Fabrication of Carboxymethylcellulose/Metal-Organic Framework Beads for Removal of Pb(II) from Aqueous Solution
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Material Preparation and Characterization
2.2.1. Preparation of MOF-5
2.2.2. Synthesis of MOF-5–CMC Beads
2.2.3. Characterization
2.2.4. Adsorption Experiments
2.2.5. Reuse Experiments
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Morphologies as Observed by SEM
3.2. Thermogravimetric Analyses
3.3. XRD Analyses
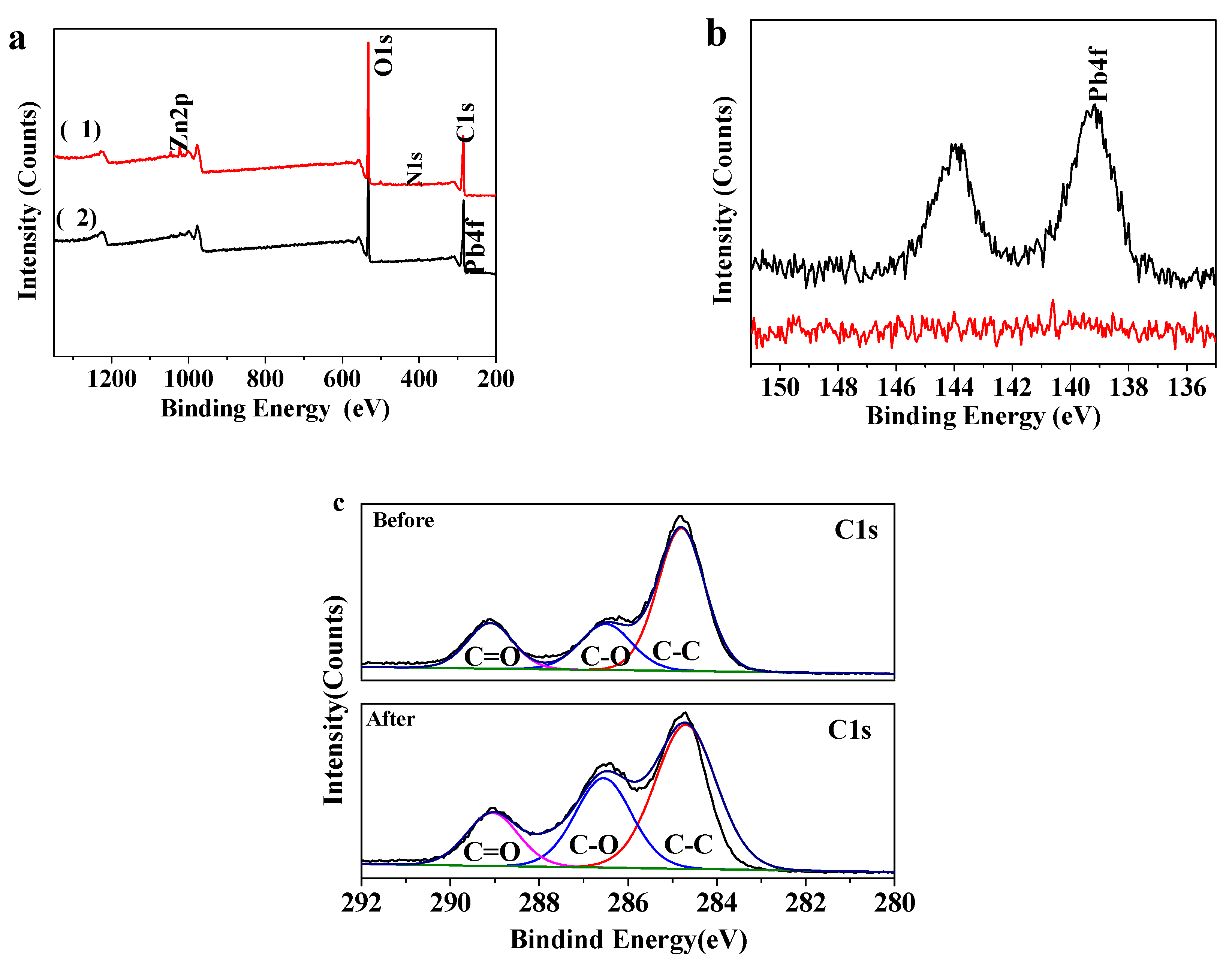
3.4. XPS Analyses
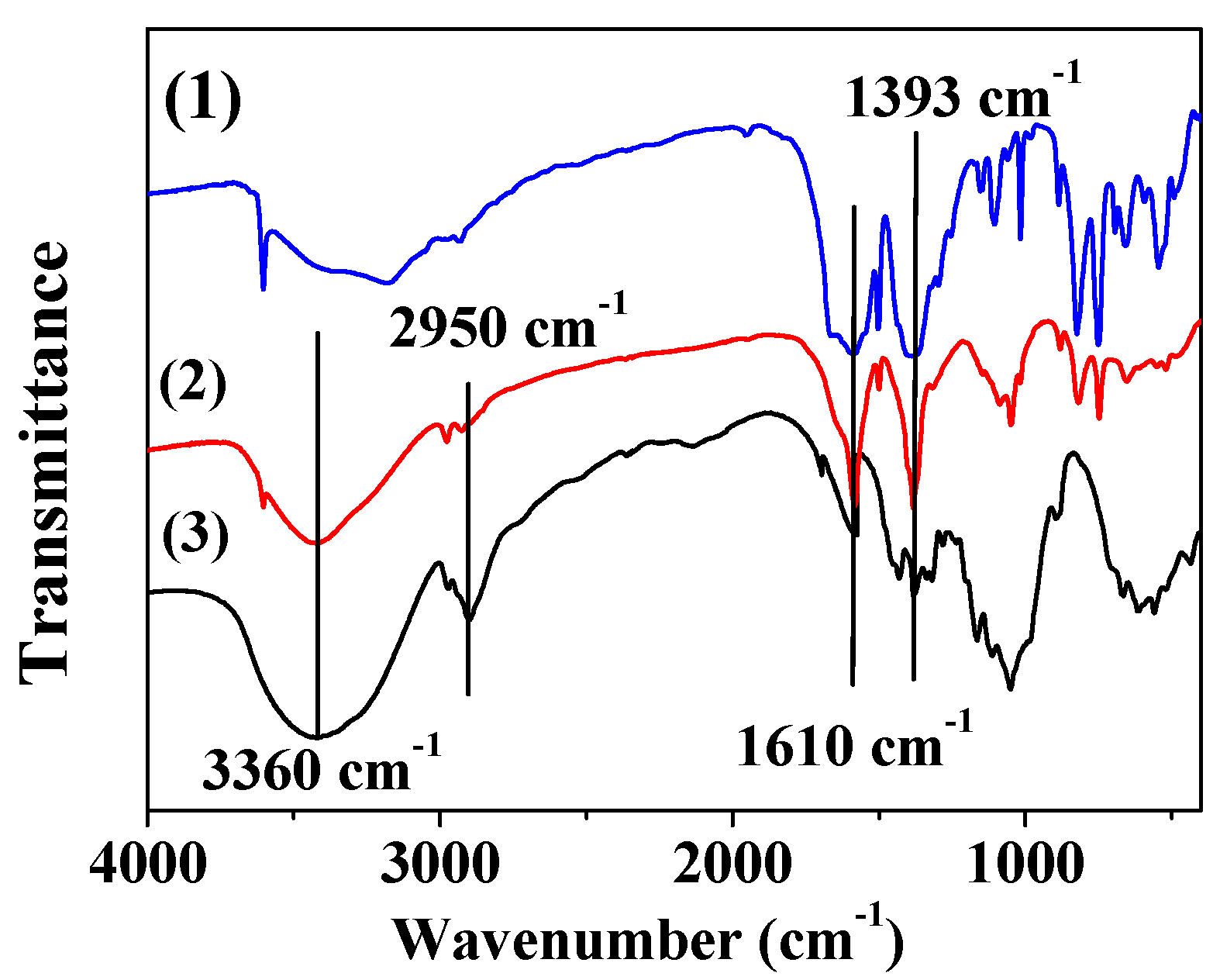
3.5. FT-IR Analyses
3.6. Adsorption Experiments
3.6.1. Effect of Contact Time
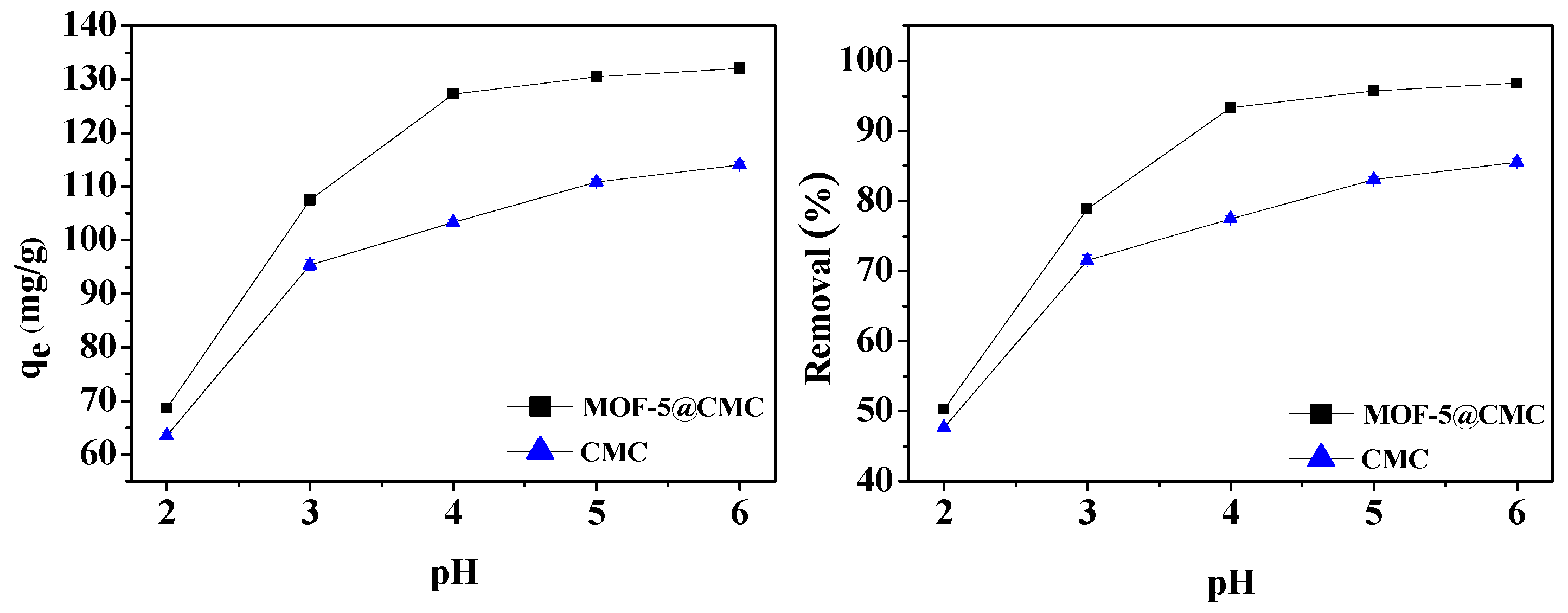
3.6.2. Effect of pH on Adsorption
3.6.3. Effect of Initial Solution Concentration
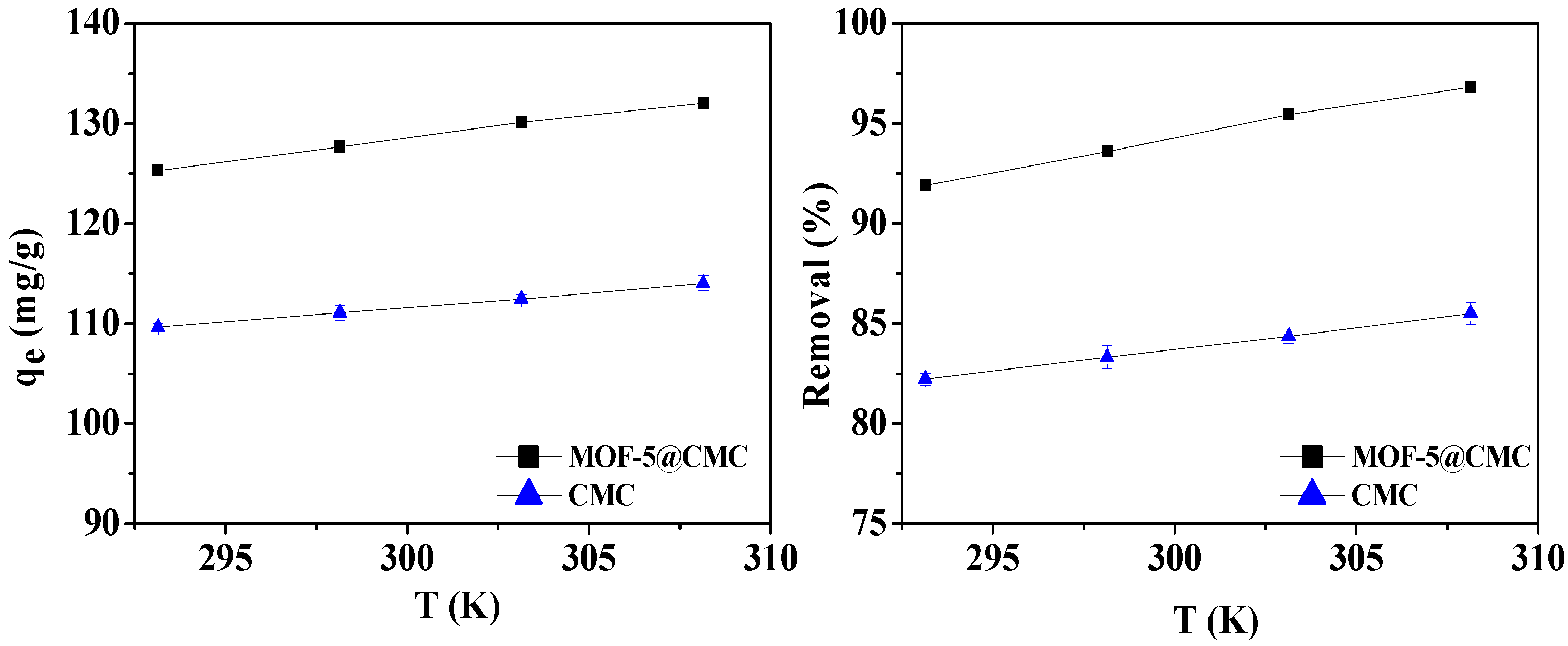
3.6.4. Effect of Temperature on Adsorption
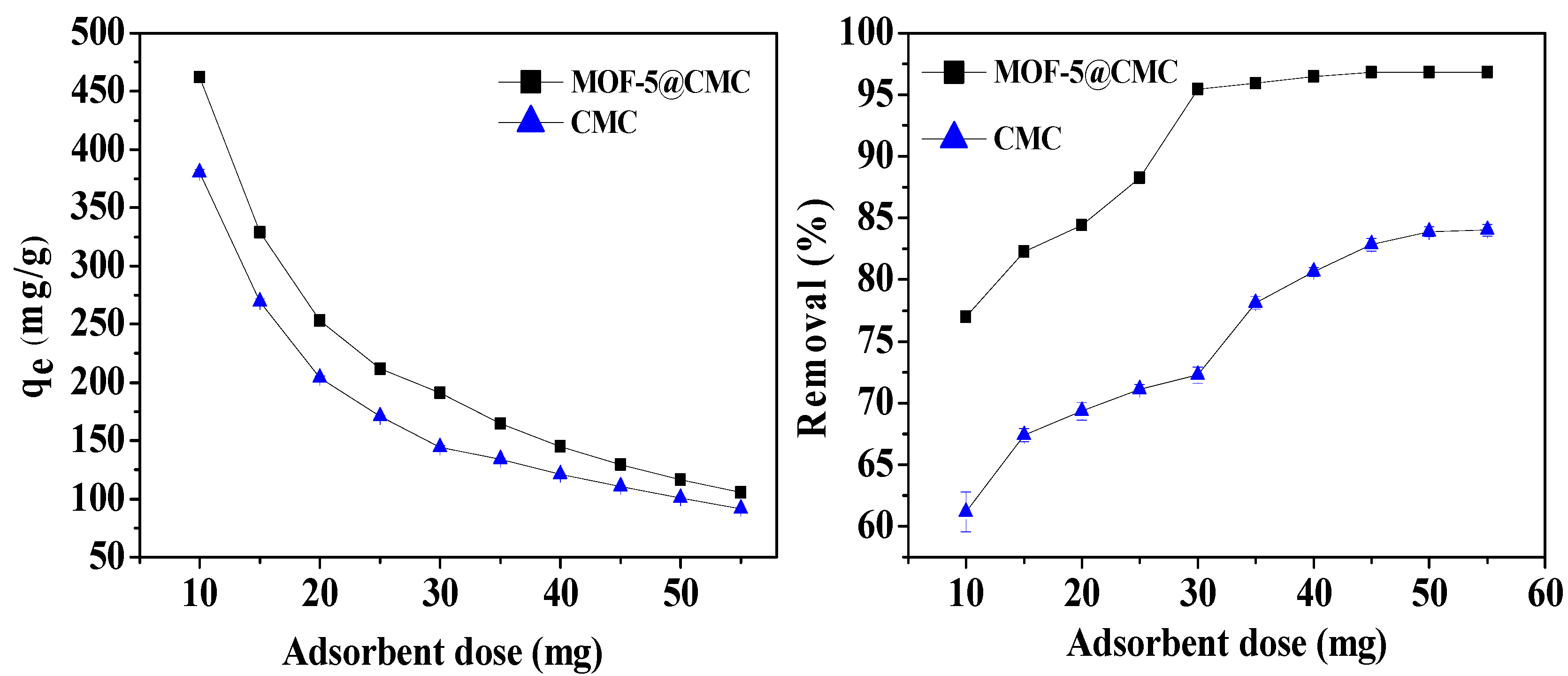
3.6.5. Effect of Adsorbent Dosage
3.7. Adsorption Mechanism
3.7.1. Adsorption Kinetics
3.7.2. Adsorption Isotherm Modeling
3.7.3. Adsorption Thermodynamics
3.8. Comparing the Pb(II)-Absorption Capacities of CMC, MOF-5, and CMC–MOF-5 Beads
3.9. Regeneration Analysis
4. Comparison of Adsorption Performance
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Predoi, D.; Predoi, M.V.; Iconaru, S.L.; el Kettani, M.E.C.; Leduc, D.; Prodan, A.M. Ultrasonic Measurements on β Cyclodextrin/Hydroxyapatite Composites for Potential Water Depollution. Materials 2017, 10, 681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Q.; Wang, Y.; Jin, L.; Wang, Y.; Qin, M. Adsorption of Cu (II), Pb (II) and Cr (VI) from aqueous solutions using black wattle tannin-immobilized nanocellulose. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 339, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, N.; Jin, R.N.; Omer, A.M.; Ouyang, X.K. Adsorption of Pb(II) from fish sauce using carboxylated cellulose nanocrystal: Isotherm, kinetics, and thermodynamic studies. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 102, 232–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samuel, M.S.; Shah, S.S.; Bhattacharya, J.; Subramaniam, K.; Pradeep Singh, N.D. Adsorption of Pb(II) from aqueous solution using a magnetic chitosan/graphene oxide composite and its toxicity studies. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 115, 1142–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, W.; Li, H.; Liu, Y.; Song, S. Comparison of Pb(II) adsorption onto graphene oxide prepared from natural graphites: Diagramming the Pb(II) adsorption sites. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 364, 620–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, H.; Gao, Z.; Wu, D.; Jiang, J.; Sun, Y.; Luo, C. Efficient Pb(II) removal using sodium alginate-carboxymethyl cellulose gel beads: Preparation, characterization, and adsorption mechanism. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 137, 402–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, X.; Wei, G.; Xiong, J.; Tan, F.; He, H.; Qu, C.; Yin, H.; Zhu, J.; Zhu, R.; Qin, Z.; et al. Adsorption isotherm, mechanism, and geometry of Pb(II) on magnetites substituted with transition metals. Chem. Geol. 2017, 470, 132–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Chai, F.; Chen, Q. Soft magnetic nanocomposite microgels by in-situ crosslinking of poly acrylic acid onto superparamagnetic magnetite nanoparticles and their applications for the removal of Pb(II) ion. Eur. Polym. J. 2017, 89, 468–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-Y.; Liu, Y.-X.; Lu, H.-H.; Yang, R.-Q.; Yang, S.-M. Competitive adsorption of Pb(II), Cu(II), and Zn(II) ions onto hydroxyapatite-biochar nanocomposite in aqueous solutions. J. Solid State Chem. 2018, 261, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Fu, Y.; Qin, Q.; Lu, X.; Shi, X.; Zhao, C.; Xu, G. Synthesis of magnetic mesoporous Fe3O4@PEI-MOF-5 for the effective enrichment of malachite green and crystal violet in fish samples. J. Chromatogr. A 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stene, R.E.; Scheibe, B.; Pietzonka, C.; Karttunen, A.J.; Petry, W.; Kraus, F. MoF 5 revisited. A comprehensive study of MoF 5. J. Fluor. Chem. 2018, 211, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Z.; Li, H.; Yu, Z.; Wang, P.; Fan, X. Densification of MOF-5 synthesized at ambient temperature for methane adsorption. Mater. Lett. 2011, 65, 2445–2447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, D.K.; Ganesan, V.; Marken, F.; Gupta, R.; Sonkar, P.K. Metal@MOF Materials in Electroanalysis: Silver-Enhanced Oxidation Reactivity Towards Nitrophenols Adsorbed into a Zinc Metal Organic Framework—Ag@MOF-5(Zn). Electrochim. Acta 2016, 219, 482–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wang, C.; Sun, Y.; Shi, K.; Deng, S.; Lu, H. Large negative thermal expansion provided by metal-organic framework MOF-5: A first-principles study. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2016, 175, 138–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakhtiari, N.; Azizian, S. Adsorption of copper ion from aqueous solution by nanoporous MOF-5: A kinetic and equilibrium study. J. Mol. Liquids 2015, 206, 114–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cendrowski, K.; Skumial, P.; Spera, P.; Mijowska, E. Thermally induced formation of zinc oxide nanostructures with tailoring morphology during metal organic framework (MOF-5) carbonization process. Mater. Des. 2016, 110, 740–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Wang, C.; Li, H.; Li, X.; Liu, B.; Singh, V.; Wang, S.; Sun, L.; Gref, R.; Zhang, J. Evaluation of drug loading capabilities of gamma-cyclodextrin-metal organic frameworks by high performance liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2017, 1488, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Y.; Yu, H.; Xu, P.; Xu, J.; Li, X. Metal organic framework of MOF-5 with hierarchical nanopores as micro-gravimetric sensing material for aniline detection. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 256, 639–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ataur, R.; Tirmizi, S.A.; Badshah, A.; Ammad, H.M.; Jawad, M.; Abbas, S.M.; Rana, U.A.; Khan, S.U.-D. Synthesis of highly stable MOF-5@MWCNTs nanocomposite with improved hydrophobic properties. Arabian J. Chem. 2018, 11, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhivkov, A.M.; Hristov, R.P. Adsorption of carboxymethyl cellulose on alumina particles. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 447, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, Z.; Ge, H.; Liu, L.; Zhu, C.; Min, L.; Liu, M.; Fan, L.; Li, D. Carboxymethyl cellulose modified graphene oxide as pH-sensitive drug delivery system. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 107, 1184–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, M.; Guo, C.; Liu, H.; Zeng, H.; Duan, X.; Zhou, Y.; Tang, Z. Direct electrodeposition of carboxymethyl cellulose based on coordination deposition method. Cellulose 2018, 25, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi Pour, S.; Shaterian, H.R.; Afradi, M.; Yazdani-Elah-Abadi, A. Carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC)-loaded Co-Cu doped manganese ferrite nanorods as a new dual-modal simultaneous contrast agent for magnetic resonance imaging and nanocarrier for drug delivery system. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2017, 438, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bicak, O.; Ekmekci, Z.; Bradshaw, D.J.; Harris, P.J. Adsorption of guar gum and CMC on pyrite. Miner. Eng. 2007, 20, 996–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zengin Kurt, B.; Uckaya, F.; Durmus, Z. Chitosan and carboxymethyl cellulose based magnetic nanocomposites for application of peroxidase purification. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 96, 149–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shui, T.; Feng, S.; Chen, G.; Li, A.; Yuan, Z.; Shui, H.; Kuboki, T.; Xu, C. Synthesis of sodium carboxymethyl cellulose using bleached crude cellulose fractionated from cornstalk. Biomass Bioenergy 2017, 105, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakshmi, D.S.; Trivedi, N.; Reddy, C.R.K. Synthesis and characterization of seaweed cellulose derived carboxymethyl cellulose. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 157, 1604–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamthai, S.; Magaraphan, R. Mechanical and barrier properties of spray dried carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC) film from bleached bagasse pulp. Ind. Crops Prod. 2017, 109, 753–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khodadadi, M.; Malekpour, A.; Ansaritabar, M. Removal of Pb (II) and Cu (II) from aqueous solutions by NaA zeolite coated magnetic nanoparticles and optimization of method using experimental design. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2017, 248, 256–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Wang, J.; Yang, Q.; Pei, H.; Hu, N.; Suo, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhang, D.; Wang, J. Facile fabrication of robust MOF membranes on cloth via a CMC macromolecule bridge for highly efficient Pb(II) removal. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 339, 230–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Pang, H.; Yao, W.; Wang, X.; Yu, S.; Yu, Z.; Wang, X. Synthesis of rod-like metal-organic framework (MOF-5) nanomaterial for efficient removal of U(VI): Batch experiments and spectroscopy study. Sci. Bull. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Qiu, F.; Li, P. Synthesis and characterization of β-cyclodextrin–carboxymethyl cellulose–graphene oxide composite materials and its application for removal of basic fuchsin. J. Iran. Chem. Soc. 2017, 14, 1827–1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liuyun, J.; Yubao, L.; Chengdong, X. A novel composite membrane of chitosan-carboxymethyl cellulose polyelectrolyte complex membrane filled with nano-hydroxyapatite I. Preparation and properties. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2009, 20, 1645–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joshi, G.; Naithani, S.; Varshney, V.K.; Bisht, S.S.; Rana, V.; Gupta, P.K. Synthesis and characterization of carboxymethyl cellulose from office waste paper: A greener approach towards waste management. Waste Manag. 2015, 38, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, S.M.; Mousaa, I.M.; Ibrahim, M.S. Characterization of gamma irradiated plasticized carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC)/gum arabic (GA) polymer blends as absorbent for dyestuffs. Bull. Mater. Sci. 2014, 37, 603–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Jin, R.-N.; Ouyang, X.-K.; Wang, Y.-G. Adsorption behavior of carboxylated cellulose nanocrystal—Polyethyleneimine composite for removal of Cr(VI) ions. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 408, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seoane, B.; Téllez, C.; Coronas, J.; Staudt, C. NH2-MIL-53(Al) and NH2-MIL-101(Al) in sulfur-containing copolyimide mixed matrix membranes for gas separation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2013, 111, 72–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuba-Chiem, L.T.; Huynh, L.; Ralston, J.; Beattie, D.A. In situ particle film ATR-FTIR studies of CMC adsorption on talc: The effect of ionic strength and multivalent metal ions. Miner. Eng. 2008, 21, 1013–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.H.; Omer, A.M.; Ouyang, X.K.; Yu, D. Fabrication of carboxylated cellulose nanocrystal/sodium alginate hydrogel beads for adsorption of Pb(II) from aqueous solution. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 108, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Valdivieso, A.; Lozano-Ledesma, L.A.; Robledo-Cabrera, A.; Orozco-Navarro, O.A. Carboxymethylcellulose (CMC) as PbS depressant in the processing of Pb-Cu bulk concentrates. Adsorption and floatability studies. Miner. Eng. 2017, 112, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yáñez-S, M.; Matsuhiro, B.; Maldonado, S.; González, R.; Luengo, J.; Uyarte, O.; Serafine, D.; Moya, S.; Romero, J.; Torres, R. Carboxymethylcellulose from bleached organosolv fibers of Eucalyptus nitens: Synthesis and physicochemical characterization. Cellulose 2018, 25, 2901–2914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Jin, R.N.; Liu, C.; Wang, Y.F.; Ouyang, X.K. Magnetic carboxylated cellulose nanocrystals as adsorbent for the removal of Pb(II) from aqueous solution. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 93, 547–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Javadian, H.; Koutenaei, B.B.; Shekarian, E.; Sorkhrodi, F.Z.; Khatti, R.; Toosi, M. Application of functionalized nano HMS type mesoporous silica with N-(2-aminoethyl)-3-aminopropyl methyldimethoxysilane as a suitable adsorbent for removal of Pb (II) from aqueous media and industrial wastewater. J. Saudi Chem. Soc. 2017, 21, S219–S230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatehi, M.H.; Shayegan, J.; Zabihi, M.; Goodarznia, I. Functionalized magnetic nanoparticles supported on activated carbon for adsorption of Pb(II) and Cr(VI) ions from saline solutions. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 1754–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, F.; Orcajo, G.; Briones, D.; Leo, P.; Calleja, G. Catalytic advantages of NH 2 -modified MIL-53(Al) materials for Knoevenagel condensation reaction. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2017, 246, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araújo, C.S.T.; Almeida, I.L.S.; Rezende, H.C.; Marcionilio, S.M.L.O.; Léon, J.J.L.; de Matos, T.N. Elucidation of mechanism involved in adsorption of Pb(II) onto lobeira fruit ( Solanum lycocarpum ) using Langmuir, Freundlich and Temkin isotherms. Microchem. J. 2018, 137, 348–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayati, B.; Maleki, A.; Najafi, F.; Daraei, H.; Gharibi, F.; McKay, G. Super high removal capacities of heavy metals (Pb(2+) and Cu(2+)) using CNT dendrimer. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 336, 146–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, C.; Zhu, P.; Cai, M.; Hu, H.; Fu, Q. Comparative adsorption of Pb(II), Cu(II) and Cd(II) on chitosan saturated montmorillonite: Kinetic, thermodynamic and equilibrium studies. Appl. Clay Sci. 2017, 143, 320–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, B.; Ye, L. Structure of polyvinyl alcohol-g-acrylic acid-2-acrylamido-2-methyl-1-propanesulfonic acid hydrogel and adsorption mechanism for advanced Pb(II) removal. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2016, 35, 309–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Qian, P.; Yu, Y.; Yu, B.; Wang, Y.; Ye, S.; Chen, Y. Preparation and characterization of a novel hybrid chelating material for effective adsorption of Cu(II) and Pb(II). J. Environ. Sci. (China) 2018, 67, 224–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui, S.H.; Ahmad, R. Pistachio Shell Carbon (PSC)—An agricultural adsorbent for the removal of Pb(II) from aqueous solution. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2017, 4, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, X.; Ren, J.; Zhong, C. Magnetic Multi-porous Bio-adsorbent Modified with Amino siloxane for Fast Removal of Pb(II) from Aqueous Solution. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, S0169433217324480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Dong, W.; Ma, S.; Chen, J.; Ling, J.; Wang, P. A new, low-cost adsorbent: Preparation, characterization, and adsorption behavior of Pb(II) and Cu(II). J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 445, 294–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Fu, S.; Zhang, L.; Zhan, H.; Levit, M.V. Use of carboxylated cellulose nanofibrils-filled magnetic chitosan hydrogel beads as adsorbents for Pb(II). Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 101, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Lin, D.; Luo, J. Adsorptive Removal of Pb(II) Ions from Aqueous Samples with Amino-Functionalization of Metal–Organic Frameworks MIL-101(Cr). J. Chem. Eng. Data 2015, 60, 1732–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, W.; Gu, J.; Na, Y. Efficient removal of Pb (II) and Cd (II) using NH2-functionalized Zr-MOFs via rapid microwave-promoted synthesis. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2017, 56, 1880–1887. [Google Scholar]
- Rivera, J.M.; Rincón, S.; Youssef, C.B.; Zepeda, A. Highly Efficient Adsorption of Aqueous Pb(II) with Mesoporous Metal-Organic Framework-5: An Equilibrium and Kinetic Study. J. Nanomater. 2016, 2016, 8095737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Concentration (mg/L) | Pseudo-First-Order Model | Pseudo-Second-Order Model | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qe,exp | k1 | R2 | qe,cal | k2 | R2 | |
| 300 | 132.03 | 0.0242 | 0.945 | 133.64 | 0.0098 | 0.999 |
| T (K) | Langmuir Isotherm | Freundlich Isotherm | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qm (mg/g) | b (L/mg) | R2 | KF | n | R2 | |
| 293.15 | 322.58 | 0.061 | 0.988 | 1.75 | 3.22 | 0.961 |
| C0 (mg/L) | RL |
|---|---|
| 100 | 0.14 |
| 200 | 0.075 |
| 300 | 0.052 |
| 500 | 0.032 |
| 800 | 0.02 |
| 1000 | 0.016 |
| Concentration (mg/L) | ΔG (KJ/mol) T (K) | ΔH (KJ/mol) | ΔS (J/mol·K) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 300 | 293.15 −3.99 | 298.15 −4.67 | 303.15 −5.69 | 308.15 −6.74 | 50.09 | 0.814 |
| Adsorbents | qmax (mg/g) | Adsorption Time | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| AS-ACI | 133.3 | 150 | [52] |
| Mg2Al-CO3-LDH | 123 | 120 | [53] |
| m-CS/PVA/CCNFs | 175.4 | 200 | [54] |
| ED-MIL-101 | 81.09 | 30 | [55] |
| Zr-MOF | 166.74 | 120 | [56] |
| MOF-5 | 658.5 | 30 | [57] |
| MOF-5–CMC | 322.58 | 120 | This work |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jin, H.-X.; Xu, H.P.; Wang, N.; Yang, L.-Y.; Wang, Y.-G.; Yu, D.; Ouyang, X.-K. Fabrication of Carboxymethylcellulose/Metal-Organic Framework Beads for Removal of Pb(II) from Aqueous Solution. Materials 2019, 12, 942. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12060942
Jin H-X, Xu HP, Wang N, Yang L-Y, Wang Y-G, Yu D, Ouyang X-K. Fabrication of Carboxymethylcellulose/Metal-Organic Framework Beads for Removal of Pb(II) from Aqueous Solution. Materials. 2019; 12(6):942. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12060942
Chicago/Turabian StyleJin, Huo-Xi, Hong Ping Xu, Nan Wang, Li-Ye Yang, Yang-Guang Wang, Di Yu, and Xiao-Kun Ouyang. 2019. "Fabrication of Carboxymethylcellulose/Metal-Organic Framework Beads for Removal of Pb(II) from Aqueous Solution" Materials 12, no. 6: 942. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12060942
APA StyleJin, H.-X., Xu, H. P., Wang, N., Yang, L.-Y., Wang, Y.-G., Yu, D., & Ouyang, X.-K. (2019). Fabrication of Carboxymethylcellulose/Metal-Organic Framework Beads for Removal of Pb(II) from Aqueous Solution. Materials, 12(6), 942. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12060942





