Systematic Investigation of the Synergistic and Antagonistic Effects on the Removal of Pyrene and Copper onto Mesoporous Silica from Aqueous Solutions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Chemicals
2.2. The Preparation of Adsorbents
2.3. Characterization Techniques
2.4. Adsorption Experiments
3. Results and Discussion
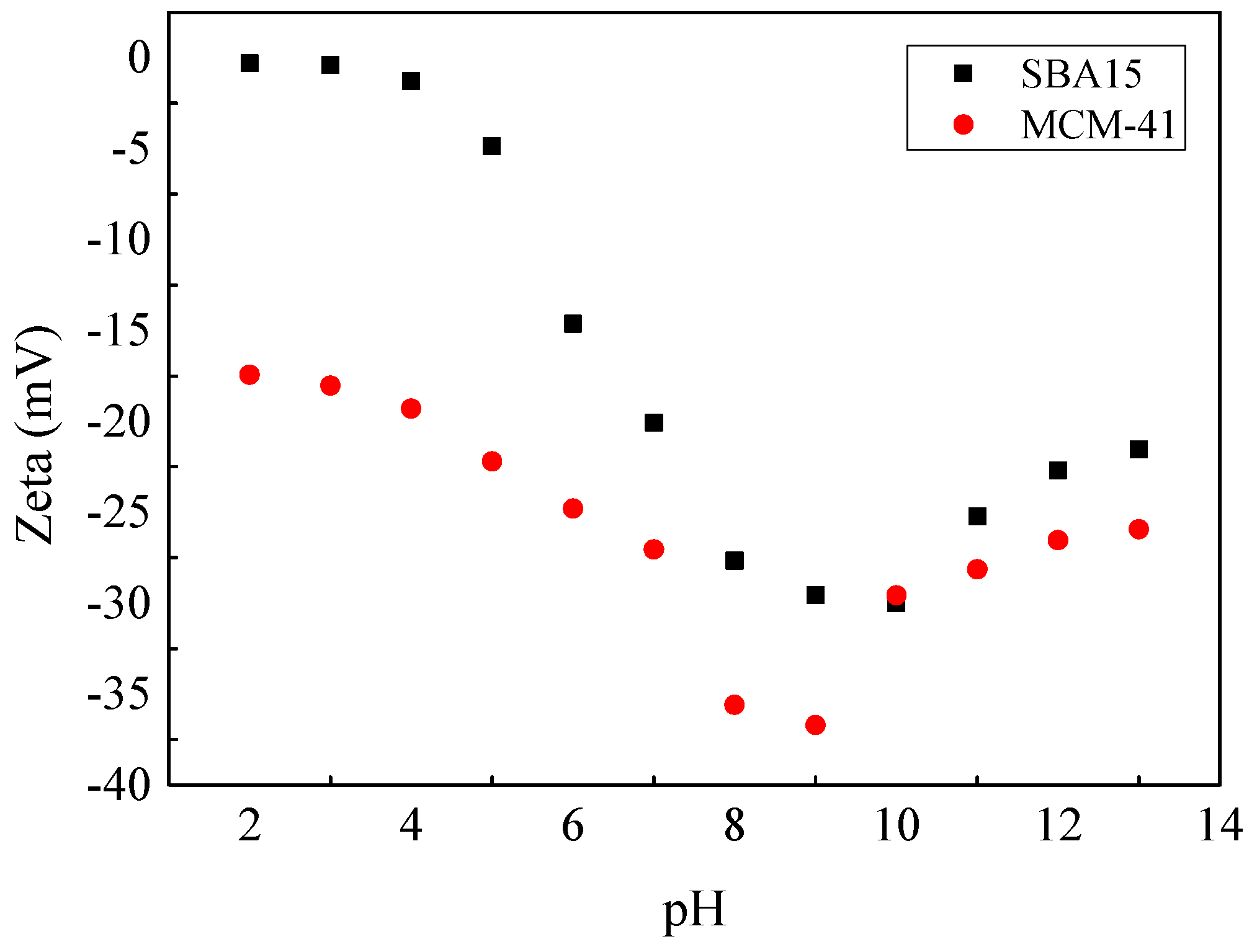
3.1. Structure, Textural and Morphological Properties of Adsorbents
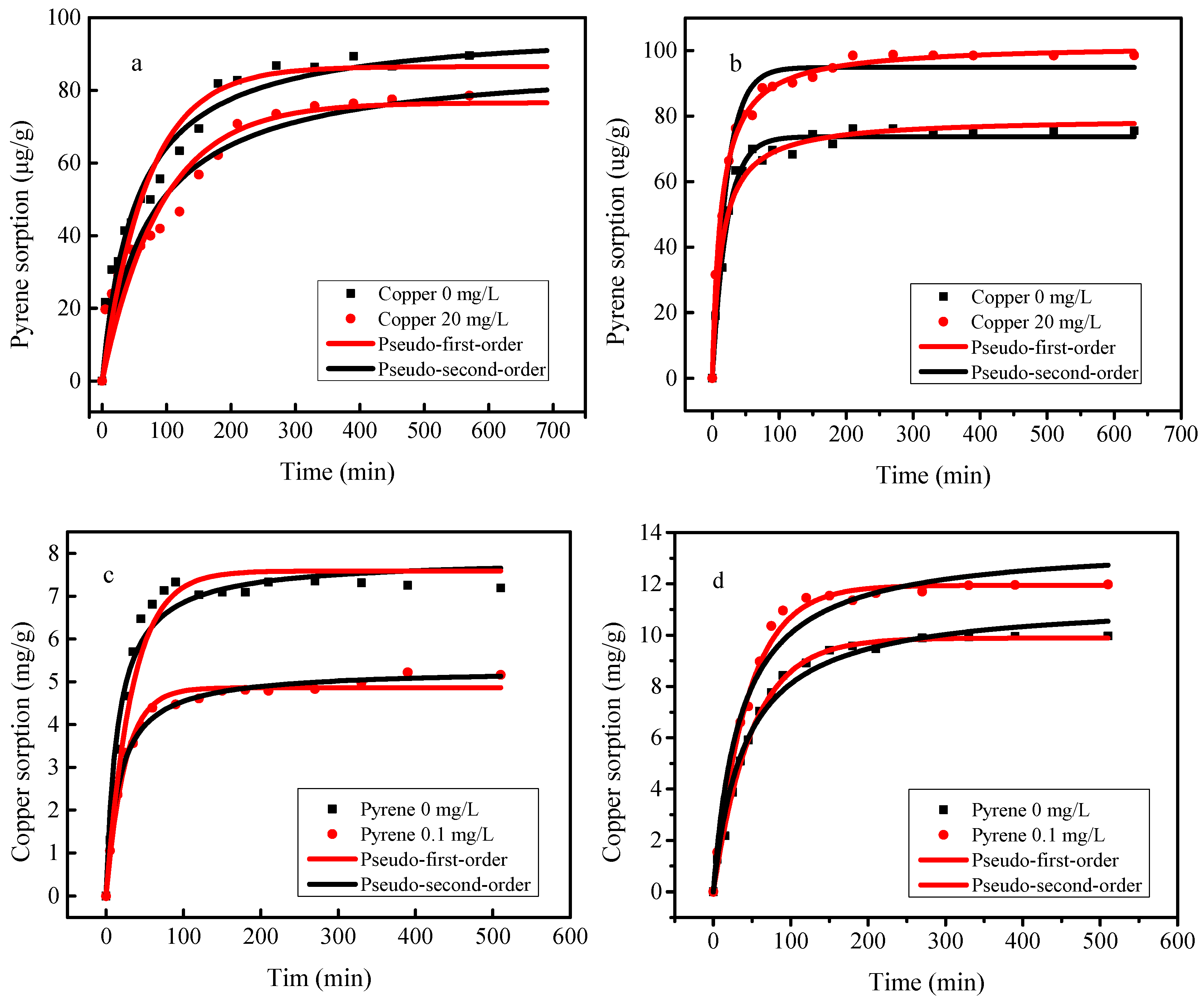
3.2. The Adsorption Kinetics of Pyrene and Copper onto SBA15 and MCM-41
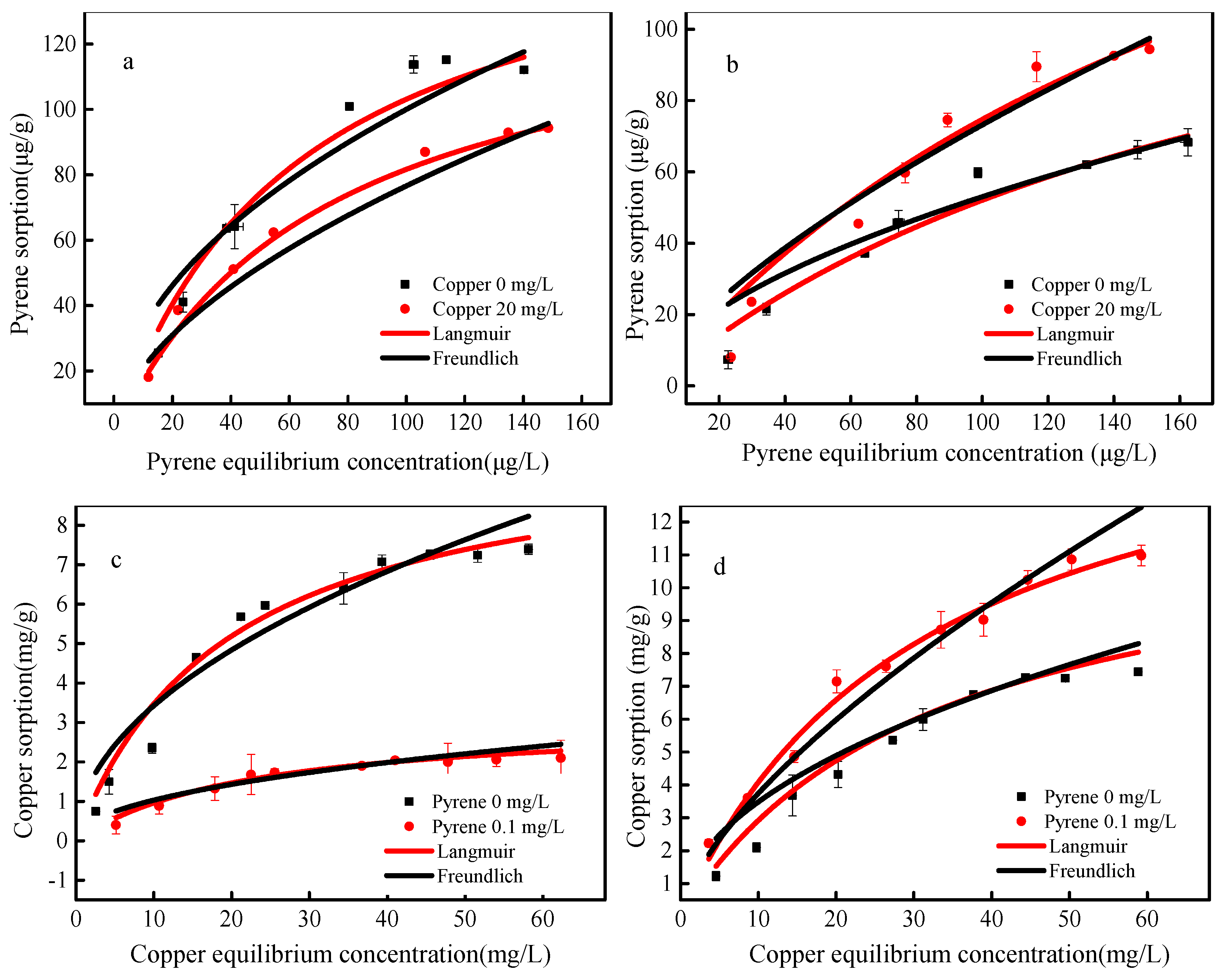
3.3. The Adsorption Isotherms of Pyrene and Copper onto SBA15 and MCM-41
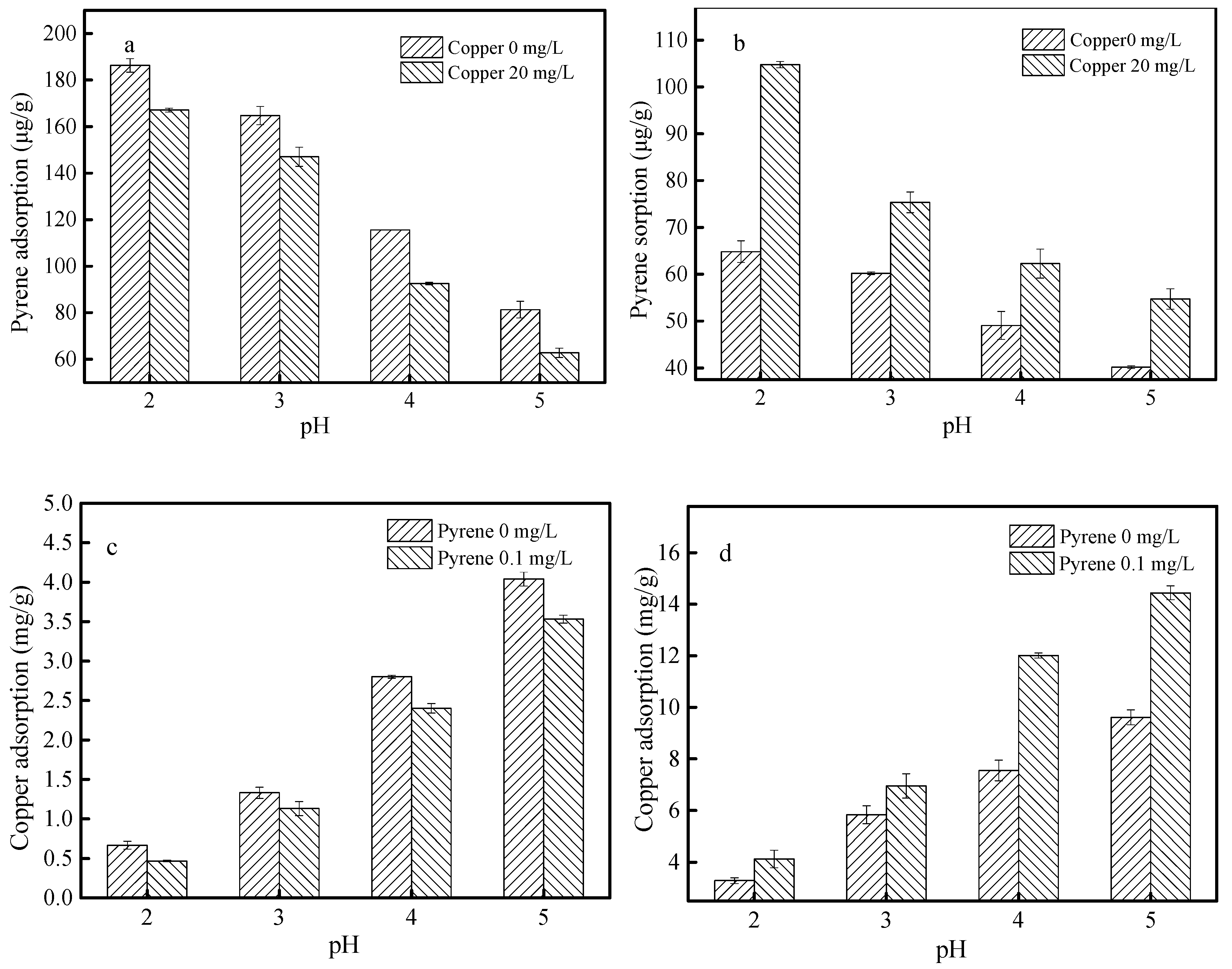
3.4. Effects of pH
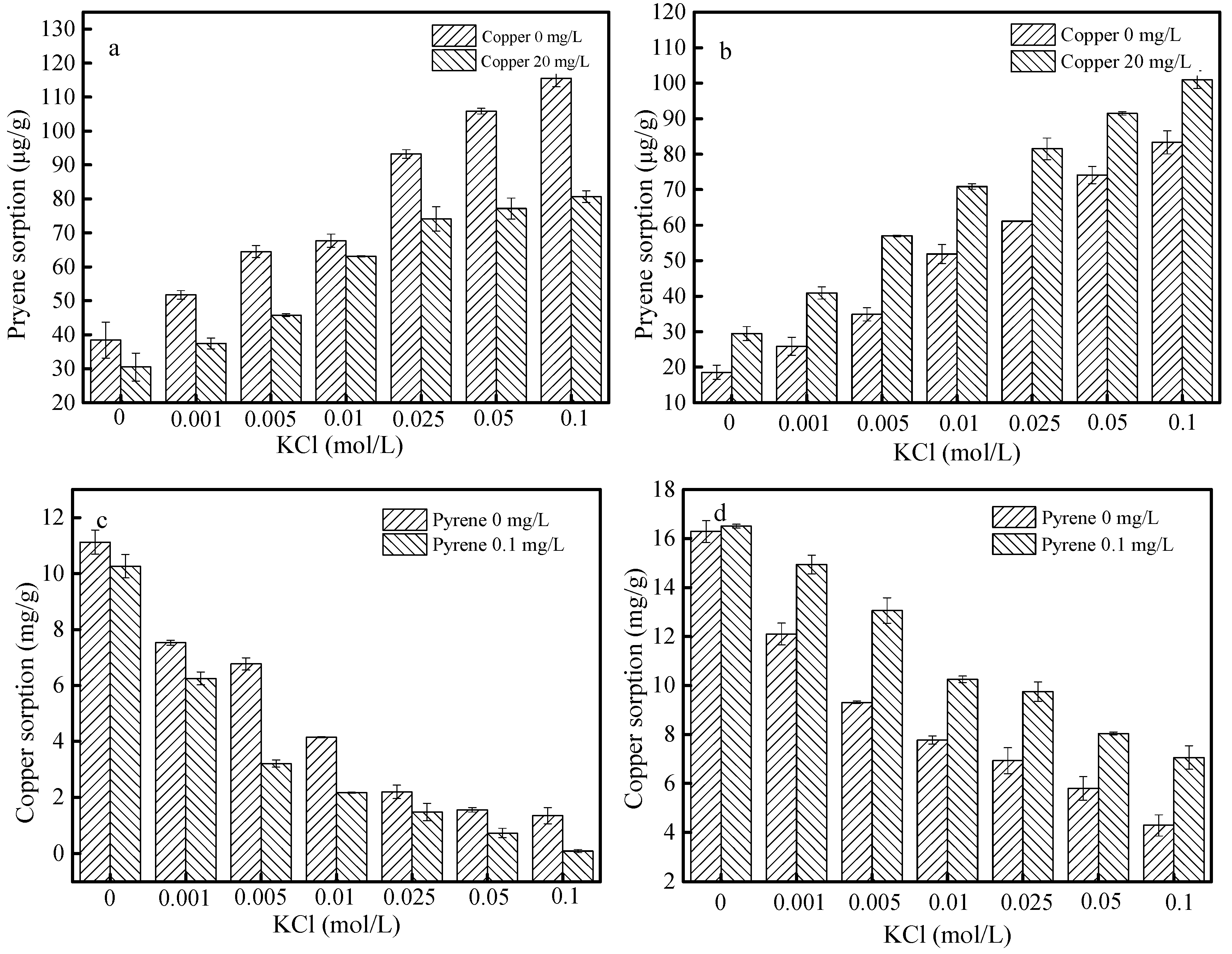
3.5. Effects of Ionic Strength
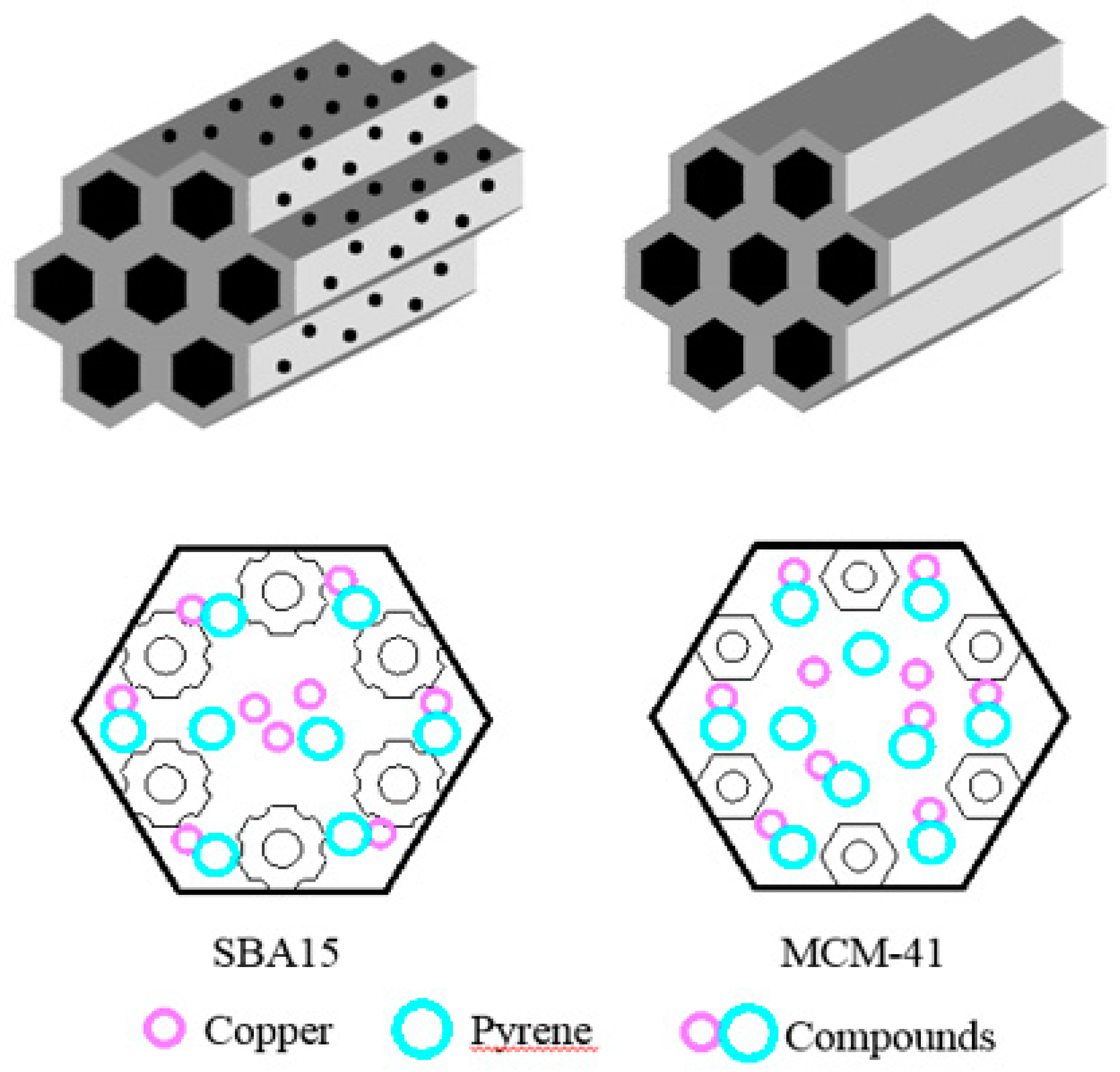
3.6. Adsorption Mechamism
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Costa, J.A.S.; de Jesus, R.A.; da Silva, C.M.P.; Romão, L.P.C. Efficient adsorption of a mixture of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) by Si-MCM-41 mesoporous molecular sieve. Powder Technol. 2017, 308, 434–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Park, S.; Han, Y.; Choi, J.; Park, J. Adsorption of Co(II) and Mn(II) Ions on Mesoporous Silica SBA15 Functionalized with Amine Groups. Mater. Trans. 2014, 55, 1494–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koedrith, P.; Kim, H.; Weon, J.-I.; Seo, Y.R. Toxicogenomic approaches for understanding molecular mechanisms of heavy metal mutagenicity and carcinogenicity. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2013, 216, 587–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; de Brauwere, A.; Elskens, M.; Croes, K.; Baeyens, W.; Leermakers, M. Evolution of trace metal and organic pollutant concentrations in the Scheldt River Basin and the Belgian Coastal Zone over the last three decades. J. Mar. Syst. 2013, 128, 52–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gauthier, P.T.; Norwood, W.P.; Prepas, E.E.; Pyle, G.G. Metal–PAH mixtures in the aquatic environment: A review of co-toxic mechanisms leading to more-than-additive outcomes. Aquat. Toxicol. 2014, 154, 253–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrella, A.; Spasiano, D.; Acquafredda, P.; De Vietro, N.; Ranieri, E.; Cosma, P.; Rizzi, V.; Petruzzelli, V.; Petruzzelli, D. Heavy metals retention (Pb(II), Cd(II), Ni(II)) from single and multimetal solutions by natural biosorbents from the olive oil milling operations. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2018, 114, 79–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, J.; Loh, G.; Gwie, C.G.; Dewiyanti, S.; Tasrif, M.; Borgna, A. Desulfurization of diesel fuels by selective adsorption on activated carbons: Competitive adsorption of polycyclic aromatic sulfur heterocycles and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 166, 207–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemić, J.; Tomašević-Čanović, M.; Adamović, M.; Kovačević, D.; Milićević, S. Competitive adsorption of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons on organo-zeolites. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2007, 105, 317–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Shao, T.; Bekaroglu, S.S.K.; Karanfil, T. Adsorption of synthetic organic chemicals by carbon nanotubes: Effects of background solution chemistry. Water Res. 2010, 44, 2067–2074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrella, A.; Petruzzelli, V.; Ranieri, E.; Catalucci, V.; Petruzzelli, D. Sorption of Pb(II), Cd(II), and Ni(II) From Single- and Multimetal Solutions by Recycled Waste Porous Glass. Chem. Eng. Commun. 2015, 203, 940–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salih, S.S.; Ghosh, T.K. Adsorption of Zn(II) ions by chitosan coated diatomaceous earth. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 106, 602–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Gao, C.; Wu, Y.; Sun, L.; Huang, X.; Ran, W.; Shen, Q. Removal of heavy metals from aqueous solution by lipopeptides and lipopeptides modified Na-montmorillonite. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 147, 378–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letina, D.; Letshwenyo, W.M. Investigating waste rock, tailings, slag and coal ash clinker as adsorbents for heavy metals: Batch and column studies. Phys. Chem. Earth Parts ABC 2018, 105, 184–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da’na, E. Adsorption of heavy metals on functionalized-mesoporous silica: A review. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2017, 247, 145–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esparza, J.M.; Ojeda, M.L.; Campero, A.; Domínguez, A.; Kornhauser, I.; Rojas, F.; Vidales, A.M.; López, R.H.; Zgrablich, G. N2 sorption scanning behavior of SBA-15 porous substrates. Coll. Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2004, 241, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wloch, J.; Rozwadowski, M.; Lezanska, M.; Erdmann, K. Analysis of the pore structure of the MCM-41 materials. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2002, 191, 368–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gouze, B.; Cambedouzou, J.; Parrès-Maynadié, S.; Rébiscoul, D. How hexagonal mesoporous silica evolves in water on short and long term: Role of pore size and silica wall porosity. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2014, 183, 168–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; He, Y.; Wang, X.; Wei, C. Efficient adsorption of phenanthrene by simply synthesized hydrophobic MCM-41 molecular sieves. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 311, 825–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mureseanu, M.; Reiss, A.; Stefanescu, I.; David, E.; Parvulescu, V.; Renard, G.; Hulea, V. Modified SBA-15 mesoporous silica for heavy metal ions remediation. Chemosphere 2008, 73, 1499–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Morales, V.; Nava, R.; Acosta-Silva, Y.J.; Macías-Sánchez, S.A.; Pérez-Bueno, J.J.; Pawelec, B. Adsorption of lead (II) on SBA-15 mesoporous molecular sieve functionalized with –NH2 groups. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2012, 160, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Huang, Q.; Xiao, H.; Eić, M. Effect of cationic template on the adsorption of aromatic compounds in MCM-41. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2007, 98, 330–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pajarre, R.; Koukkari, P. CALPHAD aqueous solution model based on the BET approach: General theory. Calphad 2018, 63, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papynov, E.K.; Portnyagin, A.S.; Modin, E.B.; Mayorov, V.Y.; Shichalin, O.O.; Golikov, A.P.; Pechnikov, V.S.; Gridasova, E.A.; Tananaev, I.G.; Avramenko, V.A. A complex approach to assessing porous structure of structured ceramics obtained by SPS technique. Mater. Charact. 2018, 145, 294–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguado, J.; Arsuaga, J.M.; Arencibia, A.; Lindo, M.; Gascón, V. Aqueous heavy metals removal by adsorption on amine-functionalized mesoporous silica. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 163, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, S.-W.; Lin, H.-L.; Yu, T.L.; Lee, L.-P.; Weng, B.-J. Hydrogen release from ammonia borane embedded in mesoporous silica scaffolds: SBA-15 and MCM-41. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2012, 37, 14393–14404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidari, A.; Younesi, H.; Mehraban, Z. Removal of Ni(II), Cd(II), and Pb(II) from a ternary aqueous solution by amino functionalized mesoporous and nano mesoporous silica. Chem. Eng. J. 2009, 153, 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, F.; He, Y.; Lian, Z.; Xu, J. The impact of solution chemistry of electrolyte on the sorption of pentachlorophenol and phenanthrene by natural hematite nanoparticles. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 466, 577–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Zhu, D. Effect of heavy metals on the sorption of hydrophobic organic compounds to wood charcoal. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 2536–2541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, X.; Li, F. Removal of Cu(II) from aqueous solution by adsorption onto functionalized SBA-16 mesoporous silica. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2008, 116, 116–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, H.; Gao, J.; Qu, Z. Effect of Morphology and Pore Structure of SBA-15 on Toluene Dynamic Adsorption/Desorption Performance. Proced. Environ. Sci. 2013, 18, 366–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kosuge, K.; Kubo, S.; Kikukawa, N.; Takemori, M. Effect of Pore Structure in Mesoporous Silicas on VOC Dynamic. Langmuir 2007, 23, 3095–3102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

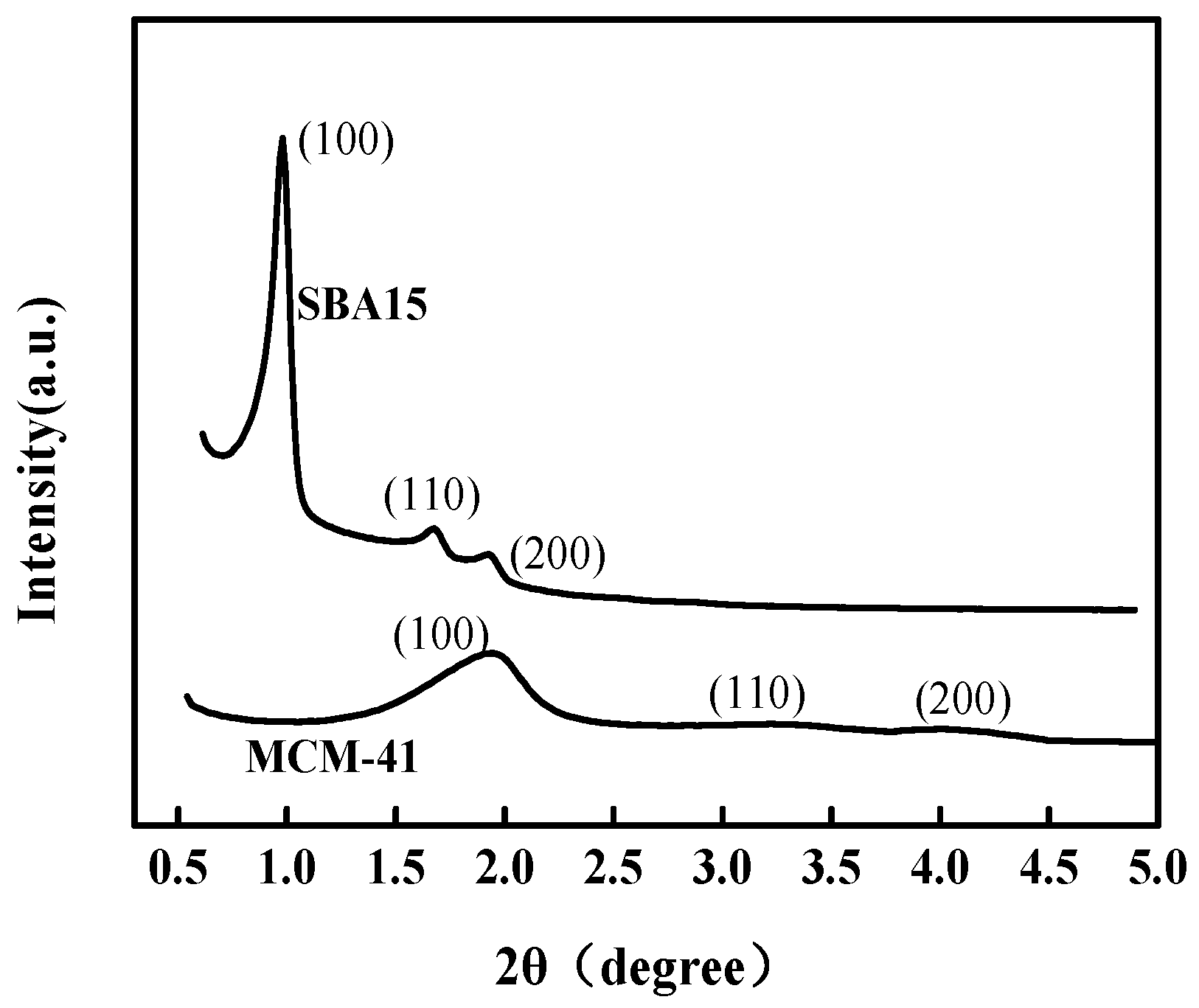

| Materials | BET (m2 g−1) | Pore Volume (cm3 g−1) | Pore Size (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| SBA15 | 409.45 | 0.83 | 4.12 |
| MCM-41 | 969.94 | 1.09 | 3.74 |
| Adsorbent | Initial Concentration (mg L−1) | Pseudo-First-Order | Pseudo-Second-Order | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Qe (mg g−1) | K1 | R2 | Qe (mg g−1) | K2 (10−4) | R2 | |||
| SBA15 | Pyrene = 0.1 | Copper = 0 | 0.087 | 0.014 | 0.94 | 0.098 | 1.96 | 0.96 |
| Copper = 20 | 0.077 | 0.011 | 0.92 | 0.089 | 1.56 | 0.95 | ||
| Copper = 20 | Pyrene = 0 | 7.36 | 0.050 | 0.97 | 7.88 | 84.6 | 0.97 | |
| Pyrene = 0.1 | 4.86 | 0.041 | 0.98 | 5.29 | 114 | 0.99 | ||
| MCM-41 | Pyrene = 0.1 | Copper = 0 | 0.072 | 0.050 | 0.98 | 0.081 | 8.22 | 0.98 |
| Copper = 20 | 0.091 | 0.053 | 0.97 | 0.102 | 7.38 | 0.99 | ||
| Copper = 20 | Pyrene = 0 | 9.22 | 0.028 | 0.97 | 11.80 | 19.1 | 0.99 | |
| Pyrene = 0.1 | 11.31 | 0.030 | 0.97 | 14.10 | 18.4 | 0.97 | ||
| Adsorbent | Initial Concentration (mg L−1) | Langmuir | Freundlich | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Qmax (mg g−1) | b (L mg−1) | R2 | n | Kf | R2 | |||
| SBA15 | Pyrene = 0.1 | Copper = 0 | 0.168 | 0.016 | 0.98 | 2.08 | 19.93 | 0.94 |
| Copper = 20 | 0.141 | 0.014 | 0.99 | 1.78 | 5.74 | 0.98 | ||
| Copper = 20 | Pyrene = 0 | 10.28 | 0.051 | 0.98 | 2.01 | 1.09 | 0.94 | |
| Pyrene = 0.1 | 3.080 | 0.045 | 0.96 | 0.35 | 2.12 | 0.90 | ||
| MCM-41 | Pyrene = 0.1 | Copper = 0 | 0.157 | 0.005 | 0.97 | 1.77 | 3.91 | 0.94 |
| Copper = 20 | 0.198 | 0.005 | 0.97 | 1.44 | 2.96 | 0.97 | ||
| Copper = 20 | Pyrene = 0 | 10.53 | 0.030 | 0.92 | 2.04 | 1.13 | 0.85 | |
| Pyrene = 0.1 | 15.09 | 0.031 | 0.98 | 1.48 | 0.79 | 0.97 | ||
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, H.; Zhai, M.; Chen, H.; Tan, C.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Z. Systematic Investigation of the Synergistic and Antagonistic Effects on the Removal of Pyrene and Copper onto Mesoporous Silica from Aqueous Solutions. Materials 2019, 12, 546. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12030546
Li H, Zhai M, Chen H, Tan C, Zhang X, Zhang Z. Systematic Investigation of the Synergistic and Antagonistic Effects on the Removal of Pyrene and Copper onto Mesoporous Silica from Aqueous Solutions. Materials. 2019; 12(3):546. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12030546
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Haiyan, Mengyun Zhai, Hongrui Chen, Chaohong Tan, Xiaoran Zhang, and Ziyang Zhang. 2019. "Systematic Investigation of the Synergistic and Antagonistic Effects on the Removal of Pyrene and Copper onto Mesoporous Silica from Aqueous Solutions" Materials 12, no. 3: 546. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12030546
APA StyleLi, H., Zhai, M., Chen, H., Tan, C., Zhang, X., & Zhang, Z. (2019). Systematic Investigation of the Synergistic and Antagonistic Effects on the Removal of Pyrene and Copper onto Mesoporous Silica from Aqueous Solutions. Materials, 12(3), 546. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12030546