Colorimetric Detection of Mercury Ions in Water with Capped Silver Nanoprisms
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
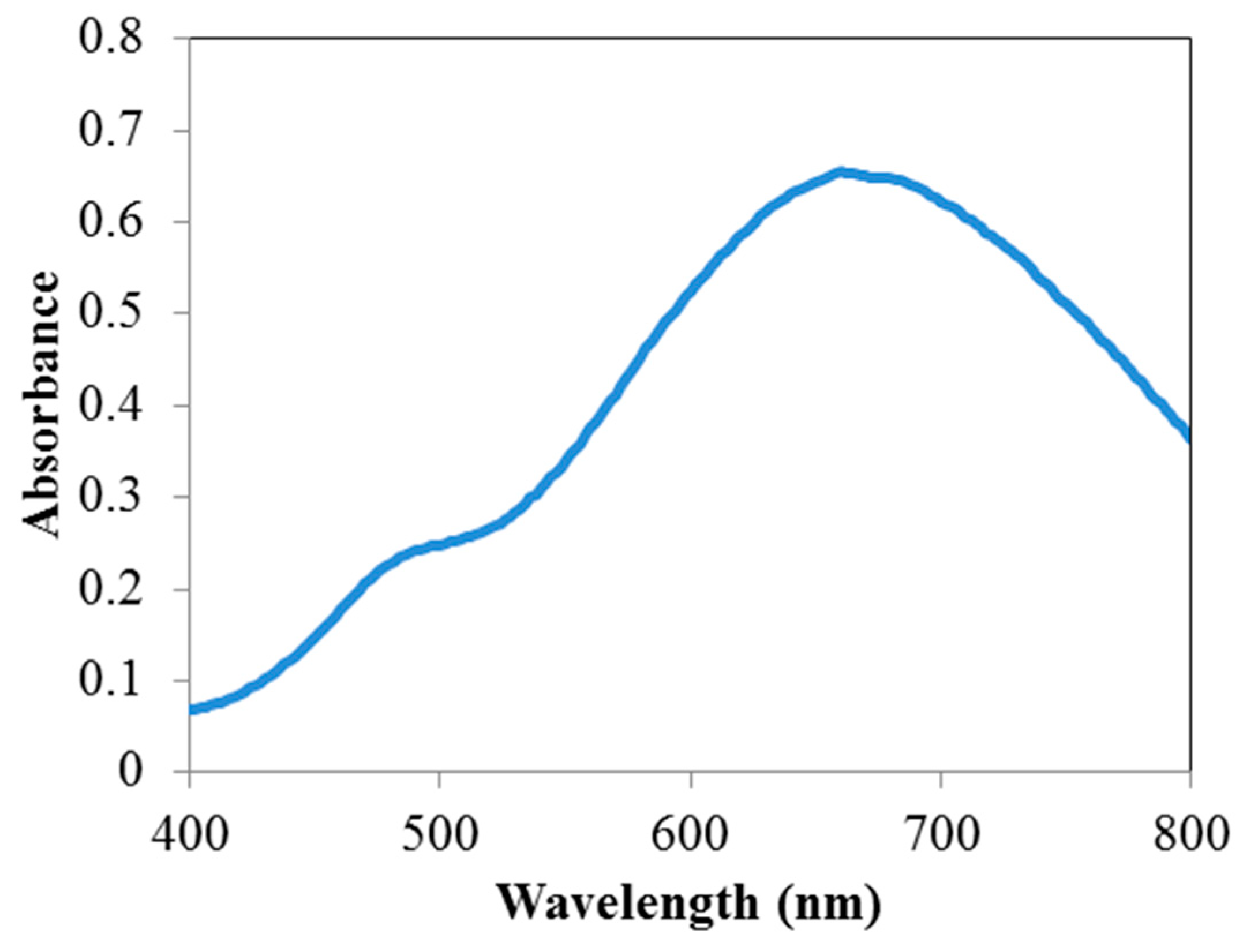
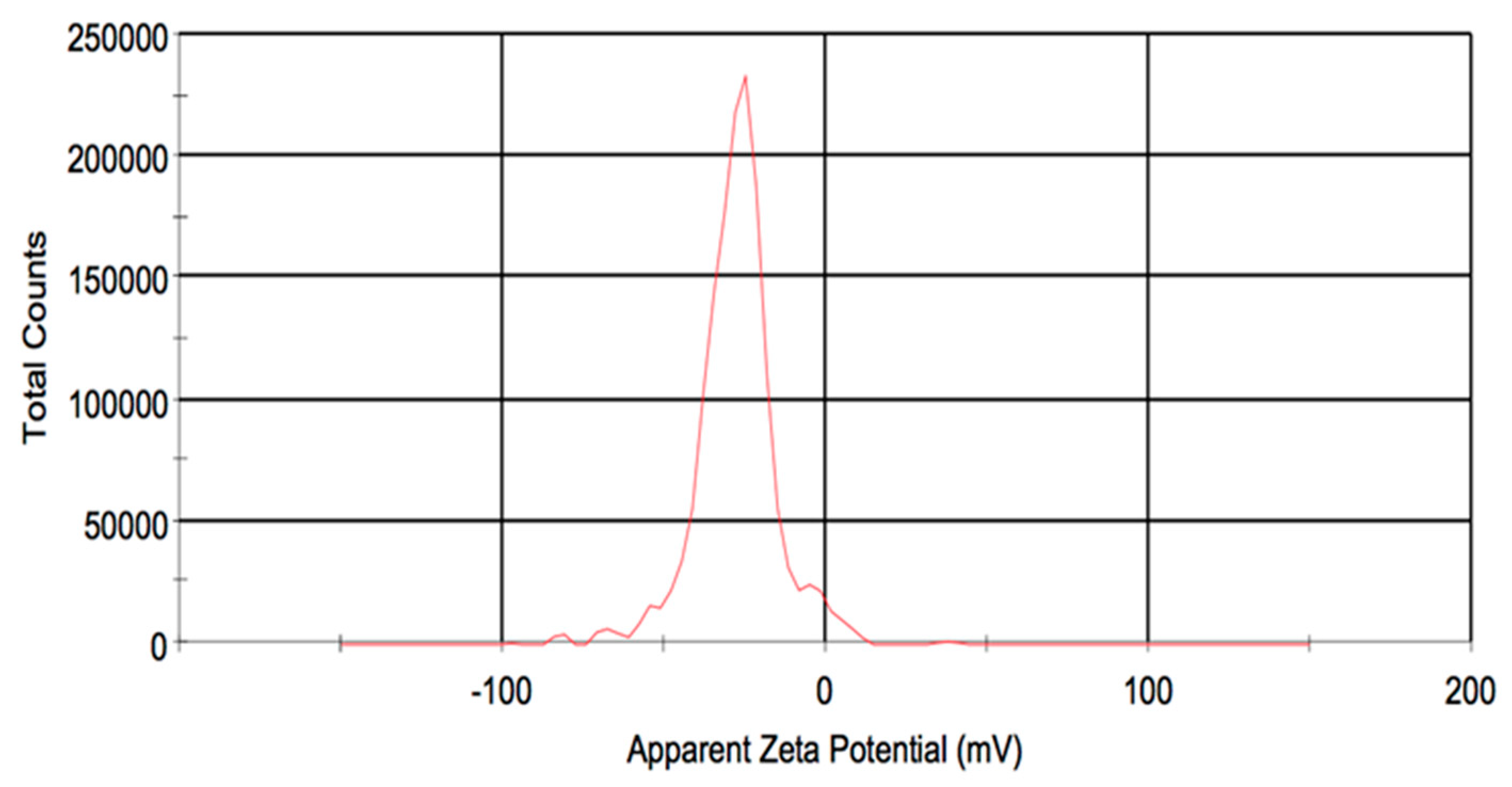
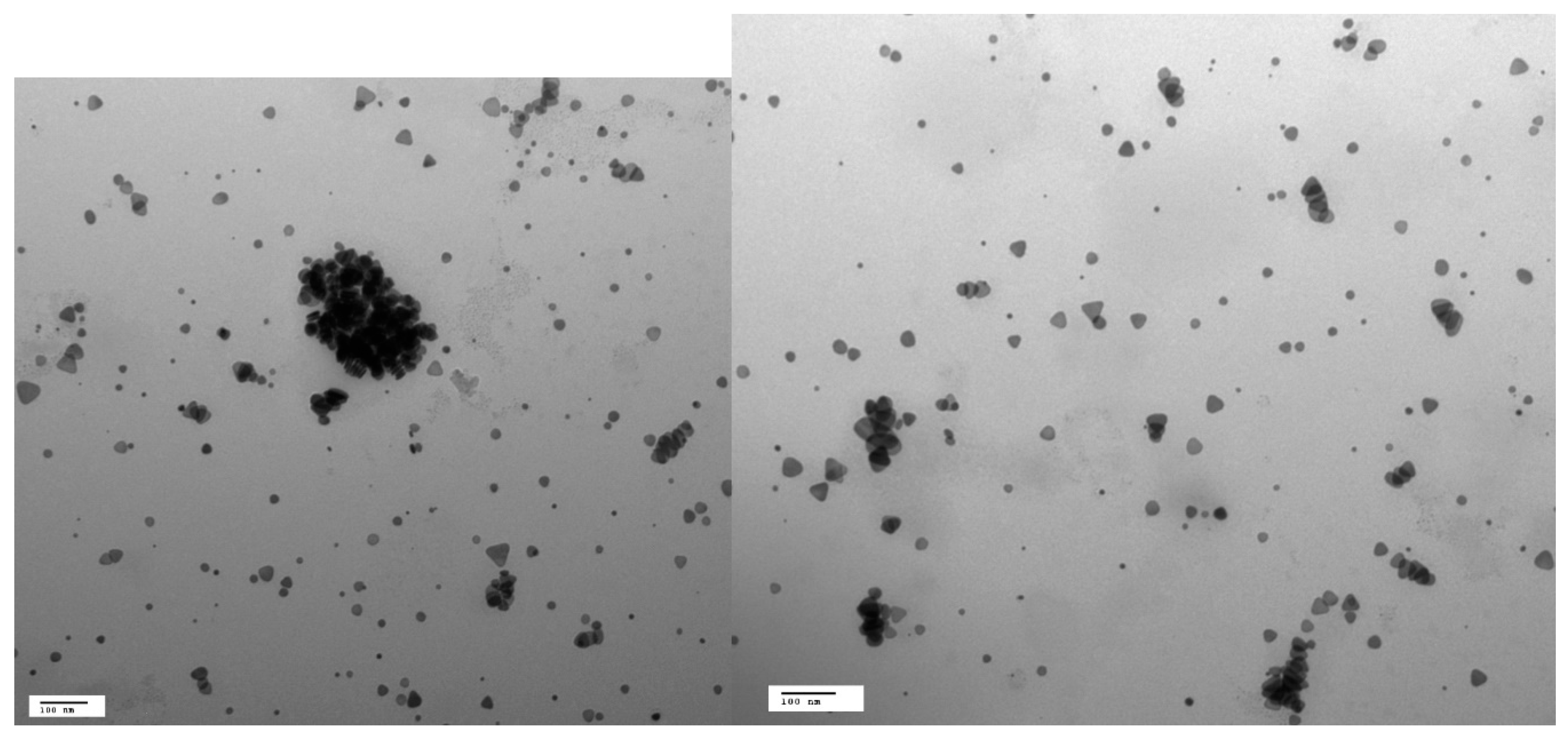
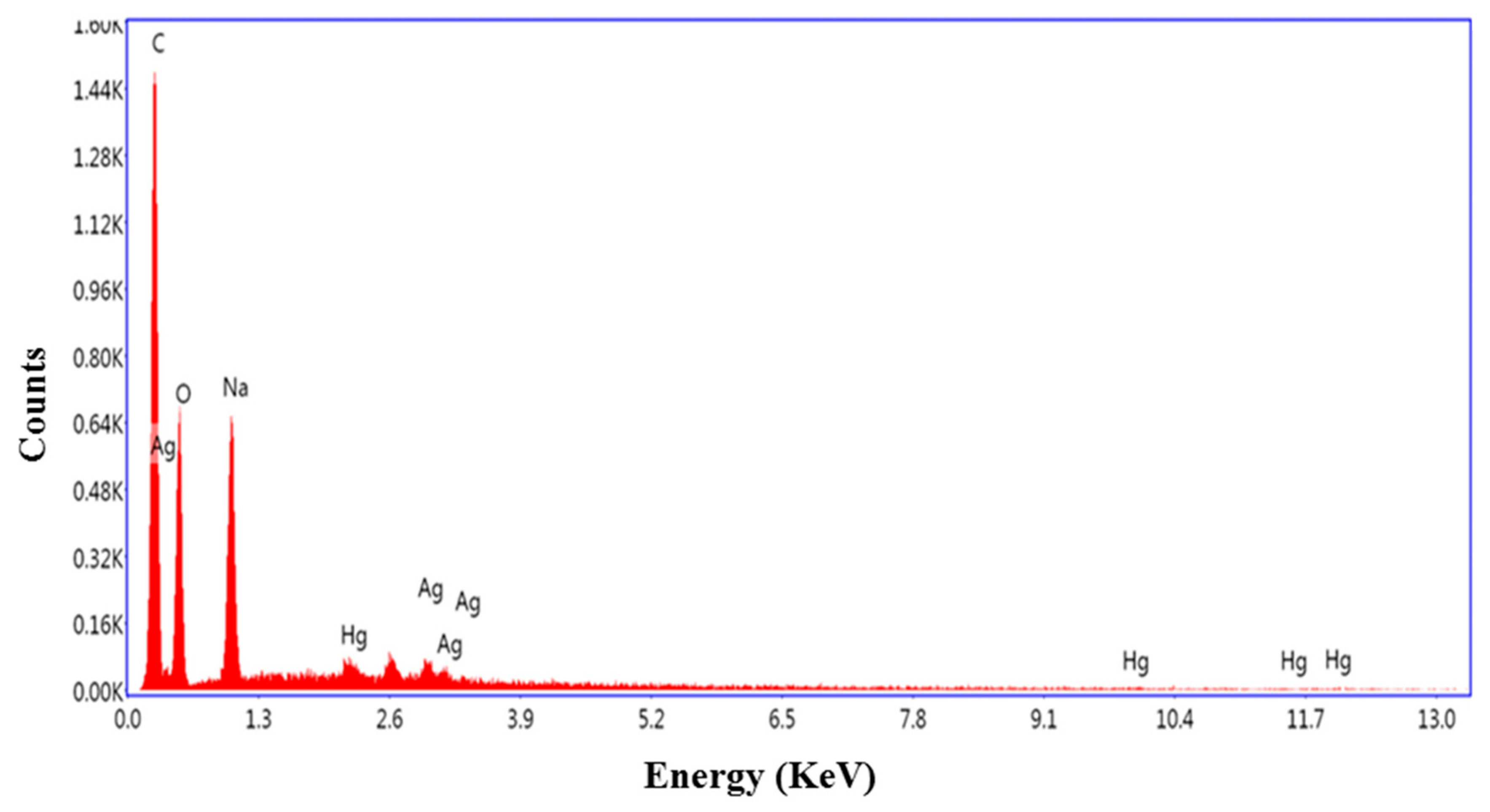
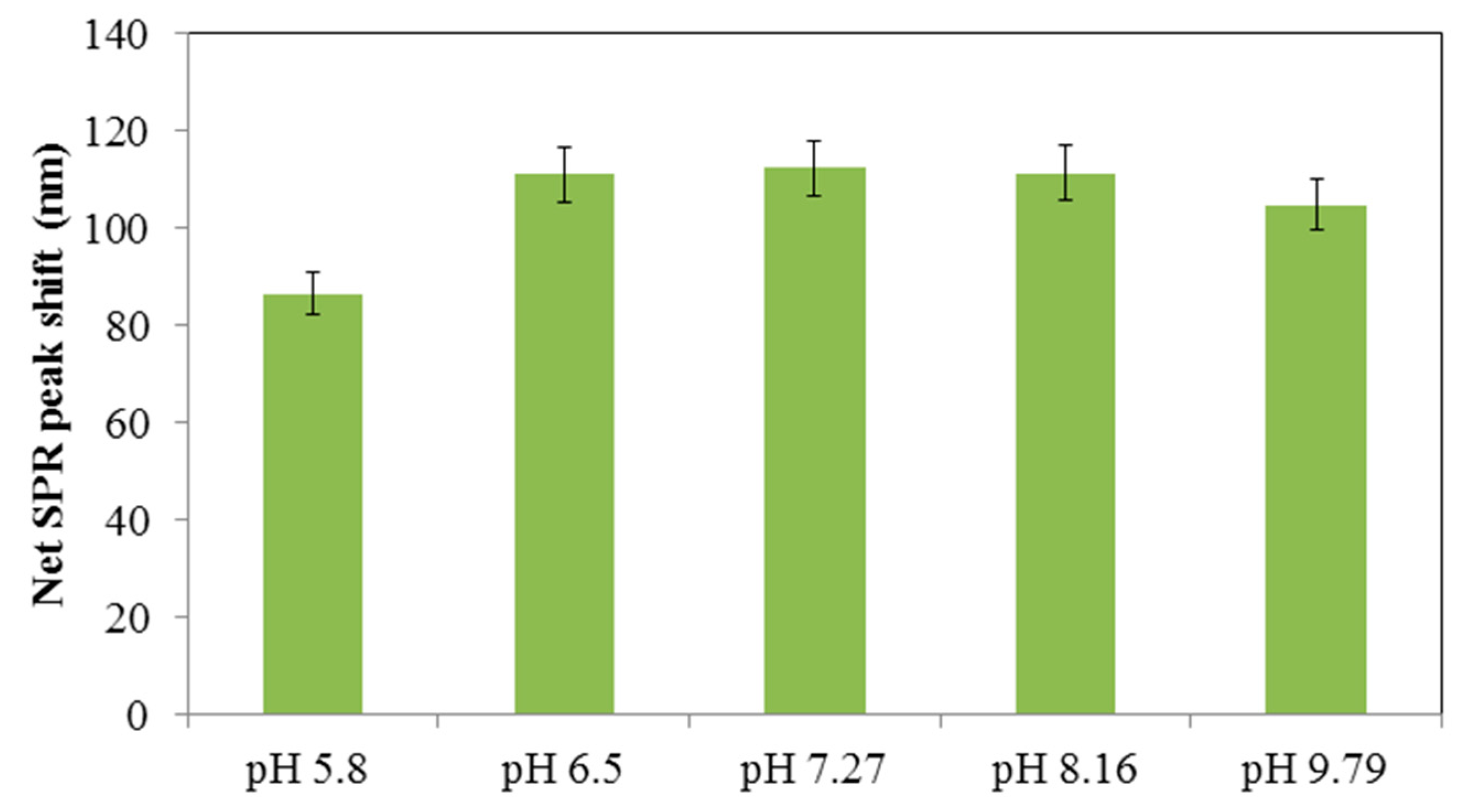
3.1. Characterization of the Nanoparticles
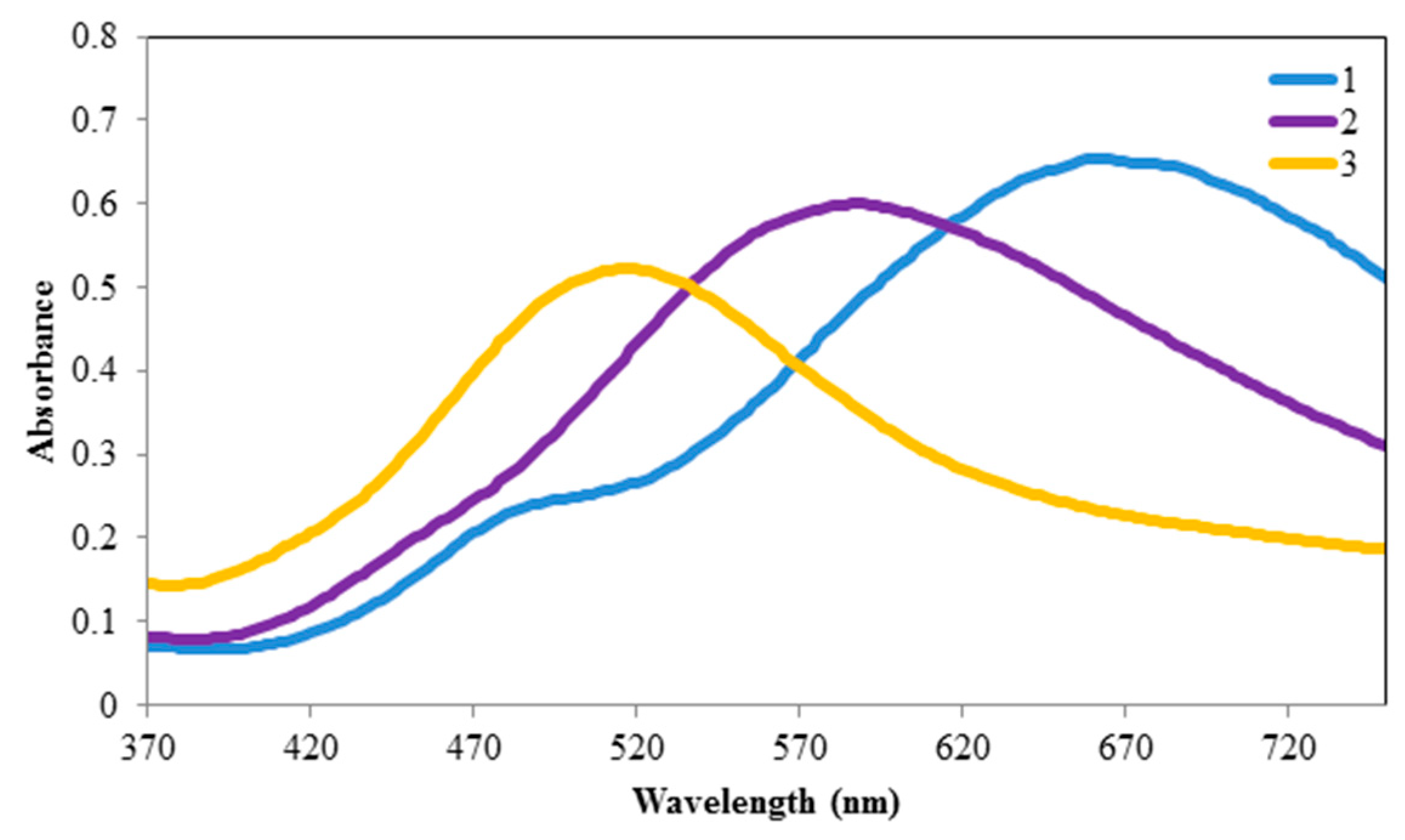
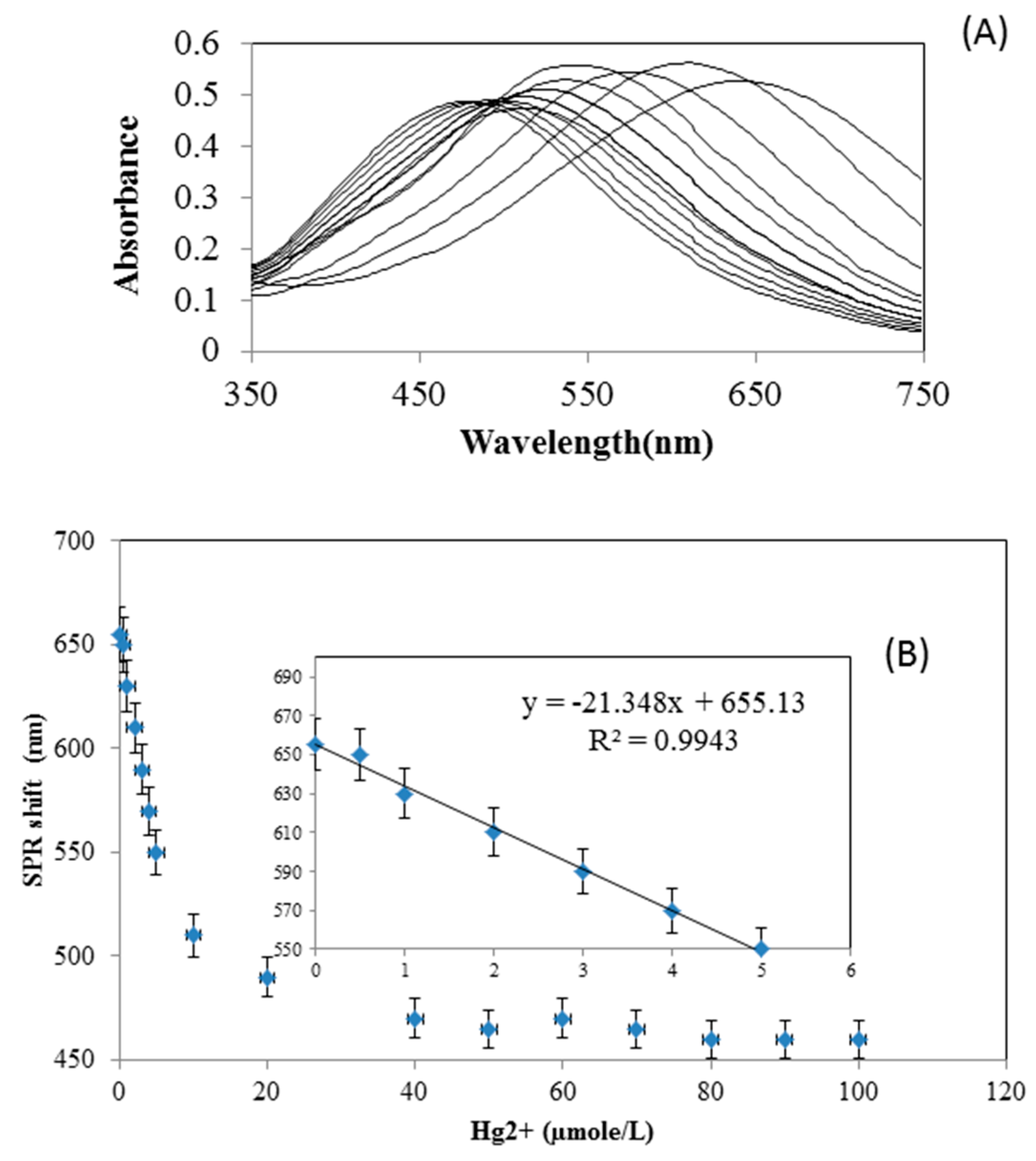
3.2. Spectral Shifts in the Presence of Hg+
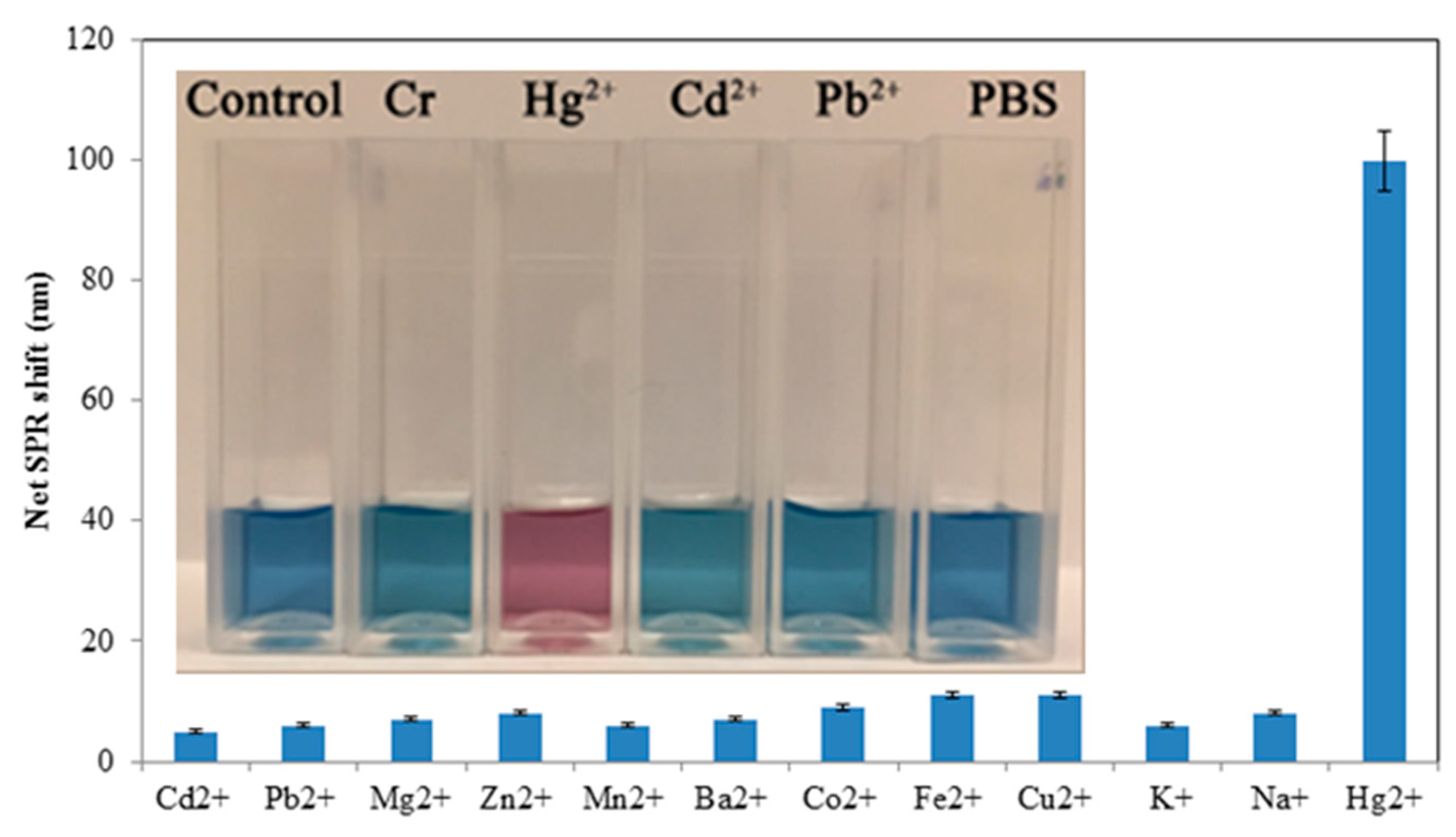
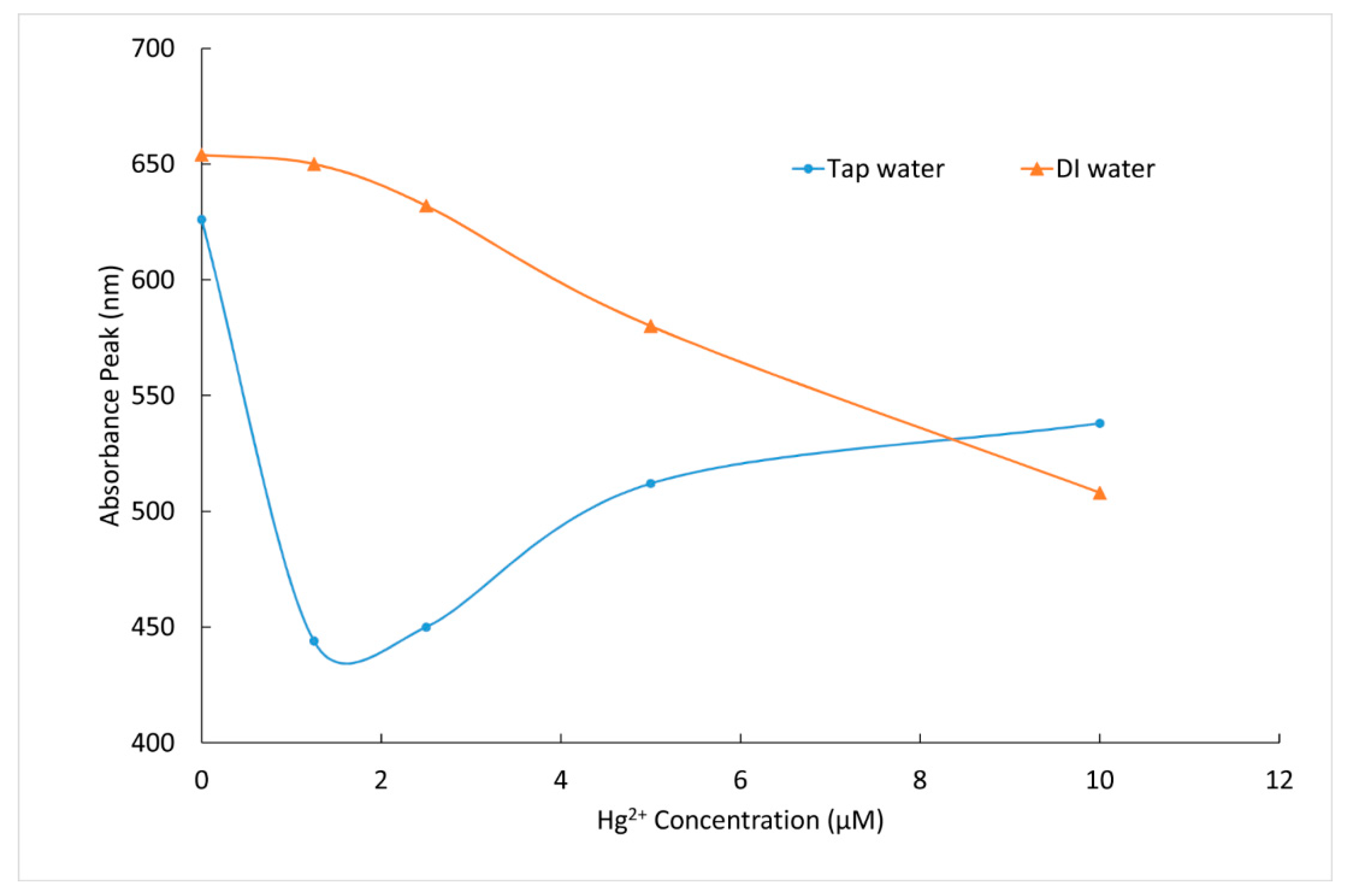
3.3. Sensitivity and Selectivity
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Streets, D.G.; Horowitz, H.M.; Lu, Z.; Levin, L.; Thackray, C.P.; Sunderland, E.M. Global and regional trends in mercury emissions and concentrations, 2010–2015. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 201, 417–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, S.; Wu, Q.; Wang, F.; Lin, C.J.; Zhang, L.; Hui, M.; Yang, M.; Su, H.; Hao, J. Mercury transformation and speciation in flue gases from anthropogenic emission sources: A critical review. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 2417–2433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- US EPA. Available online: https://safewater.zendesk.com/hc/en-us/articles/212076077-4-What-are-EPA-s-drinking-water-regulations-for-mercury- (accessed on 18 April 2019).
- Leopold, K.; Foulkes, M.; Worsfold, P. Methods for the determination and speciation of mercury in natural waters—A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2010, 663, 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín-Yerga, D.; González-García, M.B.; Costa-García, A. Electrochemical determination of mercury: A review. Talanta 2013, 116, 1091–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uglov, A.N.; Bessmertnykh-Lemeune, A.; Guilard, R.; Averin, A.D.; Beletskaya, I.P. Optical methods for the detection of heavy metal ions. Russ. Chem. Rev. 2014, 83, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Guo, Z.; Zeng, G.; Tang, L. Fluorescent and colorimetric sensors for environmental mercury detection. Analyst 2015, 140, 5400–5443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bui, M.P.N.; Brockgreitens, J.; Ahmed, S.; Abbas, A. Dual detection of nitrate and mercury in water using disposable electrochemical sensors. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 85, 280–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Yang, F.; Yang, X. Colorimetric biosensing of mercury (II) ion using unmodified gold nanoparticle probes and thrombin-binding aptamer. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2010, 25, 1994–1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, K.N.; Choi, J.S.; Kwon, J. Gold nanozyme-based paper chip for colorimetric detection of mercury ions. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 2806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, R.; Li, J.; Yang, W. Aggregation of glutathione-functionalized Au nanoparticles induced by Ni 2+ ions. J. Nanopart. Res. 2012, 14, 929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Cui, Z.; Han, C. Glutathione-stabilized silver nanoparticles as colorimetric sensor for Ni2+ ion. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2009, 143, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Agostino, A.; Taglietti, A.; Bassi, B.; Donà, A.; Pallavicini, P. A naked eye aggregation assay for Pb 2+ detection based on glutathione-coated gold nanostars. J. Nanopart. Res. 2014, 16, 2683. [Google Scholar]
- Sung, H.K.; Oh, S.Y.; Park, C.; Kim, Y. Colorimetric detection of Co2+ ion using silver nanoparticles with spherical, plate, and rod shapes. Langmuir 2013, 29, 8978–8982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.S.; Han, M.S.; Mirkin, C.A. Colorimetric detection of mercuric ion (Hg2+) in aqueous media using DNA-functionalized gold nanoparticles. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 4093–4096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zarlaida, F.; Adlim, M. Gold and silver nanoparticles and indicator dyes as active agents in colorimetric spot and strip tests for mercury (II) ions: A review. Microchim. Acta 2017, 184, 45–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Fu, X.; Lu, W.; Chen, L. Highly sensitive and selective colorimetric sensing of Hg2+ based on the morphology transition of silver nanoprisms. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2012, 5, 284–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhadi, K.; Forough, M.; Molaei, R.; Hajizadeh, S.; Rafipour, A. Highly selective Hg2+ colorimetric sensor using green synthesized and unmodified silver nanoparticles. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2012, 161, 880–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yang, F.; Yang, X. Colorimetric detection of mercury (II) ion using unmodified silver nanoparticles and mercury-specific oligonucleotides. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2010, 2, 339–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alam, A.; Ravindran, A.; Chandran, P.; Khan, S.S. Highly selective colorimetric detection and estimation of Hg2+ at nano-molar concentration by silver nanoparticles in the presence of glutathione. Spectrochim. Acta A 2015, 137, 503–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manivel, P.; Ilanchelian, M. Selective and Sensitive Colorimetric Detection of Hg 2+ at Wide pH Range Using Green Synthesized Silver Nanoparticles as Probe. J. Clust. Sci. 2017, 28, 1145–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, L.; Yang, T.; Zhen, S.J.; Huang, C.Z. Cytosine triphosphate-capped silver nanoparticles as a platform for visual and colorimetric determination of mercury (II) and chromium (III). Microchim. Acta 2017, 184, 3171–3178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeevika, A.; Shankaran, D.R. Functionalized silver nanoparticles probe for visual colorimetric sensing of mercury. Mater. Res. Bull. 2016, 83, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Gui, L.; Li, W. A colorimetric silver nanoparticle-based assay for Hg (II) using lysine as a particle-linking reagent. Microchim. Acta 2015, 182, 1977–1981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Detsri, E. Novel colorimetric sensor for mercury (II) based on layer-by-layer assembly of unmodified silver triangular nanoplates. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2016, 27, 1635–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanvir, F.; Yaqub, A.; Tanvir, S.; Anderson, W. Poly-l-arginine coated silver nanoprisms and their anti-bacterial properties. Nanomaterials 2017, 7, 296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panzarasa, G. Just What Is It That Makes Silver Nanoprisms so Different, so Appealing? J. Chem. Educ. 2015, 92, 1918–1923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, V.; Popa, M.; Crespo, D.; Moreno, J.M.C. Silver nanoprism coatings on optical glass substrates. Microelectron. Eng. 2007, 84, 1665–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Agostino, A.; Taglietti, A.; Desando, R.; Bini, M.; Patrini, M.; Dacarro, G.; Cucca, L.; Pallavicini, P.; Grisoli, P. Bulk surfaces coated with triangular silver nanoplates: Antibacterial action based on silver release and photo-thermal effect. Nanomaterials 2017, 7, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rex, M.; Hernandez, F.E.; Campiglia, A.D. Pushing the limits of mercury sensors with gold nanorods. Anal. Chem. 2006, 78, 445–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamali, K.Z.; Pandikumar, A.; Jayabal, S.; Ramaraj, R.; Lim, H.N.; Ong, B.H.; Bien, C.S.D.; Kee, Y.Y.; Huang, N.M. Amalgamation based optical and colorimetric sensing of mercury (II) ions with silver@ graphene oxide nanocomposite materials. Microchim. Acta 2016, 183, 369–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.L.; Zhu, X.Y.; Jiao, H.J.; Dong, Y.M.; Li, Z.J. Ultrasensitive and dual functional colorimetric sensors for mercury (II) ions and hydrogen peroxide based on catalytic reduction property of silver nanoparticles. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2012, 31, 337–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Mosher, B.P.; Lyons, K.; Zeng, T. Reducing ability and mechanism for polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) in silver nanoparticles synthesis. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2010, 10, 2342–2347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wen, G.; Ye, L.; Liang, A.; Jiang, Z. Label-free SERS study of galvanic replacement reaction on silver nanorod surface and its application to detect trace mercury ion. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 19650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badawy, A.M.E.; Luxton, T.P.; Silva, R.G.; Scheckel, K.G.; Suidan, M.T.; Tolaymat, T.M. Impact of environmental conditions (pH, ionic strength, and electrolyte type) on the surface charge and aggregation of silver nanoparticles suspensions. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 1260–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haynes, W.M. The CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, 97th ed.; CRC Press/Taylor & Francis: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2017; p. 192+. [Google Scholar]
- Metreveli, G.; Philippe, A.; Schaumann, G.E. Disaggregation of silver nanoparticle homoaggregates in a river water matrix. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 535, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tanvir, F.; Yaqub, A.; Tanvir, S.; An, R.; Anderson, W.A. Colorimetric Detection of Mercury Ions in Water with Capped Silver Nanoprisms. Materials 2019, 12, 1533. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12091533
Tanvir F, Yaqub A, Tanvir S, An R, Anderson WA. Colorimetric Detection of Mercury Ions in Water with Capped Silver Nanoprisms. Materials. 2019; 12(9):1533. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12091533
Chicago/Turabian StyleTanvir, Fouzia, Atif Yaqub, Shazia Tanvir, Ran An, and William A. Anderson. 2019. "Colorimetric Detection of Mercury Ions in Water with Capped Silver Nanoprisms" Materials 12, no. 9: 1533. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12091533
APA StyleTanvir, F., Yaqub, A., Tanvir, S., An, R., & Anderson, W. A. (2019). Colorimetric Detection of Mercury Ions in Water with Capped Silver Nanoprisms. Materials, 12(9), 1533. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12091533





