Flexible Carbon Nanotube-Based Polymer Electrode for Long-Term Electrocardiographic Recording
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
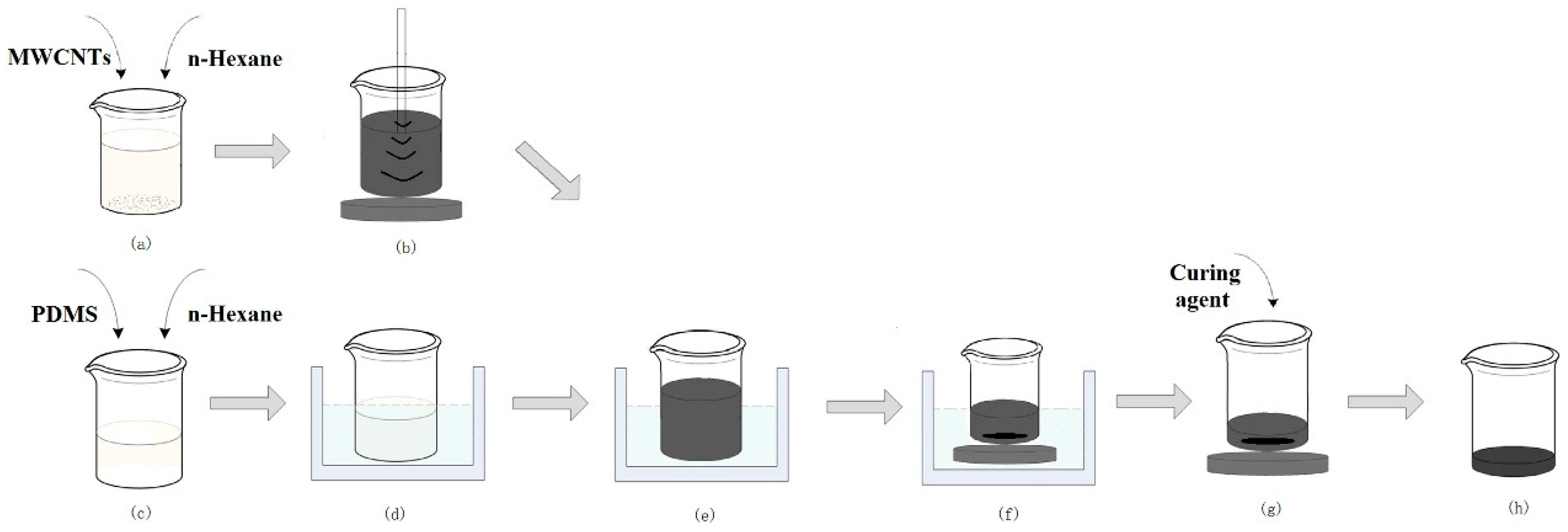
2.1. MWCNT/PDMS Composite Preparation
2.2. Fabrication of the MWCNT/PDMS Electrode
3. Results and Discussion
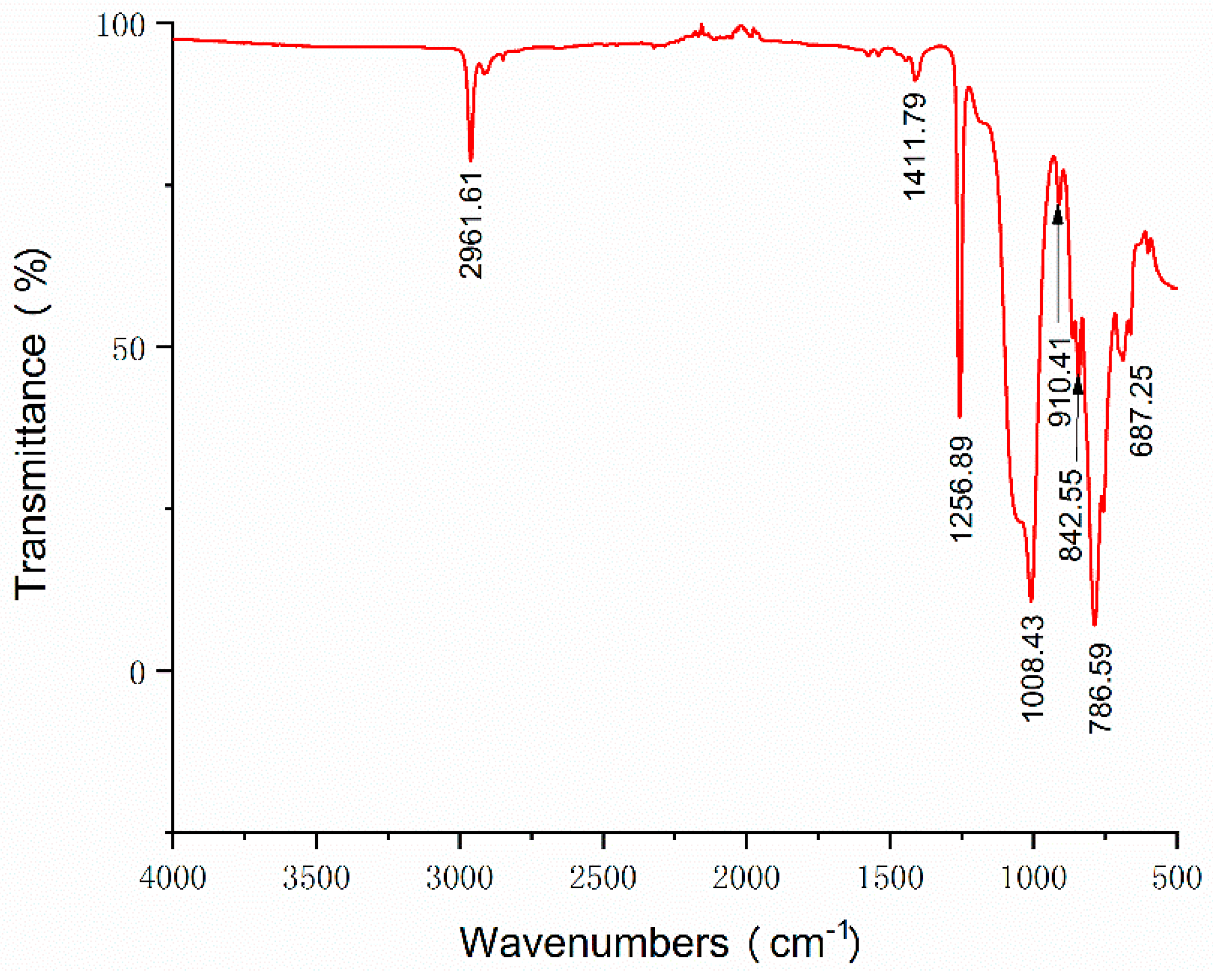
3.1. Structural Characterization
3.2. Skin-Electrode Contact Impedance Measurement
3.3. Short-Term ECG Measurement
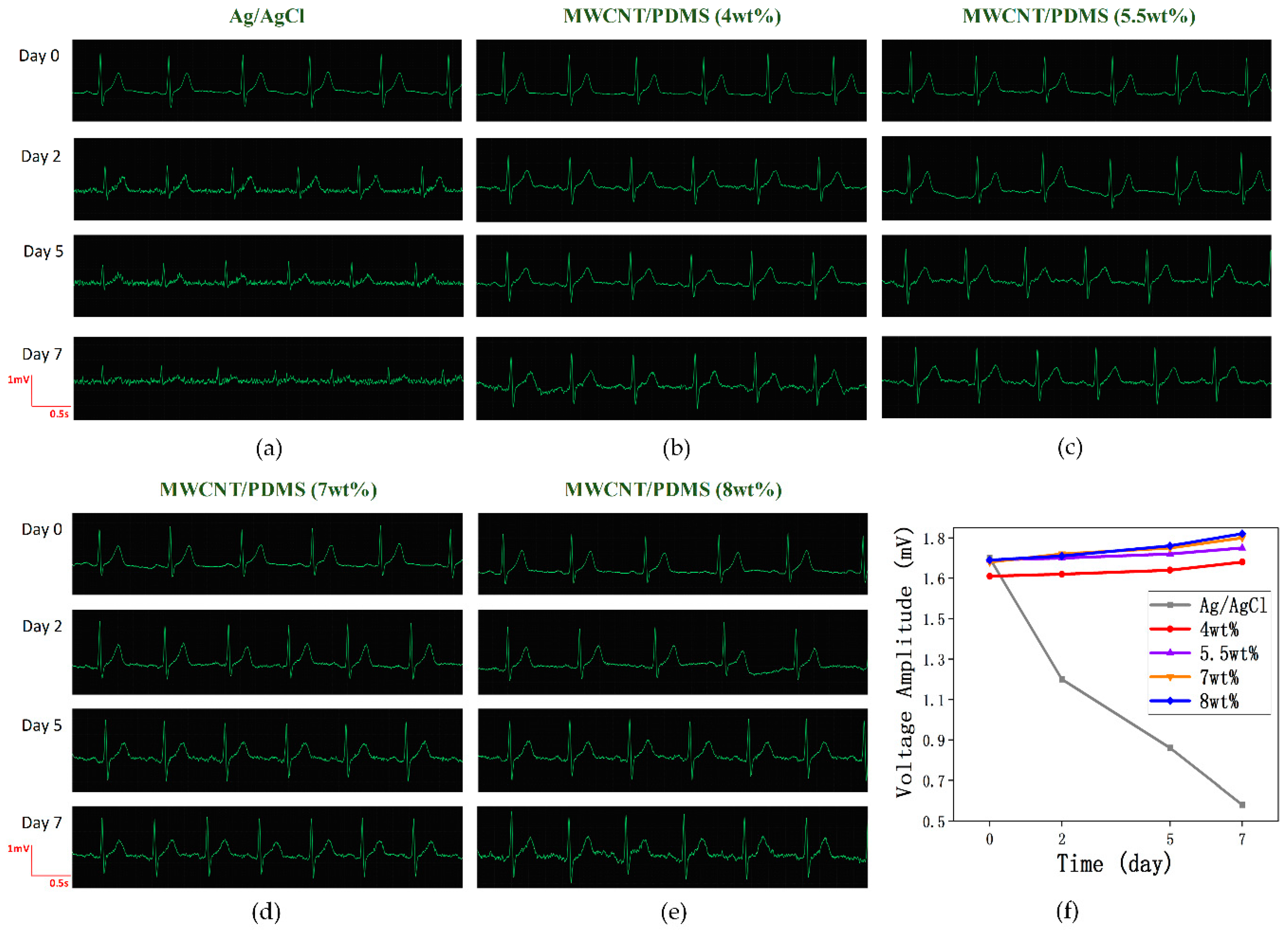
3.4. Long-Term ECG Measurement
3.5. Cytotoxicity and Skin Compatibility Tests
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization. Available online: https://www.who.int/hepatitis/publications/global-hepatitis-report2017/en/ (accessed on 15 July 2018).
- Peng, H.L.; Liu, J.Q.; Tian, H.C. Flexible dry electrode based on carbon nanotube/polymer hybrid micropillars for biopotential recording. Sens. Actuator A Phys. 2015, 235, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Yu, X.B. Capacitive biopotential measurement for electrophysiological signal acquisition: A review. IEEE Sens. J. 2016, 16, 2832–2853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.M.; Pearce, F.; Hibbs, A.D. Evaluation of a Capacitively-Coupled, Non-Contact (Through Clothing) Electrode or ECG Monitoring and Life Signs Detection for the Objective Force Warfighter; Walter Reed Army Inst of Research Silver Spring Md, St.: Pete Beach, FL, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Aleksandrowicz, A.; Leonhardt, S. Wireless and Non-contact ECG Measurement System—The “Aachen SmartChair”. Acta Polytech. 2007, 47, 4–5. [Google Scholar]
- Chamadiya, B.; Mankodiya, K.; Wagner, M. Non-contact, non-obtrusive electrocardiography in clinical environements. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Pervasive Computing Technologies for Healthcare, Dublin, Ireland, 23–26 May 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Chi, Y.M.; Deiss, S.R.; Cauwenberghs, G. Non-contact Low Power EEG/ECG Electrode for High Density Wearable Biopotential Sensor Networks. In Proceedings of the Sixth International Workshop on Wearable and Implantable Body Sensor Networks IEEE Computer Society, Berkeley, CA, USA, 3–5 June 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Chi, Y.M.; Cauwenberghs, G. Micropower non-contact EEG electrode with active common-mode noise suppression and input capacitance cancellation. In Proceedings of the Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Minneapolis, MN, USA, 2–6 September 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, L.M.; Tay, F.E.H.; Guo, D.G. A microfabricated electrode with hollow microneedles for ECG measurement. Sens. Actuator A Phys. 2009, 151, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Mahony, C.; Pini, F.; Blake, A. Microneedle-based electrodes with integrated through-silicon via for biopotential recording. Sens. Actuator A Phys. 2012, 186, 130–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matteucci, M.; Carabalona, R. Preliminary technological assessment of microneedles-based dry electrodes for biopotential monitoring in clinical examinations. Sens. Actuator A Phys. 2012, 180, 177–186. [Google Scholar]
- Salvo, P.; Raedt, R.; Carrette, E. A 3D printed dry electrode for ECG/EEG recording. Sens. Actuator A Phys. 2012, 174, 96–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, L.S.; Tung, S.W. Developing Barbed Microtip-Based Electrode Arrays for Biopotential Measurement. Sensors 2014, 14, 12370–12386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griss, P.; Enoksson, P. Micromachined electrodes for biopotential measurements. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 2001, 10, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, K.P.; Ruff, R. Flexible dry surface-electrodes for ECG long-term monitoring. In Proceedings of the Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Lyon, France, 23–26 August 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, B.; Luo, Z. Carbon nanotube-based self-adhesive polymer electrodes for wireless long-term recording of electrocardiogram signals. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2016, 27, 1899–1908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myers, A.; Huang, H. Wearable silver nanowire dry electrodes for electrophysiological sensing. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 11627–11632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, S.; Myers, A. A Wearable Hydration Sensor with Conformal Nanowire Electrodes. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2017, 6, 1601159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandes, M.S.; Lee, K.S. Flexible PDMS-based dry electrodes for electro-optic acquisition of ECG signals in wearable devices. In Proceedings of the Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Buenos Aires, Argentina, 31 August–4 September 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, S.; Schwalb, W. A wearable and highly sensitive pressure sensor with ultrathin gold nanowires. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, Y.; Chen, X. A flexible dry micro-dome electrode for ECG monitoring. Microsyst. Technol. 2015, 21, 1241–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Y.; Li, Z.B. A flexible dry electrode based on APTES-anchored PDMS substrate for portable ECG acquisition system. Microsyst. Technol. 2015, 22, 2027–2034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.M.; Byeon, H.J. Self-adhesive epidermal carbon nanotube electronics for tether-free long-term continuous recording of biosignals. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 6074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Her, S.C.; Lai, C.Y. Dynamic behavior of nanocomposites reinforced with multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs). Materials 2013, 6, 2274–2284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sankar, N.; Reddy, M.N.; Prasad, R.K. Carbon nanotubes dispersed polymer nanocomposites: Mechanical, electrical, thermal properties and surface morphology. Bull. Mater. Sci. 2016, 39, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murudkar, V.; Gaonkar, A.; Deshpande, V.D.; Mhaske, S.T. Study of nano mechanical properties polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS)/MWCNT composites. In AIP Conference Proceedings; AIP Publishing: Melville, NY, USA, 2018; Volume 1953, p. 090055. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, J.; Kim, B.; Jeong, Y.G. Thermomechanical and electrical properties of PDMS/MWCNT composite films crosslinked by electron beam irradiation. J. Mater. Sci. 2015, 50, 5599–5608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nour, M.; Berean, K.; Balendhran, S. CNT/PDMS composite membranes for H2 and CH4 gas separation. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2013, 38, 10494–10501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, N.; Cheng, D.; Yang, J.; Liu, L. New insight on the interfacial interaction between multiwalled carbon nanotubes and elastomers. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2017, 142, 214–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, H.C.; Moon, J.H. CNT/PDMS composite flexible dry electrodes for long-term ECG monitoring. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2012, 59, 1472–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reyes, B.A.; Posada-Quintero, H.F. Novel electrodes for underwater ECG monitoring. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2014, 61, 1863–1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chi, M.; Zhao, J.; Dong, Y.; Wang, X. Flexible Carbon Nanotube-Based Polymer Electrode for Long-Term Electrocardiographic Recording. Materials 2019, 12, 971. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12060971
Chi M, Zhao J, Dong Y, Wang X. Flexible Carbon Nanotube-Based Polymer Electrode for Long-Term Electrocardiographic Recording. Materials. 2019; 12(6):971. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12060971
Chicago/Turabian StyleChi, Miao, Jingjing Zhao, Ying Dong, and Xiaohao Wang. 2019. "Flexible Carbon Nanotube-Based Polymer Electrode for Long-Term Electrocardiographic Recording" Materials 12, no. 6: 971. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12060971
APA StyleChi, M., Zhao, J., Dong, Y., & Wang, X. (2019). Flexible Carbon Nanotube-Based Polymer Electrode for Long-Term Electrocardiographic Recording. Materials, 12(6), 971. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12060971




