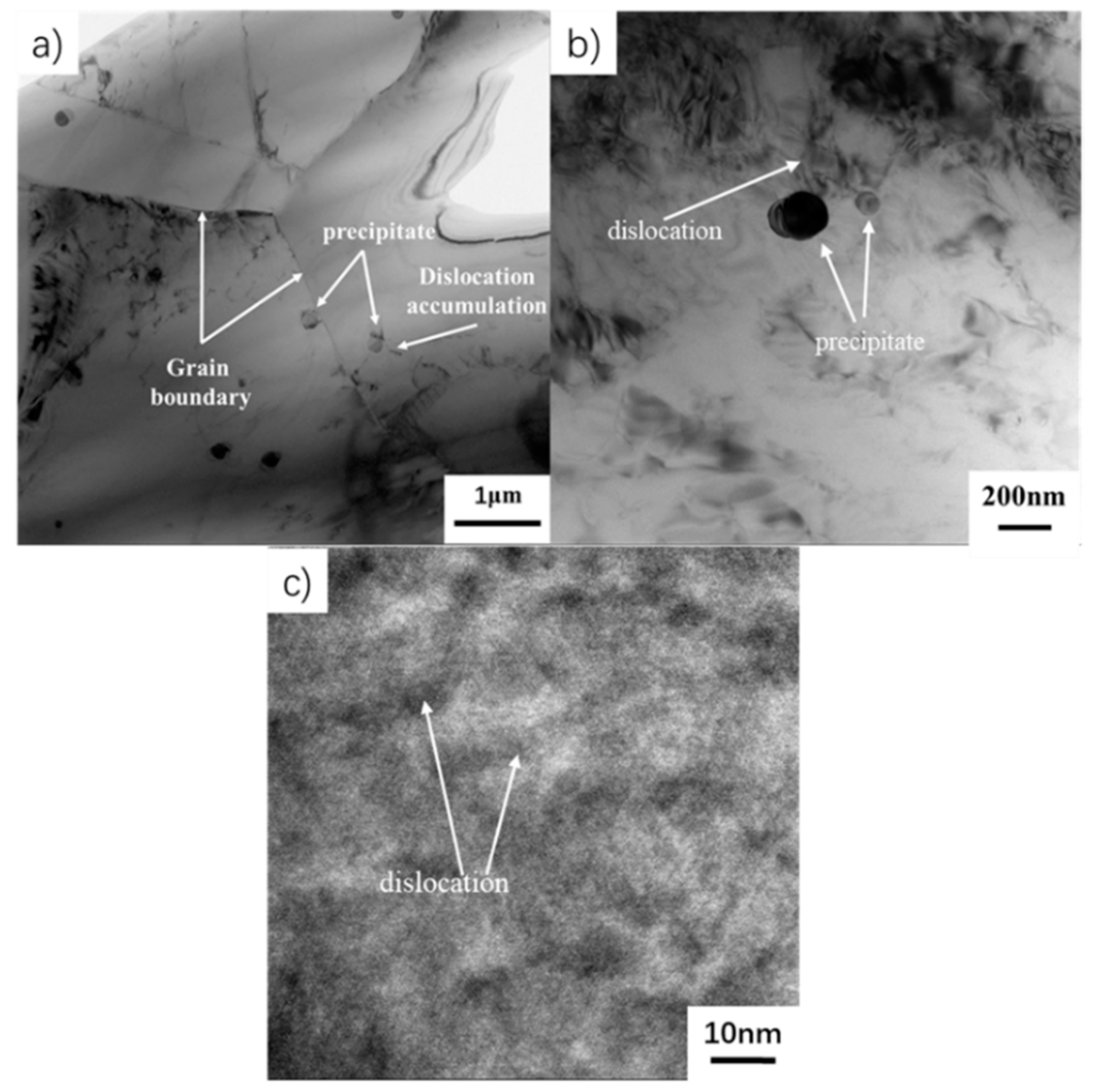
3.3. EBSD Investigation
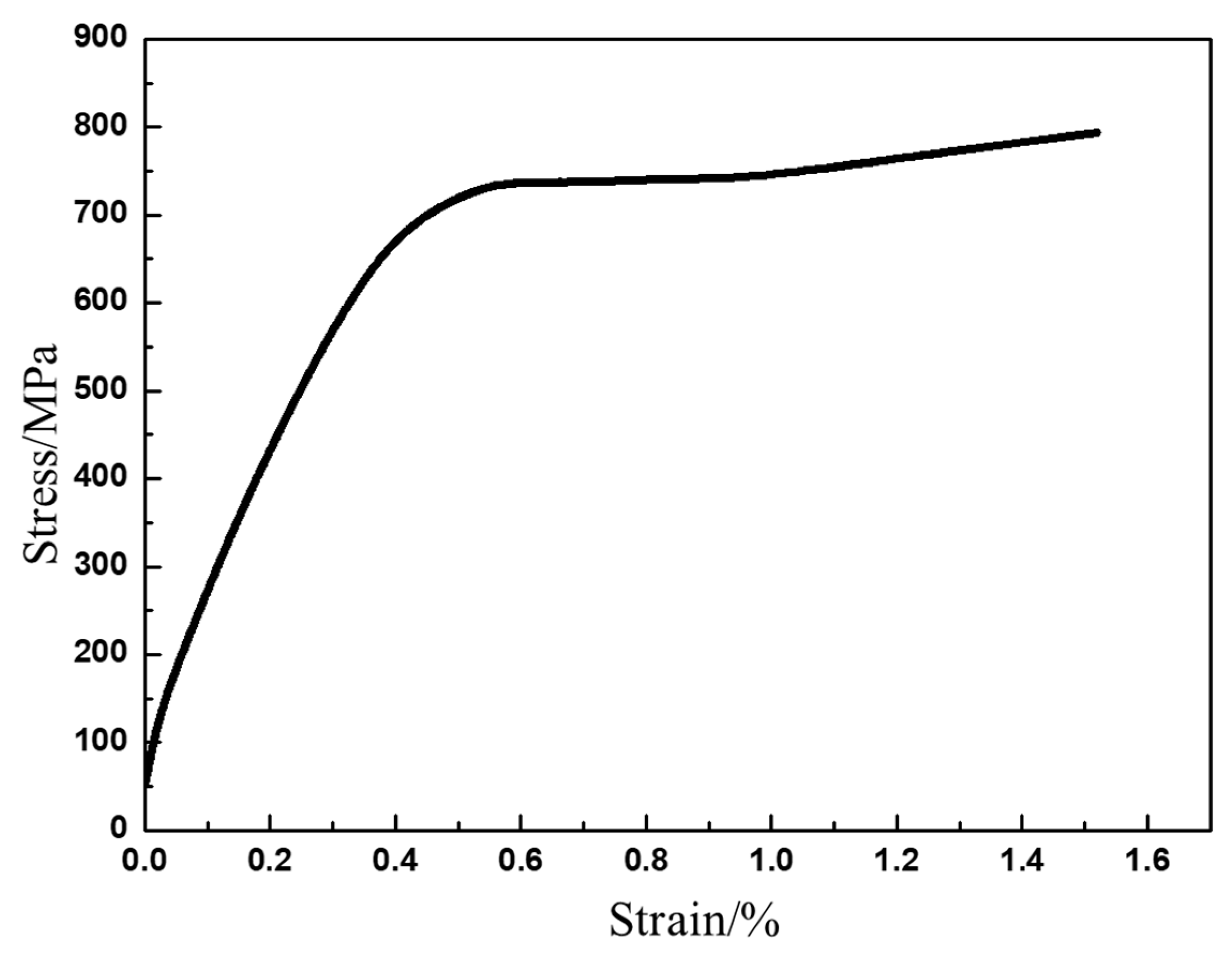
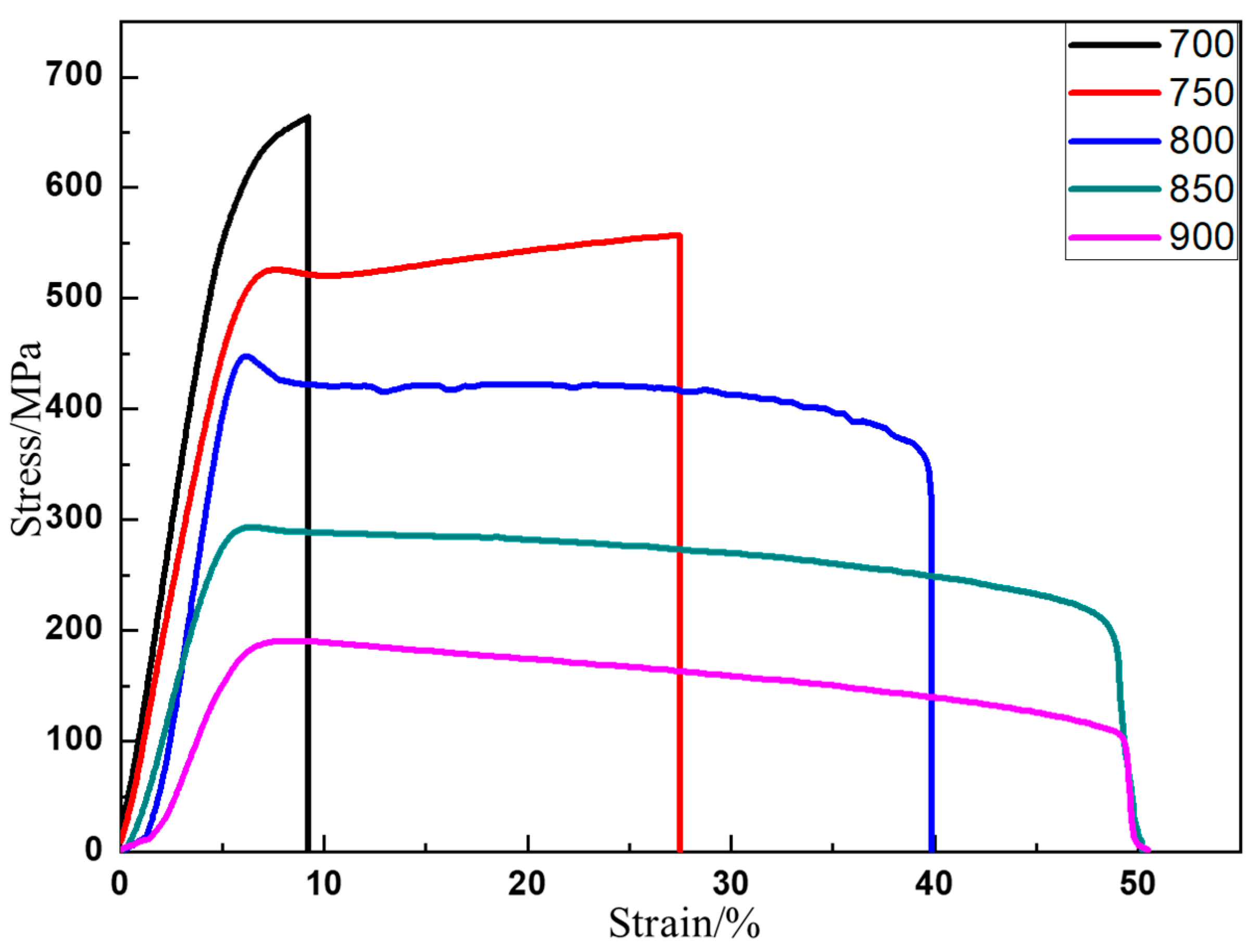
3.4. Mechanical Behaviors
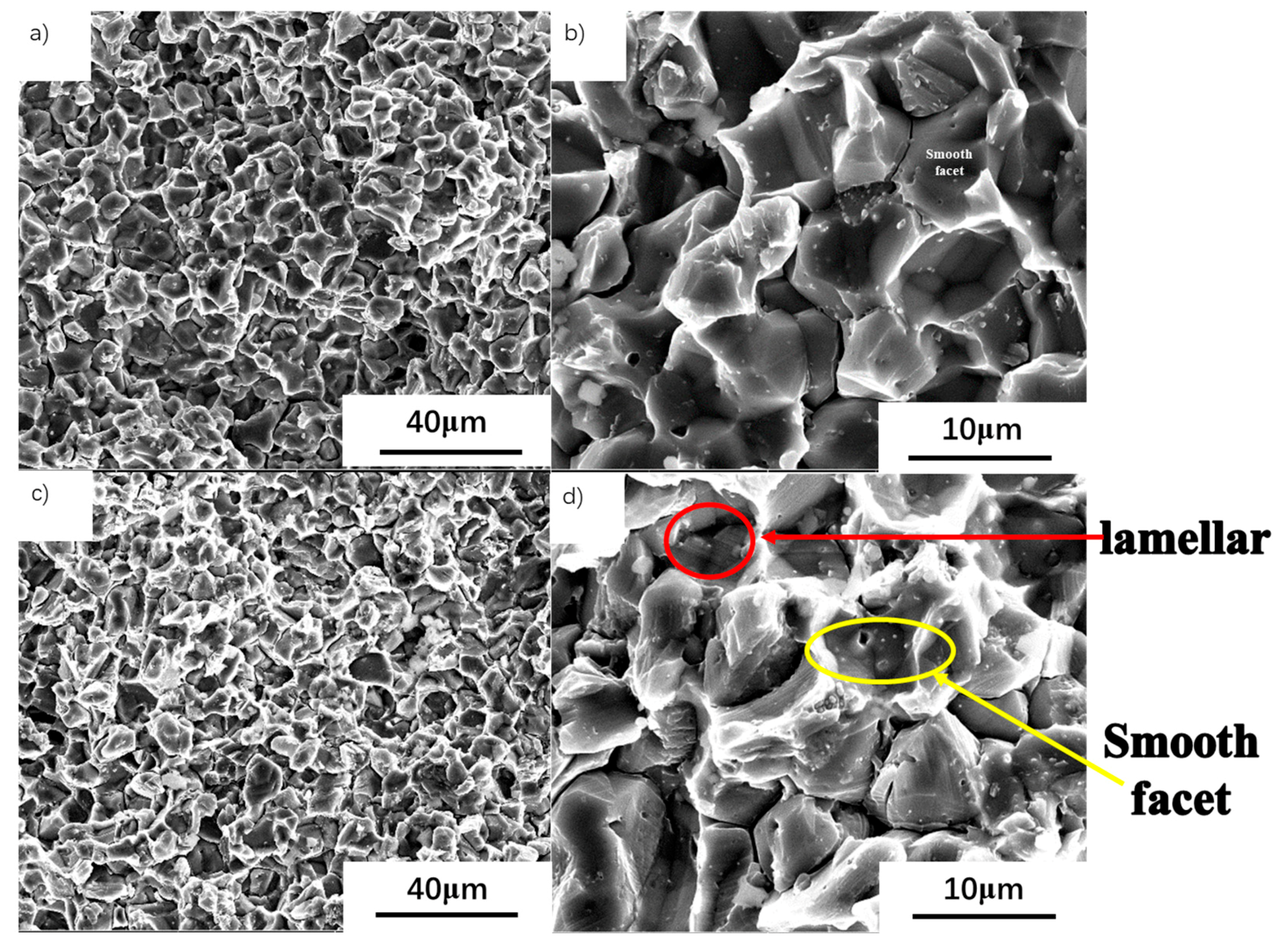
3.5. Study of the Fracture Surfaces
4. Conclusions
- The TiAl powder prepared by gas atomization has high sphericity. The small powder is smooth and the large one exhibits a dendritic appearance. Although the alloy contains high β stabilizer V, the powder mainly consists of α2 due to the fast cooling rate.
- The phase composition of as-HIPed TiAl and TiAl powder varies greatly. The microstructural evolution is as follows: α2 + trace B2 → γ + B2 from powder to billet. The microstructure is fine and uniform and the grain diameter is about 7 μm. Many γ phases and fine grain are beneficial to the plasticity of the TiAl.
- TiAl is mainly deformed when the grain boundary slips below 700 °C. When the temperature reaches 750 °C, both TiAl grains and grain boundaries start to contribute to deformation. The hard-to-soft transition temperature inside the grain is between 700 °C and 750 °C. It is the reason that the plasticity of TiAl alloy is greatly improved between 700 °C and 750 °C.
- The YS and UTS of the as-HIPed TiAl at room temperature are 669 MPa and 793 MPa, respectively. The plastic elongation to fracture is 1%. At 700 °C, the YS and UTS still reach 589 MPa and 664 MPa, respectively. Fine grain and submicron Y2O3 precipitates enhance the room-temperature and high-temperature strength and plasticity.
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Data Availability Statement
References
- Dong, S.L.; Chen, R.R.; Guo, J.J.; Ding, H.S.; Su, Y.Q.; Fu, H.Z. Microstructure and room temperature tensile property of as-cast Ti44Al6Nb1.0Cr2.0V alloy. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2015, 25, 1097–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.; Lu, Z.; Zhang, K.; Deng, L.; Wang, C. Microstructure evolution and mechanical properties of γ-TiAl honeycomb structure fabricated by isothermal forging and pulse current assisted diffusion bonding. Intermetallics 2018, 99, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clemens, H.; Mayer, S. Design, processing, microstructure, properties, and applications of advanced intermetallic TiAl alloys. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2013, 15, 191–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Chen, R.; Yang, Y.; Guo, J.; Su, Y.; Ding, H.; Fu, H. Effects of V and B, Y additions on the microstructure and creep behaviour of high-Nb TiAl alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 747, 640–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ping-Ping, J. High-temperature Antioxidation of TiAl-Nb Based Alloys. Surf. Technol. 2018, 47, 224–230. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, J.; Liang, L.; Liu, Z.; Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Gao, H.; Wu, S.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X. Recent research and development of mould materials for casting TiAl alloys. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2019, 35, 891–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Microstructure stability and micro-mechanical behavior of as-cast gamma-TiAl alloy during high-temperature low cycle fatigue. Acta Mater. 2018, 145, 504–515. [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.T.; Maziasz, P.J.; Clemens, D.R.; Kim, Y.W.; Wagner, R.; Yamaguchi, M. (Eds.) Gamma Titanium Aluminides; TMS: Warrendale, PA, USA, 1995; p. 679. [Google Scholar]
- Gerling, R.; Bartels, A.; Clemens, H.; Kestler, H.; Schimansky, F.P. Structural characterization and tensile properties of a high niobium containing gamma TiAl sheet obtained by powder metallurgical processing. Intermetallics 2004, 12, 275–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liang, X.; Liu, B.; He, W.; Li, J.; Gan, Z.; He, Y. Investigations on processing powder metallurgical high-Nb TiAl alloy sheets. Intermetallics 2014, 55, 80–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawabata, T.; Tadano, M.; Izumi, O. Effect of purity and second phase on ductility of TiAl. Scripta Metallurgica. Scr. Metall. 1988, 22, 1725–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Z.; Zhang, K.; Lu, Z.; Jiang, S. Microstructure and mechanical properties of vacuum diffusion bonding joints for γ-TiAl based alloy. Vacuum 2018, 150, 96–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathabathe, M.N.; Bolokang, A.S.; Govender, G.; Mostert, R.J.; Siyasiya, C.W. The vacuum melted γ-TiAl (Nb, Cr, Si)-doped alloys and their cyclic oxidation properties. Vacuum 2018, 154, 82–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, S.K. Microstructural refinement and improvement of mechanical properties and oxidation resistance in EPM TiAl-based intermetallics with yttrium addition. Acta Mater. 2002, 50, 1479–1493. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.Y.; Li, B.H.; Kong, F.T. Microstructural refinement and mechanical properties of Y-bearing TiAl alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2008, 457, 265–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gourdet, S.; Montheillet, F. An experimental study of the recrystallization mechanism during hot deformation of aluminium. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2000, 283, 274–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trivedi, P.B.; Patankar, S.N.; Froes, F.S.; Baburaj, E.G.; Genç, A.; Ovecoglu, L. Grainsize control in Ti-48Al-2Cr-2Nb with yttrium additions. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2002, 33, 2729–2736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Criss, J.W.; Birks, L.S. Calibration of chemical element EDS. In The Electron Microprobe; McKinley, T.D., Heinrich, K.F.J., Wittry, D.B., Eds.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1966; p. 217. [Google Scholar]
- Appel, F.; Oehring, M.; Paul, J.D.H. Nano-scale design of TiAl alloys based on β phase decomposition. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2006, 8, 371–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeyama, M.; Kobayashi, S. Physical metallurgy for wrought gamma titanium aluminides: Microstructure control through phase transformations. Intermetallics 2005, 13, 993–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Kong, F.; Chen, Y.; Gao, N.; Zhang, D. Microstructure and mechanical properties of large size Ti-43Al-9V-0.2Y alloy pancake produced by pack-forging. Intermetallics 2013, 34, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, Y.; Duan, H.; Sun, Y. Effect of yttrium and erbium on the microstructure and mechanical properties of Ti–Al–Nb alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2010, 528, 220–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, F.T.; Chen, Y.Y.; Tian, J. Effect of Yttrium on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Ti-43Al-9V Alloy. Chin. J. Rare Met. 2004, 28, 75–77. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, W.J.; Xiao, L.; Xu, D.; Qin, J.N.; Zhang, D. Microstructural characterization of Y2O3 in in situ synthesized titanium matrix composites. J. Alloys Compd. 2007, 433, 140–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Kong, F.; Chen, Y. A high-performance β-stabilized Ti-43Al-9V-0.2Y alloy sheet with a nano-scaled, antiphase domain. Mater. Lett. 2018, 214, 182–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Kong, F.; Chen, Y. Effect of Yttrium Addition on Microstructures and Room Temperature Tensile Properties of Ti-47 Al Alloy. J. Rare Earths 2006, 24, 352–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.Y.; Li, B.H.; Kong, F.T. Effects of minor yttrium addition on hot deformability of lamellar Ti-45Al-5Nb alloy. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2007, 17, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Niu, H.; Kong, F.; Xiao, S. Microstructure and fracture toughness of a β phase containing TiAl alloy. Intermetallics 2011, 19, 1405–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trivedi, P.B.; Patankar, S.N.; Froes, F.S.; Baburaj, E.G. Formation of Al–Y oxide during processing of γ-TiAl. J. Alloys Compd. 2002, 340, 231–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, N.; Kong, F.; Wang, X.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, H. Microstructural evolution, hot workability, and mechanical properties of Ti–43Al–2Cr–2Mn–0.2Y alloy. Mater. Des. 2016, 89, 1020–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Kong, F.; Wu, K.; Wang, X.; Chen, Y. Hot pack rolling nearly lamellar Ti-44Al-8Nb-(W, B, Y) alloy with different rolling reductions: Lamellar colonies evolution and tensile properties. Mater. Des. 2017, 121, 202–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, Y.; Wen, D.; Liu, Z.; Shan, D. γ-Phase transformation, dynamic recrystallization and texture of a forged TiAl-based alloy based on plane strain compression at elevated temperature. Mater. Des. 2016, 91, 321–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenel, C.; Dasargyri, G.; Bauer, T.; Colella, A.; Spierings, A.B.; Leinenbach, C.; Wegener, K. Selective laser melting of an oxide dispersion strengthened (ODS) γ-TiAl alloy towards production of complex structures. Mater. Des. 2017, 134, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Long, Y.; Liang, X.; Che, Y.; Liu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Xu, H.; Wang, L. Effects of multiaxial forging on microstructure and high temperature mechanical properties of powder metallurgy Ti-45Al-7Nb-0.3W alloy. Intermetallics 2020, 116, 106647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, Y.; Wen, D.; Liu, Z.; Shan, D. Molina-Aldareguia. Slip transfer across γ-TiAl lamellae in tension. Mater. Des. 2018, 146, 81–95. [Google Scholar]
- Erdely, P.; Staron, P.; Maawad, E.; Schell, N.; Klose, J.; Clemens, H.; Mayer, S. Design and control of microstructure and texture by thermomechanical processing of a multi-phase TiAl alloy. Mater. Des. 2017, 131, 286–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartels, A.; Hartig, C.; Uhlenhut, H. Influence of the deformation conditions on the texture evolution in γ –TiAl. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 1997, 239, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanani, M.; Hartmaier, A.; Janisch, R. Stacking fault based analysis of shear mechanisms at interfaces in lamellar TiAl alloys. Acta Mater. 2016, 106, 208–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hang, D.Y.; Li, H.Z.; Liang, X.P.; Wei, Z.W.; Liu, Y. Microstructure characteristic for high temperature deformation of powder metallurgy Ti–47Al–2Cr–0.2Mo alloy. Mater. Des. 2014, 59, 415–420. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, D.Y.; Li, H.Z.; Liang, X.P.; Wei, Z.W.; Liu, Y. Brittle-to-ductile transition temperature and its strain rate sensitivity in a two-phase titanium aluminide with near lamellar microstructure. J. Mater. Sci. 1999, 34, 3155–3159. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Samman, T.; Molodov, K.D.; Molodov, D.A.; Gottstein, G.; Suwas, S. Softening and dynamic recrystallization in magnesium single crystals during c-axis compression. Acta Mater. 2012, 60, 537–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, F.; Xu, X.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, D. Microstructure and mechanical properties of large size as-cast Ti–43Al–9V–0.2Y (at.%) alloy ingot from brim to centre. Mater. Des. 2012, 33, 485–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
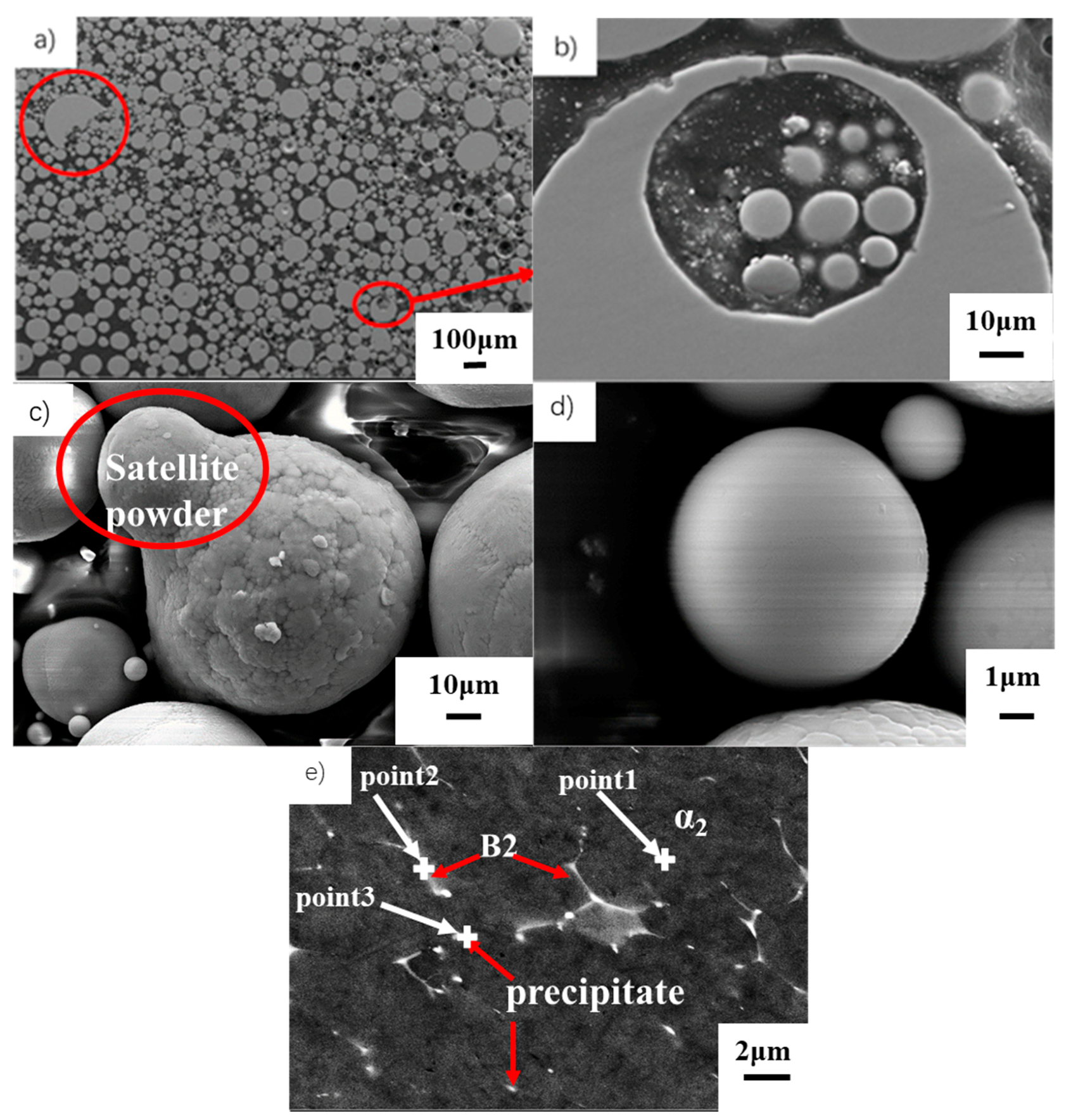

| Select Points | Point 1 (at%) | Point 2 (at%) | Point 3 (at%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Al | 42.81 | 42.34 | 26.58 |
| Ti | 48.74 | 48.33 | 32.37 |
| V | 8.32 | 9.18 | 5.49 |
| Y | 0.05 | 0.08 | 13.51 |
| O | 0.08 | 0.07 | 22.05 |
| Total | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 |
| RT | 700 °C | 750 °C | 800 °C | 850 °C | 900 °C | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| σs (MPa) | 669 ± 23 | 589 ± 12 | 505 ± 21 | 440 ± 15 | 279 ± 8 | 172 ± 6 |
| σb (MPa) | 793 ± 35 | 664 ± 20 | 556 ± 29 | 448 ± 10 | 292 ± 7 | 190 ± 5 |
| strain (%) | 1.52 ± 0.17 | 9.2 ± 0.6 | 27.4 ± 1.1 | 39.5 ± 1.3 | 48.4 ± 1.6 | 49.2 ± 1.1 |
| Alloys | Room Temperature | 700 °C | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UTS (MPa) | Strain (%) | UTS (MPa) | Strain (%) | |||
| Ti-43Al-9V-0.2Y | rolling | 826 | 1.4 | 674 | 27.1 | |
| Ti-43Al-9V-0.2Y | casting | 561–634 | 0.45–0.76 | / | / | |
| Ti-43Al-2Cr-2Mn-0.2Y | forging | 657 | 0.86 | 496 | 10 | |
| Ti-43Al-9V-0.3Y | as-HIPed | 793 | 1.5 | 664 | 9.2 | current alloy |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, D.; Liu, N.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, G.; Tian, J.; Kong, F.; Xiao, S.; Sun, J. Microstructure Evolution and Mechanical Properties of PM-Ti43Al9V0.3Y Alloy. Materials 2020, 13, 198. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13010198
Zhang D, Liu N, Chen Y, Zhang G, Tian J, Kong F, Xiao S, Sun J. Microstructure Evolution and Mechanical Properties of PM-Ti43Al9V0.3Y Alloy. Materials. 2020; 13(1):198. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13010198
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Dongdong, Na Liu, Yuyong Chen, Guoqing Zhang, Jing Tian, Fantao Kong, Shulong Xiao, and Jianfei Sun. 2020. "Microstructure Evolution and Mechanical Properties of PM-Ti43Al9V0.3Y Alloy" Materials 13, no. 1: 198. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13010198
APA StyleZhang, D., Liu, N., Chen, Y., Zhang, G., Tian, J., Kong, F., Xiao, S., & Sun, J. (2020). Microstructure Evolution and Mechanical Properties of PM-Ti43Al9V0.3Y Alloy. Materials, 13(1), 198. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13010198






